Unsupervised Image Dedusting via a Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The D-CycleGAN is the first work that successfully introduces unpaired training to sand-dust image restoration. This work eliminates the dependence on paired data and does not require the estimation of any physical model parameters and can be well generalized to realistic applications;
- (2)
- We propose a jointly optimized guided module (JOGM) and a hidden layer adversarial branch to constrain the network model from the outside and inside of the network, which can improve the quality of the generated image;
- (3)
- Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method exhibits better image quality and outperforms other advanced comparison algorithms. We also contribute sand-dust datasets including some aerial sand-dust datasets to promote research in the field of sand-dust images.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Image Dedusting Methods
2.2. Learning-Based Methods
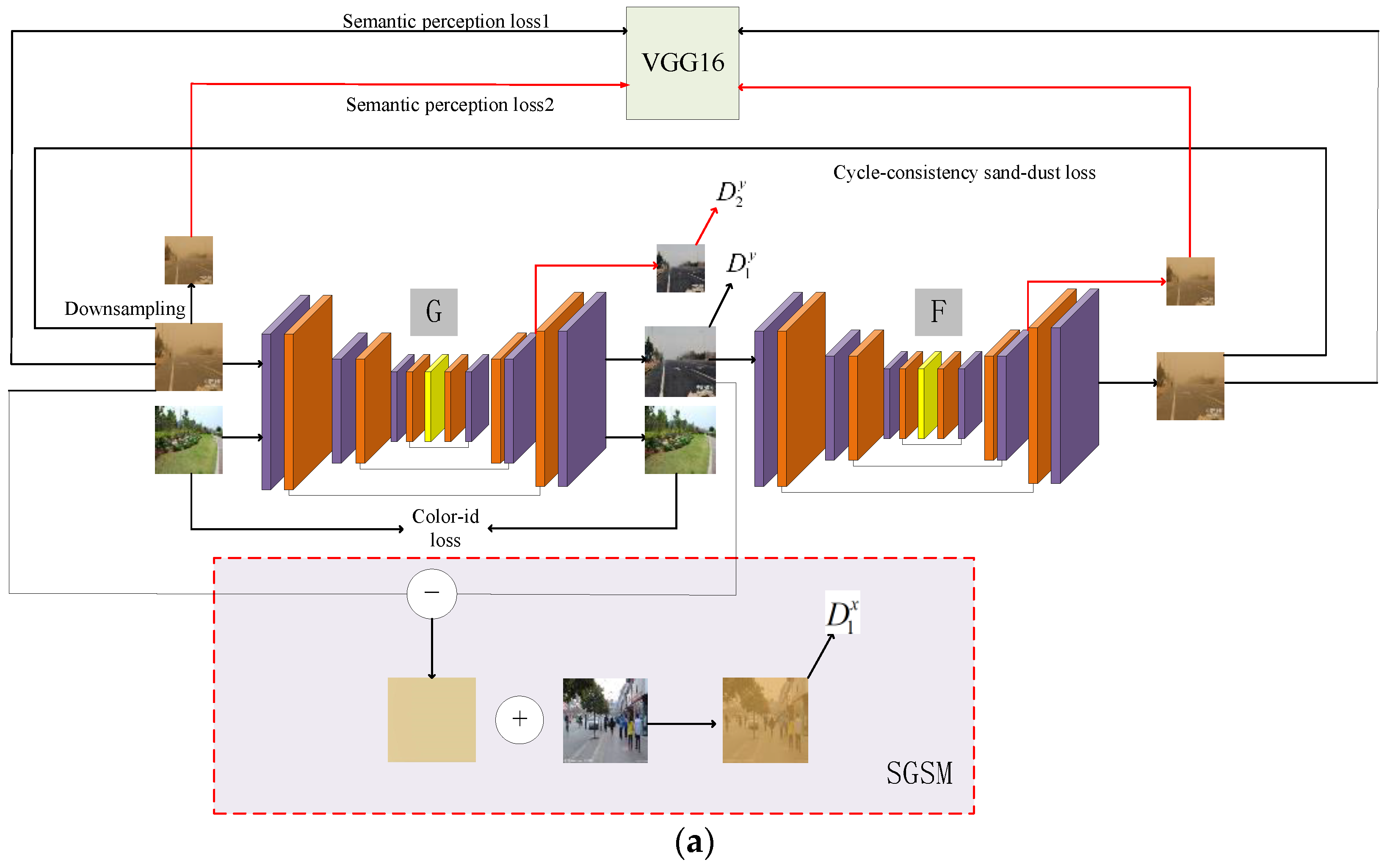
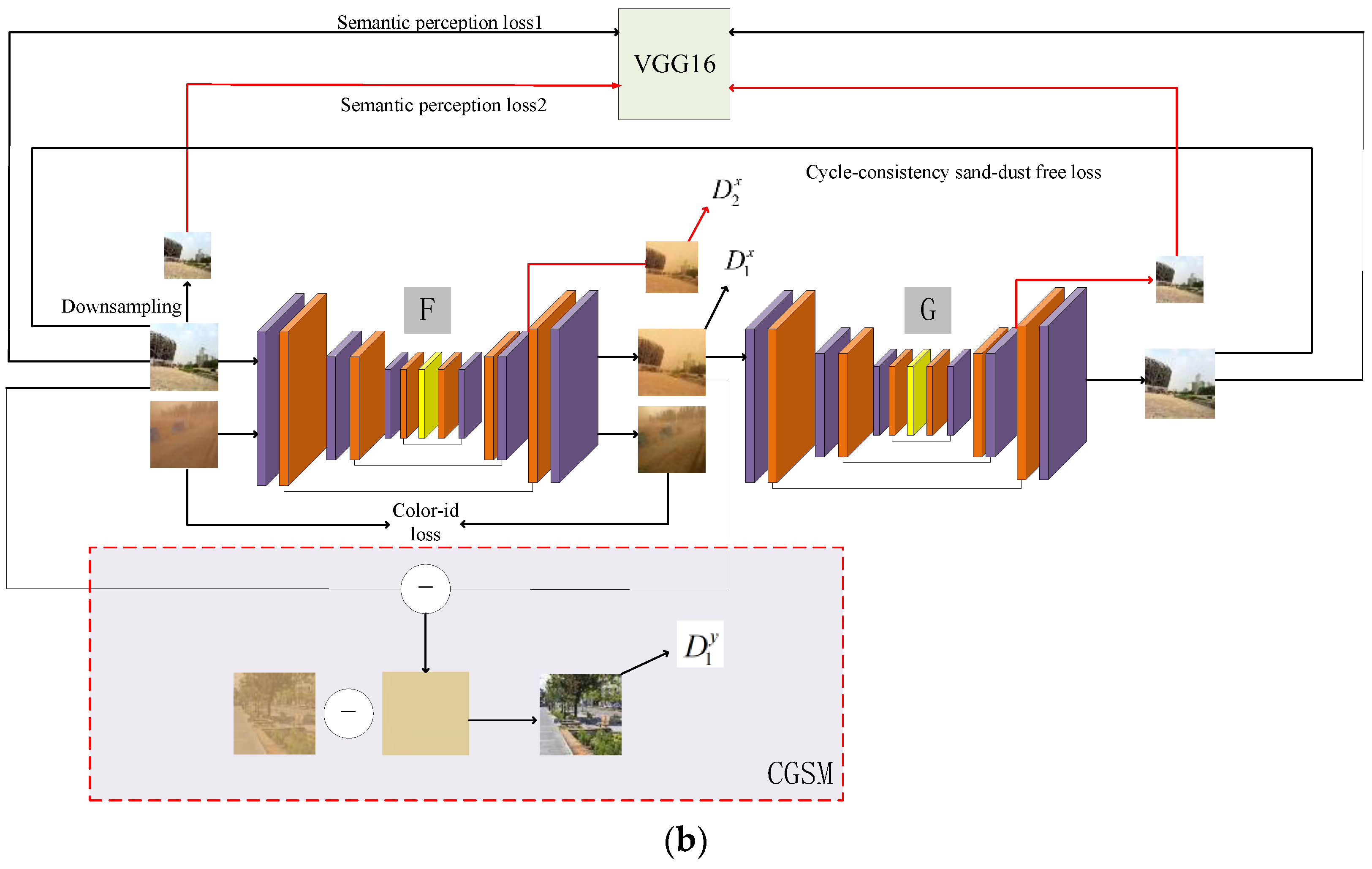
3. The Proposed Method
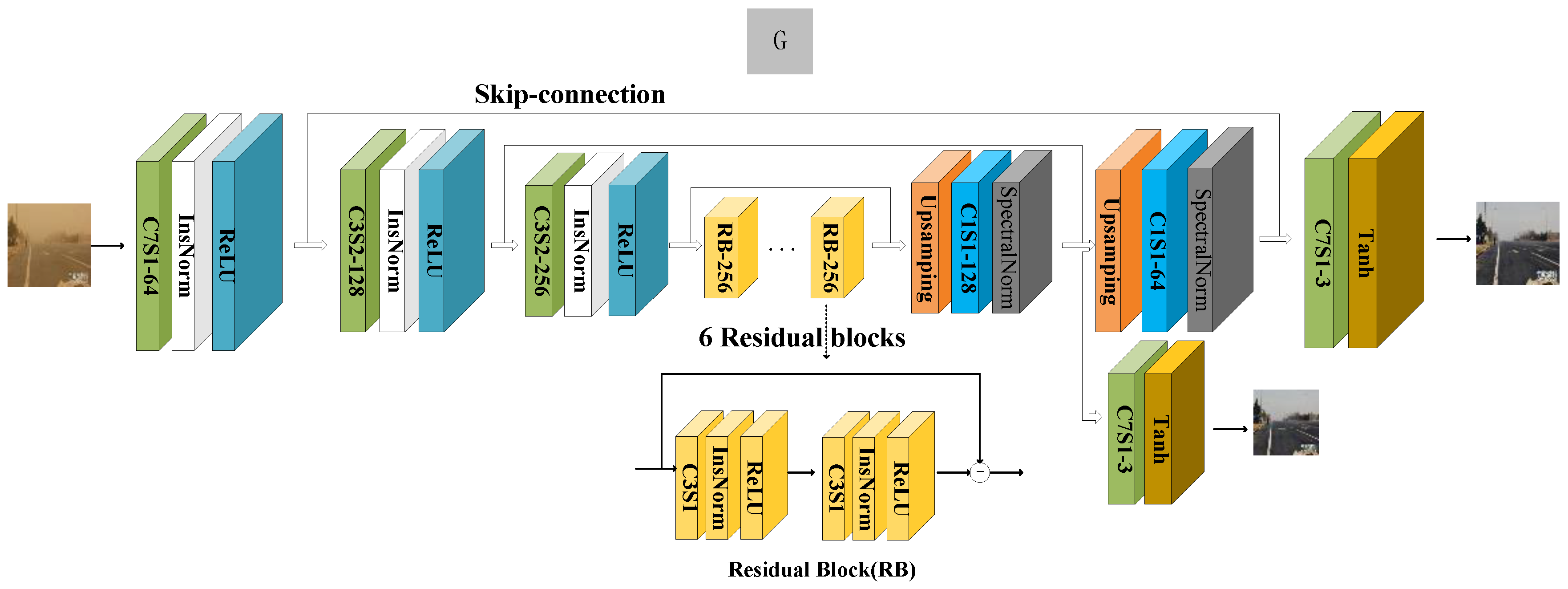
3.1. Generator
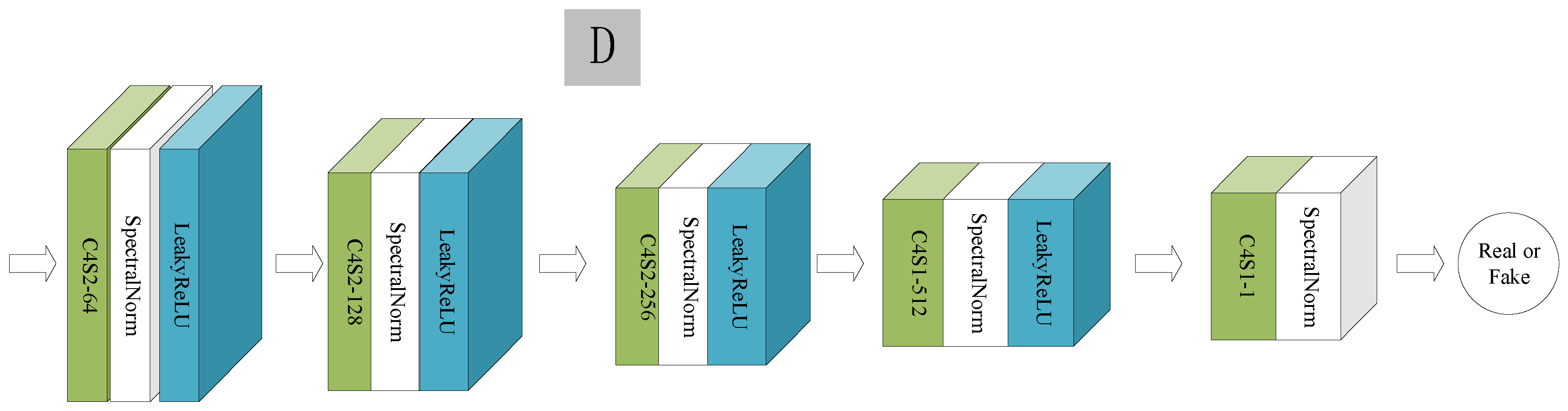
3.2. Discriminator
3.3. Joint Optimization Guidance Module
3.4. Loss Function
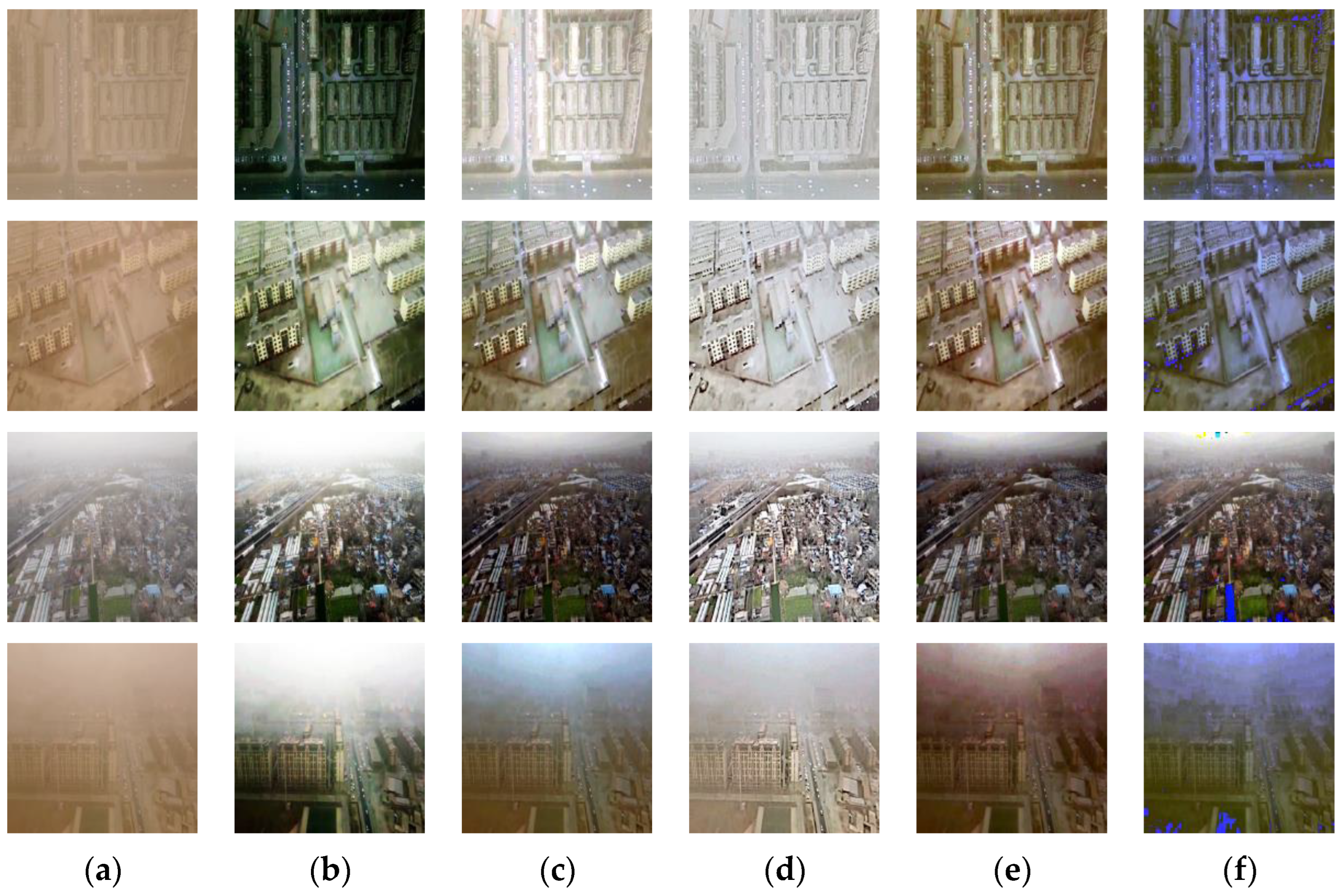
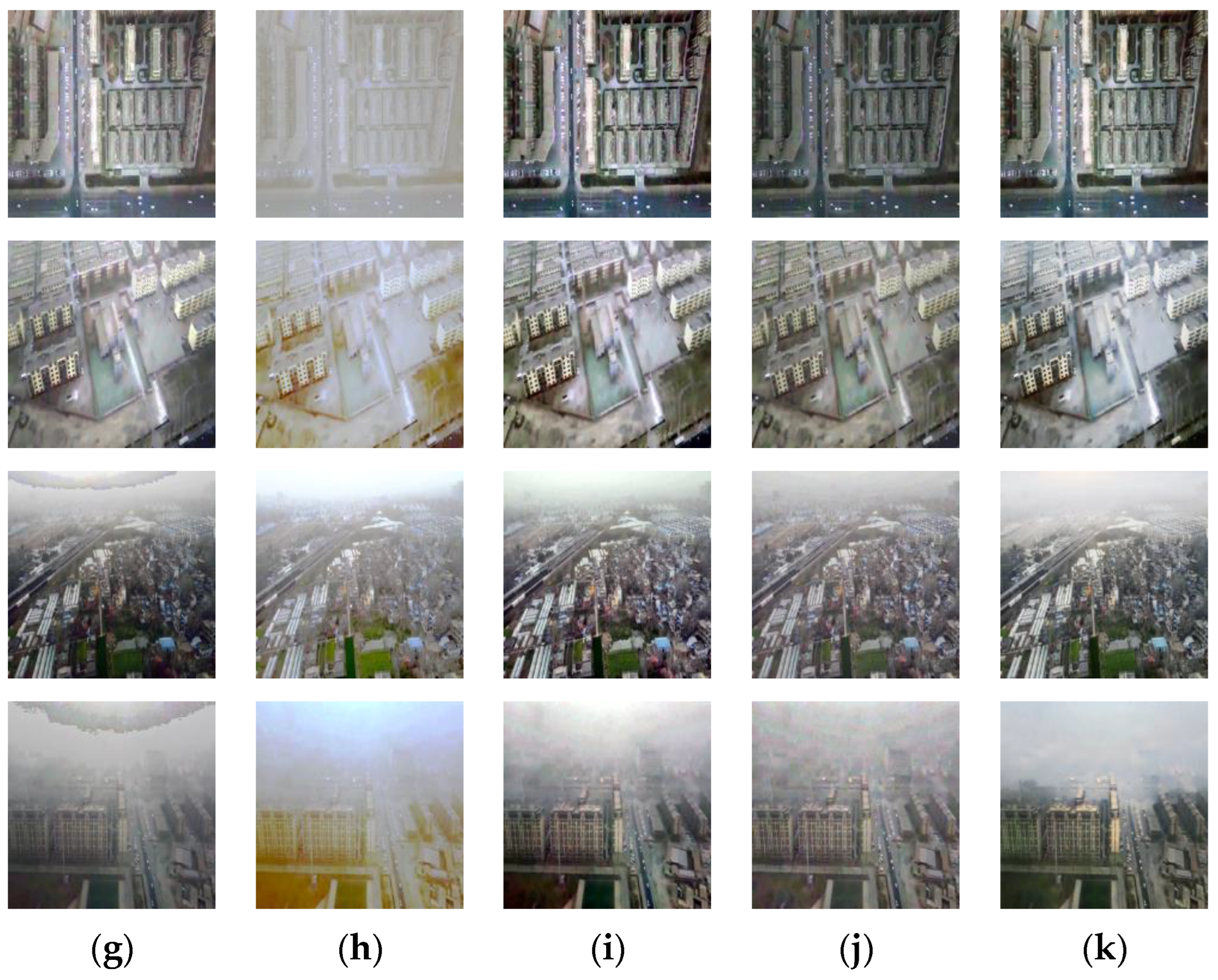
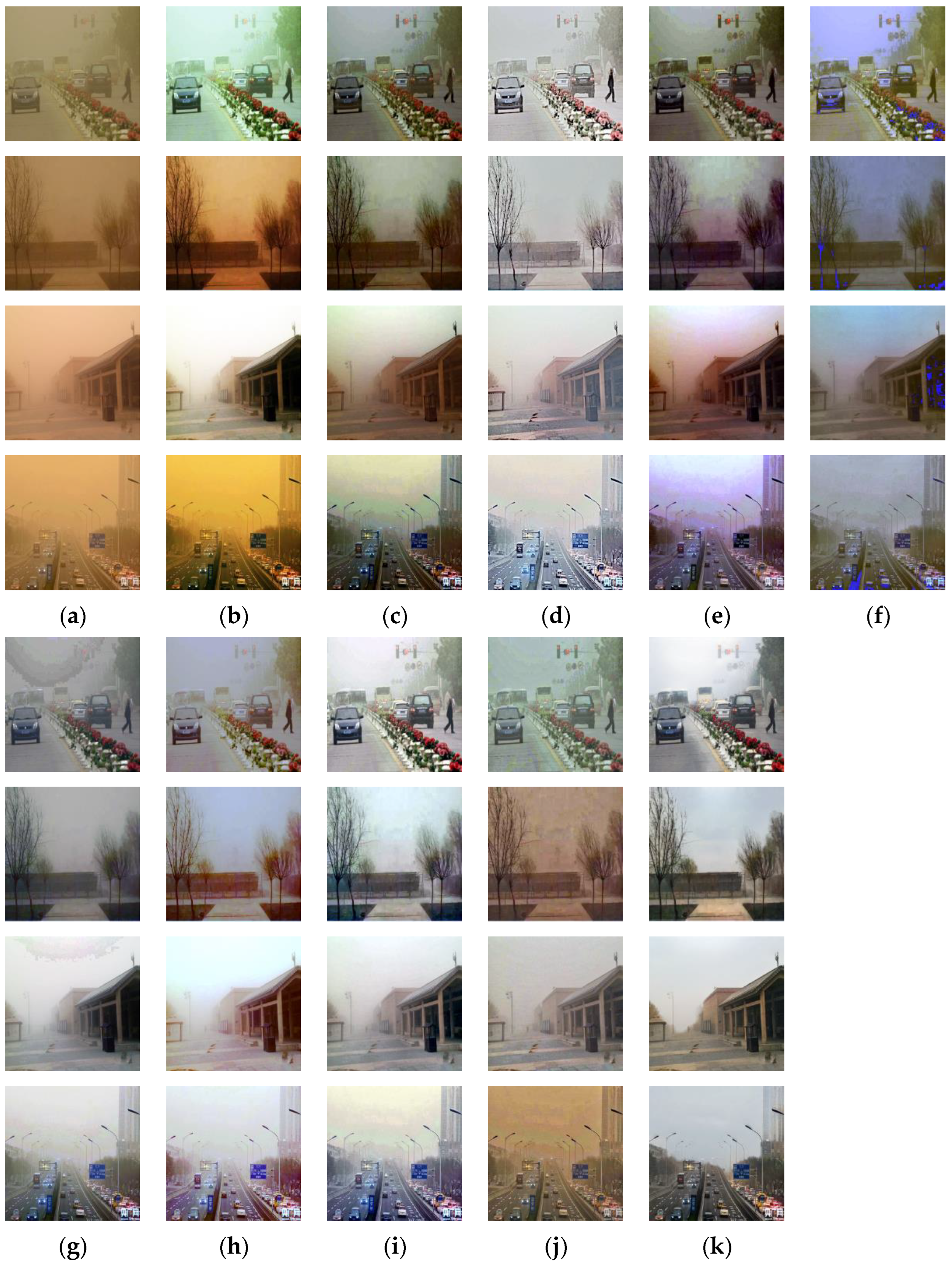
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Dataset and Application Details
4.2. Ablation Studies
4.3. Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation
4.4. Run Time
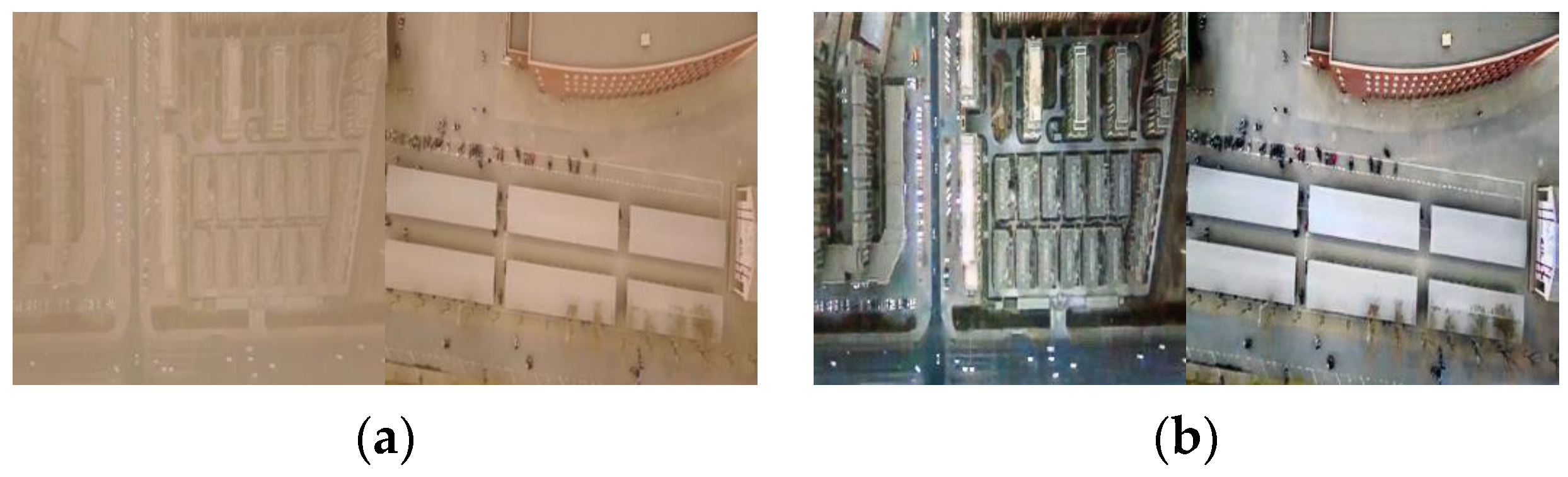
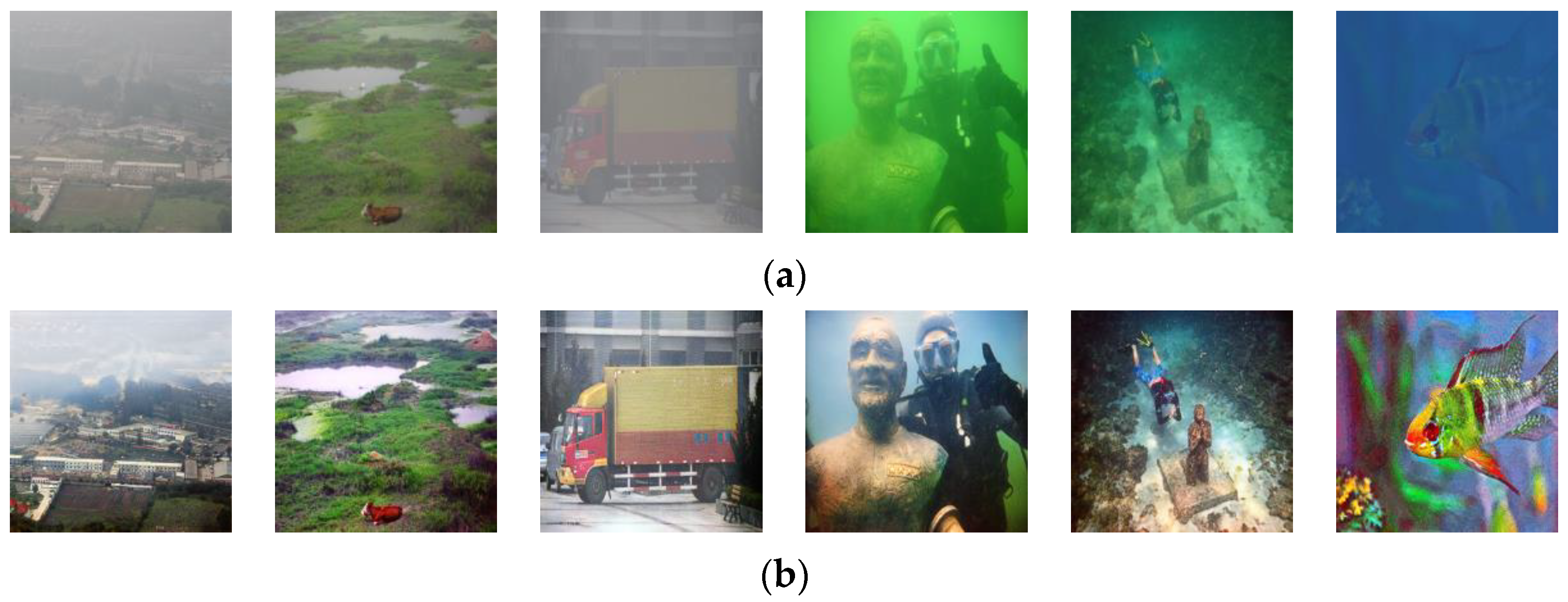
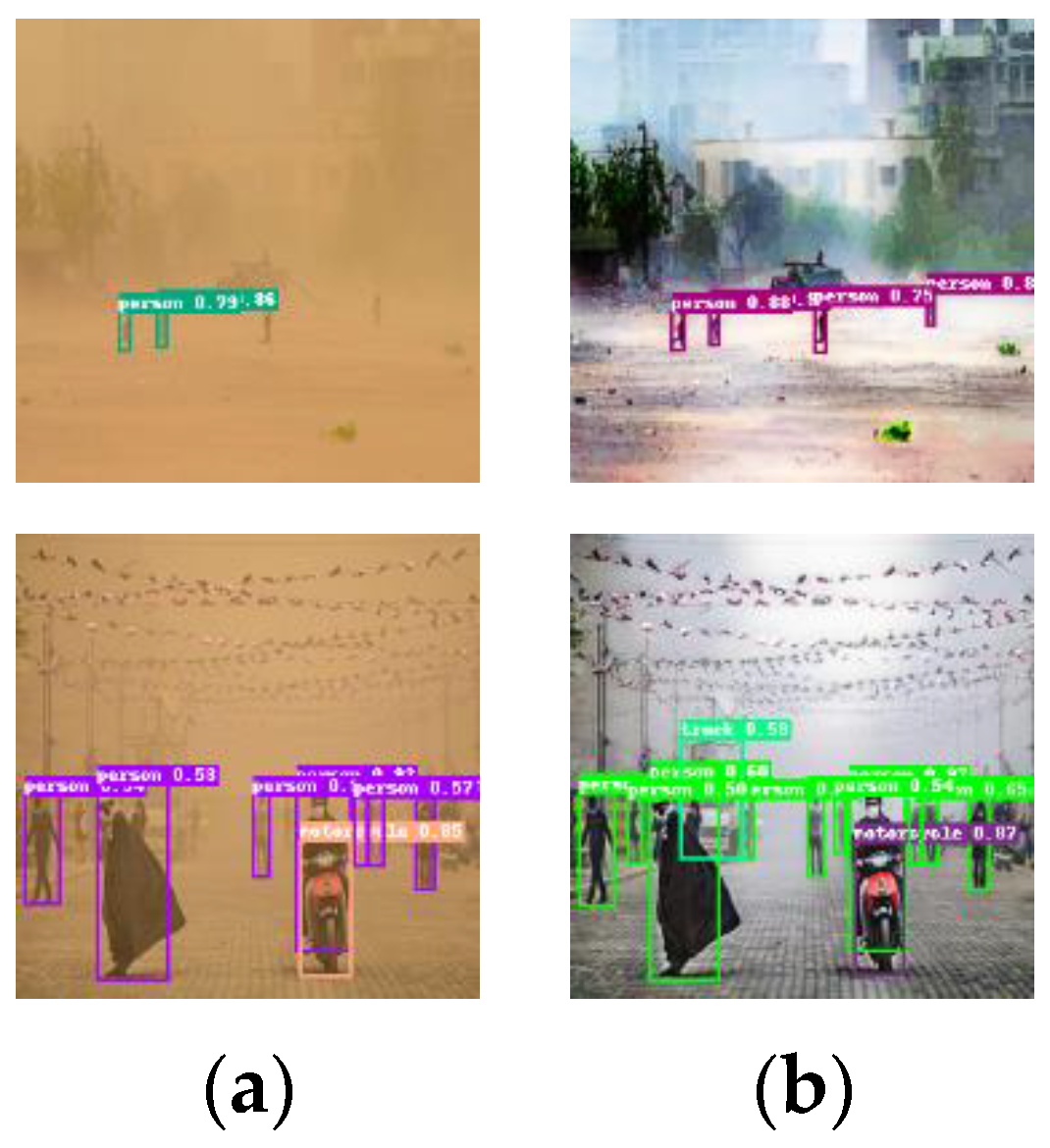
4.5. Other Applications
4.5.1. Application One: Application in Image Dehazing and Underwater Image Enhancement
4.5.2. Application Two: Application in Object Detection
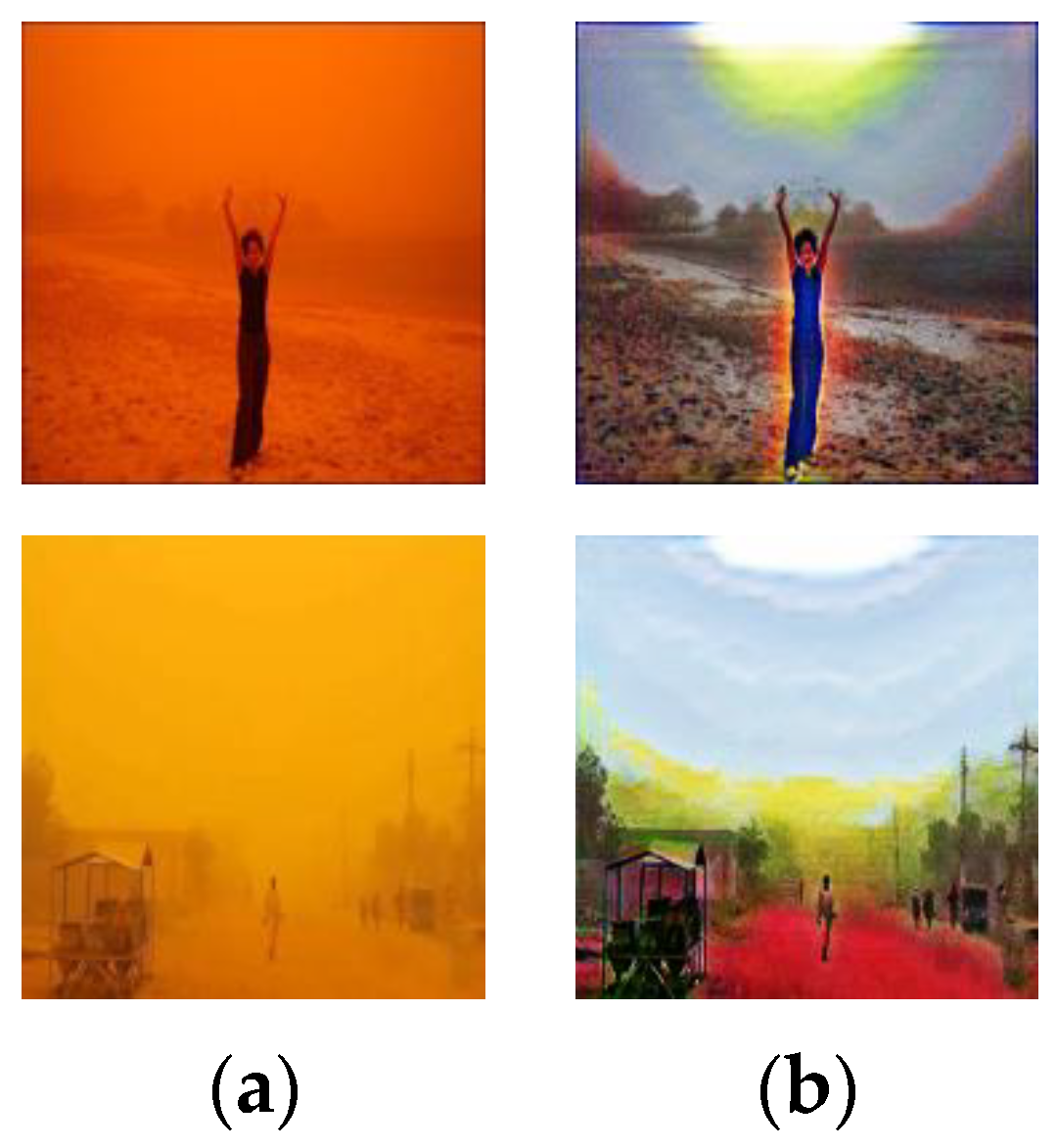
4.6. Failure Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.U.; Park, S.; Ro, Y.M. Robust small-scale pedestrian detection with cued recall via memory learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 17 October 2021; pp. 3050–3059. [Google Scholar]
- Lamssaggad, A.; Benamar, N.; Hafid, A.S.; Msahli, M. A survey on the current security landscape of intelligent transportation systems. IEEE Access. 2021, 9, 9180–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Praveen, S.; Ahamad, F. Automatic Driving System by Recognizing Road Signs Using Digital Image Processing. In Computer Vision and Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 329–339. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ameen, Z. Visibility enhancement for images captured in dusty weather via tuned tri-threshold fuzzy intensification operators. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2016, 8, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, X.; Xu, X. Single image enhancement in sandstorm weather via tensor least square. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1649–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Eom, I.K. Sand-dust image enhancement using successive color balance with coincident chromatic histogram. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 19749–19760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, G.; Yue, H. Visibility restoration of single image captured in dust and haze weather conditions. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 31, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Lai, H.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Sand-Dust Image Restoration Based on Reversing the Blue Channel Prior. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 3900216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, E.; He, L. Let You See in Sand Dust Weather: A Method Based on Halo-Reduced Dark Channel Prior Dehazing for Sand-Dust Image Enhancement. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116722–116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liang, D.; Hang, B.; Gao, H. Aerial Image Dehazing Using Reinforcement Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, T. Transformer for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 24 June 2022; pp. 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Fang, Z. Single-image deraining via a recurrent memory unit network. Knowl. Based Syst. 2021, 218, 106832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Li, Z. SIDNet: A Single Image Dedusting Network with Color Cast Correction. Signal Process. 2022, 199, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, Z.; Cao, X. FFNet: A simple image dedusting network with feature fusion. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2021, 33, e6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Far, D.; Ozai, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Jia, Z.; Lai, H.; Yang, J.; Kasabov, N.K. A fast sand-dust image enhancement algorithm by blue channel compensation and guided image filtering. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 196690–196699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wei, B.; Kang, Z.; Hu, L.; Li, C. Fast color balance and multi-path fusion for sandstorm image enhancement. Signal Image Video Process. 2021, 15, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, X.P.; Ding, X. A fusion-based enhancing approach for single sandstorm image. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 16th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Process (MMSP), Jakarta, Indonesia, 22–24 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.X.; Lai, H.C.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Jia, Z.H. Sandstorm image enhancement based on YUV space. Optik 2021, 226, 165659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single Image Haze Removal Using Dark Channel Prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.T.; Cao, K.; Cosman, P.C. Generalization of the Dark Channel Prior for Single Image Restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2856–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Park, T.H.; Eom, I.K. Fast Single Image Dehazing Using Saturation Based Transmission Map Estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, S.K.; Roy, M.; Sen, D.; Biswas, P.K. Color Cast Dependent Image Dehazing via Adaptive Airlight Refinement and Non-linear Color Balancing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartani, A.; Abdollahpouri, A.; Ramezani, M.; Tab, F.A. An adaptive optic-physic based dust removal method using optimized air-light and transfer function. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 33823–33849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Xu, X.; Jia, K.; Qing, C.; Tao, D. Dehazenet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5187–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Xie, X.; Jia, H. FFA-Net: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 11908–11915. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Xie, Y. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8160–8168. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Y.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive benchmark analysis for sand dust image reconstruction. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 89, 103638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Dong, P.; Wang, F.; Ma, P.; Bai, J.; Wang, B.; Li, C. Learning to remove sandstorm for image enhancement. Vis. Comput. 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, D.; Genç, A.; Kemal Ekenel, H. Cycle-dehaze: Enhanced cyclegan for single image dehazing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 825–833. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Luo, J. Towards perceptual image dehazing by physics-based disentanglement and adversarial training. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Hou, X.; Duan, J.; Qiu, G. End-to-end single image fog removal using enhanced cycle consistent adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7819–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osakabe, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kiya, H. CycleGAN without checkerboard artifacts for counter-forensics of fake-image detection. In International Workshop on Advanced Imaging Technology (IWAIT); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; pp. 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:180205957. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitanya, B.; Mukherjee, S. Single image dehazing using improved cycleGAN. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2021, 74, 103014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Hwang, J.N.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Huang, B. Dd-cyclegan: Unpaired image dehazing via double-discriminator cycle-consistent generative adversarial network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 82, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, X. DCA-CycleGAN: Unsupervised single image dehazing using Dark Channel Attention optimized CycleGAN. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 82, 103431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Li, Q.; Xie, H.; Lau, R.Y.K.; Wang, Z.; Paul Smolley, S. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2794–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14091556. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ren, W.; Fu, D.; Tao, D.; Feng, D.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Z. Benchmarking Single-Image Dehazing and Beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, B.; Huang, H.; Bovik, A.C. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2014, 29, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, A.K.; Bovik, A.C. A modular framework for constructing blind universal quality indices. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2009, 17, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatanath, N.; Praneeth, D.; Bh, M.C.; Channappayya, S.S.; Medasani, S.S. Blind image quality evaluation using perception based features. In Proceedings of the 2015 Twenty First National Conference on Communications (NCC), Mumbai, India, 27 February–1 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Deng, K.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Shen, H.; Ren, J.; Han, S.; Ding, E.; et al. PP-YOLO: An effective and efficient implementation of object detector. arXiv 2020, arXiv:200712099. [Google Scholar]





| SSEQ↓ | BIQI↓ | |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 14.58 | 21.06 |
| Baseline+a | 14.76 | 21.34 |
| Baseline+b | 14.04 | 19.89 |
| Baseline+a+b | 13.56 | 19.70 |
| Baseline+a+b+adv | 13.50 | 19.62 |
| Baseline+a+b+adv+ploss | 13.41 | 19.50 |
| SSEQ↓ | BIQI↓ | |
|---|---|---|
| No vgg | 14.96 | 19.60 |
| No color | 16.09 | 22.04 |
| Ours | 13.41 | 19.50 |
| SSEQ↓ | BIQI↓ | PIQUE↓ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TF | 25.24 | 22.55 | 37.94 |
| GDCP | 23.60 | 28.77 | 41.62 |
| RDCP | 15.23 | 37.11 | 37.72 |
| CC | 21.17 | 31.45 | 40.73 |
| FSS | 20.40 | 25.22 | 36.59 |
| VR | 24.56 | 31.48 | 42.38 |
| RBCP | 22.61 | 31.04 | 42.63 |
| SES | 19.83 | 24.02 | 39.02 |
| AOP | 19.85 | 31.60 | 33.94 |
| Proposed | 18.21 | 21.30 | 26.65 |
| SSEQ↓ | BIQI↓ | PIQUE↓ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TF | 20.24 | 25.34 | 41.13 |
| GDCP | 18.00 | 26.37 | 41.79 |
| RDCP | 13.32 | 27.13 | 41.12 |
| CC | 16.72 | 27.22 | 42.25 |
| FSS | 14.87 | 25.22 | 40.45 |
| VR | 18.56 | 25.47 | 41.86 |
| RBCP | 18.05 | 24.85 | 41.16 |
| SES | 14.80 | 24.20 | 40.02 |
| AOP | 15.57 | 26.03 | 36.79 |
| Proposed | 13.41 | 19.50 | 33.28 |
| Methods | Platform | Time (Seconds) |
|---|---|---|
| TF | MATLAB/CPU | 0.074 |
| GDCP | MATLAB/CPU | 0.279 |
| RDCP | MATLAB/CPU | 0.756 |
| CC | MATLAB/CPU | 0.132 |
| FSS | Python/CPU | 0.059 |
| VR | MATLAB/CPU | 0.165 |
| RBCP | MATLAB/CPU | 0.190 |
| SES | Python/CPU | 0.258 |
| AOP | MATLAB/CPU | 0.168 |
| Proposed | PyTorch/CPU | 0.424 |
| Proposed | PyTorch/GPU | 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, G.; Lai, H.; Jia, Z. Unsupervised Image Dedusting via a Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051311
Gao G, Lai H, Jia Z. Unsupervised Image Dedusting via a Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051311
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Guxue, Huicheng Lai, and Zhenhong Jia. 2023. "Unsupervised Image Dedusting via a Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051311
APA StyleGao, G., Lai, H., & Jia, Z. (2023). Unsupervised Image Dedusting via a Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051311






