Interpretation of Latent Codes in InfoGAN with SAR Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background Knowledge and Motivation
2.1. Basic SAR Principles
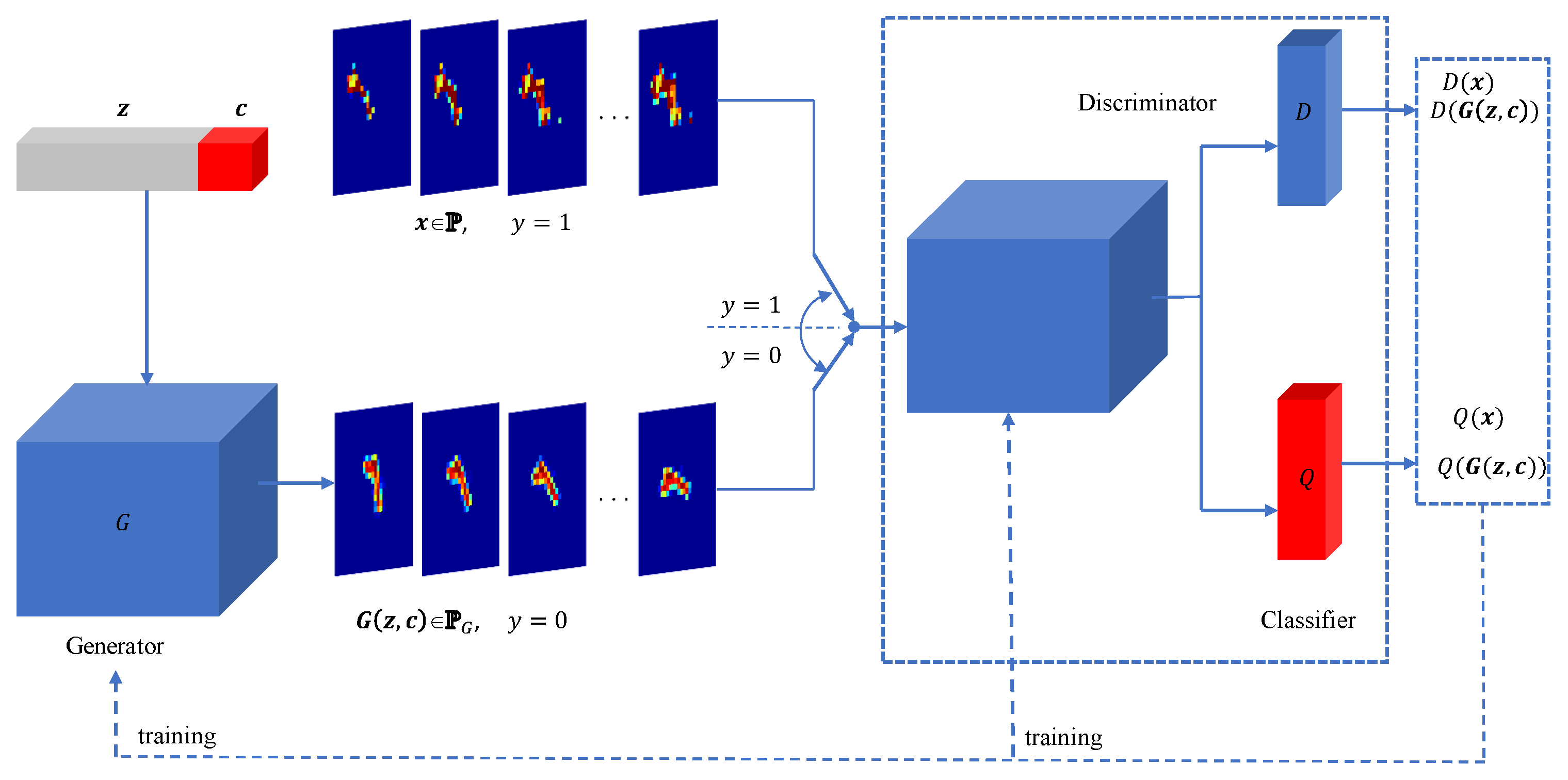
2.2. GAN and InfoGAN
- if the input to the discriminator is a real image from the set ;
- if the input to the discriminator is a synthesized image, , being output from the generator.
3. Methodology
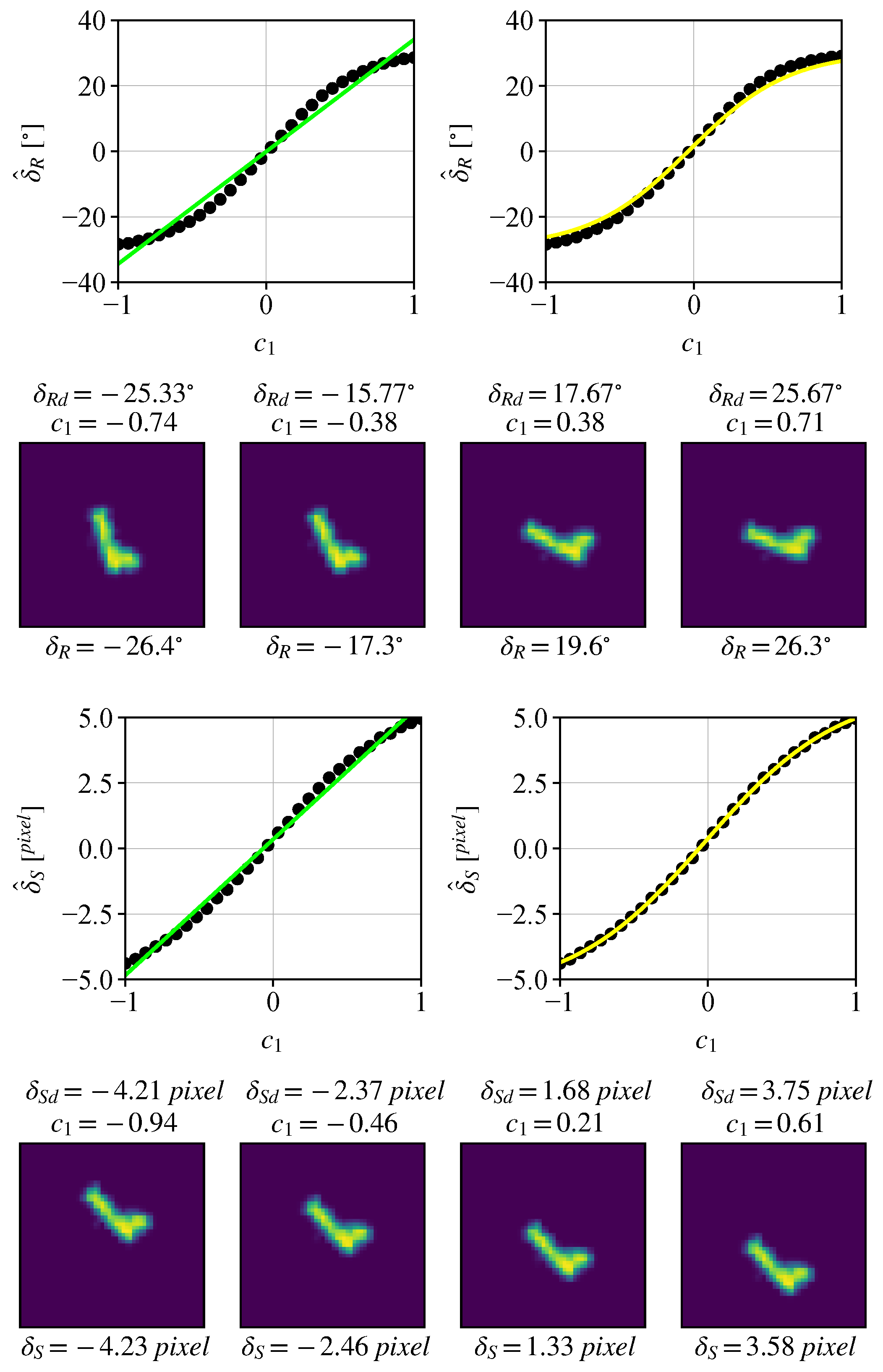
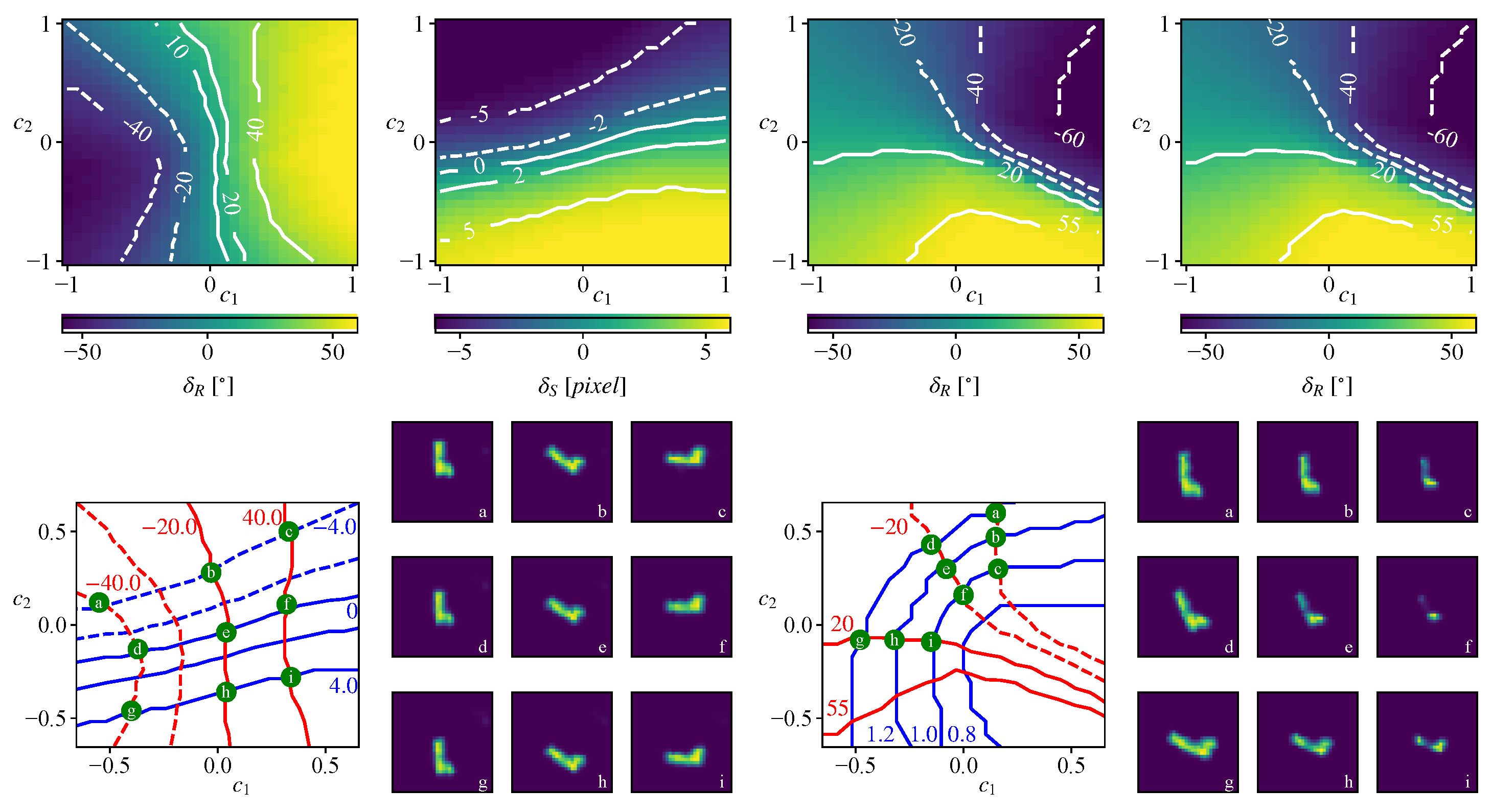
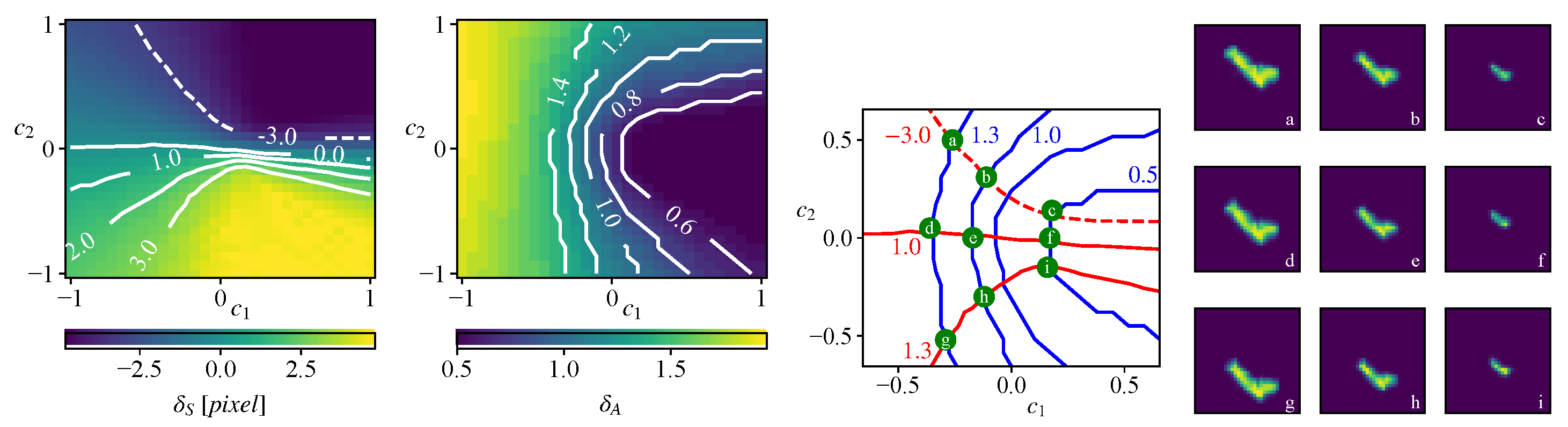
3.1. Property Measurement
3.2. Relation of the Properties and Latent Codes
4. Experiments
- Simulated SAR images: This dataset contains SAR images produced by a simulation model, retaining the scattering characteristics with rotation, translation, and scaling.
- Semi-simulated SAR images: In this dataset, real images are manually rotated, translated, and scaled; thus, it is termed semi-simulated SAR images. It is worth noting the purpose of this dataset without scattering characteristics is to demonstrate the validity of our method in a clear and intuitive manner. The conclusions are also applicable to other datasets.
- Real SAR images without background: This dataset concludes SAR images from MSTAR that is a popular and open-access dataset of SAR images. The background of SAR images is removed by self-matching CAM.
- Real SAR images with background: This dataset is the same as the above except for the maintained background.
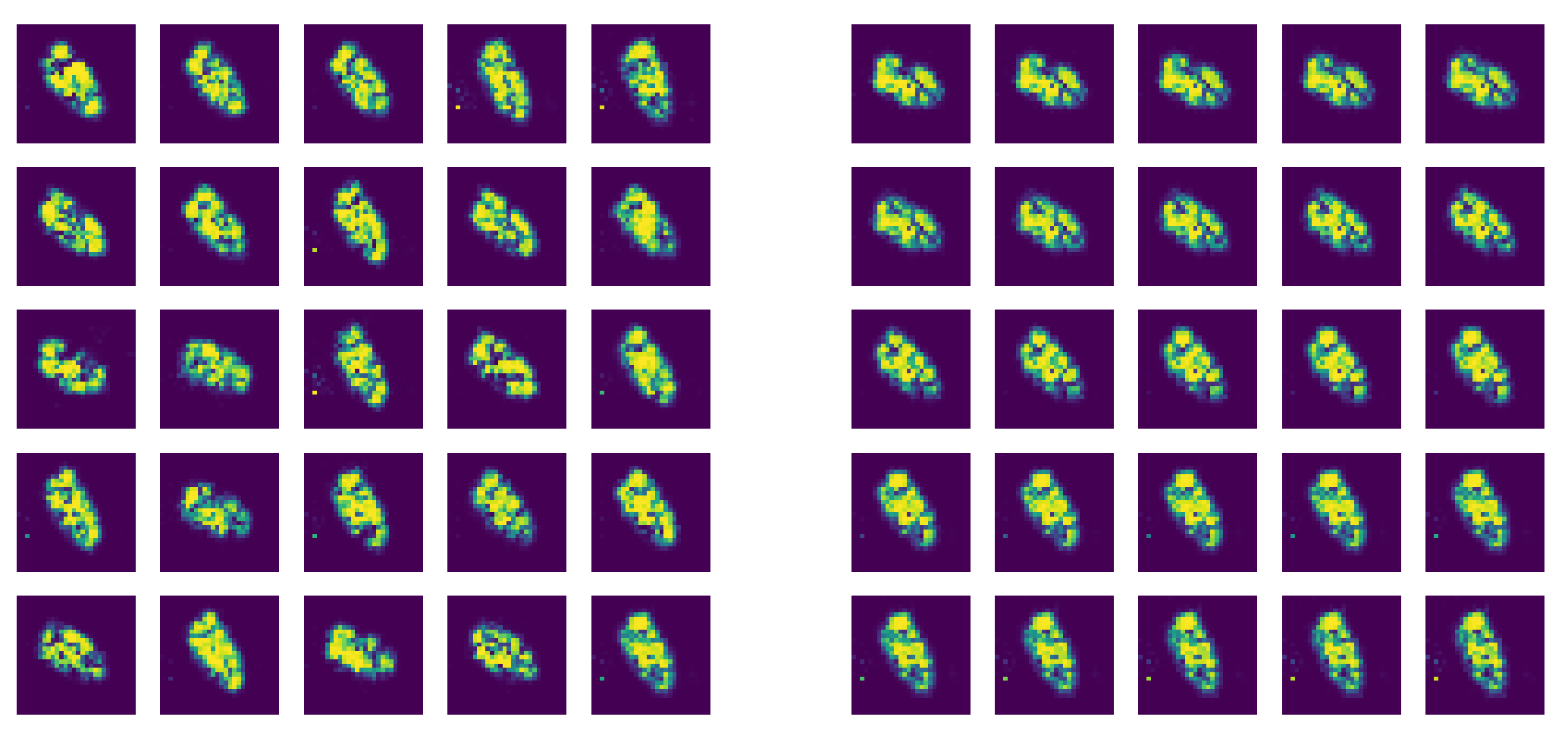
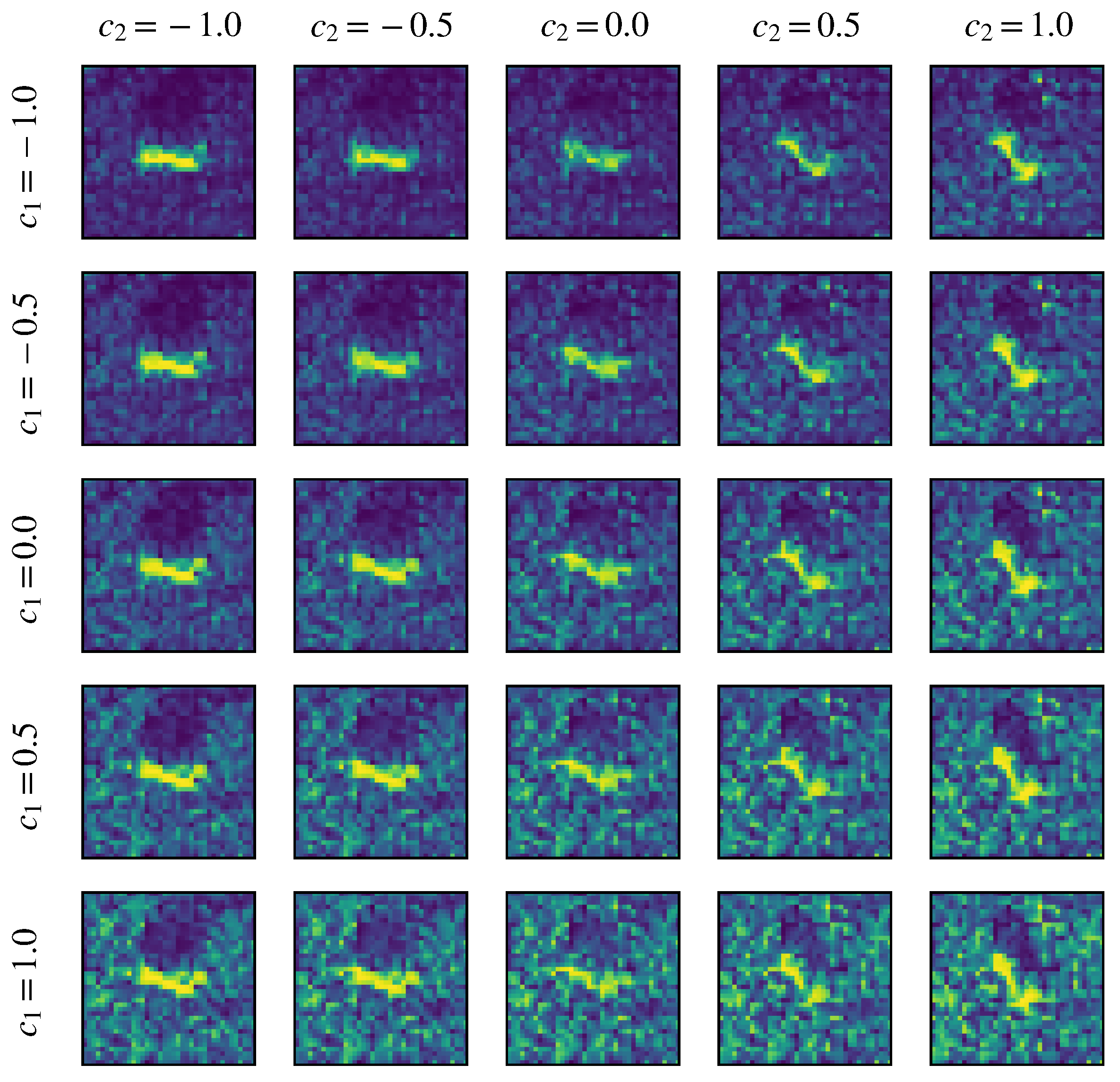
4.1. Simulated SAR Images
4.2. Real Object from a SAR Image with Simulated Properties
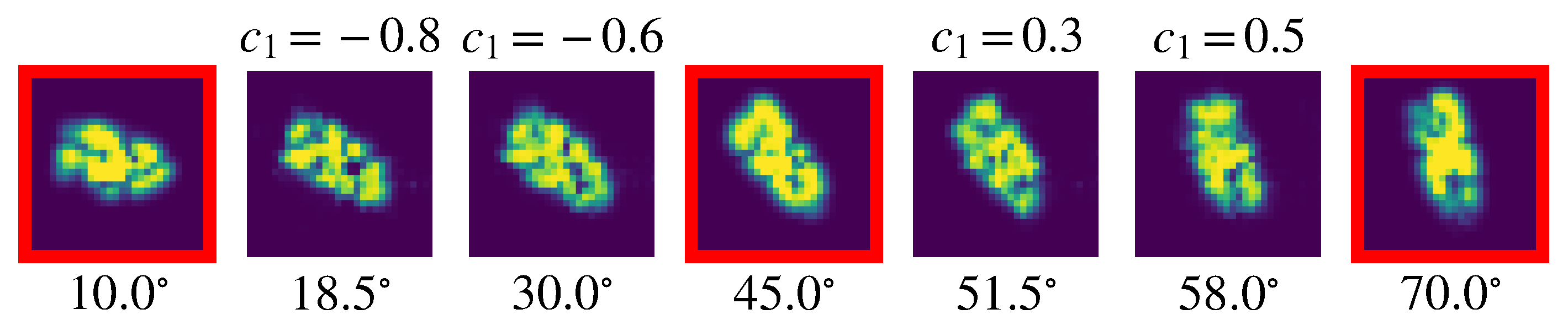
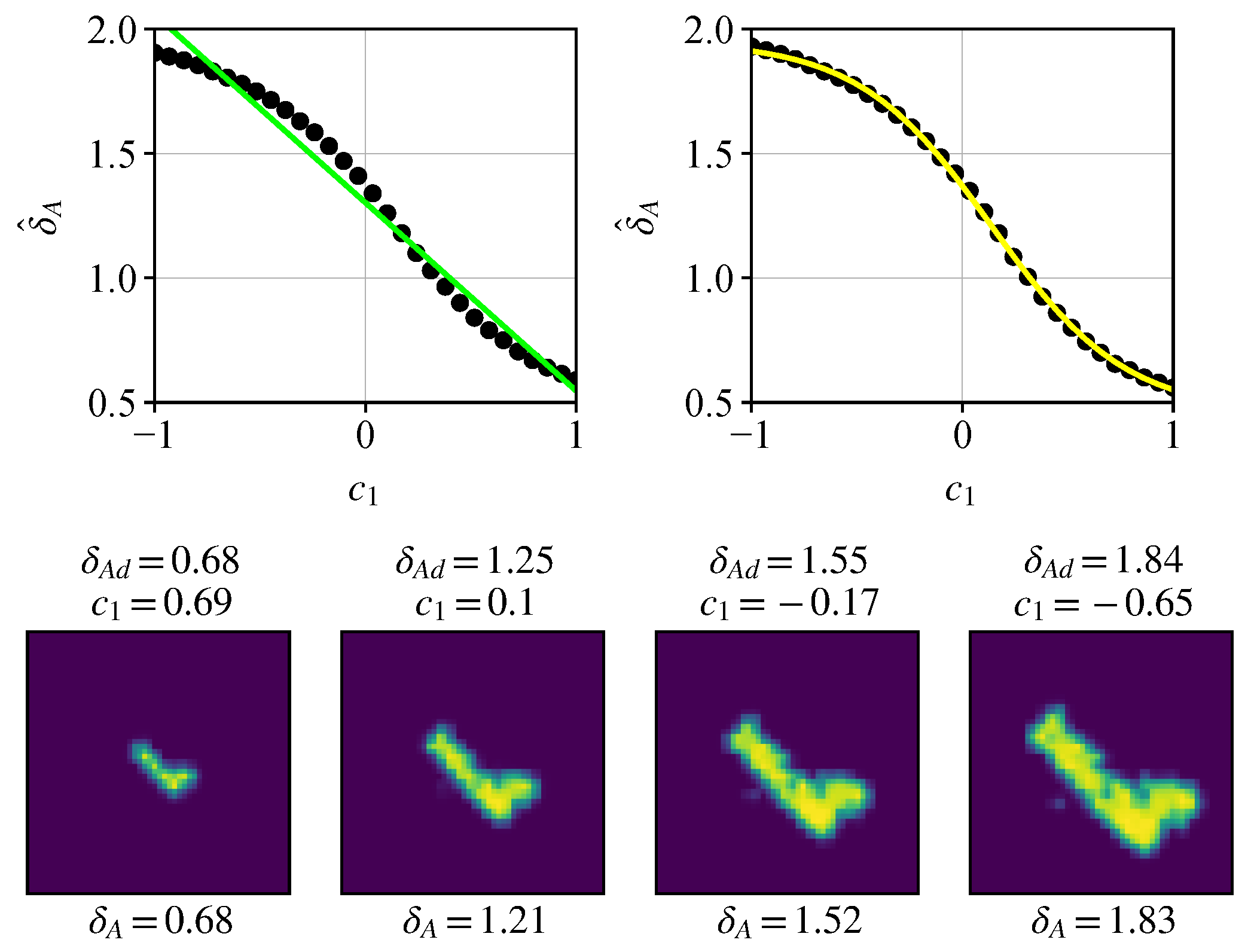
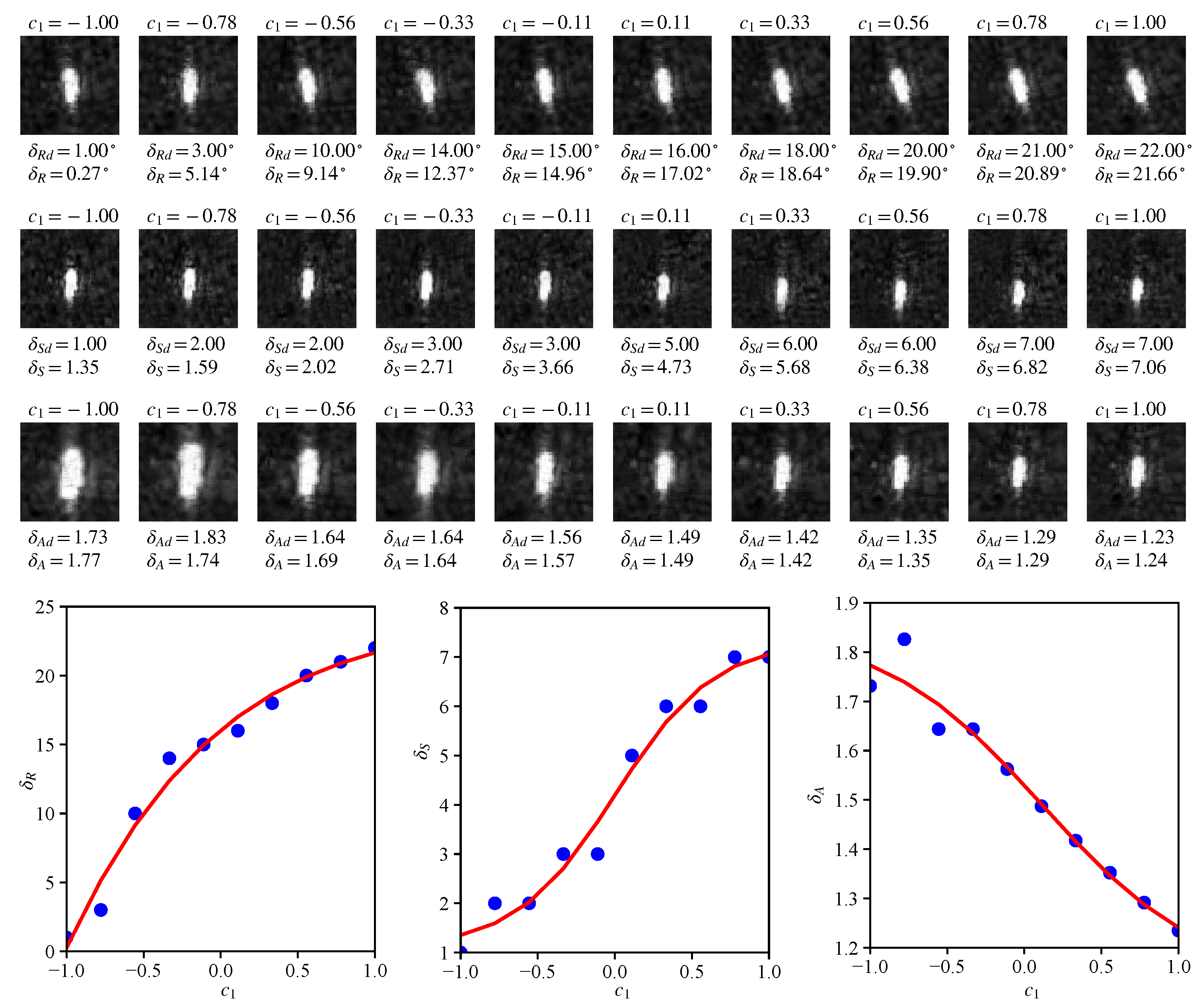
4.2.1. One Property—One Latent Code
4.2.2. One Property—Two Latent Codes
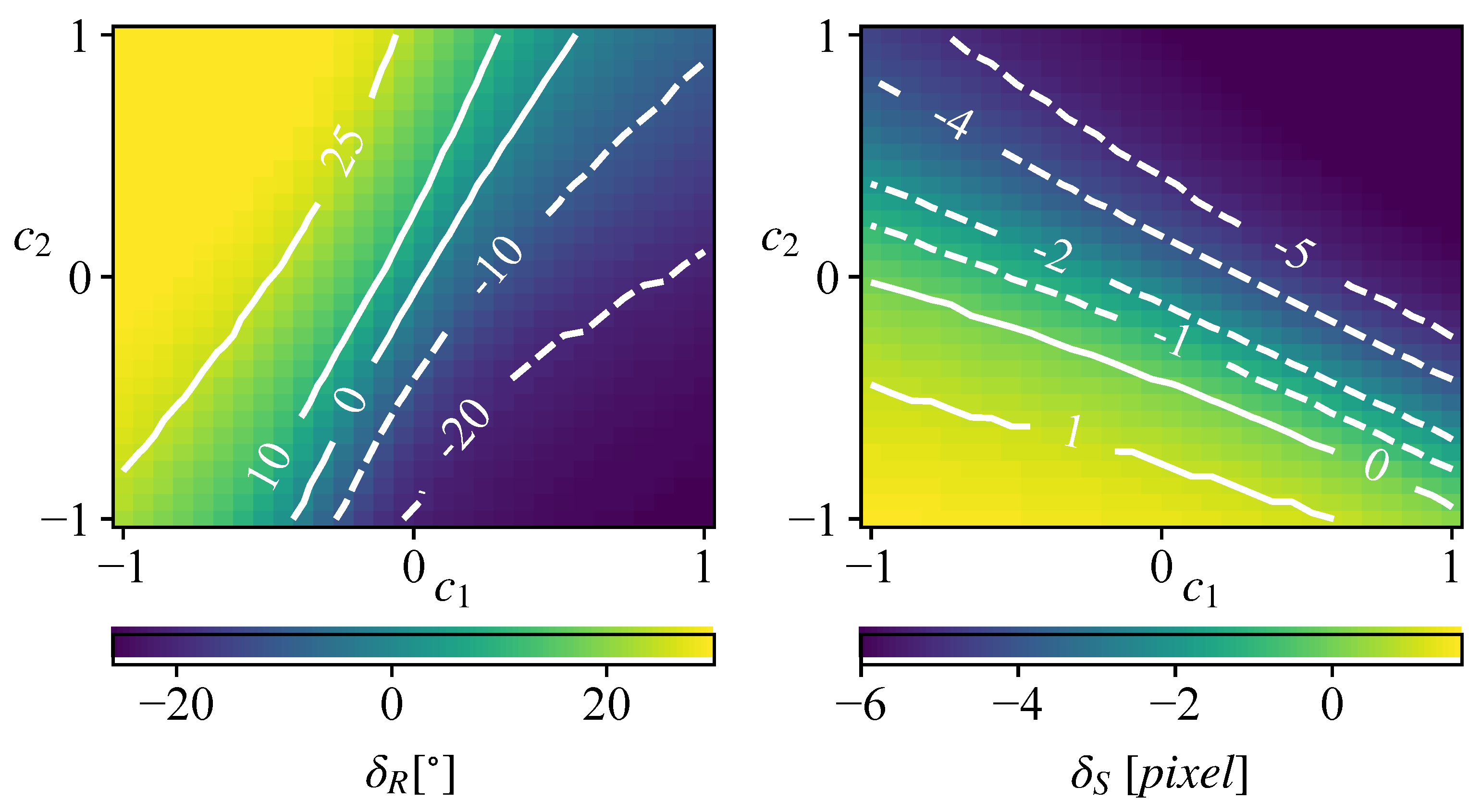
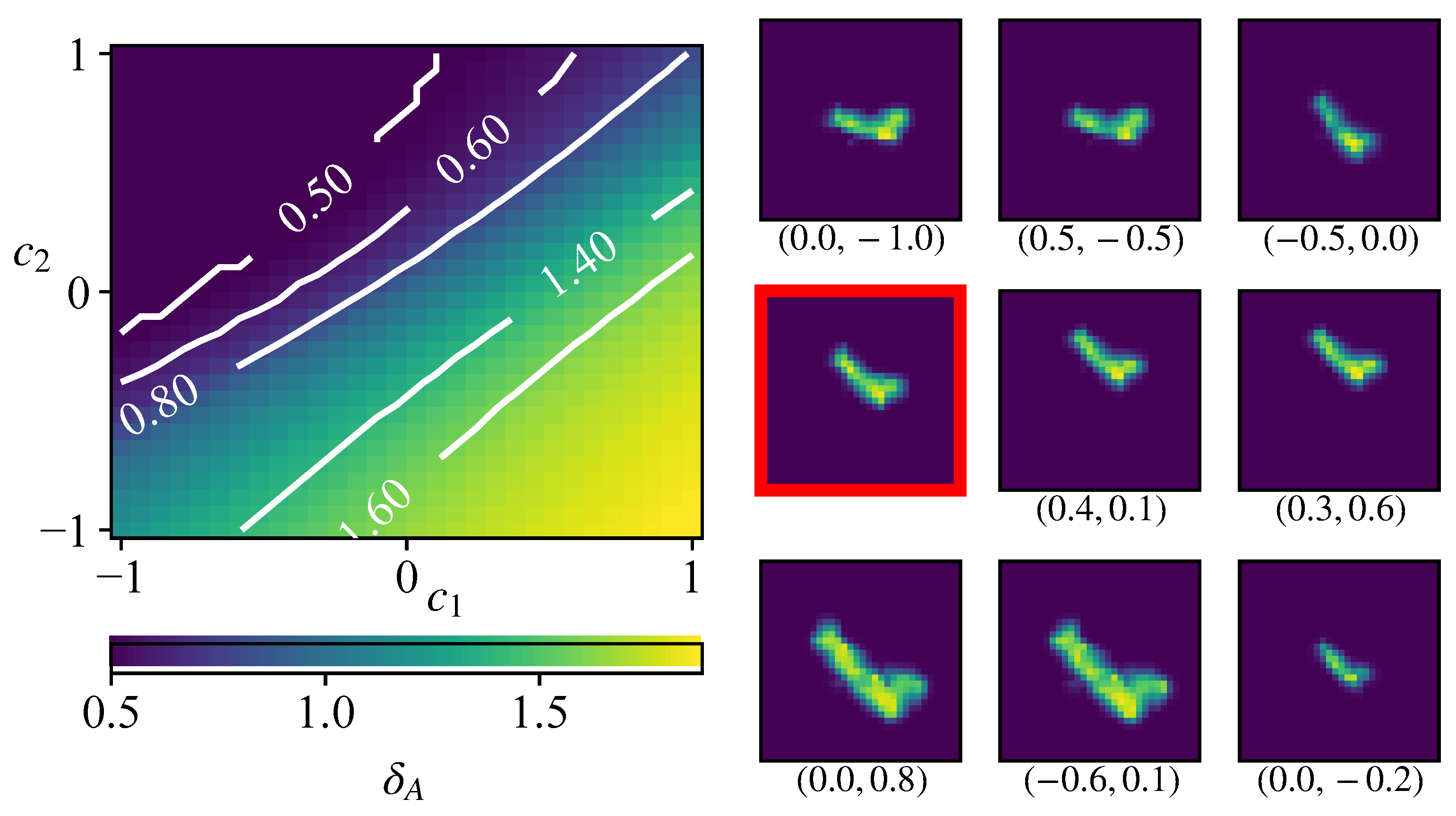
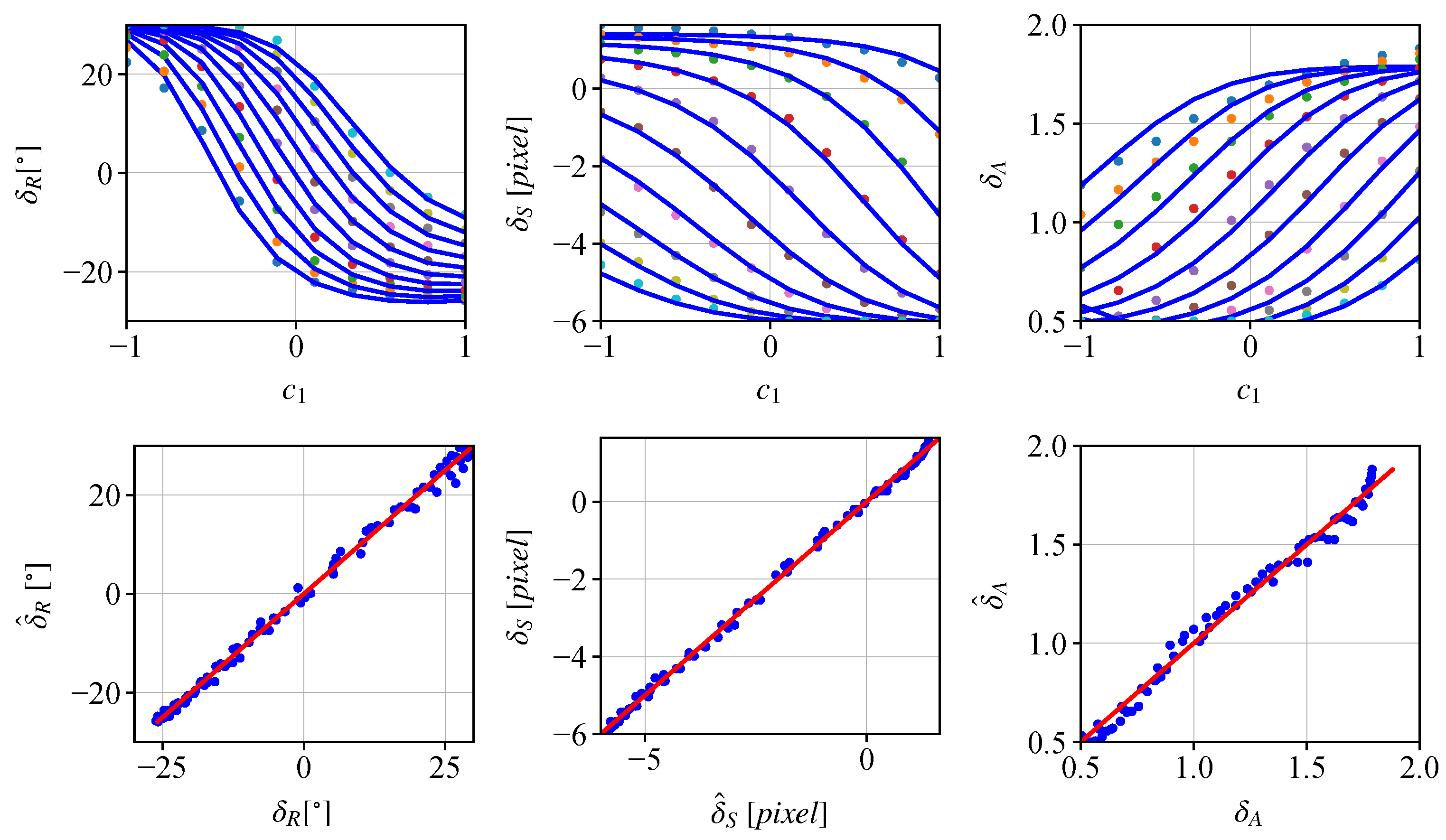
4.2.3. Two Properties—Two Latent Codes
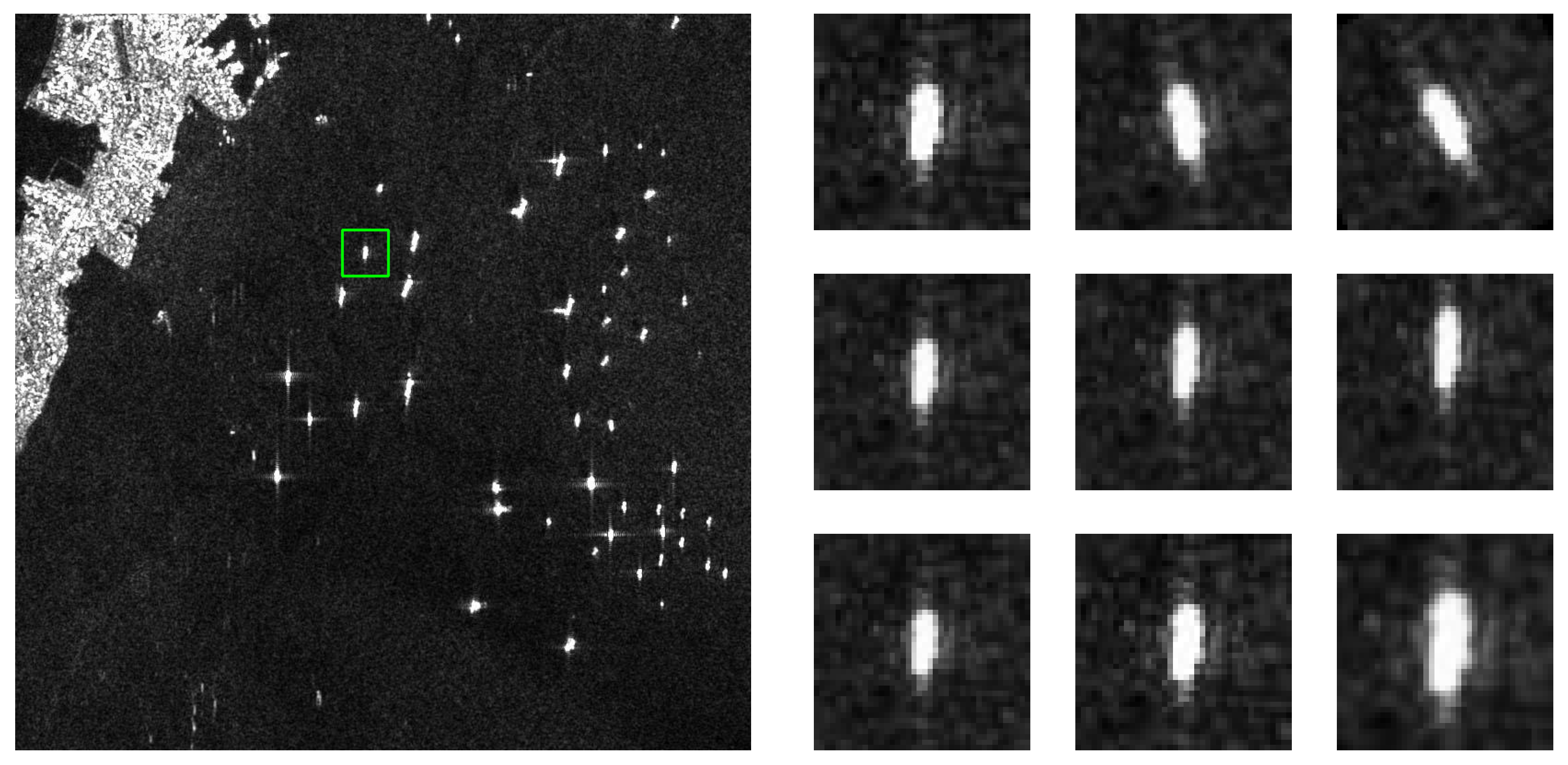
4.3. Real SAR Images with Suppressed Background
4.4. SAR Images with Background
4.5. Robustness and Generalization Analysis on Other SAR Datasets
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ender, J.; Amin, M.G.; Fornaro, G.; Rosen, P.A. Recent Advances in Radar Imaging. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A Tutorial on Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Bai, B.; Li, X.; Niu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L. Space-Time Varying Plasma Sheath Effect on Hypersonic Vehicle-borne SAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 4527–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; An, D.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Feng, D.; Zhou, Z. Ground Moving Target Detection and Trajectory Reconstruction Methods for Multi-Channel Airborne Circular SAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 2900–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berizzi, F.; Martorella, M.; Giusti, E. Radar Imaging for Maritime Observation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, V.; Djurović, I.; Stanković, L.; Thayaparan, T.; Daković, M. Autofocusing of SAR Images Based on Parameters Estimated from the PHAF. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Guida, R.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Efficient Simulation of Hybrid Stripmap/Spotlight SAR Raw Signals from Extended Scenes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wen, G.; Huang, X.; Ma, C.; Yang, X. Data Augmentation by Multilevel Reconstruction Using Attributed Scattering Center for SAR Target Recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederik, P.; Kingma, M.W. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, D.; Cheung, W.K. Learning Hierarchical Variational Autoencoders With Mutual Information Maximization for Autoregressive Sequence Modeling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 1949–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Sengupta, A.; Cao, S. mmFall: Fall Detection Using 4-D mmWave Radar and a Hybrid Variational RNN AutoEncoder. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 19, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, K.; Sakurada, K.; Onishi, M.; Iwasaki, A. GAN-Based SAR-to-Optical Image Translation with Region Information. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2069–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Hong, J.; Wang, Y.; Qi, Y. A High-Quality Multicategory SAR Images Generation Method With Multiconstraint GAN for ATR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. PSGAN: A Generative Adversarial Network for Remote Sensing Image Pan-Sharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 10227–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Lei, J.; Du, Q.; Li, J. HPGAN: Hyperspectral Pansharpening Using 3-D Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Ramesh, A.; Shyam, P.; Sishkin, P.; McGrew, B.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, M. GLIDE: Towards Photorealistic Image Generation and Editing with Text-Guided Diffusion Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.10741v3. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, M. Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06125. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Denton, E.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Ayan, B.K.; Madhavi, S.S.; Lopez, R.G.; et al. Photorealistic Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Deep Language Understanding. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.11487. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Yu, W.; Yi, X.; Khan, A.; Yuan, F.; Zheng, Y. Recent Progress on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36322–36333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, B. Semantic hierarchy emerges in deep generative representations for scene synthesis. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Duan, Y.; Houthooft, R.; Schulman, J.; Sutskever, I.; Abbeel, P. Infogan: Interpretable Representation Learning by Information Maximizing Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2016), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Schwegmann, C.P.; Kleynhans, W.; Salmon, B.P.; Mdakane, L.W.; Meyer, R.G. Synthetic Aperture Radar Ship Discrimination, Generation and Latent Variable Extraction using Information Maximizing Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2263–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, M.; Giusti, E.; Demi, L.; Zhou, Z.; Cacciamano, A.; Berizzi, F.; Bates, B. Target Recognition by Means of Polarimetric ISAR Images. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2011, 47, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.D.; Amin, M.G.; Himed, B. High-resolution Passive SAR Imaging Exploiting Structured Bayesian Compressive Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papson, S.; Narayanan, R.M. Classification via the Shadow Region in SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, L.; Brajović, M.; Stanković, I.; Ioana, C.; Daković, M. Reconstruction Error in Nonuniformly Sampled Approximately Sparse Signals. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, L. ISAR Image Analysis and Recovery with Unavailable or Heavily Corrupted Data. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisken, S.; Martorella, M.; Mathy, T.; Wasserzier, C.; Worms, J.G.; Ender, J.H. Motion Estimation and Imaging with a Multistatic ISAR System. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnous, F.I.; Narayanan, R.M.; Li, B.C. Application of Multidomain Data Fusion, Machine Learning and Feature Learning Paradigms Towards Enhanced Image-based SAR Class Vehicle Recognition. In Proceedings of the Radar Sensor Technology XXV, International Society for Optics and Photonics, Online, 12–17 April 2021; Volume 11742, p. 1174209. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti, G.; Schirinzi, G. A SAR Processor Based on Two-dimensional FFT Codes. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1990, 26, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pavel, M.S.R.; Zhang, Y.D. Crossterm-free Time-frequency Representation Exploiting Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Signal Process. 2022, 192, 108372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, C.; Balleri, A.; Aouf, N.; Le Caillec, J.M.; Merlet, T. Explainability of Deep SAR ATR Through Feature Analysis. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimi, F.; Dosen, S.; Ang, K.K.; Mrachacz-Kersting, N.; Guan, C. Generative Adversarial Networks-Based Data Augmentation for Brain–Computer Interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4039–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Ye, X.; Li, C.; Chen, X. Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering With Perceptual Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.A.; Asadi, F. Pre-trained vs. Random Weights for Calculating Fréchet Inception Distance in Medical Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Ayutthaya, Thailand, 19–21 November 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sekar, A.; Perumal, V. CFC-GAN: Forecasting Road Surface Crack Using Forecasted Crack Generative Adversarial Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 21378–21391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Shen, H.L. Multispectral Image Out-of-Focus Deblurring Using Interchannel Correlation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 4433–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W. SAE-Net: A Deep Neural Network for SAR Autofocus. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sensor Data Management System, MSTAR Database. Available online: https://www.sdms.afrl.af.mil/index.php?collection=mstar (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Feng, Z.; Zhu, M.; Stanković, L.; Ji, H. Self-matching CAM: A Novel Accurate Visual Explanation of CNNs for SAR Image Interpretation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ji, H.; Stanković, L.; Fan, J.; Zhu, M. SC-SM CAM: An Efficient Visual Interpretation of CNN for SAR Images Target Recognition. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Model | FID |
|---|---|
| GAN | 18.74 |
| InfoGAN | 17.59 |
| Dataset | Property | Spatial Size | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| simulated | rotation | ||
| semi-simulated | rotation | 601 | |
| semi-simulated | translation | 151 | |
| semi-simulated | scaling | 301 | |
| semi-simulated | rotation and translation | 3721 | |
| semi-simulated | rotation and scaling | 1891 | |
| semi-simulated | translation and scaling | 3751 | |
| real without background | rotation | 60 | |
| real with background | rotation | 60 |
| Layer | Input Shape | Output Shape | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully connected | 6272 | ||
| Reshape | 6272 | ||
| BatchNormalize | Sigmoid | ||
| TransposedConv2D | |||
| BatchNormalize | Sigmoid | ||
| TransposedConv2D | |||
| BatchNormalize | Sigmoid | ||
| TransposedConv2D | |||
| BatchNormalize | Sigmoid | ||
| TransposedConv2D | Sigmoid |
| Layer | Input Shape | Output Shape | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conv2D | Leaky ReLU | ||
| Conv2D | Leaky ReLU | ||
| Conv2D | Leaky ReLU | ||
| Conv2D | Leaky ReLU | ||
| Flatten | 4096 | ||
| D: Fully connected | 4096 | 1 | Sigmoid |
| Q: Fully connected | 4096 | 128 | |
| Fully connected | 128 | Sigmoid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Daković, M.; Ji, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, M.; Cui, X.; Stanković, L. Interpretation of Latent Codes in InfoGAN with SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051254
Feng Z, Daković M, Ji H, Zhou X, Zhu M, Cui X, Stanković L. Interpretation of Latent Codes in InfoGAN with SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051254
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zhenpeng, Miloš Daković, Hongbing Ji, Xianda Zhou, Mingzhe Zhu, Xiyang Cui, and Ljubiša Stanković. 2023. "Interpretation of Latent Codes in InfoGAN with SAR Images" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051254
APA StyleFeng, Z., Daković, M., Ji, H., Zhou, X., Zhu, M., Cui, X., & Stanković, L. (2023). Interpretation of Latent Codes in InfoGAN with SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051254








