Abstract
Chlorophyll-a concentration (Chl-a) is a crucial parameter for monitoring the water quality in coastal waters. The principal aim of this study is to evaluate the performance of existing Chl-a band ratio inversion models for estimating Chl-a from Sentinel2-MSI and Sentinel3-OLCI observation. This was performed using an extensive in situ Rrs-Chl-a dataset covering contrasted coastal waters (N = 1244, Chl-a (0.03–555.99) µg/L), which has been clustered into five optical water types (OWTs). Our results show that the blue/green inversion models are suitable to derive Chl-a over clear to medium turbid waters (OWTs 1, 2, and 3) while red/NIR models are adapted to retrieve Chl-a in turbid/high-Chl-a environments. As they exhibited the optimal performance considering these two groups of OWTs, MuBR (multiple band ratio) and NDCI (Normalized Difference Chlorophyll-a Index)-based models were merged using the probability values of the defined OWTs as the blending coefficients. Such a combination provides a reliable Chl-a prediction over the vast majority of the global coastal turbid waters (94%), as evidenced by a good performance on the validation dataset (e.g., MAPD = 21.64%). However, our study further illustrated that none of the evaluated algorithms yield satisfying Chl-a estimates in ultra-turbid waters, which are mainly associated with turbid river plumes (OWT 5). This finding highlights the limitation of multispectral ocean color observation in such optically extreme environments and also implies the interest to better explore hyperspectral Rrs information to predict Chl-a.
1. Introduction
Phytoplankton biomass, estimated through the Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) concentration, represents a key parameter for monitoring the response of the coastal domain to environmental changes of natural or anthropogenic origins. The evaluation of human impacts on coastal ecosystems’ structure and functioning leading for instance to eutrophication processes (e.g., [1]) represents a crucial scientific and societal objective, which strongly relies on the availability of long-lasting consistent Chl-a times series. Satellite ocean observation represents in this context a relevant tool since it provides a continuous synoptic view of the coastal waters over more than two decades. At the same time, the spatial and temporal resolutions of ocean color observations are fine enough for allowing local studies or capturing episodic events advantageously complementing classical in situ monitoring. Recent ocean color sensors onboard satellites from the ESA Sentinel constellation (i.e., Sentinel2-MSI and Sentinel3-OLCI) have further increased the availability of ocean satellite data. These satellite archives are now considered an essential observation tool for supporting the development of sustainable environmental policies (EU Water Framework Directive and Marine Strategy Framework Directive, [2,3]).
While Chl-a concentration represents the pioneer product of ocean color observation, efforts are still required for improving the accuracy of Chl-a estimation in optically complex waters [4,5]. Chl-a inversion algorithms have indeed been first dedicated to the oceanic (Case-1) waters where the variability of optical properties is mainly driven by phytoplankton [6]. The ocean color (OC) chlorophyll-a models and related offspring algorithms [7,8] are typically based on the use of a maximum band ratio in the blue–green domain of the visible spectrum. Such algorithms have been widely validated over clear environments and are now operationally used for deriving Chl-a in open ocean waters (e.g., [9,10,11]). Estimating Chl-a from space still, however, represents a challenging task in coastal waters (Case-2 waters, [5,12]). This is related to the high optical diversity of these environments [13] where water optical properties are diversely driven by a variable contribution of phytoplankton, suspended particulate matter (SPM), and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM). In high-CDOM and/or -SPM phytoplankton conditions, the co-occurrence of different water constituents presents impacts on the reflectance signal, especially at the shortest wavelengths of the visible range. This feature tends to impair the performance of classical blue/green ratio-based inversion models [14,15,16].
For this reason and considering the crucial need to monitor Chl-a over turbid coastal environments, specific Chl-a algorithms have been developed taking advantage of the impacts of phytoplankton on the water optical properties in the red and near-infrared (NIR) regions. These models rely on the negligible impacts of CDOM and SPM absorption as well as the optical signature of phytoplankton absorption or chlorophyll fluorescence over the red–NIR domain of the electromagnetic spectrum (e.g., [17,18,19,20]). Such red–NIR approaches are, however, failing in clear waters, where the phytoplankton signal can be masked in relationships to the high contribution of pure water absorption at higher wavelengths [21,22].
Regional inversion models have been considered to be a convenient way for optimizing ocean color products over a defined coastal area. Such approaches present, however, numerous limitations being dependent on the representativeness of the dataset used and are intrinsically limited in terms of spatial applicability [23]. Alternative approaches based on the applications of a defined model on a pixel-per-pixel basis according to the water optical characteristics have been shown to represent a valuable alternative for combining different algorithms for estimating ocean color satellite products in coastal waters [23,24,25]. An extensive study by Neil et al. [26] has further illustrated the interest in an adaptive framework for dynamically selecting and optimizing Chl-a inversion models in inland waters based on optical water types (OWTs). With the main objective to provide ocean color data users a simple way to evaluate the reliability of the Chl-a estimates derived from blue/green and red/NIR inversion models, Lavigne et al. [12] developed quality control tests for improving MERIS and OLCI Chl-a estimates in coastal waters. In addition to these recent studies, new alternative approaches that rely on machine learning, which may be more computing-time-consuming than standard reflectance ratios, are now developed for deriving Chl-a over a large range of Chl-a contents and considering a variety of bio-optical regimes in inland and coastal waters [27]. Although there were numerous efforts performed during the last decades for accurately estimating Chl-a concentration from the remote sensing reflectance using adapted inversion, there is still no consensus on the algorithm or the set of algorithms to be applied for deriving Chl-a for large-scale applications in coastal waters.
This study contributes to ongoing efforts to optimize the retrieval of Chl-a from ocean color observations in coastal waters, with a specific focus on Sentinel-2/MSI and Sentinel-3/OLCI observations. A comprehensive global in situ remote sensing reflectance (Rrs)–Chl-a dataset (N = 1244) of samples collected in contrasted environments has been gathered. This dataset was classified into five OWTs ranging from clear to ultra-turbid waters. Using OWTs as a general framework, this work first aims at illustrating the limitations of historical band-ratio-based algorithms for deriving Chl-a and selecting the most appropriate inversion models by evaluating novel formulations and state-of-the-art algorithms adapted for different OWTs considered. This study further presents the interest and requirements (e.g., compatibility of inversion algorithms to provide accurate Chl-a estimates, discontinuities in the map when merging Chl-a models) of band-ratio-based blending approaches to provide reliable Chl-a across diverse coastal environments. The applicability of band-ratio-based approaches at a global scale, as well as possible future improvements in Chl-a retrieval, especially in ultra-turbid environments, by exploiting the potential of upcoming hyperspectral observations, is specifically discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
An overview of the study process, including the performed development and processing, can be seen in the flow chart (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
Flow chart of the present study illustrating the general methodology for development and validation of the combined Chl-a model.
2.1. In Situ Dataset
The in situ dataset (DS-W, N = 1244, mean Chl-a = 12.14 µg/L) combines concomitant measurements of Chl-a and remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) collected between 1997 and 2016 in the frame of diverse worldwide distributed field campaigns in contrasted coastal areas (European coastal waters [28,29,30,31], French Guiana [23,32], Eastern Viet Nam Sea [15,33], South Shetland Islands, the US coastal waters, The Sea of Japan [34], Beaufort Sea North Canada [35], and Brazil (Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro) [36]) (Figure 2). This dataset covers a wide range of Chl-a concentrations with values ranging over 4 orders of magnitude (0.03–555.99 µg/L, Table 1) from oligotrophic waters (e.g., Mediterranean Sea, clear polar waters) to ultra-eutrophic environments (Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro; [36]). The DS-W was further randomly split into a development dataset (DS-D, N = 831, mean Chl-a = 13.63 µg/L) and a validation dataset (DS-V, N = 356, mean Chl-a = 9.45 µg/L), representing 70 and 30% of the DS-W, respectively; these three datasets follow a similar distribution (Figure 3). It is worth noting that the proportion of DS-D/DS-V partition was performed excluding the points corresponding to OWT5 (N = 57), for which no band-ratio-based model development has been performed (see Section 3.2.1 and Section 3.3.1).

Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of in situ Rrs-Chl-a measurements gathered within the DS-W dataset (N = 1244) collected in (a) the Beaufort Sea, (b) the United States coastal waters, (c) the French Guiana coastal waters, (d) Guanabara Bay, (e) the South Shetland Islands, (f) European coastal waters, (g) Vietnamese coastal waters, and (h) the Sea of Japan: colors indicate the optical water types each in situ sample is associated with (see Section 2.3).

Table 1.
Description of the in situ dataset of Chl-a (µg/L) considered in the frame of this study: number of samples (N), minimum (Min), maximum (Max), mean (Mean), and standard deviation (StdDev).

Figure 3.
Chl-a absolute frequency distribution for (a) the whole in situ dataset DS-W (N = 1244), (b) the development dataset (DS-D, N = 831), and the validation dataset (DS-V, N = 356). The number of data points corresponding to OWT 5 is not considered in the DS-D and DS-V.
The Chl-a/SPM ratio has been calculated for the whole dataset for providing rough information on the relative importance of the Chl-a signal associated with the different water masses considered in this study. Considering that the SPM concentration was not available for all the in situ samples in the DS-W, SPM was estimated from the Rrs(665) using the model by Han et al. [37], which has had a reliable performance illustrated from various former studies in contrasted coastal waters (e.g., [38,39]).
2.2. Satellite and Matchup Dataset
Data in the DS-W have been acquired before the S2 and S3 time period (from June 2015 and February 2016, respectively). An external and independent in situ dataset, which encompasses only Chl-a measurements, has been therefore considered in addition to the DS-W for validation purposes (Figure 4). In practice, Chl-a samples collected along the French coast are in the frame of the SOMLIT (Coastal Environment Observation Service, https://www.somlit.fr/, accessed on 15 June 2021) and REPHY (Observation and Monitoring Network for Phytoplankton and Hydrology in coastal waters, https://www.seanoe.org/data/00361/47248/, accessed on 15 June 2021) French national survey programs. These long-lasting in situ datasets (e.g., continuous monthly data since 1997 for SOMLIT) present the advantage of being acquired following a standardized protocol.

Figure 4.
Distribution of the REPHY and SOMLIT stations considered in the matchup dataset DS-M.
In practice, Satellite Sentinel2-MSI A/B (60 m resolution) and Sentinel3-OLCI A/B (300 m resolution) Rrs data have been extracted for both SOMLIT and REPHY Chl-a samples over the time periods from 7 September 2015 to 19 March 2021 and from 24 May 2016 to 7 April 2021 for MSI and OLCI, respectively). Specifically, top-of-atmosphere Level 1 products have been processed considering three atmospheric correction schemes including POLYMER (version 4.13, [40]), C2RCC [41], and ACOLITE [42]. The matchup extraction was performed considering a 3 × 3 window around each in situ sampling point. Several quality control criteria were then applied [43] considering the following: (1) the number of valid pixels (at least 5 valid pixels among the 9 pixels extracted), (2) the spatial homogeneity of the matchup subsets assessed from the variation coefficient within the subset window (CV = standard deviation/mean. 100 < 30%), and (3) the time difference between in situ and satellite measurements (lower than 3 h).
After the application of all these criteria, the final matchup dataset (DS-M) is then composed of a maximal number of 194 matchup points for MSI and 362 for OLCI with Chl-a concentrations ranging between 0.19 and 34.12 µg/L (mean = 2.48 µg/L, standard deviation = 3.79 µg/L) and 0.05 and 52.93 µg/L (mean = 2.52 µg/L, standard deviation = 3.7 µg/L), respectively. The Chl-a statistic of the DS-M is further illustrated in Figure 5.

Figure 5.
Box plot showing Chl-a range of the final matchup dataset (DS-M) regarding OLCI and MSI sensors.
In addition to the Sentinel2 and Sentinel3 matchup dataset, the global MERIS GlobCoast dataset (monthly 1 km spatial resolution, [15,33]) was further considered for illustrating and discussing the potential applicability of the models selected with the frame of this study with a global-scale perspective.
2.3. Optical Classification
2.3.1. Optical Water Types Definition
Optical water types (OWTs) were defined using the procedure defined in [23] applied to the DS-W Rrs dataset. In practice, normalized Rrs data were considered to cluster the reflectance data focusing on the shape of the spectra. The normalization was applied to multispectral Rrs data considering 6 wavelengths in the visible part of the spectrum (412, 443, 490, 510, 560, and 665 nm) centered on the OLCI bands. The normalized Rrs was determined by the ratio between its original value and the surface below the spectral shape as follows:
where represents the normalized remote sensing reflectance.
An unsupervised classification was then applied to the dataset using Ward’s clustering method [44], which presents the advantage of being less sensitive to outliers compared to other approaches [23].
This classification led to the definition of 5 optical water types showing different Rrs spectral shapes (Figure 6a). OWTs 1 and 2 (N = 269 and 185, respectively) are associated with clear oligotrophic to mesotrophic waters (mean Chl-a = 0.38 ± 0.36 and 0.96 ± 0.74 µg/L, respectively) with Rrs spectra typically peaking in the blue part of the visible spectrum. OWT 3 samples correspond to mesotrophic waters characterized by high Rrs in the green part of the visible spectrum with an Rrs plateau ranging between 490 and 560 nm (N = 426, mean Chl-a = 2.33 ± 3.09 µg/L). The Chl-a/SPM ratio for these 3 OWTs increases from OWT 1 (2.25 × 10−3) to OWT 3 (4.04 × 10−3).

Figure 6.
(a) Average spectra corresponding to the optical water types defined from the DS-W dataset (N = 1244); box plots illustrating the distribution of Chl-a (b) and Chl-a/SPM ratio (c) associated with each optical class. While all the samples considered in DS-W are available for all the visible wavelengths corresponding to Sentinel2−MSI and Sentinel3−OLCI bands, it is worth noticing that the spectral coverage of the Rrs in situ dataset in the NIR part of the spectrum is unequal. For most of the samples associated with OWTs 1, 2, and 3, little information was available in the NIR (12.8% for OWTs 1, 2, and 3, respectively) while this information was present for most (98%) of the samples associated with OWTs 4 and 5, for which red and NIR algorithms are devoted (see Section 2.4).
OWTs 4 and 5 are associated with highly turbid/eutrophic coastal waters. OWT 4 corresponds to high-Chl-a waters with an Rrs peak at 560 nm (N = 307, mean Chl-a = 43.72 ± 80.89 µg/L) and shows the maximal Chl-a/SPM ratio among the different OWTs (Chl-a/SPM = 13 × 10−3) related to ultra-eutrophic for these samples. Conversely, OWT 5 samples (N = 57) are more likely associated with turbid waters showing a higher proportion of non-algal particles (sediments and detritus) when compared to OWT 4 as emphasized from the lower average Chl-a (7.15 ± 10.46 µg/L) and the lowest Chl-a/SPM ratio (1.43 × 10−3) found for these samples (Figure 6c).
2.3.2. Satellite Pixel Optical OWT Labeling, OWT Membership Calculation
The five OWTs defined in the previous section were used for labeling the satellite Rrs spectra. This labeling consists of computing the OWT membership of an input Rrs spectrum (e.g., satellite Rrs) to each of the OWTs defined from the in situ dataset, which are characterized by specific mean (µ) and covariance ( matrices [23,25]. The Mahalanobis distance ∆2 applied to the log-transformed is then used to estimate the distance between input spectrum x and a given OWT ic as follows:
where T indicates the matrix transpose.
The OWT membership of satellite pixels to each of the defined OWTs was then estimated as in [23]. The probability density function (PDF), corresponding to each targeted pixel associated with , is calculated based on its Mahalanobis distance () to the distribution of OWT ic and can be expressed as below:
The computed probability values are then normalized (p*) so that the sum of OWT memberships equals 1 by taking the ratio between P for ic OWT and the total P for all OWTs considering such as follows [13]:
2.4. Chl-a Candidate Inversion Algorithms
A variety of empirical band-ratio-based bio-optical algorithms have been developed for estimating Chl-a concentration from satellite ocean remote sensing observation. Here, a selection of “standard” models based on different input Rrs data and formulations have been performed among the number of different methods available considering models whose performances have already been shown to be relevant to the diverse types of coastal environments taking into account results provided from recent extensive intercomparison exercises (e.g., [26]). In practice, historical models considered here can be split into two categories: blue/green(Red) ratio-based models more likely adapted to clear to moderately turbid waters [8,45] and red/NIR ratio-based methods specifically developed for turbid environments [17,18,21,46].
It is important to mention that all the considered models (except the model OC5, [45]) have been considered in their original and tuned versions fitting the different formulations to the DS-D data corresponding to the optical water types they have been designed for (see Section 3.2 and Section 3.3). These coefficients are here provided for each original model.
2.4.1. Blue/Green (Red) Band-Ratio-Based Models
Considering the radiometric resolution of Sentinel2-MSI and Sentinel3-OLCI sensors, two models have been selected for clear to medium turbid waters. These models correspond to the empirical NASA OC-family algorithms developed from the NOMAD dataset extensively used to produce standard Chl-a products from satellite observation.
- (1)
- OC6
This recent algorithm OC6 [8] corresponds to an adaptation of the OC4 model [7], which includes additional bands at 412 and 665 nm to extend the applicability of this approach, typically applied to open ocean waters, towards coastal waters. This model can be described as follow:
where
The original coefficients for this model are a0 = 0.2424, a1 = −2.2146, a2 = 1.5193, a3 = −0.7702, and a4 = −0.4291
- (2)
- OC3
The main equation of the OC3 model to compute Chl-a remains the same as in Equation (5). However, this algorithm uses a different blue/green ratio input that is established by 3 spectral bands in the visible part of the spectrum [8]. Such a ratio can be expressed as below:
and the coefficients are a0 = 0.41712, a1 = −2.56402, a2 = 1.22219, a3 = 1.02751, and a4 = −1.56804.
- (3)
- OC5—Gohin
The five channels model by Gohin et al. [45] was developed in order to correct the overestimation of the Chl-a estimated from the OC4 model in coastal waters presenting moderate turbidity levels and highCDOM loads, based on sensor-specific LUTs empirically developed from an extensive in situ dataset. It has been considered here using the LUTs defined for MERIS.
2.4.2. Red–NIR Algorithms
- (1)
- Gurlin11
The empirical model developed by Gurlin et al. [17] consists of a second-order polynomial function based on the Rrs(709)/Rrs(665) band ratio:
where a = 25.28; b = 14.85; c = −15.18.
- (2)
- Gilerson10
The model proposed for MERIS by Gilerson et al. [18] is based on a linear relationship between in situ Chl-a and the NIR/red ratio of MERIS, such as the following:
where a = 35.745; b = −19.295; c = 1.124.
- (3)
- Gons08
The Chl-a inversion algorithm developed by Gons et al. [47] for turbid environments is a semi-analytical approach considering IOPs information along with the red–NIR reflectance ratio and the reflectance at 779 nm. The version proposed in [21] is considered here and is expressed as follows:
where aw(709) and aw(665), the water absorption coefficients at 709 nm and 665 nm, were estimated as 0.7 m−1 and 0.4 m−1, respectively [48]. is the chlorophyll-specific absorption that was defined as 0.016 m2 mg−1. The calculation of the back-scattering coefficient is estimated from the water-leaving reflectance at 779 nm as follows:
where Rw (779) is the water-leaving reflectance (Rw = Rrs × pi).
- (4)
- Mishra12
The model proposed by Mishra and Mishra [46] is an empirical model developed for application in estuarine and coastal waters. It is based on the calculation of the Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index (NDCI) as an input variable to derive Chl-a:
where a = 42.197; b = 236.5; c = 314.97.
2.5. Statistical Indicators for Algorithm Performance Assessment
The performance of the considered Chl-a models was evaluated considering a set of statistical descriptors including the following:
where represents the in situ Chl-a observations and the Rrs-based Chl-a estimates.
In addition, a linear regression between and was performed for each considered model leading to the estimation of a slope and coefficient of determination (R2) as additional statistical descriptors.
Radar charts have been further used to compare the performance of the Chl-a inversion algorithms. This graphical display allows the representation of multiple statistical parameters summarized in the form of a two-dimensional chart [49]. Here, an overview of the normalized MAPD, RMSD, MRAD, MB, slope, and R2 (Equations (14)–(18)) is provided, and the normalization is computed as follows:
where j represents each individual Chl-a model considered in a defined intercomparison exercise.
In addition to a synthetic visual examination, radar plots were also used to compute a unique statistical indicator outlining the general performance of the considered Chl-a inversion methods. This consists in practice to compute the area associated with the polygons linking the normalized indicators indicated from (19) to (24) as below:
3. Results
3.1. Performances of Historical Models
The performances of the historical models described in Section 2.4 in their original version were first illustrated considering the whole dataset (DS-W, Figure 7 and Figure 8) gathering a maximum of 1244 values considering the Rrs input wavelengths for the OC3, OC5, and OC6 models (i.e., Rrs at 412, 443, 490, 510, 560, and 665 nm) and 470 values for the one used in Gurlin11, Gilerson10, Mishra12, and Gons08 (i.e., Rrs at 665, 709, and 779 nm).

Figure 7.
Scatterplot (log–log scale) of the in situ Chl-a (DS-W) vs. the Chl-a estimated from the different historical band-ratio-based models (a) OC3, (b) OC6, (c) OC5−Gohin, (d) Gurlin11, (e) Gilerson10, (f) Mishra12, and (g) Gons08 considered in their original formulations (see Section 2.4).

Figure 8.
Determination coefficient (R2) of the linear relationships between the in situ Chl-a and the estimated Chl-a corresponding to each OWT subset in DS-W (Figure 6) for the different band-ratio-based historical models considered in the frame of this study in their original versions (Section 2.4).
As already documented, models based on the use of the band ratios in the visible part of the spectrum (OC6, OC3, and OC5, Figure 7a–c) provide reliable Chl-a estimates for clear to medium turbid waters (OWTs 1, 2, and 3) with R2 values of 0.59, 0.61, and 0.57, respectively (Figure 8). The models, however, show limitations for estimating Chl-a in the most turbid environments (OWTs 4 and 5) as illustrated by the high scattering found in Figure 7 as well as by the low R2 (<0.28) found for the OWT 4 samples when applying these models (Figure 8). The OC5 model, which has been designed for moderately coastal waters providing a correction of the overestimation generally provided from the OC4 algorithm, also shows clear limitations for the OWT 4 (Figure 7) in agreement with the previous studies [12,15]. Loisel et al. [15], for instance, documented an exponential increase in the uncertainties related to OC5-derived Chl-a with increasing turbidity (i.e., SPM concentration > 60 mg·L−1). As expected, the OC3, OC4, and OC5 models (not based on the NIR band) are totally saturated over the whole range of Chl-a for the OWT 5 samples generating quasi-invariant Chl-a estimates.
Red–NIR-based approaches (Gurlin11, Gilerson10, Mishra12, and Gons08; Figure 7d–g) are conversely showing poor performances for OWT 1, 2, and 3 samples with the R2 remaining below 0.1 (see Figure 8) for these waters whatever the model considered. These models have, however, not been developed for these waters with a relatively low level of turbidity. A general better performance is, however, found for Gilerson10, Gurlin11, Mishra12, and Gons08 models for the OWT 4 samples. This confirms the reliable applicability of the latter methods for estimating Chl-a over highly turbid and high-Chl-a waters [26]. These models, in their original formulations, still, however, show limitations, more likely related to the data range they have been developed. This is emphasized, for instance, by the saturation pattern found for the lower-end Chl-a values for Mishra12 (Figure 7f) already pointed out by previous studies [46]. The model of Gons08 while providing relatively good Chl-a estimates for high Chl-a values (>10 g·L−1) tends to fail for low Chl-a for the OWT 4 samples, highly underestimating the Chl-a value (Figure 7g), and further generates negative Chl-a (N = 287 vs. N = 299, 298, and 300 for Gurlin11, Gilerson10, and Mishra12, respectively) in agreement with former studies (e.g., [12,21]).
None of the red–NIR models evaluated are able to produce reliable Chl-a estimates for the ultra-turbid waters represented by the OWT 5 samples, due to the very low impact of the Chl-a on the reflectance signal for these waters [12]. A clear saturation is found for Gilerson10, Gurlin11, and Mishra12 (Figure 7d–f) and low R2 values were obtained for these models (Figure 8), emphasizing the limitation of these red–NIR-based methods towards ultra-turbid waters. The model by Gons et al. [21] is globally able to reproduce the Chl-a gradient found in OWT 5 data although it has an overall high uncertainty level as illustrated by the scattering in Figure 7d for these samples. As previously mentioned for OWT 4, this model tends to produce negative Chl-a values as illustrated by the lower estimated Chl-a for the Gons08 model when compared to Gurlin11, Gilerson10, and Mishra12 algorithms for OWT 5 (N = 35 and 57, 57, and 57, respectively).
These results are confirming the relative limitations of the different band-ratio formulations usually considered for estimating Chl-a over contrasted coastal environments. Considering the performance of the considered models in their original formulations, an optimization of historical models as well a development of a new formulation was further performed, subsetting the in situ dataset into two groups: (1) one gathering oligotrophic to mesotrophic waters (OWTs 1, 2, 3) for which visible wavelengths have been considered and (2) one gathering highly turbid/high-Chl-a samples corresponding to OWT 4.
Further considering that all the band-ratio-based evaluated methods were failing for OWT 5 samples, no adaptation of these existing methods was performed for the corresponding samples.
3.2. Chl-a Estimates for Clear to Medium Turbid Waters
3.2.1. Development of a New Algorithm for OWTs 1, 2, and 3
Considering the previous results, OC3 and OC6 models (OC3-Tuned and OC6-Tuned), which are the most adapted for clear to medium turbid waters (OWTs 1, 2, and 3), have been optimized on the DS-D dataset (N = 617, Table 2) using the QR decomposition method where the input matrix of the regression problem can be presented as a product of the orthogonal matrix (Q) and a triangular matrix (R). This optimization approach is available as the “fitlm” function in Matlab version 2022a.

Table 2.
Coefficients of the OC3 and OC6 models adapted to the DS-D dataset for OWTs 1, 2, and 3 (N = 617).
In addition to these adapted historical formulations, an alternative model for oligotrophic to mesotrophic waters was developed by exploiting the DS-D dataset. This model named MUBR is based on a combination of multiple band ratios, which have been shown to provide the best performance for estimating Chl-a from DS-D (Figure 9). It is worth noticing that the Rrs(412) was not considered in the development of the MUBR model considering that this wavelength is not available for MSI and that this band is susceptible to be affected by large uncertainties related to the atmospheric correction processes [50]. The MUBR algorithm is in practice based on the combination of three band ratios using four visible bands from the blue to the red available for both Sentinel2-MSI and Sentinel3-OLCI. This formulation is expressed as follows:
where
and where a0 = 0.665, a1 = −3.506, a2 = 3.590, and a3 = −0.019.

Figure 9.
(a) Relationship between the in situ vs. estimated Chl-a from the MUBR model developed on the samples corresponding to OWTs 1, 2, and 3 in the DS-D dataset (N = 617). (b) Histograms of distribution of the Chl-a values corresponding to OWT 1, 2, and 3 samples in DS-D and for the Chl-a values estimated from the MUBR model.
3.2.2. Model Selection for Clear to Medium Turbid Waters
The intercomparison on the performance of the Chl-a estimates on clear to medium turbid waters (OWTs 1, 2, and 3) was performed on the independent validation dataset DS-V (N = 263) considering, in addition to the MUBR, classical clear waters band-ratio models adapted on DS-D (OC3-Tuned and OC6-Tuned) as well as considering the model OC5 in its original version. The results in Figure 10a–c show that the MUBR model provides the best performance considering our validation dataset when compared to OC3-Tuned and OC6-Tuned models with an overall lower dispersion (e.g., MRAD = 66.72% vs. 97.12% and 86.24%, respectively) as well as with a general better estimation of Chl-a value over the whole range of Chl-a for the considered subset (e.g., slope = 0.76 vs. 0.69 and 0.64, respectively). We observed a similar performance of the OC5 original model in the clear to medium turbid waters on the validation dataset (Figure 10c) to that obtained for OC3 (e.g., area of 2.109). The better performance for the MUBR model is further underlined in the radar plot provided in Figure 10d where the area found for the MUBR, representing a summary of the statistical parameters considered, is lower (1.24) than that for the other three methods considering both their original and adapted versions (OC3-Tuned: 2.45 and 2.09, respectively; OC6-Tuned: 2.45 and 2.05, respectively). The lower performance of the OC3 and OC6 methods on the DS-V subset for OWTs 1, 2, and 3 can be explained by an overestimation of the very low Chl-a values as well as by a saturation of the Chl-a estimated for the highest Chl-a values (Figure 10).

Figure 10.
Intercomparison of the performance of the Chl-a inversion models for the OWT 1, 2, and 3 samples in the in situ validation dataset DS-V (N = 263): relationships between in situ vs. estimated Chl-a applying (a–c) the OC3, OC6, and OC5−Gohin models adapted to the development dataset DV−D and (d) for the MUBR model; (e) summary of the performance of the Chl-a inversion models where the lowest area of the polygon associated with each model represented in the radar plot corresponds to the best model. Note that the statistics for the original versions of OC3 and OC6 are also shown for completeness.
Our results, therefore, tend to indicate that the model MUBR represents a valuable alternative for estimating Chl-a focusing on the clear to moderate turbid waters gathered using the dataset considered in the frame of the present study (OWTs 1, 2, and 3 data).
3.3. Chl-a Estimation in Turbid/high-Chl-a Waters (OWT 4)
3.3.1. Development of a New Algorithm
Considering the results of the previous section, a focus was performed to define the model most adapted for estimating Chl-a over highly turbid/high-Chl-a waters corresponding to OWT 4 samples only. This is also due to the fact that none of the adapted models has been found to provide accurate Chl-a retrieval for OWT 5 samples (not shown). In practice, the Red-NIR-based models by Gurlin11, Gilerson10, Mishra12, and Gons08 were adapted to our dataset defining new coefficients for each model refitting the corresponding formulation on the DS-D samples (not shown, Table 3).

Table 3.
The tuned coefficients for the Gurlin10, Gilerson11, Gons08, and Mishra12 models adapted to the DS-D dataset for OWT 4 (N = 210).
In addition, a new formulation (referred to as the NDCI-based model) was developed for OWT 4 samples (Figure 11) considering the saturation pattern towards low Chl-a values already reported for models using the NDCI parameter as an input value [26,46,51] and is expressed as follows:
where a0 = 1.179, a1 = 2.689, and a2 = −1.083.
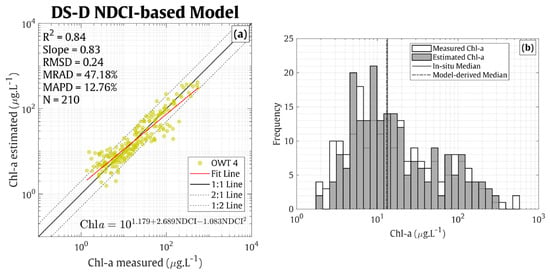
Figure 11.
(a) Relationship between the in situ vs. estimated Chl-a from the NDCI-based model developed on the OWT 4 samples in the DS-D dataset (N = 210). (b) Histograms of distribution of the OWT 4 Chl-a in DS-D and for the Chl-a values estimated from the NDCI-based model.
3.3.2. Model Selection for Highly Turbid/High-Chl-a Waters
The relative performances of these red–NIR models were then evaluated on the DS-V dataset for OWT 4 (Nmax = 90, Figure 12). Although very similar statistics are found for all the tuned versions of the models evaluated, the new NDCI-based model presents the best performances (area = 0.472, Figure 12f). As previously pointed out from the DS-W dataset (Figure 7g), Gons08 tends to generate an underestimation of the lower-end Chl-a concentration (i.e., Chl-a < 5 µg/L) in OWT 4, potentially leading to the generation of negative values (Figure 12c, N = 86 for the original and tuned versions vs. N = 90 for the other models). It is worth mentioning that the tuned version of Gons08 does not provide better estimates than the original one, which is probably related to the difference in the Chl-a range presented in our development dataset (1.37–556 µg/L) and the one in [21] (0.37–131 µg/L) as the adapted coefficients and the performances corresponding to different inversion models in the DS-V might vary according to Chl-a level. The tuned versions of Gilerson10 and Gurlin11 (Figure 12a,b) globally show satisfactory performances (area = 0.602 and 0.577, respectively), confirming the effectiveness of these models to derive Chl-a in turbid environments [26]. Interestingly the tuned version of Mirshra12 (Figure 12d), although exhibiting a generally reliable performance, still shows a saturation pattern towards the smallest Chl-a for the OWT 4 samples (<5 µg/L). Such a saturation pattern is not found when applying the modification of this model corresponding to the NDCI-based formulation proposed here (Figure 12e).

Figure 12.
Intercomparison of the performance of the adapted versions of Red-NIR model on highly turbid/high-Chl-a validation data corresponding to the OWT 4 samples in DS-V (N = 90): scatterplots of the in situ Chl-a vs. the Chl-a estimated from (a) Gilerson10, (b) Gurlin11, (c) Gons08, (d) Mishra12, and (e) NDCI-based models; a summary of the performance of the considered model for estimating Chl-a is provided in the radar plot (f) where the performance of both original and tuned versions of these 4 models is also provided for completeness.
This intercomparison exercise thus suggests that the NDCI-based model represents the most adapted model for estimating Chl-a over highly turbid/high-Chl-a (OWT 4) waters gathered in our in situ dataset.
3.4. Class-Based Combination of Multiple Chl-a Models for OWTs 1, 2, 3, and 4
The previous algorithm evaluation exercises clearly confirm the inability for a unique simple band ratio to deliver reliable estimates over the whole range of Chl-a values found in coastal waters [12,15,26]. We further illustrate the use of two band-ratio formulations considering a first model combining band ratios in the visible domain for clear to medium turbid waters (MUBR for OWTs 1, 2, 3) and a red–NIR model (NDCI-based) for highly turbid/high-Chl-a waters (OWT 4).
Different methods can be used for producing Chl-a maps by applying different bio-optical algorithms on a pixel-per-pixel basis. Diverse former studies have, for instance, illustrated the interest of using a weighted average to provide smooth Chl-a gradients in transition areas between different inversion algorithms. Such weighting approaches were diversely based on the use of Chl-a values [52] or on the exploitation of the optical characteristics of the water masses provided from optical water types defined from the reflectance spectra [25,26,53].
Such an optical-based weighted approach was considered in the frame of this study using weights based on the belonging probability of each sampling point (in situ sample or satellite pixel) to each optical group of optical water types to which a specific Chl-a model should be applied (i.e., MUBR for OWTs 1, 2, and 3 and Mishra12-Tuned for OWT 4). The combination of algorithms from two groups of OWTs was performed following the equation [23]:
where the terms are defined as follows:
- , , , and correspond to the normalized probability for OWTs 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively (Equation (4), [13]).
- Chl-a123 is the Chl-a estimated from MuBR designed for OWTs 1, 2, and 3. Chl4 is the Chl-a estimated by using red/NIR models designed for OWT 4. The tuned coefficients are used for the calculation of Chl-a123 and Chl-a4 (Equations (26) and (30)).
The evaluation of this weighted combination is provided in Figure 13. It is worth mentioning that the number of points presented in Figure 13 (N = 147) corresponds to the maximal number of points in DS-V with available information from the visible to the NIR for samples corresponding to OWTs 1, 2, 3, and 4. An overall good performance is found for the MUBR-NDCI-based combination (MAPD = 21.64%, RMSD = 0.25).

Figure 13.
Performance of the combined model between the MUBR model for clear/moderate turbid waters (OWTs 1, 2, and 3) and the NDCI-based model on the DS-V (N = 147).
3.5. Matchup Exercise
The validation of the Chl-a estimates performed using the MUBR-NDCI-based combination proposed in this study was performed through a matchup exercise based on the DS-M dataset for both OLCI and MSI (Section 2.2). Our results emphasize a general expected degradation in the accuracy of the Chl-a estimates for these two sensors (Figure 14) when compared to the performance of the Chl-a inversion performed using the in situ validation dataset (Figure 13). Globally, the best performance is here found when applying the MUBR-NDCI-based combination using satellite Rrs(λ) derived from the POLYMER processing for both sensors. The Chl-a derived with POLYMER yields the highest number of valid matchups for both OLCI (N = 358 vs. N = 184 and 225 for ACOLITE and C2RCC, respectively) and MSI (N = 188 vs. N = 138 and 143 for ACOLITE and C2RCC, respectively). This result is in agreement with former intercomparison exercises (e.g., [54]). Although it has an overall high scattering level in the matchups, POLYMER globally provides better estimates from the clear to the highly turbid waters with a better performance found for OLCI when compared to MSI (Figure 14b,e). For both sensors, ACOLITE processing tends to generate an overestimation of the retrieved Chl-a also found for C2RCC, especially for the OWT 4 samples, suggesting the probable need to improve atmospheric correction in the NIR domain. The patterns depicted in Figure 13 remain globally valid when considering the common matchup points (not shown) for the three atmospheric correction schemes applied to both sensors. A general better performance in retrieving Chl-a is still found when applying the MUBR-NCDI-based combination to POLYMER data to OLCI (e.g., MAPD = 114, 172, and 116% for POLYMER, ACOLITE, and C2RCC, respectively; N = 214) and MSI (e.g., MAPD = 68, 149, and 148% for POLYMER, ACOLITE, and C2RCC, respectively; N = 99) Rrs(λ).

Figure 14.
Chl-a matchup validation (DS-M dataset, Section 2.2) computed applying the MUBR-Mishra12-Tuned combination (Section 3.4) on the Rrs(λ) generated applying three atmospheric corrections schemes (ACOLITE, POLYMER, and C2RCC) for Sentinel3−OLCI (a–c) and Sentinel2−MSI (d–f), respectively.
Our results therefore relatively differ from previous works [54] where POLYMER was not found to provide the best performance when evaluating different atmospheric correction schemes (and Chl-a models) for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 applications over lakes, rivers, and coastal waters. However, this better performance might be related to the general good performance of POLYMER when considering band ratios as illustrated from former studies in coastal waters [50,55,56]. This might also be explained by the fact that the current matchup dataset (DS-M) does not contain many very highly turbid or high-Chl-a waters (max Chl-a = 34.12 µg/L and 52.93 µg/L for MSI and OLCI, respectively) underlining the need to perform additional matchup exercises on a larger dataset. Investigating in more detail the relative impact of the considered atmospheric correction schemes is out of the scope of this study considering that the matchup dataset DS-D contains Chl-a data only. However, it should be mentioned that up to now no consensual atmospheric correction scheme is currently recommended for Sentinel2-MSI and Sentinel3-OLCI applications in coastal waters, as the performance of the different approaches is susceptible to vary widely according to the wavelength as well as according to the water type considered [50,54,57].
4. Discussion
4.1. Chl-a Algorithms Combination
The results obtained in the previous sections have illustrated that the red–NIR formulations globally demonstrated their ability to retrieve Chl-a values in highly turbid/high-Chl-a waters with a satisfying accuracy (Figure 13). Our results further emphasize the necessity to consider compatible models when applying weighting approaches, such as the one depicted in Section 3.4, taking care of the applicability of the approaches to be merged especially in transition areas. A limitation was, for instance, found for the formulation by Gons et al. [21], which tends to generate negative Chl-a values for the low Chl-a levels (<5 µg/L) for the OWT 4 waters. Such limitations might represent an issue when merging multiple algorithms on a pixel-per-pixel basis. As a matter of fact, the application of a combination based on MUBR and Gons08 will lead to a generation of bias or even create negative Chl-a in the transition area between OWT 3 and OWT 4 (not shown) where pixels can show relatively high OWT membership values for both OWTs.
To avoid such issues; a possible way would consist of considering other approaches than the one based on the weighting methods based on pixel OWT membership (Equation (31)) for combining multiple bio-optical models. Lavigne et al. [12], for instance, recently proposed pixel-per-pixel-based quality control tests (diversely based on the Chl-a as well as on thresholds applied on different MERIS Rrs(λ)) for selecting the most appropriate models for estimating Chl-a [8,21,45]. As mentioned by these authors, the main objective of such a quality-control-based approach is more likely to provide the users with a way to evaluate the reliability of the models applied to a defined area. These authors further illustrate the possibility to use this selection procedure to eventually merge multiple algorithms although such an approach might generate discontinuity in the Chl-a maps when switching from one algorithm to another.
The interest of using the OWT membership information to merge the two inversion models considered here was further illustrated from a Sentinel2-MSI map in the Vietnamese coastal waters close to the Mekong River and Nha Be River estuaries (East Vietnam Sea, Figure 15a), which shows contrasted water masses ranging from clear (OWT 2) to ultra-turbid (OWT 5) waters (Figure 15c). The MUBR-NDCI-based combination was here applied considering for each pixel the best model according to the pixel OWT (i.e., without weighting the models, not shown) as well as applying the weighing approach described in Equation (31) (Figure 15d). The need to consider the pixel OWT membership to combine MUBR- and NDCI-based models is illustrated in Figure 15e where the relative difference between the Chl-a map produced without and with a weighting function is shown. It appears that the simple juxtaposition of the most pertinent model can generate significant discontinuities in the final Chl-a estimates. As a matter of fact, maximum differences reaching 10% are observed in the transition areas between OWTs 3 and 4. Such possible spatial artifacts induced using an unweighted function can represent a significant issue when using high-spatial-resolution data, such as from Sentinel2-MSI (or Landsat8-OLI), which are susceptible to capturing fine-scale transition gradients in coastal waters [12,23].

Figure 15.
Illustration of the interest of using a weighting function based on the OWT membership probability for blending multiple Chl-a from a Sentinel2−MSI (60 m, POLYMER processing) image capturing the Vietnamese coastal waters: (a) Location of the Sentinel2 (Tile 48PYS) (b) true color image; (c) optical water types distribution; (d) Chl-a estimated from the MUBR-NDCI-based combination where masked gray areas are those belonging to OWT 5; (e) relative difference (%) in the Chl-a estimated from the MUBR-NDCI-based combination with and without using pixel OWT belonging probability as a weighting function (see Equation (31)).
4.2. Applicability of Band-Ratio-Based Chl-a Models at Global Scale and Current Limitations and Perspectives
To summarize the results developed in the previous sections regarding the relative performance of the different Chl-a inversion methods selected for the different optical OWTs defined in the frame of this study, global monthly MERIS 1 km Rrs data were associated with the five optical OWTs defined in this work. Figure 16 shows the most frequent OWTs observed for each pixel over the MERIS time period. The coastal domain was here defined considering a global mask proposed by Mélin and Vantrepotte [13] for characterizing the optical diversity of coastal waters, which is based on the combination of criteria based on bathymetry and distance to the coast. It appears that pixels corresponding to OWTs 1, 2, and 3 represent 63, 21, and 14% of the considered coastal domain, meaning that the MUBR model can be applied in the vast majority (98%) of the considered waters. OWT 4 pixels, where the use of red/NIR models such as the NDCI-based model defined here are the most suitable, represent only 2% of the whole domain, often corresponding to coastal margins impacted by the dilution of terrestrial inputs, including waters offshore river plume or mangrove areas, for instance. The OWT 5 waters, for which none of the tested band-ratio-based Chl-a inversion methods provide accurate Chl-a estimates, represent 1% of the global domain here considered. Focusing on moderate to ultra-turbid waters (OWTs 3, 4, and 5), our results indicate that Chl-a can be estimated with a satisfying accuracy (OWTs 3 and 4) over 94% of the coastal margins and shelf waters.

Figure 16.
Global distribution of the most frequent optical water type among the 5 optical water types considered in the frame of this study observed from the monthly MERIS 1 km observation between 2002 and 2012. The histogram chart provides an illustration of the relative spatial coverage (in %) associated with each optical water type over the whole domain considered here.
The main limitations in estimating Chl-a from ocean color observation are therefore related to ultra-turbid waters corresponding to OWT 5, mainly associated with the proximal part of most of the large rivers. Despite the restricted spatial extension of OWT-5 regions, an accurate monitoring of the recent evolution of the biogeochemical quality of these water masses is, however, essential considering their vulnerability to environmental changes of a natural and anthropic origin impacting the transfer of matter along the land–sea continuum [1]. Our results, however, clearly question the pertinence of considering Chl-a concentration as a relevant indicator for monitoring from satellite ocean color observation such environments where the phytoplankton signal on the marine reflectance seems to be too low for being detected considering band-ratio-based methods on both visible and NIR wavelengths.
The present study only allows the pixels for which Chl-a estimates are not reliable, considering the evaluated models to be dynamically identified using optical water types information to potentially mask the corresponding areas. A possible way to overcome this issue could consist of adopting alternative methods, for instance, taking advantage of the new potential offered by upcoming hyperspectral satellite sensors (e.g., the NASA PACE mission). Cheng et al. [58], for instance, documented the interest of an Rrs derivative-based approach for estimating Chl-a in turbid inland waters. More specifically, these authors demonstrated that the first Rrs derivative at 699 nm was a good proxy for estimating Chl-a in turbid lakes. The pertinence of this approach was evaluated on the OWT 5 dataset testing the best combination considering wavelengths ranging from 412 to 740 nm [58]. Our preliminary results show that the highest correlation with Chl-a (R2 = 0.40, N = 57) is obtained when using the second derivative at 671 nm (; using Rrs(l) measurements at X and Y nm, these two parameters follow a linear relationship indicated in Figure 17.

Figure 17.
Illustration of the potential of an Rrs(671) second derivative-based model for estimating Chl-a concentration in ultra-turbid waters (OWT 5).
The derivative-based approach, although it has potential interest, will not fully allow for the solving of the issue represented by the Chl-a inversion in ultra-turbid OWT 5 waters (Figure 17). Indeed, a clear overestimation of the Chl-a concentration is observed for the low Chl-a samples in OWT 5 (<1 µg/L), for which the data correspond to samples showing extremely to fairly low values for the Chl-a/SPM ratio (<3.9 × 10−5). However, the performance of this latter model has proven a significant improvement in retrieving Chl-a over such optically complex water when comparing the R2 value to that of the traditional approaches (see Figure 8). It is also important to recognize that additional in situ observations are required to further confirm the latter statement and deliver more robust information on the current limitations of ocean-color-based observation for depicting Chl-a in such ultra-turbid environments.
5. Conclusions
This work aimed at evaluating the performance of band-ratio-based algorithms for estimating Chl-a in coastal waters from Sentinel2-MSI and Sentinel3-OLCI observation from an extensive in situ dataset covering a large spectrum of coastal environments in terms of optical characteristics (from clear to ultra-turbid waters) and trophic status (from oligotrophic to ultra-eutrophic environments). The best combination found from our dataset consists of mixing a visible band-ratio model (MUBR) for clear to medium turbid waters (OWTs 1, 2, and 3) and an adapted version of the red–NIR model (NDCI-based) for highly turbid/high-Chl-a waters. Such a combination can provide relevant Chl-a estimates covering four orders of magnitude from oligotrophic to ultra-eutrophic waters covering the vast part of the coastal domain. From our dataset, POLYMER processing was the most adapted to derive Chl-a from the proposed approach although additional matchups should be performed considering more data, especially towards higher turbidity/Chl-a levels. While the methodology proposed in this work can be transposed to other sensors (e.g., MERIS), future works should be performed for other sensors (e.g., MODIS) for which less information is available in the NIR domain, which is, however, crucial for coastal waters applications. Finally, classical band-ratio-based methods show clear limitations, failing, whatever the model considered, for delivering Chl-a in ultra-turbid environments (e.g., proximal part of main river plumes). While optical water types information could allow for the dynamic flagging of the corresponding pixels, this work further emphasizes the necessity to develop specific approaches for these waters (e.g., exploiting the potential offered by future hyperspectral missions).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.T. and V.V.; methodology, M.D.T., V.V. and H.L.; formal analysis, M.D.T. and V.V.; in situ data collection: E.N.O., R.P. and X.M.; satellite data processing: M.D.T., K.T.T. and D.J.; writing—original draft preparation, V.V., M.D.T. and H.L.; supervision, V.V. and H.L.; project administration, V.V.; funding acquisition, V.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Office de l’eau Guyane, OFB and DEAL M.T PhD support, as well as by the ANR-FAPESP COCOBRAZ (ANR-21-CE01-0026) and the CNES-TOSCA OSYNICO projects. Guanabara Bay sampling and analyses were funded by CNPq (PELD-BG) and FAPERJ (several projects).
Data Availability Statement
The database used in this study encompasses the SeaBASS dataset (https://seabass.gsfc.nasa.gov/wiki/NOMAD accessed on: 15 June 2021), the LOG’s dataset (included in GLORIA dataset: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-023-01973-y accessed on: 15 June 2021), and the dataset collected in Guanabara Bay, Brazil (only available for specific requests).
Acknowledgments
This work has benefited of the CNRS International Research Project VELITROP research projects for gathering parts of the in situ dataset.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abril, G.; Cotovicz, L.C., Jr.; Nepomuceno, A.; Erbas, T.; Costa, S.; Ramos, V.V.; Moser, G.; Fernandes, A.; Negri, E.; Knoppers, B.A.; et al. Spreading Eutrophication and Changing CO2 Fluxes in the Tropical Coastal Ocean: A few lessons from Rio de Janeiro Propagação da Eutrofização e Mudanças Nos Fluxos de CO2 No Oceano Costeiro Tropical: Algumas Lições Do Rio de Janeiro. Espec. Labomar 2022, 55, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasopoulou, E.; Simis, S.G.H.; Alikas, K.; Ansper, A.; Anttila, S.; Jenni, A.; Barillé, A.-L.; Barillé, L.; Brando, V.; Bresciani, M.; et al. Satellite-Assisted Monitoring of Water Quality to Support the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive. EOMORES White Pap. 2019. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/3903776#.ZBbiEnZByUk (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Gohin, F.; Van der Zande, D.; Tilstone, G.; Eleveld, M.A.; Lefebvre, A.; Andrieux-Loyer, F.; Blauw, A.N.; Bryère, P.; Devreker, D.; Garnesson, P.; et al. Twenty Years of Satellite and in Situ Observations of Surface Chlorophyll-a from the Northern Bay of Biscay to the Eastern English Channel. Is the Water Quality Improving? Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Jamet, C.; Dinh Ngoc, D. Challenges and New Advances in Ocean Color Remote Sensing of Coastal Waters. In Topics in Oceanography; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-1179-5. [Google Scholar]
- Groom, S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Ban, Y.; Bernard, S.; Brewin, R.; Brotas, V.; Brockmann, C.; Chauhan, P.; Choi, J.; Chuprin, A. Satellite Ocean Colour: Current Status and Future Perspective. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of Variations in Ocean Color. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C. Ocean Color Chlorophyll Algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Werdell, P.J. Chlorophyll Algorithms for Ocean Color Sensors—OC4, OC5 & OC6. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, D.; Barciela, R. Global Marine Biogeochemical Reanalyses Assimilating Two Different Sets of Merged Ocean Colour Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnesson, P.; Mangin, A.; D’Andon, O.F.; Demaria, J.; Bretagnon, M. The CMEMS GlobColour Chlorophyll a Product Based on Satellite Observation: Multi-Sensor Merging and Flagging Strategies. Ocean Sci. 2019, 15, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Losa, S.N.; Mangin, A.; Soppa, M.A.; Garnesson, P.; Demaria, J.; Liu, Y.; d’Andon, O.H.F.; Bracher, A. Global Retrieval of Phytoplankton Functional Types Based on Empirical Orthogonal Functions Using CMEMS GlobColour Merged Products and Further Extension to OLCI Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, H.; Zande, D.; Ruddick, K.; Santos, J.; Gohin, F.; Brotas, V.; Kratzer, S. Quality-Control Tests for OC4, OC5 and NIR-Red Satellite Chlorophyll-a Algorithms Applied to Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Vantrepotte, V. How Optically Diverse Is the Coastal Ocean? Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Ishizaka, J.; Goes, J.I.; Gomes, H.D.R.; Maúre, E.D.R.; Hayashi, M.; Katano, T.; Fujii, N.; Saitoh, K.; Mine, T.; et al. Improved MODIS-Aqua Chlorophyll-a Retrievals in the Turbid Semi-Enclosed Ariake Bay, Japan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Ouillon, S.; Ngoc, D.D.; Herrmann, M.; Tran, V.; Mériaux, X.; Dessailly, D.; Jamet, C.; Duhaut, T.; et al. Assessment and Analysis of the Chlorophyll-a Concentration Variability over the Vietnamese Coastal Waters from the MERIS Ocean Color Sensor (2002–2012). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, F.H.; Dierssen, H.M. Evaluating the Seasonal and Decadal Performance of Red Band Difference Algorithms for Chlorophyll in an Optically Complex Estuary with Winter and Summer Blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurlin, D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Moses, W.J. Remote Estimation of Chl-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters—Return to a Simple Two-Band NIR-Red Model? Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3479–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.A.; Gitelson, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.; Ioannou, I.; Ahmed, S.A. Algorithms for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Coastal and Inland Waters Using Red and near Infrared Bands. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Borstad, G.; Brown, L. Detection of Intense Plankton Blooms Using the 709 Nm Band of the MERIS Imaging Spectrometer. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, S.T.; Kucharik, C.J.; Norman, J.M. Direct and Indirect Estimation of Leaf Area Index, FAPAR, and Net Primary Production of Terrestrial Ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J.; Auer, M.T.; Effler, S.W. MERIS Satellite Chlorophyll Mapping of Oligotrophic and Eutrophic Waters in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4098–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of Constituent Retrieval in Optically Deep and Complex Waters from Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantrepotte, V.; Loisel, H.; Dessailly, D.; Mériaux, X. Optical Classification of Contrasted Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alimonte, D.; Zibordi, G. Phytoplankton Determination in an Optically Complex Coastal Region Using a Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Vantrepotte, V.; Clerici, M.; D’Alimonte, D.; Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.-F.; Canuti, E. Multi-Sensor Satellite Time Series of Optical Properties and Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Adriatic Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N. A Global Approach for Chlorophyll-a Retrieval across Optically Complex Inland Waters Based on Optical Water Types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Hà, N.; et al. Seamless Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in Inland and Coastal Waters: A Machine-Learning Approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Stramski, D.; Ferrari, G.M.; Claustre, H.; Bricaud, A.; Obolensky, G.; Hoepffner, N. Variations in the Light Absorption Coefficients of Phytoplankton, Nonalgal Particles, and Dissolved Organic Matter in Coastal Waters around Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2003, 108(C7), 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubac, B.; Loisel, H.; Guiselin, N.; Astoreca, R.; Artigas, L.F.; Mériaux, X. Hyperspectral and Multispectral Ocean Color Inversions to Detect Phaeocystis Globosa Blooms in Coastal Waters. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C06026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubac, B.; Loisel, H. Variability and Classification of Remote Sensing Reflectance Spectra in the Eastern English Channel and Southern North Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 110, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukermans, G.; Ruddick, K.; Loisel, H.; Roose, P. Optimization and Quality Control of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentration Measurement Using Turbidity Measurements. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantrepotte, V.; Danhiez, F.-P.; Loisel, H.; Ouillon, S.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A.; Dessailly, D. CDOM-DOC Relationship in Contrasted Coastal Waters: Implication for DOC Retrieval from Ocean Color Remote Sensing Observation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Mangin, A.; Vantrepotte, V.; Dessailly, D.; Ngoc Dinh, D.; Garnesson, P.; Ouillon, S.; Lefebvre, J.P.; Mériaux, X.; Minh Phan, T. Variability of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentration in Coastal Waters under the Mekong’s Influence from Ocean Color (MERIS) Remote Sensing over the Last Decade. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W. An Improved Bio-Optical Data Set for Ocean Color Algorithm Development and Satellite Data Product Variation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 122–140. [Google Scholar]
- Be, S.; Babin, M.; Larouche, P.; Seas, N. An Empirical Ocean Color Algorithm for Estimating the Contribution of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter to Total Light Absorption in Optically Complex Waters. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, E.N.; Fernandes, A.M.; Kampel, M.; Cordeiro, R.C.; Brandini, N.; Vinzon, S.B.; Grassi, R.M.; Pinto, F.N.; Fillipo, A.M.; Paranhos, R. Assessment of Remotely Sensed Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Guanabara Bay, Brazil. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Bryère, P.; Ouillon, S.; Dessailly, D.; Xing, Q.; Zhu, J. Development of a Semi-Analytical Algorithm for the Retrieval of Suspended Particulate Matter from Remote Sensing over Clear to Very Turbid Waters. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensac, E.; Martinez, J.M.; Vantrepotte, V.; Anthony, E.J. Seasonal and Inter-Annual Dynamics of Suspended Sediment at the Mouth of the Amazon River: The Role of Continental and Oceanic Forcing, and Implications for Coastal Geomorphology and Mud Bank Formation. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 118, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, N.A.; Vantrepotte, V.; Ngoc, D.D.; Huybrechts, N.; Gardel, A. Automated SWIR Based Empirical Sun Glint Correction of Landsat 8-OLI Data over Coastal Turbid Water. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A294–A318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric Correction in Presence of Sun Glint: Application to MERIS. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, C.; Doerffer, R.; Peters, M.; Kerstin, S.; Embacher, S.; Ruescas, A. Evolution of the C2RCC Neural Network for Sentinel 2 and 3 for the Retrieval of Ocean Colour Products in Normal and Extreme Optically Complex Waters. In Proceedings of the Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; Volume 740, p. 54. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the Dark Spectrum Fitting Atmospheric Correction for Aquatic Applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 Archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Harding Jr, L.W.; Feldman, G.C.; McClain, C.R. Regional and Seasonal Variability of Chlorophyll-a in Chesapeake Bay as Observed by SeaWiFS and MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical Grouping to Optimize an Objective Function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohin, F.; Druon, J.N.; Lampert, L. A Five Channel Chlorophyll Concentration Algorithm Applied to SeaWiFS Data Processed by SeaDAS in Coastal Waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 1639–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index: A Novel Model for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J. A Chlorophyll-Retrieval Algorithm for Satellite Imagery (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer) of Inland and Coastal Waters. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, R.M.; Fry, E.S. Absorption Spectrum (380–700 Nm) of Pure Water. II. Integrating Cavity Measurements. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 8710–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.K.; Duforět-Gaurier, L.; Vantrepotte, V.; Ferreira Jorge, D.S.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A.; d’Andon, F.; Loisel, H. Deriving Particulate Organic Carbon in Coastal Waters from Remote Sensing: Inter-Comparison Exercise and Development of a Maximum Band-Ratio Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mograne, M.; Jamet, C.; Loisel, H.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A. Evaluation of Five Atmospheric Correction Algorithms over French Optically-Complex Waters for the Sentinel-3A OLCI Ocean Color Sensor. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Song, K.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.; Cai, X.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; Lyu, H. Assessment of Algorithms for Estimating Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters: A Round-Robin Scoring Method Based on the Optically Fuzzy Clustering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.E.; Lain, L.R.; Bernard, S. An Optimized Chlorophyll a Switching Algorithm for MERIS and OLCI in Phytoplankton-Dominated Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieronymi, M.; Müller, D.; Doerffer, R. The OLCI Neural Network Swarm (ONNS): A Bio-Geo-Optical Algorithm for Open Ocean and Coastal Waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Mangin, A.; Balasubramanian, S.V.; Smith, B.; Alikas, K.; Arai, K.; Barbosa, C.; Bélanger, S.; Binding, C.; Bresciani, M.; et al. ACIX-Aqua: A Global Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Methods for Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 over Lakes, Rivers, and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Evaluation of Seven Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for OLCI Images over the Coastal Waters of Qinhuangdao in Bohai Sea. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 102711. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Poser, K.; Bresciani, M.; Alikas, K.; Spyrakos, E.; Giardino, C.; Ansper, A. Assessment of Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for the Sentinel-2A MultiSpectral Imager over Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.-T.; Jamet, C.; Vantrepotte, V.; Mériaux, X.; Cauvin, A.; Mograne, M.A. Evaluation of Sentinel-2/MSI Atmospheric Correction Algorithms over Two Contrasted French Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wei, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Lake Using Spectral Smoothing and Derivative Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2979–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).