An Interstation Undifferenced Real-Time Time Transfer Method with Refined Modeling of Receiver Clock
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Traditional PPP Model
2.2. Interstation Undifferenced Time Transfer Model
2.3. Receiver Clock Offset Constraint Model
- The CSRS-PPP service provided by Natural Resources Canada was used to calculate the receiver clock offset series of the previous day for each observation station. For example, for the KOKV-MKEA time link, the receiver clock offsets dtk and dtm of the two observatories on day j are calculated, respectively. The obtained receiver clock offset sampling interval is 30 s.
- The receiver clock offset data from the two stations that performed the time transfer are differenced to obtain the time transfer result for the jth day. The Allan variance at a sampling rate of 30 s is obtained directly using the following equation:where m is the number of data in the smoothing time, N is the number of clock offset data, x is the clock offset data, τ is the sampling interval (30 s), and is the number of data when the sampling interval is 30 s.
- Equation (6) was used to obtain the priori variance, and the priori variance was substituted into the calculation for day j + 1.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Data Preparation and Processing Strategies
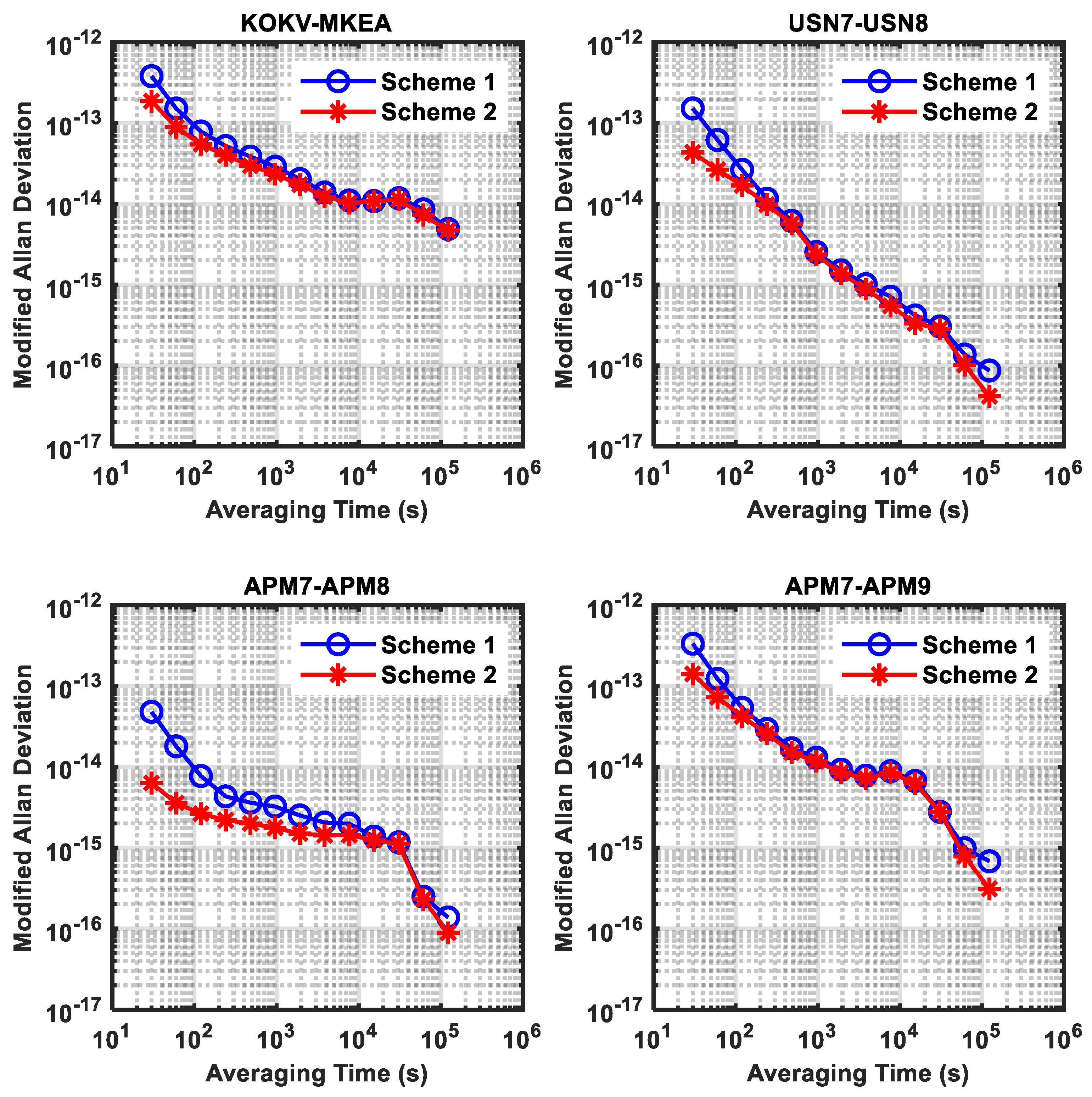
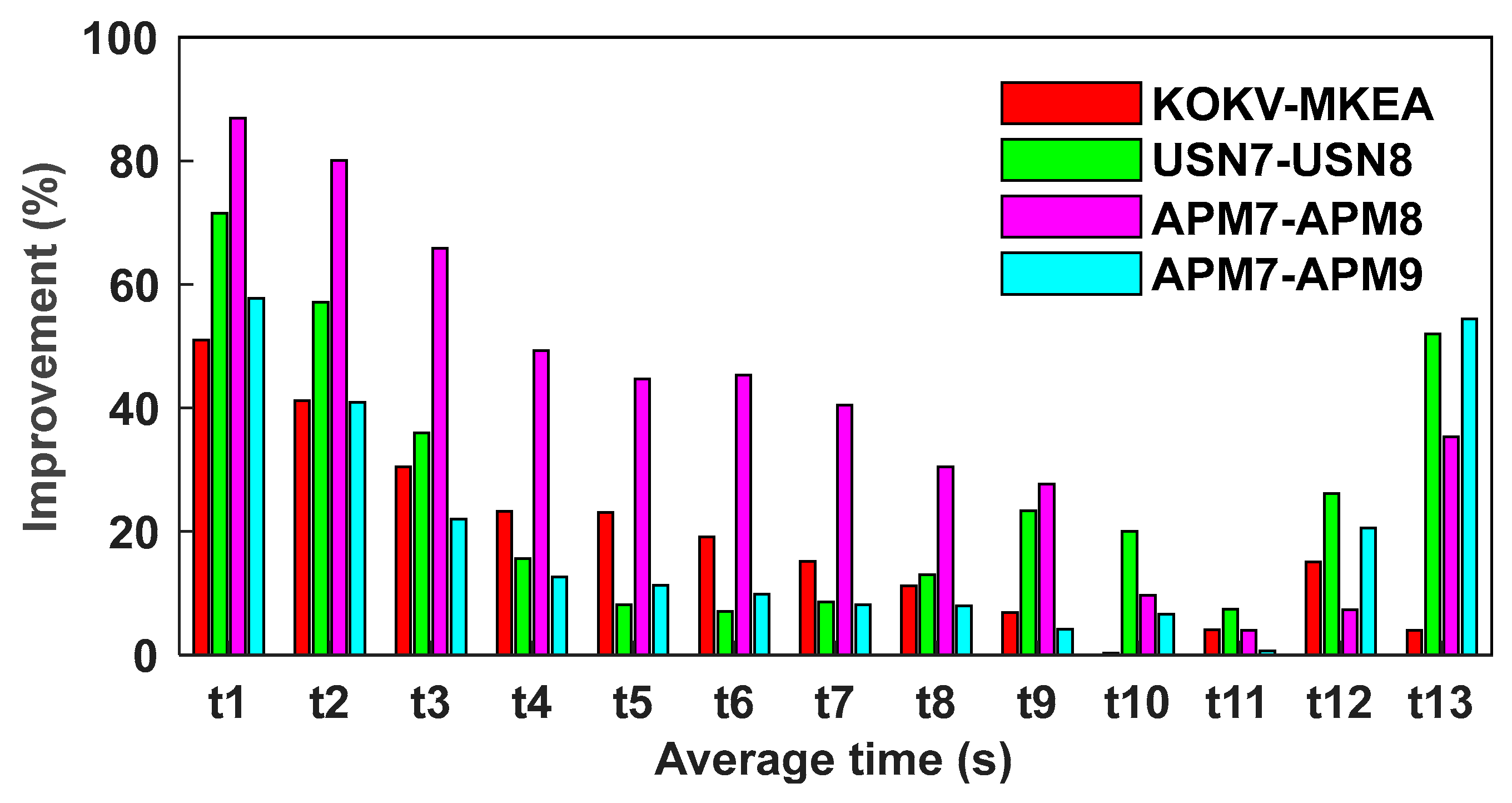
3.2. Experiment 1
- Scheme 1:
- Scheme 2:
- Scheme 3:
- Scheme 4:
3.3. Experiment 2
3.4. Experiment 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milner, W.R.; Robinson, J.M.; Kennedy, C.J.; Bothwell, T.; Kedar, D.; Matei, D.G.; Legero, T.; Sterr, U.; Riehle, F.; Leopardi, H.; et al. Demonstration of a Timescale Based on a Stable Optical Carrier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 173201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, B.M.; Blewitt, G.; Dailey, C.; Murphy, M.; Pospelov, M.; Rollings, A.; Sherman, J.; Williams, W.; Derevianko, A. Search for Domain Wall Dark Matter with Atomic Clocks on Board Global Positioning System Satellites. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.; Zhang, B.; El-Mowafy, A.; Wang, K.; Yuan, Y. On the Potential of Undifferenced and Uncombined GNSS Time and Frequency Transfer with Integer Ambiguity Resolution and Satellite Clocks Estimated. GPS Solut. 2022, 27, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Czubla, A.; Nawrocki, J.; Lewandowski, W.; Arias, E.F. Comparing a GPS Time Link Calibration with an Optical Fibre Self-Calibration with 200 Ps Accuracy. Metrologia 2015, 52, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, V.; Huang, Y.-J.; Achkar, J.; Piester, D.; Lin, S.-Y.; Wu, W.; Naumov, A.; Yang, S.; Nawrocki, J.; et al. Use of Software-Defined Radio Receivers in Two-Way Satellite Time and Frequency Transfers for UTC Computation. Metrologia 2018, 55, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, M.; Piester, D.; Gotoh, T.; Becker, J.; Aida, M.; Bauch, A. Carrier-Phase Two-Way Satellite Frequency Transfer over a Very Long Baseline. Metrologia 2014, 51, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, G.; Gao, M.; Zhang, B.; Hu, S.; Lyu, M. A New Inter-System Double-Difference RTK Model Applicable to Both Overlapping and Non-Overlapping Signal Frequencies. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W. GNSS/RNSS Integrated PPP Time Transfer: Performance with Almost Fully Deployed Multiple Constellations and a Priori ISB Constraints Considering Satellite Clock Datums. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G. Sub-10-16 Accuracy GNSS Frequency Transfer with IPPP. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuanxi, Y. Resilient PNT Concept Frame. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2018, 47, 893–898. [Google Scholar]
- Harmegnies, A.; Defraigne, P.; Petit, G. Combining GPS and GLONASS in All-in-View for Time Transfer. Metrologia 2013, 50, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Ge, Y.; Yang, X. Investigation of Real-Time Carrier Phase Time Transfer Using Current Multi-Constellations. Measurement 2020, 166, 108237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Cao, F.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, X.; Qin, W. Common-View Time Transfer Using Geostationary Satellite. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; He, L.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Synchronization Performance between Two Stations with Satellite Single-Frequency Close-Range Common View and Dual-Frequency One-Way Timing. J. Time Freq. 2020, 43, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Lu, X. Modeling and Performance Analysis of Precise Time Transfer Based on BDS Triple-Frequency Un-Combined Observations. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyninx, C.; Defraigne, P.; Sleewaegen, J.-M. Time and Frequency Transfer Using GPS Codes and Carrier Phases: Onsite Experiments. GPS Solut. 1999, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise Point Positioning for the Efficient and Robust Analysis of GPS Data from Large Networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pireaux, S.; Defraigne, P.; Wauters, L.; Bergeot, N.; Baire, Q.; Bruyninx, C. Higher-Order Ionospheric Effects in GPS Time and Frequency Transfer. GPS Solut. 2010, 14, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Shen, W.; Cai, C.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Ning, A.; Shen, Z. Comparison and Evaluation of Carrier Phase PPP and Single Difference Time Transfer with Multi-GNSS Ambiguity Resolution. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraigne, P.; Aerts, W.; Harmegnies, A.; Petit, G.; Rovera, D.; Uhrich, P. Advances in Multi-GNSS Time Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2013 Joint European Frequency and Time Forum & International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFC), Prague, Czech Republic, 21–25 July 2013; pp. 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Jiang, Z. Precise Point Positioning for TAI Computation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium Joint with the 21st European Frequency and Time Forum, Geneva, Switzerland, 29 May–1 June 2007; pp. 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, J.A.R.; Watson, R.J.; Allain, D.J.; Mitchell, C.N. Ionospheric Corrections for GPS Time Transfer. Radio Sci. 2014, 49, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavella, P.; Petit, G. Precise Time Scales and Navigation Systems: Mutual Benefits of Timekeeping and Positioning. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Skakun, I.; Jiang, Z.; Levine, J. A Detailed Comparison of Two Continuous GPS Carrier-Phase Time Transfer Techniques. Metrologia 2015, 52, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, G.; Moore, A.W.; Mueller, I.I. The International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Service (IGS): Development and Achievements. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.M.; Neilan, R.E.; Rizos, C. The International GNSS Service in a Changing Landscape of Global Navigation Satellite Systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Geng, J. GPS Satellite Clock Determination in Case of Inter-Frequency Clock Biases for Triple-Frequency Precise Point Positioning. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Arias, E.F. Use of IGS Products in TAI Applications. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. GNSS Precise Point Positioning. In Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century: Integrated Satellite Navigation, Sensor Systems, and Civil Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, S.; Li, X.; Guo, F. Accuracy Analysis of Time and Frequency Transfer Based on Precise Point Positioning. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2010, 35, 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Gao, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, R. Evaluation of Carrier-Phase Precise Time and Frequency Transfer Using Different Analysis Centre Products for GNSSs. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 65003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defraigne, P.; Aerts, W.; Pottiaux, E. Monitoring of UTC(k)’s Using PPP and IGS Real-Time Products. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Cao, X.; Lyu, D.; He, Z.; Ye, F.; Xiao, G.; Shen, F. An Investigation of PPP Time Transfer via BDS-3 PPP-B2b Service. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, M.; Yin, X.; Xiao, G.; Lv, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, R. High-Precision Cloud Platform Timing Based on GNSS Precise Point Positioning. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Song, W.; Niu, X.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S.; Zhang, S.; Shi, C. Foundation and Performance Evaluation of Real-Time GNSS High-Precision One-Way Timing System. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Dai, P.; Qin, W.; Yang, X.; Zhou, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X. Performance of Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning Time and Frequency Transfer with Clock Modeling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Feng, Y. Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning with Raw Single-Frequency and Dual-Frequency Measurement Models. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise Point Positioning Using IGS Orbit and Clock Products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzum, B.; Petit, G. The IERS Conventions (2010): Reference systems and new models. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2012, 10, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Station Name | Receiver Type | Antenna Type | Clock |
|---|---|---|---|
| USN7 | SEPT POLARX5TR | TPSCR.G5 | H-MASER |
| USN8 | SEPT POLARX5TR | ||
| KOKV | JAVAD TRE_G3TH DELTA | ASH701945G_M | H-MASER |
| MKEA | SEPT POLARX5 | JAVRINGANT_DM | H-MASER |
| APM7 | SEPT POLARX5TR | HX-CGX601A | CESIUM |
| APM8 | SEPT POLARX5TR | ||
| APM9 | TRIMBLE ALLOY | HX-CSX601A |
| Product Type | Accuracy | Sample Interval | Update Rate | Latency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broadcast | orbits | ~100 cm | daily | — | real time |
| clocks | ~5 ns | ||||
| Ultrarapid (predicted half) | orbits | ~5 cm | 15 min | 4 times a day | real time |
| clocks | ~3 ns | ||||
| Ultrarapid (observed half) | orbits | ~3 cm | 15 min | 4 times a day | 3~9 h |
| clocks | ~0.15 ns | ||||
| Rapid | orbits | ~2.5 cm | 15 min | Once a day | 17~41 h |
| clocks | ~0.075 ns | 5 min | |||
| Final | orbits | ~2.5 cm | 15 min | Once a week | 12~18 days |
| clocks | ~0.075 ns | 30 s |
| Processing Strategies | ||
|---|---|---|
| Traditional PPP Model | Interstation Undifferenced Time Transfer Model | |
| Satellite orbit | IGS orbit products | |
| Satellite clock offset | IGS clock offset products | — |
| Tropospheric delay | Model corrected dry delay, parameter estimated wet delay | |
| Ionospheric delay | Ionosphere-free combination model | |
| Satellite antenna phase center | Antenna file correction | |
| Satellite antenna phase wind-up | Model correction [39] | |
| Tide | Model correction [39] | |
| Earth rotation | Model correction [39] | |
| Relativistic effect | Model correction [39] | |
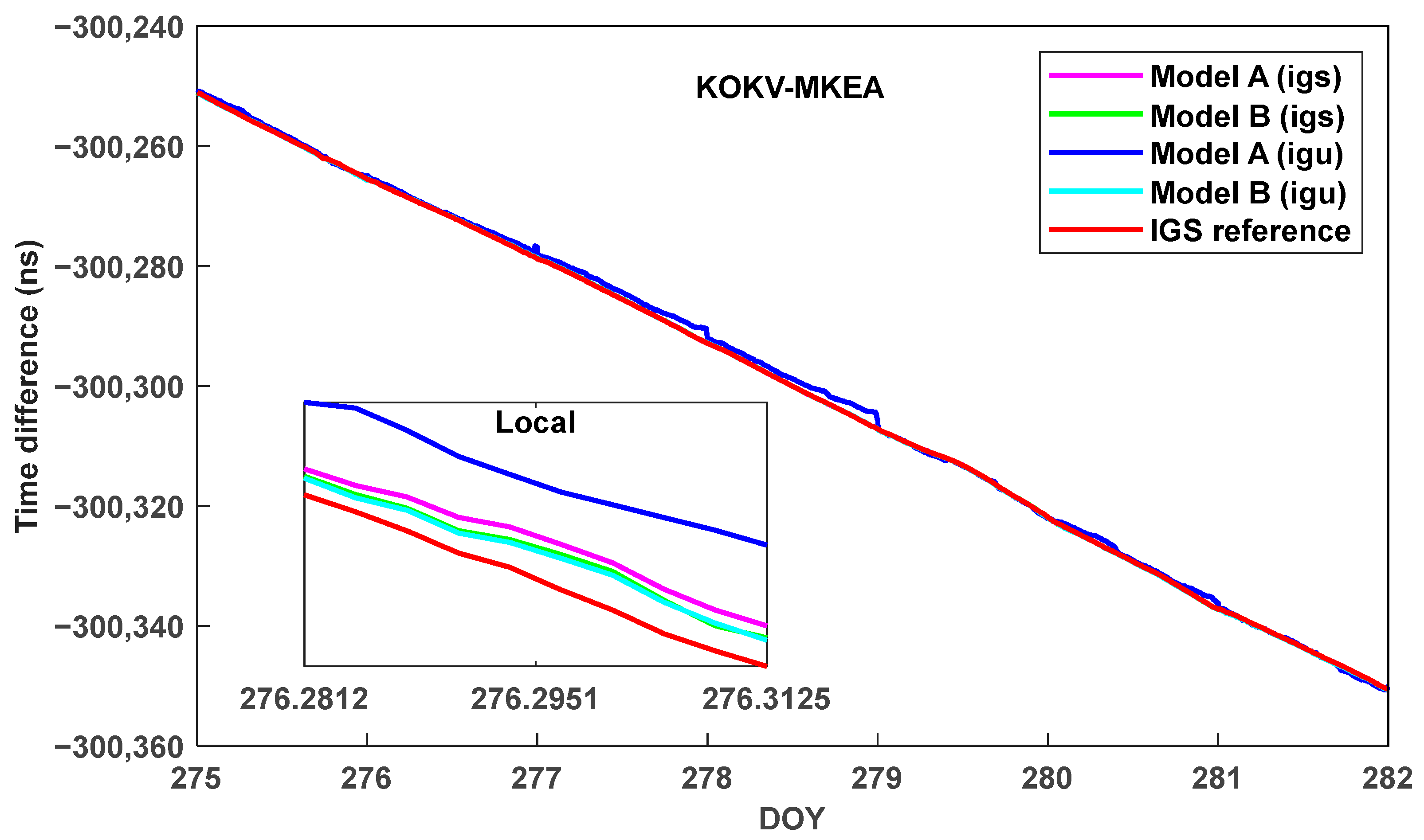
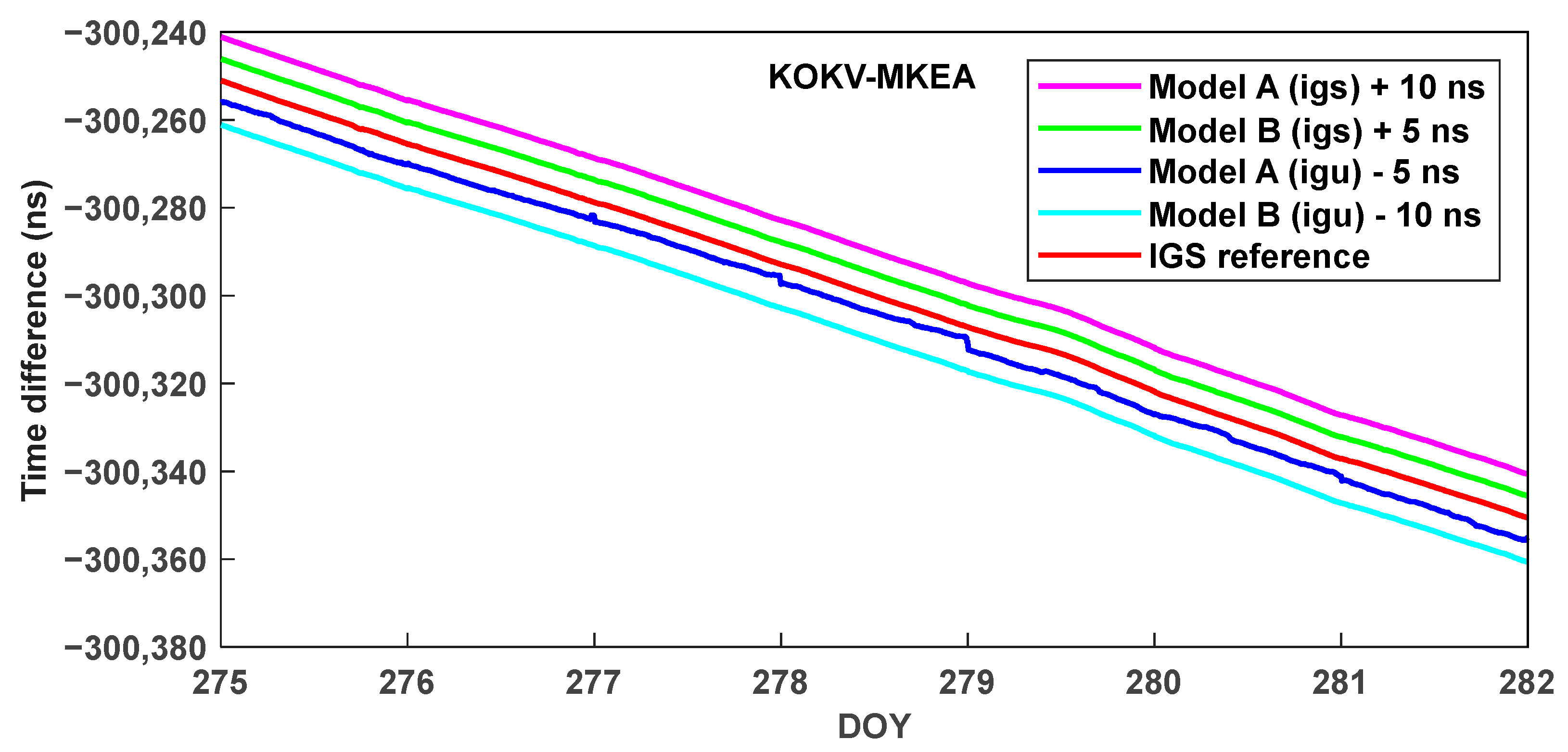
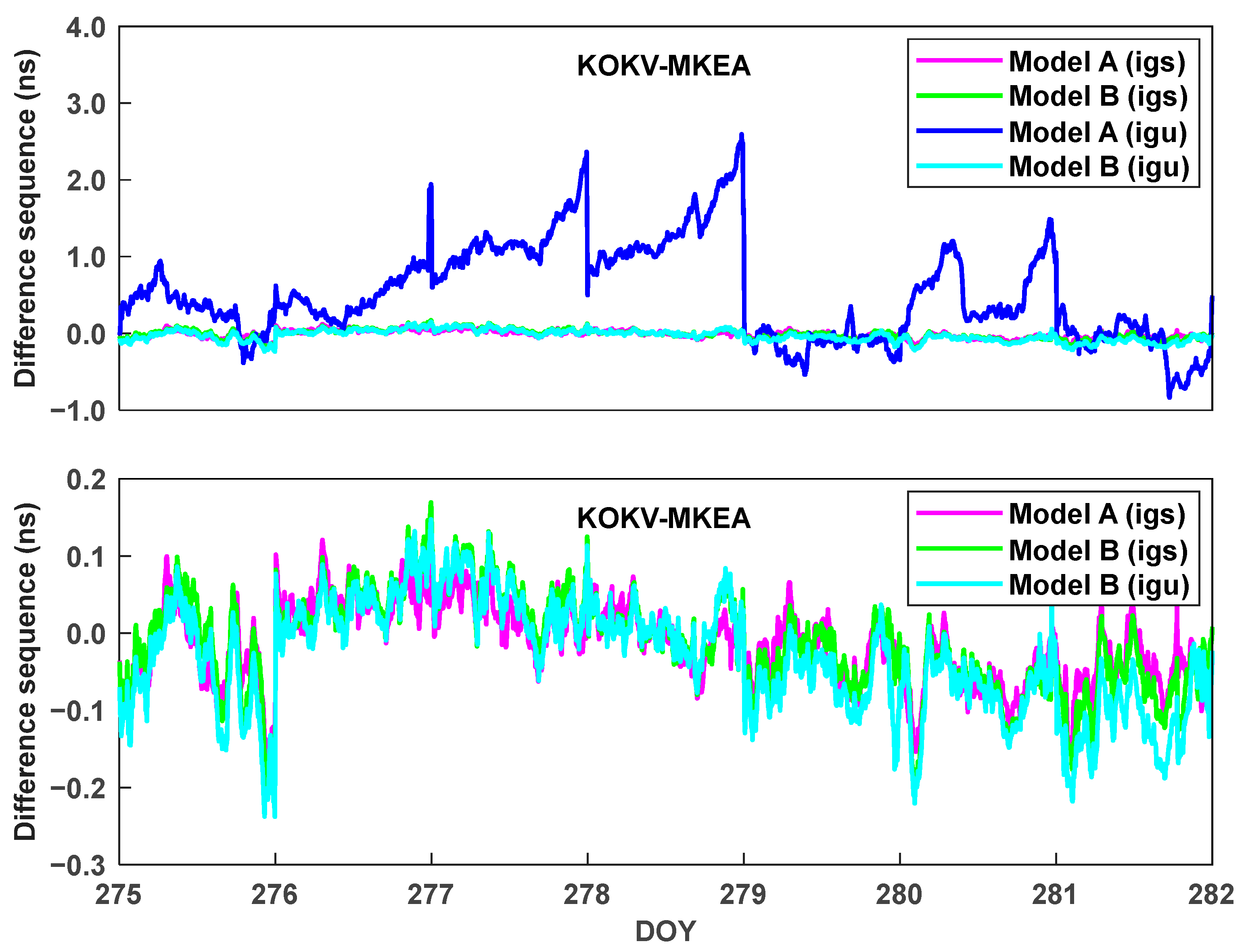
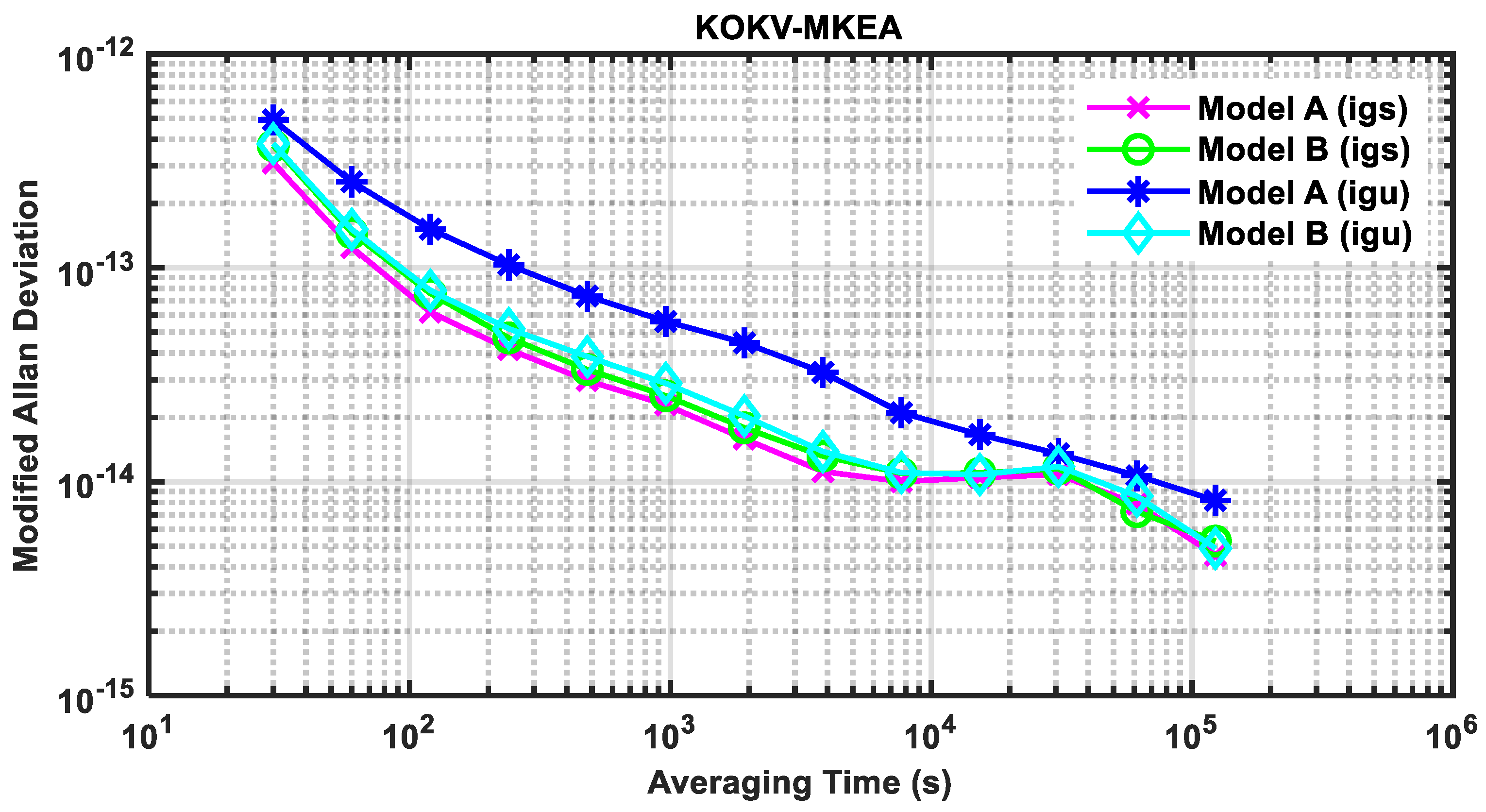
| Statistics | Model A (igs) | Model B (igs) | Model A (igu) | Model B (igu) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.520 | 0.032 |
| STD | 0.052 | 0.063 | 0.629 | 0.073 |
| RMS | 0.054 | 0.064 | 0.816 | 0.079 |
| STD | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Model B | Improved | |
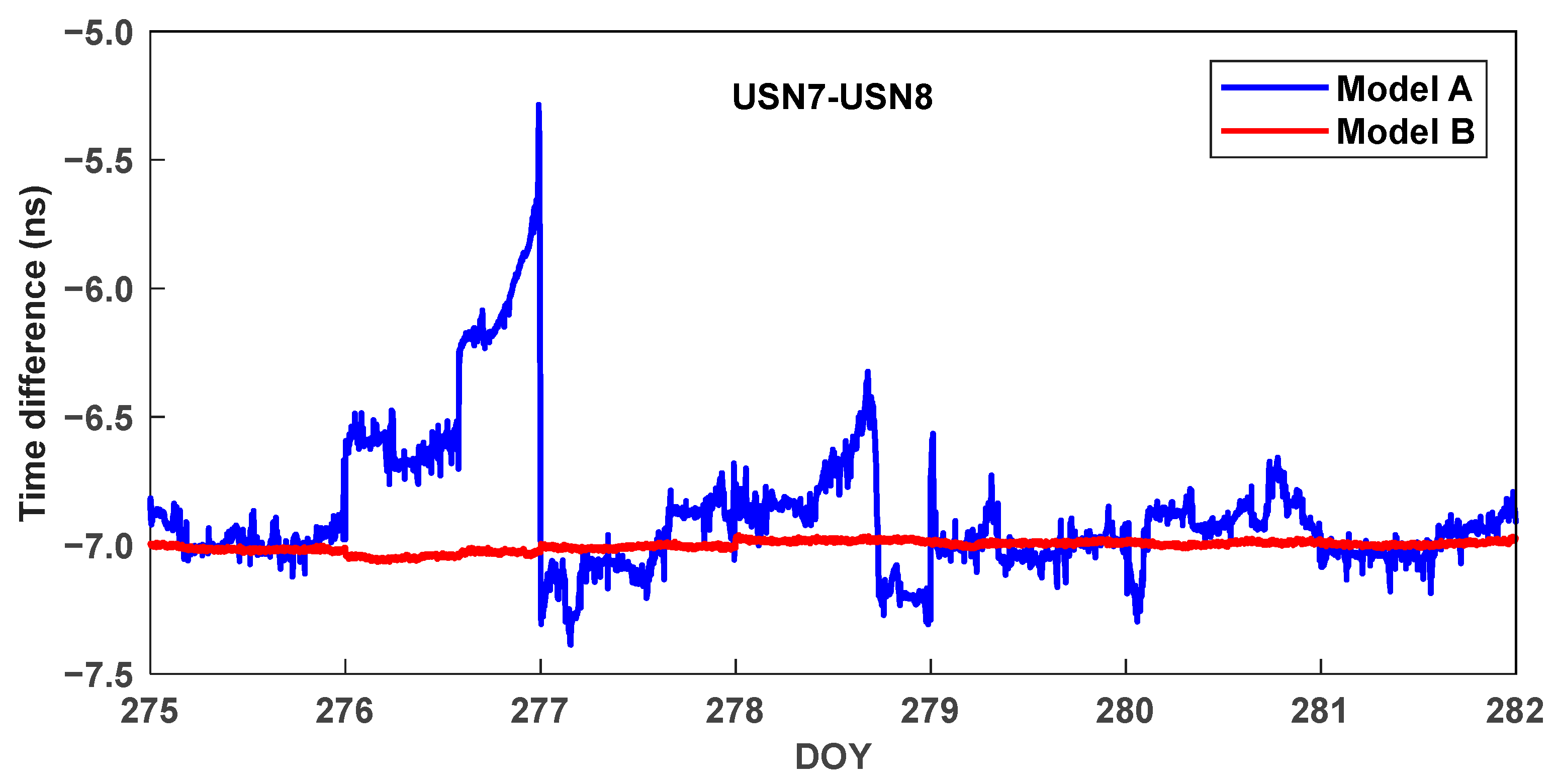
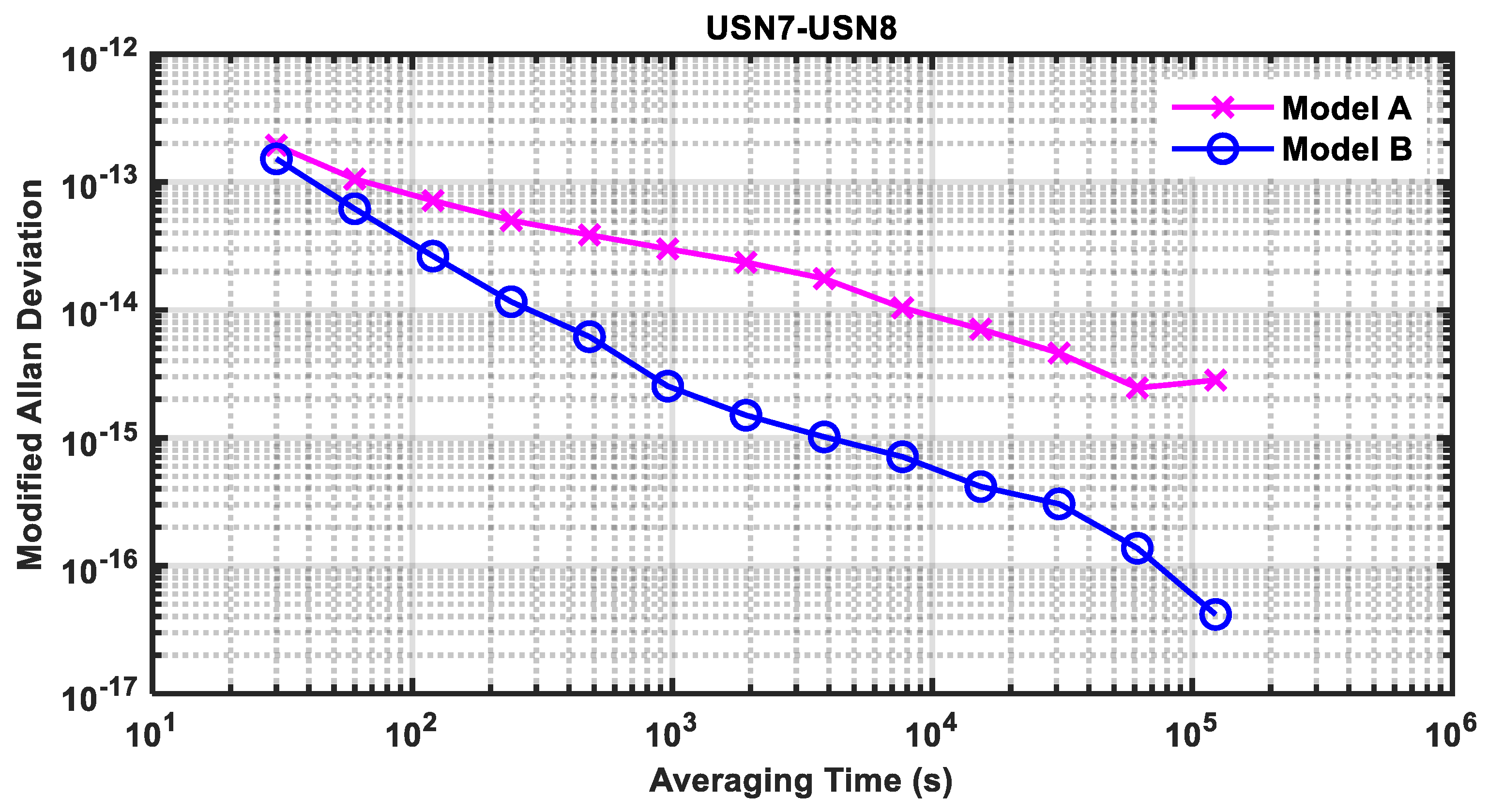
| USN7-USN8 | 0.266 | 0.019 | 92.9% |
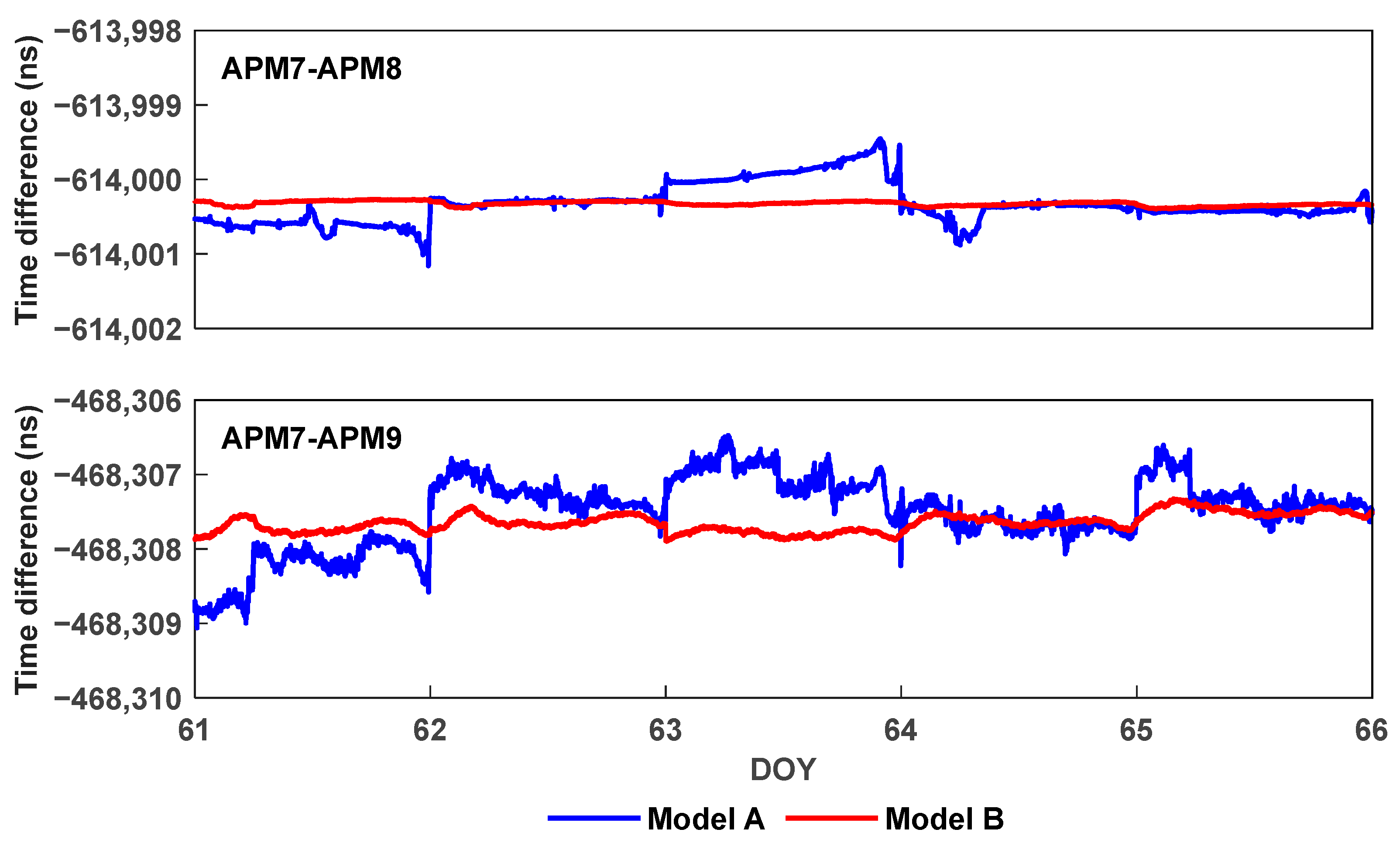
| APM7-APM8 | 0.263 | 0.030 | 88.6% |
| APM7-APM9 | 0.483 | 0.123 | 74.5% |
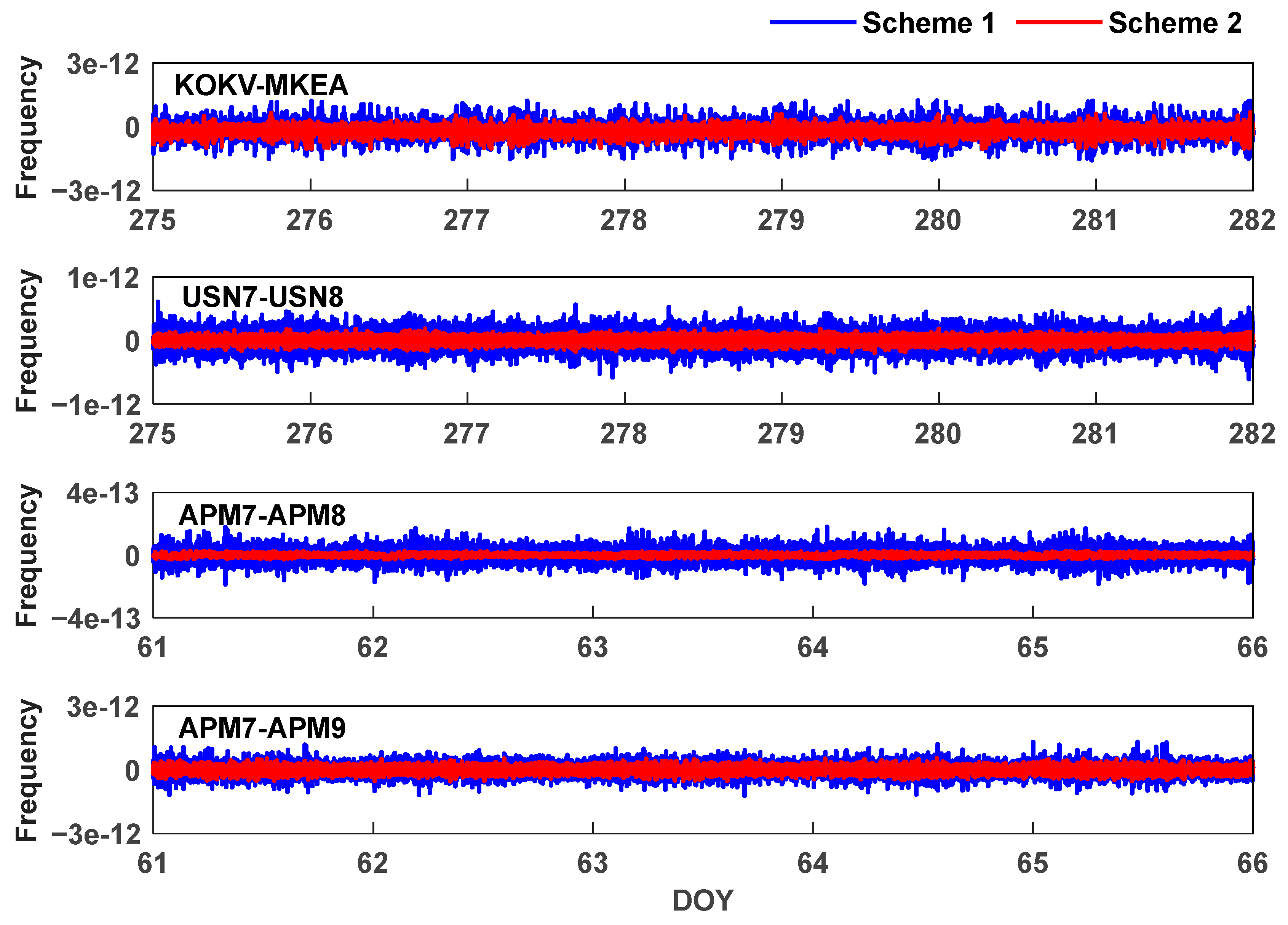
| Statistics | Scheme 1 | Scheme 2 |
|---|---|---|
| STD | 0.073 | 0.069 |
| RMS | 0.079 | 0.079 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, D.; Liu, G.; Zhao, W.; Liao, W.; Zhang, B.; Lyu, M. An Interstation Undifferenced Real-Time Time Transfer Method with Refined Modeling of Receiver Clock. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010168
Lyu D, Liu G, Zhao W, Liao W, Zhang B, Lyu M. An Interstation Undifferenced Real-Time Time Transfer Method with Refined Modeling of Receiver Clock. Remote Sensing. 2024; 16(1):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010168
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Dong, Genyou Liu, Wenhao Zhao, Wei Liao, Bo Zhang, and Minghui Lyu. 2024. "An Interstation Undifferenced Real-Time Time Transfer Method with Refined Modeling of Receiver Clock" Remote Sensing 16, no. 1: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010168
APA StyleLyu, D., Liu, G., Zhao, W., Liao, W., Zhang, B., & Lyu, M. (2024). An Interstation Undifferenced Real-Time Time Transfer Method with Refined Modeling of Receiver Clock. Remote Sensing, 16(1), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010168





