Analysis and Simulation of a Sequential Rotationally Excited Circular Polarized Multi-Dipole Array for a Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle of SRE Circular Polarization
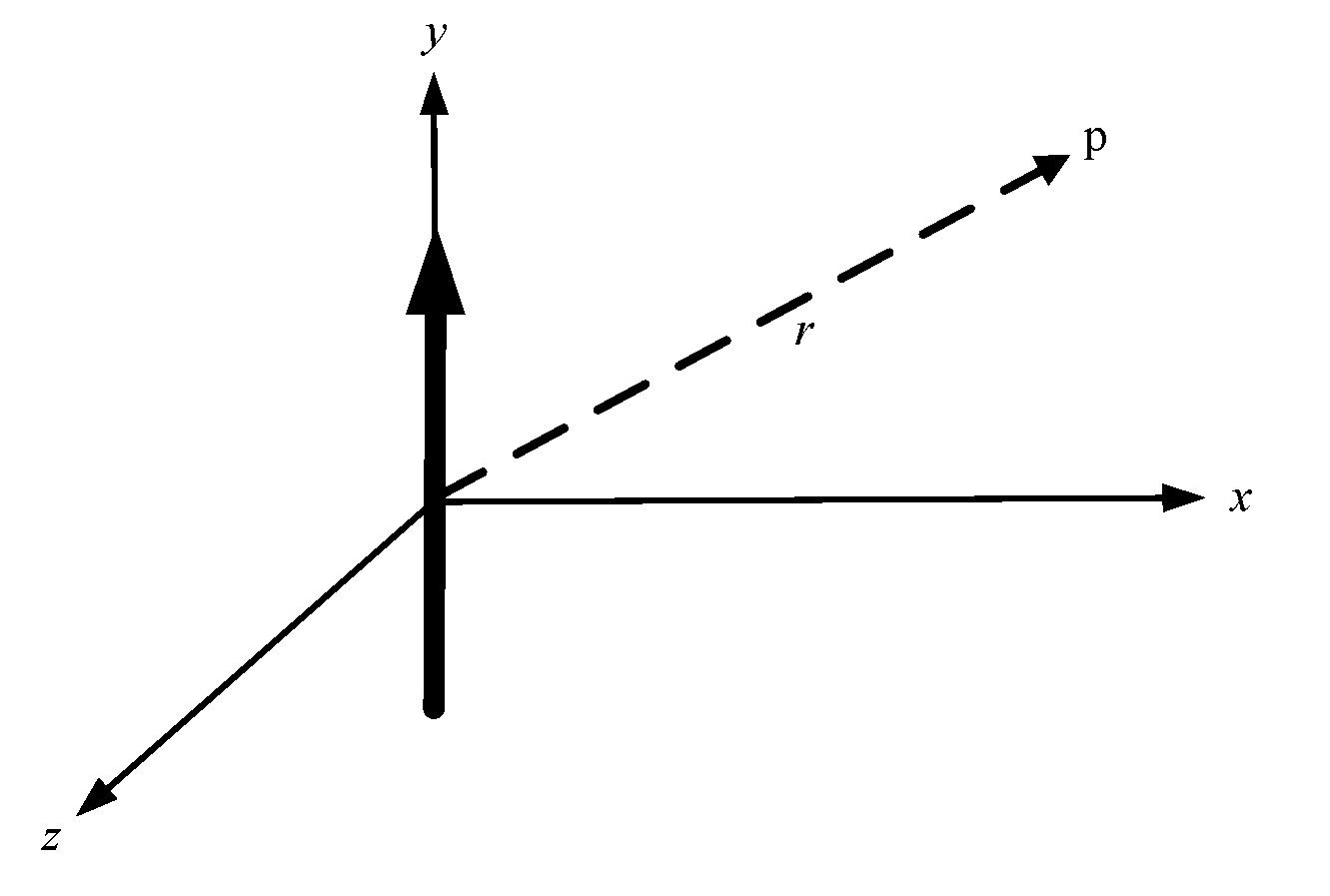
2.1. Interference and Superposition Principle for Electromagnetic Waves
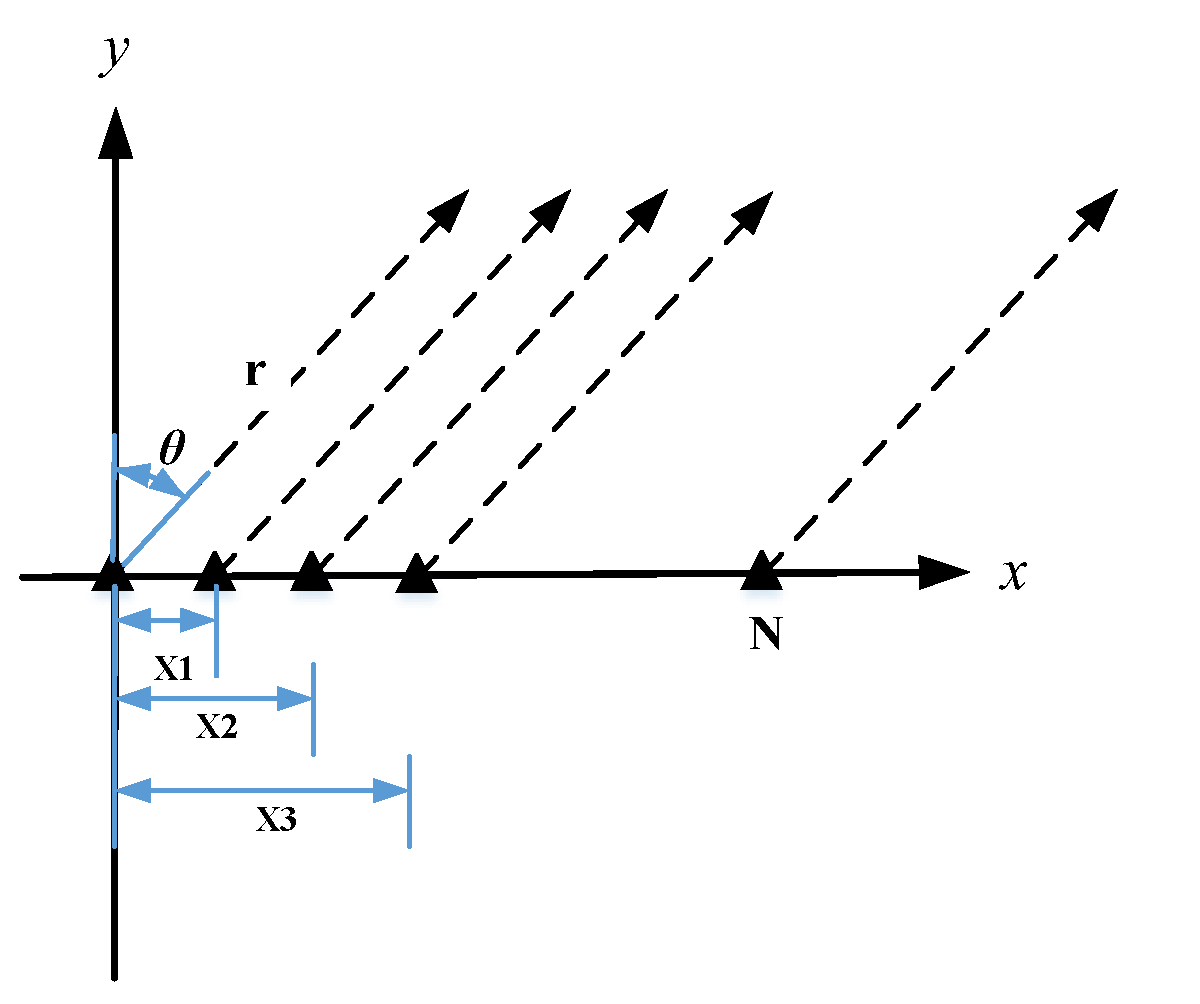
2.2. Principle of Pattern Multiplication
2.3. Principle of Sequential Rotationally Excited Circular Polarization
3. Simulation of Dipole Antenna
4. Simulation of SRE Circular Polarization Based on the MD Array
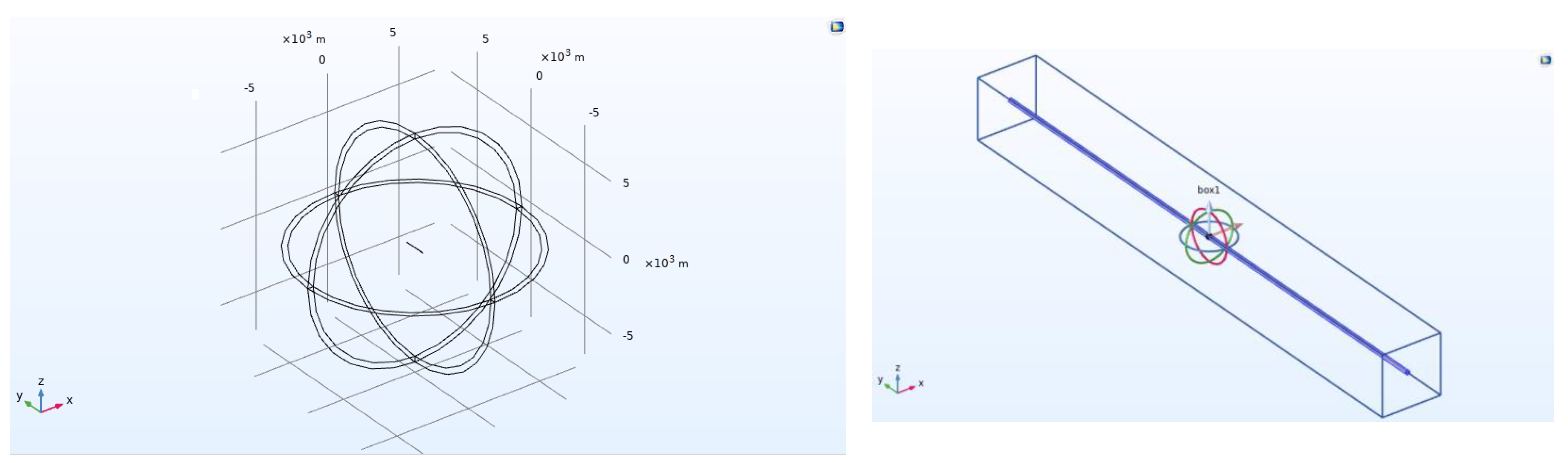
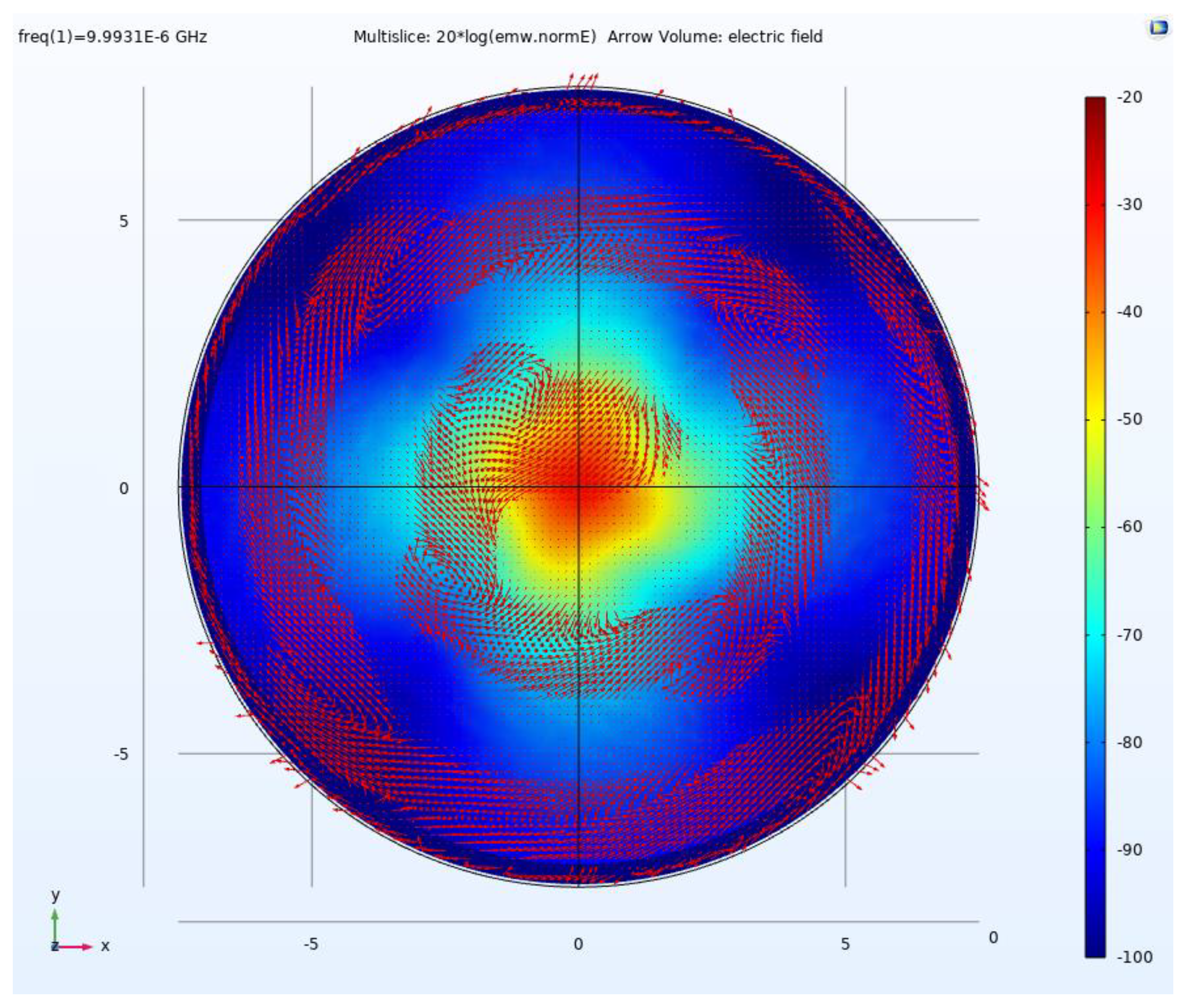
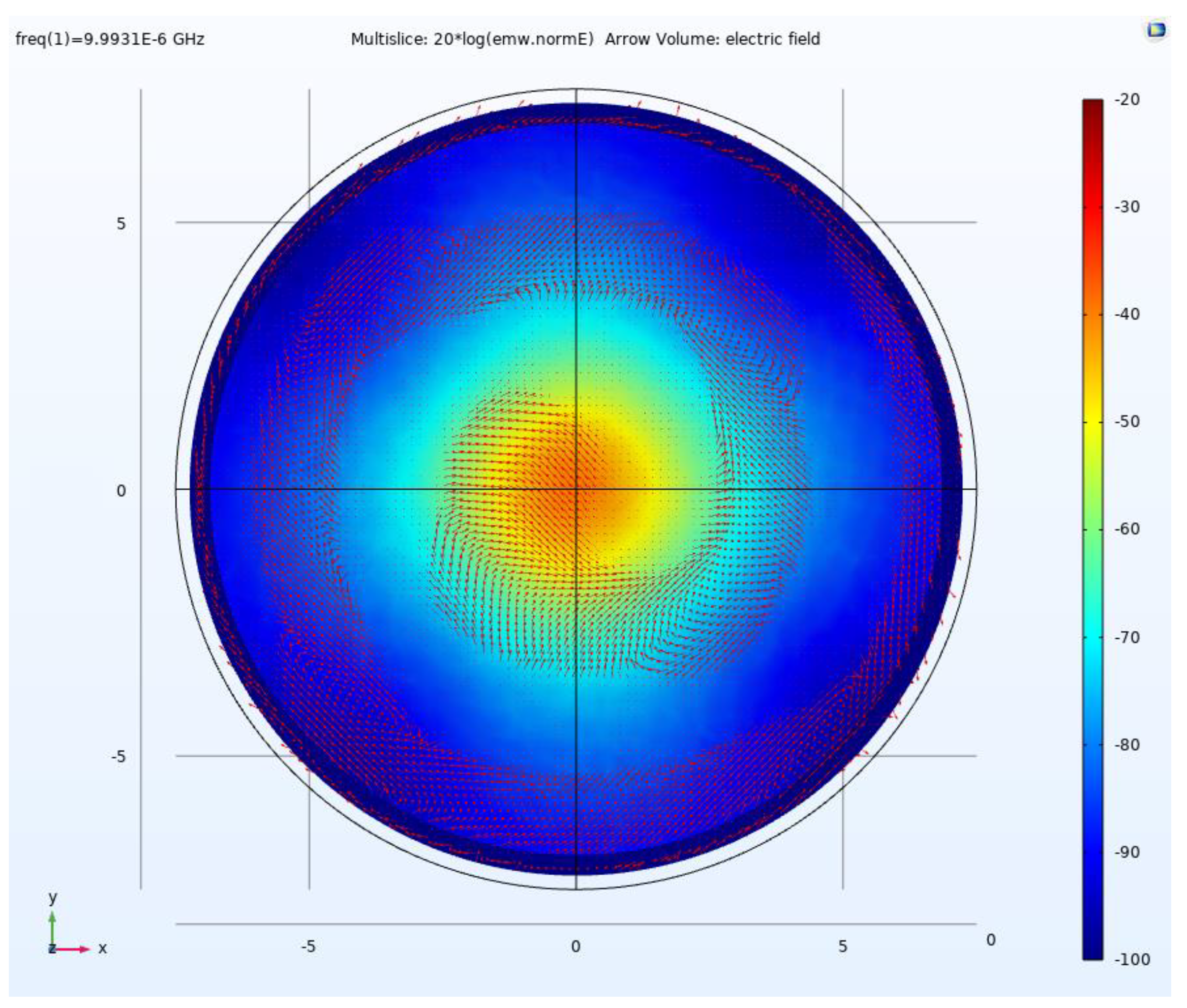
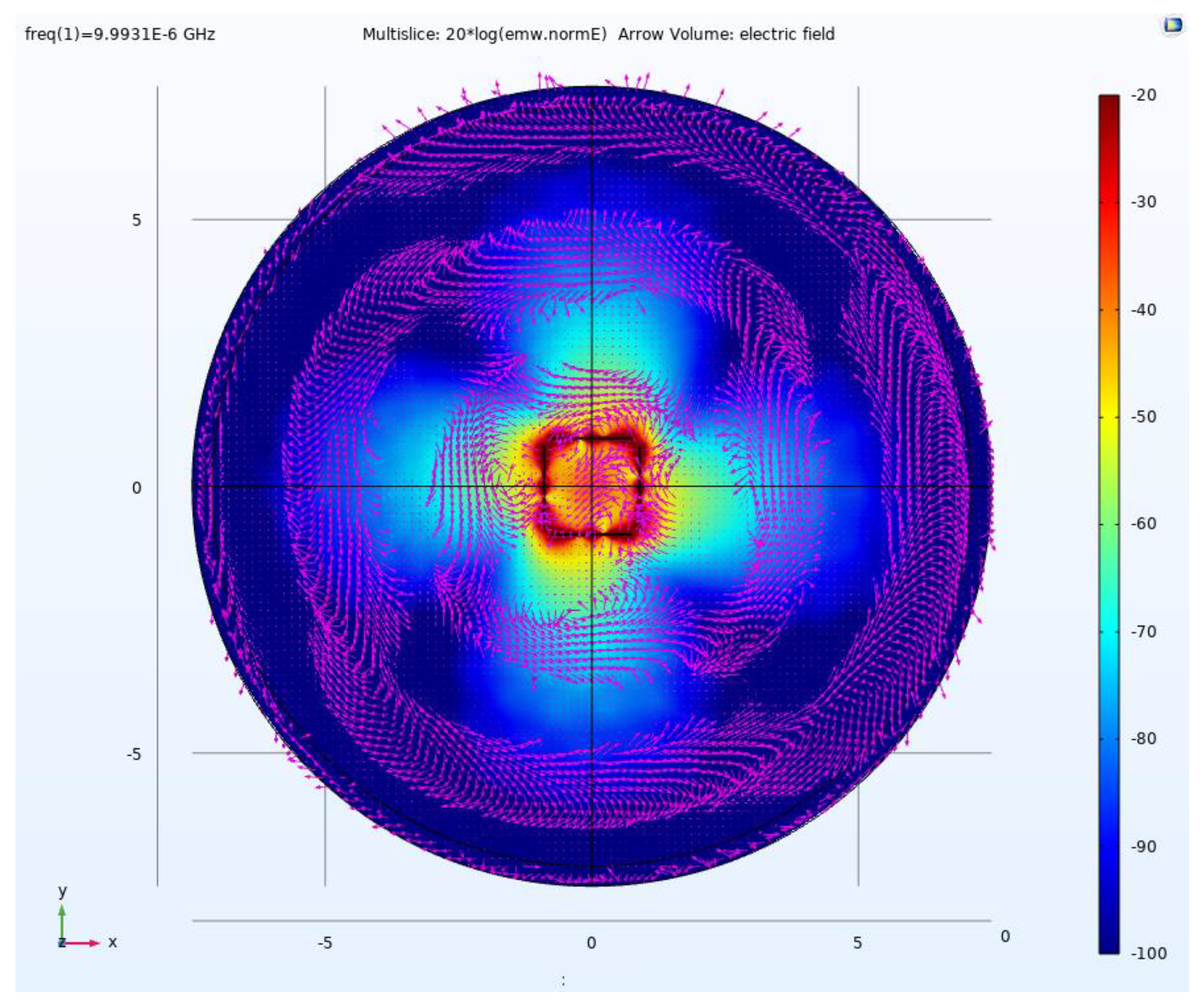
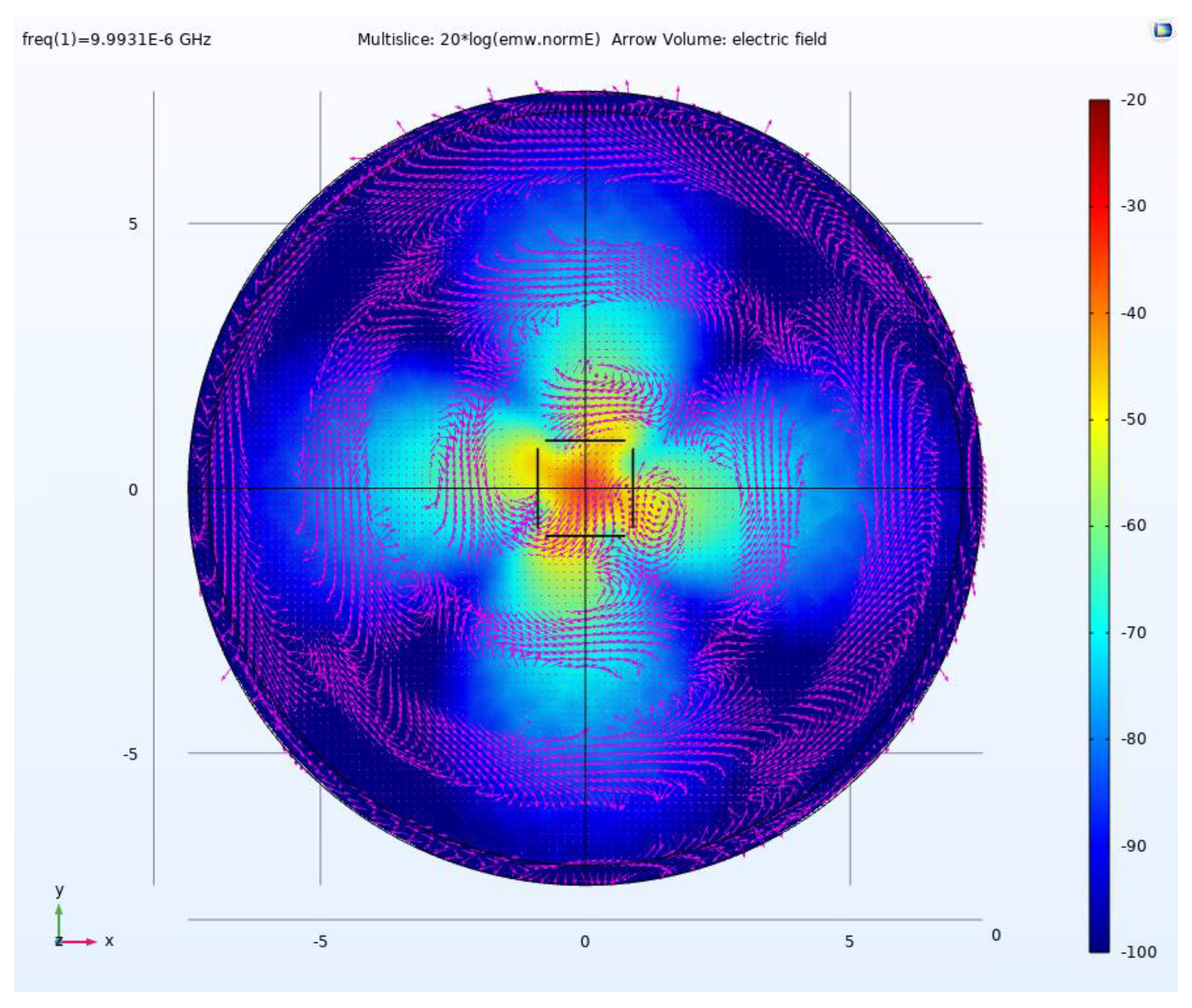
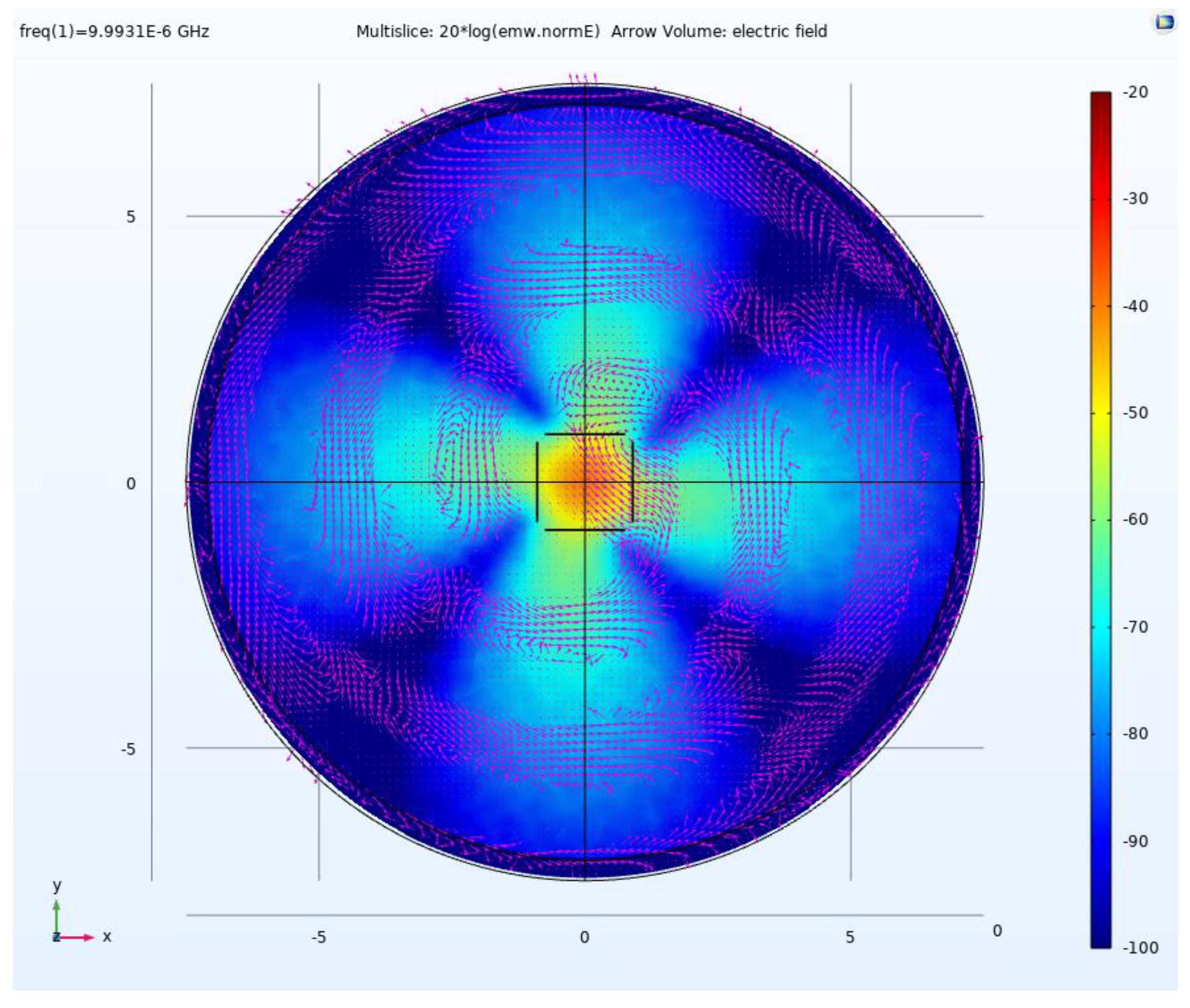
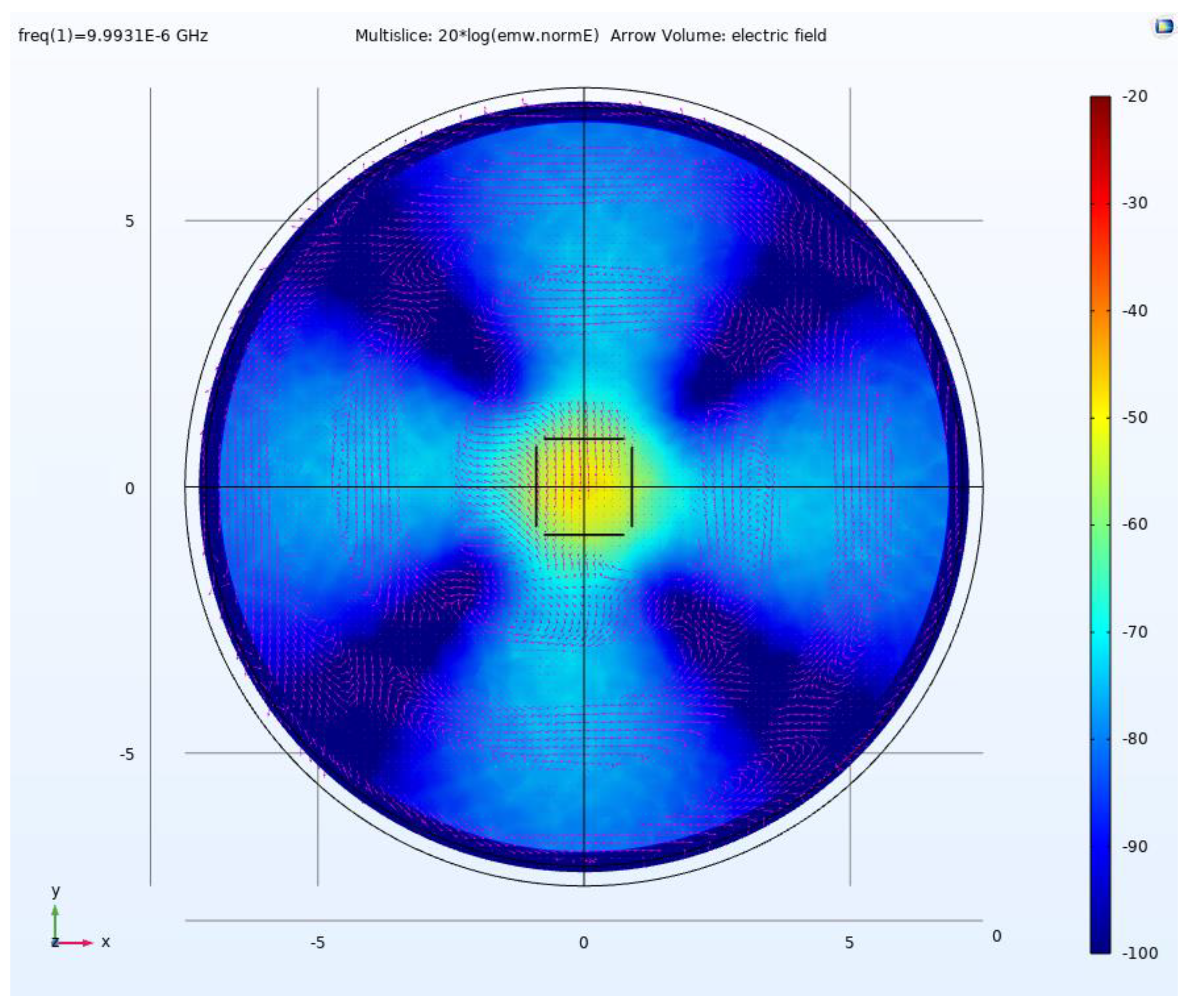
4.1. Electric Field Simulation for SRE Circular Polarization
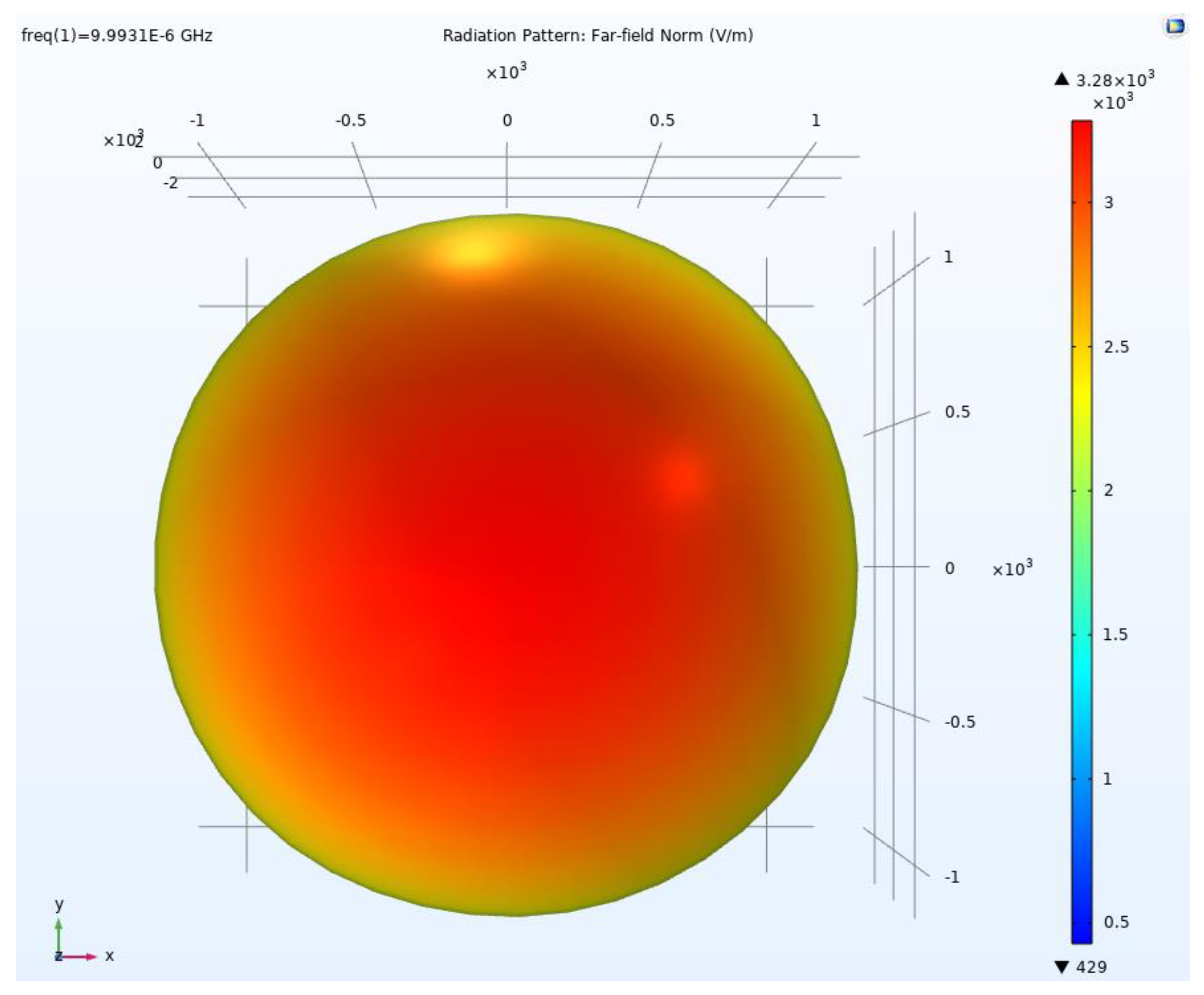
4.2. Far-Field Simulation of SRE Circular Polarization
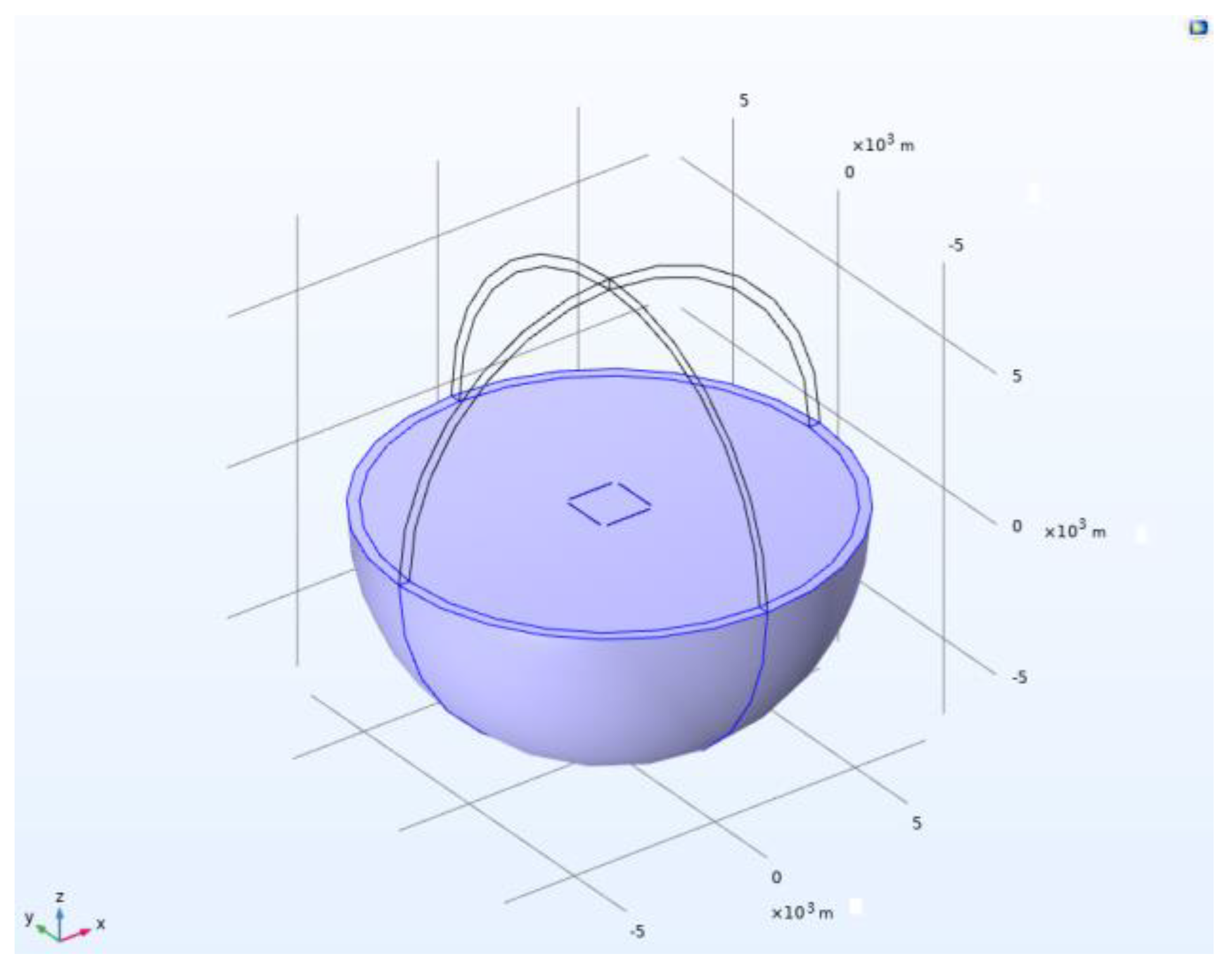
5. Simulation of an SRE CP MD Antenna Array for Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration
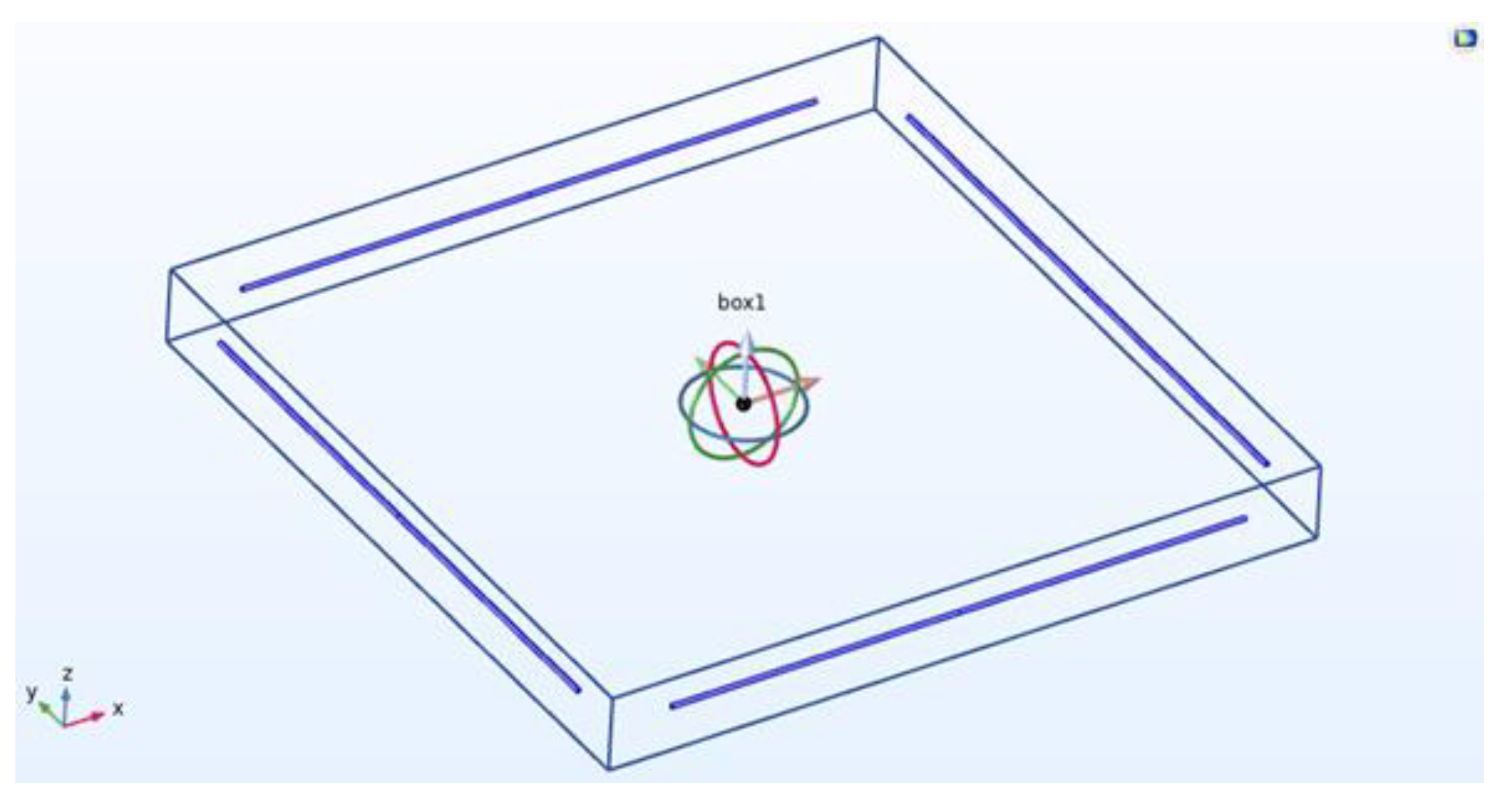
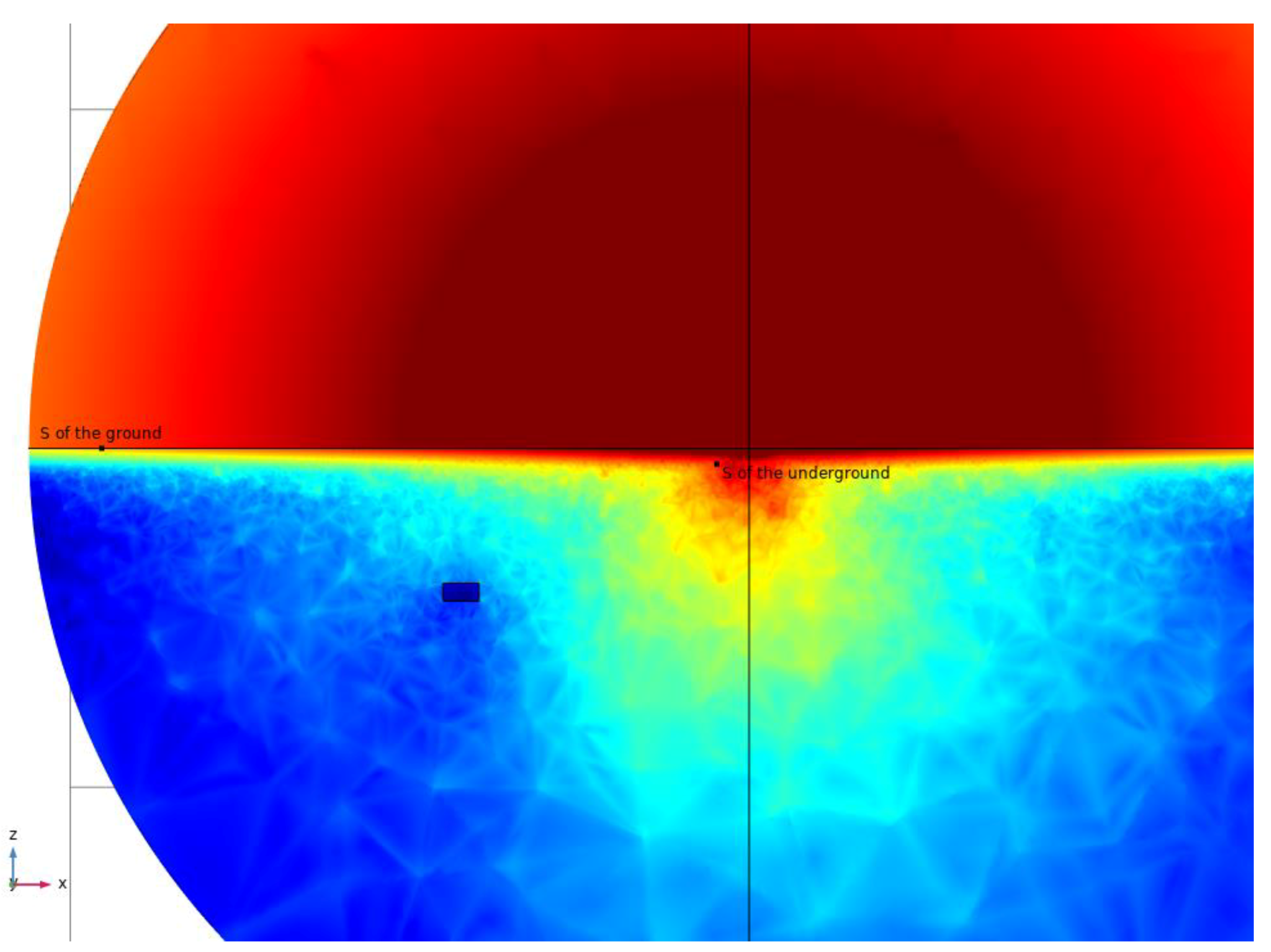
5.1. Electric Field Simulation of an SRE CP MD Antenna Array for Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration
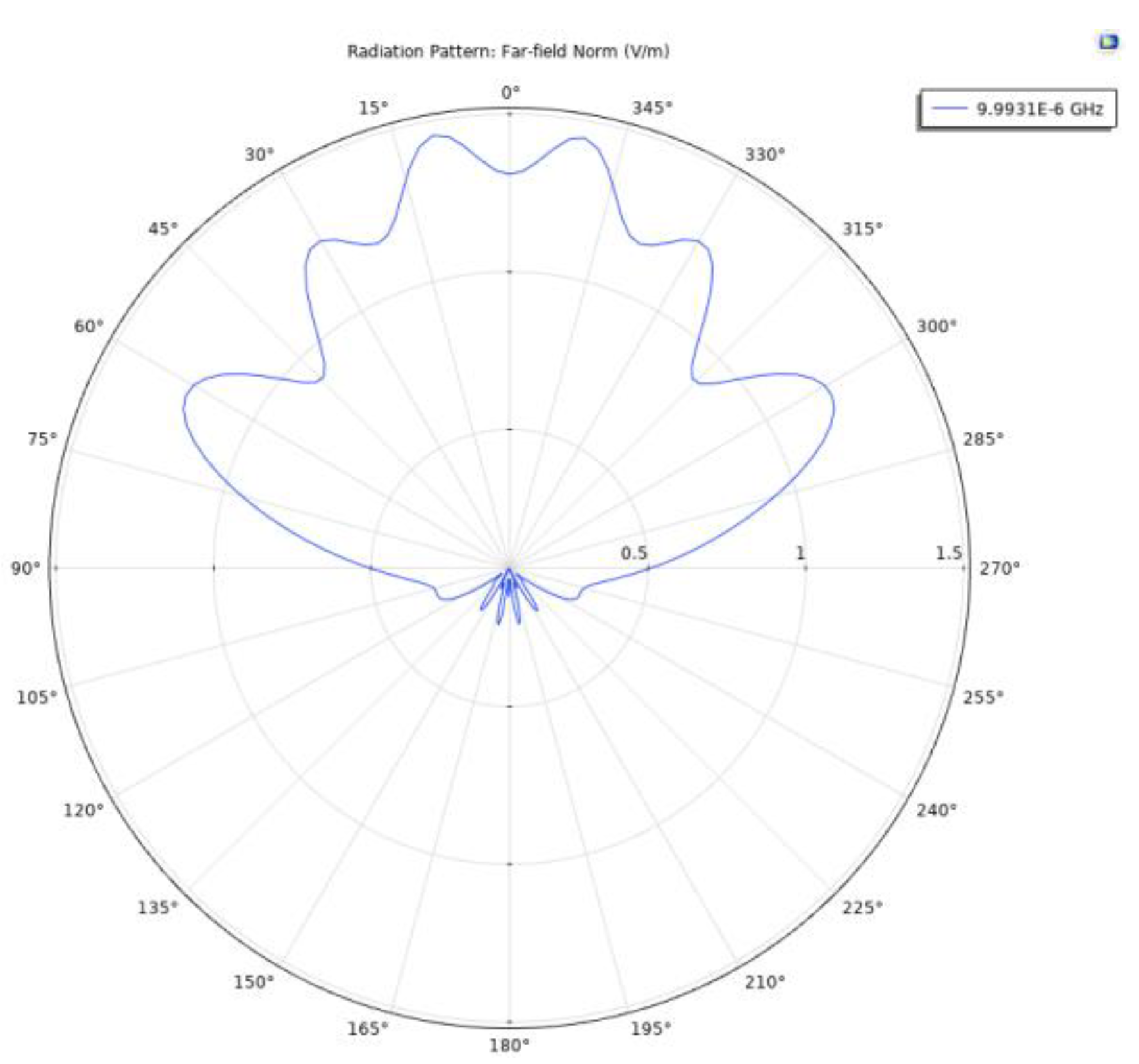
5.2. Far-Field Simulation of an SRE CP MD Antenna Array for Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration
6. Discussion
6.1. Comparison of SNRs of LP Dipole Antenna and CP MD Array for Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration
6.2. Comparison of Remote Sensing Depths of the Large-Aperture CP MD Array and Small-Size LP Dipole Antenna for Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GPR | Ground-penetrating radar |
| LP | Linear polarized |
| CP | Circular polarized |
| MD | Multiple-dipole |
| SRE | Sequential rotationally excited |
| SNR | Signal to noise ratio |
| MIMO | Multiple-input multiple-output |
| TP | Transmitting power |
| Wav | Energy density time average |
References
- Cui, F.; Bao, J.; Cao, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Q. Soil hydraulic parameters estimation using ground penetrating radar data via ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, E.; Saintenoy, A.; Coquet, Y. Hydrodynamic parameters of a sandy soil determined by ground-penetrating radar inside a single ring infiltrometer. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5459–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzsche, A.; Jonard, F.; Looms, M.C.; van der Kruk, J.; Huisman, J.A. Measuring Soil Water Content with Ground Penetrating Radar: A Decade of Progress. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 180052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Weihermüller, L.; Klotzsche, A.; Lärm, L.; Vereecken, H.; Huisman, J.A. Sequential and coupled inversion of horizontal borehole ground penetrating radar data to estimate soil hydraulic properties at the field scale. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaumann, S.; Roth, K. Soil hydraulic material properties and layered architecture from time-lapse GPR. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2551–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Slob, E.C.; Bosch, I.v.d.; Stockbroeckx, B.; Vanclooster, M. Modeling of ground-penetrating Radar for accurate characterization of subsurface electric properties. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Ground-penetrating radar for high-resolution mapping of soil and rock stratigraphy1. Geophys. Prospect. 1989, 37, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.P.; Bogaert, P.; Wiaux, F.; Vanclooster, M.; Lambot, S. High-resolution space–time quantification of soil moisture along a hillslope using joint analysis of ground penetrating radar and frequency domain reflectometry data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huisman, J.A.; Klotzsche, A.; Vereecken, H.; Weihermüller, L. Coupled full-waveform inversion of horizontal borehole ground penetrating radar data to estimate soil hydraulic parameters: A synthetic study. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ren, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X. Joint acoustic full-waveform inversion of crosshole seismic and ground-penetrating radar data in the frequency domain. Geophysics 2017, 82, H41–H56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbin, G.; Or, D. Ground-penetrating radar measurement of soil water content dynamics using a suspended horn antenna. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.F.; Li, J.; Huang, L.; Feng, X.; Liu, F.S. Improving Target Detection Accuracy Based on Multi polarization MIMO GPR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L. Development of Vehicle Mounted Ground Penetrating Radar System and Experimental Research on Its Application; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.P.; Xiao, L.; Yan, Q.; Meng, X.; Zhou, B.; Dong, Z.H.; Zhao, D. Comparison of Dielectric Properties and Structure of Lunar Regolith at Chang’e-3 and Chang’e-4 Landing Sites Revealed by Ground-Penetrating Radar. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 12783–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, M. Modelling of GPR wave for lossy media obeying a complex power law of frequency for dielectric permittivity. Geophys. Prospect. 2004, 52, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosten, T.R.; Day-Lewis, F.D.; Schultz, G.M.; Curtis, G.P.; Lane, J.W. Inversion of multi-frequency electromagnetic induction data for 3D characterization of hydraulic conductivity. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 73, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, M.; Tsend-Ayush, N.; Schlupp, A.; Munkhuu, U. Ground-Penetrating Radar Imaging of Near-Surface Deformation along the Songino Active Fault in the Vicinity of Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoué, F.; Brossier, R.; Métivier, L.; Garambois, S.; Virieux, J. Two-dimensional permittivity and conductivity imaging by full waveform inversion of multi offset GPR data: A frequency-domain quasi-Newton approach. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 197, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.; van der Kruk, J.; Bikowski, J.; Vereecken, H. Quantitative conductivity and permittivity estimation using full-waveform inversion of on-ground GPR data. Geophysics 2012, 77, H79–H91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Lee, K.S. Investigation of Forest Fire Characteristics in North Korea Using Remote Sensing Data and GIS. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlykov, A.A.; Saraev, A.K. Wave effects in the field of a high frequency horizontal electric dipole. Izv.-Phys. Solid Earth 2014, 50, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, M.J.; Travis, B.J.; Chave, A.D. Electromagnetic induction by a finite electric dipole source over a 2D earth. Geophysics 1993, 58, 198–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, B.; Ziolkowski, A.; Wright, D. Multi-Transient Electromagnetics (MTEM)-controlled source equipment for subsurface resistivity investigation. 18th IAGA WG 2006, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetzov, A.N. Distorting effects during electromagnetic sounding of horizontally non-uniform media using an artificial field source. Earth Physics. 1982, 18, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.X.; Di, Q.Y.; Xu, C. Characteristics of Multiple Dipole Sources and Tensor Measurement in CSAMT. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Radzevicius, S.J.; Daniels, J.J.; Guy, E.D.; Vendl, M.A. Significance of crossed-dipole antennas for high noise environments. In 13th EEGS Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Houten, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, C. Two-dimensional DOA estimation based on polarization sensitive array and uniform linear array. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2019, 41, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Barkat, M. Near-field multiple source localization by passive sensor array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1991, 39, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Tao, H.; Xie, J. Mixed far-field and near-field source localization using a linear tripole array. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Tao, H.; Kang, H. Mixed far-field and near-field source localization using a linear electromagnetic-vector-sensor arraywith gain/phase uncertainties. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 132412–132428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tao, H.; Chen, W.; Song, D. Maneuvering target detection based on subspace subaperture joint coherent integration. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ahmad, M.O.; Swamy, M.N.S. Near-field localization of partially polarized sources with a cross-dipole array. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. Coherent sources direction finding and polarization estimation with various compositions of spatially spread polarized antenna arrays. IEEE Signal Process. 2014, 102, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, B. Frequency diversity array MIMO track-before-detect in coherent repeated interference. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electronics. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2018, 10, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, L.; Shu, T. Near-field parameter estimation for polarized source using spatial amplitude ratio. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 1961–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, S.; Rao, B.; Ottersten, B. An asymptotically efficient weighted least squares estimator for co-array-based DOA Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.F.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, X.H. An Asymmetric Beamforming Method Based on Arithmetic Phase Difference Weighting in CSAMT. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, F.; Boerner, D.E.; Holliger, K.; Green, A.G. Multicomponent georadar data: Some important implications for data acquisition and processing. Geophysics 2000, 65, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Source Mode | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Phase (deg) | Total Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP MD array | Dipole antenna1 250 | 12.5 | 0 | 50 |
| Dipole antenna2 250 | 12.5 | 90 | ||
| Dipole antenna3 250 | 12.5 | 180 | ||
| Dipole antenna4 250 | 12.5 | 270 | ||
| LP dipole antenna | 1000 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| Position (x, y, z) | Wav of CP MD Array | Wav of LP Dipole Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| (10,000, 0, 0) | 2.03 × 10−23 J/m3 | 3.86 × 10−24 J/m3 |
| (9000, 0, 0) | 3.59 × 10−23 J/m3 | 7.22 × 10−24 J/m3 |
| (8000, 0, 0) | 5.23 × 10−23 J/m3 | 1.06 × 10−23 J/m3 |
| (7000, 0, 0) | 6.93 × 10−23 J/m3 | 1.32 × 10−23 J/m3 |
| (6000, 0, 0) | 8.55 × 10−23 J/m3 | 1.69 × 10−23 J/m3 |
| (5000, 0, 0) | 1.39 × 10−22 J/m3 | 2.75 × 10−23 J/m3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, X.; Meng, H. Analysis and Simulation of a Sequential Rotationally Excited Circular Polarized Multi-Dipole Array for a Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041134
Fan H, Zhang Y, Tian Q, Wang X, Meng H. Analysis and Simulation of a Sequential Rotationally Excited Circular Polarized Multi-Dipole Array for a Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(4):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041134
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Haifeng, Yiming Zhang, Qianqian Tian, Xuhong Wang, and Hongyan Meng. 2023. "Analysis and Simulation of a Sequential Rotationally Excited Circular Polarized Multi-Dipole Array for a Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration" Remote Sensing 15, no. 4: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041134
APA StyleFan, H., Zhang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, X., & Meng, H. (2023). Analysis and Simulation of a Sequential Rotationally Excited Circular Polarized Multi-Dipole Array for a Bi-Static Antenna GPR for Deep Exploration. Remote Sensing, 15(4), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15041134





