Abstract
Accurate monitoring of the spatiotemporal dynamics of snow and ice is essential for under-standing and predicting the impacts of climate change on Arctic ecosystems and their feedback on global climate. Traditional optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) remote sensing still have limitations in the long-time series observation of polar regions. Although several studies have demonstrated the potential of moonlight remote sensing for mapping polar snow/ice covers, systematic evaluation on applying moonlight remote sensing to monitoring spatiotemporal dynamics of polar snow/ice covers, especially during polar night periods is highly demanded. Here we present a systematic assessment in Svalbard, Norway and using data taken from the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (SNPP) Day/Night Band (DNB) sensor to monitor the spatiotemporal dynamics of snow/ice covers during dark Arctic winters when no solar illumination available for months. We successfully revealed the spatiotemporal dynamics of snow/ice covers from 2012 to 2022 during polar night/winter periods, using the VIIRS/DNB time series data and the object-oriented Random Forests (RF) algorithm, achieving the average accuracy and kappa coefficient of 96.27% and 0.93, respectively. Our findings indicate that the polar snow/ice covers show seasonal and inter-seasonal dynamics, thus requiring more frequent observations. Our results confirm and realize the potential of moonlight remote sensing for continuous monitoring of snow/ice in the Arctic region and together with other types of remote sensing data, moonlight remote sensing will be a very useful tool for polar studies and climate change.
1. Introduction
Snow/ice cover consists of the precipitation that results from the freezing of water vapor. Due to its highly reflective properties, it is an extremely important component of the Earth’s climate system, affecting the energy balance, atmospheric and oceanic cycles, ecology, and natural resources, reflecting incoming sunlight into space, and cooling the Earth [1]. As one vital freshwater resource, the area of permanent snow/ice cover on Earth covers approximately 11.00% of the land area, and the total area covered by snow/ice is 23.00% of Earth’s surface area yearly [2,3]. However, snow/ice cover has experienced more serious melting with global warming in recent years [4,5,6,7], especially in the high-latitude Polar regions. It has been found that Arctic snow/ice is melting faster than expected [8], and one-third of the polar ice caps have been reduced since the first related studies began in 1979 [9]. Therefore, it is urgent to monitor polar snow/ice cover changes with more spatiotemporal details to analyze and predict global climate change, and assess the impacts of global climate change on polar snow/ice.
Optical remote sensing datasets are widely used for snow/ice cover detection, due to their advantages of large area coverage and low economic and labor costs [10]. Snow/ice covers often show strong seasonal and circadian fluctuation, such as dynamics of snow/ice cover duration, thickness, and areas, dry snow and wet snow, avalanches, and glacial debris [11,12,13,14,15]. Thus, monitoring it requires an increased frequency of data acquisition using remote sensing sensors. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) remote sensing imagery, with a specific snow-detecting band around 1.64 μm [16], is currently the most popular optical dataset for studying snow/ice cover and for generating global or regional snow/ice cover datasets [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24], mainly due to the shorter revisit cycle using single and double-satellite observations (Terra and Aqua). However, the quality of these products is easily influenced by cloud cover and their low applicability in forest cover regions [16,25], and these influences are more serious during nighttime and twilight periods because the satellite observations are limited to one infrared channel only, and low clouds, inversions, and shallow lapse rates are often present [26]. Although the thermal infrared band of MODIS can be used to distinguish forest and snow cover and several methods are proposed to solve the cloud gap-filling problem [25], challenges still exist in polar regions during polar winter periods because of the issue of MODIS sensor instrument switching and the lack of sunlight [27]. Due to the instrument operation being switched from daytime mode to nighttime mode as the satellite passes a terminator, an apparent discontinuity of MODIS visible and filled data passing through dark regions leads to no observations. Although the NPP/VIIRS DNB is loaded, only daytime data are currently used for snow/ice products [25,28,29]. Therefore, traditional daytime optical remote sensing is limited to solar irradiation, but the North and South Poles face long polar winters every year, resulting in obvious observation gaps.
With all-day and all-weather observation capabilities, satellite passive microwave radiometers [30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] have greater advantages for monitoring snow/ice cover in polar regions during polar winter periods. However, the coarse resolution (6.25–25.00 km) is the biggest problem with passive microwave radiometers [38,39,40]. SAR remote sensing data enable the acquisition of higher-resolution polar snow/ice images [41,42,43], and many studies have widely discussed mapping snow/ice cover using different polarized mechanisms, backscattering coefficients, and polarimetric decomposition methods of SAR remote sensing. However, the limitation of long revisit periods and limited spatial coverage make it difficult to use only SAR remote sensing data for timely data acquisition and application in polar regions [44]. SAR remote sensing data also have significant accessibility limitations due to substantial speckle noise and difficult interpretation [45]. In summary, both satellite passive microwave radiometers and SAR remote sensing also have some deficiencies in snow/ice study in the polar regions.
Recently, studies have reported that nightlight remote sensing provides a reliable tool for acquiring land surface data under low-light conditions at night [46,47,48], and it has been confirmed that moonlight can be a stable light source for the detection of non-luminous objects at night, especially snow/ice cover and forests, using nightlight remote sensing data [47]. Additionally, snow/ice cover detection from polar and mid-latitude mountains in short cycles is also obtained under moonlight illumination [49]. It is known that the Earth is one of the planets of the solar system and revolves around the Sun every 365.26 days, with an axial tilt of about 23.5 degrees. It is this “angle offset” that leads to the polar summer(day)/winter(night) period in the North and South Poles of the Earth, a phenomenon where the center of the Sun is below a free horizon in the polar circles. On the other hand, the Moon, as the only natural satellite of the Earth, travels once around the Earth every 29.5 days. Due to the moon’s unique materials and special space locations, moonlight is the periodic source of light to the Earth at night. The Moon glows as its surface reflects light from the Sun. Thereby, moonlight can periodically illuminate the polar regions during the polar winter period, as shown in Figure 1. The perceived brightness of the Moon from Earth is dependent on its orbit around the Earth, its terrain, and Sun/Moon (S/M) and Earth/Moon (E/M) distances [46], and the differences in brightness between the entire moon phases are, thus, relatively complex, causing multi-temporal moonlight remote sensing data to be difficult to process.
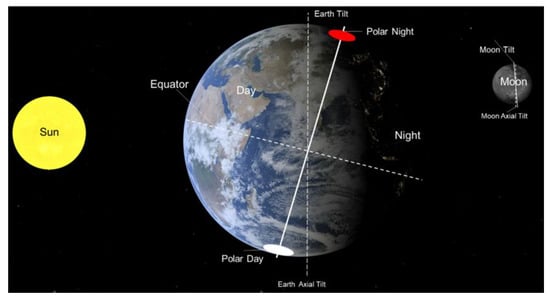
Figure 1.
Moonlight, the light source in the Arctic during the polar night period.
In summary, as a key characterization and modelling parameter for climate change, the Arctic snow/ice should be more frequently monitored to analyze and predict global climate changes. However, there is a half-year polar night period, and traditional optical and SAR remote sensing still have limitations in the long-time series observation of polar regions. Recently, although several studies have demonstrated the potential of moonlight remote sensing for mapping polar snow/ice covers, a systematic evaluation of applying moonlight remote sensing to monitoring spatiotemporal dynamics of polar snow/ice covers, especially during polar night periods when no solar illumination is available for months, is still lacking. To address the above issues, this study proposes data processing to integrate different brightness levels of long-time series moonlight remote sensing images under various lunar phases and reduce thick clouds and aurora, explores the potential of continuous moonlight for polar observation of snow/ice cover detection in the Northern Hemisphere, and maps a decade of Arctic snow/ice cover during the polar winter period (2012–2021) as a parameter for the modelling of global climate changes.
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
The study area, which covers a total of 318,141.00 km2 of land, includes Svalbard, Norway, and its surrounding seas. Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic region, located in the north of the European continent, about midway between the Norwegian mainland and the North Pole (Figure 2). The archipelago, which is north of the Arctic Research and Policy Act (ARPA) boundary area, covers a total area of 61,000 km2, of which 60.00% is glaciated and the remaining area is covered by barren rock and vegetation. The archipelago spans latitudes from 74.00° to 81.00°N and longitudes from 10.00° to 35.00°E. Due to its high latitude, the polar winter usually lasts from 84 to 128 days from October to March each year [50]. Svalbard is located within the Arctic Circle and is covered by snow/ice all year round, as well as experiencing long polar winter periods each year, making it an ideal study area. In addition, we included the surrounding marine areas around the Svalbard archipelago to explore the floating ice changes.
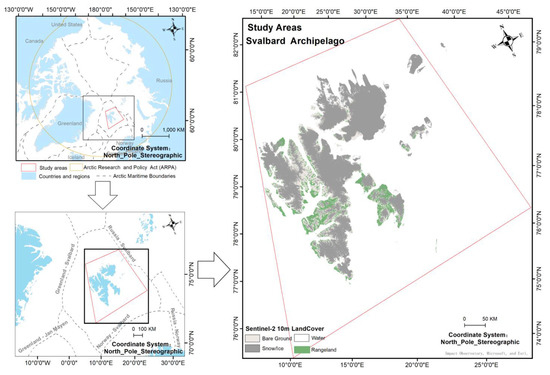
Figure 2.
Study areas in Svalbard, Arctic region.
2.2. Data
2.2.1. The VNP46A1 Nighttime Remote Sensing Dataset
The daily at-sensor top-of-atmosphere (TOA) nighttime radiance of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Black Marble product (VNP46A1) from 22 September 2012 to 21 March 2022 was retrieved from https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/missions-and-measurements/products/VNP46A1/ (accessed on 1 July 2020) (Figure 3). The VNP46A1 product is generated from nighttime light remote sensing data recorded by the DNB sensor of the VIIRS/DNB, after atmospheric, terrain, lunar bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF), thermal, and straylight effects corrections [51,52]. The VIIRS/DNB sensor is a daily, top-of-atmosphere, at-sensor nighttime radiance product called VIIRS/NPP Daily Gridded Day Night Band 15 arc-second Linear Lat Lon Grid Night [53], and the corresponding radiance unit is nW·cm−2·sr−1. Compared with the commonly used daily composite VIIRS data, the superiority of VNP46A1 lies in its improved data quality [54].
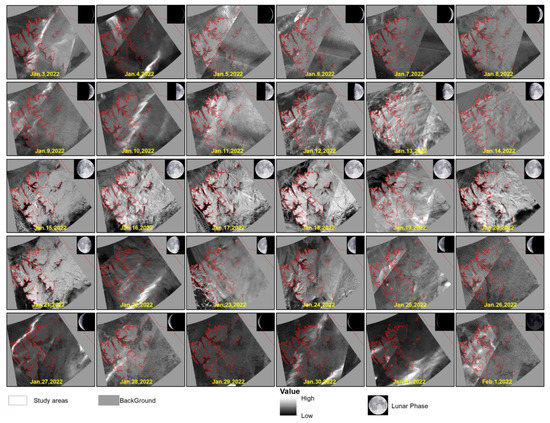
Figure 3.
Moonlight remote sensing images during lunar December 2021.
2.2.2. The Auxiliary Datasets
We used conventional snow/ice cover data as auxiliary data to evaluate our results (Table 1). (1) The VNP10A1F Snow datasets, which contain daily cloud-free snow cover produced from the VIIRS/NPP Snow Cover Daily L3 Global 375 m SIN Grid snow cover product, and are provided daily in a 375 m sinusoidal grid format from 2019 to 2020 [29]; (2) the Modis/Aqua Sea ice extent Daily L3 Global 1 km EASE-Grid Night datasets (MYD29P1N), used to capture tiles of daily 1 km resolution nighttime ice surface temperatures and quality assessment data [26]; (3) the NASA Making Earth System Data Records for Use in Research Environments (MEaSUREs) Global Record of Daily Landscape Freeze/Thaw Status, consisting of two global records of the daily freeze/thaw (F/T) status of the landscape [31]; (4) AMSR-E/AMSR3 Unified L3 Global 25 km EASE-Grid snow water equivalent (SWE) datasets, containing SWE data and quality assurance flags mapped to Northern and Southern Hemisphere 25 km equal-area scalable earth grids (EASE-Grids) [35,36]; (5) The Near-Real-Time SSM/I-SSMIS EASE-Grid Global Ice Concentration and Snow Extent datasets (NISE) [30], containing daily global maps of sea ice concentrations and snow extent; and (6) with all-day and all-weather observation capabilities, Sentinel-1 (S1) VV (single co-polarization, vertical transmit/vertical receive) images, captured by a dual-polarization C-band SAR instrument [55], used for comparison in mapping snow/ice cover during polar winter periods. We obtained the corrected images from the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform (https://developers.google.com/earthengine/datasets/catalog/COPERNICUS_S1_GRD (accessed on 3 October 2014.) [56]. Then, The Refine Lee speckle filter was employed to suppress the speckle noise [57] with a 7 × 7 sliding window and a 3 × 3 target window. A total of 702 S1 ground range detected (GRD) scenes covering the study area were taken from 2016 to 2022, with 248 scenes being acquired during the polar winter periods. Finally, the S1 mosaic images from 22 December 2019 to 21 March 2020 (astronomical “winter”, 2019) and from 21 September to 21 December 2020 (astronomical “fall”, 2020) were used to evaluate the quality of moonlight remote sensing data.

Table 1.
Auxiliary images.
3. Method
This study was mainly divided into three parts: data pre-processing, the processing of integrating moon phase difference and eliminating clouds and aurora cover, and snow/ice cover classification based on the object-oriented random forests (RF) algorithm (Figure 4).
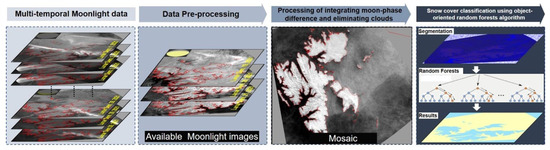
Figure 4.
Flow chart of moonlight remote sensing images for monitoring snow/ice cover.
Due to the limitations in both moon phase shifting and remote sensor minimum detection sensitivity, not all moonlight remote sensing data could be used. The data brightness value varied periodically during a full Lunar month, with the maximum brightness value under the full moon. We analyzed the entire polar winter data and found the applicable data that between the first quarter and third quarter moon, and moon altitude was over the horizon in Figure 5. Since the VIIRS/NDB data was obtained at 1:30 local time, if the moon phase angle at around 1:30 was below the horizon the data was also deleted.
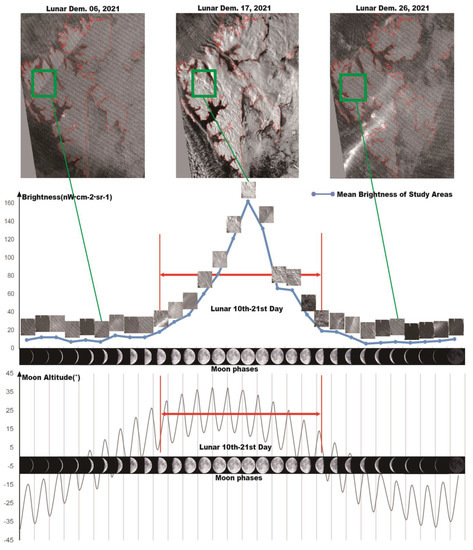
Figure 5.
The brightness values and characteristics of moonlight remote sensing data during an entire lunar month.
The first process was to reduce the brightness difference caused by moon phase shifting as well as to remove cloud cover for long-time series snow/ice extraction. It is well known that the moon has periodic changes in brightness, and orbital angle, as well as cloud and aurora effects that make moonlight remote sensing data very difficult to process. Moreover, polar regions are susceptible to clouds and often experience a large amount of aurora. In contrast to snow/ice, aurora and cloud cover tends to vary in space, thickness, and area in different images taken within a relatively short period. In this study, we fused one-month remote sensing data into a single mosaic image as shown in Figure 6, and the moonlight remote sensing images from the 10th to the 22nd day of each Lunar month were selected to make the entire Lunar month mosaic image. After overlapping different images from multiple scenes, it enhanced the difference between stable land cover and non-stationary phenomena (clouds, aurora, etc.). Such treatment allowed for generating relatively stable Arctic snow/ice cover data. As shown in Figure 3 and Figure 5, it was found that the image quality captured on the other days of each Lunar month was too poor to identify land covers, mainly because of the low brightness of moonlight, and the low sensitivity of the VIIIRS/DNB sensor. One thing to be pointed out was that the cloud and aurora effects still exist even in the one-month mosaic (Figure 6), and the satellite orbits of the sensor also made it difficult to obtain consistent data in polar regions (Figure 6). Consequently, the three-month Lunar mosaic images were used to better reduce the influences of clouds and auroras, and satellite orbit shifting as shown in Figure 7. We further divided the entire polar night period into two parts according to the difference in astronomical orbits in the northern hemisphere, i.e., astronomical “Fall” and “Winter” in the polar winter period (22 September–21 December; 22 December–21 March, respectively). Finally, a total of 20 mosaic images for the polar winter periods in 2012–2022 were obtained.
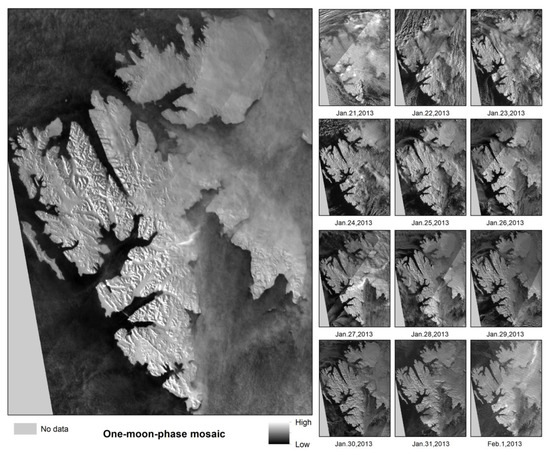

Figure 6.
One-moon-phase mosaic image and every single lunar day image (lunar 10 December–21 December 2012).
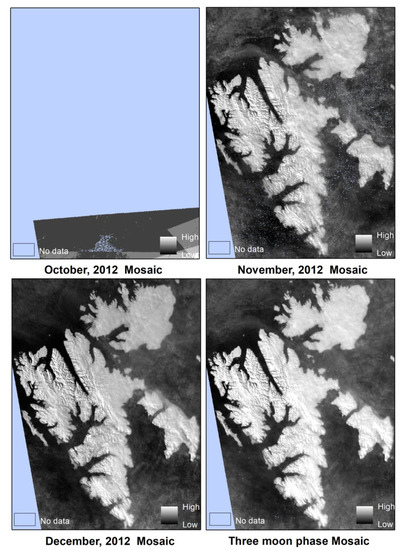

Figure 7.
Every one-moon-phase mosaic image (October–December 2012) and three-moon-phase mosaic.
Finally, we adopted an object-oriented image classification scheme, by first applying the multi-resolution segmentation algorithm on the moonlight images to delineate ground objects. The multi-resolution segmentation scale parameter greatly influences the segmentation results, and the optimal scale parameter is commonly determined using a heuristic process [58,59]. By trying different scale (10, 15, 20) parameters, we found that the optimal segmentation scales, shape, and compactness of 20 layers of moonlight remote sensing images were finally set to 15, 0.1, and 0.5 in delineating accurate land parcels and avoiding fragmental image objects, respectively.
To accurately extract snow/ice covers and analyze the characteristics of snow/ice change in different periods, we used object-oriented RF algorithms for snow/ice cover classification. RF is an ensemble learning method for classification, based on decision trees (DTs) and built randomly. These DTs are trained by randomly sampling both training samples and the components of the feature vector. Compared with SVM (support vector machines) and DT methods, RF algorithms are widely used in various studies due to their flexible and practical characteristics [60,61]. We first randomly selected 512 samples in the study area, of which 280 were snow/ice cover and 232 are others. The ratio between training samples and verification samples was 1:1.
4. Results
We extracted and mapped the snow/ice covers from 2012 to 2021 during the whole polar winter periods (both astronomical fall and winter seasons in the Northern Hemisphere) as shown in Figure 8. During the entire polar night period, we find in the astronomical fall of 2014, 2017, and 2021, snow/ice covers increased the areas by 47,145.59, 117,713.51, and 19,314.45 km2 in the astronomical winter of the previous year, respectively. And the snow/ice covering the area in 2019 is the largest in the ten years during polar night periods.
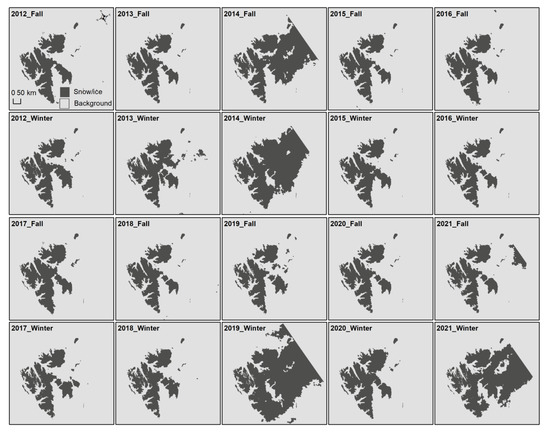

Figure 8.
Snow/ice cover maps from 2012 to 2021.
In addition, it is found that the seasonal changes in the snow/ice in the east of the Svalbard Islands are very obvious. Comparing the moonlight remote sensing images in the astronomical fall season between 2019 and 2020 proves that there is also a wide variability in the spatial distribution and timing of the snow/ice cover. There are areas of 104,130.58 km2 of floating snow/ice found in the east of the Svalbard Islands in the astronomical fall and winter of 2019 that disappeared in the next astronomical fall during the polar night periods (Figure 9).
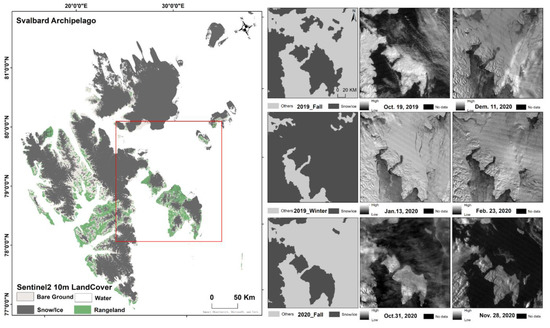
Figure 9.
Snow/ice cover change maps from fall 2019 to fall 2020.
The snow/ice cover classification accuracy is shown in Figure 10, with the highest classification accuracy being 100.00% in the fall of 2012, 2013, 2018, and 2020. The lowest classification accuracy is 79.75%, and the kappa coefficient is below 0.7 in the winter of 2019. Overall, the moonlight remote sensing images can be used to map the snow/ice cover, with a 96.27% average accuracy and a 0.93 kappa coefficient, respectively.
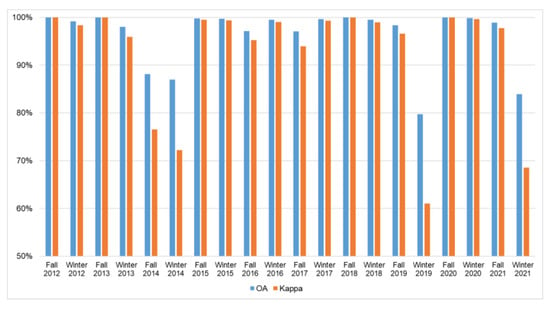
Figure 10.
Snow/ice cover classification accuracies using RF algorithm from 2012 to 2022.
The temporal change in the snow/ice cover areas is shown in Figure 11. The smallest snow/ice cover of 60,708.98 km2 occurred in the fall of 2013, with the largest area of snow/ice cover occurring in the winter of 2019, covering an area of 169,739.80 km2, and this is also the year of the greatest difference in snow/ice coverage during the autumn and winter. Overall, the snow/ice cover in winter will be larger than that in autumn. In addition, the difference between snow/ice gradually increasing throughout the year and the overall snow/ice cover for 2012–2021 shows a downward trend in fall and an upward trend in winter.
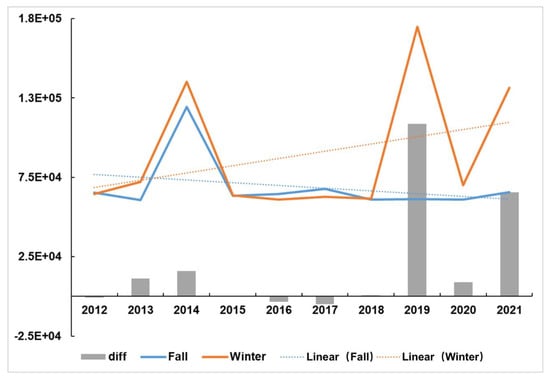
Figure 11.
Snow/ice cover areas of Svalbard, Arctic region, from 2012 to 2022.
Finally, we explored the relationship between historical temperatures (Average/MAX/MIN) and snow/ice cover areas of Svalbard, Arctic region (Figure 12). We find that the snow/ice coverage area and temperature of the Arctic have a strong correlation. R2 is equal to 0.73, 0.82, and 0.54, respectively. All curve lines on the figure show that as the temperature rose, the area of the snow/ice decreased.
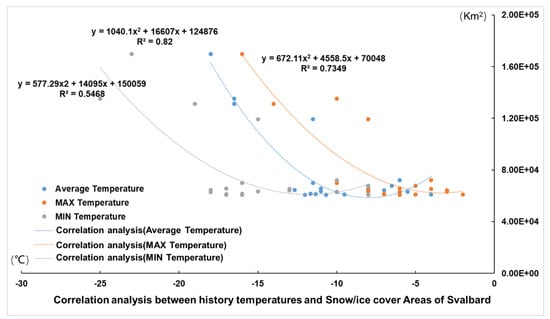
Figure 12.
Correlation analysis between historical temperatures and snow/ice cover areas of Svalbard, Arctic region.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Potential of Moonlight Remote Sensing for Monitoring Spatiotemporal Patterns of Polar Snow/Ice
Moonlight remote sensing [47] has huge potential in detecting polar snow/ice cover [48,62,63], and is first used to observe snow/ice, first demonstrated by studies using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Line-Scan System (DMSP/OLS) remote sensing [64,65]. Recently, studies with VIIRS/DNB images [49,66] and multi-spectral photos taken by astronauts from the International Space Station (ISS) [47] obtained between the first quarter and third quarter moon, and above the horizon also further confirmed that. Although our work implemented a practical framework for applying time series of moonlight remote sensing data to monitor polar snow/ice spatiotemporal dynamics during polar night periods for the first time, the application of moonlight remote sensing data in extracting snow and ice dynamics over shorter time scales has not been discussed. Additionally, with this aim, three scenes of moonlight images are used to classify the snow/ice, with accuracies over 75.00% (Table 2). However, we find that cloud cover is a major limitation for using moonlight remote sensing to extract the intra-month dynamics of snow cover (Figure 13).

Table 2.
The classification accuracy of the 31 October, 6 November, and 28 November 2020 moonlight images.
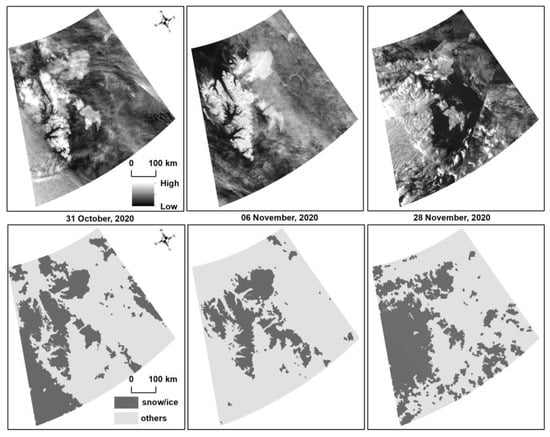
Figure 13.
The potential of moonlight remote sensing for monitoring intra-month polar snow/ice changes.
5.2. Comparison with Other Snow/Ice Products
In this study, we have discussed the difference between moonlight remote sensing images and other types of optical remote sensing images (Figure 14). Compared with moonlight remote sensing images, the availability of VNP10A1F data is limited [29]. There are only 30 scenes imaged during the polar night period from 2019 to 2020, and the dataset acquisition dates are 23 September 2019–6 October, 9 March 2020–21 March 2020, and 24 September 2020–6 October 2020, respectively. Furthermore, the available images were obtained at the beginning or the end of the polar night period, or under sunlight conditions over the Svalbard archipelago. Therefore, these VNP10A1F data cannot be applied to the entire extreme night period, especially under a faint light environment. On the other hand, although the MDY29P1N [26] dataset has a large amount of data during the polar night period, the spatiotemporal quality of the products is relatively poor, and they cannot be used for snow/ice monitoring, especially in Svalbard’s surrounding seas.

Figure 14.
VNP46A1 moonlight images, and VNP10A1F and MDY29P1N optical remote sensing snow/ice products during 2019–2020.
Compared with satellite passive microwave radiometer data, moonlight remote sensing images have great potential for monitoring winter polar snow/ice cover. Microwave radiometer remote sensing, with a passive sensor, can capture snow/ice images under all-day and all-weather conditions (Figure 15) (MEaSUREs [31], AMSR_U2_L3 [35,36], NISE_SSMISF18 [30]). However, the spatial and radiometric resolution of these sensors are their main drawbacks. Despite being susceptible to clouds and fog, the short revisit period of moonlight remote sensing makes it possible to obtain more land cover images and, thus, obtain more useful data for short-period land cover detection.
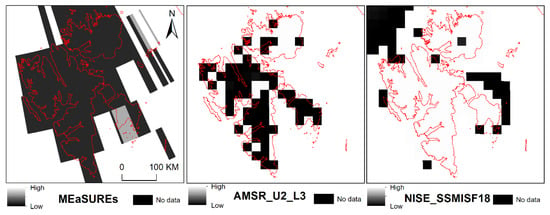
Figure 15.
Passive microwave radiometer remote sensing images (MEaSUREs, AMSR_U2_L3, NISE_SSMISF18).
Finally, the moonlight remote sensing results were validated in combination with the 2020 SAR mosaic images [44,55] as shown in Figure 16. The results during the fall of 2020 demonstrate that moonlight remote sensing datasets are more available during the polar winter period due to the shorter revisit period, thus making it possible to obtain data for polar snow/ice areas. Moonlight remote sensing data have advantages in the number of available images despite the influence of clouds, sensor orbits, and different lunar months. Moonlight remote sensing datasets are more useful to monitor short-period ice changes in polar ice areas during the polar winter period. Compared with the moonlight remote sensing data, SAR images have a higher resolution and the ability to penetrate and identify land surfaces, and the SAR data provide good access to the perennial ice cover on mountain ridges during the winter of 2019. However, the SAR mosaic cannot cover the entire research area in 2020 due to limited swath width and less frequent data acquisition. Thereby, moonlight remote sensing data provide more diverse data support for multi-source remote sensing data to enable the extraction of polar snow/ice data in the future.
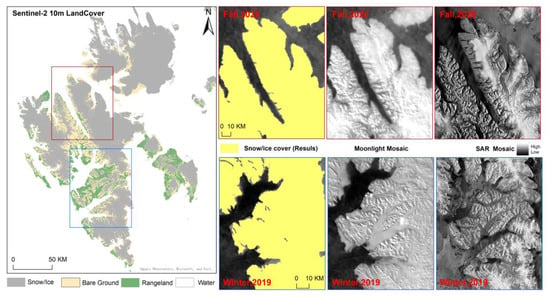
Figure 16.
Comparison of snow/ice cover classification using moonlight and Sentinel-1 SAR mosaic images in 2019 and 2020.
5.3. Limitations and Future Works
Researchers are trying to quantitatively process nightlight remote sensing data, especially VIIRS/DNB nightlight remote sensing data. Although VNP46A1 products [52,53] are produced with cloud-free, atmospheric-, terrain-, vegetation- and stray light-corrected radiances, there are still clouds and aurora cover in the study data. To deal with this issue, we have fused three lunar month datasets into one composite image to reduce the variability of data between different lunar months. Consequently, the three-month lunar mosaic images are used to better reduce the influences of clouds, aurora, temporal moonlight brightness differences, and satellite orbit shifting. However, as a lot of moonlight remote sensing images are fused, it is difficult to achieve the extraction of non-stationary snow/ice cover in a short duration with this method, so there are some drawbacks in our exploration of the intra-month snow/ice cover changes, and it is also difficult to distinguish clouds and snow/ice cover. Additionally, a more effective moonlight radiative transfer quantitative model [47,67] to deal with moonlight illumination variation is imperative to accurately retrieve land surface reflectance. We will focus on these key issues in the future.
On the other hand, what must be pointed out here is that currently only mono-spectral moonlight remote sensing data are publicly available, which limits information on snow/ice that can be retrieved. Additionally, another limitation is that only 10 years of moonlight remote sensing data are analyzed for the evolution of global climate changes. Timely satellite observations on the spatiotemporal dynamics of Arctic snow/ice covers, especially related information from moonlight remote sensing during the polar night, is otherwise very hard to obtain. Luckily, with more and more multiple-spectral satellite moonlight sensors, Jilin-1, Qimingxing-1(QMX-1), and SDGSAT-1 [68,69,70,71,72], launched into orbit, we expect richer information on arctic snow/ice to be obtained shortly. Additionally, we also believe that these problems may be better addressed by cloud screening in every single multiple-spectral moonlight remote sensing image. Furthermore, it is necessary to integrate multiple sources of remote sensing data, such as optical, satellite passive microwave radiometers, SAR, moonlight, and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) remote sensing [63,73] and geographic information science (GIS) products for accurately evaluating and simulating the potential impacts of climate change on snow/ice cover areas [74].
In addition, rapid sea ice retreat in the Arctic Ocean attracted more and more attention in the search for new opportunities for the navigation of commercial and scientific ships through the Arctic routes, which can significantly reduce shipping distances from Asia to Europe to save both time and shipping costs [75]. The increase in shipping activities in the Arctic, however, requires great efforts in improving the reliability of sea ice forecasts [76]. We expect that moonlight remote sensing can make contributions to such applications.
6. Conclusions
Arctic snow/ice covers show diurnal variation and their formation during polar winter periods is a very dynamic process. Here we proposed a practical framework to monitor Arctic winter snow/ice covers with moonlight remote sensing time series data collected from VIIRS/DNB observations. The seasonal and inter-seasonal dynamics of polar snow/ice covers are found during polar night periods. The smallest snow/ice cover of 60,708.98 km2 occurred in the fall of 2013, with the largest area of snow/ice cover occurring in the winter of 2019, covering an area of 169,739.80 km2. And there are areas of 104130.58 km2 floating snow/ice found in the east of the Svalbard Islands in the astronomical and winter of 2019 and disappeared in the next astronomical fall during the polar night periods. In addition, the difference between snow/ice gradually increasing throughout the year and the overall snow/ice cover for 2012–2021 shows a downward trend in fall and an upward trend in winter. We find this difference and temperature in Svalbard has a strong correlation, the highest R2 equals 82.00%. Thereby, there is an urgent need for continuous monitoring of them to improve climate models’ prediction accuracy and the assessment of climate change’s effect on them.
Our evaluation results on applying time series of moonlight remote sensing data to monitor polar snow/ice covers further confirm that moonlight remote sensing together with other types of remote sensing data can be very useful tools for polar study. We encourage efforts in the future to take full advantages of multisource remote sensing for polar studies, and future efforts should pay more attention to develop new generation of low light sensors to take full advantages of moonlight as a new and important type of satellite remote sensing illumination source besides sunlight and microwaves.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L. and Q.Z.; methodology, D.L., Y.S., Y.W. and Z.M.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L., Q.Z. and Y.W.; writing—review and editing, D.L., Y.W., Y.S., Z.W., Z.M. and Q.Z.; supervision, Q.Z.; project administration, Q.Z.; funding acquisition, Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFE0209300), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (No. ZDSYS20210623091808026), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Project (No. JSGG20191129145212206) and supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program, No. 42071351), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2020YFA0608501).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank reviewers and the editor for their constructive comments and suggestions, and also thank the VIIRS Land Science Investigator-led Processing System (VNP46A1), European Space Agency (Sentinel-1), VNP10A1F, MYD29P1N MEaSUREs, AMSR_U2_L3, NISE_SSMISF18, Sentinel-1, and ESRI (Sentinel-2 10m Land cover) for providing data support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rumpf, S.B.; Gravey, M.; Brönnimann, O.; Luoto, M.; Cianfrani, C.; Mariethoz, G.; Guisan, A. From white to green: Snow cover loss and increased vegetation productivity in the European Alps. Science 2022, 376, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.A.; Dewey, K.F.; Heim, R.R., Jr. Global Snow Cover Monitoring: An Update. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.D.; Robinson, D.A. Northern Hemisphere spring snow cover variability and change over 1922–2010 including an assessment of uncertainty. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eythorsson, D.; Gardarsson, S.M.; Ahmad, S.K.; Hossain, F.; Nijssen, B. Arctic climate and snow cover trends—Comparing Global Circulation Models with remote sensing observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 80, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppä, J. Characterizing ecosystem phenological diversity and its macroecology with snow cover phenology. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khani, H.M.; Kinnard, C.; Lévesque, E. Historical Trends and Projections of Snow Cover over the High Arctic: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Holland, M.M.; Meier, W.; Scambos, T.; Serreze, M. Arctic Sea ice decline: Faster than forecast. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comiso, J.C. Large Decadal Decline of the Arctic Multiyear Ice Cover. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Du, P.; Xia, J.; Tang, P.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal changes of glacier and seasonal snow fluctuations over the Namcha Barwa–Gyala Peri massif using object-based classification from Landsat time series. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 177, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, E.H.; Stillinger, T.; Dozier, J. Snow Property Inversion from Remote Sensing (SPIReS): A Generalized Multispectral Unmixing Approach with Examples from MODIS and Landsat 8 OLI. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 7270–7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, M.; Musselman, K.N.; Essery, R.L.H. Data Assimilation Improves Estimates of Climate-Sensitive Seasonal Snow. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2020, 6, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, L. Evaluation of snow depth and snow cover represented by multiple datasets over the Tianshan Mountains: Remote sensing, reanalysis, and simulation. Int. J. Clim. 2021, 42, 4223–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Liu, T.; Li, T.; Yue, L.; Shi, X.; Zhang, L. Estimating snow depth by combining satellite data and ground-based observations over Alaska: A deep learning approach. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Geldsetzer, T.; Yackel, J. Snow thickness estimation on first-year sea ice using microwave and optical remote sensing with melt modelling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, X.; Ji, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X. Development and validation of a new MODIS snow-cover-extent product over China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, A.; Lüdtke, S.; Unger-Shayesteh, K.; Vorogushyn, S.; Schöne, T.; Schmidt, S.; Kalashnikova, O.; Merz, B. MODSNOW-Tool: An operational tool for daily snow cover monitoring using MODIS data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascoin, S.; Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Jarlan, L.; Dejoux, J.-F.; Szczypta, C.; Marti, R.; Sánchez, R. A snow cover climatology for the Pyrenees from MODIS snow products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2337–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; O’Leary, D.S.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Miller, W.; Kang, D.H. The role of declining snow cover in the desiccation of the Great Salt Lake, Utah, using MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jing, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The recent developments in cloud removal approaches of MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2401–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Zaphu, V.V.; Monica, N.; Bhadra, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Accuracy Assessment of MODIS Fractional Snow Cover Product for Eastern Himalayan Catchment. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Chen, G.; Saruta, K.; Terata, Y. Snow cover detection based on two-dimensional scatter plots from MODIS imagery data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 096083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Che, H.-Z.; Tan, S.-C.; Shi, G.-Y.; Yao, X.-P.; Zhao, H.-J. Improvement of snow/haze confusion data gaps in MODIS Dark Target aerosol retrievals in East China. Atmospheric Res. 2020, 245, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Radeloff, V.C.; Ives, A.R. Characterizing global patterns of frozen ground with and without snow cover using microwave and MODIS satellite data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Román, M.O. MODIS cloud-gap filled snow-cover products: Advantages and uncertainties. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss 2019, 123, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Trepte, Q.; Minnis, P.; Arduini, R.F. Daytime and nighttime polar cloud and snow identification using MODIS data. In Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere and Clouds III; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 4891, pp. 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Kelly, R.E.J.; Riggs, G.A.; Chang, A.T.C.; Foster, J.L. Assessment of the relative accuracy of hemispheric-scale snow-cover maps. Ann. Glaciol. 2002, 34, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.; Hall, D. Continuity of MODIS and VIIRS Snow Cover Extent Data Products for Development of an Earth Science Data Record. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K. NASA S-NPP VIIRS Snow Cover Products Collection 2 User Guide; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brodzik, M.J.; Stewart, J.S. Near-Real-Time SSM/I-SSMIS EASE-Grid Daily Global Ice Concentration and Snow Extent, Version 5; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kimball, J.S.; Glassy, J.; McDonald, K.C. MEaSUREs Polar EASE-Grid 2.0 Daily 6 km Land Freeze/Thaw Status from AMSR-E and AMSR2, Version 2; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Metsämäki, S.; Böttcher, K.; Pulliainen, J.; Luojus, K.; Cohen, J.; Takala, M.; Mattila, O.-P.; Schwaizer, G.; Derksen, C.; Koponen, S. The accuracy of snow melt-off day derived from optical and microwave radiometer data—A study for Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ke, C.-Q.; Li, H. Snow depth product over Antarctic Sea ice from 2002 to 2020 using multisource passive mi-crowave radiometers. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, M.; Jeyaratnam, J. A new operational snow retrieval algorithm applied to historical AMSR-E brightness tem-peratures. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Cui, H.; Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Su, X. Evaluation and analysis of SMAP, AMSR2 and MEaSUREs freeze/thaw products in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, M.; Liang, T. AMSR2 snow depth downscaling algorithm based on a multifactor approach over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, X.; Shao, W.; Li, X. Support vector regression snow-depth retrieval algorithm using passive microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Yin, X. Quantitative Measurement of Radio Frequency Interference for SMOS Mission. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Variability and Uncertainty of Satellite Sea Surface Salinity in the Subpolar North Atlantic (2010–2019). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ji, Q.; Pang, X.; Su, J.; Liu, C. Comparison of passive microwave remote-sensing snow-depth products on Arctic Sea ice. Polar Res. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Z. Seasonal snow cover classification based on SAR imagery and topographic data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 13, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makynen, M.P.; Cheng, B.; Simila, M.H.; Vihma, T.; Hallikainen, M.T. Comparisons between SAR backscattering coef-ficient and results of a thermodynamic snow/ice model for the Baltic Sea land-fast sea ice. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; D’Alessandro, M.M.; Tebaldini, S.; Liao, M. Signal Processing Options for High Resolution SAR Tomography of Natural Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-L.S.; Dietz, A.; Oppelt, N.; Kuenzer, C. Remote Sensing of Snow Cover Using Spaceborne SAR: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Jeong, J. Speckle Noise Reduction Technique for SAR Images Using Statistical Characteristics of Speckle Noise and Discrete Wavelet Transform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Turner, R.E. A dynamic lunar spectral irradiance data set for NPOESS/VIIRS day/night band nighttime en-vironmental applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2316–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Shuai, Y. The Potential of Moonlight Remote Sensing: A Systematic Assessment with Multi-Source Nightlight Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W., III; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the capabilities of the suomi national polar-orbiting partnership (NPP) visible infrared imaging radiometer suite (VIIRS) day/night band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, Z.; Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Liu, H.; Che, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Shu, S.; Peng, X.; et al. Snow cover detection in mid-latitude mountainous and polar regions using nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 268, 112766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, H.; Malnes, E.; van Pelt, W.; Pohjola, V.; Killie, M.; Saloranta, T.; Karlsen, S. A Compilation of Snow Cover Datasets for Svalbard: A Multi-Sensor, Multi-Model Study. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Román, M.; Kalb, V. Continuous Monitoring of Nighttime Light Changes Based on Daily NASA’s Black Marble Product Suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Román, M.O.; Kalb, V.L.; Miller, S.D.; Zhang, J.; Shrestha, R.M. Quantifying uncertainties in nighttime light retrievals from Suomi-NPP and NOAA-20 VIIRS Day/Night Band data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Kalb, V.; Miller, S.D.; Molthan, A.; Masuoka, E.J. NASA’s Black Marble nighttime lights product suite. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 113–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Weng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, B. Impact of temporal compositing on nighttime light data and its applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 274, 113016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutanga, O.; Kumar, L. Google earth engine applications. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yommy, A.S.; Liu, R.; Wu, S. SAR image despeckling using refined Lee filter. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, Hangzhou, China, 26–27 August 2015; Volume 2, pp. 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Bhadauria, H.S. Object based information extraction from high resolution satellite imagery using eCognition. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues 2014, 11, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Happ, P.N.; Ferreira, R.S.; Bentes, C.; Costa GA, O.P.; Feitosa, R.Q. Multiresolution segmentation: A parallel approach for high resolution image segmentation in multicore architectures. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, C7. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Samat, A.; Waske, B.; Liu, S.; Li, Z. Random Forest and Rotation Forest for fully polarized SAR image classification using polarimetric and spatial features. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Yeh, A.G.-O.; Wang, J. Investigation of the capability of multitemporal RADARSAT-2 fully polarimetric SAR images for land cover classification: A case of Panyu, Guangdong province. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 54, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.D.; Combs, C.L.; Kidder, S.Q.; Lee, T.F. Assessing Moonlight Availability for Nighttime Environmental Ap-plications by Low-Light Visible Polar-Orbiting Satellite Sensors. J. Atmos. Ocean Technol. 2012, 29, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collados-Lara, A.-J.; Pardo-Igúzquiza, E.; Pulido-Velazquez, D. A distributed cellular automata model to simulate potential future impacts of climate change on snow cover area. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 124, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.L. Night-time observations of snow using visible imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1983, 4, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.L.; Hall, D.K. Observations of snow and ice features during the polar winter using moonlight as a source of illu-mination. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopic, R.; Dias, E. Examining Thresholding and Factors Impacting Snow Cover Detection Using Nighttime Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinman, J.A.; Masutani, M. Radiative transfer models of the appearance of city lights obscured by clouds observed in nocturnal satellite images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1987, 92, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, L. A low-light radiative transfer model for satellite obser-vations of moonlight and earth surface light at night. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Ra. 2020, 247, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barentine, J.C.; Walczak, K.; Gyuk, G.; Tarr, C.; Longcore, T. A Case for a New Satellite Mission for Remote Sensing of Night Lights. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guk, E.; Levin, N. Analyzing spatial variability in night-time lights using a high spatial resolution color Jilin-1 im-age—Je-rusalem as a case study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SDGSAT-1. Available online: http://www.cbas.ac.cn/kypt/casearthxwx/ (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Qimingxing-1(QMX-1). Available online: https://qmx.whu.edu.cn/ (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- Li, X.; Levin, N.; Xie, J.; Li, D. Monitoring hourly night-time light by an unmanned aerial vehicle and its implications to satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Igúzquiza, E.; Collados-Lara, A.J.; Pulido-Velazquez, D. Estimation of the spatiotemporal dynamics of snow cover area by using cellular automata models. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Liang, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zheng, F. Arctic Ice Ocean Prediction System: Evaluating sea-ice forecasts during Xuelong’s first trans-Arctic Passage in summer 2017. J. Glaciol. 2019, 65, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Gordon, N.D.; Bauer, P.; Bromwich, D.H.; Chevallier, M.; Day, J.J.; Dawson, J.; Doblas-Reyes, F.; Fairall, C.; Goessling, H.; et al. Advancing Polar Prediction Capabilities on Daily to Seasonal Time Scales. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1631–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).