Multi-Step Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Image and Feature Space for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Terrain Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A multi-step unsupervised domain adaptive SAR image terrain classification model framework based on Style Transformation and Domain Metrics (STDM-UDA) is proposed. The framework reduces the domain differences in both image space and feature space through two independent domain adaptation networks to enhance the generalization of the model.
- STDM-UDA transfers source domain knowledge to an unlabeled target domain, avoiding the need for labeled data in the target domain.
- The effectiveness of STDM-UDA is convincingly demonstrated by the terrain classification results in three high-resolution broad scenes without labels.
2. Related Works
2.1. SAR Image Terrain Classification
2.2. Deep Domain Adaptation in SAR Image
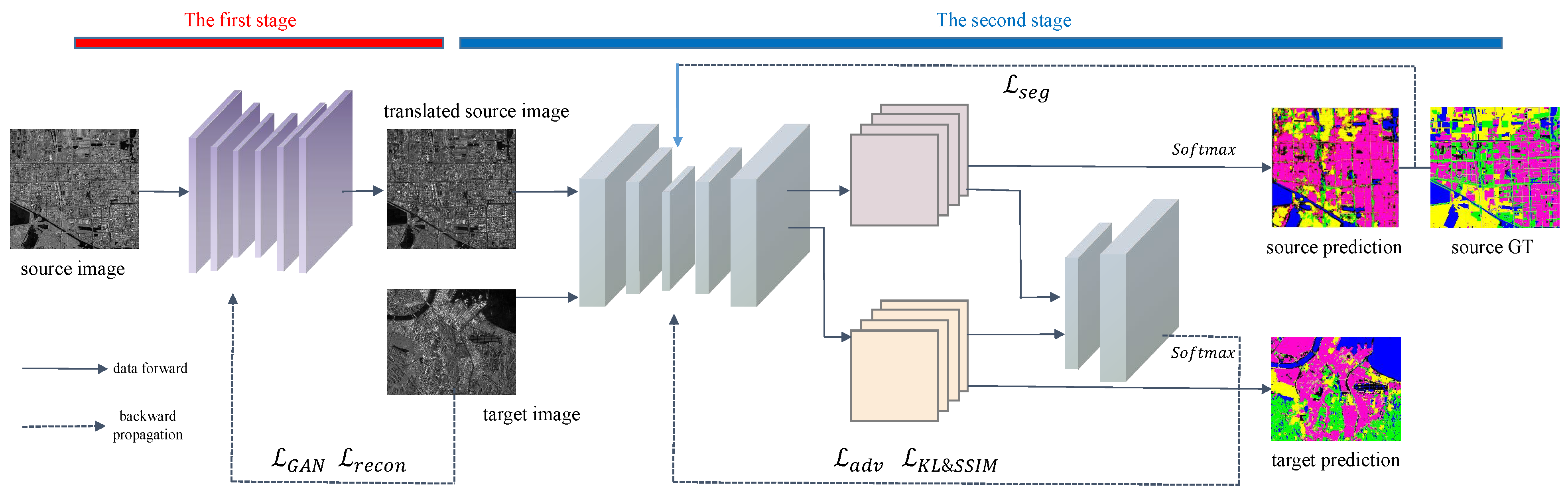
3. Methods
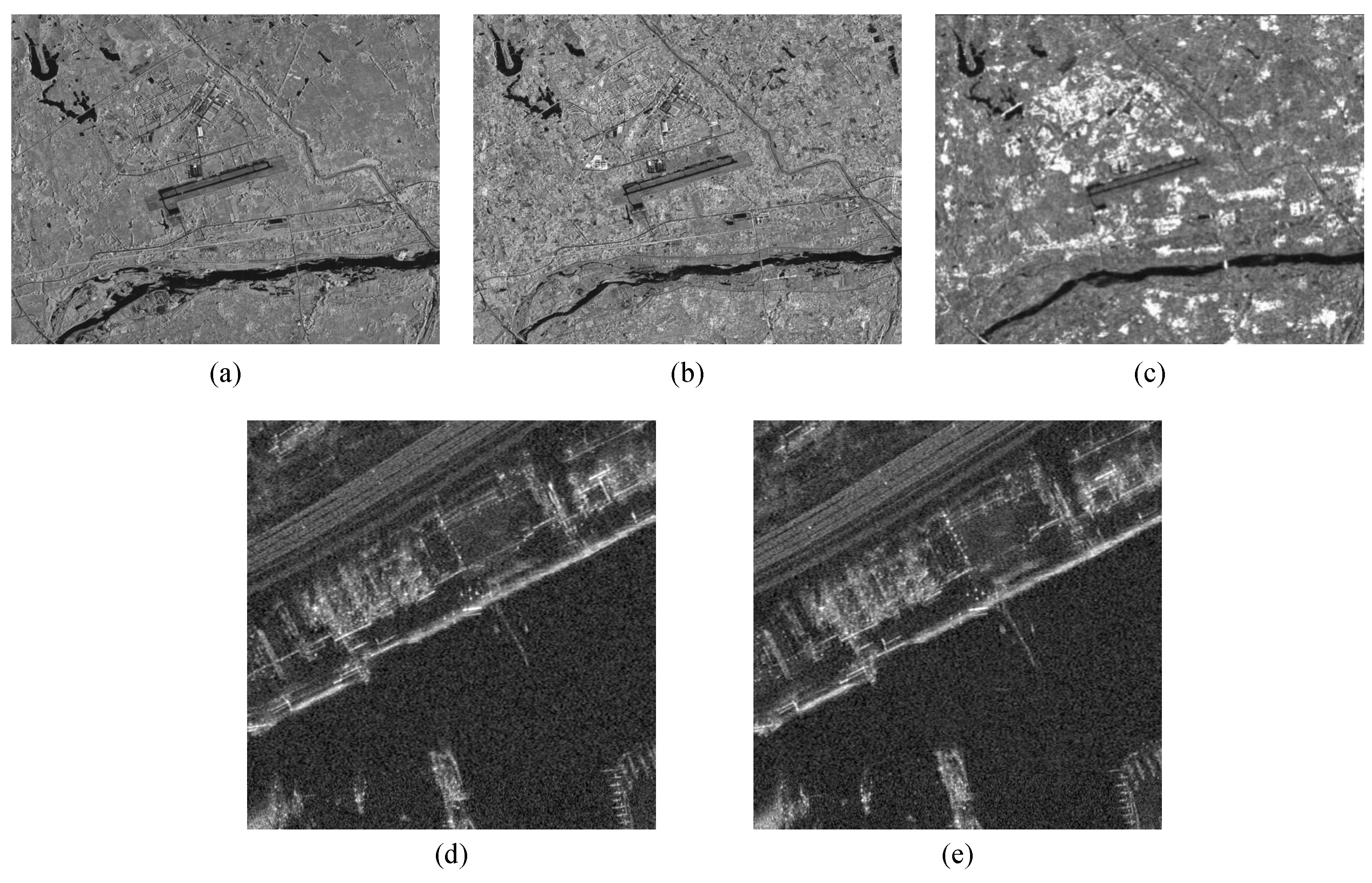
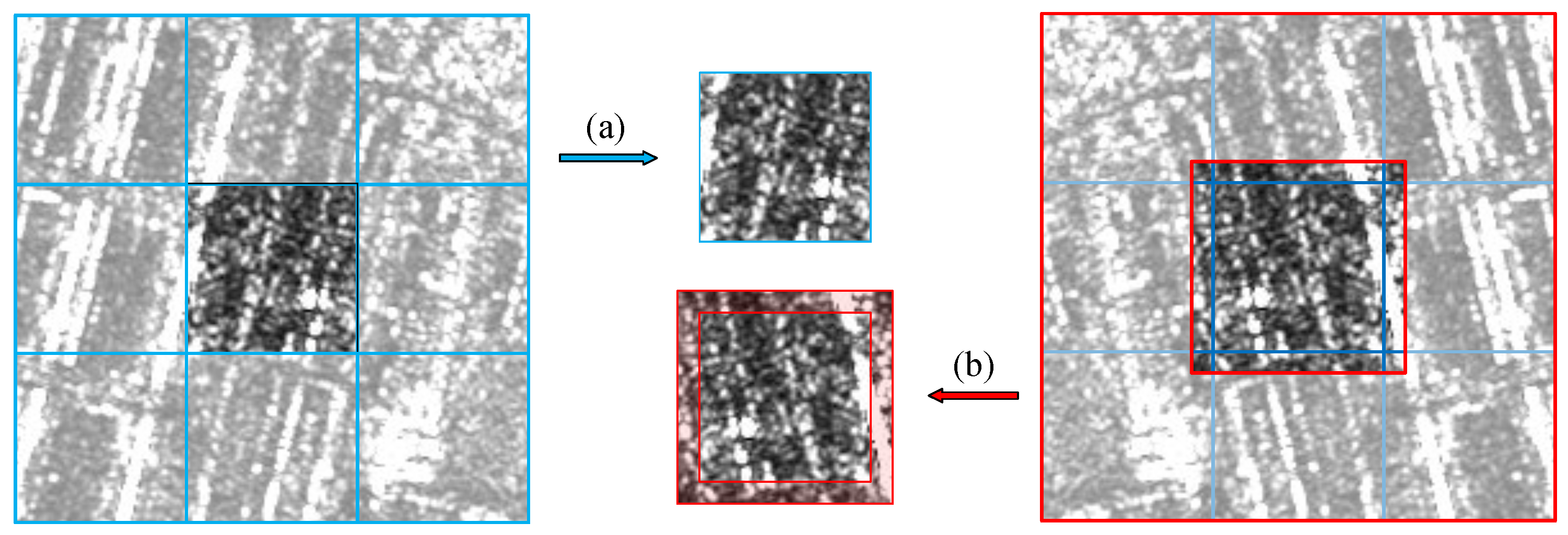
3.1. Data Preprocessing
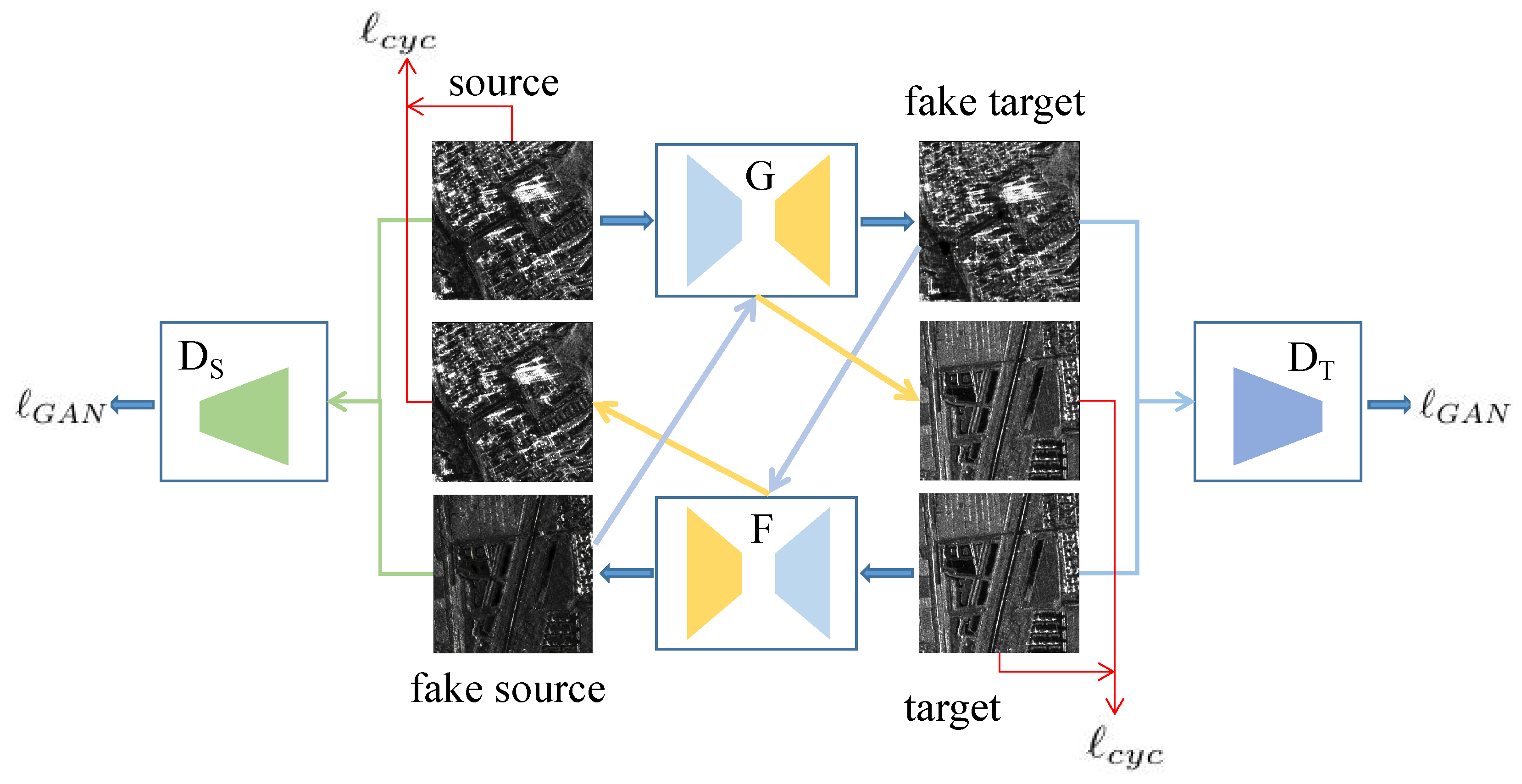
3.2. Image Style Transfer Network
3.2.1. Adversarial Loss
3.2.2. Cycle Consistency Loss
3.2.3. Identity Loss
3.2.4. Full Objective
3.3. Adversarial Adaptive Segmentation Network
| Algorithm 1 The training process of STDM-UDA. | |
| 1: | , , and the . |
| 2: | |
| 3: | Initialize image translation network . |
| 4: | for number of image translation iterations do |
| 5: | train with Formula (7). |
| 6: | end for |
| 7: | Get the by the . |
| 8: | |
| 9: | Initialize the M and the D. |
| 10: | for number of segmentation iterations do |
| 11: | train M with Formula (10). |
| 12: | train D with Formula (11). |
| 13: | end for |
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
4.2.1. Data Preprocessing
4.2.2. Architecture
4.2.3. Training Details
4.3. Classification Accuracy Index
4.4. Results and Comparison
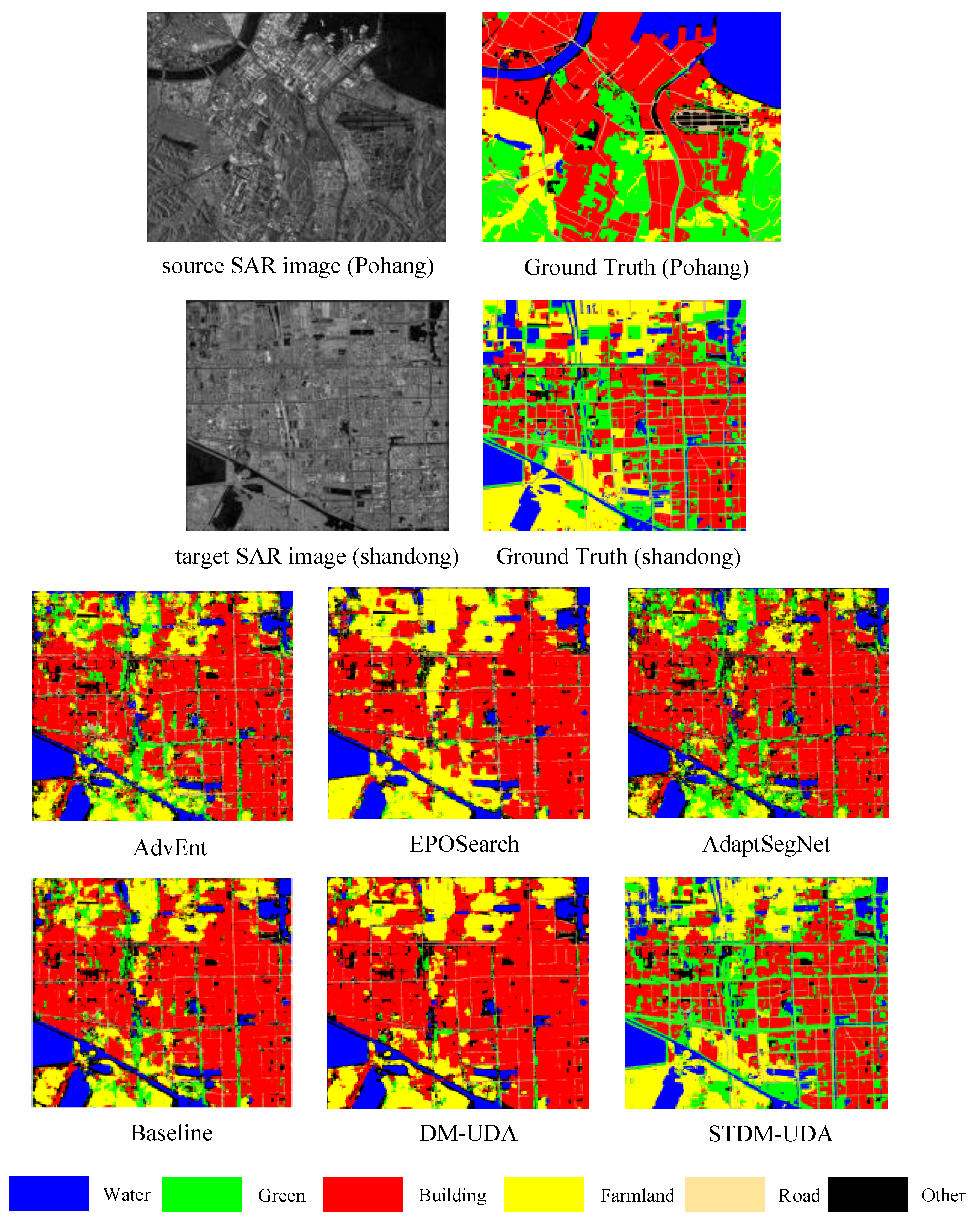
4.4.1. Comparison Results on Shandong
4.4.2. Comparison Results on Rosenheim
4.4.3. Comparison Results on JiuJiang
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, P.; Li, L.; Tian, T.; Tian, J. Two-Stage Cross-Modality Transfer Learning Method for Military-Civilian SAR Ship Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, R.; Thiel, C.; Thiel, C.; Eckardt, R.; Richter, N.; Schmullius, C. Multisensor SAR analysis for forest monitoring in boreal and tropical forest environments. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 5, pp. V-126–V-129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Uemoto, J.; Umehara, T.; Kojima, S.; Matsuoka, T.; Nadai, A.; Uratsuka, S. Damage estimation of the Great East Japan earthquake with airborne SAR (PI-SAR2) data. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 1190–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q. Extraction of Sea Ice Cover by Sentinel-1 SAR Based on Support Vector Machine With Unsupervised Generation of Training Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 3040–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhang, K. A Globally Statistical Active Contour Model for Segmentation of Oil Slick in SAR Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Schenk, A.; Ullmann, T.; Thiel, M.; Roth, A.; Dech, S. Characterization of Land Cover Types in TerraSAR-X Images by Combined Analysis of Speckle Statistics and Intensity Information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1911–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satalino, G.; Panciera, R.; Balenzano, A.; Mattia, F.; Walker, J. COSMO-SkyMed multi-temporal data for land cover classification and soil moisture retrieval over an agricultural site in Southern Australia. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 5701–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Aldrighi, M. SAR Data Classification of Urban Areas by Means of Segmentation Techniques and Ancillary Optical Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampe, E.M.; Vanhamel, I.; Salvadore, E.; Dams, J.; Bashir, I.; Demarchi, L.; Chan, J.C.W.; Sahli, H.; Canters, F.; Batelaan, O. Impact of Urban Land-Cover Classification on Groundwater Recharge Uncertainty. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Montazeri, S.; Ali, M.; Hua, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mou, L.; Shi, Y.; Xu, F.; Bamler, R. Deep learning meets SAR: Concepts, models, pitfalls, and perspectives. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 9, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Cao, W.; Yu, T.; Gu, X. SAR Image Classification Using Greedy Hierarchical Learning With Unsupervised Stacked CAEs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5721–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Jiang, W.; Deng, X. Multi-scale deep feature learning network with bilateral filtering for SAR image classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gu, H.; Su, W. SAR Image Classification Using Contrastive Learning and Pseudo-Labels With Limited Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shermeyer, J.; Hogan, D.; Brown, J.; Van Etten, A.; Weir, N.; Pacifici, F.; Hansch, R.; Bastidas, A.; Soenen, S.; Bacastow, T.; et al. SpaceNet 6: Multi-sensor all weather mapping dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Vasconcelos, N. Bidirectional Learning for Domain Adaptation of Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Yang, X.; Fang, S.; Ai, J. Region level SAR image classification using deep features and spatial constraints. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Dong, Q. SAR Image Classification Using CNN Embeddings and Metric Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Ma, X. SAR Image Classification via Deep Recurrent Encoding Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2255–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Du, Y. Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network With Autoencoder for Semisupervised SAR Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Saha, J.; Mukherjee, J.; Aikat, S.; Misra, A. Unsupervised Land Cover Classification of Hybrid and Dual-Polarized Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Yazid Boudaren, M.E.; Song, W.; Wu, Y. High-Order Triplet CRF-Pcanet for Unsupervised Segmentation of SAR Image. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020–2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 17 February 2020; pp. 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, M. A deep vector quantization clustering method for polarimetric SAR images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lei, B.; Qiu, X.; Ding, C. Winner Takes All: A Superpixel Aided Voting Algorithm for Training Unsupervised PolSAR CNN Classifiers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 16000–16009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xing, C.; Yin, J.; Yang, J. Land Cover Classification for Polarimetric SAR Images Based on Vision Transformer. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Lu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, X.; He, Q.; Li, J.; Rong, X.; Yang, Z.; Chang, H.; et al. RingMo: A Remote Sensing Foundation Model with Masked Image Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2023, 61, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, E.; Hoffman, J.; Darrell, T.; Saenko, K. Simultaneous Deep Transfer Across Domains and Tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bousmalis, K.; Silberman, N.; Dohan, D.; Erhan, D.; Krishnan, D. Unsupervised Pixel-Level Domain Adaptation With Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Luo, Y. Transferable SAR Image Classification Crossing Different Satellites Under Open Set Condition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, E.; Hoffman, J.; Zhang, N.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Deep domain confusion: Maximizing for domain invariance. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3474. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jordan, M. Learning Transferable Features with Deep Adaptation Networks. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 37, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Deng, X.; Ma, X.; Jiang, W. Transfer Learning for SAR Image Classification Via Deep Joint Distribution Adaptation Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5377–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Kolouri, S.; Eaton, E.; Kim, K. Deep transfer learning for few-shot SAR image classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y. EO-Augmented Building Segmentation for Airborne SAR Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Dumitru, C.O.; Pan, Z.; Lei, B.; Datcu, M. Classification of Large-Scale High-Resolution SAR Images With Deep Transfer Learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-To-Image Translation Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Tao, R.; Wang, S. Transfer Learning for Optical and SAR Data Correspondence Identification With Limited Training Labels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.; Sheikh, H.; Simoncelli, E. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NE, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Hou, B.; Wu, Q.; Wen, Z.; Jiao, L. A distribution and structure match generative adversarial network for SAR image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3864–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F.; Hou, B.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Coarse-to-fine contrastive self-supervised feature learning for land-cover classification in SAR images with limited labeled data. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6502–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.H.; Hung, W.C.; Schulter, S.; Sohn, K.; Yang, M.H.; Chandraker, M. Learning to Adapt Structured Output Space for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.H.; Jain, H.; Bucher, M.; Cord, M.; Perez, P. ADVENT: Adversarial Entropy Minimization for Domain Adaptation in Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mahapatra, D.; Rajan, V. Multi-Task Learning with User Preferences: Gradient Descent with Controlled Ascent in Pareto Optimization. Proc. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 119, 6597–6607. [Google Scholar]


| Area | Imaging Time | Source | Image Sizes | Resolution | Band | Polarization | S1 | S2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoDelta | 27 September 2007 | Cosmo-SkyMed | 18,308 × 16,716 | 2.5 m | X | HH | 1120 | 3074 |
| Rosenheim | 27 January 2008 | TerraSAR-X | 7691 × 7224 | 1.75 m | X | HH | 210 | 552 |
| JiuJiang | 24 November 2016 | GF-3 | 8000 × 8000 | 3 m | C | DV | 224 | 625 |
| Shandong | 16 April 2017 | GF-3 | 10,240 × 9216 | 1 m | C | VV | 360 | 928 |
| Pohang | 13 July 2018 | GF-3 | 9728 × 7680 | 1 m | C | HH | 285 | 744 |
| Layers | Input → Output Shape | Layer Information |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CONV-(N64, K4 × 4, S2, P1), LeakyReLU (0.2) | |
| 2 | CONV-(N128, K4 × 4, S2, P1), LeakyReLU (0.2) | |
| 3 | CONV-(N256, K4 × 4, S2, P1), LeakyReLU (0.2) | |
| 4 | CONV-(N512, K4 × 4, S2, P1), LeakyReLU (0.2) | |
| 5 | CONV-(N1, K4 × 4, S2, P1) |
| Method | Precision | OA | Kappa | MIoU | FWIoU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Green | Building | Farmland | Road | |||||
| AdaptSegNet | 90.3 | 30.9 | 67.8 | 67.3 | 44.7 | 55.4 | 40.4 | 36.6 | 41.6 |
| AdvEnt | 85.0 | 35.4 | 69.1 | 66.8 | 37.2 | 57.6 | 43.6 | 33.6 | 43.4 |
| EPOSearch | 88.0 | 41.0 | 70.1 | 63.8 | 49.3 | 63.4 | 50.3 | 41.2 | 46.7 |
| Baseline | 92.0 | 35.3 | 64.0 | 71.6 | 56.5 | 58.9 | 44.3 | 34.1 | 43.5 |
| DM-UDA | 90.0 | 40.2 | 62.1 | 71.0 | 60.4 | 60.6 | 45.9 | 39.7 | 43.6 |
| STDM-UDA | 89.7 | 64.3 | 88.5 | 82.5 | 74.2 | 80.0 | 73.2 | 63.4 | 68.0 |
| Method | Precision | OA | Kappa | MIoU | FWIoU | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Forest | Building | Farmland | |||||
| AdaptSegNet | 81.6 | 80.5 | 57.1 | 79.4 | 66.9 | 51.4 | 51.3 | 51.5 |
| AdvEnt | 61.2 | 94.8 | 68.9 | 71.0 | 66.3 | 51.5 | 51.3 | 53.0 |
| EPOSearch | 94.4 | 84.0 | 70.6 | 72.6 | 66.6 | 50.2 | 52.3 | 52.2 |
| Baseline | 99.1 | 61.8 | 58.5 | 85.7 | 66.8 | 52.1 | 50.7 | 52.6 |
| DM-UDA | 88.0 | 96.0 | 77.5 | 71.8 | 67.5 | 51.2 | 50.6 | 53.6 |
| STDM-UDA | 86.6 | 94.7 | 78.6 | 71.9 | 69.0 | 53.1 | 52.3 | 55.0 |
| Method | Precision | OA | Kappa | MIoU | FWIoU | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Forest | Building | Farmland | |||||
| AdaptSegNet | 86.5 | 89.1 | 98.3 | 85.5 | 65.0 | 50.8 | 45.7 | 59.0 |
| AdvEnt | 88.2 | 89.4 | 97.7 | 84.4 | 66.7 | 53.3 | 48.2 | 60.8 |
| EPOSearch | 99.3 | 87.7 | 93.9 | 79.6 | 76.6 | 66.7 | 63.7 | 70.2 |
| Baseline | 98.4 | 91.2 | 98.9 | 84.6 | 77.7 | 67.7 | 60.4 | 73.3 |
| DM-UDA | 99.2 | 99.6 | 98.8 | 76.3 | 79.9 | 69.8 | 55.7 | 72.6 |
| STDM-UDA | 97.8 | 96.6 | 96.9 | 89.7 | 83.7 | 75.9 | 50.4 | 79.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Z.; Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sha, F.; Li, W.; Hou, B. Multi-Step Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Image and Feature Space for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Terrain Classification. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111901
Ren Z, Du Z, Zhang Y, Sha F, Li W, Hou B. Multi-Step Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Image and Feature Space for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Terrain Classification. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(11):1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111901
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Zhongle, Zhe Du, Yu Zhang, Feng Sha, Weibin Li, and Biao Hou. 2024. "Multi-Step Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Image and Feature Space for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Terrain Classification" Remote Sensing 16, no. 11: 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111901
APA StyleRen, Z., Du, Z., Zhang, Y., Sha, F., Li, W., & Hou, B. (2024). Multi-Step Unsupervised Domain Adaptation in Image and Feature Space for Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Terrain Classification. Remote Sensing, 16(11), 1901. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16111901






