Abstract
This paper presents a circularly polarized turnstile antenna for a meteor radar system. The antenna employs a pair of turnstile radiators, a 1:2 power divider and a 90° phase shifter. After a series of simulations and optimizations, the maximum circularly polarized gain at 39 MHz is 5.9 dBic with 96° 3 dB beam width. The simulated axial ratio below 3 dB is from −39° to 39° within the band of interest. Then, the proposed antenna is fabricated and applied to a meteor radar system. Two tests are carried out for radiation characteristics demonstration. In the first test, the VSWR of the proposed antenna is below 1.2 at 38.5–39.5 MHz and keeps good agreement with simulation results. However, the meteor azimuth distribution is illogical when the output results are compared with the Australian meteor detection radar (ATRAD) meteor detection. To address the problem, baluns are investigated and introduced for balanced feeding. The 1:1 unbalance–balance transformer has been used to improve the radiation characteristics of the designed antenna. The final test results show that the meteor radar system with the improved antenna achieves better performances in meteor counts and meteor azimuth distribution.
1. Introduction
In the last decade, meteor detection technologies and equipment have rapidly developed with a need for better understanding of the aeronomy and dynamics of the mesospheric and lower Thermosphere (MLT) region [1] and its role in determining the revolution of the climate of the Earth [2,3].
Polarization is a fundamental property of electromagnetic waves, and it describes the orientation of the electric field vector relative to the Earth’s surface. A polarized antenna is designed to receive or transmit electromagnetic waves with a specific polarization. The use of polarized antenna can reduce interference and increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the received signal [4,5]. Considering the polarization matching condition, circularly polarized transmit antenna and receive antenna are designed and applied in most meteor detection radar systems [6]. Circularly polarized (CP) antennas are usually preferred owning to the immunity against multipath fading [7]. They can receive circularly and linearly polarized waves and can be used in many wireless communication systems, including broadcasting services, satellite communications [8], mobile communications [9], global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) [10] and detection radars [6,11].
Generally, the necessary and sufficient condition for CP is that [12]: the E-field must have 2 orthogonal linear components with the same magnitude and a time-phased difference of odd multiples of 90°. The most popular method to achieve CP is an orthogonal dipole antenna with equal amplitude and 90° phase-shift feeding. Considering the unbalanced characteristics caused by coaxial cable [13], unbalance–balance (balun) technology is necessary for the dipole antenna feeding network. The term balun is a portmanteau of balance and unbalance, indicating that a balun can transition between a balanced transmission line and an unbalanced transmission line.
For any asymmetric antenna feeding with coaxial cable, a balun is essential and significant to ensure the radiation characteristics of the antenna. Balun can not only be used as an unbalance-to-balance converter, but can also be used as an impedance transformer. There are many kinds of baluns, such as coaxial [14,15], microstrip [16] and LC baluns, currently applied in the antennas industry. Microstrip baluns are low profile and lightweight, easy to fabricate, conformable to mounting structures, and compatible with integrated circuit technology. Many efforts have been made to achieve ultra-wideband (UWB) microstrip baluns for antennas or low-noise amplifiers (LNA) [17,18,19,20,21,22]. However, for very high frequency (VHF) band antennas, microstrip baluns will cause more insertion loss, and elaborative design of microstrip baluns are needed to avoid the influence of distribution capacitance and inductance.
In this work, a circularly polarized turnstile antenna with baluns for meteor radar is presented. The antenna operates at 38.5~39.5 MHz and can realize unidirectional radiation by using reflection structures. In addition, a coaxial cable form Wilkinson power divider is designed as a balun. A fabricated prototype is validated in Section 3. To address the problems found in the meteor radar, a voltage balun is applied to each feeding port of the turnstile antenna, which improves the ability to search for meteor numbers and uniformity of the detection area of the meteor radar.
2. Antenna Topology and Simulation Analysis
To meet the circularly polarization demand of the meteor radar, a turnstile dipole antenna is used to provide orthogonal electric fields. The antenna can be considered as two integrated sub-units. Additionally, equal amplitude feeding and 90° phase shift can be achieved by the Wilkinson power divider and phase shifter inserted in the feeding network. The circularly polarized antenna was simulated by using the ANSYS High-Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS) software. Figure 1 shows the simulation model.
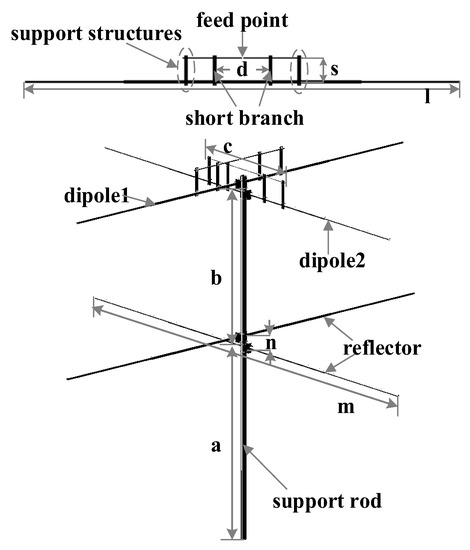
Figure 1.
The simulation model of the designed turnstile antenna.
The antenna consists of two orthogonal dipoles and two reflectors. The overall structural arrangement is more or less the same as two turnstile Yagi-Uda antennas without directors. A support rod is used to raise the antenna to a proper height, and a feeding network is fixed between the two dipoles. In the simulator, balanced feeding and 90° phase shifting are set. Therefore, the balun and Wilkinson power divider do not need to be considered at the stage of computer simulation.
Figure 1 shows that the radiator of the designed antenna has a T-match connection [12]. Dipole1 or Dipole2 is fed by a pair with a length of c and a radius of r. The parameter s and d can be conveniently changed to match the transmission line. To further understand the effects of the T-match, parametric studies on three vital parameters: b, s and d of the T-match depicted in Figure 1 are simulated. Figure 2 presents the simulation results. The simulation shows that tuning these 3 parameters will significantly affect the impedance matching of the 2 excited resonant modes, whereby the optimum impedance bandwidth is achieved when b, s and d are 1330, 182 and 235 mm, respectively.
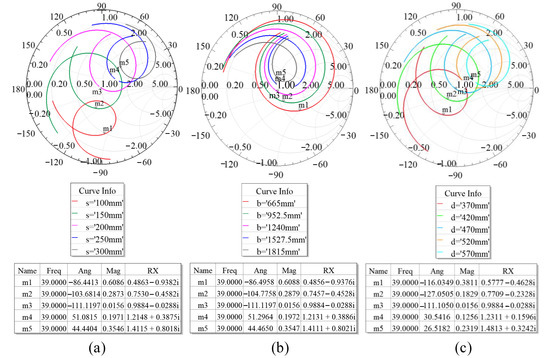
Figure 2.
The simulation results of the designed turnstile antenna with varying parameters (a) s, (b) b and (c) d.
Then, according to the system port characteristic impedance , the dipole needs impedance matching to . Thus, the impedance of the ports of the antenna is set as in the simulator.
After a series of calculations and corrections, the parameters of the turnstile dipole antenna are shown in Table 1. The simulated Smith Chart and Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) of the antenna are depicted in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Before tuning, the impedance of the antenna is about at 39 MHz (black points in Figure 3), hence capacitors are needed to be tuned. With the proper capacitors, the VSWR of the antenna decreases to below 1.2 within the operating frequency band.

Table 1.
Optimized dimensions of the antenna; all dimensions in mm.
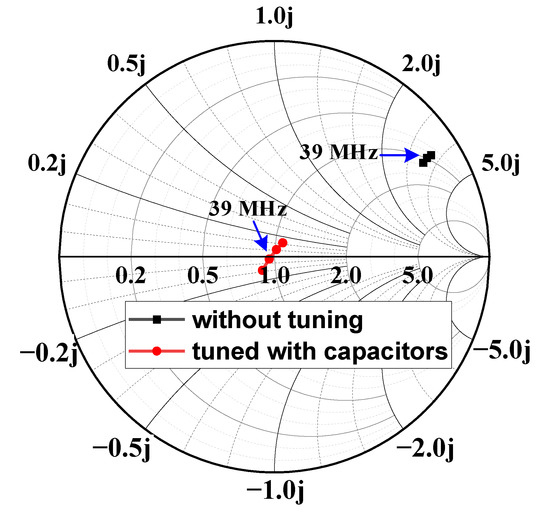
Figure 3.
The simulated Smith Chart of the designed turnstile antenna.
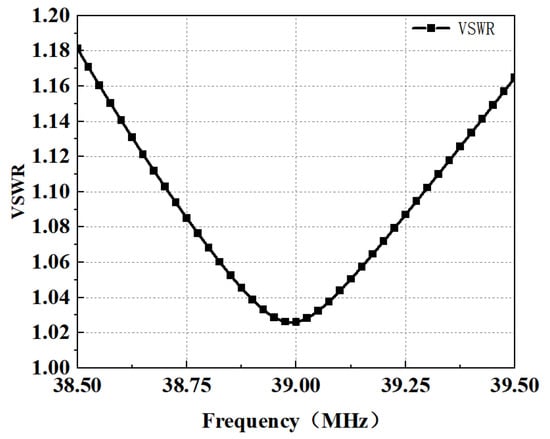
Figure 4.
The simulated VSWR of the designed turnstile antenna.
The simulated radiation patterns are shown in Figure 5. The maximum circularly polarized gain of 5.9 dBic is obtained at 39 MHz, which is quite desirable for a meteor radar antenna [6]. In Figure 5b, the simulated circular polarization (Co-pol.) and cross polarizations (X-pol.) in different vertical planes are plotted. Within the operation frequency band of 38.5~39.5 MHz, the circularly polarized radiation patterns maintain a stable shape, and the co-pol. exhibit high polarization purity. It can be seen from Figure 5b,c that the 3 dB beam width can reach about 96°. It is also found that the gain above 0 dB extends from −68° to 68° (about 136°) along the radiation direction of the antenna. These far-field characteristics, such as wide beam width and polarization gain, are well-suited for detection systems.
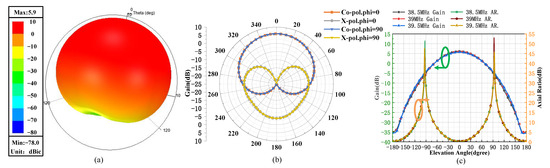
Figure 5.
The simulated far-field results of the designed turnstile antenna. (a) 3D radiation plot of the proposed antenna; (b) Results of coplanar polarization and cross polarization in two orthogonal planes; (c) Results of gain and axil ratio.
In the view of the fact that the phase difference of the feeding ports is kept stable at 90° by the simulator, the dual-feed turnstile antenna performs well in circular polarization. Additionally, we can see from Figure 5c that the axial ratio (AR) below 3 dB is from −39° to 39° within the band of interest. It is worth noticing that the phase difference between the two ports directly influences the polarization characteristics. This indicates that a feeding network must be designed to ensure good feed. To achieve the equal amplitude and 90° phase difference for the 2 ports feeding of the antenna, a Wilkinson power divider with a 90° phase shifter is introduced. The schematic diagram of the feeding network is shown in Figure 6.
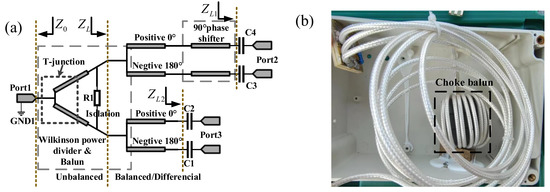
Figure 6.
(a) The schematic diagram of the designed feeding network of the proposed antenna. (b) The designed flux coupled balun.
3. Feeding Network of the Proposed Antenna
Generally, Wilkinson power divider and baluns are all based on quarter wavelength sections of transmission lines, which indicates that they need to be longer (and have a higher loss) to operate at lower frequencies. This limits the practical low end of the frequency band to around 500 MHz to 1 GHz for microstrip baluns. On low dielectric substrates, the parts will be larger (and usually have a lower loss), while on higher dielectric substrates, they will be smaller (and have a higher loss). In addition, crowded and complicated microstrip lines will cause distributed capacitances and inductances unexpectedly within a small size. As a result, the microstrip power divider and balun are no longer acceptable for VHF antenna fabrication.
To ensure that the input power of all units of the antenna is the same, a T-junction, with a 2:1 power ratio is employed in the feeding network as shown in Figure 5. Figure 6 presents the T-junction. The connector is designed for a special purpose. Its appearance is a normal N-type, but it can connect with two radio frequency cables. The impedance of the parallel cable can be treated as . The length of the two cables is a quarter wavelength (reference frequency ) for a quarter wavelength impedance transformer. The mathematical symbols utilized in this part are defined in Table 2.

Table 2.
Symbol definitions.
The impedance of the quarter wavelength impedance transformer can be calculated using the following equation:
It is clear that:
To address the issue of mismatch, fine-tuning of the T-match will solve this problem.
For VHF operation frequencies, a flux-coupled balun transformer is used to reduce the impact from the common mode current. Ideally, a flux-coupled transformer could be used whenever balun functionality is required. It is well understood, relatively simple to build, provides an arbitrary impedance ratio than can be easily tuned, and provides both DC and ground isolation [15]. Figure 6 presents the designed flux-coupled balun. With the help of the flux-coupled balun, balanced feeding can be achieved.
As for the 90° phase shifter, the demand can be satisfied with a quarter wavelength radio frequency coaxial cable.
4. Experimental Results and Improved Design
A low working frequency (less than 50 MHz) band indicates a large antenna size, and measuring the radiation pattern in an anechoic chamber can be expensive and infeasible.
The fabricated antenna and array are shown in Figure 7a,b. To verify the radiation characteristic of the antenna, the fabricated antenna is erected in the open field. VSWR was measured using the Rohde & Schwarz ZNLE3 Vector Network Analyzer, and the simulated and measured results are presented in Figure 8. The measurements are in good agreement with the simulations. The measured VSWR in the impedance bandwidth ranges from 38.5 MHz to 39.5 MHz is less than 1.2. The slight frequency shifts are attributed to fabrication and welding imperfections.

Figure 7.
The fabricated antenna unit (a) and array (b).
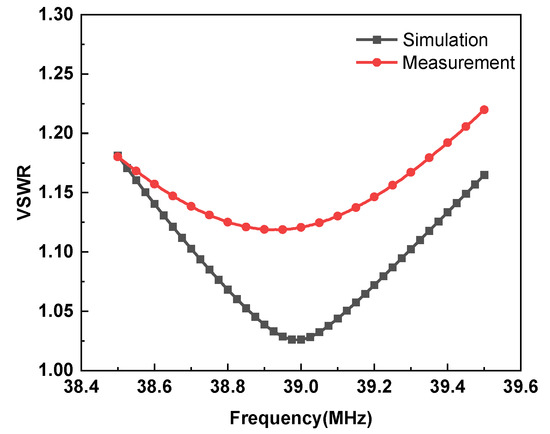
Figure 8.
Comparison of VSWR measurement results and simulation results.
- A.
- Experiment 1
To verify the antenna’s performance experimentally, an association test with a meteor detection radar system is carried out. The experimental results are compared with the Australian meteor detection radar (ATRAD). The meteor detection radar deployed in Wangjiahe Town, Huangpi District, Wuhan City, Hubei province, China, is located approximately 55 km away from ours. It consists of one transmitting antenna (left-handed circularly polarized, LHCP) and five identical receiving antennas (proposed right-handed circularly polarized antenna) designed for meteor observation. By designing the receiving antenna array, the meteor radar can be used for meteor tracking, detection of meteor trails, summarizing quantities and distributing meteors. The measured results are shown in Figure 9.
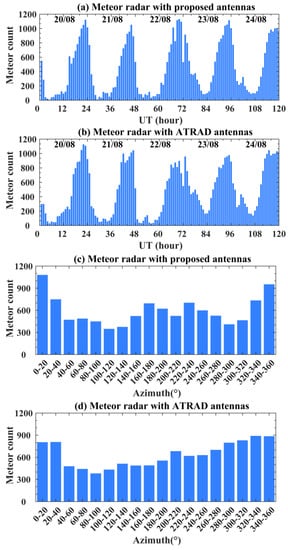
Figure 9.
Comparison of count and azimuth distribution of meteors. Meteor radar with antennas of proposed (a,c) and ATRAD (b,d).
The azimuthal distribution and counts of meteors from 3 to 7 July 2022 were observed with the proposed receiving antenna array, as shown in Figure 9. It can be seen from Figure 9a and Table 3 that the maximum of meteors reaches to 9500~13,000 per day. Figure 9 compares the universal-time distributions of meteor counts measured by the meteor radar with antennas of ATRAD and with proposed antennas. We can see from Figure 9c that the azimuthal distribution of meteors measured by the meteor radar with our proposed antennas mismatched with that observed by the ATRAD radar. Unlike the ATRAD meteor azimuth distributions that only have one depression, the system with proposed antennas shows two depressions. The disagreement in meteor azimuth distribution is unusual under the condition that the radiation pattern of the proposed antenna is approximately standard along with the direction of horizontal to the ground. The phenomenon gives an indication that the radiation patterns of the fabricated antenna at the operation frequency are distorted.

Table 3.
Statics table of meteor quantity.
- B.
- Analysis and Improved Design
Deformed pattern is often caused by reverse current. Therefore, it is possible that some reverse currents exist on the surface of the antenna. In order to solve this problem, a study was done as following:
Firstly, such pattern defects never appear in the simulated radiation pattern results of the designed turnstile antenna. Secondly, as a critical component, the balun plays a role in realizing balanced feeding for the dipole antenna. The balun used in the fabricated antenna may be insufficient to choke all the inverse currents, and its magnitude may not be equal to that of a differential port of the dipole antenna.
Generally, a balun is a three-port power splitter, similar to a Wilkinson or resistive power divider, and its two outputs will have equal magnitudes and opposite phases (a 180° phase shift).
To solve this problem, 1:1 Ferrite transmission line transformers are used in the antenna feeding network. Figure 10 shows the transform. The ferrite is ring-like with a size of 13 × 7 × 5 mm, and the initial permeability of the material is 100.
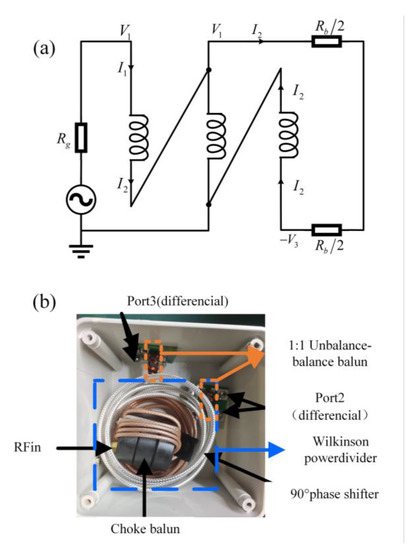
Figure 10.
The prototype of the improved feeding network. (a) the circuit principal diagram of balun and (b) photo of feeding network.
5. Results Comparison and Discussion
- C.
- Experiment 2
Figure 11 shows the measured phase difference and magnitude of ports in the improved feeding network. The measurements are taken with a vector network analyzer and only two-port scattering parameter measurements are taken with the other port terminated with a standard 50 Ω load. Within the operation band from 38.5 MHz to 39.5 MHz, the phase difference between Port2 and Port3 of the feeding network ranges from 87.3° to 90°. Achieving circular polarization or elliptical polarization is an essential prerequisite for successful feeding. The maximum phase unbalances from 180° between Port2 and Port3 are 1.3° and 1.05° at the operation band, respectively. The maximum amplitude unbalances of Port2 and Port3 are 0.215 dB and 0.24 dB.
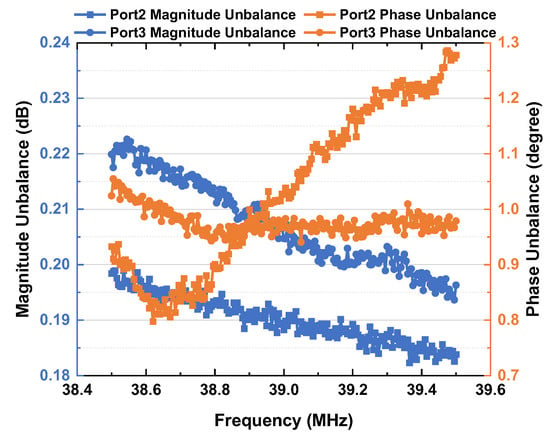
Figure 11.
Measurement results of magnitude unbalance and phase unbalance of new feeding network.
The new baluns are designed to be inserted at the two ports of the antenna. In addition, the improved antenna forms an array that can be applied in the meteor radar system. The new round of verification experiments is taken from 20 to 24 August 2022.
As shown in Figure 12 and Table 4, the antenna equipped with the new feeding network can detect a greater number of meteors, and the azimuth distribution correlation can reach 0.8467, as compared to the data from the ATRAD radar. This indicates the good radiation performance and the application ability of the designed antenna.
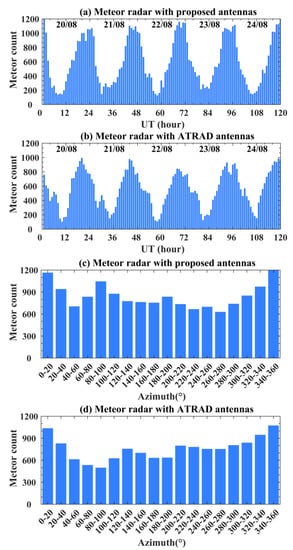
Figure 12.
Comparison of count and azimuth distribution of meteors. Meteor radar with antennas of Chinese Meridian Project (a,c) and proposed and improved (b,d).

Table 4.
Statics table of meteor quantity with improved antenna.
- D.
- Discussion
The balun plays an important role in the designed antenna. The prototype of the balun (shown in Figure 10) is proposed in reference [23]. This type of balun is similar to a single bifilar winding transformer, except for an additional length of winding being added. Under the condition of low loss and phase shifting, the characteristics of the current distribution on the three wires are as follows [24,25]:
- Equal current always flows through two of the three wires;
- The sum of the currents is equal to the current flowing through the other wire in the opposite direction;
- The points at both ends of the three wires are distributed evenly.
The equations are listed as:
where, and are termination voltages, and and are termination currents. is the odd mode impedance and is electrical length with a unit of rad of windings. is the power impedance and is the load input impedance.
Then, when , the transmission coefficient (T) of the transformer can be described as:
Equations (7) and (8) indicate that the optimum transmission condition is . This just meets the demand of the designed antenna. During the experiment, it was also found that this kind of transformer can be used for broadband RF devices. This idea will also be included in the next research.
6. Conclusions
A turnstile VHF circular polarized antenna has been designed and employed for meteor radar, utilizing a transmission line power divider and balun. A 1:1 unbalance-to-balance transformer has been implemented to enhance the radiation characteristics of the designed antenna. Considering the difficulties in radiation and gain testing, after fabricating and improving the antenna feeding network, a receiving antenna array is utilized in the meteor radar system. Better performances, such as increased meteor counts and improved azimuthal distribution of meteors, are achieved.
Author Contributions
Methodology and investigation, W.Q.; data curation and writing—original draft preparation, W.Q. and M.L.; writing—review and editing, C.Z.; W.Y.; funding acquisition, C.Z. and Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC grant No. 41574146, 41774162, 42004130, 42204161, 42104150), the fellowship of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M710941), the Foundation of National Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic Environment (Grant No. 6142403180204, 6142403200303), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Key Laboratory of Geospace Environment, University of Science and Technology of China (GE2020-01), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2042021kf0020).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in https://zenodo.org/record/7821683#.ZDaqj3ZBzEY, accessed on 14 March 2023.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the use meteor radar dataset provided by Beijing National Observatory of Space Environment, Institute of Geology and Geophysics Chinese.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ceplecha, Z.; Borovička, J.; Elford, W.G.; ReVelle, D.O.; Hawkes, R.L.; Porubčan, V. Meteor Phenomena and Bodies. Space Sci. Rev. 1998, 84, 327–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Briczinski, S.J.; Doherty, J.F.; Mathews, J.D. Genetic-Algorithm-Based Parameter Estimation Technique for Fragmenting Radar Meteor Head Echoes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.-H.; Doherty, J.F.; Mathews, J.D. Time-frequency radar processing for meteor detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangqing, W.; Junpeng, S.; Guan, G.; Gacanin, H.; Dobre, O.A. 3-D Positioning Method for Anonymous UAV Based on Bistatic Polarized MIMO Radar. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 815–827. [Google Scholar]
- Guimei, Z.; Yuwei, S.; Chen, C. Height Measurement with Meter Wave Polarimetric MIMO Radar: Signal Model and MUSIC-like Algorithm. Signal Process. 2022, 190, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.V.B.; Eswaraiah, S.; Ratnam, M.V.; Kosalendra, E.; Kumar, K.K.; Kumar, S.S.; Patil, P.T.; Gurubaran, S. Advanced meteor radar installed at Tirupati: System details and comparison with different radars. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2014, 119, 11893–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, S.X.; Park, I.; Ziolkowski, R.W. Crossed Dipole Antennas: A review. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2015, 57, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cato, C.; Lim, S. A miniaturized circularly polarized, parasitic array antenna for ground station communication with cube satellites. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, Chicago, IL, USA, 8–14 July 2012; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppettella, D.; Ali, M. A broadband directional circularly polarized spiral antenna on EBG structure. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2020, 34, 1563–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Chen, Z.N. A Compact Circularly Polarized Slotted Patch Antenna for GNSS Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 6506–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, S.; Hunt, S.M.; Minardi, M.J.; McKeen, F.M. Analysis of Perseid meteor head echo data collected using the Advanced Research Projects Agency Long-Range Tracking and Instrumentation Radar (ALTAIR). Radio Sci. 2000, 35, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Broadband Dipoles and Matching Techniques. In Antenna Theory, Analysis and Design, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 523–541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xin, H. A Dual-Band Dipole Antenna with Integrated-Balun. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 786–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, U. Wideband balun using a transmission line transformer. IEICE Electron. Express 2011, 8, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.V.; Pham, A.-V.; Leoni, R.E. Design of 600-W Low-Loss Ultra-Wideband Ferriteless Balun. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Zhang, W.; Geng, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, R.; Gao, J. Design of Compact Frequency-Tuned Microstrip Balun. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2010, 9, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaghaei, J.; Jalali, A.; Meghdadi, M. A Wideband Inductorless LNA Employing Active Complementary Current-Reuse Balun. In Proceedings of the 27th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Yazd, Iran, 30 April–2 May 2019; pp. 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fatin, G.Z.; Fatin, H.Z. A wideband balun-LNA. Aeu-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2014, 68, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geha, C.; Nguyen, C.; Silva-Martinez, J. A Wideband Low-Power-Consumption 22-32.5-GHz 0.18-mu m BiCMOS Active Balun-LNA With IM2 Cancellation Using a Transformer-Coupled Cascode-Cascade Topology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Z.G.; Xu, J. A wideband balun-LNA employing g (m)-boosting with improved gain balance. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2016, 86, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauludin, M.F.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J. A Wideband Low-Power Balun-LNA with Feedback and Current Reuse Technique. Electronics 2022, 11, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, B.; Yavari, M. A Linear Wideband CMOS Balun-LNA With Balanced Loads. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L. Dipole and Monopole antennas. In Antenna Engineering Handbook; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 218–235. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgesen, D.; Marki, C. Balun Basics Primary; Marki Microwave, Inc.: Morgan Hill, CA, USA, 2014; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Transmission Line Transformer Theory. In Broadband Devices Based on RF Ferrite; The Science Publishing Company: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 59–142. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).