Characterization of the East—West Spatial Uniformity for GOES-16/17 ABI Bands Using the Moon
Abstract
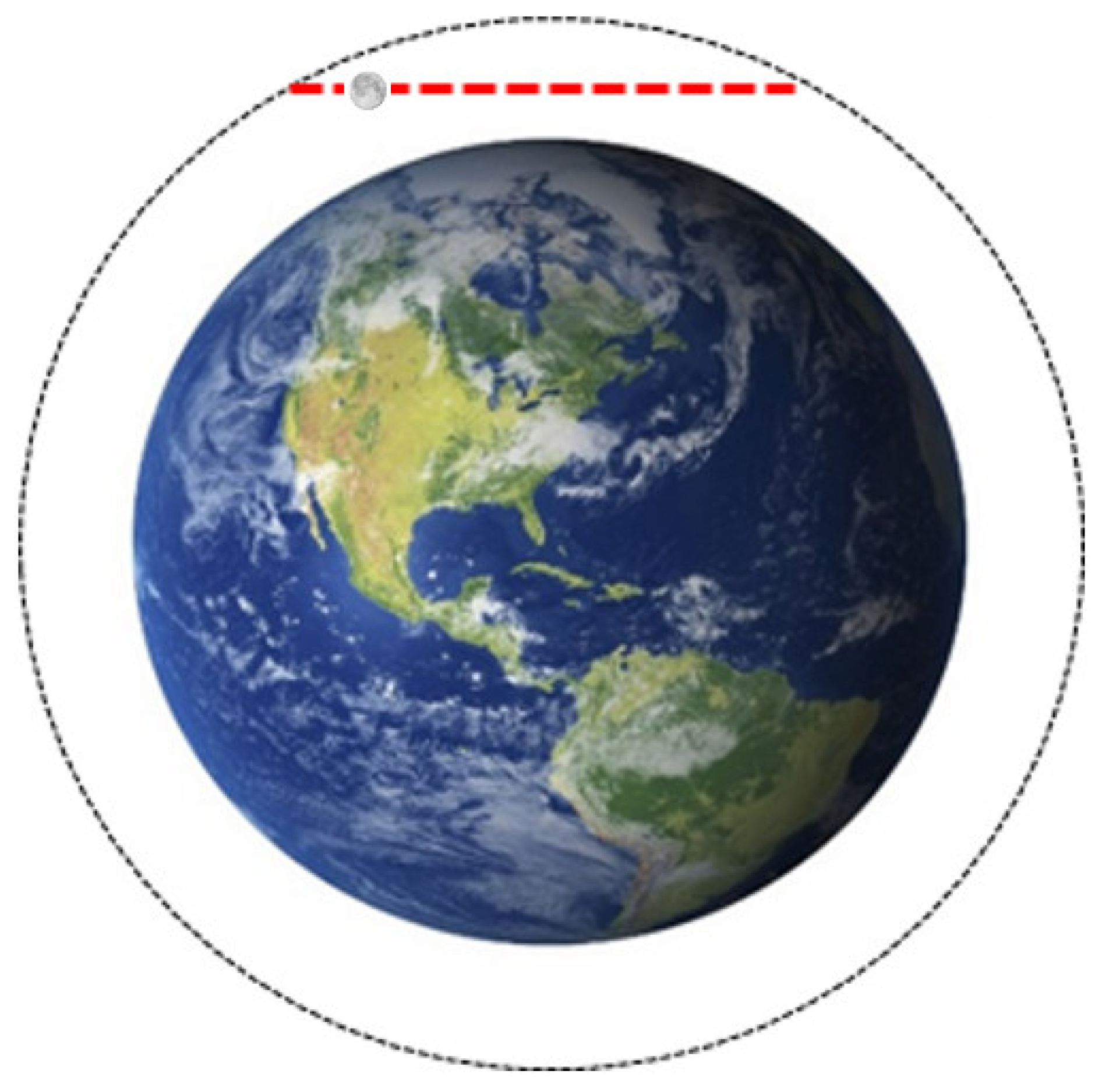
1. Introduction
2. ABI Lunar Image Collections
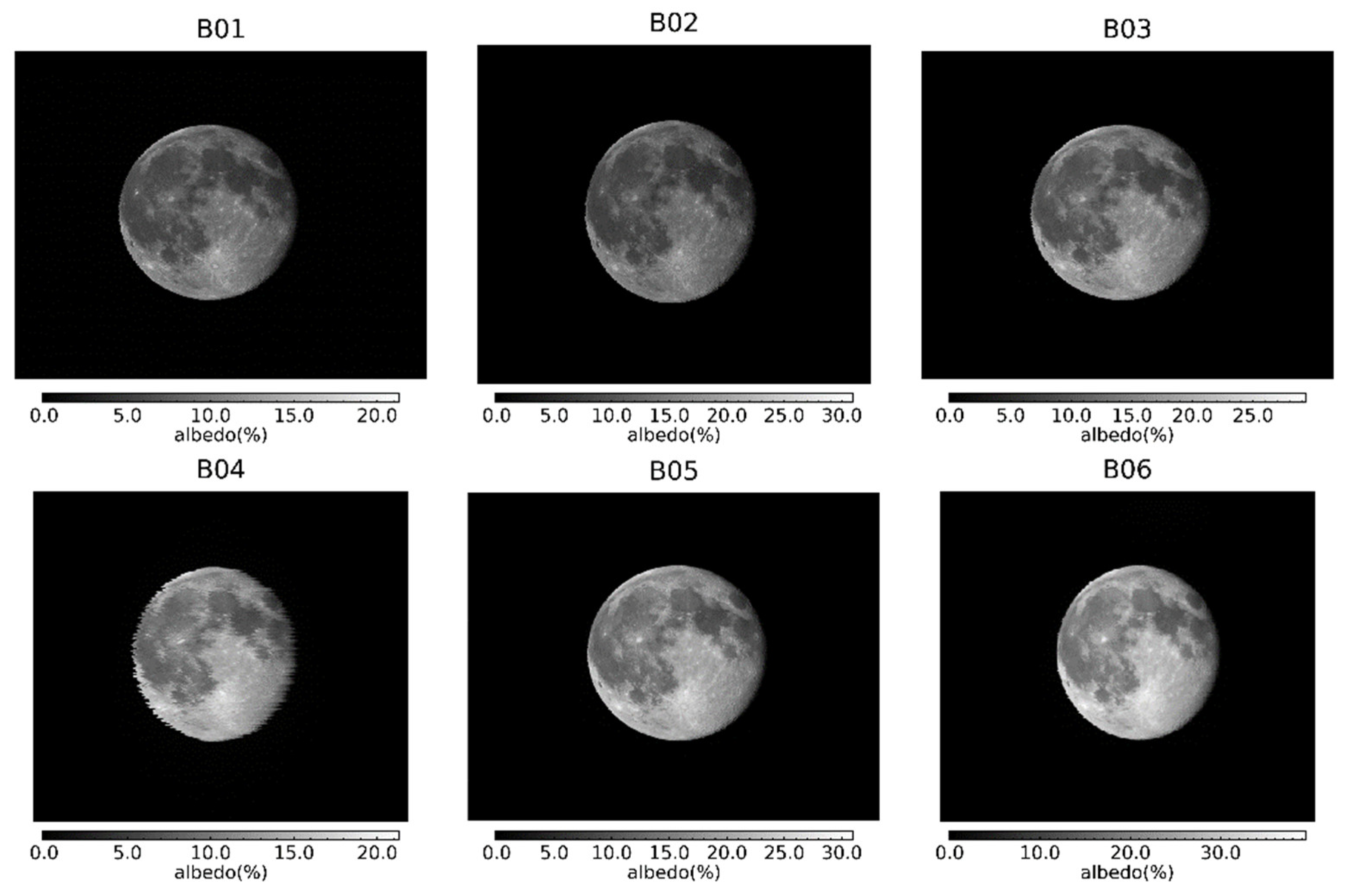
2.1. ABI VNIR Bands
2.2. Lunar Irradiance Model and ABI Lunar Phase Angle Range
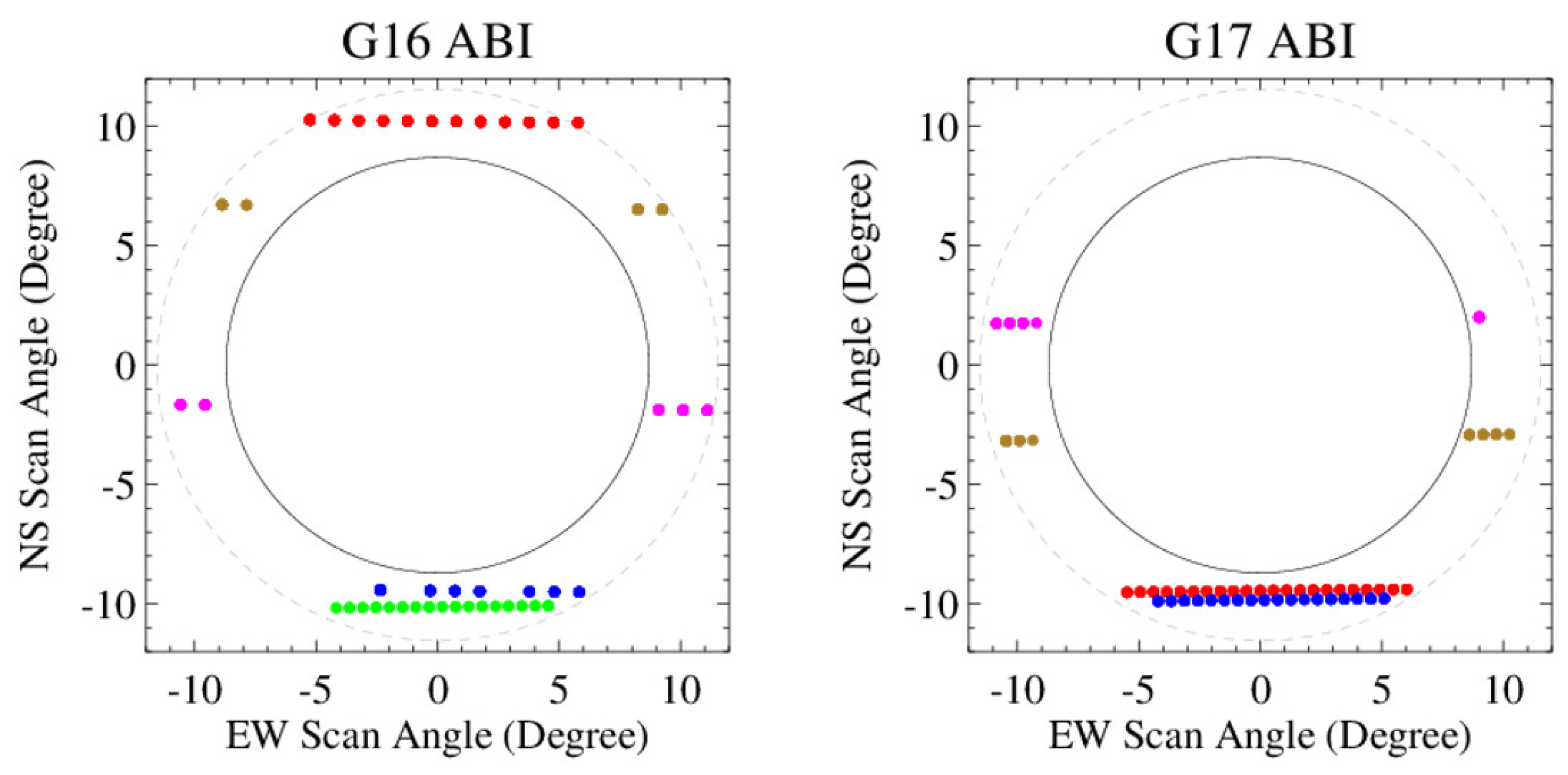
2.3. Lunar Image Collections
3. ABI VNIR Radiometric Calibration and Lunar Image Processing
3.1. ABI VNIR Radiometric Calibration
3.2. Lunar Image Processing
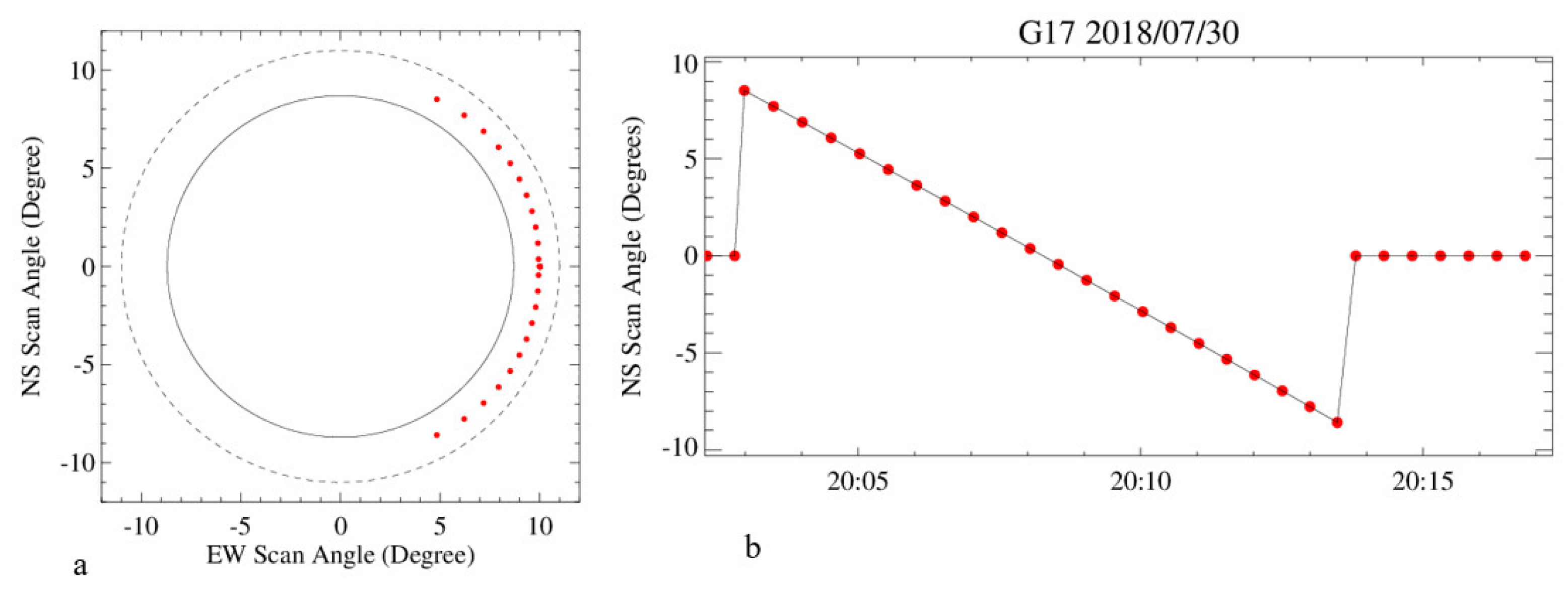
3.2.1. Data Reprocessing for the Lunar Events
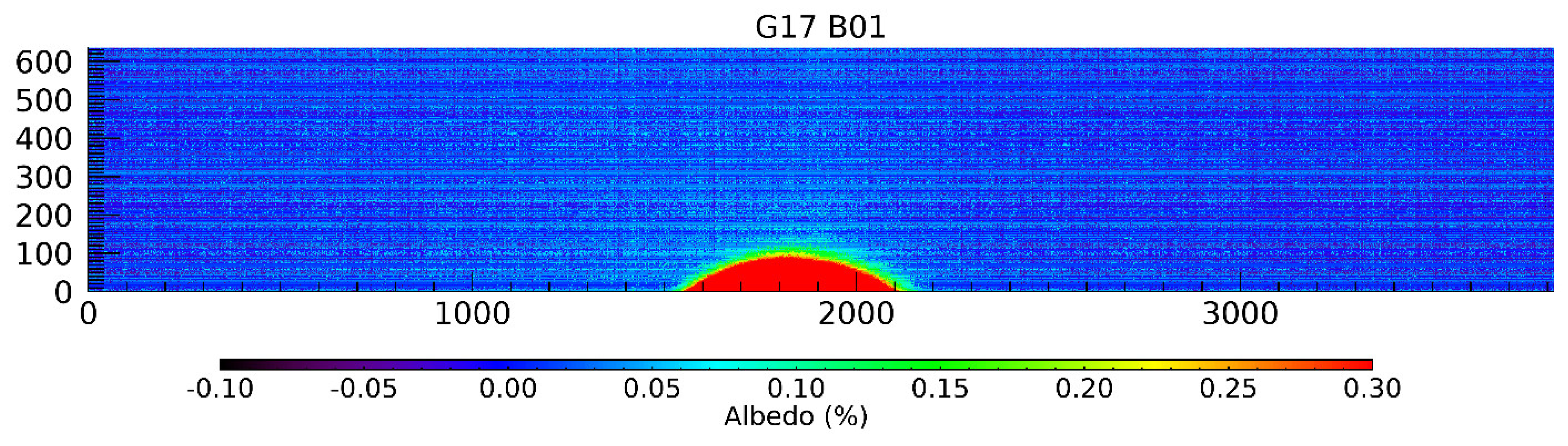
3.2.2. Lunar Image Screening and Subset
4. Data Analyses
4.1. ABI Lunar Irradiance Calculation
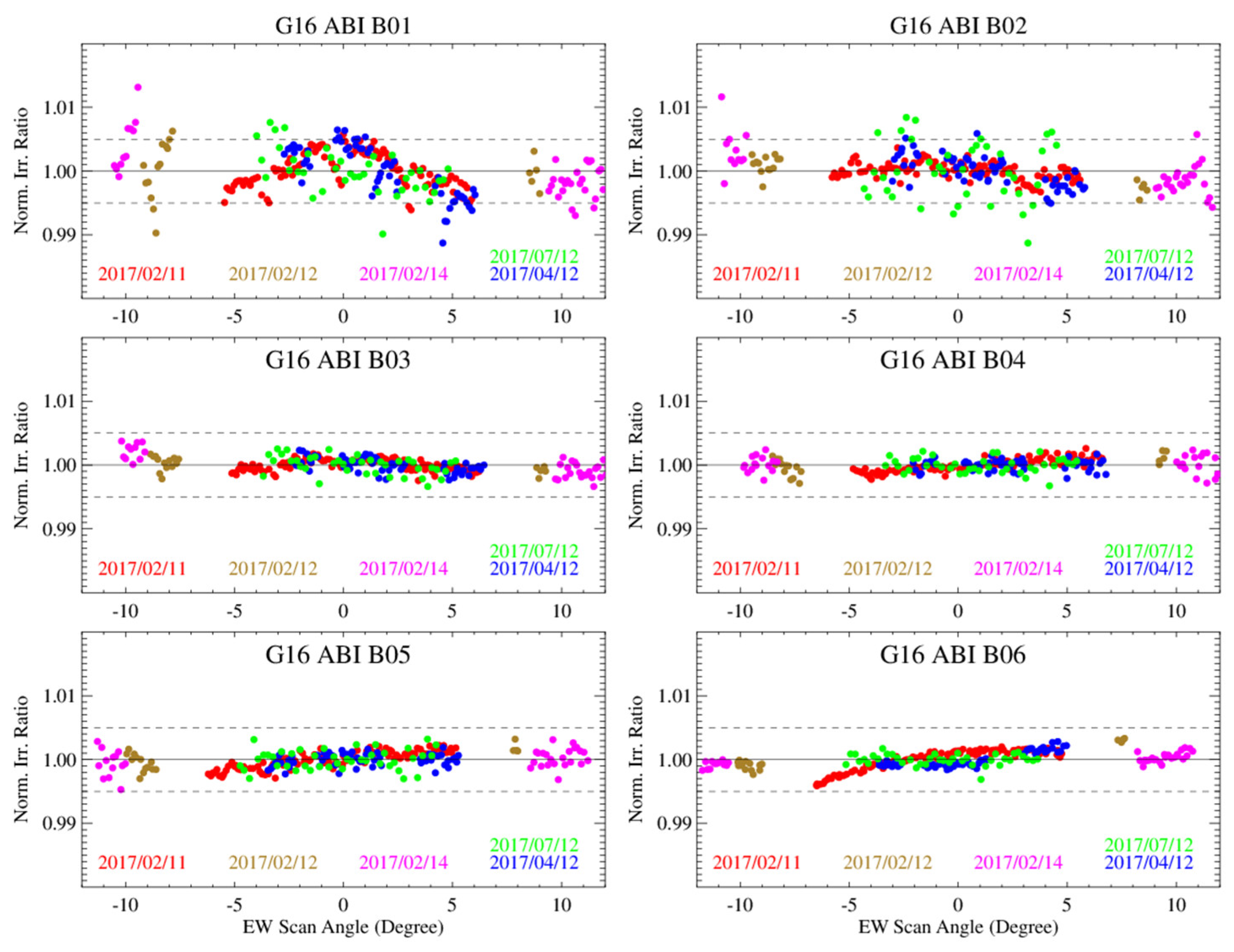
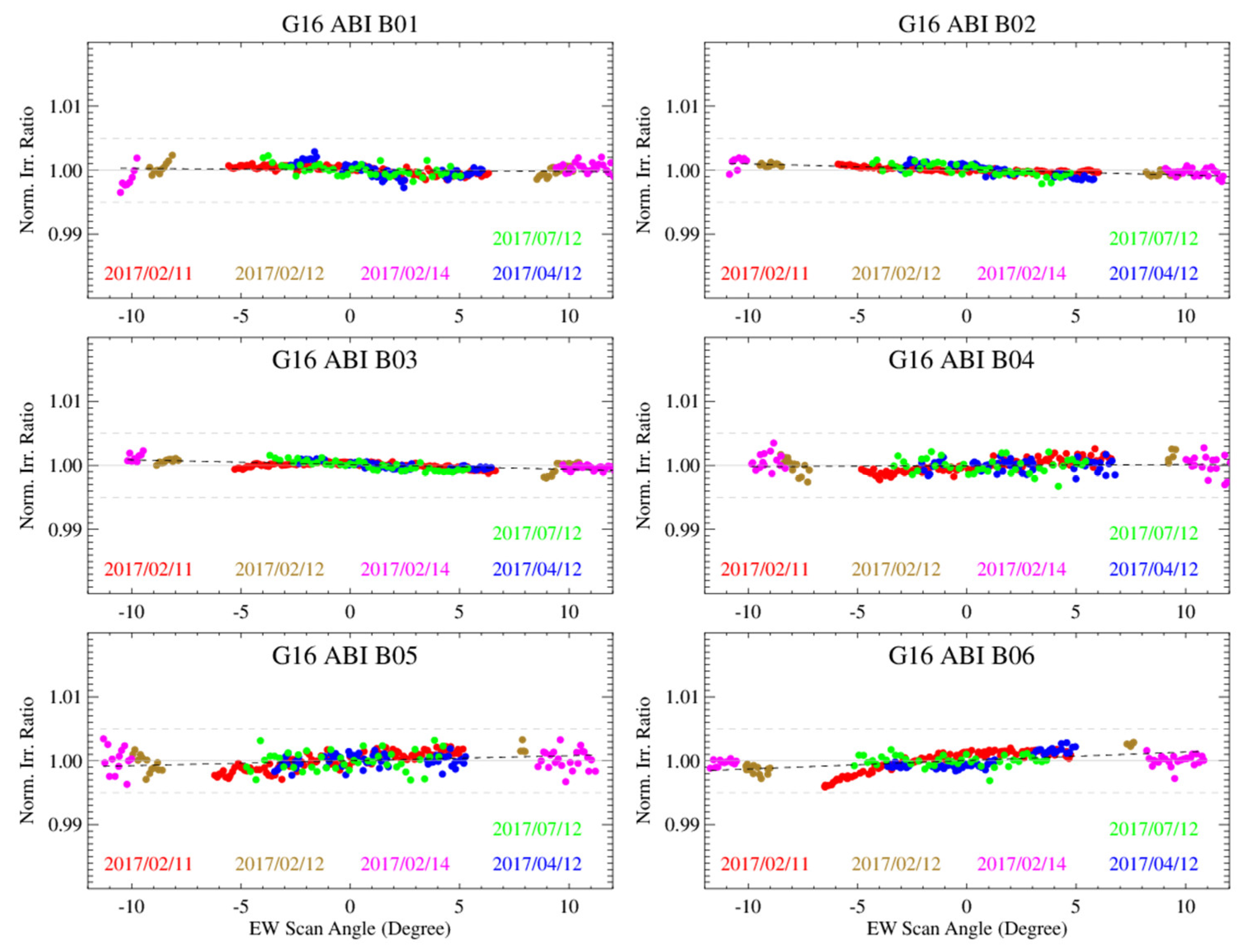
4.2. Normalized Ratios between the Measured and Simulated Lunar Irradiance
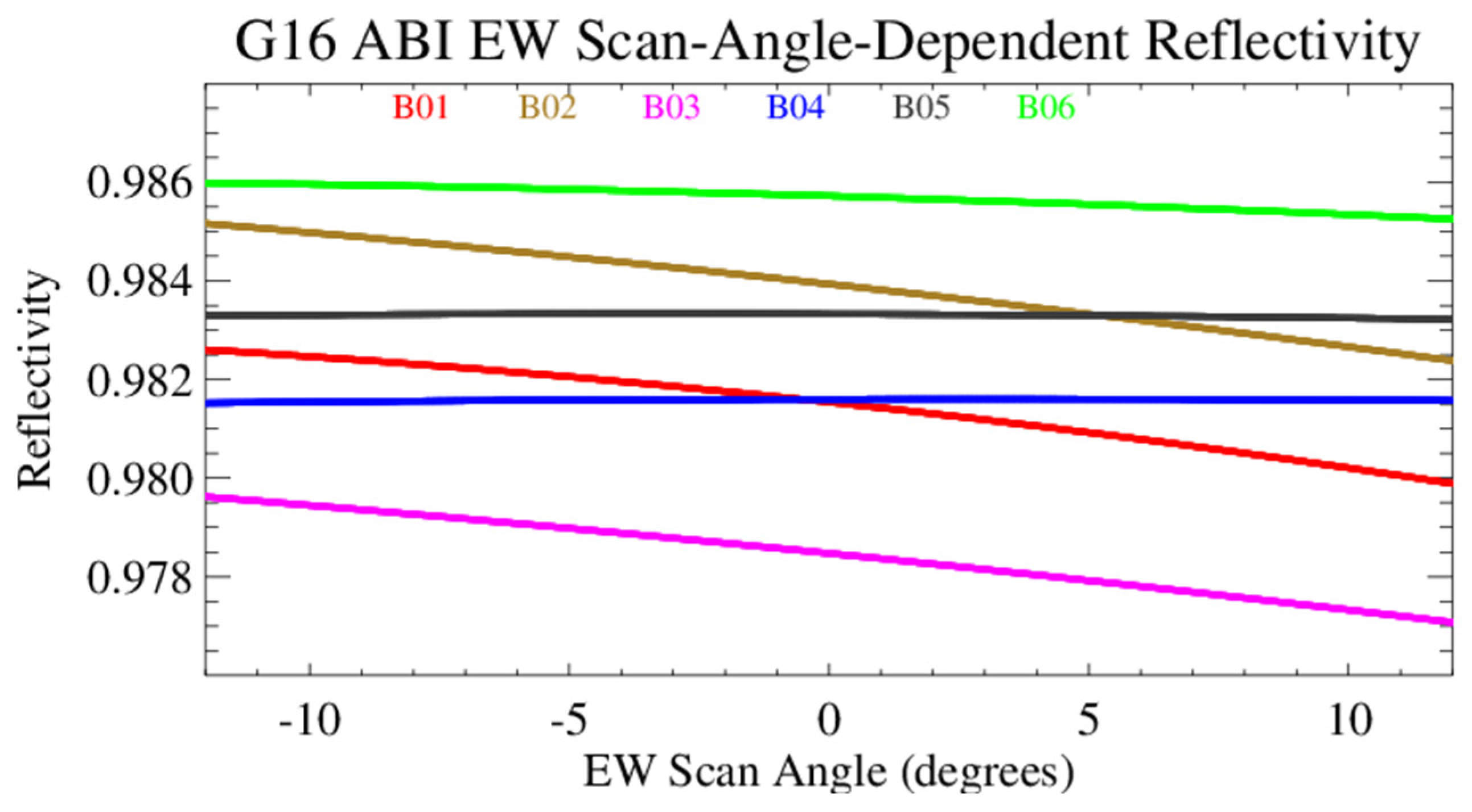
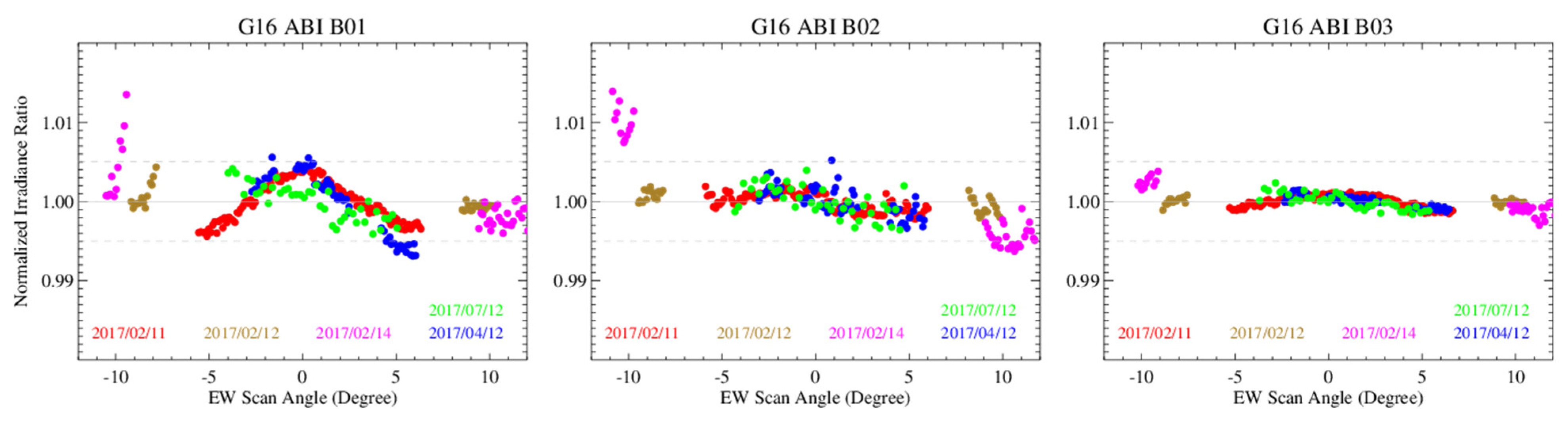
5. Initial RVS Results
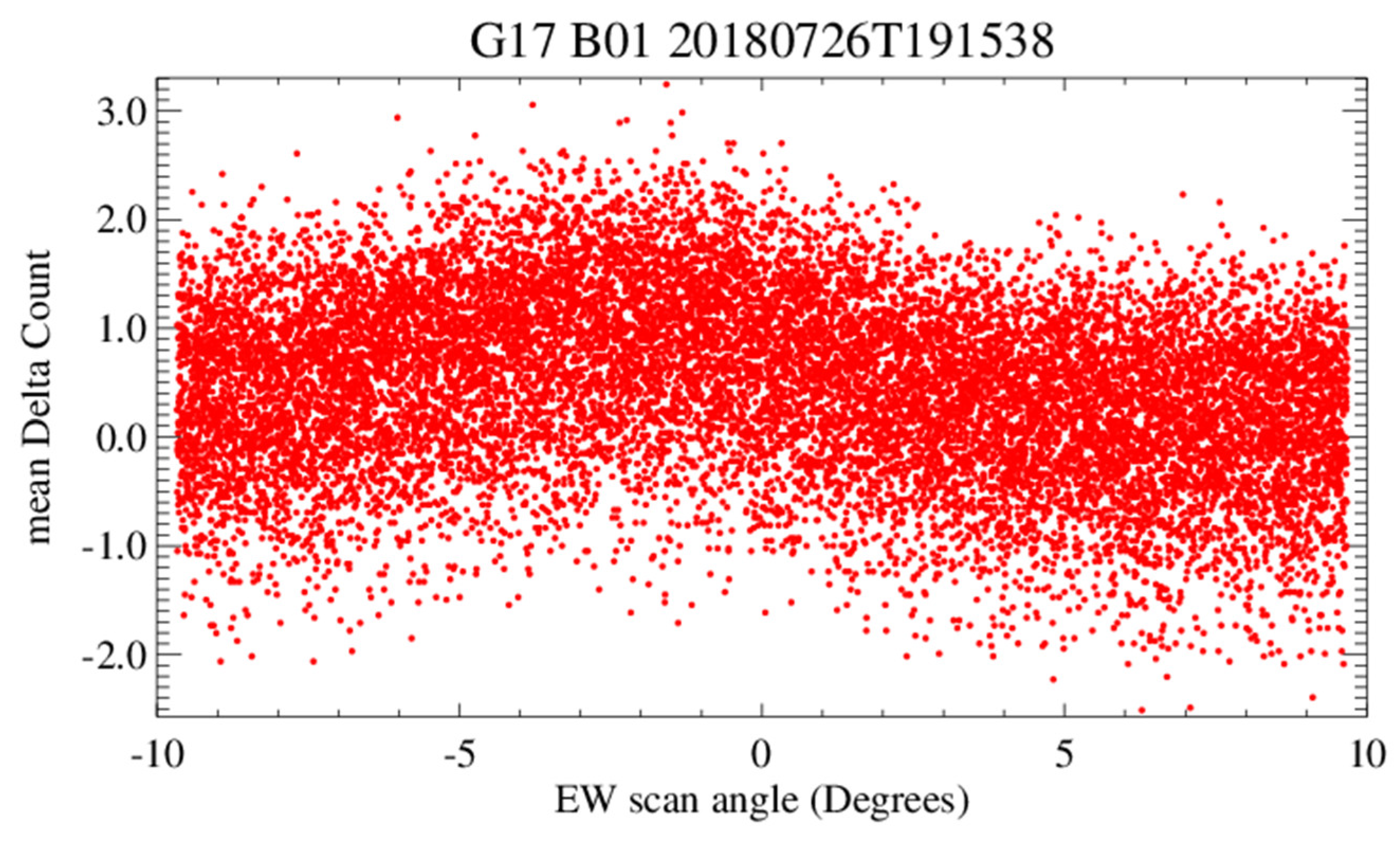
6. Straylight Corrections for B01–B03
6.1. Spacelook Corrections
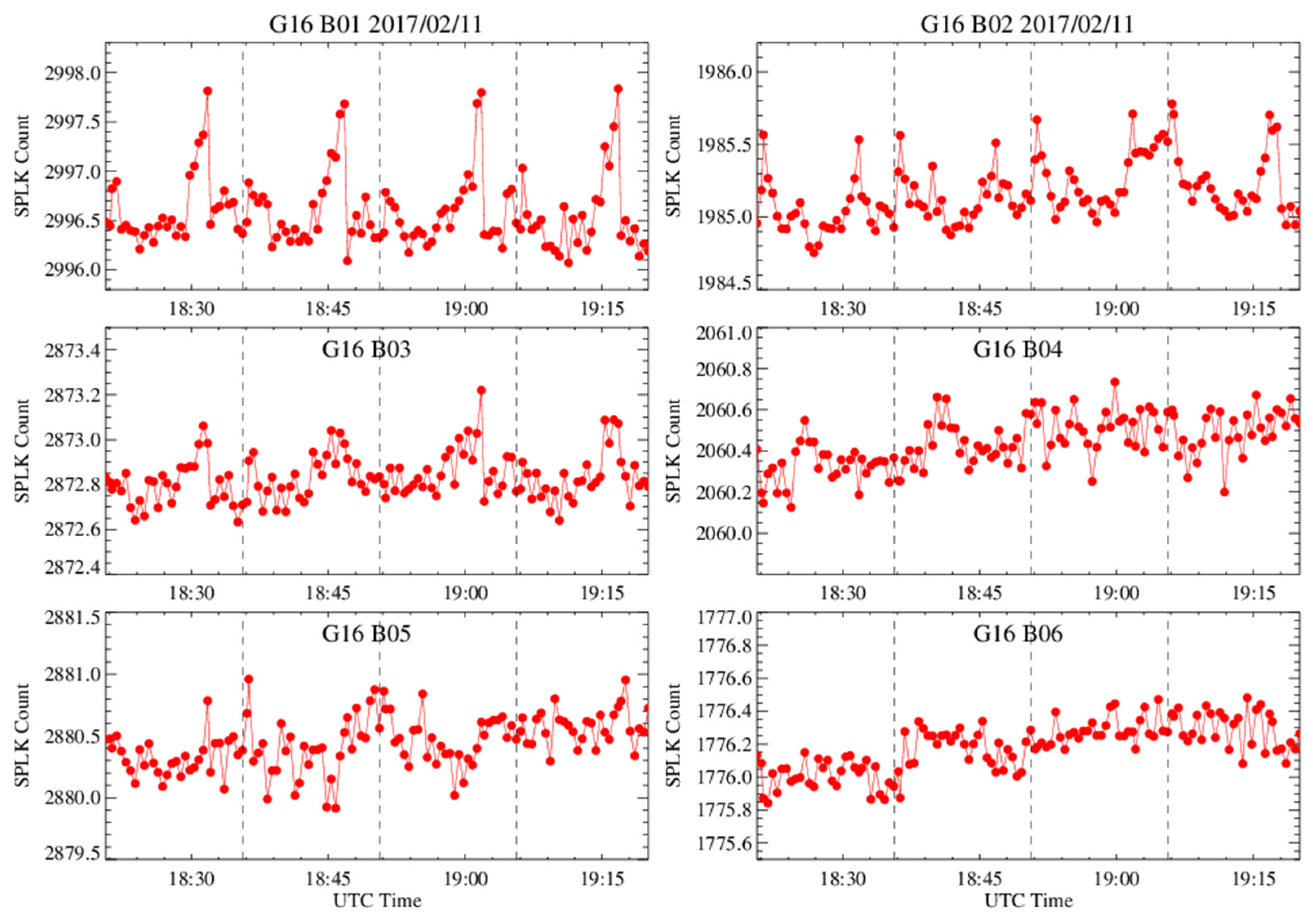
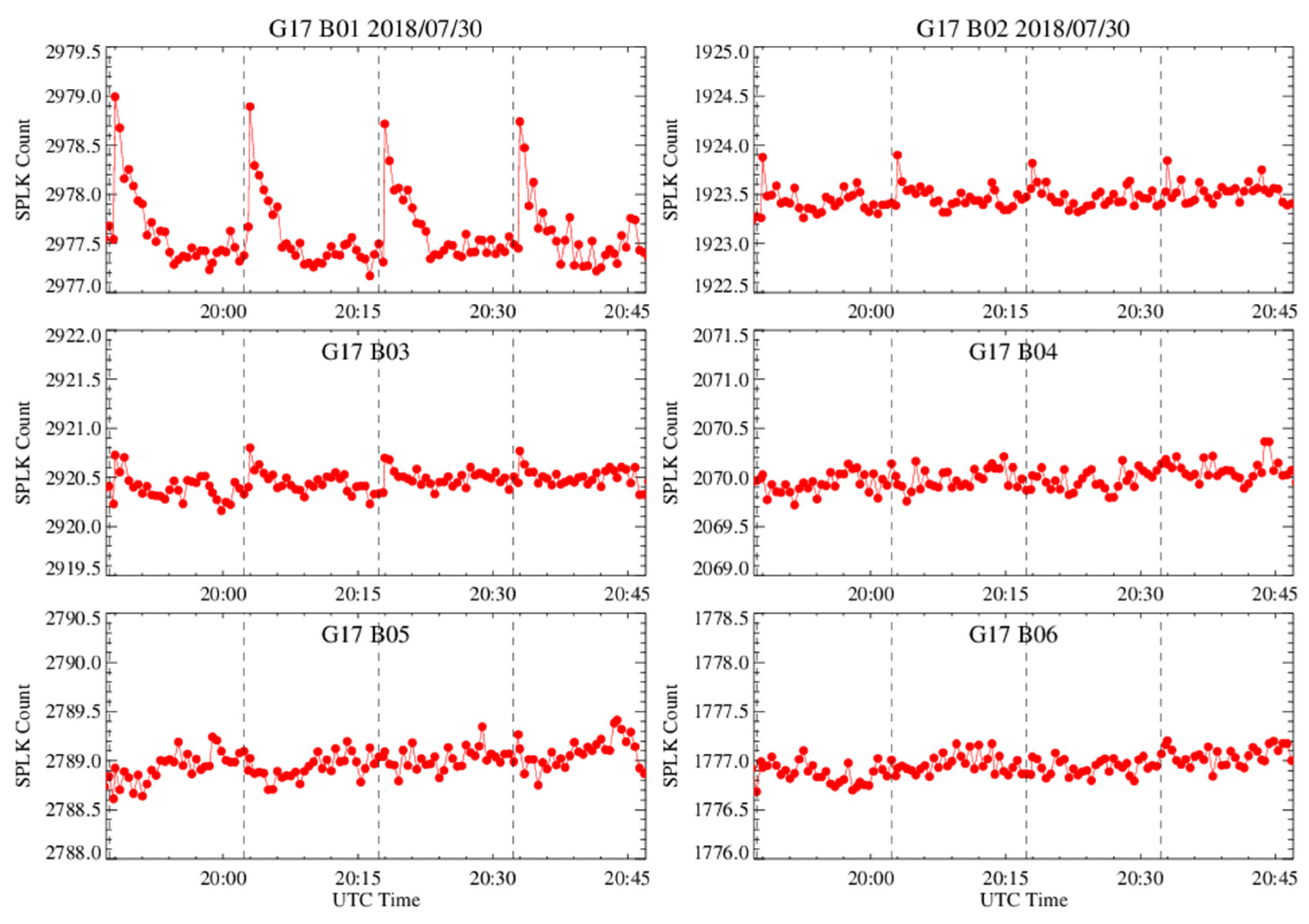
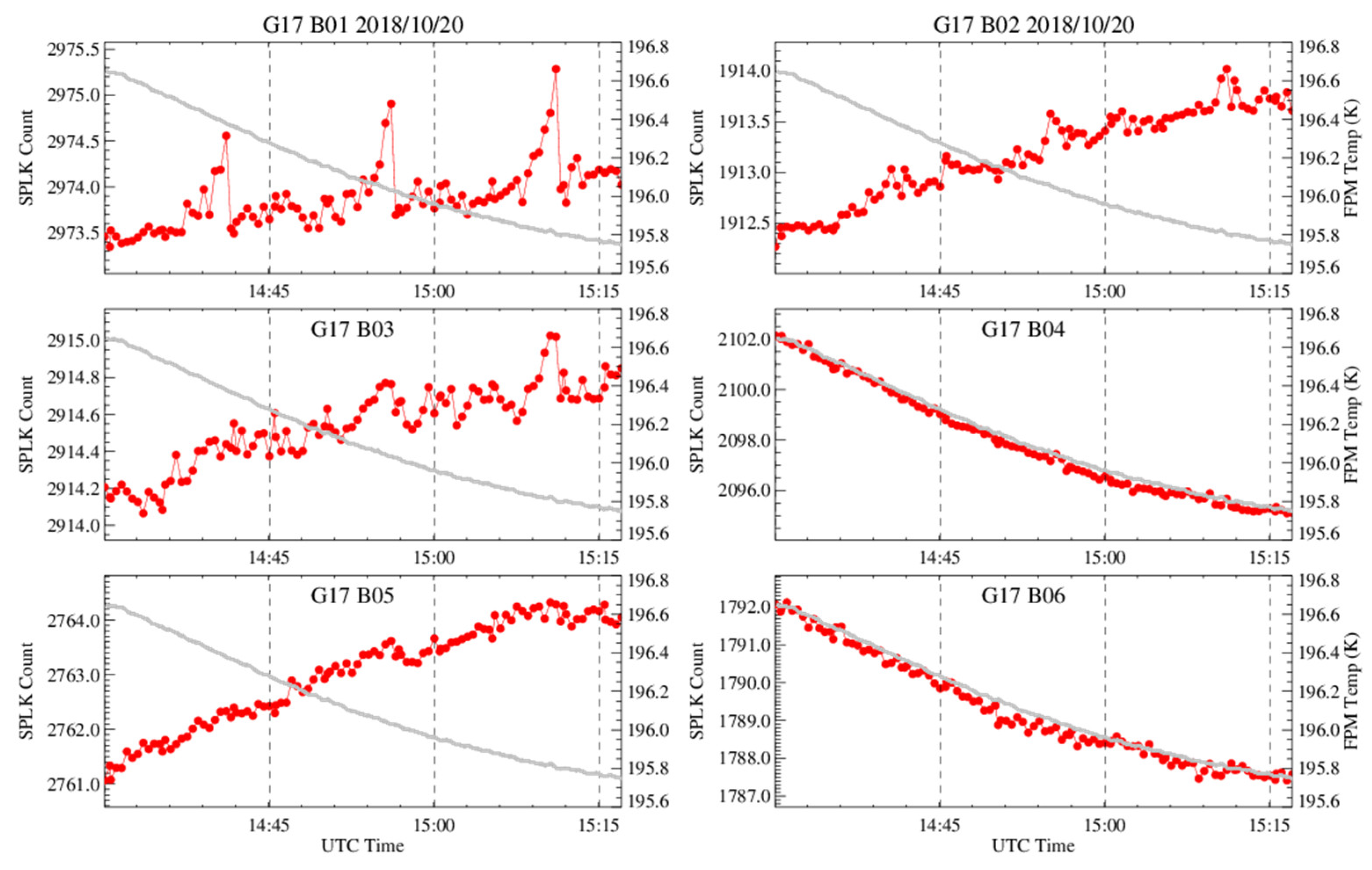
6.1.1. Time Series of Spacelook Count in the Chasing Events
6.1.2. Spacelook Corrections for B01–B03
6.1.2.1. Spacelook Correction for the Stable FPM Data
6.1.2.2. Spacelook Correction for the Unstable FPM Data
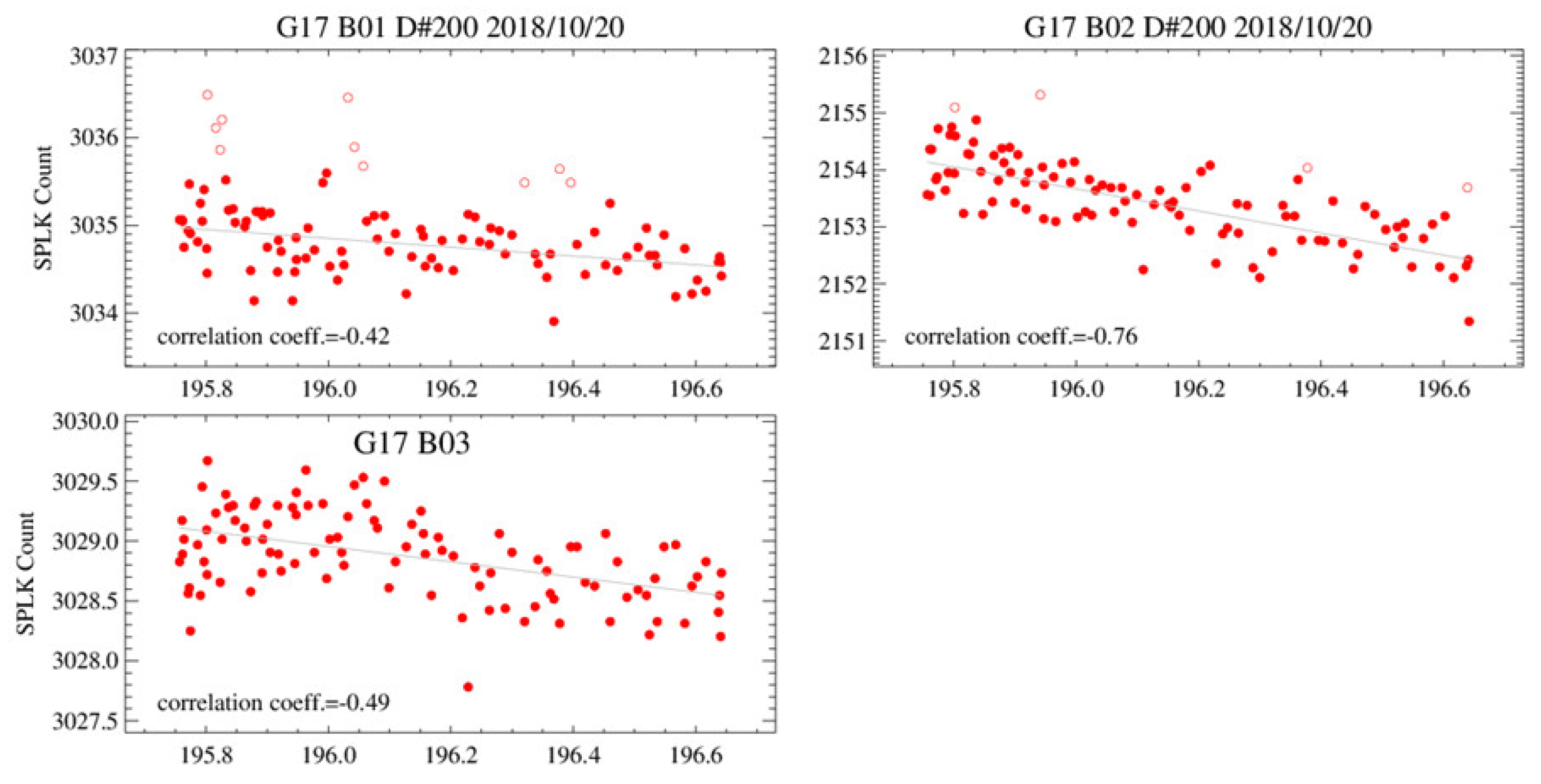
6.1.3. Results of Spacelook Correction at B01–B03
6.2. Radiance Correction for B01–B03 Lunar Images
7. Final Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABI | Advanced Baseline Imager |
| AOI | Angle of Incidence |
| BDS | Best Detector Selected |
| CNES | Centre National D’Etudes Spatiales |
| CONUS | Contiguous United Status |
| EW | East–West |
| FD | Full Disk |
| FOR | Field of Regard |
| FOV | Field of View |
| FPM | Focal Plane Module |
| G16 | GOES-16 |
| G17 | GOES-17 |
| GIRO | GSICS Implementation of the ROLO |
| GOES | Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite |
| GS | Ground Segment |
| GSICS | Global Space-Based Inter-Calibration System |
| IFOV | Instantaneous Field of View |
| L1α | L1alpha |
| L1b | Level1B |
| LOS | Light of Sight |
| LUT | Lookup Table |
| MCT | Mercury Cadmium |
| MESO | Mesoscale |
| NOAA | National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration |
| NS | North–South |
| PLT/PLPT | Post-Launch Test and Post-Launch Product Test |
| ROLO | Robotic Lunar Observatory |
| RVS | Response versus Scan Angle |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SPLK | Spacelook |
| USGS | United States Geological Survey |
| VNIR | Visible and Near-Infrared |
References
- Kalluri, S.; Alcala, C.; Carr, J.; Griffith, P.; Lebair, W.; Lindsey, D.; Race, R.; Wu, X.; Zierk, S. From photons to pixels: Processing data from the Advanced Baseline Imager. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, B. Improved GOES-R ABI image navigation and registration using maximum likelihood parameter estimation. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 032404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, T.; Gunshor, M.; Menzel, W.; Gurka, J.J.; Li, J.; Bachmeier, A.S. Introducing the next-generation advanced baseline imager on GOES-R. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1079–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, T.; Griffith, P.; Gunshor, M.; Daniels, J.; Goodman, S.; Lebair, W. A closer look at the ABI on the GOES-R Series. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, M.; Jamieson, M.; Fulton, N.; Chen, Y.; Johnson, J.; Bremer, J.; Smith, C.; Baucom, J. Operational calibration of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-8 and -9 images and sounders. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 6895–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Wu, X.; Qian, H.; Naarden, J.; Ramirez, M.; Lindsey, D.; Gravell, C.; Gunshor, M.; Schmit, T.; Shao, X.; et al. Validation of GOES-16 ABI infrared spatial response uniformity. Proc SPIE 2018, 10764, 107640F. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, H.; Stone, T. The spectral irradiance of the Moon. Astron. J. 2015, 129, 2887–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMETSAT. GIRO and GSICS Lunar Observation Dataset Usage Policy. 2015. Available online: http://gsics.atmos.umd.edu/pub/Development/LunarWorkArea/GSICS-EP-16_Doc_13_GIRO-GLOD-policy.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2015).
- Eplee, R.; Meister, G.; Patt, F.; Barnes, R.; Bailey, S.; Franz, B.; McClain, C. On-orbit calibration of SeaWiFS. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 8702–8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Sun, J.; Barnes, W.; Salomonson, V.; Esposito, J.; Erives, H.; Guenther, B. Multiyear on-orbit calibration and performance of Terra MODIS reflective solar bands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiong, X.; Barnes, W.; Guenther, B. MODIS reflective solar bands on-orbit lunar calibration. IEEE Trans. Geo. Remote Sens. 2008, 45, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Stone, T.; Yu, F.; Han, D. Vicarious calibration of GOES Imager visible channel using the Moon. In Proceedings of the SPIE 6296, Earth Observing Systems XI, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–16 August 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.; Shao, X.; Cao, C. On-orbit radiometric calibration of Suomi NPP VIIRS reflective solar bands using the Moon and solar diffuser. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 9533–9542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Lacherade, S.; Aznay, O.; Fougnie, B.; Fulbright, J.; Wang, Z. Comparison of S-NPP VIIRS and PLEIDES lunar observation. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9639, Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites XIX, Toulouse, France, 12 October 2015; p. 96390Y. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ryan-Howard, D.; Stone, T.; Sindic-Rancic, G.; Yu, F.; Weinreb, M.; Grotenhuis, M. Angular variation of GOES Imager scan mirror reflectance. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Wu, X.; Stone, T.; Sindic-Ranic, G. Angular Variation of GOES Imager scan mirror visible reflectivity. GSICS Q. 2013, 7, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, A.; Robinson, E.; Masterjohn, S.; Khalap, V.; Bhargava, S.; Rangel, E.; Babu, S.; Smith, S. Detectors and focal plane modules for weather instruments. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9854, Image Sensing Technologies: Materials, Devices, Systems, and Applications III, Baltimore, MD, USA, 26 May 2016; p. 98540H. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, P. ABI’s unique calibration and validation capabilities. In Proceedings of the EUMETSAT, Toulouse, France, 23 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, T. Radiometric calibration stability and inter-calibration of solar-band instruments in orbit using the Moon. In Proceedings of the SPIE 7081, Earth Observing Systems XIII, San Diego, CA, USA, 20 August 2008; p. 70810X. [Google Scholar]
- Lacherade, S.; Aznay, O.; Fougnie, B. POLO Pleiades Orbital Lunar Observations—Intensive study of the Moon and comparison to ROLO model. In Proceedings of the 22nd CALCON Technical Conference, Logan, UT, USA, 29 August–1 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- GOES-R Series Product Definition and User’s Guide, Volume 3: Level 1B Products, Revision 2.2. 2019. Available online: https://www.goes-r.gov/users/docs/PUG-L1b-vol3.pdf/ (accessed on 15 May 2015).
- Dalta, R.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Wu, X. Comparison of the calibration algorithms and SI traceability of MODIS, VIIRS, GOES, and GOES-R ABI Sensors. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wu, X.; Shao, X. GOES-16 ABI lunar data preparation to GIRO. In Proceedings of the 2nd GSICS/CEOS Lunar Calibration Workshop, Xi’an, China, 13–17 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Viticchie, B.; Wagner, S.; Hewison, T. EUMETSAT Moon data and GIRO calibration results. In Proceedings of the 1st GSICS/CEOS Lunar Calibration Workshop, Darmstadt, Germany, 1–4 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, M. Lunar data preparation for Himawari-8/-9 AHI. In Proceedings of the 2nd GSICS/CEOS Lunar Calibration Workshop, Xi’an, China, 13–17 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Wu, X. Some applications of ABI lunar irradiance calibration. In Proceedings of the 3rd GSICS/CEOS Lunar Calibration Workshop, Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T. GK2A AMI lunar calibration results. In Proceedings of the 3rd GSICS/CEOS Lunar Calibration Workshop, Virtual, 16–20 November 2020; Available online: http://gsics.atmos.umd.edu/bin/view/Development/LunarCalibrationWS2020 (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Harting, B. Closure memo for WR 6689—Observed lunar brightness changes west-to-east over FOR. In Harris Technical Memorandum; NASA/NOAA GOES-R Portal: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van Naardan, J.; Lindsey, D. Saving GOES-17. Aerospace America. 2019. Available online: https://aerospaceamerica.aiaa.org/departments/saving-goes-17/ (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Qian, H.; Yu, F.; Wu, X.; Yoo, H. Impact of GOES-17 ABI LHP anomaly on its VNIR calibration. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11501, Earth Observing Systems XXV, Online, 20 August 2020; p. 115011A. [Google Scholar]
- US DOC NOAA/NESDIS; NASA. GOES-R Series Mission Requirements Document (MRD). 6 January 2021. Available online: https://www.goes-r.gov/syseng/docs/MRD.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Yu, F.; Wu, X. An integrated method to improve the GOES Imager visible radiometric calibration accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Band Name | Central Wavelength (µm) | Detector Type | Nominal IFOV (µrad) | # Row | # Column | Data Application Examples [3] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EW | NS | ||||||
| B01 | 0.47 | Si | 22.9 | 22.9 | 676 | 3 | Daytime aerosol over land, coastal water mapping |
| B02 | 0.64 | Si | 12.4 | 10.5 | 1460 | 3 | Daytime clouds fog, insolation, winds |
| B03 | 0.87 | Si | 22.9 | 22.9 | 676 | 3 | Daytime vegetation/burn scar, and aerosol over water, winds |
| B04 | 1.38 | MCT | 51.5 | 42 | 372 | 6 | Daytime cirrus clouds |
| B05 | 1.61 | MCT | 22.9 | 22.9 | 676 | 6 | Daytime cloud-top phase and particle size, snow |
| B06 | 2.25 | MCT | 51.5 | 42 | 372 | 6 | Daytime land/cloud properties, particle size, vegetation, snow |
| Satellite | GOES-16 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Duration (UTC) | Phase Angles | NS Scan Angles | EW Scan Angles | No. of Nonclipped Images | FPM Temp. Change |
| 11 February 2017 | 18:19–19:17 | +9.1°–+10.8° | +9.5°–+9.4° | −6.5°–+4.7° | 110 | 0.1 K |
| 12 February 2017 | 18:54–19:04 | +21.0°–+21.4° | +5.9°–+5.9° | −10.1°–−9.0° | 13 | <0.1 K |
| 20:12–20:22 | +23.4°–+23.8° | +5.7 °–+5.7° | +7.3°–+7.6° | 16 | ||
| 14 February 2017 | 20:20–20:27 | +44.9°–+45.1° | −1.7°–−1.7° | −10.5°–−11.7° | 11 | <0.1K |
| 21:52–22:00 | +47.6°–+47.9° | −1.9°–−1.9° | +8.2°–+10.8° | 26 | ||
| 12 April 2017 | 18:57–19:38 | +17.0°–+18.7° | −9.5°–−9.4° | −3.6°–+5.0° | 57 | <0.1 K |
| 12 July 2017 | 20:32–21:16 | +41.5°–+42.8° | −10.2°–10.1° | −5.1°–+3.6° | 43 * | <0.1 K |
| Satellite | GOES-17 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Duration (UTC) | Phase Angle Range | NS Scan Angles | EW Scan Angles | No. of Nonclipped Images | FPM Temp. Change |
| 30 July 2018 | 19:50–20:45 | +32.3°–+33.9° | −9.6°–−9.4° | −6.5°–+5.3° | 112 | 0.1 K |
| 28 August 2018 | 18:53–19:01 | +25.0°–+25.3° | −3.2°–−3.1° | −10.1°–−11.7° | 15 | 0.4 K |
| 20:21–20:28 | +27.7°–+28.0 ° | −2.9°–−2.9° | +7.7°–+9.3° | 14 | ||
| 29 August 2018 | 19:37–19:42 | +36.6 °–+36.9° | +1.0°–1.0° | −11.8°–−10.5° | 11 | 0.5 K |
| 21:07–21:16 | +39.5°–+39.7° | +1.3°–+1.3° | +8.1°–+8.5° | 7 | ||
| 20 October 2018 | 14:27–15:15 | −48.1°–−46.7° | −10.0°–−9.8° | −3.3°–+6.4° | 91 | K |
| Satellite | Coefficients | B01 | B02 | B03 | B04 | B05 | B06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G16 | offset | 1.00004 | 1.00011 | 1.00014 | 0.99998 | 1.00003 | 1.00003 |
| slope | −2.44 × 10−5 | −8.80 × 10−5 | −7.37 × 10−5 | 1.75 × 10−5 | 7.79 × 10−5 | 1.33 × 10−4 | |
| RMSE | 8.91 × 10−4 | 5.39 × 10−4 | 4.77 × 10−4 | 1.17 × 10−3 | 1.31 × 10−3 | 1.14 × 10−3 | |
| F-test | 5.60 | 199.30 | 178.19 | 1.57 | 24.88 | 95.40 | |
| Error Prob. | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| EW RVS Variation (%) | −0.04 | −0.15 | −0.13 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.23 | |
| G17 | offset | 0.99998 | 1.00000 | 0.99998 | 1.00001 | 1.00001 | 1.00008 |
| slope | −7.58 × 10−5 | −1.32 × 10−4 | −6.98 × 10−5 | 1.12 × 10−4 | 3.31 × 10−5 | 1.69 × 10−4 | |
| RMSE | 1.39 × 10−3 | 5.04 × 10−4 | 8.98 × 10−4 | 1.64 × 10−3 | 1.30 × 103 | 1.14 × 10−3 | |
| F-test | 19.43 | 388.50 | 37.09 | 33.45 | 4.65 | 160.41 | |
| Error Prob. | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.00 | |
| EW RVS Variation (%) | −0.13 | −0.23 | −0.12 | 0.20 | 0.06 | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, F.; Wu, X.; Shao, X.; Qian, H. Characterization of the East—West Spatial Uniformity for GOES-16/17 ABI Bands Using the Moon. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071881
Yu F, Wu X, Shao X, Qian H. Characterization of the East—West Spatial Uniformity for GOES-16/17 ABI Bands Using the Moon. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(7):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071881
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Fangfang, Xiangqian Wu, Xi Shao, and Haifeng Qian. 2023. "Characterization of the East—West Spatial Uniformity for GOES-16/17 ABI Bands Using the Moon" Remote Sensing 15, no. 7: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071881
APA StyleYu, F., Wu, X., Shao, X., & Qian, H. (2023). Characterization of the East—West Spatial Uniformity for GOES-16/17 ABI Bands Using the Moon. Remote Sensing, 15(7), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15071881






