Sequential Seismic Anisotropic Inversion for VTI Media with Simulated Annealing Algorithm Aided by Adaptive Setting of Optimization Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Forward Modeling for VTI Media
2.2. Prestack Seismic Anisotropic Inversion
2.3. Optimization Method Based on Fast Simulated Annealing
2.4. Adaptive Optimization Parameter Setting
2.4.1. Linear Inversion Based on the Rüger Approximation
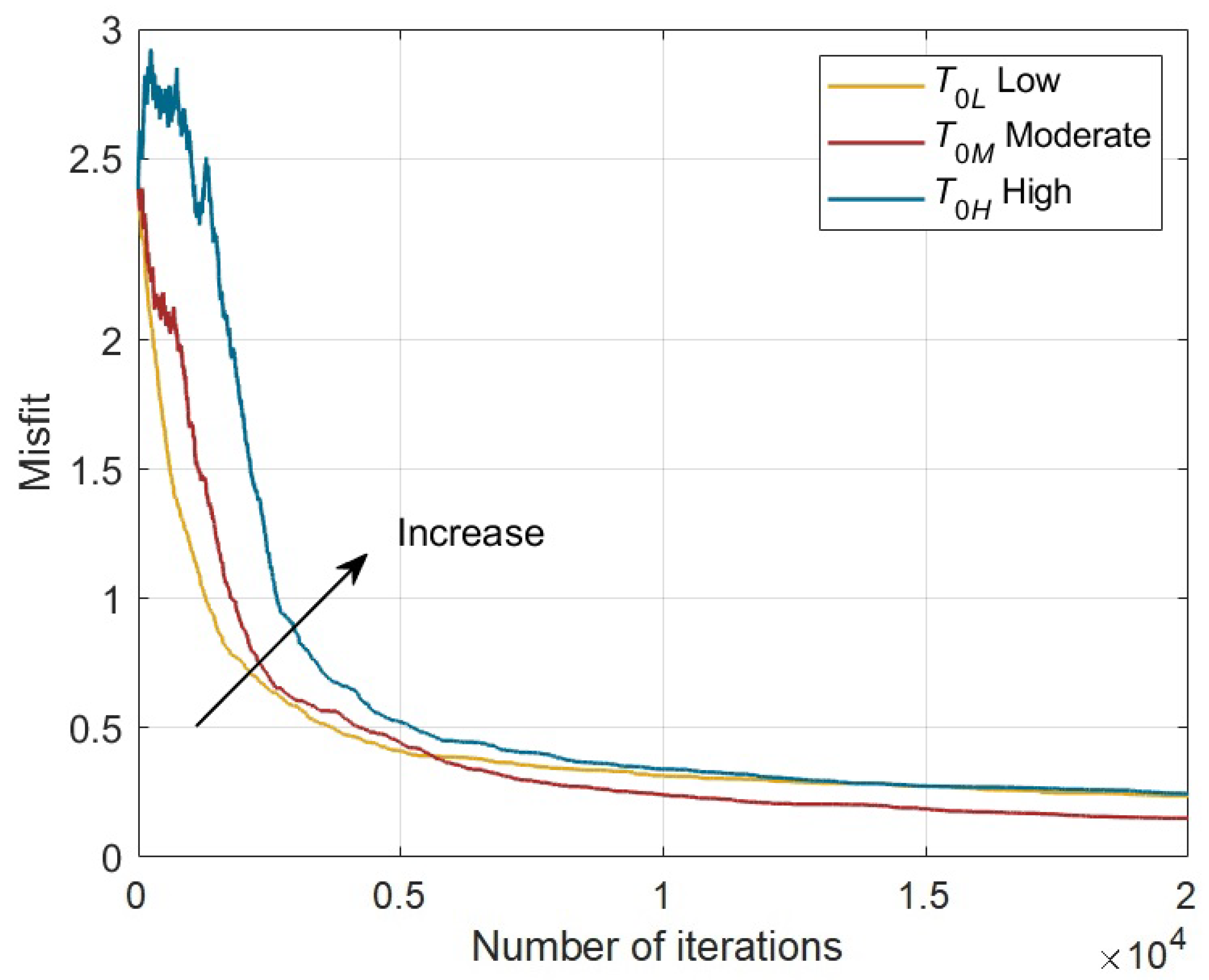
2.4.2. Initial Temperature Setting
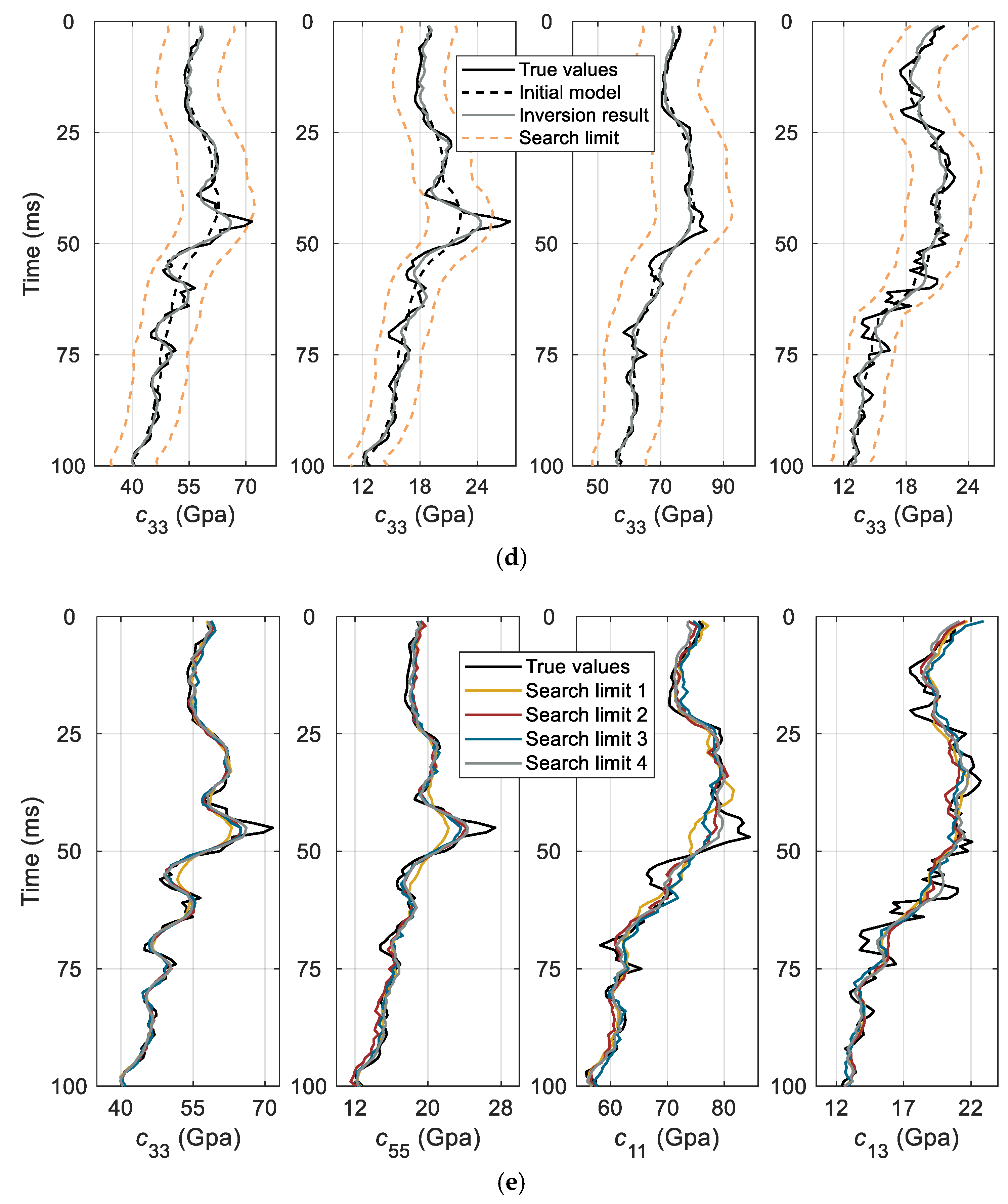
2.4.3. Search Limit and Perturbation Range Setting
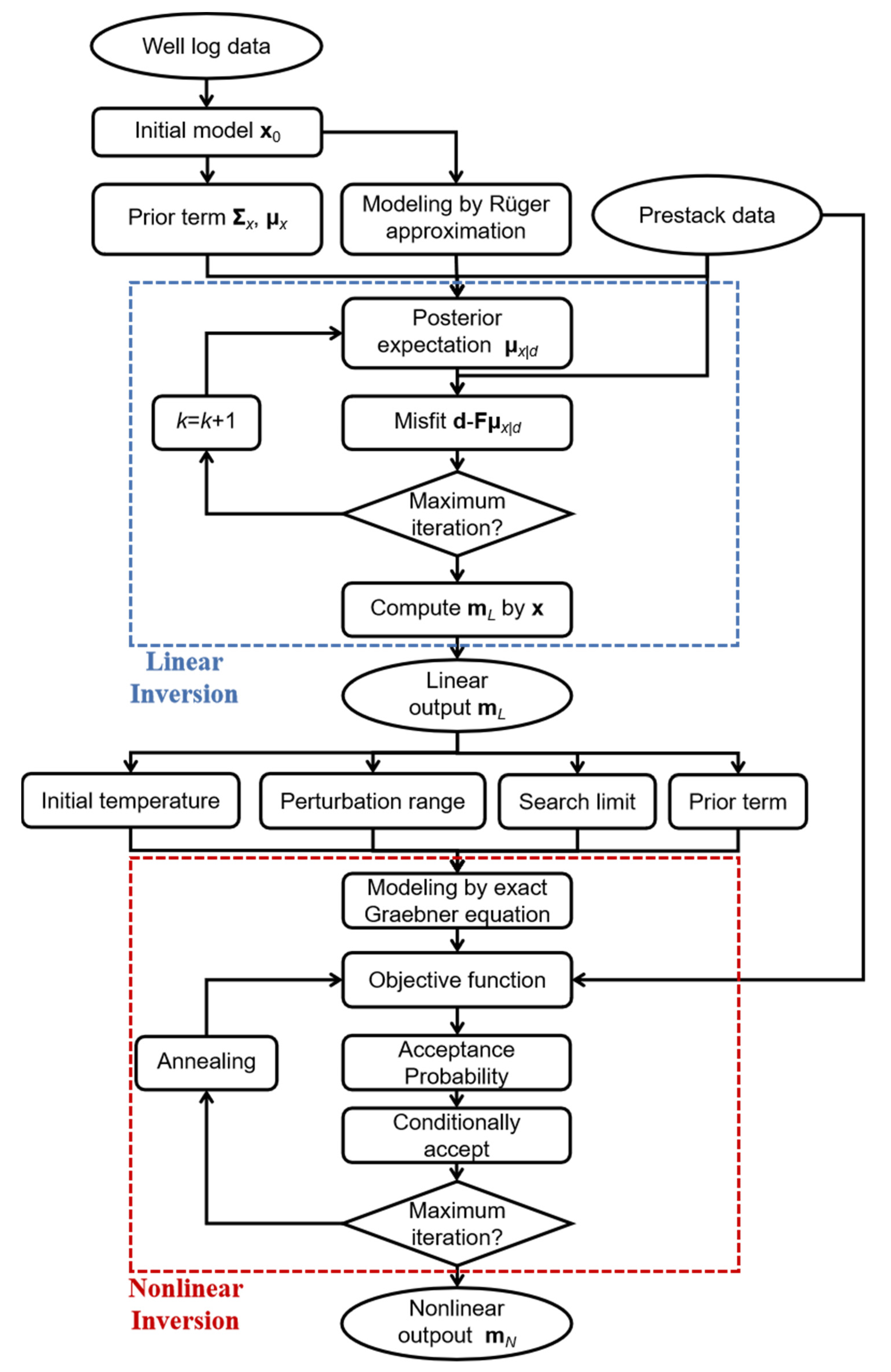
| Algorithm 1 The Proposed Sequential Prestack Anisotropic Inversion Method |
| 1. Input: the observed prestack seismic data d, and the logging data |
| 2. Initialization for linear inversion: |
| 2-1. Initialize the model vector for the linear inversion, and we obtain x0 = [vP0, vS0, ρ0, ε0, δ0] |
| 2-2. Initialize the initial statistical relations among the five parameters from x0, and we obtain Σx0 and μx0 of Equation (11) |
| 3. Stage 1 linear inversion |
| Adopt Equation (11) and start the loop: k = 1, 2, 3, ... do |
| 3-1. Compute the synthetic data based on the initial model by using the Rüger approximation of Appendix C and the forward operator matrix F according to Equation (10) |
| 3-2. Calculate the posterior expectation μx|d according to Equation (11) |
| 3-3. Compute the misfit d-μd. Output the inversion result x = μx|d if the maximum iteration is reached, or x0 = μx|d, and repeat steps 2–3 |
| 3-4. Compute the model vector mL = [c33L,c55L,c11L,c13L,ρL] according to Equation (12) based on x |
| 4. Preliminary output: the result mL of the first step |
| 5. Initialization for nonlinear inversion: |
| 5-1. Set m0 = mL as the initial model of the nonlinear inversion |
| 5-2. Initialize the statistical relations among the five target parameters from m0, and we obtain Cm0 and of Equation (5) |
| 5-3. Generate the initial temperature according to Equation (13) based on m0 |
| 5-4. Generate the search limit and perturbation range according to Equations (16) and (17) based on m0 |
| 6. Stage 2 nonlinear inversion: |
| Adopt the objective function (5) and start the loop: k = 1, 2, 3, ... do |
| 6-1. Perturb the model parameter according to Equation (6) and calculate the acceptance probability |
| 6-2. Reject or accept the perturbation according to Equation (8); repeat the process several times within the Markov chain |
| 6-3. Reduce the temperature and repeat 6-1 to 6-2 until twenty consecutive perturbations are rejected or the maximum iteration is reached |
| 7. Final output: the final result mN. |
3. Effect of Optimization Parameter
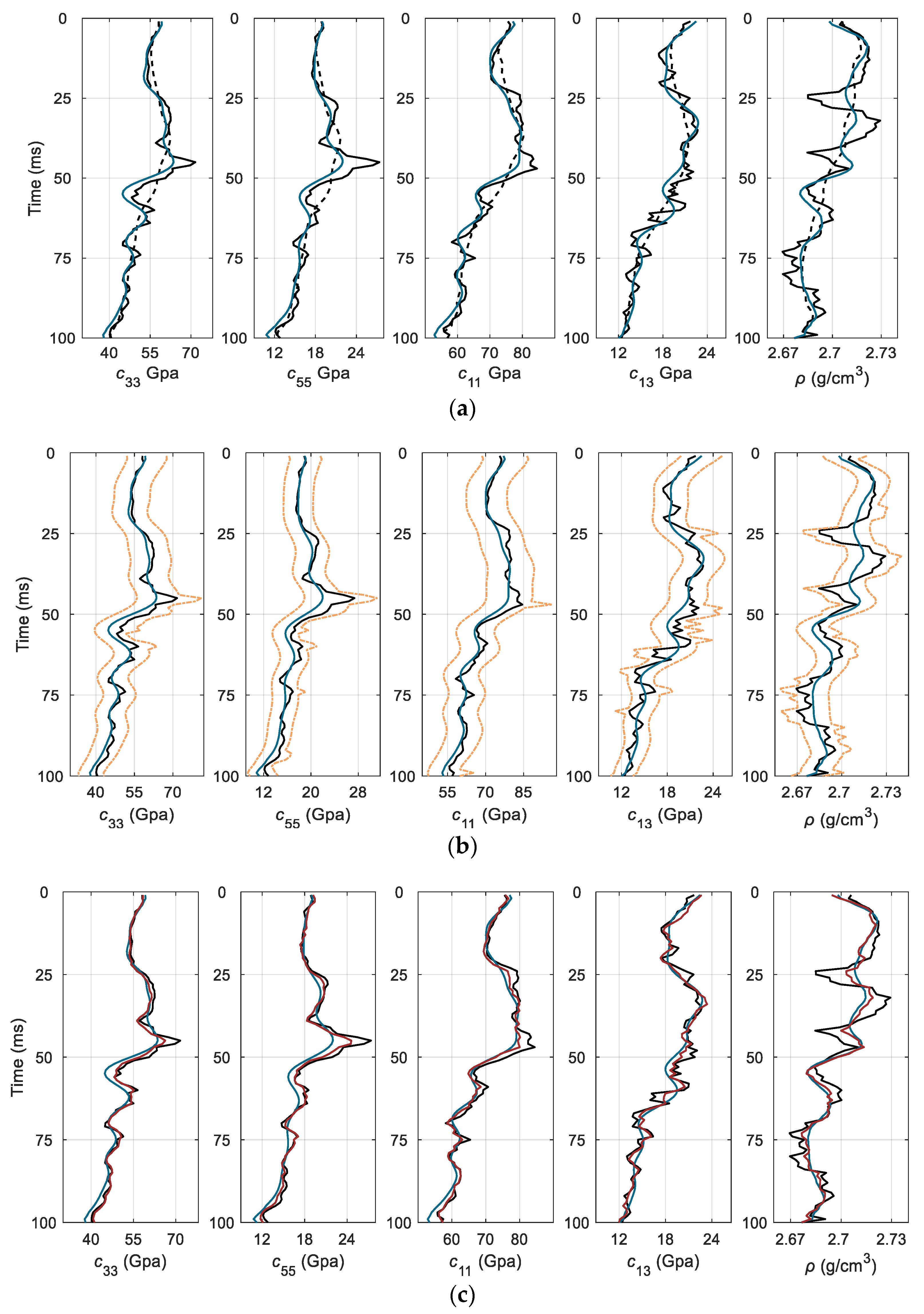
3.1. Initial Temperature
3.2. Perturbation Range
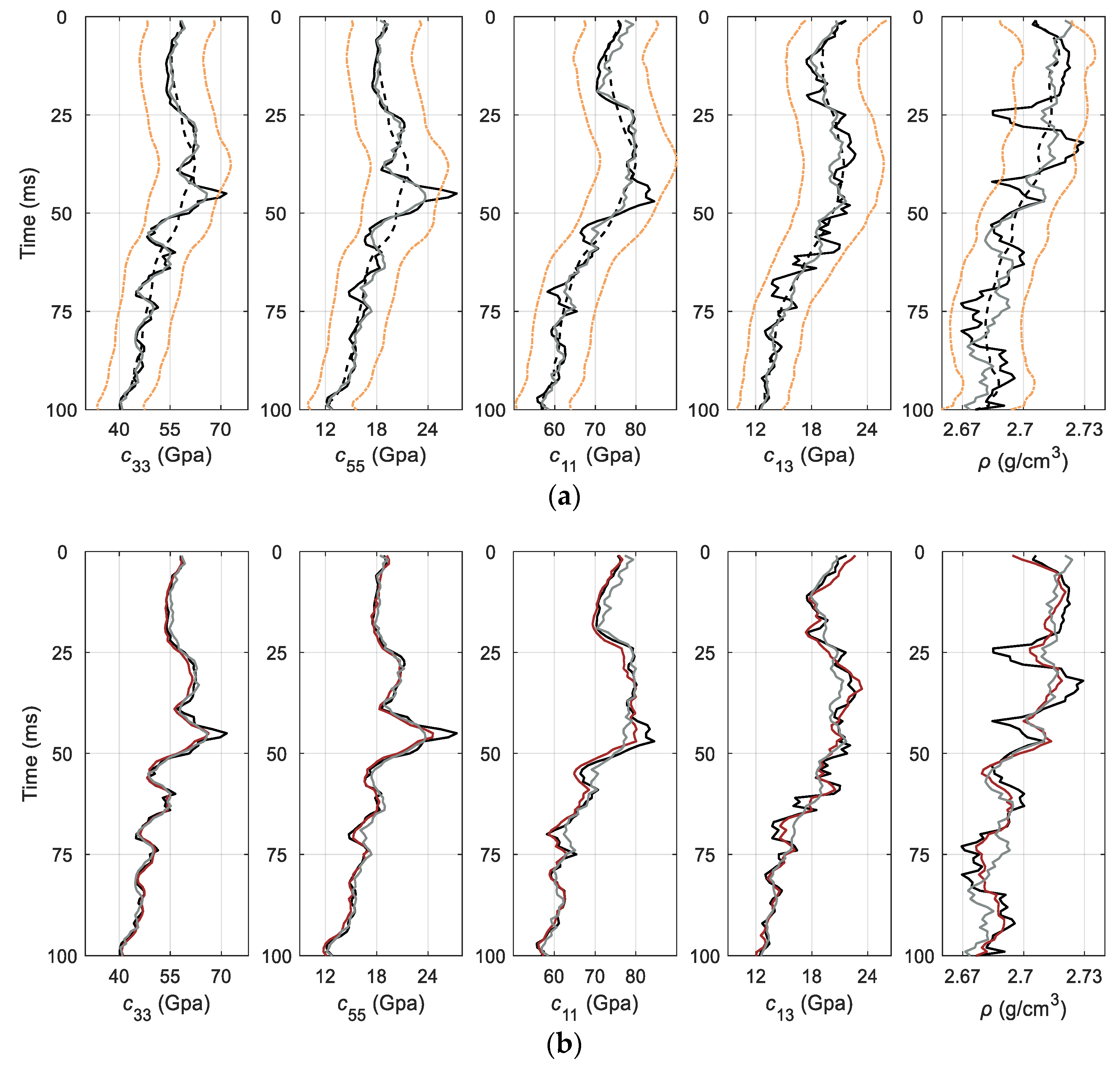
3.3. Search Limit
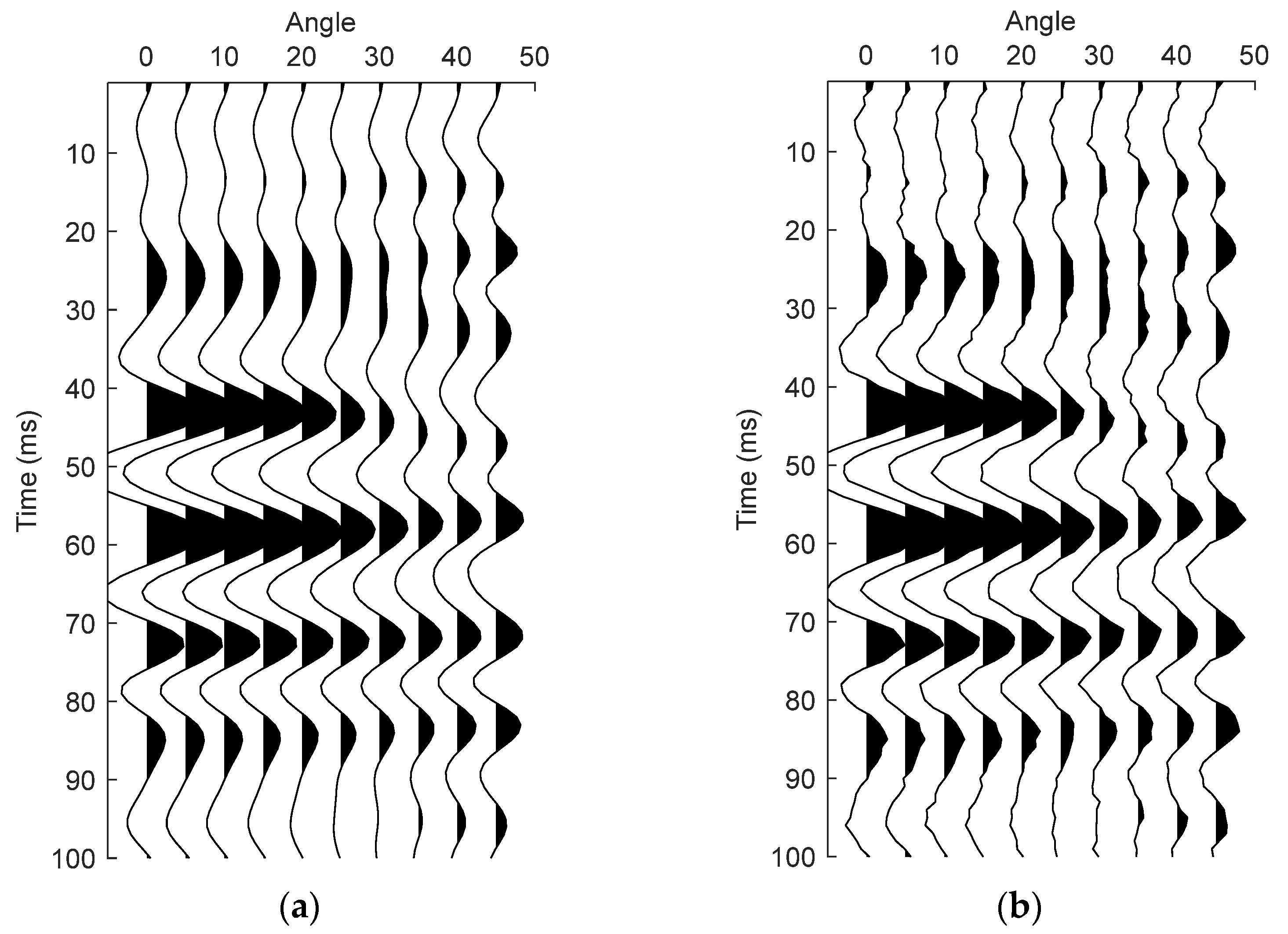
4. Synthetic Data Test
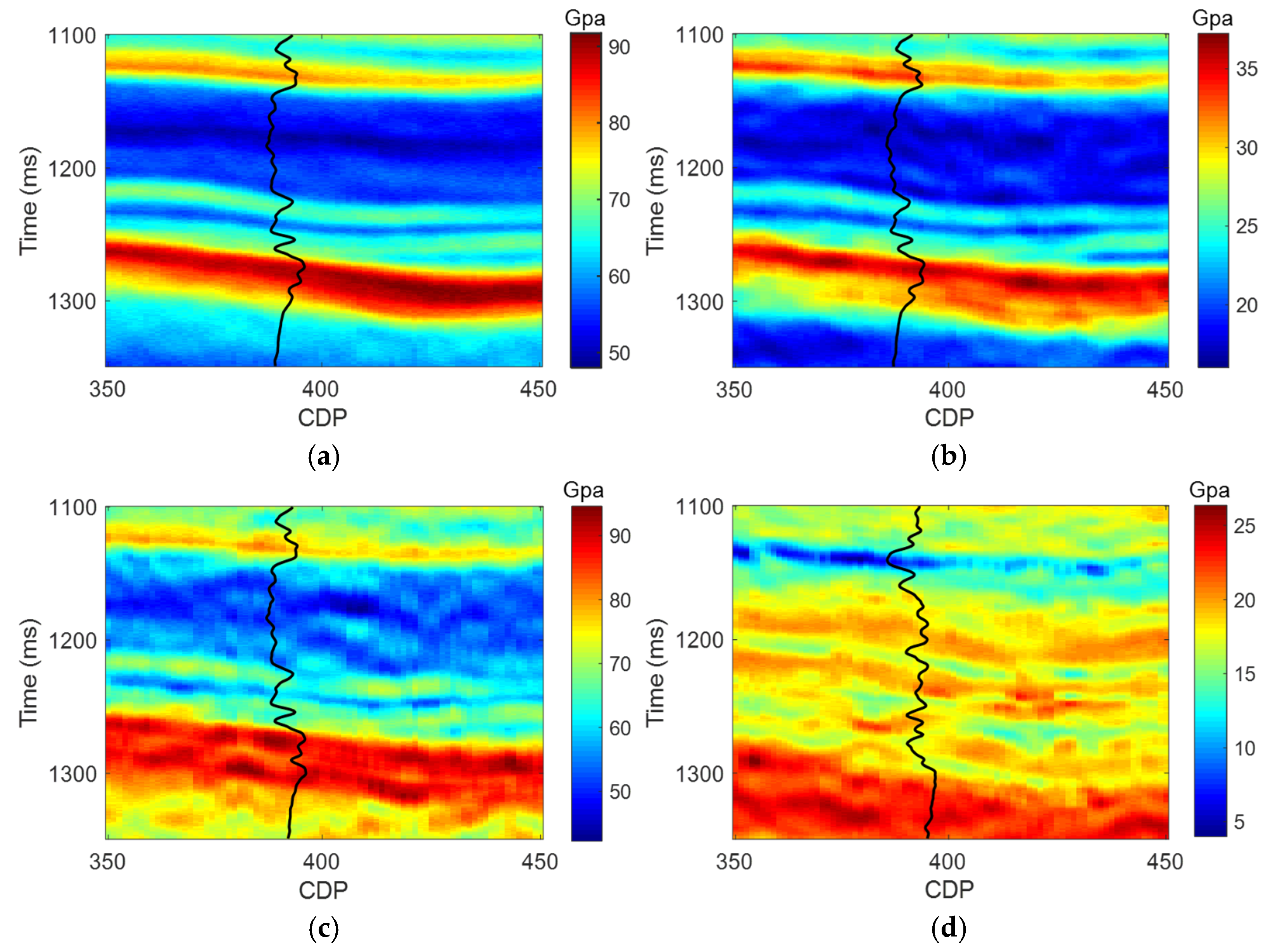
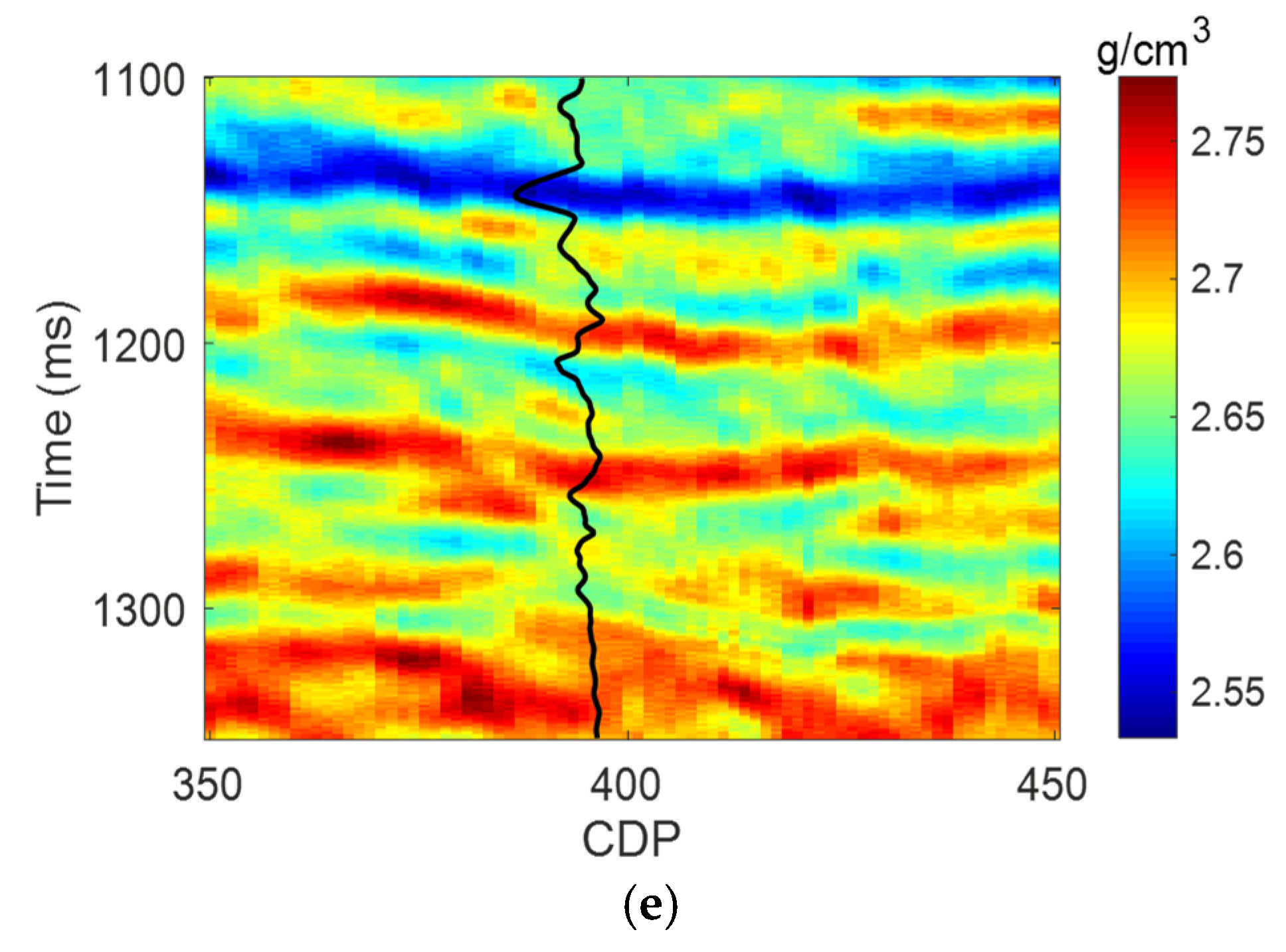
5. Real Data Application
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Chen, H. Seismic frequency component inversion for elastic parameters and maximum inverse quality factor driven by attenuating rock physics models. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 835–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ba, J.; Gei, D.; Carcione, J. A matrix-fracture-fluid decoupled PP reflection coefficient approximation for seismic inversion in tilted transversely isotropic media. Geophysics 2022, 87, M275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y. Mesoscopic wave-induced fluid flow effect extraction by using frequency-dependent prestack waveform inversion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 6510–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y. Registration free multicomponent joint AVA inversion using optimal transport. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4501513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Huang, G.; Carcione, J. A Born-WKBJ pre-stack seismic inversion based on a 3-D structural-geology model building. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4505011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Sun, Q. Density stability estimation method from pre-stack seismic data. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Li, K.; Yin, X.; Zhu, M.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, W. Broadband seismic amplitude variation with offset inversion. Geophysics 2017, 82, M43–M53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Han, J.; Geng, J.; Innanen, K. Anisotropic anelastic impedance inversion for attenuation factor and weaknesses combining Newton and Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 1845–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ba, J.; Luo, C.; Pang, M. Seismic rock physics inversion with varying pore aspect ratio in tight sandstone reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 207, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ba, J.; Carcione, J. Multi-objective petrophysical seismic inversion based on the double-porosity Biot-Rayleigh model. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 1117–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ba, J.; Luo, C. Nonlinear petrophysical AVO inversion inversion with spatially-variable pore aspect ratio. Geophysics 2022, 87, M111–M125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, D.; Liu, C. A new seismic inversion scheme using fluid dispersion attribute for direct gas identifification in tight sandstone reservoirs. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yin, X.; Zong, Z.; Grana, D. Estimation of porosity, fluid bulk modulus, and stiff-pore volume fraction using a multi-trace Bayesian AVO petrophysics inversion in multi-porosity reservoirs. Geophysics 2021, 87, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Yin, X.; Wu, G. Geofluid discrimination incorporating poroelasticity and seismic reflection inversion. Surv. Geophys. 2015, 36, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Gong, F.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. A physical model study of shale seismic responses and anisotropic inversion. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, C.; den Boer, L. Shale anisotropy and the elastic anisotropy of clay minerals. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2014; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2014; pp. 2829–2833. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J. The effects of transverse isotropy on reflection amplitudes versus offset. Geophysics 1987, 52, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Di, B.; Zeng, L. Quantitative seismic interpretation of rock brittleness based on statistical rock physics. Geophysics 2019, 84, IM63–IM75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcione, J.; Avseth, P. Rock-physics templates for clay-rich source rocks. Geophysics 2015, 80, D481–D500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, J.; Xu, W.; Fu, L.; Carcione, J.; Zhang, L. Rock anelasticity due to patchy saturation and fabric heterogeneity: A double doubleporosity model of wave propagation. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2017, 122, 1949–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcione, J. Reflflection and transmission of qP-qS plane waves at a plane boundary between viscoelastic transversely isotropic media. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 129, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graebner, M. Plane-wave reflflection and transmission coeffificients for a transversely isotropic solid. Geophysics 1992, 57, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, M.; Protazio, J. ‘Zoeppritz’ rationalized and generalized to anisotropy. J. Seism. Explor. 1992, 1, 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, L. Weak elastic anisotropy. Geophysics 1986, 51, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüger, A. P-wave reflflection coeffificients for transversely isotropic models with vertical and horizontal axis of symmetry. Geophysics 1997, 62, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüger, A. Variation of P-wave reflectivity with offset and azimuth in anisotropic media. Geophysics 1998, 63, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; An, Y. Joint anisotropic amplitude variation with offset inversion of PP and PS seismic data. Geophysics 2018, 83, N31–N50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessix, R.; Bork, P. Quantitative estimate of VTI parameters from AVA responses. Geophys. Prospect. 2000, 48, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, T.; Li, X. Seismic amplitude inversion for the transversely isotropic media with vertical axis of symmetry. Geophys. Prospect. 2019, 67, 2368–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Characterization of a shale-gas reservoir based on a seismic AVO inversion for VTI media and quantitative seismic interpretation. Interpretation 2020, 8, SA11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Carcione, J.; Huang, G.; Guo, Q. Joint PP and PS pre-stack AVA inversion for VTI medium based on the exact Graebner equation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Carcione, J. A Hierarchical Prestack Seismic Inversion Scheme for VTI Media Based on the Exact Reflection Coefficient. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4507416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Ba, J.; Luo, C. Prestack seismic inversion with data-driven MRF-based regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 7122–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingber, L. Very fast simulated re-annealing. Math. Comput. Model. 1989, 12, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Stoffa, P. Nonlinear one-dimensional seismic waveform inversion using simulated annealing. Geophysics 1991, 56, 1624–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, R. Nonlinear inversion, statistical mechanics, and residual statics estimation. Geophysics 1985, 50, 2784–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Wei, X.; Han, F. Hybrid seismic inversion based on mulit-order anisotropic Markov random field. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Kiatsupaibul, S.; Zabinsky, Z.; Smith, R. An analytically derived cooling schedule for simulated annealing. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 38, 333–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Frazer, L. Rapid determination of the critical temperature in simulated annealing inversion. Science 1990, 249, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, E.; Korst, J. Simulated Annealing and Boltzmann Machines; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Buland, A.; Omre, H. Bayesian linearized AVO inversion. Geophysics 2003, 68, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryden, N.; Park, C.B. Fast simulated annealing inversion of surface waves on pavement using phase-velocity spectra. Geophysics 2007, 71, R49–R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. Simultaneous inversion of prestack seismic data for rock properties using simulated annealing. Geophysics 2002, 67, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, E. Tutorial: Wavelet estimation for well ties. Lead. Edge 2016, 35, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, A. Inverse Problem Theory and Methods for Model Parameter Estimation; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM): Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, L.X.; Chen, S.Q.; Li, X.Y. Amplitude variation with angle inversion using the exact Zoeppritz equations—Theory and methodology. Geophysics 2016, 81, N1–N15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrych, J.T.; Sacchi, D.M.; Woodbury, A. A Bayes tour of inversion: A tutorial. Geophysics 2001, 66, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabben, E.T.; Tjelmeland, H.; Ursin, B. Non-linear Bayesian joint inversion of seismic reflection coefficients. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Carcione, M.J.; Huang, G.T.; Guo, Q. Joint PP and PS pre-stack seismic inversion for stratifified models based on the propagator matrix forward engine. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 987–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grana, D.; Mukerji, T.; Doyen, P. Seismic Reservoir Modeling: Theory, Examples, and Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Carcione, J.; Guo, Q. Basis Pursuit Anisotropic Inversion Based on the L1-L2-Norm Regularization. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8011105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


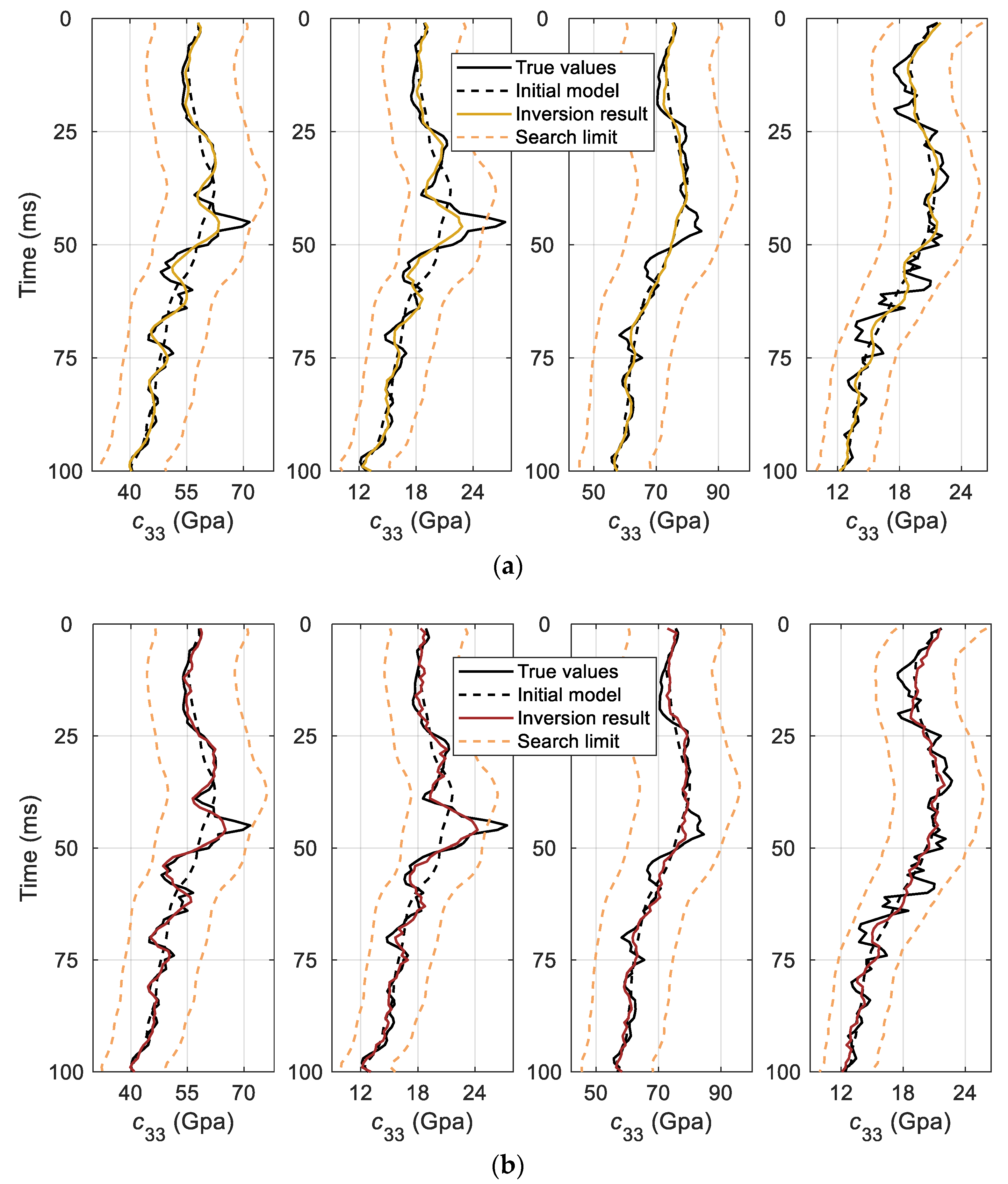
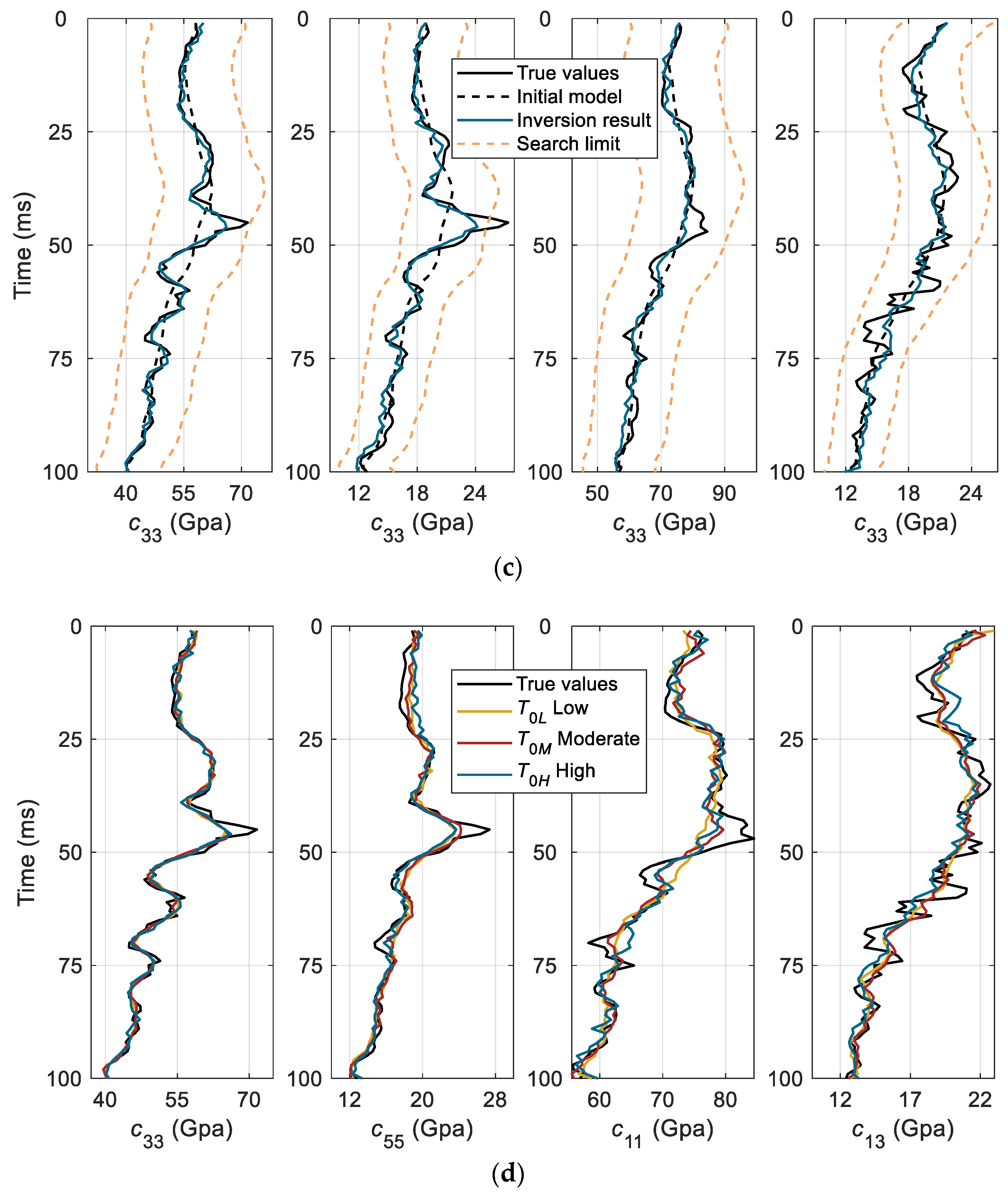
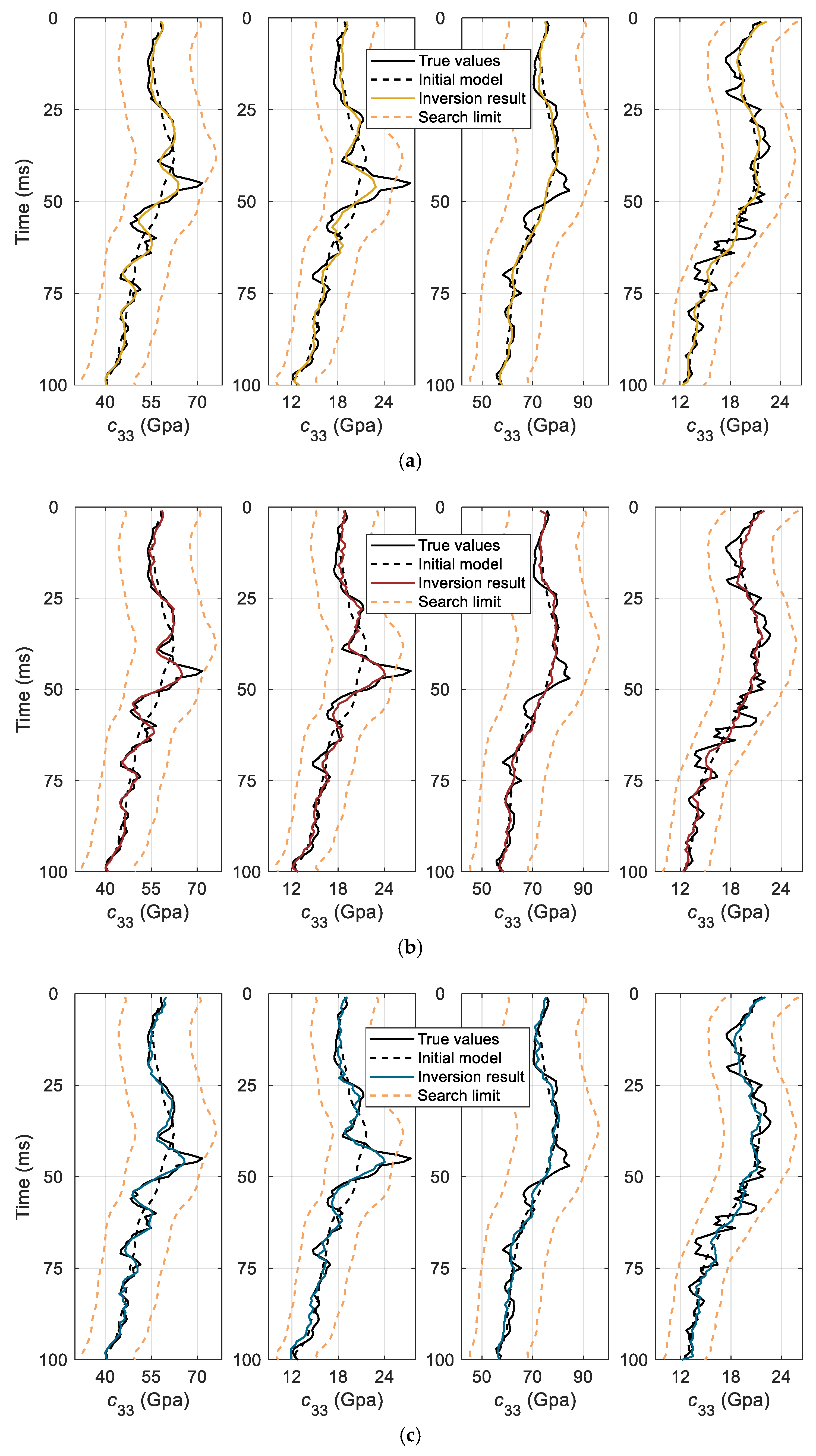
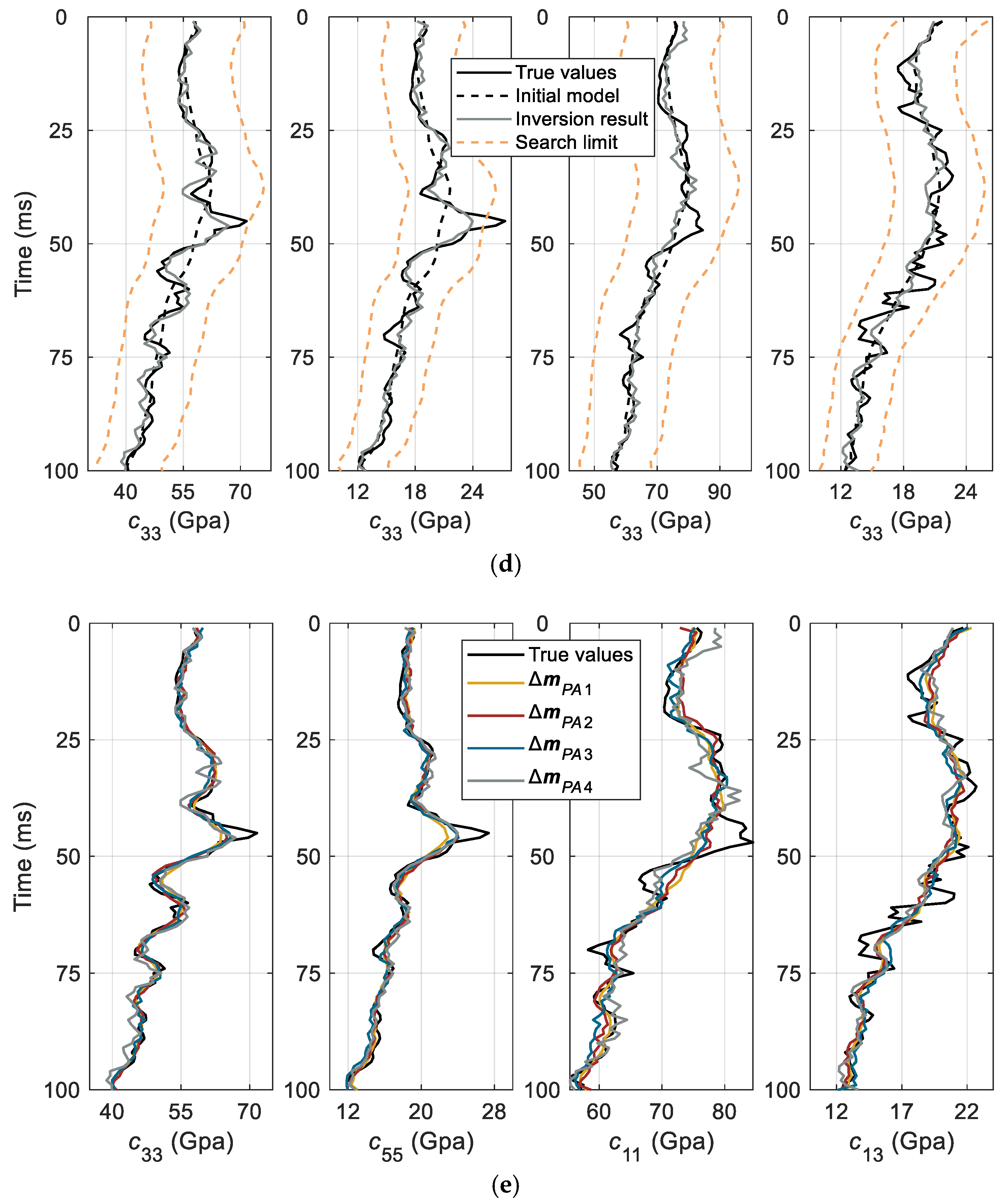
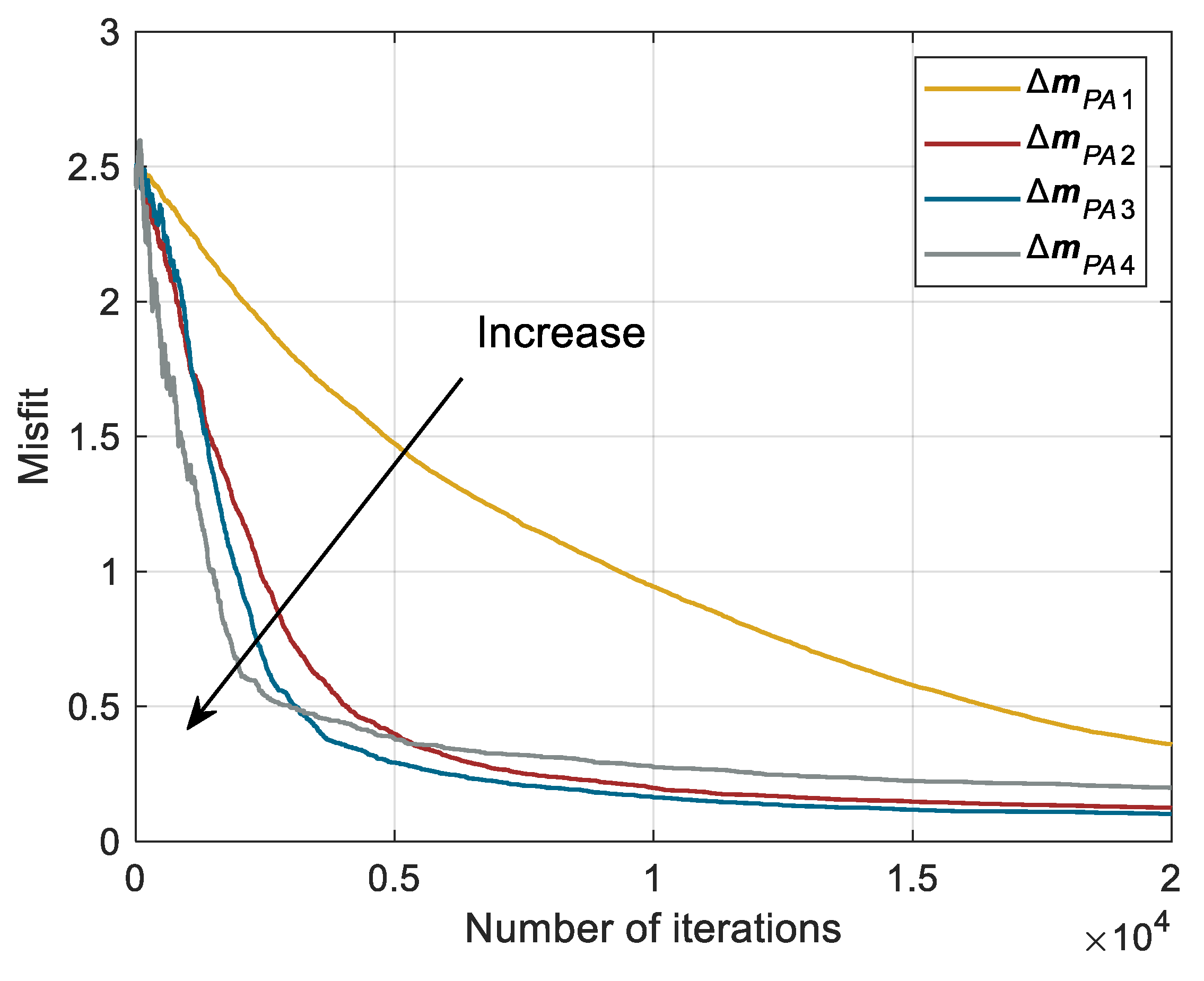
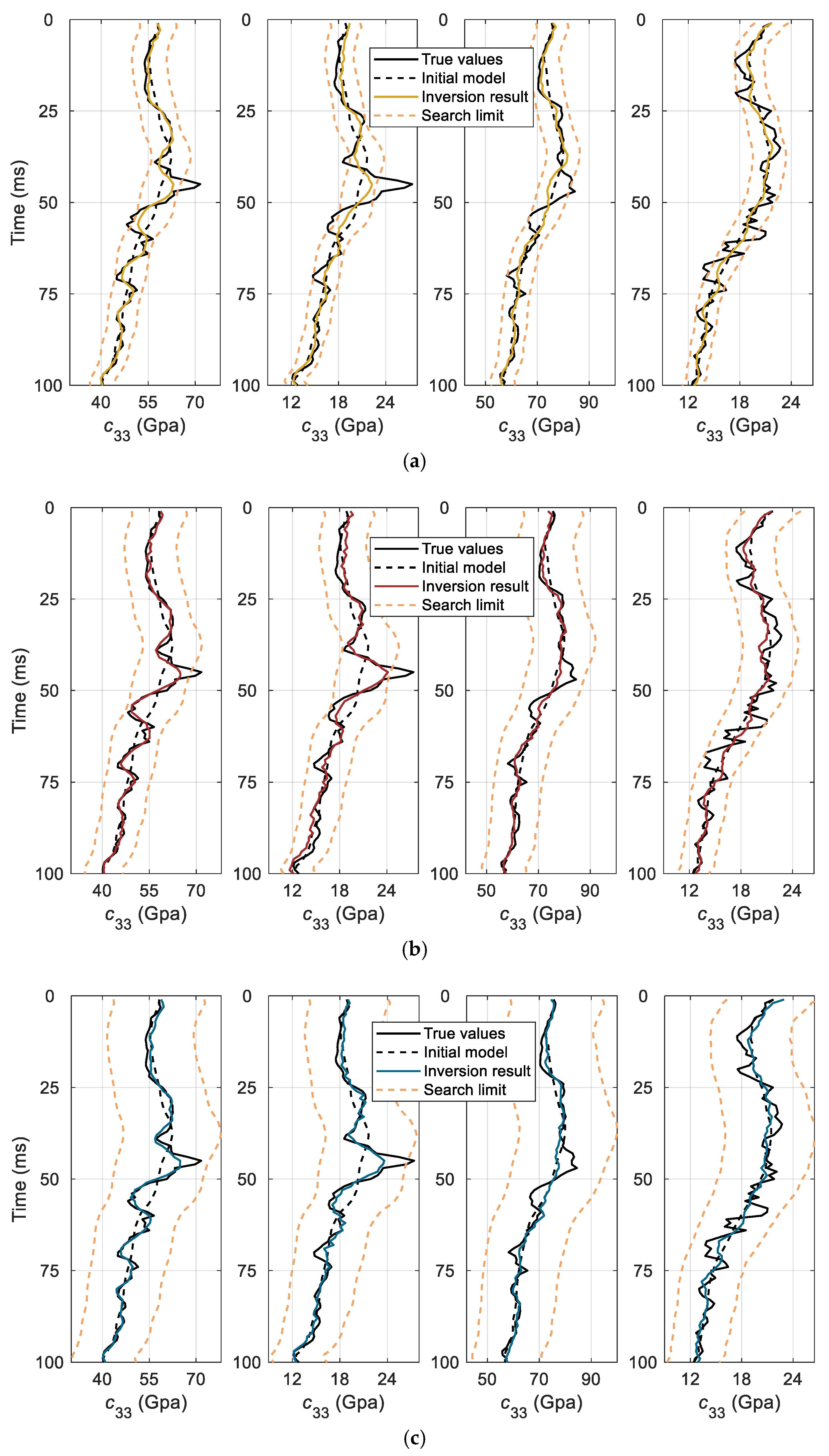

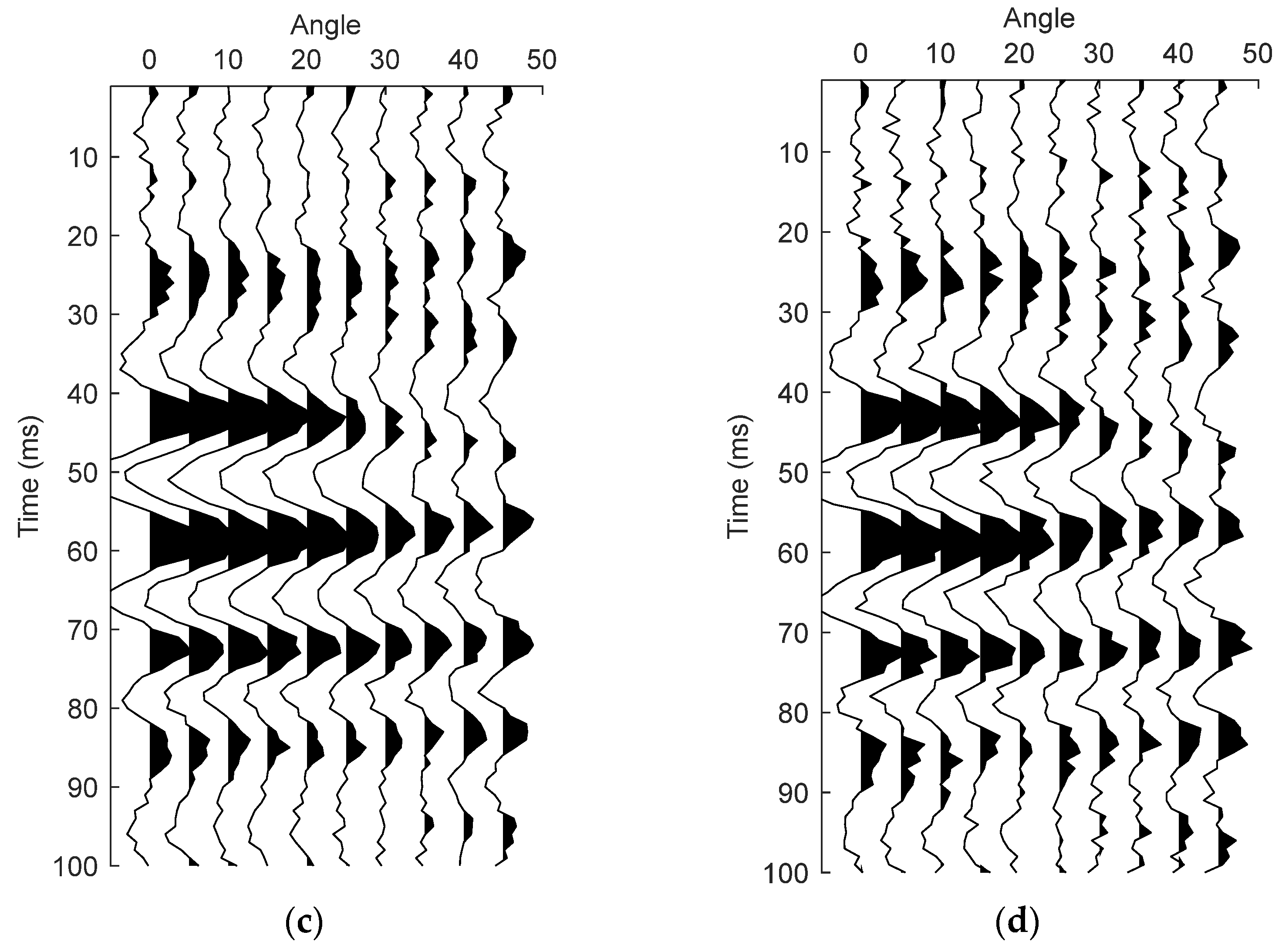


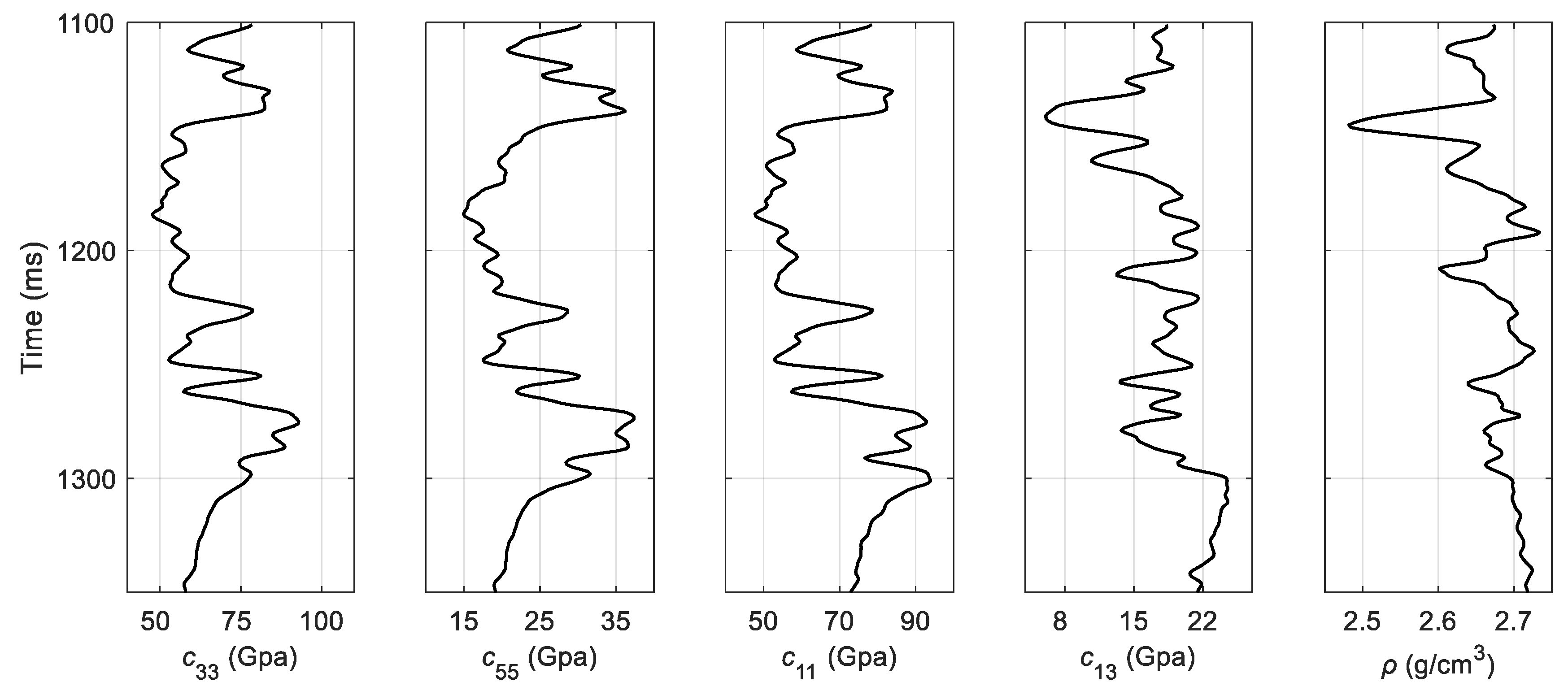
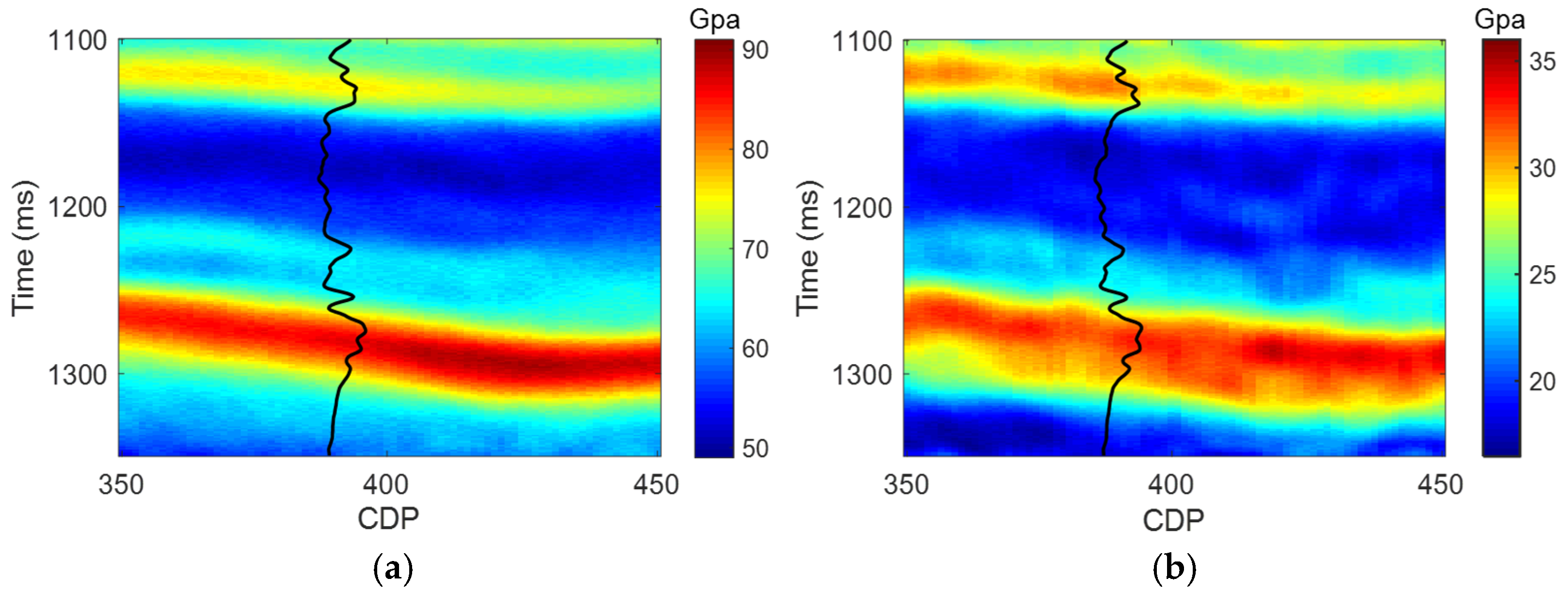
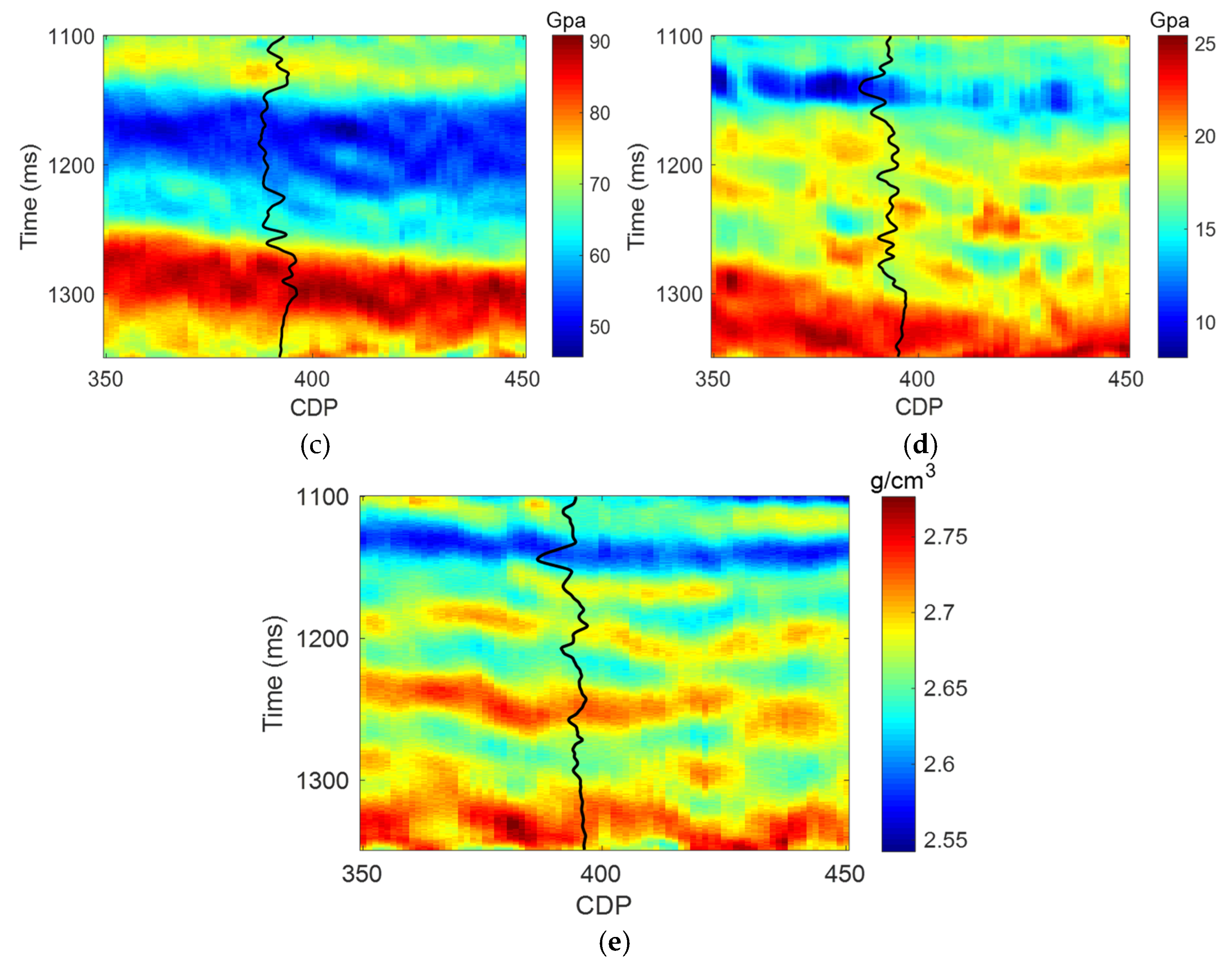
| Correlation Coefficients | c33 | c55 | c11 | c13 | ρ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rüger inversion (linear step) | 0.9605 | 0.9413 | 0.9324 | 0.9102 | 0.8731 |
| Aided FSA (nonlinear step) | 0.9932 | 0.9825 | 0.9801 | 0.9717 | 0.9201 |
| Correlation Coefficients | c33 | c55 | c11 | c13 | ρ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional FSA | 0.9806 | 0.9719 | 0.9626 | 0.9495 | 0.8737 |
| Correlation Coefficients | c33 | c55 | c11 | c13 | ρ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR = 10 | 0.9846 | 0.9731 | 0.9703 | 0.9598 | 0.8889 |
| SNR = 5 | 0.9808 | 0.9681 | 0.9611 | 0.9543 | 0.8769 |
| SNR = 3 | 0.9744 | 0.9630 | 0.9587 | 0.9501 | 0.8643 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, C.; Ba, J.; Guo, Q. Sequential Seismic Anisotropic Inversion for VTI Media with Simulated Annealing Algorithm Aided by Adaptive Setting of Optimization Parameters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071891
Luo C, Ba J, Guo Q. Sequential Seismic Anisotropic Inversion for VTI Media with Simulated Annealing Algorithm Aided by Adaptive Setting of Optimization Parameters. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071891
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Cong, Jing Ba, and Qiang Guo. 2023. "Sequential Seismic Anisotropic Inversion for VTI Media with Simulated Annealing Algorithm Aided by Adaptive Setting of Optimization Parameters" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071891
APA StyleLuo, C., Ba, J., & Guo, Q. (2023). Sequential Seismic Anisotropic Inversion for VTI Media with Simulated Annealing Algorithm Aided by Adaptive Setting of Optimization Parameters. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071891








