An Ensemble Mean Method for Remote Sensing of Actual Evapotranspiration to Estimate Water Budget Response across a Restoration Landscape
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Evapotranspiration and the Water Budget
1.2. Quantification of Evapotranspiration
1.3. Remote Sensing of Actual Evapotranspiration
1.4. Vegetation vs. Land Cover and a Restoration Landscape
1.5. Research Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
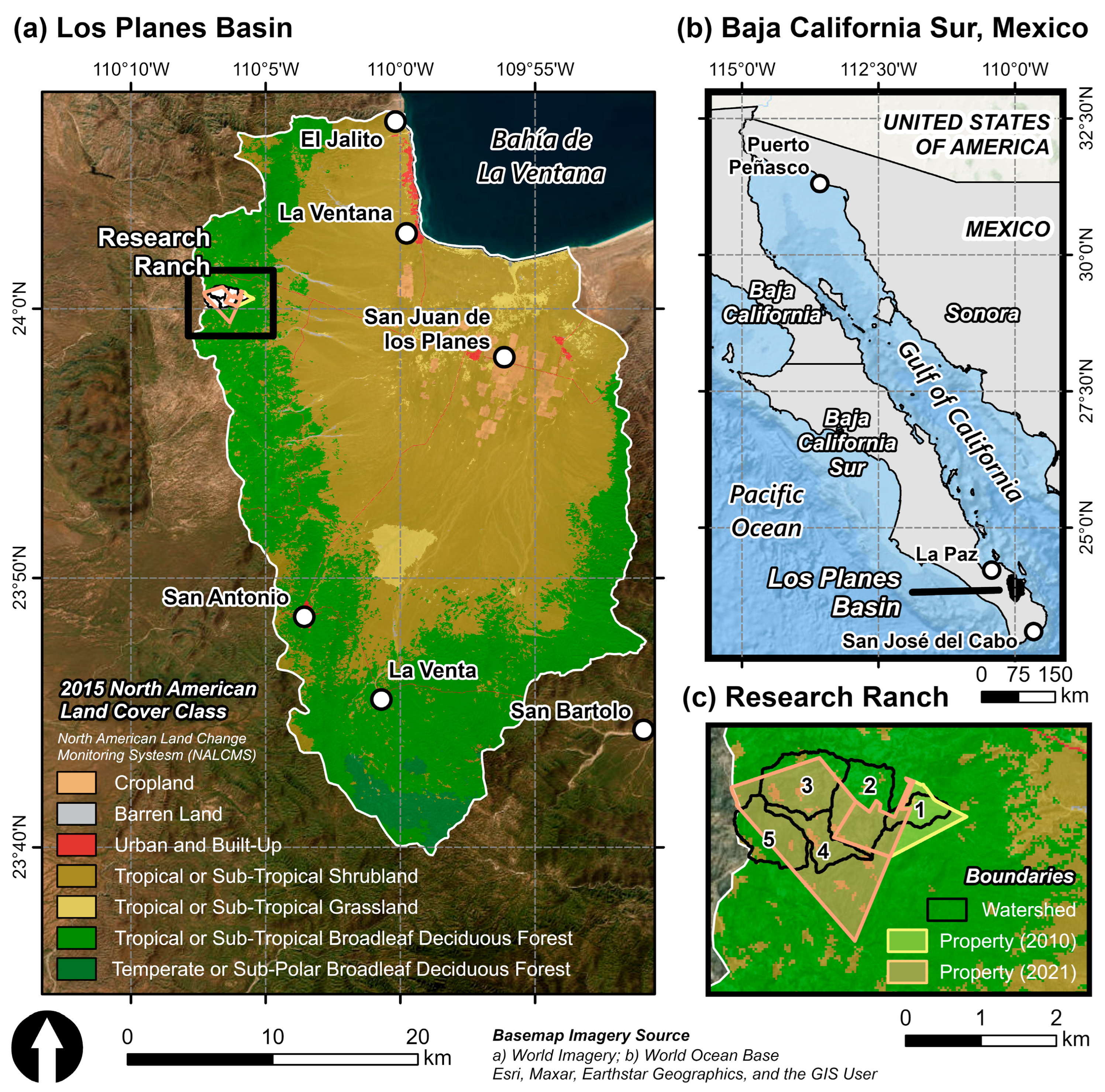
2.1. Los Planes Basin
Restoration Landscape—Paired Watersheds at the Research Ranch
2.2. Remote Sensing Analyses
2.2.1. Nagler-ET(EVI2)
2.2.2. SSEBop-LS
2.2.3. SSEBop-MOD
2.2.4. MODIS—MOD16A2
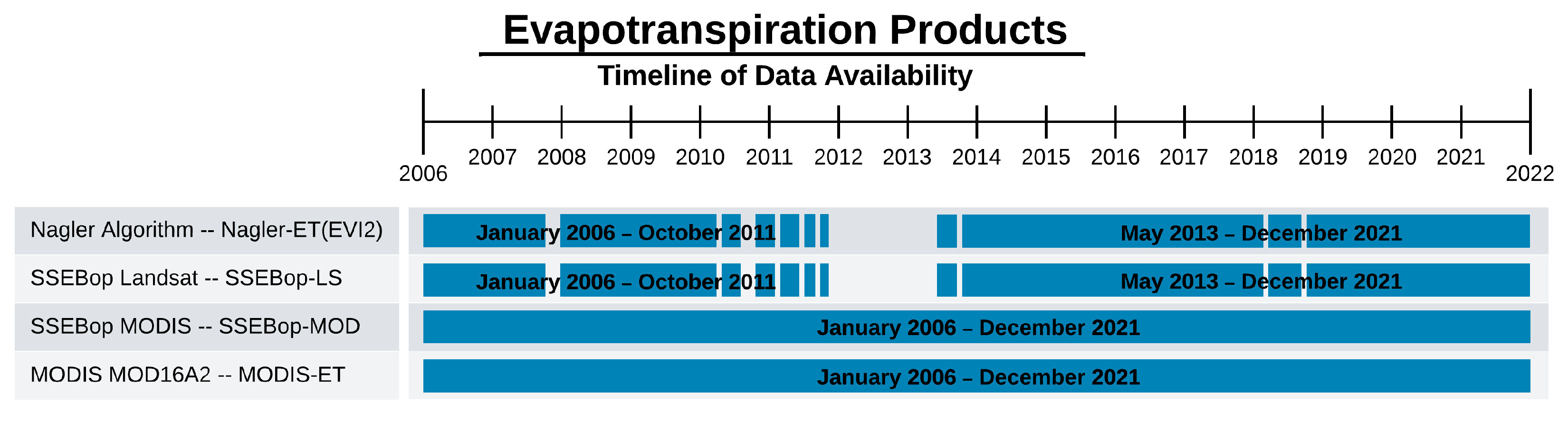
2.3. Evapotranspiration Data Harmonization
2.4. Ensemble Mean
2.5. Analysis—Comparison of Evapotranspiration Products
2.6. Change Analysis
2.6.1. Land Use/Land Cover and Evapotranspiration Rates
2.6.2. Watershed Restoration at the Research Ranch
2.6.3. Partitioning Evaporation and Transpiration
2.7. Identifying Evapotranspiration Associations with Precipitation
3. Results
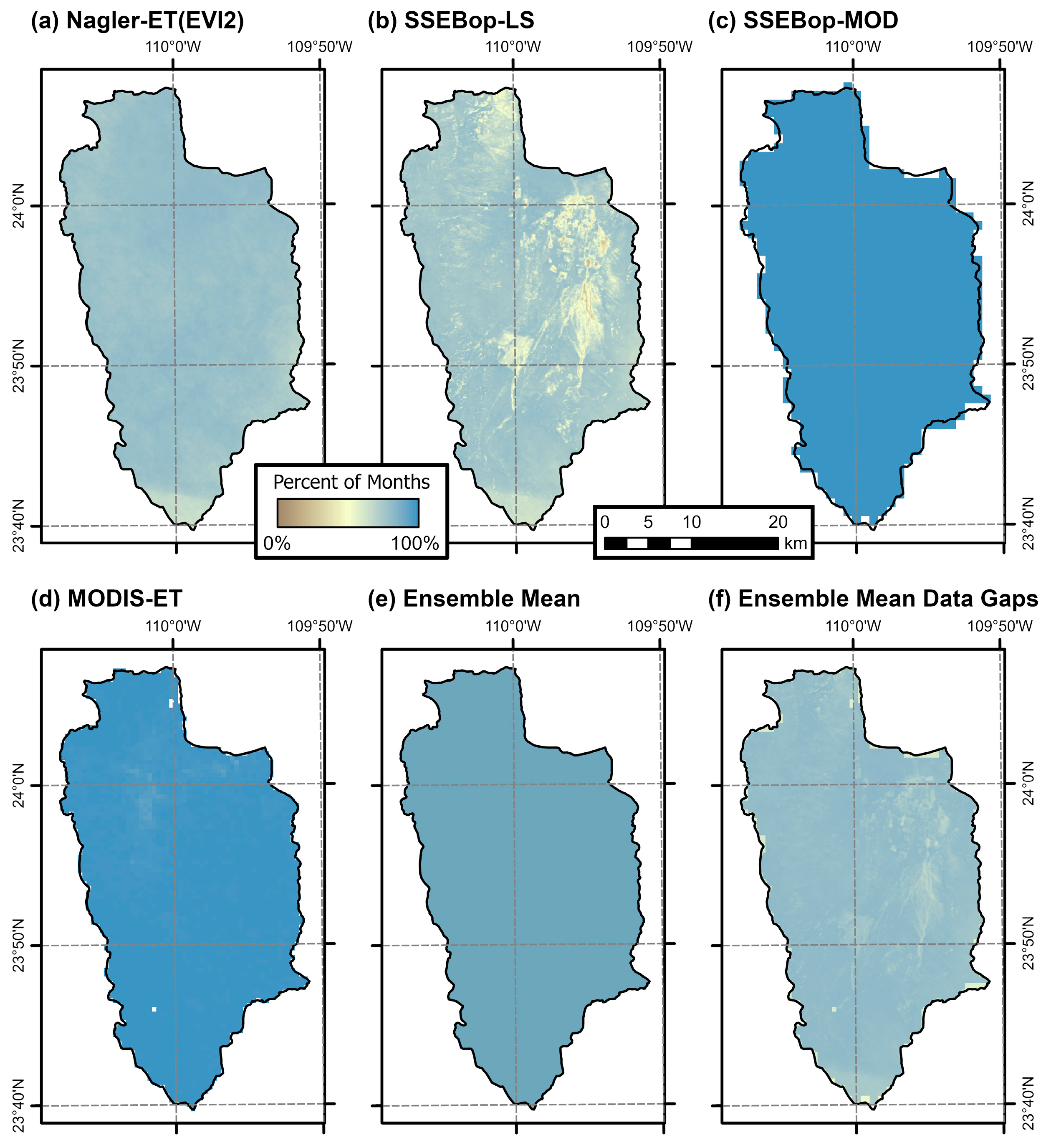
3.1. Remote Sensing Data Coverage
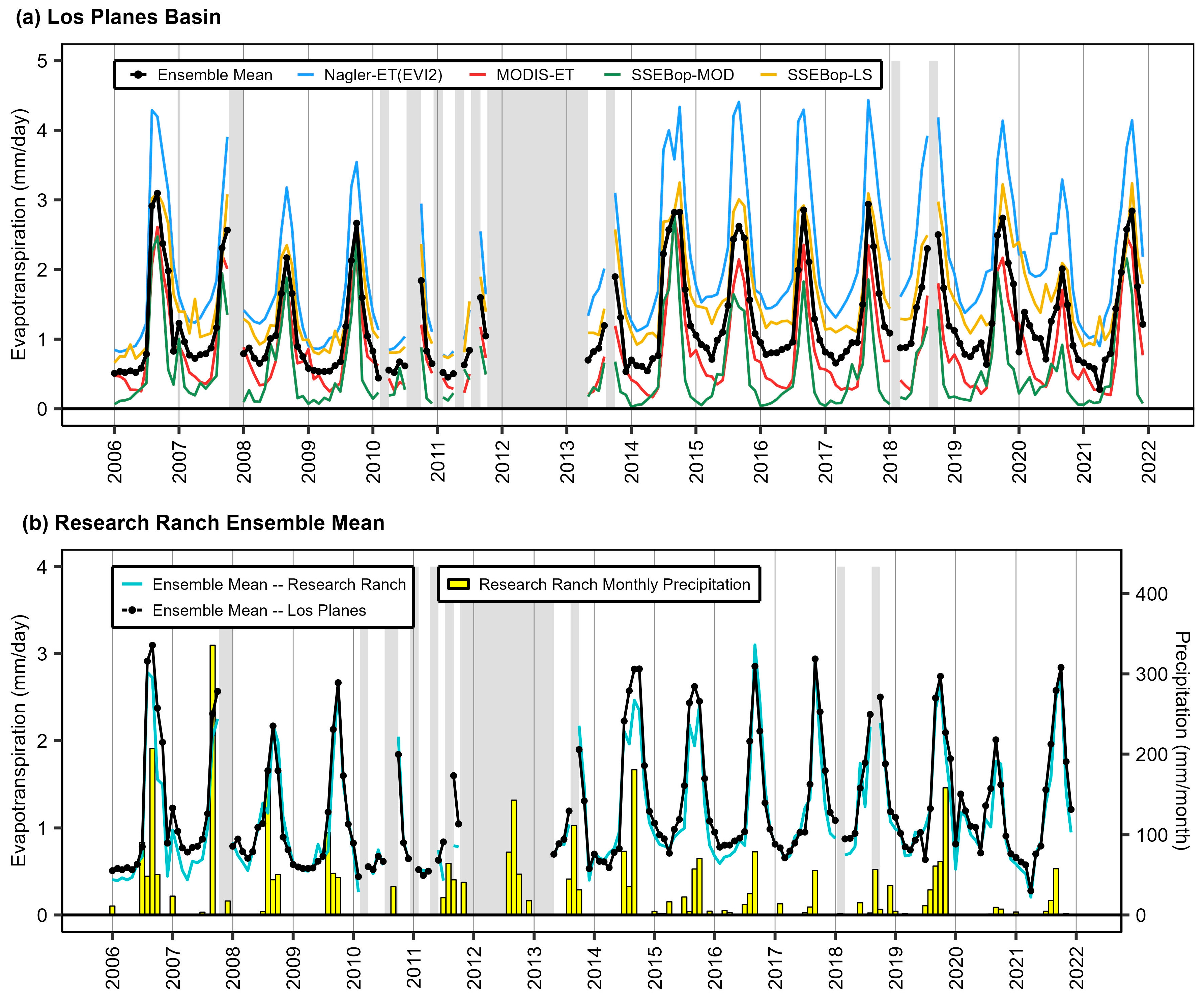
3.2. Comparison of Remote Sensing Evapotranspiration Products
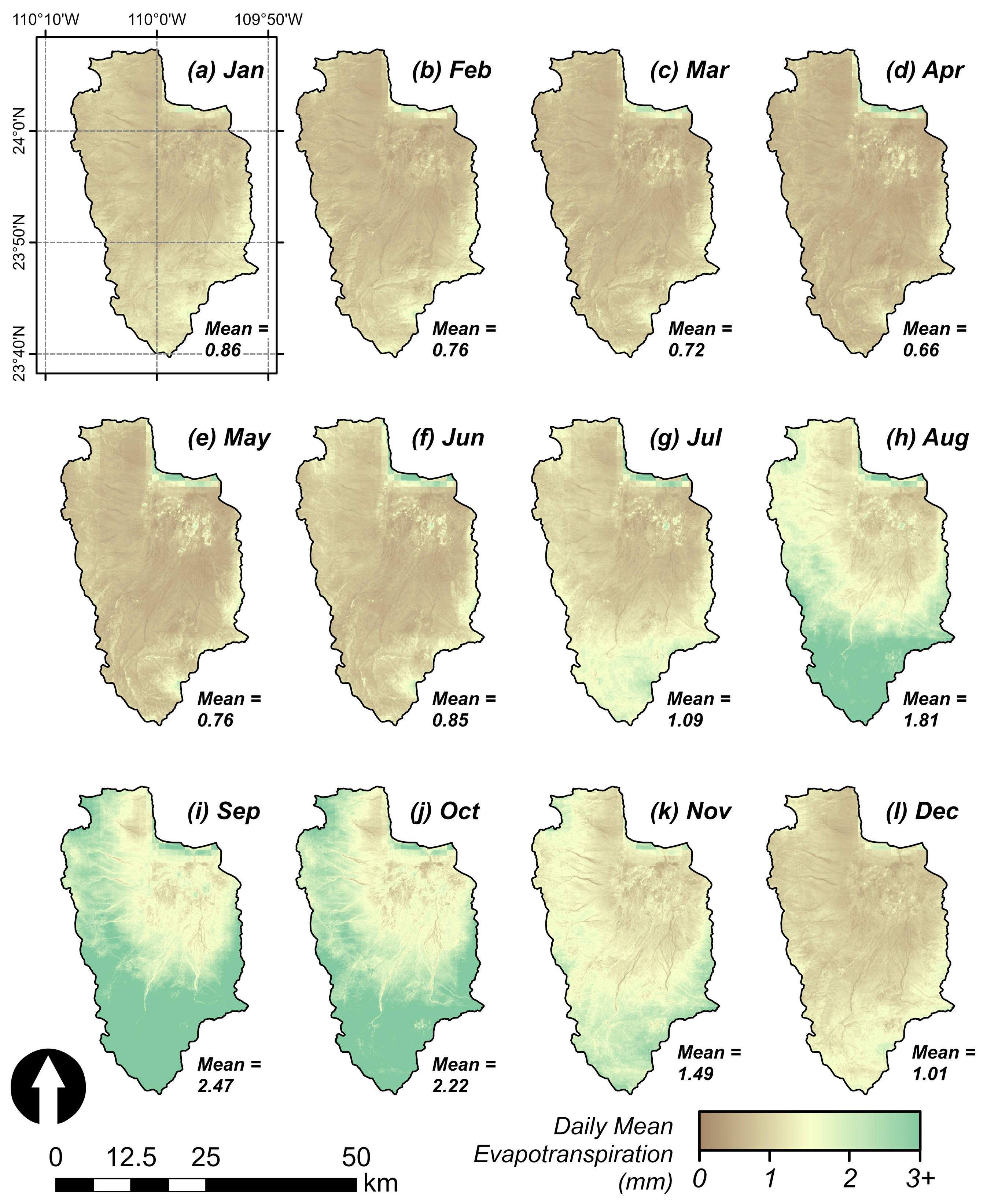
3.3. Monthly Mean Variability
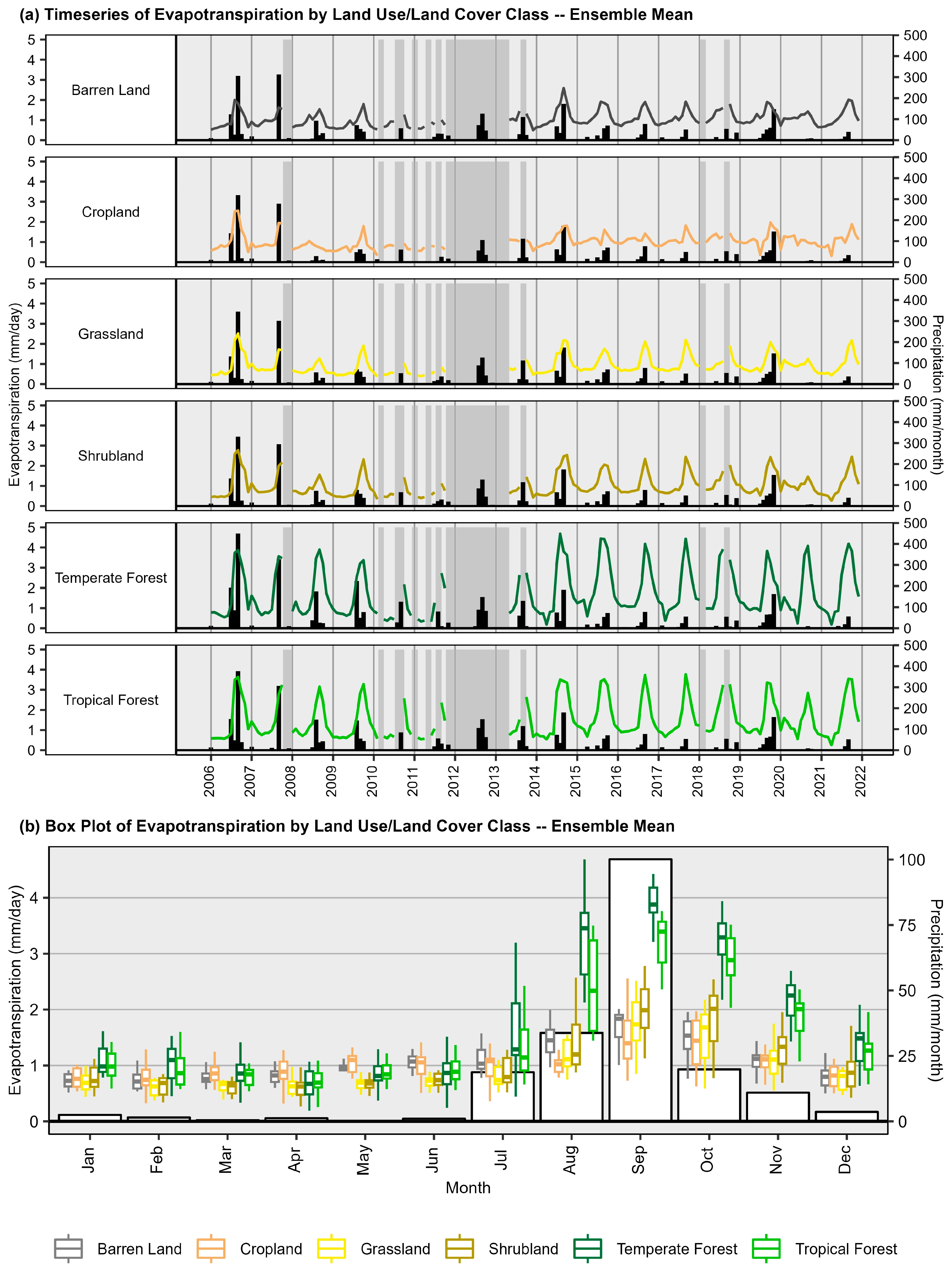
3.4. Land Use/Land Cover Variability
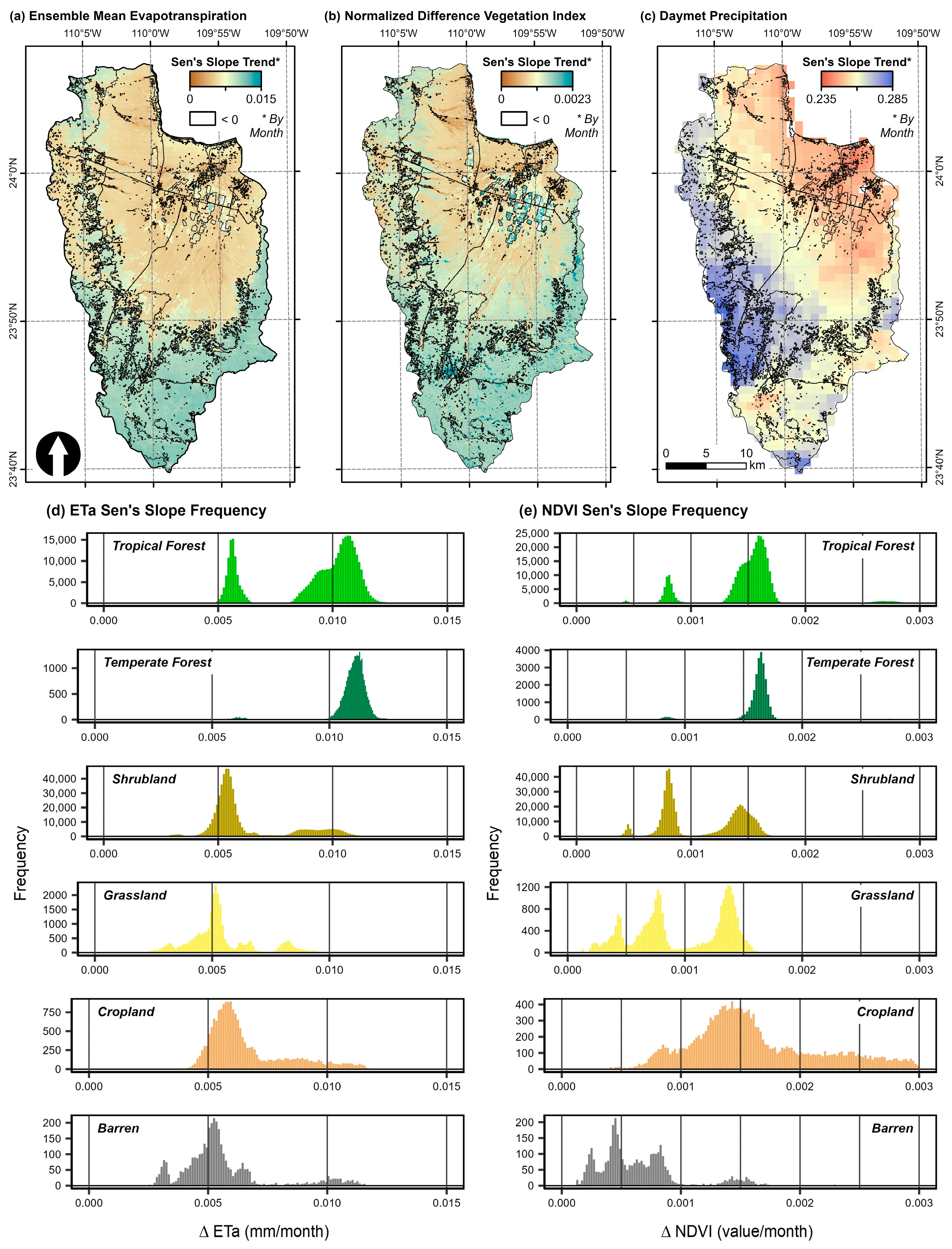
3.5. Research Ranch Watershed Case Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Using a Spatially Explicit EMET Product
4.2. Restoration Landscape
4.3. Calibration with Water Budget Models
4.4. Climate and Other Drivers
4.5. Limitations and Challenges with Remote Sensing Monitoring
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norman, L.M.; Villarreal, M.L.; Niraula, R.; Haberstich, M.; Wilson, N.R. Modelling Development of Riparian Ranchlands Using Ecosystem Services at the Aravaipa Watershed, SE Arizona. Land 2019, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.; Srivastava, P.; Piles, M.; Pearson, S. Earth Observation-Based Operational Estimation of Soil Moisture and Evapotranspiration for Agricultural Crops in Support of Sustainable Water Management. Sustainability 2018, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanniarachchi, S.; Sarukkalige, R. A Review on Evapotranspiration Estimation in Agricultural Water Management: Past, Present, and Future. Hydrology 2022, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Ren, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Effects of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change on Evapotranspiration and Water Yield in China During 1900–2000. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Brinkerhoff, F.; Gwilliam, E.; Guertin, D.P.; Callegary, J.; Goodrich, D.C.; Nagler, P.L.; Gray, F. Hydrologic Response of Streams Restored with Check Dams in the Chiricahua Mountains, Arizona. River Res. Applic. 2016, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Niraula, R. Model Analysis of Check Dam Impacts on Long-Term Sediment and Water Budgets in Southeast Arizona, USA. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2016, 16, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of Landsat Thermal Imagery in Monitoring Evapotranspiration and Managing Water Resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Schauer, M.; Friedrichs, M.; Velpuri, N.M.; Singh, R.K. Satellite-Based Water Use Dynamics Using Historical Landsat Data (1984–2014) in the Southwestern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, B.; Piasecki, M. Availability and Coverage of Hydrologic Data in the US Geological Survey National Water Information System (NWIS) and US Environmental Protection Agency Storage and Retrieval System (STORET). Earth Sci. Inf. 2008, 1, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. USGS Surface-Water Data for the Nation. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis (accessed on 23 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.L. Evapotranspiration and Droughts. In National Water Summary 1988-89—Hydrologic Events and Floods and Droughts; Paulson, R.W., Chase, E.B., Roberts, R.S., Moody, D.W., Compilers, Eds.; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1991; pp. 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Tian, S.; Wei, J.; Jia, S.; Song, Z. Multi-Scale Evaluation of Global Evapotranspiration Products Derived from Remote Sensing Images: Accuracy and Uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2022, 611, 127982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, M.B. Potential Evapotranspiration. In Principles of Soil and Plant Water Relations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 501–514. ISBN 978-0-12-420022-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, N.J.; Blad, B.L.; Verma, S.B. Microclimate: The Biological Environment, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998; ISBN 978-92-5-104219-9. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, K.; Li, Y.; Horton, R.; Feng, H. Similarity and Difference of Potential Evapotranspiration and Reference Crop Evapotranspiration—A Review. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Barreto-Muñoz, A.; Sall, I.; Lurtz, M.R.; Didan, K. Riparian Plant Evapotranspiration and Consumptive Use for Selected Areas of the Little Colorado River Watershed on the Navajo Nation. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Friedrichs, M.; Morton, C.; Parrish, G.E.L.; Schauer, M.; Khand, K.; Kagone, S.; Boiko, O.; Huntington, J. Mapping Actual Evapotranspiration Using Landsat for the Conterminous United States: Google Earth Engine Implementation and Assessment of the SSEBop Model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 275, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and Environment. In Symposia of the Society for Experimental Biology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1965; Volume 19, pp. 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, W.J. Wallace Evaporation from Sparse Crops—An Energy Combination Theory. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the Assessment of Surface Heat Flux and Evaporation Using Large-Scale Parameters. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turc, L. Water Requirements Assessment of Irrigation, Potential Evapotranspiration: Simplified and Updated Climatic Formula. Ann. Agron. 1961, 12, 13–49. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, D.K.; Pringle, H.C., III. Evaluation of Alternative Methods for Estimating Reference Evapotranspiration. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, R.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of 18 Models for Calculating Potential Evapotranspiration in Different Climatic Zones of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Glenn, E.; Nguyen, U.; Scott, R.; Doody, T. Estimating Riparian and Agricultural Actual Evapotranspiration by Reference Evapotranspiration and MODIS Enhanced Vegetation Index. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3849–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Morino, K.; Murray, R.S.; Osterberg, J.; Glenn, E. An Empirical Algorithm for Estimating Agricultural and Riparian Evapotranspiration Using MODIS Enhanced Vegetation Index and Ground Measurements of ET. I. Description of Method. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 1273–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarchow, C.J.; Waugh, W.J.; Nagler, P.L. Calibration of an Evapotranspiration Algorithm in a Semiarid Sagebrush Steppe Using a 3-ha Lysimeter and Landsat Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Data. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Jetton, A.; Fleming, J.; Didan, K.; Glenn, E.; Erker, J.; Morino, K.; Milliken, J.; Gloss, S. Evapotranspiration in a Cottonwood (Populus fremontii) Restoration Plantation Estimated by Sap Flow and Remote Sensing Methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 144, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, N.; Nouri, H.; Didan, K.; Barreto-Muñoz, A.; Chavoshi Borujeni, S.; Salemi, H.; Opp, C.; Siebert, S.; Nagler, P. Estimating Actual Evapotranspiration over Croplands Using Vegetation Index Methods and Dynamic Harvested Area. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Barreto-Muñoz, A.; Chavoshi Borujeni, S.; Jarchow, C.J.; Gómez-Sapiens, M.M.; Nouri, H.; Herrmann, S.M.; Didan, K. Ecohydrological Responses to Surface Flow across Borders: Two Decades of Changes in Vegetation Greenness and Water Use in the Riparian Corridor of the Colorado River Delta. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 4851–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courault, D.; Seguin, B.; Olioso, A. Review on Estimation of Evapotranspiration from Remote Sensing Data: From Empirical to Numerical Modeling Approaches. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A Review of Current Methodologies for Regional Evapotranspiration Estimation from Remotely Sensed Data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ge, Y.; Xu, T.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F. Upscaling Evapotranspiration Measurements from Multi-Site to the Satellite Pixel Scale over Heterogeneous Land Surfaces. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230–231, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Morino, K.; Didan, K.; Erker, J.; Osterberg, J.; Hultine, K.R.; Glenn, E.P. Wide-area Estimates of Saltcedar (Tamarix Spp.) Evapotranspiration on the Lower Colorado River Measured by Heat Balance and Remote Sensing Methods. Ecohydrology 2009, 2, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Leake, S.; Nagler, P.L.; Artan, G.; Dickinson, J.; Cordova, J.T.; Glenn, E.P. Estimating Basin Scale Evapotranspiration (ET) by Water Balance and Remote Sensing Methods. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 4037–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, A.J.; Fisher, J.B.; Goulden, M.L.; Colliander, A.; Halverson, G.; Tu, K.; Famiglietti, J.S. SMAP Soil Moisture Improves Global Evapotranspiration. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Mattersdorf, G.; Beringer, J.; Hutley, L.B.; Leuning, R.; Pipunic, R.C.; Sherman, B.S. Scaling of Potential Evapotranspiration with MODIS Data Reproduces Flux Observations and Catchment Water Balance Observations across Australia. J. Hydrol. 2009, 369, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S.; Carlson, T.N. Uncertainties in Latent Heat Flux Measurement and Estimation: Implications for Using a Simplified Approach with Remote Sensing Data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 30, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. An Intercomparison of Regional Latent Heat Flux Estimation Using Remote Sensing Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S.W.; Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Moreno, A. User’s Guide—MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration (ET) Product (MOD16A2/A3 and Year-End Gap-Filled MOD16A2GF/A3GF) NASA Earth Observing System MODIS Land Algorithm (For Collection 6). 2019. Available online: https://modis-land.gsfc.nasa.gov/pdf/MOD16UsersGuideV2.022019.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- NASA EARTHDATA. MODIS/Terra Net Evapotranspiration 8-Day L4 Global 500 m SIN Grid. 2023. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod16a2v061/ (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Fisher, J.B.; Lee, B.; Purdy, A.J.; Halverson, G.H.; Dohlen, M.B.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Wang, A.; Anderson, R.G.; Aragon, B.; Arain, M.A.; et al. ECOSTRESS: NASA’s Next Generation Mission to Measure Evapotranspiration from the International Space Station. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA ECOSTRESS. Available online: https://ecostress.jpl.nasa.gov/instrument (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- NASA EARTHDATA. Application for Extracting and Exploring Analysis Ready Samples (AρρEEARS). Available online: https://appeears.earthdatacloud.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Senay, G.B.; Bohms, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gowda, P.H.; Velpuri, N.M.; Alemu, H.; Verdin, J.P. Operational Evapotranspiration Mapping Using Remote Sensing and Weather Datasets: A New Parameterization for the SSEB Approach. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Kagone, S.; Velpuri, N.M. Operational Global Actual Evapotranspiration: Development, Evaluation, and Dissemination. Sensors 2020, 20, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senay, G.B.; Parrish, G.E.L.; Schauer, M.; Friedrichs, M.; Khand, K.; Boiko, O.; Kagone, S.; Dittmeier, R.; Arab, S.; Ji, L. Improving the Operational Simplified Surface Energy Balance Evapotranspiration Model Using the Forcing and Normalizing Operation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiminia, H.; Salehi, B.; Mahdianpari, M.; Quackenbush, L.; Adeli, S.; Brisco, B. Google Earth Engine for Geo-Big Data Applications: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 164, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Diao, C.; Xian, G.; Yin, D.; Lu, Y.; Zou, S.; Erickson, T.A. A Summary of the Special Issue on Remote Sensing of Land Change Science with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 112002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, N.; Nouri, H.; Didan, K.; Barreto-Muñoz, A.; Chavoshi Borujeni, S.; Opp, C.; Nagler, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Siebert, S. Mapping Vegetation Index-Derived Actual Evapotranspiration across Croplands Using the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bhattarai, N.; Mallick, K.; Liu, Q.; Tang, L.; Im, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J. On the Use of Machine Learning Based Ensemble Approaches to Improve Evapotranspiration Estimates from Croplands across a Wide Environmental Gradient. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 298–299, 108308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Abbaszadeh, P.; Moradkhani, H. An Ensemble Data Assimilation Approach to Improve Farm-Scale Actual Evapotranspiration Estimation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 321, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, F.S.; Huntington, J.; Grimm, R.; Herring, J.; Hall, M.; Rollison, D.; Erickson, T.; Allen, R.; Anderson, M.; Fisher, J.B.; et al. OpenET: Filling a Critical Data Gap in Water Management for the Western United States. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 58, 971–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinukollu, R.K.; Meynadier, R.; Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F. Multi-Model, Multi-Sensor Estimates of Global Evapotranspiration: Climatology, Uncertainties and Trends. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3993–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.S. Whose Probabilities? Predicting Climate Change with Ensembles of Models. Philos. Sci. 2010, 77, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainforth, D.A.; Downing, T.E.; Washington, R.; Lopez, A.; New, M. Issues in the Interpretation of Climate Model Ensembles to Inform Decisions. Philos Trans. R. Soc. A 2007, 365, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Mickley, L.J.; Logan, J.A.; Kaplan, J.O. Ensemble Projections of Wildfire Activity and Carbonaceous Aerosol Concentrations over the Western United States in the Mid-21st Century. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Batelaan, O.; Fadaee, M.; Hinkelmann, R. Ensemble Machine Learning Paradigms in Hydrology: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, J.M.; Huntington, J.L.; Melton, F.S.; Allen, R.; Anderson, M.; Fisher, J.B.; Kilic, A.; Ruhoff, A.; Senay, G.B.; Minor, B.; et al. Assessing the Accuracy of OpenET Satellite-Based Evapotranspiration Data to Support Water Resource and Land Management Applications. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Jing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G. Response of Evapotranspiration to Changes in Land Use and Land Cover and Climate in China during 2001–2013. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596–597, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Hill, M.J.; Leys, J.; Heidenreich, S. Vegetation Cover Dependence on Accumulated Antecedent Precipitation in Australia: Relationships with Photosynthetic and Non-Photosynthetic Vegetation Fractions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, S.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, D.; Li, Z. Ecological Restoration Intensifies Evapotranspiration in the Kubuqi Desert. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loheide, S.P.; Gorelick, S.M. A Local-Scale, High-Resolution Evapotranspiration Mapping Algorithm (ETMA) with Hydroecological Applications at Riparian Meadow Restoration Sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 182–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, R.M.; Waddington, J.M.; Price, J.S. Ecosystem Scale Evapotranspiration and Net CO2 Exchange from a Restored Peatland. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 2839–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingming, W.; Shan, J.; Jiaqi, Z.; Guohua, H.; Yong, Z.; Yongnan, Z.; Xin, H.; Haihong, L.; Lizhen, W.; Fan, H.; et al. Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Evapotranspiration Water Consumption in Mountainous Areas and Assessment of Its Remaining Restoration Space. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Lal, R.; Wohl, E.; Fairfax, E.; Gellis, A.C.; Pollock, M.M. Natural Infrastructure in Dryland Streams (NIDS) Can Establish Regenerative Wetland Sinks That Reverse Desertification and Strengthen Climate Resilience. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairfax, E.; Small, E.E. Using Remote Sensing to Assess the Impact of Beaver Damming on Riparian Evapotranspiration in an Arid Landscape. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.; Larsen, J.R.; Lane, S.N. Dam Builders and Their Works: Beaver Influences on the Structure and Function of River Corridor Hydrology, Geomorphology, Biogeochemistry and Ecosystems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 218, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiso, S. 4—The Significance of Subsurface Water Storage in Kenya. In Management of Aquifer Recharge and Subsurface Storage; Making Better Use of Our Largest Reservoir; Tuinhof, A., Heederik, J.P., Eds.; Netherlands National Committee for the IAH: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, L.M.; Villarreal, M.; Pulliam, H.R.; Minckley, R.; Gass, L.; Tolle, C.; Coe, M. Remote Sensing Analysis of Riparian Vegetation Response to Desert Marsh Restoration in the Mexican Highlands. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.R.; Norman, L.M. Analysis of Vegetation Recovery Surrounding a Restored Wetland Using the Normalized Difference Infrared Index (NDII) and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 3243–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.R.; Norman, L.M. Five Year Analyses of Vegetation Response to Restoration Using Rock Detention Structures in Southeastern Arizona, United States. Environ. Manag. 2022, 71, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, L.M. Ecosystem Services of Riparian Restoration: A Review of Rock Detention Structures in the Madrean Archipelago Ecoregion. Air Soil Water Res. 2020, 13, 117862212094633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Lane, J.W.; Mack, T.; Valder, J.; Briggs, M.A.; Johnson, C.; McDowell, J.; Petrakis, R.E.; Anides Morales, A.; Villarreal, M.L.; et al. Water Cycle Augmentation Project, Baja California Sur, Mexico. In Proceedings of the National Ground Water Association (NGWA) Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 24 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Western Geographic Science Center Research in the Los Planes Watershed—Water Cycle Augmentation. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/western-geographic-science-center/science/research-los-planes-watershed-water-cycle (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- CEC Commission for Environmental Cooperation. North American Land Change Monitoring System; Commission for Environmental Cooperation: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, J.R.; Turner, R.M. Seasonal Precipitation Regimes in Baja California, Mexico. JSTOR 1965, 47, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Falcón, A.; Troyo-Diguez, E.; Fraga-Palomino, H.; Vega-Mayagoiti, J. Location of the Rainfall Recharge Areas in the Basin of La Paz, BCS, México. In Water Resources Planning, Development and Management; Wurbs, R., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1092-7. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, S.C.; Touchan, R.; Swetnam, T.W. A Tree-Ring Reconstruction of Past Precipitation for Baja California Sur, Mexico. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfán, L.M.; D’Sa, E.J.; Liu, K.; Rivera-Monroy, V.H. Tropical Cyclone Impacts on Coastal Regions: The Case of the Yucatán and the Baja California Peninsulas, Mexico. Estuaries Coasts 2014, 37, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knabb, R.D. Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Henriette; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Beven, J.L. Tropical Cyclone Report—Hurricane Jimena; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Petrakis, R.E.; Norman, L.M.; Vaughn, K.; Pritzlaff, R.; Weaver, C.; Rader, A.; Pulliam, H.R. Hierarchical Clustering for Paired Watershed Experiments: Case Study in Southeastern Arizona, U.S.A. Water 2021, 13, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; McVicar, T.R.; McCabe, M.F. Estimating Land Surface Evaporation: A Review of Methods Using Remotely Sensed Surface Temperature Data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, Z.-L. A Framework of Correcting the Angular Effect of Land Surface Temperature on Evapotranspiration Estimation in Single-Source Energy Balance Models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 283, 113306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a Two-Band Enhanced Vegetation Index without a Blue Band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.J.; Roy, D.P.; Arab, S.; Barnes, C.; Vermote, E.; Hulley, G.; Gerace, A.; Choate, M.; Engebretson, C.; Micijevic, E.; et al. The 50-Year Landsat Collection 2 Archive. Sci. Remote Sens. 2023, 8, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat Collection 2 Provisional Actual Evapotranspiration Science Product. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-collection-2-provisional-actual-evapotranspiration-science-product (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Markham, B.L.; Storey, J.C.; Williams, D.L.; Irons, J.R. Landsat Sensor Performance: History and Current Status. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2691–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, H.F.; Criddle, W.D. Determining Water Requirements in Irrigated Areas from Climatological and Irrigation Data; Forgotten Books: London, UK, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Chapter 3: Crop Water Needs. In Irrigation Water Management: Irrigation Water Needs; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, M.M.; Shrestha, R.; Wei, Y.; Thornton, P.E.; Kao, S.; Wilson, B.E. Daymet: Daily Surface Weather Data on a 1-Km Grid for North America, Version 4; ORNL DAAC: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey. EROS Science Processing Architecture on Demand Interface. Available online: https://espa.cr.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Justice, C.O.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Masuoka, E.; Wolfe, R.E.; Saleous, N.; Roy, D.P.; Morisette, J.T. An Overview of MODIS Land Data Processing and Product Status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. USGS FEWS NET Data Portal. Available online: https://earlywarning.usgs.gov/fews (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Korkin, S.; Huang, D. MODIS Collection 6 MAIAC Algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5741–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Fosnight, E.A.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.G.; Roy, D.P. The Global Landsat Archive: Status, Consolidation, and Direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA. Landsat 5 Mission in Jeopardy. Available online: https://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/article/landsat-5-mission-in-jeopardy/ (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Petrakis, R.E.; Norman, L.M.; Villarreal, M.L.; Senay, G.B.; Friedrichs, M.O.; Cassassuce, F.; Gomis, F.; Nagler, P.L. Monthly Ensemble Mean Evapotranspiration (EMET) Product for the Los Planes Basin in Baja California Sur, Mexico from January 2006 through December 2021: U.S. Geological Survey Data Release. 20 January 2024. Available online: https://www.sciencebase.gov/catalog/item/656e22dcd34e7ca10833f963 (accessed on 7 February 2024). [CrossRef]
- ESRI ArcMap Desktop 2020. Available online: https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/products/arcgis-desktop/resources (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- R Core Team R Software 2022. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, R.E.; van Leeuwen, W.; Villarreal, M.L.; Tashjian, P.; Dello Russo, R.; Scott, C. Historical Analysis of Riparian Vegetation Change in Response to Shifting Management Objectives on the Middle Rio Grande. Land 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gentine, P.; Lin, C.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. A Simple and Objective Method to Partition Evapotranspiration into Transpiration and Evaporation at Eddy-Covariance Sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yoshimura, K.; Wang, L.; Miralles, D.G.; Jasechko, S.; Lee, X. Revisiting the Contribution of Transpiration to Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G. Partitioning Evapotranspiration Based on the Concept of Underlying Water Use Efficiency. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 1160–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilagyi, J.; Rundquist, D.C.; Gosselin, D.C.; Parlange, M.B. NDVI Relationship to Monthly Evaporation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1753–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbrecht, J.; Van Liew, M.; Brown, G.O. Trends in Precipitation, Streamflow, and Evapotranspiration in the Great Plains of the United States. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2004, 9, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Kagone, S.; Parrish, G.E.; Budde, M.E.; Rowland, J. SSEBop Evapotranspiration Data from 2012 to Present: Dekadal (10-Day), Monthly, Seasonal, and Annual Time Scales. 2023. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/data/ssebop-evapotranspiration-data-2012-present-dekadal-10-day-monthly-seasonal-and-annual-time (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Petrakis, R.E.; Soulard, C.E.; Waller, E.K.; Walker, J.J. Analysis of Surface Water Trends for the Conterminous United States Using MODIS Satellite Data, 2003–2019. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Ju, J.; Lewis, P.; Schaaf, C.; Gao, F.; Hansen, M.; Lindquist, E. Multi-Temporal MODIS–Landsat Data Fusion for Relative Radiometric Normalization, Gap Filling, and Prediction of Landsat Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3112–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.J.; De Beurs, K.M.; Wynne, R.H.; Gao, F. Evaluation of Landsat and MODIS Data Fusion Products for Analysis of Dryland Forest Phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, G.; Shi, H.; Arab, S.; Mueller, C.; Hussain, R.; Sayler, K.; Howard, D. Improving Temporal Frequency of Landsat Surface Temperature Products Using the Gap-Filling Algorithm; Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. MODIS Vegetation Index Products (NDVI and EVI). Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/mod13.php (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global Estimates of the Land–Atmosphere Water Flux Based on Monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II Data, Validated at 16 FLUXNET Sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Yang, Y.; Xue, J.; Knipper, K.R.; Yang, Y.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Hulley, G.; et al. Interoperability of ECOSTRESS and Landsat for Mapping Evapotranspiration Time Series at Sub-Field Scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Feng, Y.; Wu, J.; He, X.; Liang, S.; Jiang, X.; De Oliveira, G.; Qiu, J.; Zeng, Z. Evaluation of ECOSTRESS Evapotranspiration Estimates over Heterogeneous Landscapes in the Continental US. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Senay, G.B.; Singh, R.K.; Verdin, J.P. Uncertainty Analysis of the Operational Simplified Surface Energy Balance (SSEBop) Model at Multiple Flux Tower Sites. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zayed, I.S.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Satellite-Based Evapotranspiration over Gezira Irrigation Scheme, Sudan: A Comparative Study. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, L.M.; Callegary, J.B.; Lacher, L.; Wilson, N.R.; Fandel, C.; Forbes, B.T.; Swetnam, T. Modeling Riparian Restoration Impacts on the Hydrologic Cycle at the Babacomari Ranch, SE Arizona, USA. Water 2019, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.A.; Pérez-Priego, O.; Zhou, S.; Poyatos, R.; Zhang, Y.; Blanken, P.D.; Gimeno, T.E.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Desai, A.R.; Gioli, B.; et al. Ecosystem Transpiration and Evaporation: Insights from Three Water Flux Partitioning Methods across FLUXNET Sites. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 6916–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoy, P.C.; El-Madany, T.S.; Fisher, J.B.; Gentine, P.; Gerken, T.; Good, S.P.; Klosterhalfen, A.; Liu, S.; Miralles, D.G.; Perez-Priego, O.; et al. Reviews and Syntheses: Turning the Challenges of Partitioning Ecosystem Evaporation and Transpiration into Opportunities. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 3747–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, G.; Zha, T.; Wang, L.; An, J.; Shao, Y. Multi-Temporal Variations in Evapotranspiration Partitioning and Its Controlling Factors of a Xerophytic Shrub Ecosystem. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.; Agam, N.; Lazarovitch, N.; Heitman, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Ben-Gal, A. A Review of Approaches for Evapotranspiration Partitioning. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L.; Knowles, J.F.; Nelson, J.A.; Gentine, P.; Li, X.; Barron-Gafford, G.; Bryant, R.; Biederman, J.A. Water Availability Impacts on Evapotranspiration Partitioning. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 297, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Good, S.P.; Caylor, K.K. Global Synthesis of Vegetation Control on Evapotranspiration Partitioning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6753–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, P.; Wagle, P.; Kumar, M.; Banerjee, T.; Neel, J.P.S. Vegetation Index-Based Partitioning of Evapotranspiration Is Deficient in Grazed Systems. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR032067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz-Yaseef, N.; Rotenberg, E.; Yakir, D. Effects of Spatial Variations in Soil Evaporation Caused by Tree Shading on Water Flux Partitioning in a Semi-Arid Pine Forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, M.; Senay, G.; Sanford, W. Combining Remote Sensing and Water-Balance Evapotranspiration Estimates for the Conterminous United States. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Response of Mean Annual Evapotranspiration to Vegetation Changes at Catchment Scale. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part I: Model Development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westenbroek, S.M.; Engott, J.A.; Kelson, V.A.; Hunt, R.J. SWB Version 2.0—A Soil-Water-Balance Code for Estimating Net Infiltration and Other Water-Budget Components. In Book 6, Modeling Techniques; Chapter 59 of Section A, Groundwater; U.S. Department of the Interior—U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, R.L.; Cable, W.L.; Huxman, T.E.; Nagler, P.L.; Hernandez, M.; Goodrich, D.C. Multiyear Riparian Evapotranspiration and Groundwater Use for a Semiarid Watershed. J. Arid Environ. 2008, 72, 1232–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
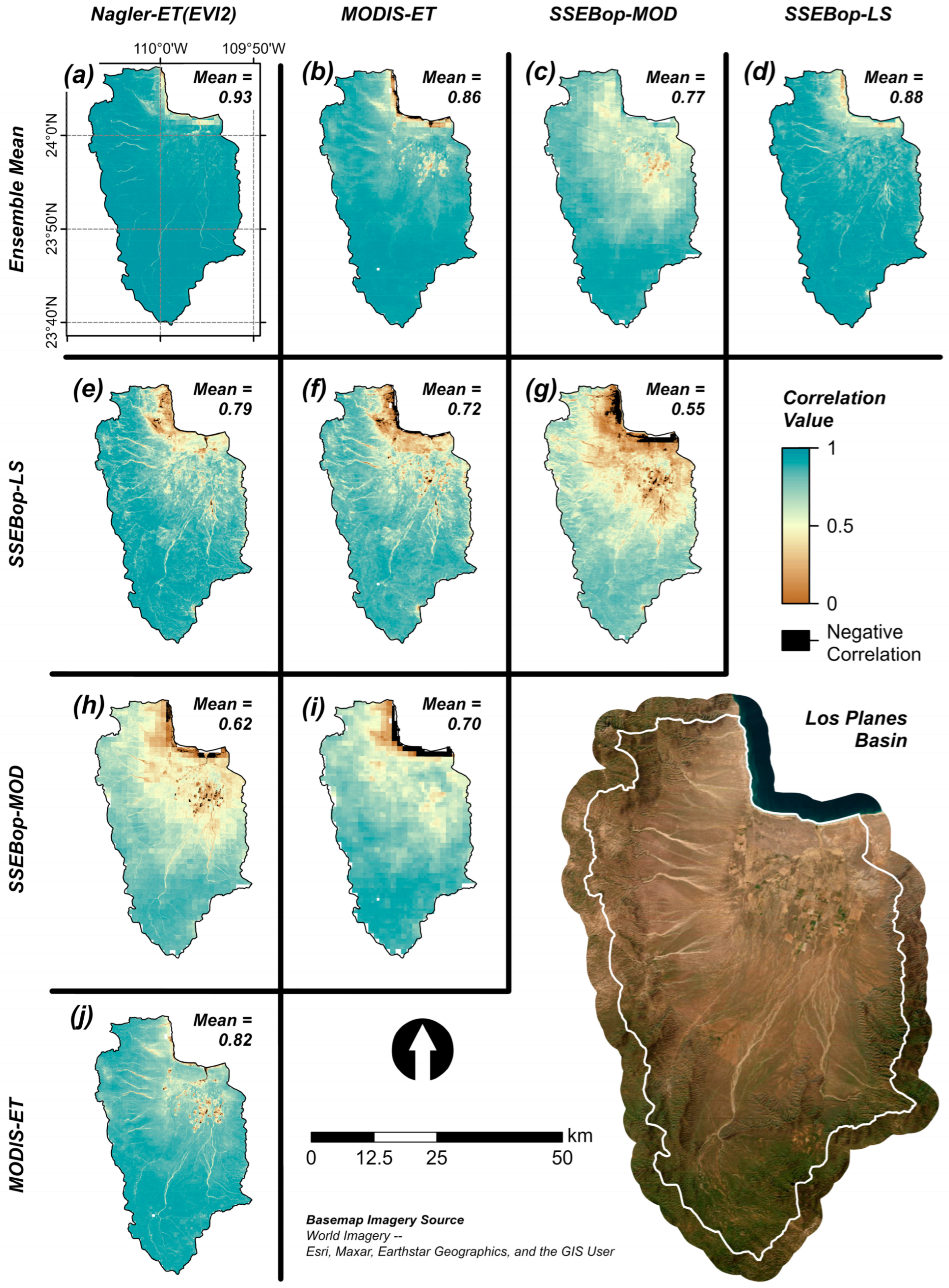

| ETa Algorithm | Source Spatial Resolution | Source Temporal Resolution | Source Temporal Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nagler-ET(EVI2) | 30 m | 16 day | August 1982–December 2021 |
| SSEBop-LS | 30 m | 16 day | August 1982–Present Day * |
| SSEBop-MOD | 1000 m | 1 month | January 2003–April 2022 |
| MODIS-ET | 500 m | 8 day | January 2003–Present Day * |
| Data Harmonization | 30 m | 1 month | January 2006–December 2021 |
| Ensemble Mean (EMET; ETa) | Nagler-ET(EVI2) | SSEBop-LS | SSEBop-MOD | MODIS-ET | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensemble Mean (EMET; ETa) | Cor = 1 RMSE = 0 MAE = 0 | ||||
| Nagler-ET(EVI2) | Cor = 0.97 RMSE = 0.92 MAE = 0.84 | Cor = 1 RMSE = 0 MAE = 0 | |||
| SSEBop-LS | Cor = 0.95 RMSE = 0.43 MAE = 0.38 | Cor = 0.97 RMSE = 0.61 MAE = 0.49 | Cor = 1 RMSE = 0 MAE = 0 | ||
| SSEBop-MOD | Cor = 0.88 RMSE = 0.75 MAE = 0.67 | Cor = 0.8 RMSE = 1.64 MAE = 1.51 | Cor = 0.76 RMSE = 1.13 MAE = 1.04 | Cor = 1 RMSE = 0 MAE = 0 | |
| MODIS-ET | Cor = 0.95 RMSE = 0.44 MAE = 0.4 | Cor = 0.9 RMSE = 1.34 MAE = 1.23 | Cor = 0.9 RMSE = 0.82 MAE = 0.76 | Cor = 0.87 RMSE = 0.42 MAE = 0.34 | Cor = 1 RMSE = 0 MAE = 0 |
| Evapotranspiration (EMET; ETa) (mm/day ∗ 1000) | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) (mm/day ∗ 1000) | Transpiration (T) (mm/day ∗ 1000) | Evaporation (E) (mm/day ∗ 1000) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Watershed | ’06–‘09 | ’10–‘21 | ’06–‘09 | ’10–‘21 | ’06–‘09 | ’10–‘21 | ’06–‘09 | ’10–‘21 |
| 1—Restoration | 0.290 0.300 | 0.185 * 0.003 | 0.033 0.404 | 0.033 * 0.001 | 0.040 0.759 | 0.094 * 0.008 | 0.145 0.240 | 0.056 * 0.008 |
| 2 | 0.234 0.384 | 0.134 * 0.011 | 0.031 0.333 | 0.019 * 0.012 | 0.041 0.678 | 0.048 0.063 | 0.124 0.329 | 0.052 * 0.027 |
| 3 | 0.248 0.395 | 0.136 * 0.017 | 0035 0.327 | 0.019 * 0.026 | 0.043 0.699 | 0.049 0.097 | 0.126 0.331 | 0.047 * 0.043 |
| 4—Control | 0.235 0.419 | 0.144 * 0.018 | 0.042 0.286 | 0.021 * 0.021 | 0.058 0.649 | 0.049 0.141 | 0.148 0.244 | 0.036 0.149 |
| 5 | 0.297 0.354 | 0.152 * 0.031 | 0.051 0.247 | 0.023 * 0.033 | 0.079 0.602 | 0.060 0.168 | 0.154 0.210 | 0.027 0.267 |
| Mean | 0.261 | 0.150 | 0.038 | 0.023 | 0.052 | 0.060 | 0.140 | 0.044 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrakis, R.E.; Norman, L.M.; Villarreal, M.L.; Senay, G.B.; Friedrichs, M.O.; Cassassuce, F.; Gomis, F.; Nagler, P.L. An Ensemble Mean Method for Remote Sensing of Actual Evapotranspiration to Estimate Water Budget Response across a Restoration Landscape. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122122
Petrakis RE, Norman LM, Villarreal ML, Senay GB, Friedrichs MO, Cassassuce F, Gomis F, Nagler PL. An Ensemble Mean Method for Remote Sensing of Actual Evapotranspiration to Estimate Water Budget Response across a Restoration Landscape. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(12):2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122122
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrakis, Roy E., Laura M. Norman, Miguel L. Villarreal, Gabriel B. Senay, MacKenzie O. Friedrichs, Florance Cassassuce, Florent Gomis, and Pamela L. Nagler. 2024. "An Ensemble Mean Method for Remote Sensing of Actual Evapotranspiration to Estimate Water Budget Response across a Restoration Landscape" Remote Sensing 16, no. 12: 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122122
APA StylePetrakis, R. E., Norman, L. M., Villarreal, M. L., Senay, G. B., Friedrichs, M. O., Cassassuce, F., Gomis, F., & Nagler, P. L. (2024). An Ensemble Mean Method for Remote Sensing of Actual Evapotranspiration to Estimate Water Budget Response across a Restoration Landscape. Remote Sensing, 16(12), 2122. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16122122







