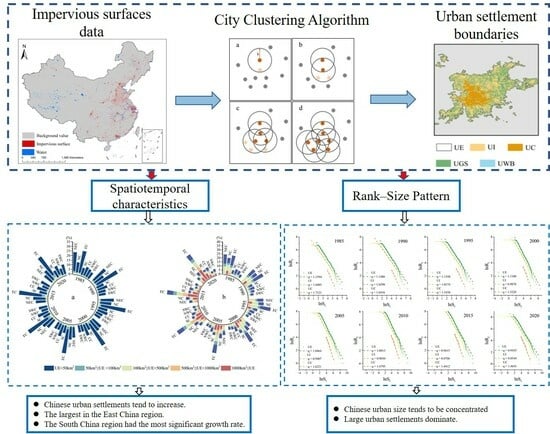
Spatiotemporal Evolution and Rank–Size Pattern of Chinese Urban Settlements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
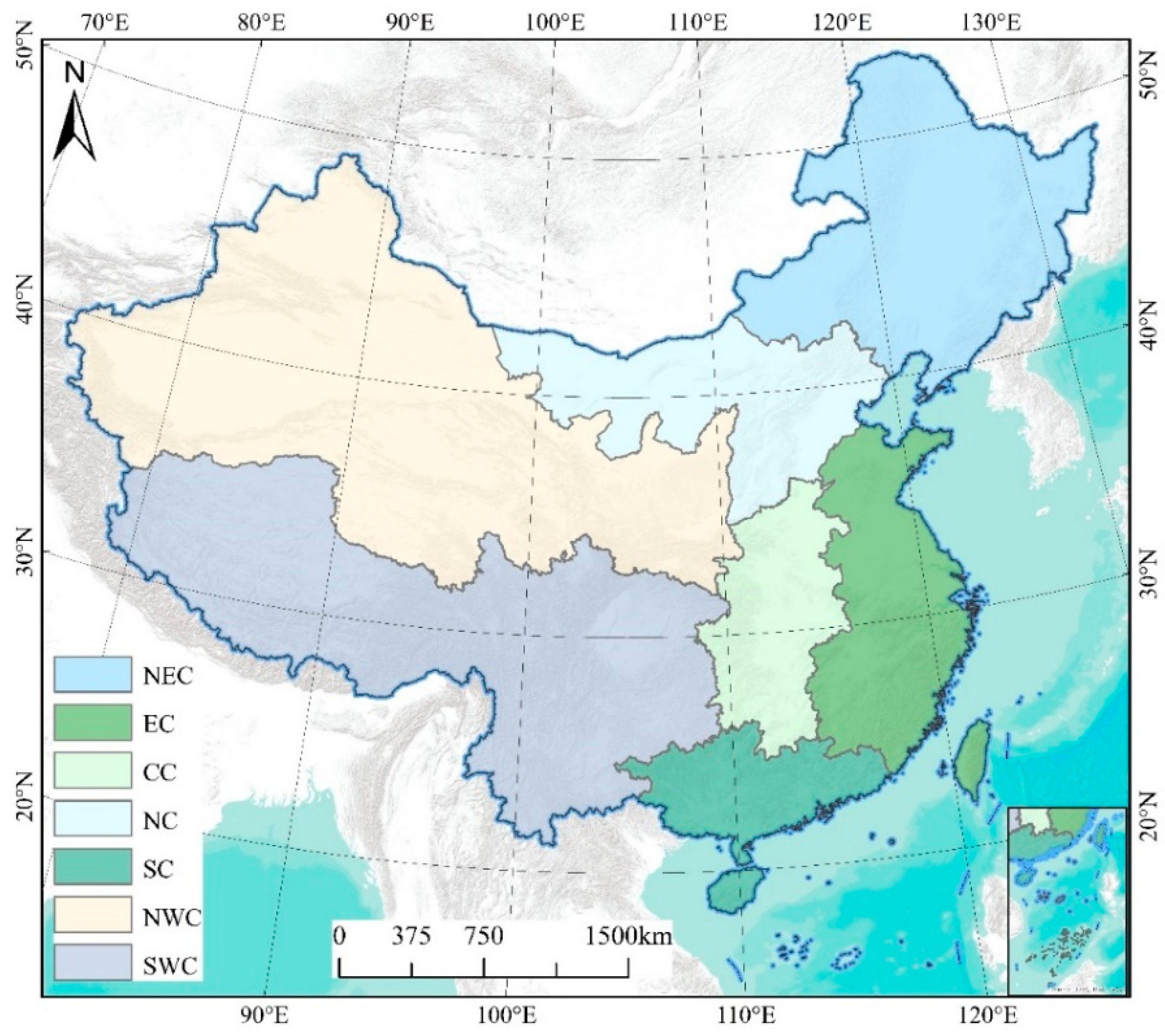
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Patch Type Identification
2.3.2. City Clustering Algorithm
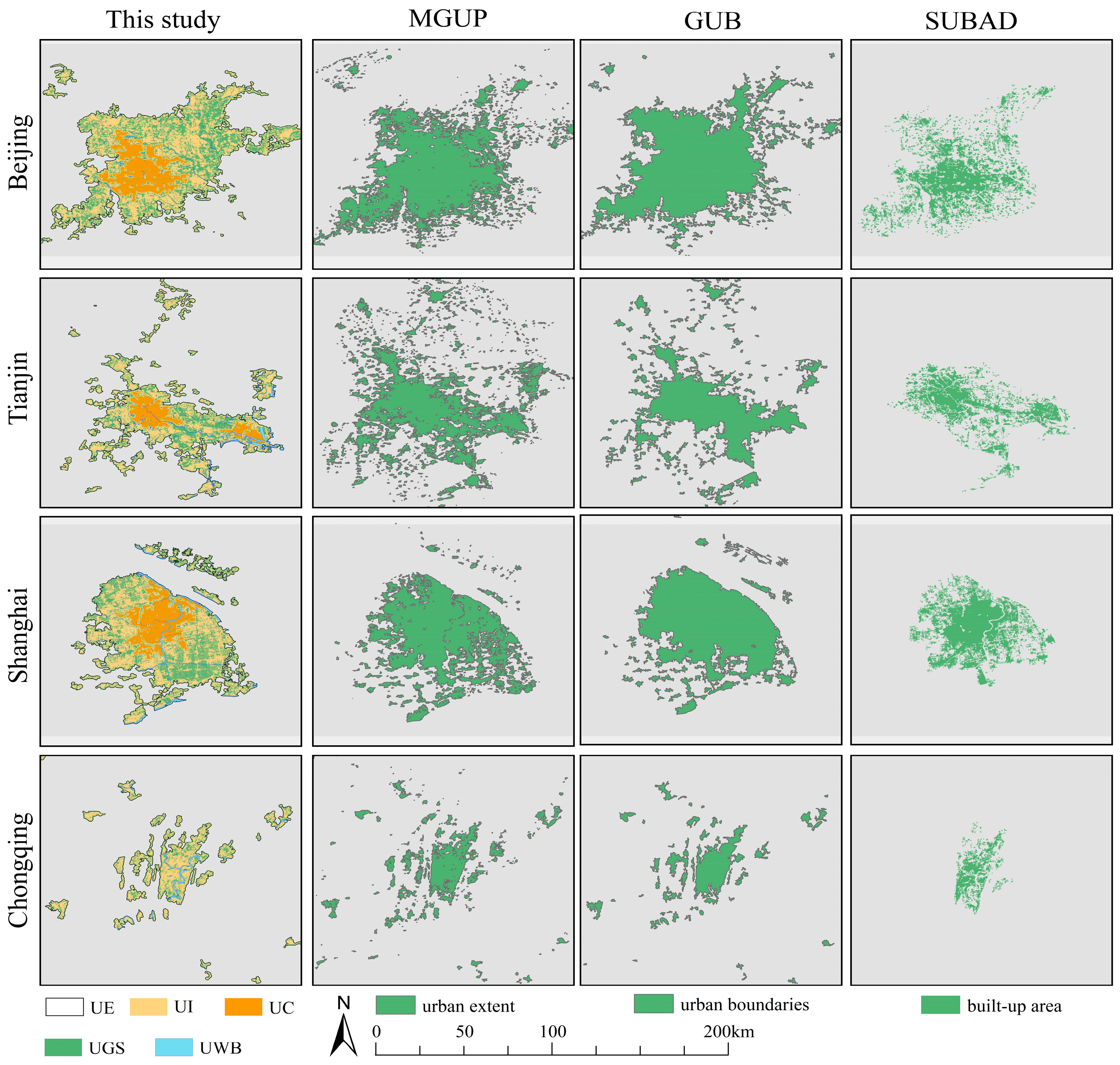
2.3.3. Accuracy Verification
2.3.4. Zipf’s Law
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Verification of Urban Settlements
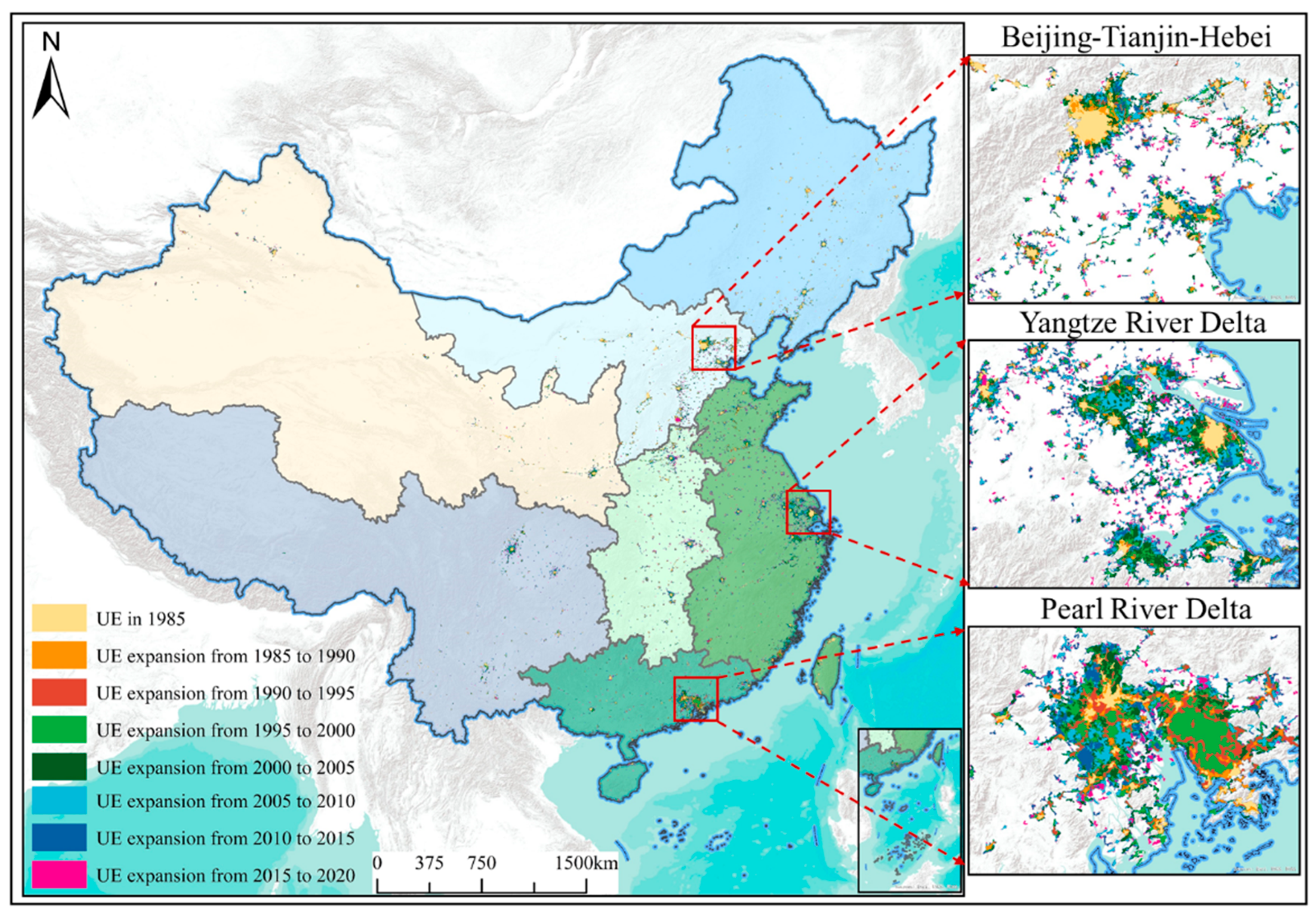
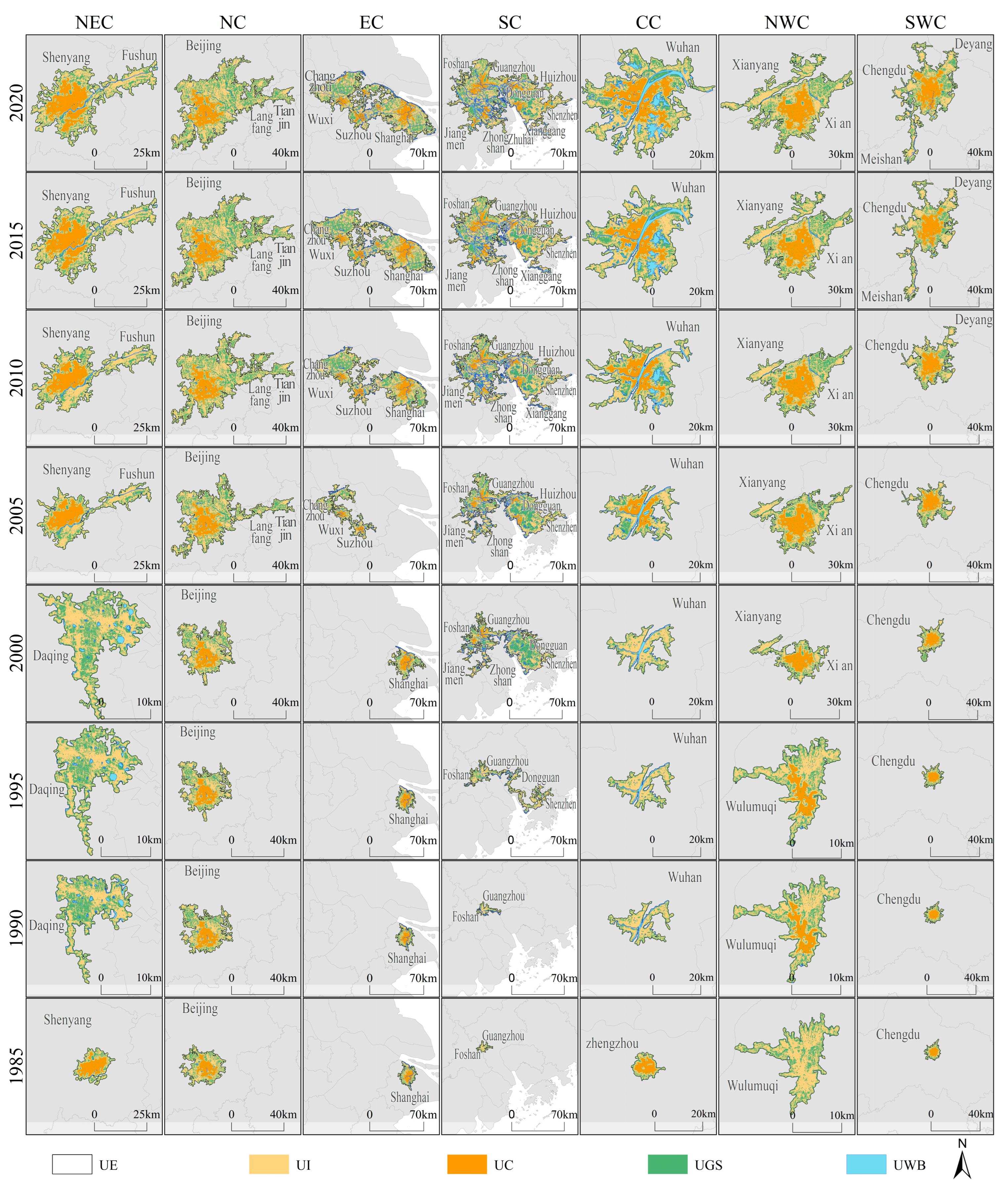
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Urban Settlements
3.3. Characteristics of Urban Settlements in Different Regions
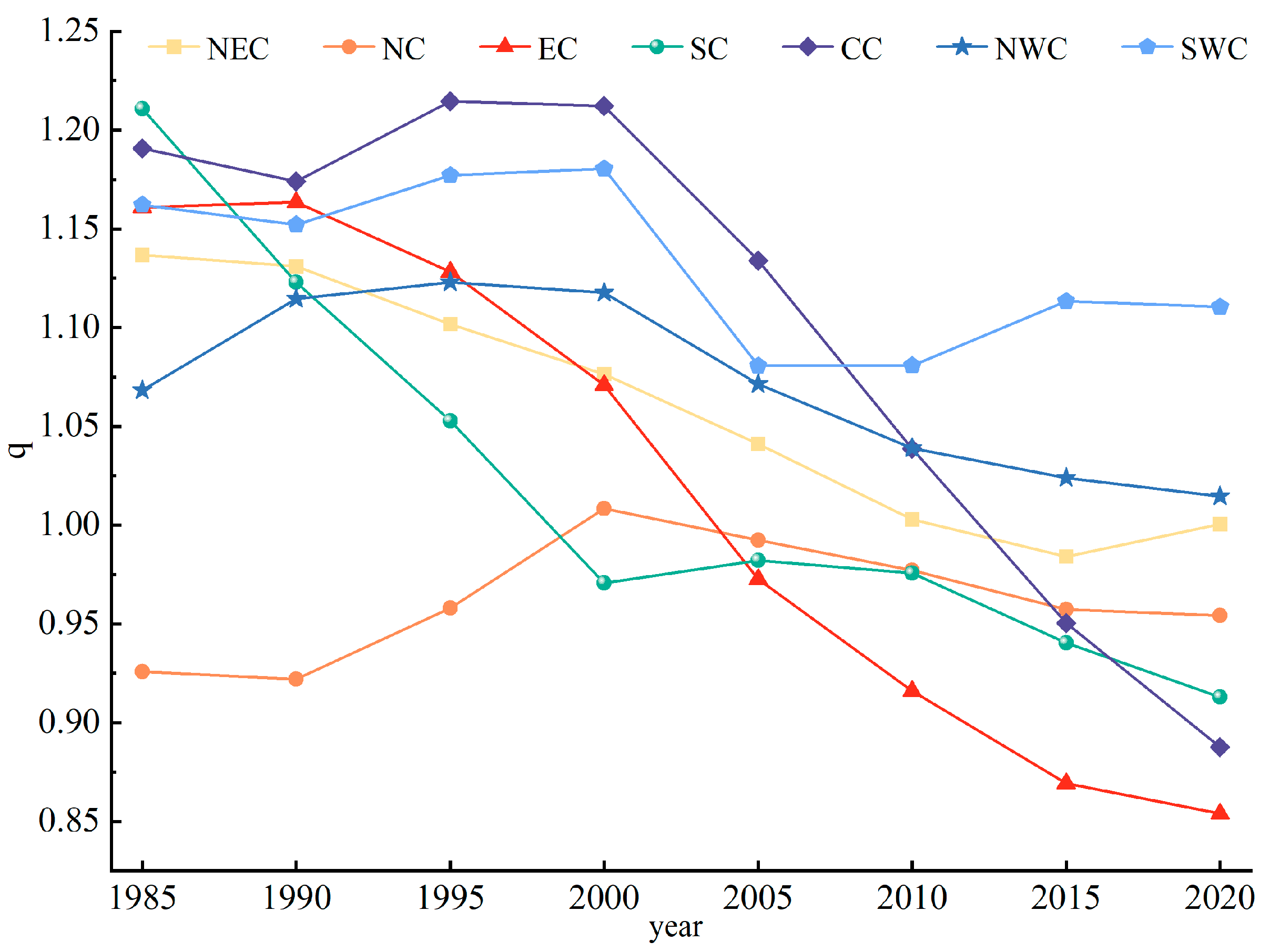
3.4. The Rank–Size Pattern of Urban Settlements
4. Discussion
4.1. Urban Spatiotemporal Evolution and Its Influencing Factors
4.2. Urban Rank–Size Patterns and Its Influencing Factors
4.3. Advantages and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN-Habitat. World Cities Report 2020: The Value of Sustainable Urbanization; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Kong, X.S.; Wang, R.; Chen, L. Identifying the relationship between urban land expansion and human activities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 94, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Yuan, M.; Yang, S.B.; Zhang, D.X.; Wang, Y.G.; Song, D.Y.; Dai, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.; Gong, J. Spatial Diffusion Waves of Human Activities: Evidence from Harmonized Nighttime Light Data during 1992–2018 in 234 Cities of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.C.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wu, X.L. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of urbanization and its coupling coordination degree in Russia—Perspectives from the population, economy, society, and eco-environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61334–61351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.Y. Construction of ecological security pattern in coastal urban areas: A case study in Qingdao, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.D.; Schneider, S.C.; Ahlers, A.A.; Miller, J.R. Categorizing wildlife responses to urbanization and conservation implications of terminology. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 29, 1246–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rega-Brodsky, C.C.; Aronson, M.F.J.; Piana, M.R.; Carpenter, E.S.; Hahs, A.K.; Herrera-Montes, A.; Knapp, S.; Kotze, D.J.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Moretti, M.; et al. Urban biodiversity: State of the science and future directions. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zheng, T.H. Establishing a “dynamic two-step floating catchment area method” to assess the accessibility of urban green space in Shenyang based on dynamic population data and multiple modes of transportation. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 82, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.K.; Xu, T. Urbanization and the informal economy: New evidence from partially linear functional-coefficient models. Cities 2021, 119, 103383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zhu, Y.M. The impact of economic development on urban livability: Evidence from 40 large and medium-sized cities of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 1767–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.F.; Silva, E.A. Understanding temporal and spatial patterns of urban activities across demographic groups through geotagged social media data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 100, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Ferguson, P. Defining city size. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2011, 38, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. The Primary Scientific Issue of Urban Research in China Is the Correctness of Basic Urban Concepts. Urban Plan. Forum 2006, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.G.; Wang, J.J.; Long, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, X.S. Defining urban boundaries by characteristic scales. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 94, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, F.; Cao, Y.; Qin, X.; Wang, B. Delineation of an urban agglomeration boundary based on Sina Weibo microblog ‘check-in’ data: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta. Cities 2017, 60, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.X.; He, C.Y.; Dou, Y.Y. Similarities and differences of city-size distributions in three main urban agglomerations of China from 1992 to 2015: A comparative study based on nighttime light data. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.; Driscoll, A.; Lobell, D.B.; Ermon, S. Using satellite imagery to understand and promote sustainable development. Science 2021, 371, eabe8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Huang, Y.H.; Xu, X.C.; Li, X.C.; Li, X.; Ciais, P.; Lin, P.R.; Gong, K.; Ziegler, A.D.; Chen, A.N.; et al. High-spatiotemporal-resolution mapping of global urban change from 1985 to 2015. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Zheng, K.; Qin, F.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhao, C.H. Deriving Urban Boundaries of Henan Province, China, Based on Sentinel-2 and Deep Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.R.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, Y.Z. Identifying and evaluating suburbs in China from 2012 to 2020 based on SNPP-VIIRS nighttime light remotely sensed data. IJAEO 2022, 114, 103401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, B.; Yang, J. Mapping global urban boundaries from the global artificial impervious area (GAIA) data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Qin, F.; Han, Z.G.; Miao, C.H. Mapping an Urban Boundary Based on Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 and POI Data: A Case Study of Zhengzhou City. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Zhou, Y.Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. IJRS 2017, 38, 6030–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I.; Jones, J.; Caruso, G.; Gerber, P. City delineation in European applications of LUTI models: Review and tests. Transp. Rev. 2018, 38, 6–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenbck, H.; Weigand, M.; Esch, T.; Staab, J.; Dech, S. A new ranking of the world’s largest cities—Do administrative units obscure morphological realities? Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.H.; Zhu, D.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. The size distribution of cities in China: Evolution of urban system and deviations from Zipf’s law. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, K.; Suedekum, J. Zipf’s law for cities in the regions and the country. J. Econ. Geogr. 2010, 11, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziqin, W. Zipf law analysis of urban scale in China. Asian J. Soc. Sci. Stud. 2016, 1, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Qi, W.; Fu, B.J.; Wang, K. Geographical transformations of urban sprawl: Exploring the spatial heterogeneity across cities in China 1992–2015. Cities 2020, 105, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.X.; He, C.Y.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Dou, Y. Detecting the 20 year city-size dynamics in China with a rank clock approach and DMSP/OLS nighttime data. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 137, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.; Eckstein, Z. Cities and growth: Theory and evidence from France and Japan. Boston Univ. Inst. Econ. Dev. 2000, 27, 443–474. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, G.; Ge, Y. The size distribution of Chinese cities. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2005, 35, 756–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.C.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.Q.; Cheng, B.; Hu, T.Y.; Liu, X.P.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 763–771. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Su, H.; Cao, G.; Wang, S.; Guan, Q. Learning from data: A post classification method for annual land cover analysis in urban areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Li, P. Annual Urban Expansion Extraction and Spatio-Temporal Analysis Using Landsat Time Series Data: A Case Study of Tianjin, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2644–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Li, H.; Wang, S.J.; Feng, Z.Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution of County-Level Land Use Structure in the Context of Urban Shrinkage: Evidence from Northeast China. Land 2022, 11, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.X.; Xue, B.; Yang, J.; Lu, C.P. Effects of the Northeast China Revitalization Strategy on Regional Economic Growth and Social Development. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Liu, A. China Statistical Yearbook; Chinese Statitical Bureau: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Mi, J. GISD30: Global 30 m impervious-surface dynamic dataset from 1985 to 2020 using time-series Landsat imagery on the Google Earth Engine platform. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1831–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, J.; Wen, D.; Li, J. An updated MODIS global urban extent product (MGUP) from 2001 to 2018 based on an automated mapping approach. IJAEO 2021, 95, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, Z.; Guo, H.; Xing, Q.; Cai, G. A standardized dataset of built-up areas of China’s cities with populations over 300,000 for the period 1990–2015. Big Earth Data 2021, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, S.; Blei, A.M.; Parent, J.; Lamson-Hall, P.; Galarza-Sanchez, N.; Civco, D.L.; Thom, K. Atlas of Urban Expansion—2016 Edition; The NYU Urbanization Project: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.Y.; Liu, Z.F.; Gou, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Xu, L.L. Detecting global urban expansion over the last three decades using a fully convolutional network. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Friedl, M.A.; Potere, D. Mapping global urban areas using MODIS 500-m data: New methods and datasets based on ‘urban ecoregions’. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenfeld, H.; Rybski, D.; Gabaix, X.; Makse, H.A. The Area and Population of Cities: New Insights from a Different Perspective on Cities. Am. Econ. Rev. 2011, 101, 2205–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florczyk, A.J.; Melchiorri, M.; Corbane, C.; Schiavina, M.; Zanchetta, L. Description of the GHS Urban Centre Database 2015. Public Release 2019, 1, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- General Office of the State Council. Notice of The State Council on Adjusting the Standards for Dividing the Size of Cities. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2014-11/20/content_9225.htm (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Zipf, G.K. Human Behavior and the Principle of Least Effort; Addison-Wesley: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1949; p. 573. [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach, F. Das gesetz der bevölkerungskonzentration. Petermanns Geogr. Mitteilungen 1913, 59, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Bai, X.; Kong, F.; Fang, J.; Gong, D.; Zhou, T.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Wei, Z. Urbanization and air quality as major drivers of altered spatiotemporal patterns of heavy rainfall in China. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zengxiang, Z.; Lifeng, S.; Xiaoli, Z.; Jinyong, X.U.; Ling, Y.I.; Bin, L. Urban expansion in China and its spatial-temporal differences over the past four decades. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1477–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Zengxiang, Z.; Xiaoli, Z.; Bin, L.; Xiao, W.; Ling, Y.I.; Lijun, Z.; Jinyong, X.U.; Shunguang, H.U.; Feifei, S. Urban Expansion of China from the 1970s to 2020 Based on Remote Sensing Technology. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 765–781. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The dimensions of global urban expansion: Estimates and projections for all countries, 2000–2050. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Ghulam, A.; Sandoval, J.S.O.; Maimaitiyiming, M. Drivers of land cover and land use changes in St. Louis metropolitan area over the past 40 years characterized by remote sensing and census population data. IJAEO 2015, 35, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Su, S. Determinants of urban expansion and their relative importance: A comparative analysis of 30 major metropolitans in China. Habitat Int. 2016, 58, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, I.; Jeleek, L.; Těpánek, V. Land-Use Changes and their Social Driving Forces in Czechia in the 19th and 20th Centuries. Land Use Policy 2001, 18, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, W.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Chi, W.; Zhang, C. The rapid and massive urban and industrial land expansions in China between 1990 and 2010: A CLUD-based analysis of their trajectories, patterns, and drivers. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 145, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zheng, Y. China’s Regional Disparity and Its Policy Responses. China World Econ. 2008, 4, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, A.; Zain, A.M.; Takeuchi, K.; Tsunekawa, A.; Yokota, S. Trends in urbanization and patterns of land use in the Asian mega cities Jakarta, Bangkok, and Metro Manila. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 70, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Wu, J. What drives urban growth in China? A multi-scale comparative analysis. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 98, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Zhang, K.H. Urbanization and City-Size Distribution in China. In The Great Urbanization of China; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, G.; Xie, S.H.; Li, H.B. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics of China’s City Size Distribution Based on New Criteria. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W. The form and evolution of city size distribution and urban growth model in China: An analysis based on Zipf’s Law and Gibrat’s Law. Prog. Geogr. 2022, 41, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, C.; Chen, X. City Size Distribution, Export-Oriented Economies, and Regional Technical Efficiency: The Case of China. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2020, 56, 1474–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egidi, G.; Salvati, L.; Vinci, S. The long way to tipperary: City size and worldwide urban population trends, 1950–2030. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.; Hu, S.G.; Ashraf, B.N. Zipf’s law and city size distribution: A survey of the literature and future research agenda. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 492, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.H.; Tong, L.J.; Mei, L. The effect of industrial agglomeration on green development efficiency in Northeast China since the revitalization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Kaufmann, R.K. Modeling the drivers of urban land use change in the Pearl River Delta, China: Integrating remote sensing with socioeconomic data. Land Econ. 2003, 79, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Wei, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.L. Economic transition and urban land expansion in Provincial China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.J.; Liu, S.R.; Wu, Y.Z.; Shi, K.F. The Regional Disparity of Urban Spatial Expansion Is Greater than That of Urban Socioeconomic Expansion in China: A New Perspective from Nighttime Light Remotely Sensed Data and Urban Land Datasets. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Dataset | Spatial Resolution | Year | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious surface dynamic data | 30 m | 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 | https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5220816 (accessed on 5 December 2022). | [40] |
| Water body dataset | 30 m | 1985, 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020 | https://global-surface-water.appspot.com (accessed on 2 December 2022). | [41] |
| MGUP | 250 m | 2001–2018 | https://www.rsearchgate.net/publication/339873537_MGUP_annual_global_2001_2018 (accessed on 25 June 2023). | [42] |
| GUB | 30 m | 1990–2018 | http://data.ess.tsinghua.edu.cn (accessed on 25 June 2023). | [21] |
| SUBAD | Vector | 1990–2015 | http://www.doi.org/10.11922/sciencedb.j00076.00004 (accessed on 25 June 2023). | [43] |
| Time | Number of UEs | UE (km2) | UI (km2) | UC (km2) | UGS (km2) | UWB (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | 870 | 25,679.19 | 14,715.96 | 1541.24 | 10,619.74 | 359.60 |
| 1990 | 1106 | 34,285.76 | 19,250.63 | 1965.85 | 14,055.86 | 1008.18 |
| 1995 | 1418 | 45,980.02 | 25,535.69 | 2377.77 | 18,881.29 | 1606.76 |
| 2000 | 1898 | 69,283.41 | 37,326.47 | 3429.58 | 29,515.09 | 2511.07 |
| 2005 | 2346 | 101,785.36 | 55,226.06 | 6244.24 | 43,072.80 | 3608.54 |
| 2010 | 2700 | 136,251.06 | 74,652.62 | 8697.47 | 57,016.67 | 4759.75 |
| 2015 | 3165 | 174,056.77 | 95,749.52 | 11,584.27 | 72,421.03 | 6054.82 |
| 2020 | 3385 | 195,995.38 | 107,905.46 | 13,547.30 | 81,641.82 | 6634.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Rank–Size Pattern of Chinese Urban Settlements. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010019
Zhang J, Li C, Zhang B, Hu Y, Wang H, Li Z, Zhang Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Rank–Size Pattern of Chinese Urban Settlements. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Chunlin Li, Baolei Zhang, Yuanman Hu, Hao Wang, Zhenxing Li, and Qian Zhang. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Rank–Size Pattern of Chinese Urban Settlements" Remote Sensing 16, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010019
APA StyleZhang, J., Li, C., Zhang, B., Hu, Y., Wang, H., Li, Z., & Zhang, Q. (2024). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Rank–Size Pattern of Chinese Urban Settlements. Remote Sensing, 16(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010019