Abstract
This paper focuses on the proof and application of discriminating between oil spills and seawater (including the “look-alikes”, named low wind areas) based on the polarization ratio. A new relative polarization ratio () method is proposed, which is based on the difference between the scattering mechanism and the dielectric constant for oil spills compared to that of seawater. The case study found that (1) numerically amplifies the contrast between oil spills and seawater, reduces the difference between low wind areas and ordinary seawater, and exhibits better details of the image; (2) the threshold method based on Euclidean distance can obtain the highest classification overall accuracy within the allowable error range, and can be widely used in the study of different incidence angles and environmental conditions; and (3) the identification of oil spills and seawater by the proposed methods can largely avoid the misjudgment of low wind areas as oil spills. Considering visual interpretation as the reference ‘ground truth’, the overall classification accuracy of all cases is more than 95%; only the edge of the diffuse thin oil slick and oil–water mixture is difficult to identify. This method can serve as an effective supplement to existing oil spill detection methods.
1. Introduction
The exploration, exploitation, processing, transportation, and storage of offshore oil is an important part of the development and utilization of oil resources. Accidents often occur during the process, resulting in oil spills, major environmental problems, and large ecological and economic losses. According to oil slick statistics (2014–2019), researchers detected a cumulative oil slick area of km2 (more than twice the area of France) in global oceans [1]. The effective identification, simulation and diffusion, dynamic monitoring, and disaster assessment of offshore oil spills is necessary to reduce the ecological damage resulting from oil spill disasters and the associated financial risk.
Satellite remote sensing has become an important means of oil spill detection based on its advantages, such as a large range, few restrictive conditions, short periods, and fast information acquisition. Although optical images have the advantages of wide coverage, bright colors, rich spectral information, and obvious contrast [2], they have low penetrability and are greatly affected by weather and sea surface conditions, so their imaging time is limited. However, active microwave sensors, such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR), can overcome these limitations and have the advantages of all-day, all-weather, large range, and high resolution, which can compensate for the limitations of optical sensors. Therefore, SAR has been widely used in rapid oil spill detection [3,4].
Driven by ocean surface winds, the sea surface may be characterized by the resulting surface wave patterns, and SAR relies on backscattering from these surface waves to image the sea surface [5]. An oil film on the sea surface has a damping effect on capillary waves and short gravity waves on the sea surface [6], reducing the roughness of the sea surface and attenuating backscattering. SAR images of the sea surface covered with oil films show a sharp contrast with the corresponding clean sea surface; the oil spill area is usually less bright than the clean sea surface area, presenting a relatively dark distribution pattern [3].
Therefore, many researchers have developed methods for remote sensing monitoring of surface films based on the difference between the normalized radar scattering cross section (NRCS) caused by the surface film medium and the clean ocean surface [7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Typical oil spill detection methods in SAR images use the following four methodologies. (1) The copolarization phase difference factor is used to distinguish the radar echo characteristics of an oil spill, or biofilm are used to automatically monitor the oil spill and calculate the oil concentration [14,15,16]. (2) Inspired by the consistency analysis method of terrestrial remote sensing classification, a type of oil spill monitoring method based on the consistency coefficient and similarity parameters of fully polarized SAR images was developed [9,11,13]. (3) The decomposition parameters of polarimetric SAR images are used to calculate entropy H, average alpha angle α, anisotropy A, and other characteristics to estimate the oil spill area [10,11,13,17]. (4) With the rise of machine learning algorithms, artificial neural network methodologies are also widely used in oil spill detection [12,18,19,20]. In addition, further investigations have proposed an effective dielectric constant model of electromagnetic backscattering from a stratified air-ocean surface film-sea water medium and studied the characteristics of the effective dielectric constant for the air-sea surface film and seawater medium [21], which has great potential for applications to retrieve film thickness.
Although scholars have made great progress in the field of sea surface oil spill algorithms, the existing electromagnetic remote sensing technology for oil film identification is still mainly based on the simple Bragg scattering model, which has certain limitations. In addition to marine oil spills, natural phenomena called “look-alikes”, such as low wind areas, biogenic slicks, precipitation, internal ocean waves, and tides, will also appear as dark areas on SAR images, resulting in false alarms. The low wind area “look-alike” has a high frequency of occurrence and can contribute large, dark areas. Most of the existing algorithms cannot effectively and automatically distinguish between oil spills and low wind areas on the sea surface [22]. When the wind speed is below 3 m/s, there are many low wind areas, and the detection of oil spills is not completely successful [3]. Xie et al. [23] discriminated sea ice and open water based on the theoretical polarization ratio model, which depends on the surface roughness and the relative dielectric constant of the surface. Based on the theoretical polarization ratio model, our paper explains the feasibility of identifying oil spills and seawater based on the polarization ratio and proposes the relative polarization ratio () feature to discriminate oil spills and seawater. However, the low wind area “look-alikes” are still sea water, which has little difference from clean seawater compared with oil spills; that is, the distinction among oil spills, clean seawater, and low wind areas can be regarded as the difference problem among substances. This method can effectively identify oil spills and seawater, and avoid the misjudgment of low wind areas as oil spills.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the experimental data and preprocessing and the theoretical methods. Section 3 contains the experimental results and analyses of these results, and Section 4 presents the discussion. Finally, the conclusions are presented in Section 5.
2. Data and Methodology
This study proposes a relative polarization ratio feature methodology for oil spill detection and classification, and Figure 1 is a flowchart for the proposed method. After SAR image preprocessing, the backscattering coefficients of VV polarization and HH polarization are converted to decibel (dB), and then the decibel polarization ratio is obtained. After mean filtering on , the relative polarization ratio characteristic is obtained from the filtered decibel polarization ratio. Thereafter, we perform Euclidean Distance-based thresholds for images, which can effectively identify oil spills and seawater and largely avoid misjudging low wind areas as oil spills.
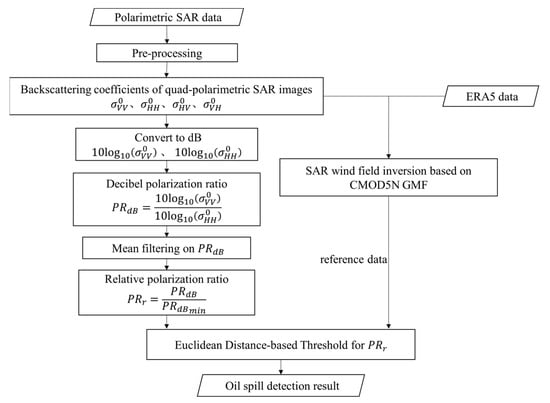
Figure 1.
The flow chart for the proposed method.
2.1. SAR Data and Preprocessing
RADARSAT-2 is equipped with C-band fully polarized SAR, which is widely used in oil spill-related studies. RADARSAT-2 provides multiple polarization characteristic parameters, which provides more information than single-polarized SAR and has higher detection accuracy than single-polarized SAR. Thus, RADARSAT-2 has a better oil spill detection and oil film identification capability than RADARSAT-1, to take one example. The data used in this study are RADARSAT-2 quad fine, single-look complex (SLC) SAR images. SLC complex processing is adopted to obtain data with lower noise, and the good signal-to-noise ratio enables the extraction of complex sea surface information, which plays an important role in the accurate acquisition of sea surface environmental parameters [24]. The spatial resolution of the data is approximately 5 m × 8 m in range and azimuth, respectively, and the swath is 25 km × 25 km. In this study, four SAR images of oil spills and two SAR images of clean sea surfaces with low wind areas were selected for a total of six cases. The detailed data acquisition information is shown in Table 1. In particular, the detailed material information for Case 3 is shown in Table 2 and Figure 2.

Table 1.
SAR data acquisition information, indicated by series number. Slicks of emulsion refer to mixtures of crude oil and seawater [25].

Table 2.
Detailed material information for Case 3 [25].
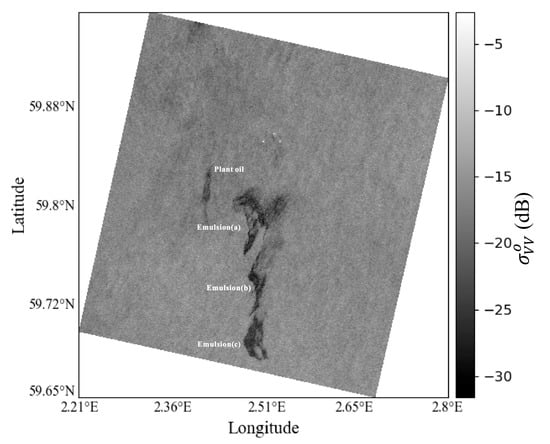
Figure 2.
Detailed material information for Case 3 on preprocessed image [25].
The SAR data selected in this paper are all unprocessed original RADARSAT-2 image data. These data need to be preprocessed to obtain image data that can meet the requirements of this study.
First, we perform radiometric calibration of the original SAR images to eliminate systematic errors, convert the grayscale values in the original image into the radar backscattering coefficient , and then obtain the dB values of the NRCSs to quantitatively describe the relationship between the radar backscattering intensity and the target backscattering cross section. Thus, the noise generated in the imaging process has been corrected and eliminated from the SLC data, and the calibration parameters can be directly used for radiometric calibration. The calibration method comes from the RADARSAT-2 product format definition given by Dettwiler and Associates Ltd., Richmond, BC, Canada. [26].
To accurately obtain the spatial information position for the ground features in the SAR images, it is necessary to conduct geometric correction processing of the SAR images. In this investigation, the research object is the vast ocean, and the ocean surface has only small and gentle fluctuations under the action of seawater gravity and is not prone to local regional distortions caused by slant imaging. Moreover, the objective of the research is only the detection of oil films on the sea surface. Therefore, during geometric correction processing of the SAR images, only the control points provided by the individual RADARSAT-2 products are used for geocode correction of the image.
The interference effect of the radar waves will produce coherent speckle noise on the SAR images, which will greatly impact the subsequent oil spill target identification. Noise information needs to be reduced and removed. At present, the main denoising method for high-resolution SAR images is speckle noise suppression technology based on spatial filtering techniques, such as the Lee filter, median filter, mean filter, and Frost filter. Therefore, we have compared the characteristics of each filtering algorithm and the related literature [27,28] and selected the Lee filter [28] for this analysis. The Lee filter is an adaptive linear filtering algorithm model based on the least mean square error [29]. It is a classical method for speckle noise filtering based on the local statistical characteristics of SAR images.
In practical calculations, it is possible to ignore areas of seawater that are deemed too small to be of interest and do not require a high resolution. To improve the running speed and filter out the seawater for a very small area, we reconstructed the SAR image resolution based on the original resolution, using pixels as a new pixel for reconstruction [23]. Figure 3 shows the final preprocessed VV polarization images for all cases. The incidence angles of the images vary from 25° to 44°. Details related to the six SAR images are presented in Table 1.
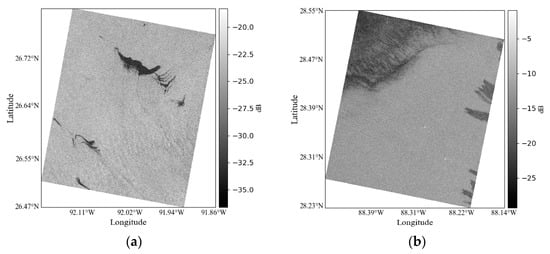
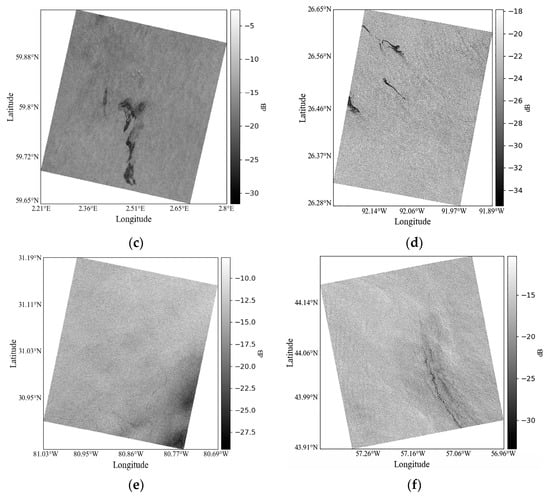
Figure 3.
Preprocessed VV polarization images: (a–d) are oil spill Cases 1–4, respectively; (e,f) are low wind area Cases 5 and 6, respectively. RADARSAT-2 data MacDonald, Dettwiler, and Associates, Ltd., all rights reserved.
2.2. ERA5 Reanalysis Data and SAR Wind Inversion Method
As the identification of oil spills is affected by wind speed, we perform wind field inversion based on ERA5 reanalysis data from the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), which is operated by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF). ERA5 is the latest generation of reanalysis data, which provides a large amount of atmospheric wave and surface volume data from 1950 to the present. ERA5 has been greatly improved compared to its predecessor ERA-Interim. Thus, in ERA5, the vertical layering has been increased from 60 layers to 137 layers, the spatiotemporal resolution has been greatly improved, the horizontal resolution has been increased to 31 km (approximately 0.28°), the vertical resolution has been increased to 0.01 h Pa (approximately 80 km from the ground), and the time resolution has been increased from 6 h to 1 h [30,31]. In addition, ERA5 incorporates more historical data, especially satellite data, and uses an advanced data and model system to provide up to 240 accurate estimates of atmospheric and oceanic states [32]. In our study, we use the meridional and zonal winds at 10 m above the sea surface.
The identification of oil spills is affected by wind speed. It is difficult for existing algorithms to effectively and automatically identify oil spills on the sea surface amid low wind speed areas. Therefore, the wind field information corresponding to the study area is very important. Studies have shown that in low wind speed events, wind speed inversion based on the CMOD5.N geophysical model function (GMF) can achieve high accuracy [33]. The CMOD5.N GMF is a further development of the CMOD5 GMF methodology and retains the internal algorithm formula, modifies 28 adjustable parameters, corrects the 0.5 m/s underestimation error of previous CMOD5 GMF formulations, and therefore more effectively expresses the sea surface conditions, thereby avoiding errors that may be introduced by atmospheric stratification. In this study, building on the recent literature [33], ERA5 data and VV polarization SAR data were selected, and SAR wind field inversion was performed based on COMD5.N GMF. Thus, the SAR wind field inversion results were used as experimental reference data.
2.3. Oil Spill Detection Method Based on Relative Polarization Ratio Characteristics
2.3.1. Polarization Ratio Methods
An oil film on the sea surface reduces the roughness of the sea surface, attenuates backscattering, and weakens the radar echo scattering signal. When low wind speed occurs over the sea surface, the radar echo scattering signal is small. In this situation, it is difficult to identify whether the dark area in the SAR image is an oil spill or a low wind area. The radar scattering at the sea surface without the oil spill is dominated by Bragg scattering, whereas the scattering from the oil spill area is dominated by non-Bragg scattering [9]. Thus, the backscattering cross sections of the different polarization channels can be used for the study of oil film detection on the sea surface, and the Bragg scattering theory can be used for modeling in the medium incidence angle range (approximately 20°~60°) [5].
Previously, we showed that the theoretical polarization ratio (PR) model derived from the X-Bragg model is used to discriminate sea ice from open water, which is related to the surface roughness and the relative dielectric constant of the surface [23]. The theoretical PR model is defined as follows [23]:
where and are the averages of the NRCS in VV and HH polarization, respectively, which are related to the radar look angle , the wavenumber spectra density of the surface roughness , the average orientation angle shift , Bragg scattering coefficients for vertical polarization , and Bragg scattering coefficients for horizontal polarization .
and can be expressed as follows:
A and B can be expressed as follows:
where the average orientation angle shift can be substituted by Equation (6), where is the standard deviation of the orientation angle shift, and and are related to radar look angle and the relative dielectric constant of the surface , respectively, as shown in Equations (7) and (8):
Real-value solutions for are difficult to obtain; however, we can eliminate this term using the ratio, which simplifies in Equation (1) to A divided by B, that is
The numerical simulation is presented in Figure 4, where increases with increasing incidence angle. Under most incidence angle conditions, monotonically increases with increasing relative dielectric constant. Moreover, with a low incidence angle and high roughness, as shown in Figure 4a, when , shows a weak decrease with increasing relative dielectric constant. That is, is a monotone function of the relative incidence angle at a certain incidence angle.
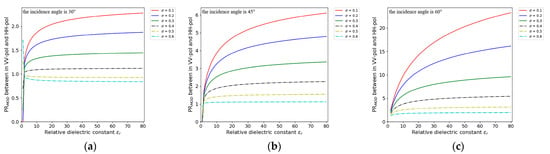
Figure 4.
Numerical simulation of . Incidence angles are (a) 30°, (b) 45°, and (c) 60°. The standard deviation of the orientation angle shift varies from 0.1 to 0.6 in steps of 0.1 [23].
Studies have shown that oil–water mixture exists in a variety of states, and its states are unstable and irregular. The main types can be summarized as oil-in-water (O-W), oil-in-water (O-W-O), oil-in-water (W-O), and oil-in-water (W-O-W). The relationship between water content and the dielectric constant of the oil–water mixture in the corresponding four states is shown in Figure 5 [34]. Studies have shown that the dielectric constant of different types of oil–water mixtures increases with the increase in water content and is lower than that of water but higher than that of oil [34]. Therefore, oil spills and seawater can be classified based on the theoretical PR model and related PR characteristics.
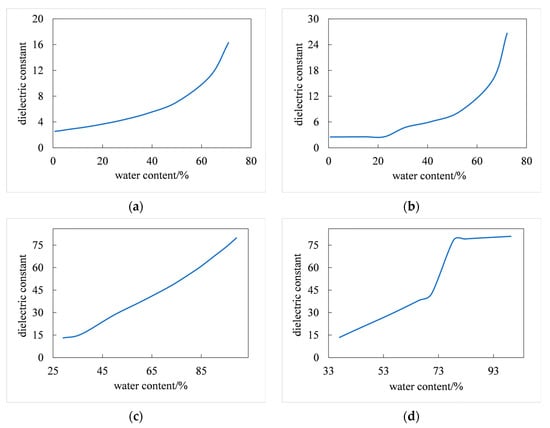
Figure 5.
Relationships between water content and dielectric constant in different states. The states are (a) O-W, (b) O-W, (c) W-O, and (d) W-O-W.
At low wind speeds, the measured PR (the ratio of NRCS for vertical polarization, VV, to NRCS for horizontal polarization, HH) over the water surface covered by the surface film is larger than that calculated using a simple Bragg scattering model. Gade et al. [35] proposed a three-scale model consisting of a short Bragg wave, long wavelength, and medium wavelength coupled ocean-wave model to explain this phenomenon. Based on this theory, the polarization ratio () can be used to identify oil spills and seawater. is expressed in SAR-measured data as follows:
where and are NRCSs in VV and HH polarizations, respectively.
To improve the contrast between oil spill areas and clean seawater and to facilitate data analysis, the NRCS of SAR data are taken logarithmically in decibels. Thus, the decibel PR is calculated as follows:
We perform mean filtering on of each case to reduce noise. To further improve the contrast between oil spill areas and clean seawater, the relative PR is defined, which is expressed by the ratio operation between of the image and the minimum of this image. The formula for is given as follows:
Performing threshold segmentation on , we determine that the threshold is T, where is identified as the oil spill, and is identified as clean seawater. T is greater than for low wind areas, which avoids the misidentification of low wind areas as oil spill areas.
2.3.2. Euclidean Distance-Based Threshold for
In SAR oil spill identification, the commonly used methods of image processing, such as the Otsu method [36,37] and the iterative thresholding method [38,39], can obtain good threshold values to identify dark areas for each image. However, low wind areas and oil films are both shown as dark areas in the image, and it is difficult to exclude low wind areas from the identification results. As shown in Figure 6, the image of each case shows that the of the oil spill is larger than that of the low wind area and ordinary seawater. The of the low wind area is slightly higher than that of ordinary seawater but lower than that of oil spills. In essence, the “look-alike” of low wind area is also seawater, which is the same kind of substance. The properties of the oil–water mixture are closer to those of seawater. The value of the oil–water mixture is smaller than that of the thick oil film, and the value is closer to the low wind area, which is still greater than that of ordinary seawater. If the difference between oil spills, ordinary seawater, and low wind areas cannot be found quantitatively, it is difficult to obtain a threshold that can effectively distinguish oil spills from seawater (including ordinary seawater and low wind areas).
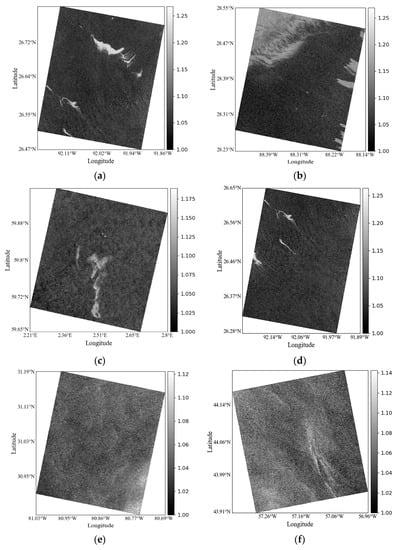
Figure 6.
Feature images of . (a–f) are Cases 1–6, respectively.
Euclidean distance () is a commonly used definition of distance. Mathematically, it refers to the straight-line distance between two points in Euclidean space, and the greater the distance between two points is, the greater the difference between two points is. is introduced to study the material difference between the oil spill and the seawater as well as to find the appropriate threshold, calculating the between the oil spill pixel, the oil–water mixture pixel, and the low wind area “look-alike” pixel and the ordinary seawater pixel of the corresponding case for further research.
As shown in Table 2 and Figure 2, due to the small volume and long timeframe of plant oil in Case 3, a thin plant oil–water mixture should exist in the image. In other words, in Case 3, there are ordinary seawater and two types of oil–water mixtures, including plant oil–water mixtures and crude oil–water mixtures, with a total of approximately 20,000 pixels.
Since there are approximately 20,000 pixels in oil–water mixture Case 3, based on the image of Cases 2, 3, 5, and 6, the maximum 20,000 pixels are selected, and the between them is calculated; the average of the ordinary seawater pixels in their images is also calculated, as shown in Figure 7a. The kernel density estimate (KED) curve and rug plot of are drawn between the dark area and ordinary seawater corresponding to the image in Cases 2, 3, 5, and 6, and the distributions corresponding to Cases 3, 5, and 6 are shown in Figure 7b–d, respectively. The between the oil spill pixels and ordinary seawater () is significantly greater than the between the low wind area and ordinary seawater (). The low wind area and ordinary seawater are essentially the same substance while oil spill and ordinary seawater are completely two different substances; therefore, it is consistent with the actual situation that is smaller than . In addition, the property of the oil–water mixture is closer to that of seawater rather than the oil spill, and the Euclidean distance between the oil–water mixture and ordinary seawater () is smaller than , with its value closer to . As shown in Figure 7b, the KDE curve of the oil–water mixture has two peak points: the first peak corresponds to the plant oil–water mixture, and the second peak (red dot in Figure 7b) corresponds to the crude oil–water mixture, with a value of 0.0665, which is less than 0.07. Furthermore, in Figure 7c,d, only less than 1.9% of and less than 1.7% of are more than 0.07, that is, is mostly less than 0.07. Therefore, we take 0.07 as the characteristic value. Based on the image, the threshold is assumed to be , the number of pixels of the oil spill and oil-water mixture is n, and the of them and ordinary seawater is calculated in the same image. If , T is the recognition threshold, that is, if , it is an oil spill or oil-water mixture; otherwise, it is seawater.
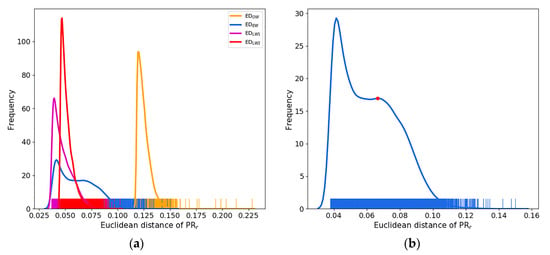
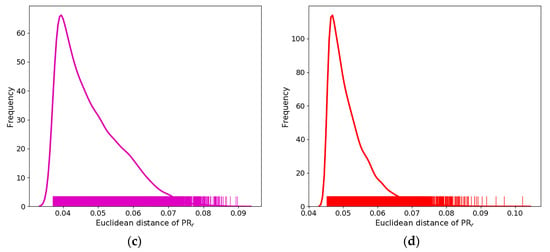
Figure 7.
Distribution of between oil spill, emulsion, or low wind area and ordinary seawater based on images, including KED curve and rug plot. , , , and in (a) correspond to Cases 2, 3, 5, and 6, respectively. The distributions corresponding to Cases 3, 5, and 6 are shown in (b–d), respectively. The red dot indicates the second peak in the KDE curve for the oil–water mixture, with a value of 0.0665.
Accordingly, the thresholds for discriminating oil spills and seawater-based are shown in Table 3. Based on the methods, we can effectively identify oil spills and seawater and largely avoid misjudging low wind areas as oil spills. The discrimination result is shown in Section 3. This method is used for the ratio of each case, it excludes the impact of environmental factors, and it returns to the essence. Based on the differences in the targets of different material types, this method can be widely applied to studies of different incident angles and environmental conditions.

Table 3.
Thresholds of the images, the values of which are obtained according to the Euclidean distance-based threshold method, with four decimal points retained in the table.
3. Results
3.1. SAR Wind Field Inversion Results and Analysis
Since the detection of oil spills is affected by wind speed, especially when the wind speed is below 3 m/s, many low wind areas act as “look-alikes”, which greatly interfere with the detection of oil spills. Figure 8a–d show the SAR wind field inversion results for the oil spill areas in Cases 1–4, respectively. Figure 8e,f show the wind field inversion results for the low wind area in Cases 5 and 6. The inversion results for winds in Cases 5 and 6 can be used to screen the low wind areas below 3 m/s.
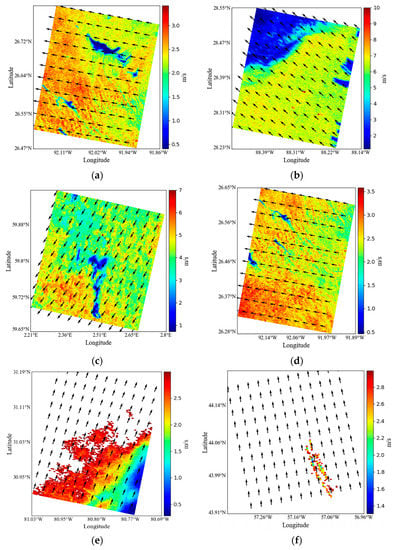
Figure 8.
SAR wind field inversion results, (a–f) are Cases 1–6, respectively. In Cases 5 and 6, the area with wind speeds above 3 m/s is white.
Our analysis showed that wind speeds in all cases are no more than 10 m/s. The overall wind speeds in Cases 1 and 4 are very low, below 3 m/s. The wind speed of the ordinary seawater area in Case 2 is between 6 m/s and 10 m/s, and the oil spill and some nearby areas have low wind speeds, below 3 m/s. In Case 3, the wind speed over a small seawater area upper left is less than 3 m/s, whereas the wind speed over most of the seawater area is between 4 m/s and 7 m/s. However, the wind speeds over the oil spill area and some nearby areas are less than 3 m/s. Case 5 consists mostly of an area below 5 m/s; in particular, the wind speed in the lower right area of the image is extremely low, below 2 m/s, which appears to be an obvious low wind area in the SAR image. Case 6 consists mostly of an area below 8 m/s, whereas the wind speed in the lower right area of the image is extremely low, below 3 m/s, which appears to be a low wind area in the SAR image.
3.2. Analysis of Oil Spill Detection Results
The images of Cases 1–4, as calculated according to Equation (12), are shown in Figure 6 in Section 2.3.2. As shown in Figure 6, increases the contrast between oil spill areas and ordinary seawater, with values being significantly larger than those of seawater, while in the low wind areas, narrows the difference between the “look-alike” areas and the surrounding ordinary seawater, and the values for these low wind areas are not very different from those of the surrounding ordinary seawater areas. In particular, the emulsions in Figure 6c show that the value of the oil–water mixture is between the oil spill and ordinary seawater, and it is still greater than the low wind area. Moreover, according to Figure 3 and Figure 6, preserves the details of the target sea surface areas well.
The oil spill detection result based on is shown in Figure 9, where the white area is seawater and the black area is the oil spill. Figure 9e–h correspond to oil spill Cases 1–4, respectively; Figure 9i–l correspond to low wind area Cases 5–6, respectively. To further verify the identification results, the cases were visually interpreted, and the accuracy was analyzed in reference to the visual interpretation results. The overall accuracy of oil spills and seawater in Cases 1–4 is 98.6%, 95.9%, 97.5%, and 99.3%, respectively, indicating that the overall accuracy of oil spills and seawater in these cases can reach more than 95%. However, compared with the actual distribution of oil spills from the visual interpretation results, our analysis found that the unidentified oil spills were thin oil slicks and oil–water mixtures that spread around the edges. For Case 3, only a small portion of the thin plant oil–water mixture in the upper left corner is unidentified, and only part of the slicks of the crude oil–water mixture is identified. Compared with Figure 9c, the unrecognized ones should be thin oil films with lower oil content, which have higher relative dielectric constants and are more similar to seawater than oil spills. For Cases 5–6, a very small number of low wind areas are misidentified as oil spills.
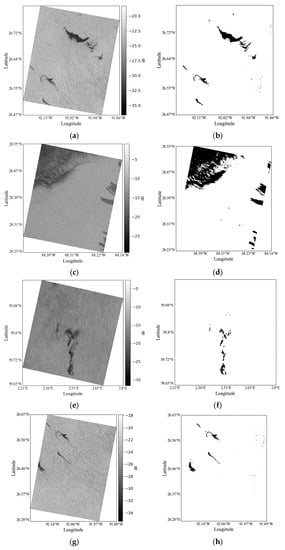
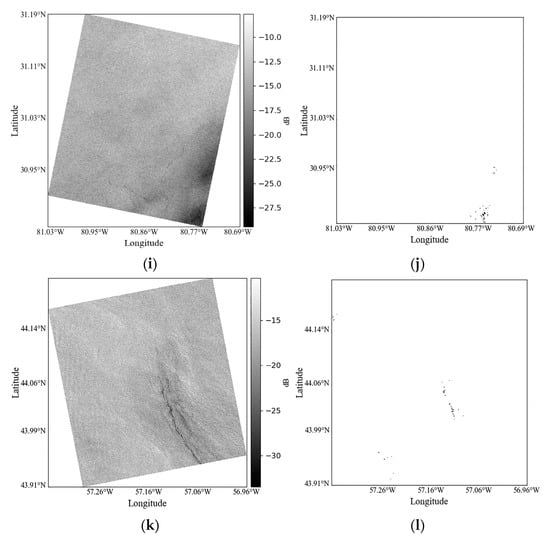
Figure 9.
The preprocessed VV polarization images and oil spill detection results based on and the Euclidean distance-based threshold method (a,c,e,g) are preprocessed of oil spill Cases 1–4, respectively; (b,d,f,h) are oil spill detection results of oil spill Cases 1–4, respectively; (i,k) are preprocessed of Cases 5 and 6, respectively; and (j,l) are detection results of Cases 5 and 6 based on the threshold method, respectively. The white area is seawater, and the black area is oil spill.
When the oil film is thin w.r.t. the penetration depth of the microwave (which is dependent on the band), this commonly happens because the dielectric constant of the oil film is much smaller and the dielectric constant difference is not large enough to alter the , and maybe this is the reason why the proposed method cannot work well. Previous studies have shown that radar scattering from the slick-covered sea surface with a weak damping characteristics is similar to that from the slick-free sea surface, and that Bragg scattering is the dominant scattering mechanism. This finding may be related to its weak damping characteristics and the associated weathering state. Thus, thin oil slicks with weak damping characteristics and oil–water mixtures are generally difficult to detect with various algorithms [40,41,42,43]. This is consistent with the cases of oil–water mixtures and the cases of low wind areas in this study. In the actual oil spill accident, there must be a large amount of oil–water mixture, and its edge must be thin oil slicks with weak damping characteristics and oil–water mixtures. Therefore, this research is indeed to maximize the identification of oil spills while minimizing the interference in the “look-alike” low wind area, to reduce misjudgment and identify the oil spill most accurately in the actual work. It is inevitable to sacrifice a small number of thin oil slicks and oil–water mixtures with weak damping characteristics, as well as allow a very small amount of “look-alike” low wind areas with relatively high damping characteristics to be misjudged as oil spills. These low wind areas are actually similar to thin oil slicks and oil–water mixtures with weak damping characteristics, which are determined by the properties of substances and cannot be avoided. This is also consistent with Figure 6 in Section 2.3.2. These weakly damped thin slicks and spill-seawater mixtures are still the minority of offshore spills, and these misidentified “look-alike” low wind areas with relatively high damping characteristics are also the minority, as shown in Figure 9i–l.
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages Analysis of
is a physical feature that can effectively detect oil spills and distinguish oil spills from ordinary seawater because of their differing dielectric constants and scattering mechanisms. To further demonstrate the advantage of the methodology in the differentiation of seawater (including low wind areas) from oil spill areas, the preprocessed , polarimetric entropy and average alpha angle of the six cases are further investigated. The polarimetric entropy and the average alpha angle are based on the Cloude polarization decomposition algorithm [44].
Considering the differences between different target scenarios, three types of feature maps are drawn for Cases 2, 3 and 5, which include oil film, oil–water mixture, and low wind areas. As shown in Figure 10, the three feature values of the oil spill and low wind area are greater than those of ordinary seawater. Visually, and both describe the data scene well and can distinguish the oil film from other targets. However, compared with the two, in a sense, the detailed information of is too rich. It is required that the identification features reflect the difference between the oil spill and seawater. can clearly describe many details while reflecting on the difference, which is very good, but the ’s scene description ability to such a degree has met our research needs. In addition, retains good local characteristics, reduces the difference between the “special seawater” low wind area and ordinary seawater, and magnifies the difference between the oil spill and seawater to a certain extent. This result greatly facilitates the identification of oil spills and seawater and eliminates the interference of low wind areas on oil spill identification. However, for , the difference between the low wind area and ordinary seawater is as obvious as that between the oil spill and seawater, which is not conducive to us eliminating the interference of low wind areas on oil spill identification. has a relatively poor ability to describe the data scene, and it is difficult to see the details of the data.
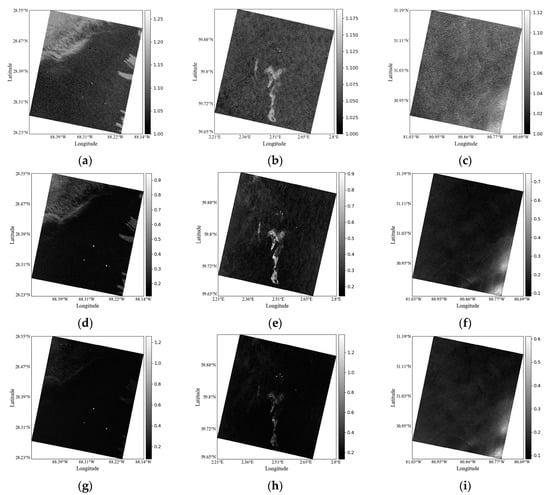
Figure 10.
Feature images for Case 2, Case 3, and Case 5. (a–c) are images. (d–f) are images. (g–i) are images.
To show the numerical situation of the identification features more directly, numerical statistical analyses of , , , and of six cases are carried out. Combined with Figure 10 and Figure 11, considering the characteristics of and , the values of the low wind area and oil spill are smaller/greater than those of ordinary seawater, but there is no obvious difference between the low wind area and the oil spill. Therefore, it is difficult to obtain a suitable threshold to identify oil spills effectively, and low wind areas can inevitably be misjudged as oil spills. The value of the oil spill is much larger than that of ordinary seawater and the low wind area, and compared with the oil spill, the numerical difference between the low wind area and ordinary seawater is relatively small. Therefore, although ’s ability to describe data scenes is relatively poor, it can still be used as important auxiliary information to determine whether the target is a low wind area or oil spill in actual application. In addition, and the low wind area value is still greater than the ordinary seawater, but the oil spill values are higher than the ordinary seawater and low wind area; therefore, it can be based on effective identification of oil spill and seawater, largely avoiding misjudgment of low wind areas as oil spills.
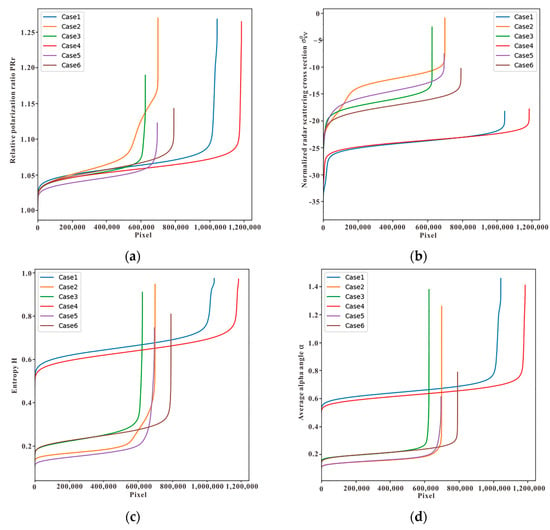
Figure 11.
Numerical statistical comparison of different characteristics of six cases. (a–d) are based on , , , and , respectively.
Since the Euclidian distance can directly reflect the similarity degree of the target, the Euclidian distances between oil spill pixels, oil–water mixture pixels, low wind area pixels, and ordinary seawater pixels under , and are calculated, as shown in Figure 12. For and , there is no clear difference in the Euclidian distance between the oil spill and low wind area and ordinary seawater. Under these two polarization features, based on Euclidian distance, oil spills and low wind areas cannot be distinguished, and they cannot effectively express the law that low wind areas are “special seawater” and that their difference from ordinary seawater should be smaller than that between oil spills and ordinary seawater. For , and are larger than ; that is, can effectively describe the difference between oil spills and seawater. As “special seawater”, the feature of the low wind area is smaller than that of the oil spill. Therefore, appropriate thresholds can be selected in combination with the Euclidian distance to effectively identify oil spills and seawater, largely avoiding misjudgments in low wind areas.
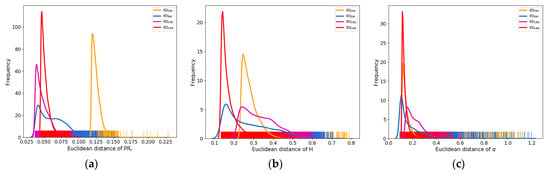
Figure 12.
Distribution of between oil spill, emulsion, or low wind area and ordinary seawater based on different features images, including KED curve and rug plot. , , , and correspond to Cases 2, 3, 5, and 6, respectively. (a–c) are based on , and , respectively.
4.2. Accuracy and Uncertainty
Taking visual interpretation as a reference, the relationship between the oil spill detection accuracy and the threshold value based on can be obtained for Cases 1–4, as shown in Figure 13. Accordingly, the threshold ranges are defined by for each case. The results show that this method has a good oil spill detection capability and can achieve very high accuracy. However, due to the subjectivity of visual interpretation, SAR wind field inversion has certain systematic errors, which can result in inevitable errors. Therefore, with Figure 13 as an effective reference and within the allowable error range, we conclude that the thresholds in Table 3 can achieve the highest oil spill detection accuracy for this method.
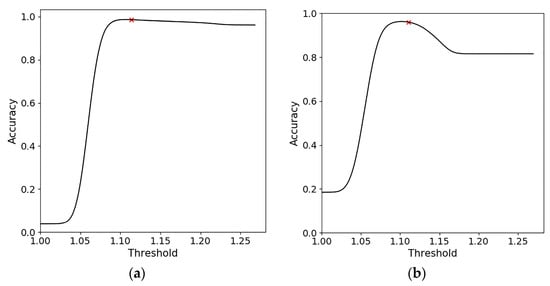
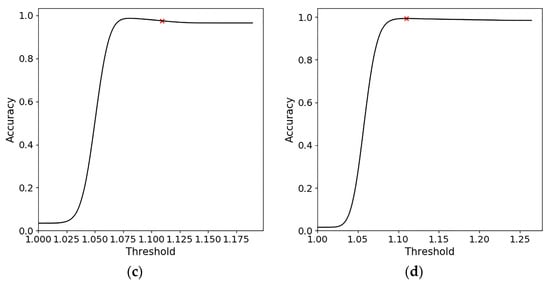
Figure 13.
Relationship between oil spill detection accuracy and threshold based on . (a–d) are Cases 1–4, respectively. The red symbol × indicates the thresholds for our method.
An additional consideration is that marine oil spills on the ocean surface are affected by weathering, including evaporation, emulsification, diffusion, dissolution, oxidation, etc. Thus, the physical and chemical properties of the oil can change, and the scattering mechanism can be affected. For this reason, it is difficult to detect marginally thin oil slicks and oil–water mixtures on the ocean surface using this method.
5. Conclusions
This study focuses on the ambiguity in the identification of oil spills and low wind areas on the ocean surface. To solve the ambiguity problem, whereby low wind areas and oil spills both appear as dark areas on SAR images, making it difficult to distinguish them, a relative PR variable is proposed. The main features are described as follows:
- is a physical characteristic based on the difference in dielectric constants and scattering mechanisms for oil spill and clean seawater areas.
- can numerically increase the contrast between oil spill areas and clean seawater, thereby narrowing the difference between the “look-alike” low wind areas and the surrounding seawater. In addition, the details of the target sea surface are well preserved.
- The of pixels in low wind areas and oil spills is higher than that of ordinary seawater, while the of low wind areas is smaller than that of oil spills. Therefore, based on , oil spills and seawater can be effectively discriminated, and we can largely avoid misidentification of oil spills and low wind areas.
Combined with the four cases of oil spills, using visual interpretation as a “truth” reference, the results show that the overall accuracy rate of oil spills and seawater based on is over 95%. The Euclidean distance-based threshold for can effectively identify oil spills and seawater and largely avoid misjudging low wind areas as oil spills. When the oil film is thin w.r.t. the penetration depth of the microwave (which is dependent on the band), this commonly happens because the dielectric constant of the oil film is much smaller and the dielectric constant difference is not large enough to alter the , and maybe this is the reason why the proposed method cannot work well. A limitation of the methodology is that the edges of areas that are defined as diffuse, thin oil slicks, and oil–water mixture features are not well identified, which is related to their weak damping characteristics and weathering states. A few low wind areas with relatively high damping characteristics are also still misidentified, which are similar to thin oil slicks and oil–water mixtures with weak damping characteristics. It is determined by the properties of substances, and these slicks, mixtures, and areas are still in the minority, so it is inevitable and allowable. Considering additional factors, such as interpretation error and systematic errors in wind field inversion, we conclude that the proposed method and threshold T value can achieve the highest oil spill detection accuracy; this is within the allowable error range and considers the other methodologies used in this study.
In addition, this paper proposes a threshold method based on Euclidean distance, which uses Euclidean distance to measure the similarity degree among materials. Using the ratio of different pixels in the same image, the influence of environmental factors is excluded and returns to the essence. Based on the material differences among different types of targets, the method can be widely used in the study of different incidence angles and different environmental conditions.
Oil spill identification is affected by different sensor parameters, such as image mode, band, incidence angle, payload, etc., and different environmental conditions (weather, climate, sea state, etc.); these problems deserve further study, and we will apply our identification methods to more types of sensor data in the future. We are also committed to exploring whether there is a specific response relationship between and oil spill thickness in our future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.X.; methodology, T.X. and R.O.; software, R.O. and L.Z.; validation, R.O. and L.Z.; formal analysis, R.O.; investigation, T.X. and R.O.; resources, T.X. and R.O.; data curation, T.X., R.O., W.P., L.Z. and X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, R.O.; writing—review and editing, R.O., T.X. and W.P.; visualization, R.O., L.Z. and X.Z.; supervision, T.X.; project administration, T.X.; funding acquisition, T.X. and R.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China project (41776181), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_1174), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC2803302), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grants No JSZRHYKJ202114, YJGL-YF-2020-16). Additional funding support is acknowledged from the Canadian Space Agency, Canada’s Ocean Frontier Institute (OFI), Marine Environmental Observation Prediction and Response (MEOPAR) network, and Canada’s Competitive Science Research Fund.
Acknowledgments
RADARSAT-2 Data and Products from MacDonald, Dettwiler, and Associates Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; MacDonald, I.R.; Lu, Y. Chronic oiling in global oceans. Science 2022, 376, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, T.; Xu, H.; Meng, L.; Chen, W. Comparative analysis of oil spill recognition based on TM remote sensing image. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (IAME) 2019, 3, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Brekke, C.; Solberg, A.H. Oil spill detection by satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Perrie, W.; Wu, J. Retrieval of oil–water mixture ratio at ocean surface using compact polarimetry synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. Progress in research on marine oil spills detection using synthetic aperture radar. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2019, 41, 751–762. [Google Scholar]
- Dabboor, M.; Singha, S.; Topouzelis, K.; Flett, D. Oil Spill Detection Using Simulated Radarsat Constellation Mission Compact Polarimetric SAR Data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 4582–4585. [Google Scholar]
- Latini, D.; Del Frate, F.; Jones, C.E. Multi-frequency and polarimetric quantitative analysis of the gulf of mexico oil spill event comparing different SAR systems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Alpers, W.; Hühnerfuss, H.; Masuko, H.; Kobayashi, T. Imaging of biogenic and anthropogenic ocean surface films by the multifrequency/multipolarization SIR-C/X-SAR. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 18851–18866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Perrie, W.; Li, X.; Pichel, W.G. Mapping sea surface oil slicks using RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization SAR image. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchew, B.; Jones, C.E.; Holt, B. Polarimetric analysis of backscatter from the deepwater horizon oil spill using L-Band synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3812–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrunes, S.; Brekke, C.; Eltoft, T. Characterization of Marine Surface Slicks by Radarsat-2 Multipolarization Features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 5302–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghany, M. Utilization of a Genetic Algorithm for the Automatic Detection of Oil Spill from RADARSAT-2 SAR Satellite Data. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, G. Multi-Feature Based Ocean Oil Spill Detection for Polarimetric SAR Data Using Random Forest and the Self-Similarity Parameter. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velotto, D.; Migliaccio, M.; Nunziata, F.; Lehner, S. Dual-Polarized TerraSAR-X Data for Oil-Spill Observation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4751–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivonin, D.V.; Skrunes, S.; Brekke, C.; Ivanov, A.Y. Interpreting Sea Surface Slicks on the Basis of the Normalized Radar Cross-Section Model Using RADARSAT-2 Copolarization Dual-Channel SAR Images. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2748–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelliaume, S.; Boisot, O.; Guérin, C.-A. Dual-Polarized L-Band SAR Imagery for Temporal Monitoring of Marine Oil Slick Concentration. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. An Experiment for Oil Spill Recognition Using RADARSAT-2 Image. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 2761–2764. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y. Application of Deep Networks to Oil Spill Detection Using Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, M. Ocean Oil Spill Classification with RADARSAT-2 SAR Based on an Optimized Wavelet Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, L.; Xu, J.; Fanucci, L. Oil Spill Identification from SAR Images for Low Power Embedded Systems Using CNN. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Perrie, W.; Fang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yu, W.-J.; He, Y.-J. Effective Dielectric Constant Model of Electromagnetic Backscattering from Stratified Air–Sea Surface Film–Sea Water Medium. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 054102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, T.; Fang, H.; Meng, L.; Zhao, L.; Ai, R. Sea surface oil spill identification method based on SAR polarization ratio and texture feature. Haiyang Xuebao 2019, 9, 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, T.; Perrie, W.; Wei, C.; Zhao, L. Discrimination of Open Water from Sea Ice in the Labrador Sea Using Quad-Polarized Synthetic Aperture Radar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Vachon, P.W.; Wolfe, J. Requirement on Antenna Cross-Polarization Isolation for the Operational Use of C-Band SAR Constellations in Maritime Surveillance. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, C.; Brekke, C.; Eltoft, T. Retrieval of Marine Surface Slick Dielectric Properties from Radarsat-2 Data via a Polarimetric Two-Scale Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5162–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RADARSAT-2 Product Format Definition MacDonald; Dettwiler and Associates Ltd.: Richmond, BC, Canada, 2008.
- Yommy, A.S.; Liu, R.; Wu, S. SAR Image Despeckling Using Refined Lee Filter. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, Hangzhou, China, 26–27 August 2015; Volume 2, pp. 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-S.; Jurkevich, L.; Dewaele, P.; Wambacq, P.; Oosterlinck, A. Speckle Filtering of Synthetic Aperture Radar Images: A Review. Remote Sens. Rev. 1994, 8, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benes, R.; Riha, K. Medical Image Denoising by Improved Kuan Filter. Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2012, 10, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Dee, D. ERA5 Reanalysis Is in Production. ECMWF Newsl. 2016, 147, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Sabater, J.M.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; Soci, C. Global Reanalysis: Goodbye ERA-Interim, Hello ERA5. ECMWF Newsl. 2019, 159, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Guo, J.; Han, Y. Preliminarily assessment of ERA5 reanalysis data. J. Mar. Meteor. 2018, 38, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Xie, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, L.; He, Y. Evaluation of SAR wind speed retrieved based on C-2PO model and CMOD5.N geophysical model functions. Haiyang Xuebao 2018, 40, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Pei, X. Measurement of water-oil ratio in crude oil based on modes classification. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2008, 59, 970–976. [Google Scholar]
- Gade, M.; Alpers, W.; Hühnerfuss, H.; Lange, P.A. Wind Wave Tank Measurements of Wave Damping and Radar Cross Sections in the Presence of Monomolecular Surface Films. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 3167–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G. An Improved Otsu Method for Oil Spill Detection from SAR Images. Oceanologia 2017, 59, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Teng, X.; Cao, L.; Li, J. Oil Spill Detection Based on a Superpixel Segmentation Method for SAR Image. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1725–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Magid, A.; Rotman, S.R.; Weiss, A.M. Comments on Picture Thresholding Using an Iterative Selection Method. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1990, 20, 1238–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trussell, H.J. Comments on “Picture Thresholding Using an Iterative Selection Method”. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Perrie, W.; Garcia-Pineda, O. Compact Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar for Marine Oil Platform and Slick Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 1407–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.J.; Migliaccio, M.; Hargrove, J.T.; Garcia-Pineda, O.; Graber, H.C. Oil Spills and Slicks Imaged by Synthetic Aperture Radar. Oceanography 2013, 26, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunziata, F.; Gambardella, A.; Migliaccio, M. A Unitary Mueller-Based View of Polarimetric SAR Oil Slick Observation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 6403–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunziata, F.; Migliaccio, M.; Li, X. Sea Oil Slick Observation Using Hybrid-Polarity SAR Architecture. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 40, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. An Entropy Based Classification Scheme for Land Applications of Polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).