Characteristics of Optical Properties and Heating Rates of Dust Aerosol over Taklimakan Desert and Tibetan Plateau in China Based on CALIPSO and SBDART
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. CALIPSO
2.2. SBDART
2.3. Dust Heating Rate and Efficiency
3. Results and Analysis
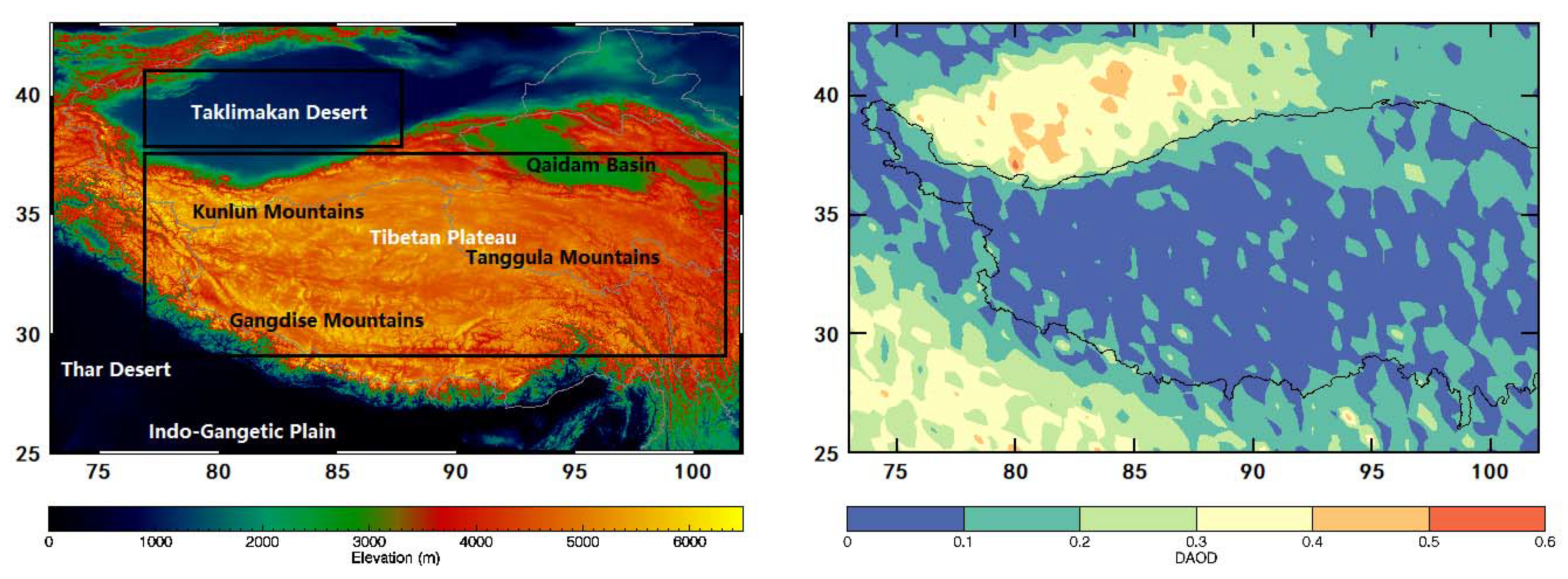
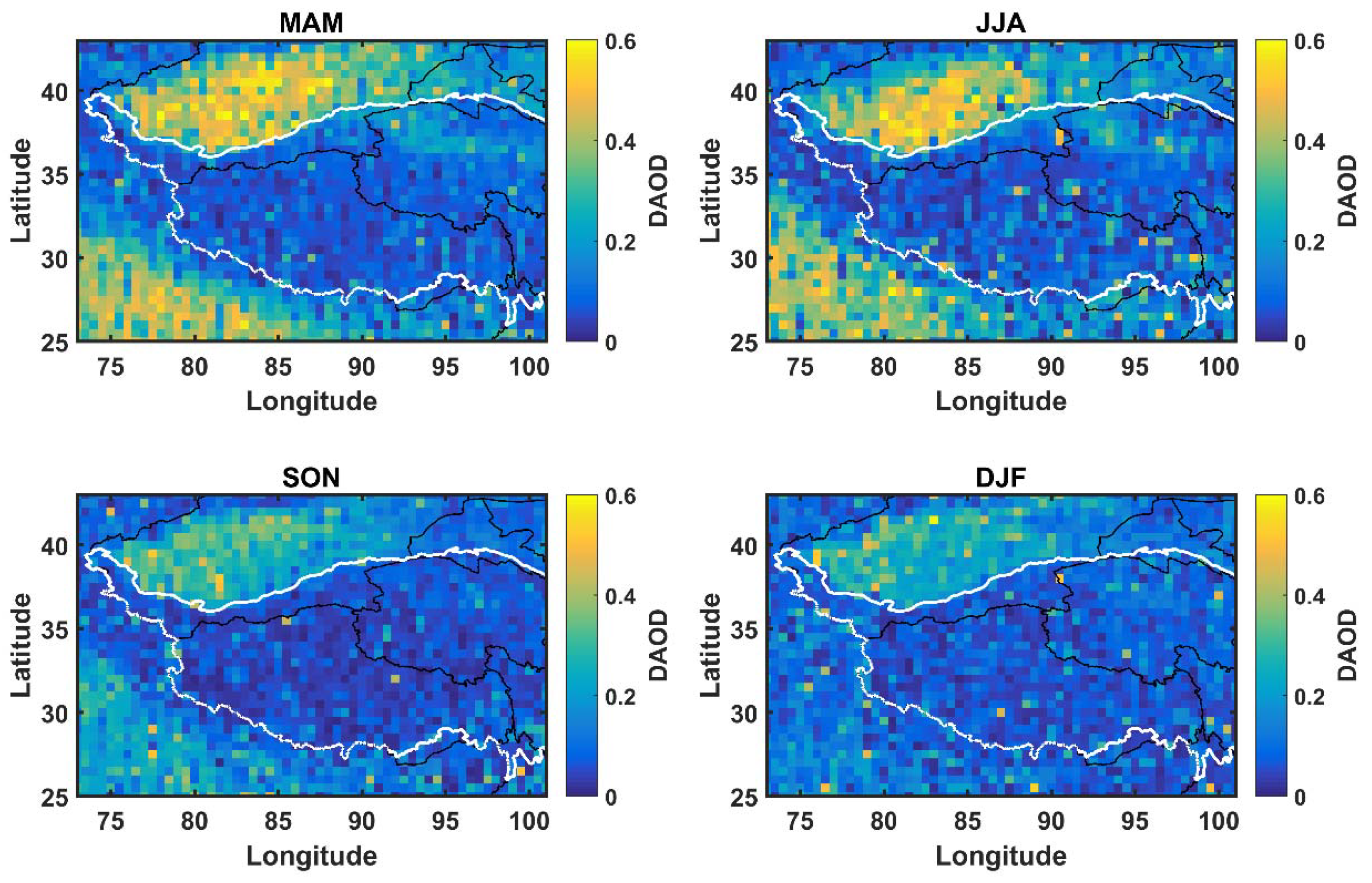
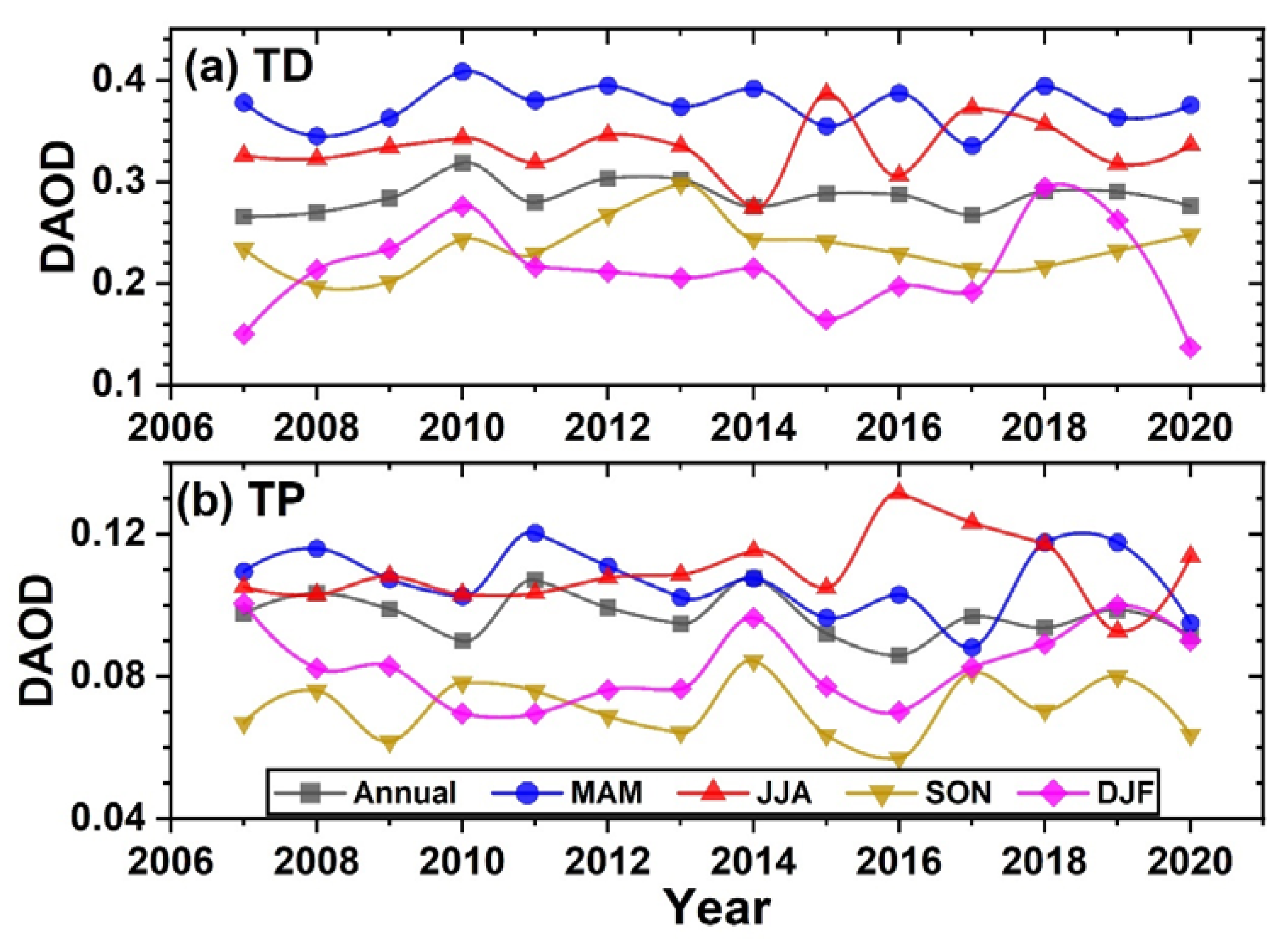
3.1. Dust AOD
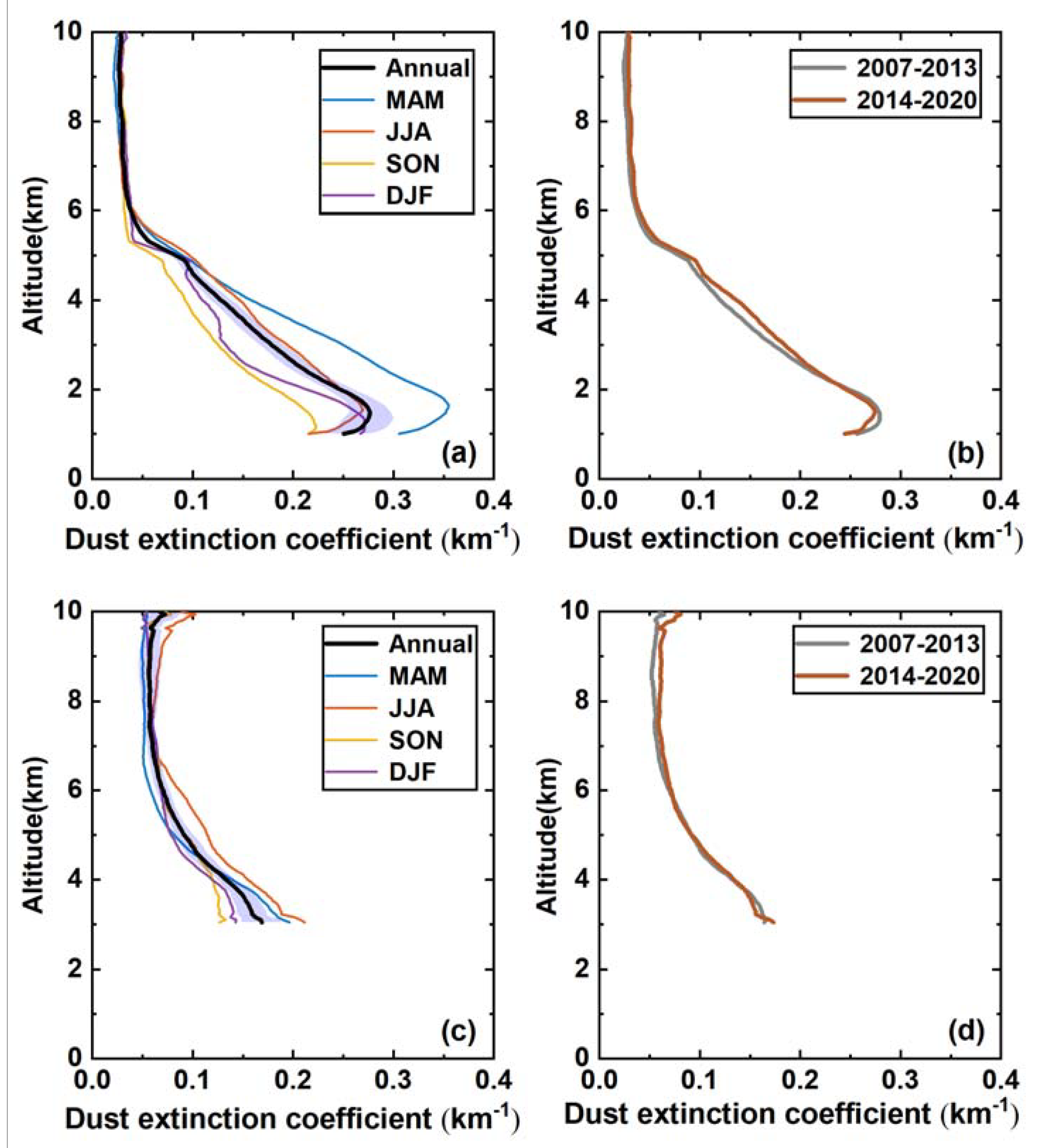
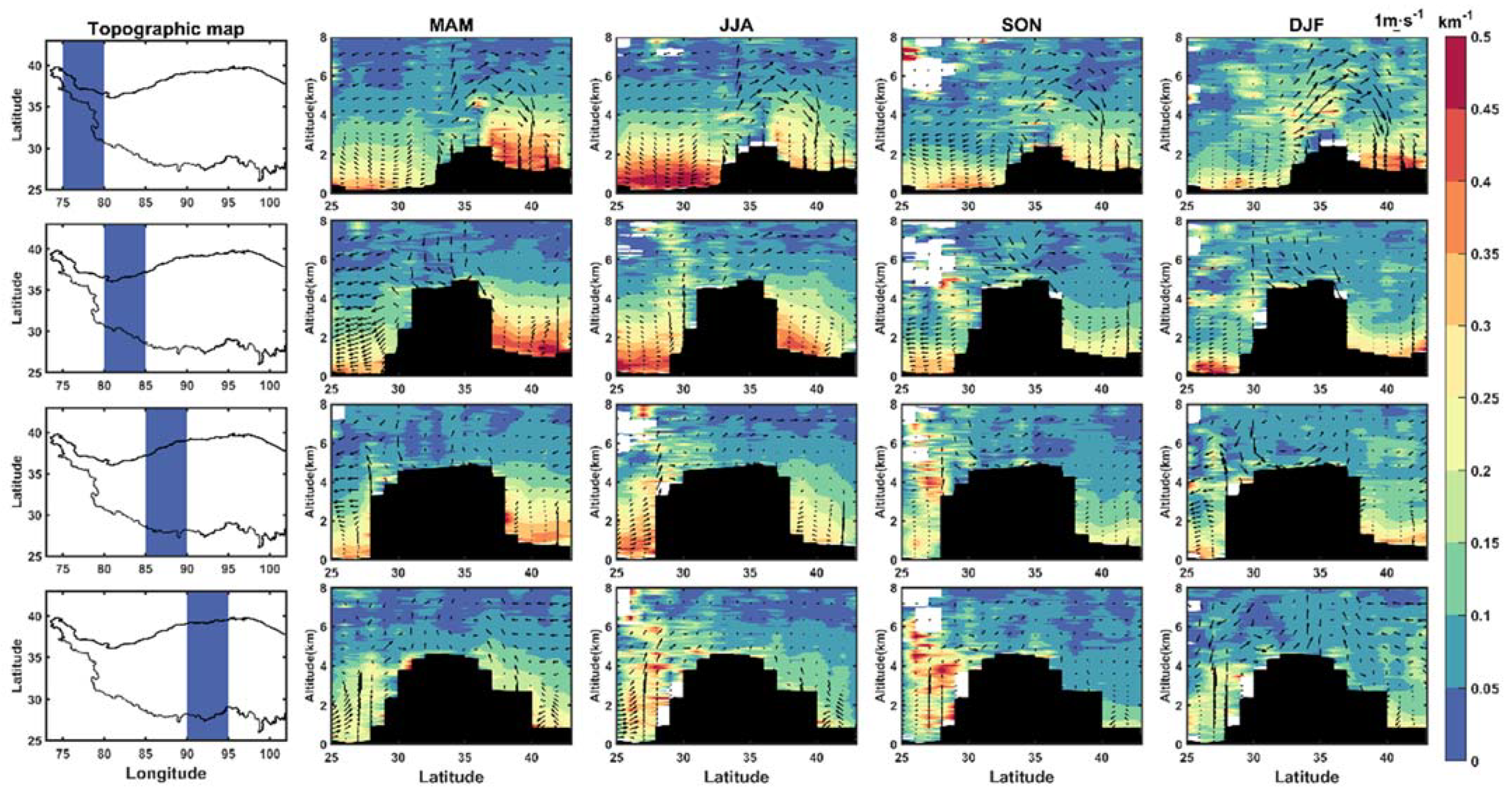
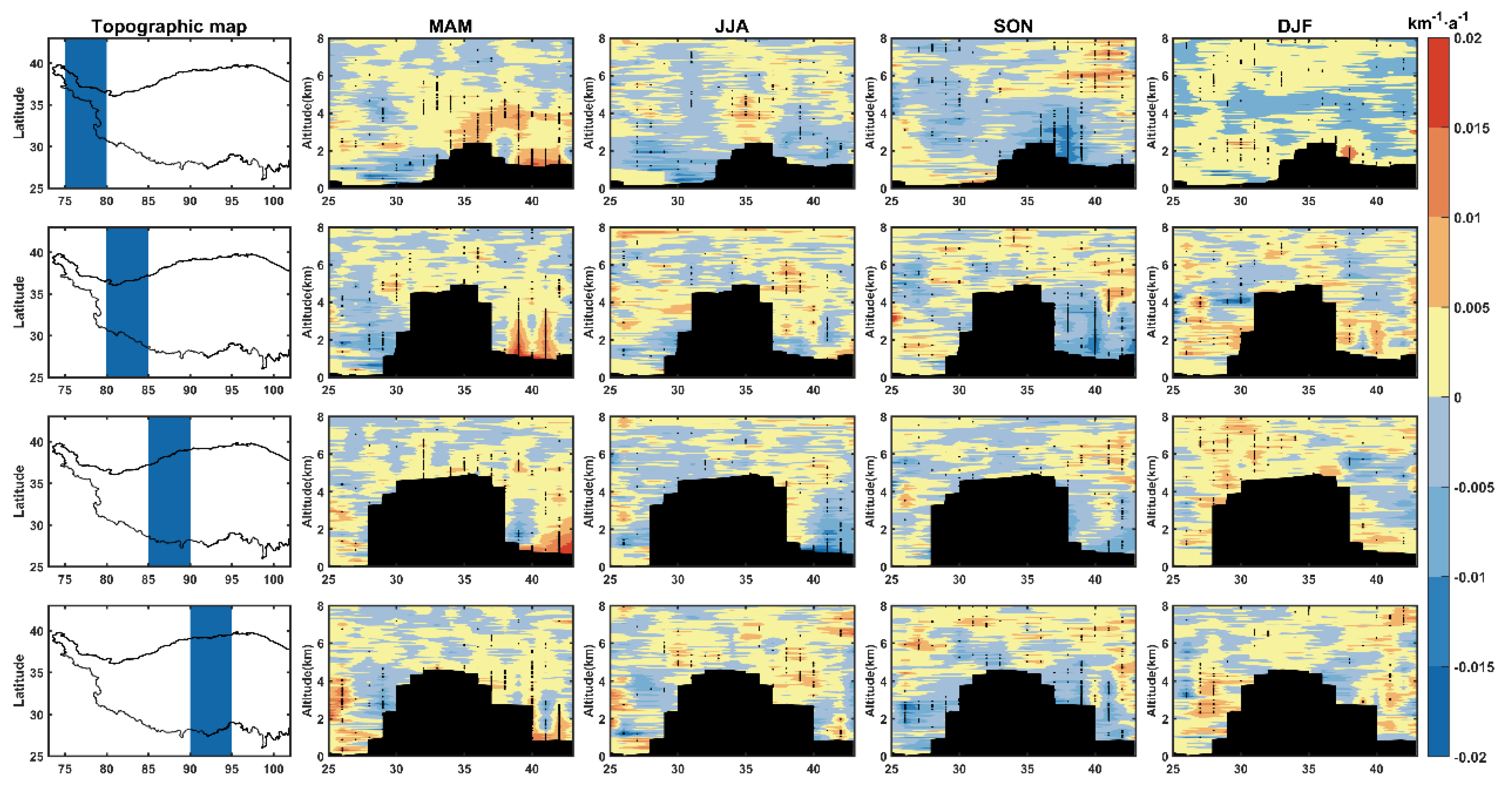
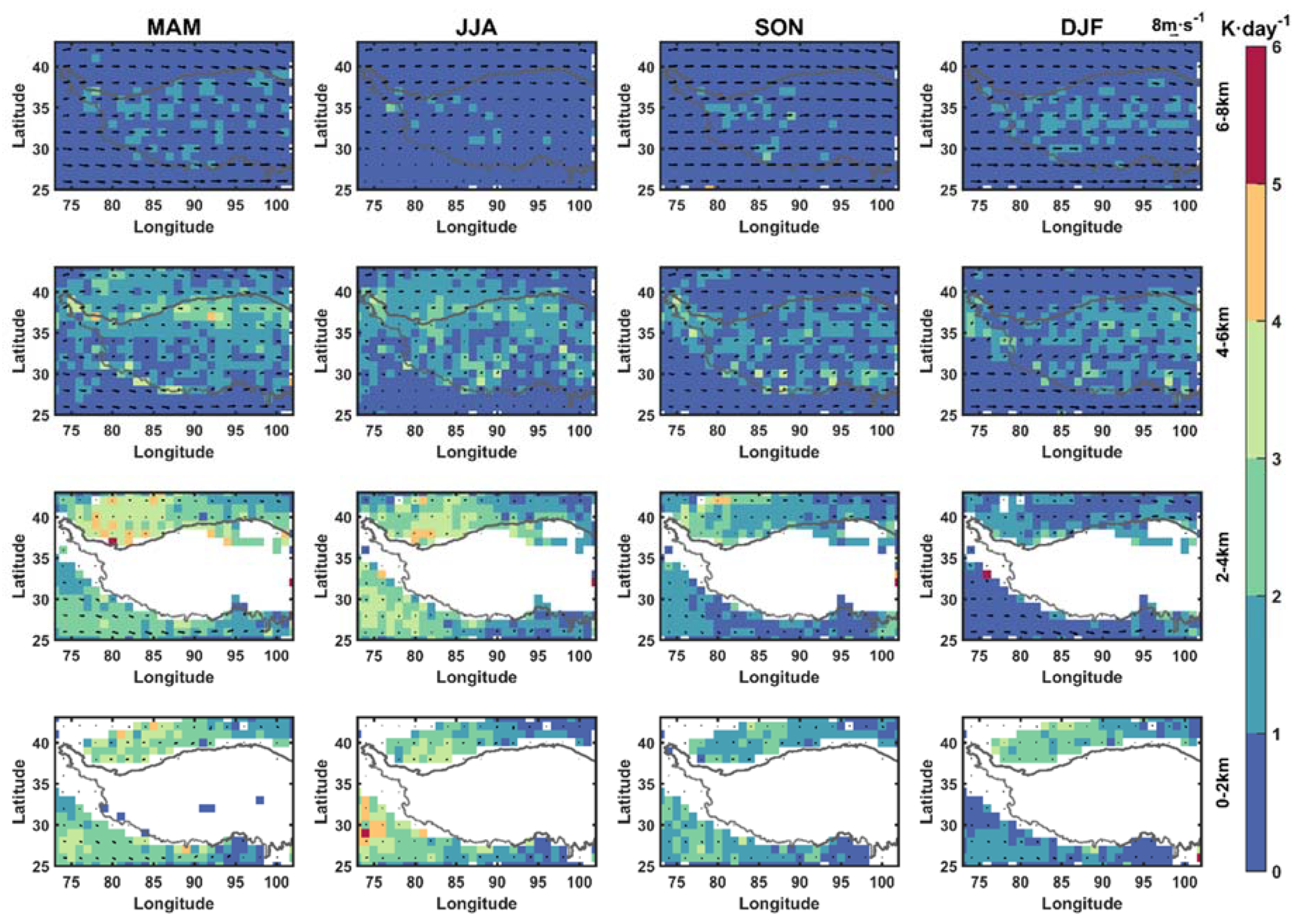
3.2. Vertical Distributions of Dust
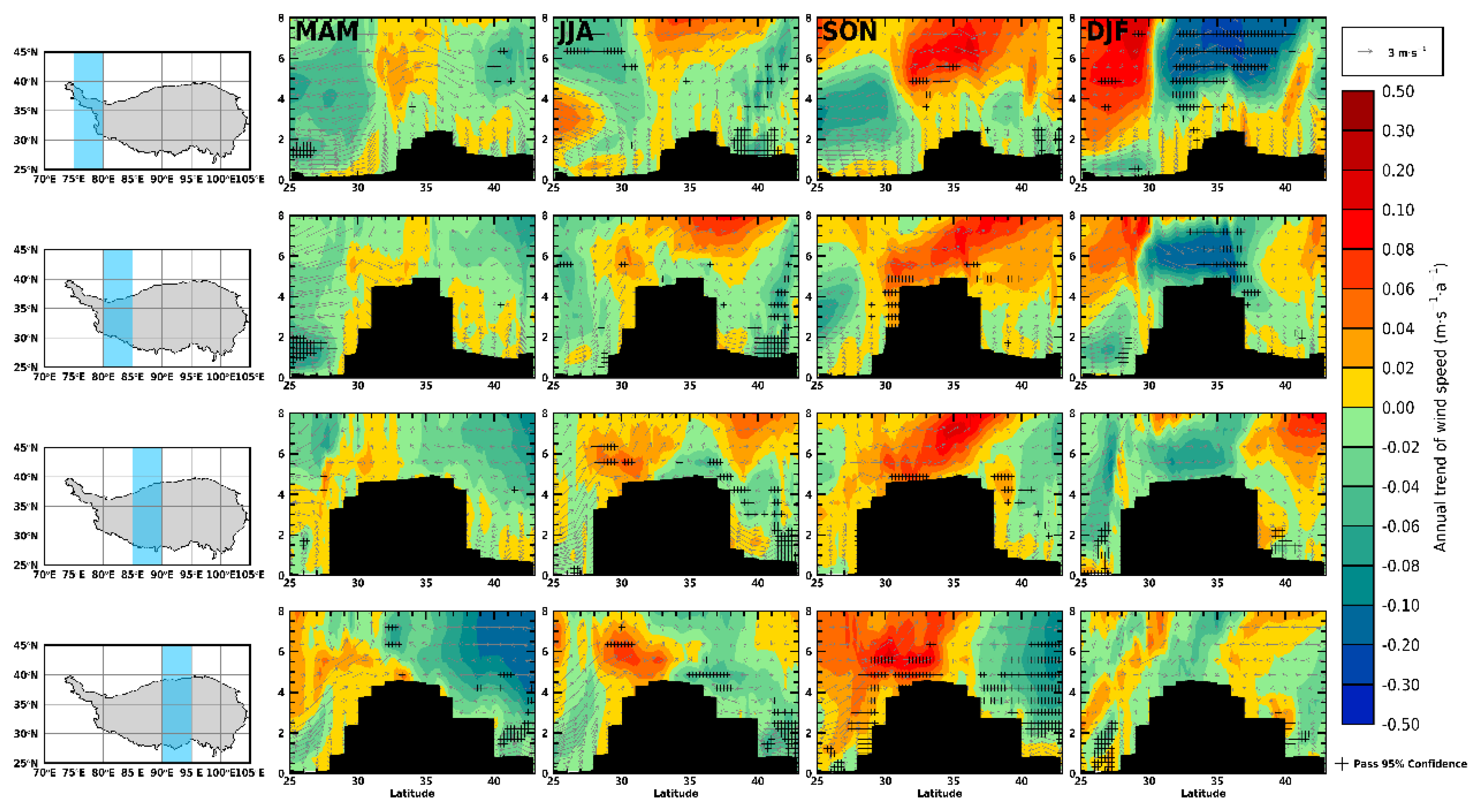
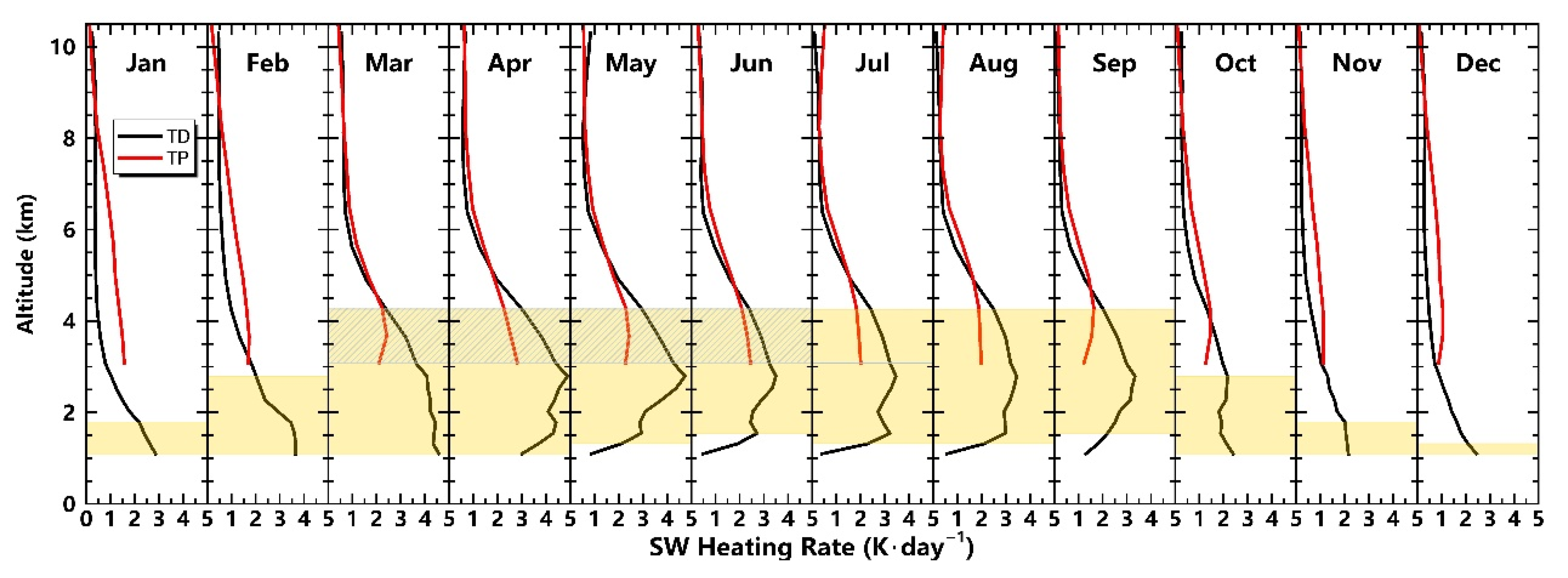
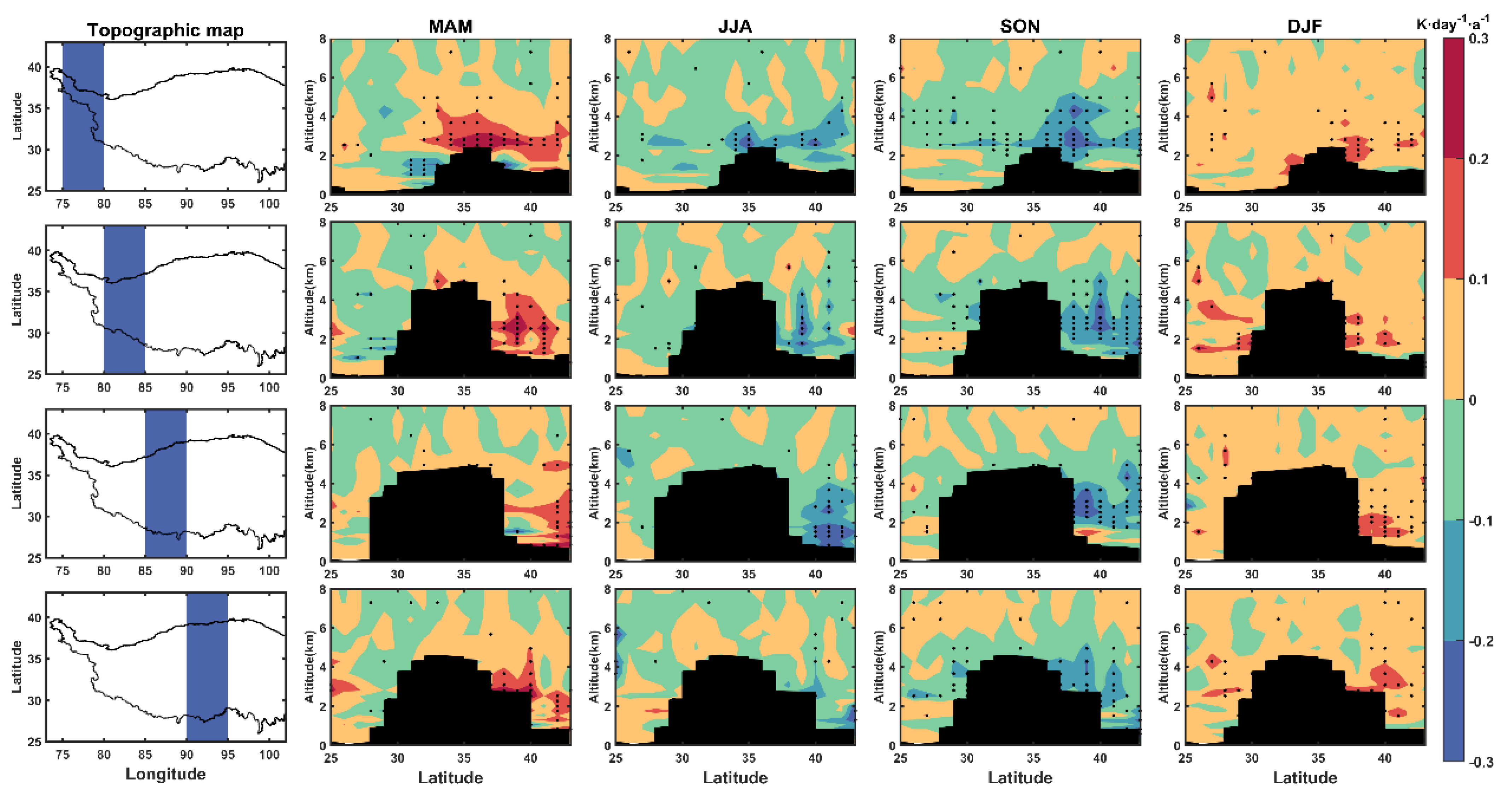
3.3. Dust Heating Rate
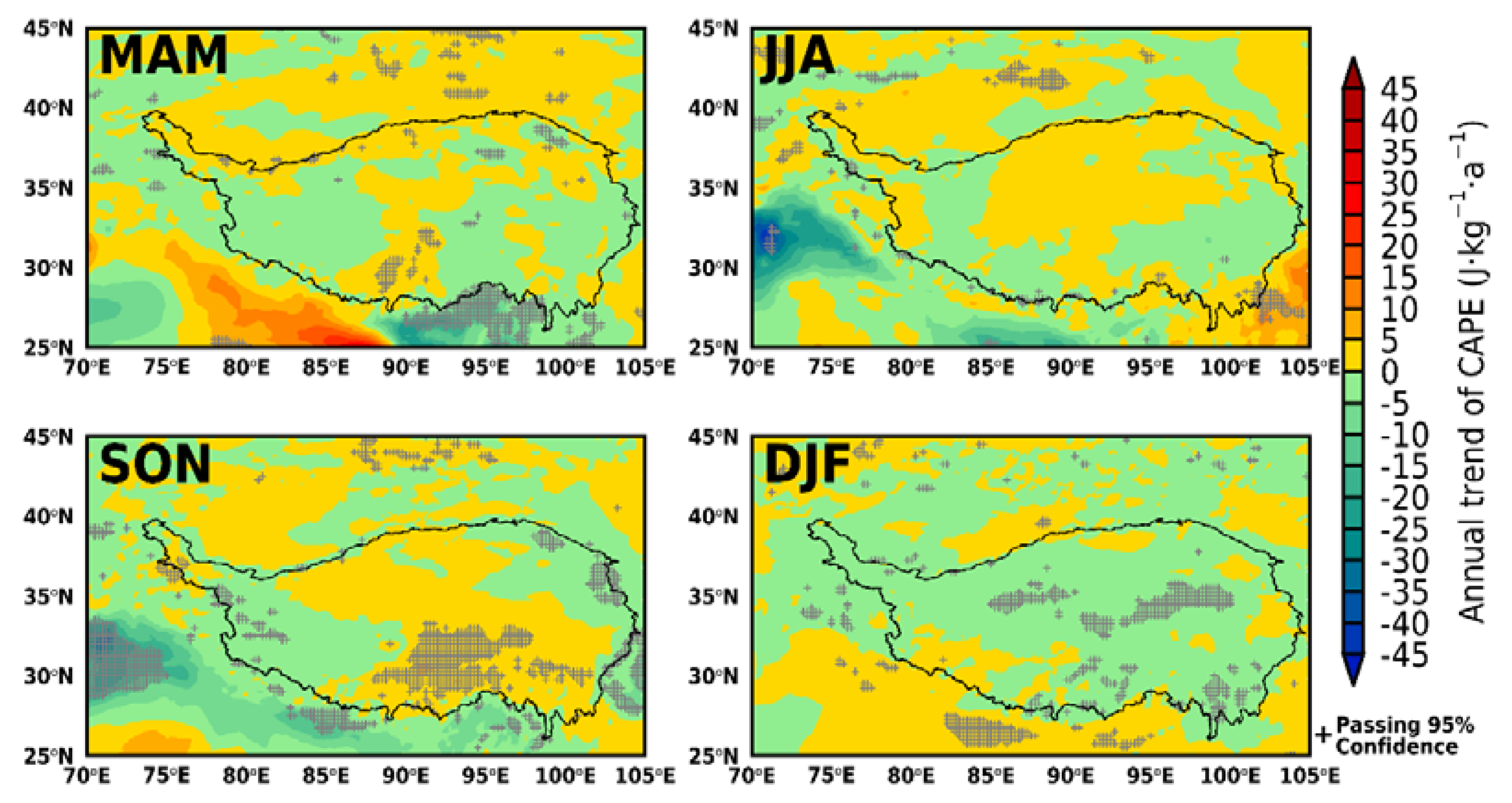
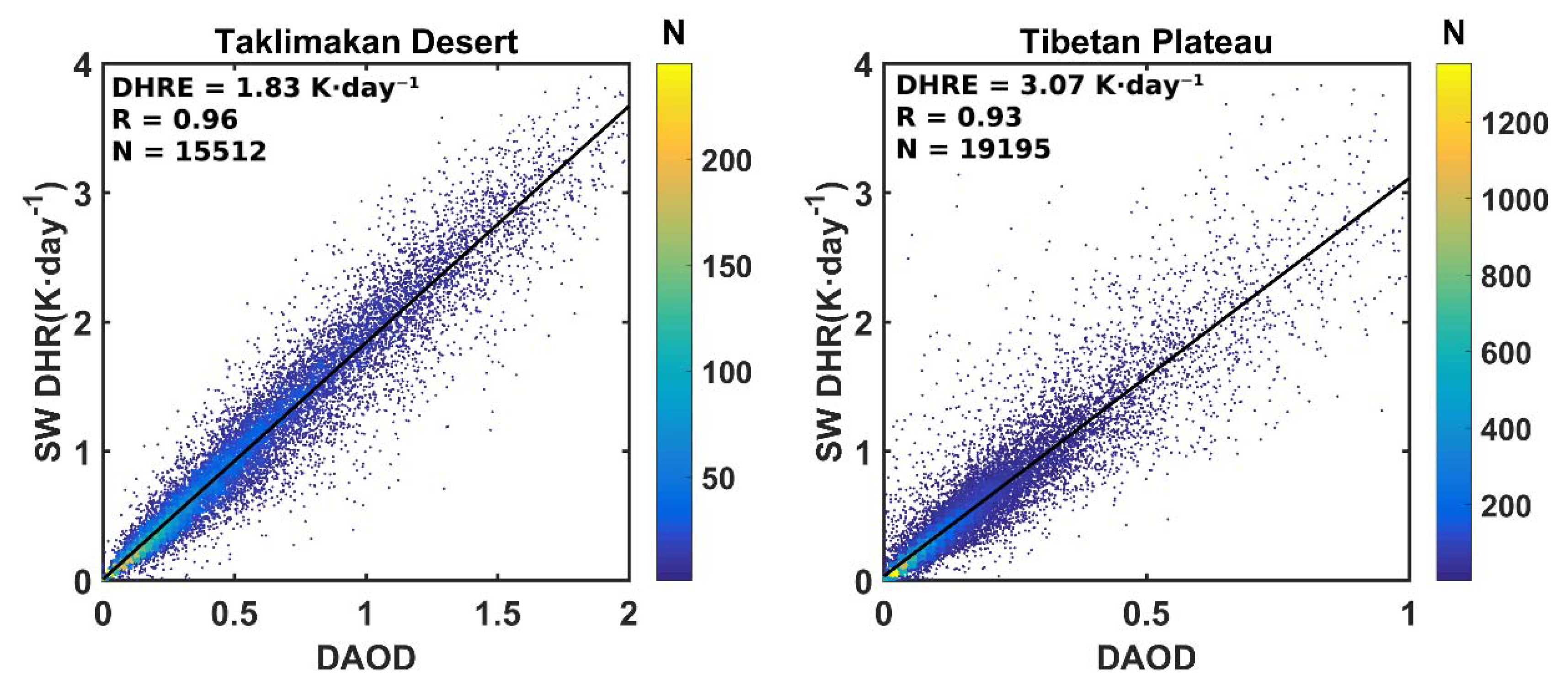
3.4. Dust Heating Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Mao, J.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Q. Current progresses in study of impacts of the Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer climate. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2006, 20, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Lu, C.; Shi, X.; Gao, S. World water tower: An atmospheric perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s Water Tower: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Jianping, H.; Mingxia, J.; Kaz, H. Variability of East Asia dust events and their long-term trend. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; You, Q.; Flügel, W.-A.; Pepin, N.; Yao, T. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Su, J.; Tang, Q.; Minnis, P.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Q. Taklimakan dust aerosol radiative heating derived from CALIPSO observations using the Fu-Liou radiation model with CERES constraints. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Duan, K.; Kang, S.; Shi, P.; Ji, Z. Potential feedback between aerosols and meteorological conditions in a heavy pollution event over the Tibetan Plateau and Indo-Gangetic Plain. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 2901–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, D.; Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X. Influence of Dynamic and Thermal Forcing on the Meridional Transport of Taklimakan Desert Dust in Spring and Summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-C.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Physics 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Minnis, P.; Yi, Y.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ayers, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D. Summer dust aerosols detected from CALIPSO over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L18805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Gan, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, J. Assessment of dominating aerosol properties and their long-term trend in the pan-third pole region: A study with 10-year multi-sensor measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 239, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sato, Y.; Jia, R.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J.; Nakajima, T. Modeling study on the transport of summer dust and anthropogenic aerosols over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12581–12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X. Ten-year global particulate mass concentration derived from space-borne CALIPSO lidar observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.M.; Kim, K.M. Observational relationships between aerosol and Asian monsoon rainfall, and circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L21810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, J.; Quaas, J. How can aerosols affect the Asian summer monsoon? Assessment during three consecutive pre-monsoon seasons from CALIPSO satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4673–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, W.-S. Enhanced surface warming and accelerated snow melt in the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau induced by absorbing aerosols. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 025204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, P.; Ramaswamy, V.; Artaxo, P.; Berntsen, T.; Betts, R.; Fahey, D.; Haywood, J.; Lean, J.; Lowe, D.; Myhre, G.; et al. Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in Radiative Forcing. In The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 131–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Tan, S. The Radiative and Climatic Effects of Atmospheric Aerosols. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 32, 826–840. [Google Scholar]
- Choobari, O.A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Sturman, A. The global distribution of mineral dust and its impacts on the climate system: A review. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claquin, T.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.; Boucher, O. Uncertainties in assessing radiative forcing by mineral dust. Tellus B 1998, 50, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Ramanathan, V.; Li, F.; Kim, D. Dust plumes over the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic oceans: Climatology and radiative impact. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D16208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComiskey, A.; Schwartz, S.E.; Schmid, B.; Guan, H.; Lewis, E.R.; Ricchiazzi, P.; Ogren, J.A. Direct aerosol forcing: Calculation from observables and sensitivities to inputs. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D09202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycki, C.M.; Bond, T.C. How much can the vertical distribution of black carbon affect its global direct radiative forcing? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L20807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Kotamarthi, V.R.; Coulter, R.; Zhao, C.; Cadeddu, M. Radiative and thermodynamic responses to aerosol extinction profiles during the pre-monsoon month over South Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuolo, M.R.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.; Takemura, T. A new method for evaluating the impact of vertical distribution on aerosol radiative forcing in general circulation models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Winker, D.; Vaughan, M.; Noel, V.; Bissonnette, L.; Roy, G.; McGill, M. A simple relation between depolarization and multiple scattering of water clouds and its application for lidar calibration. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 1809–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.; Vaughan, M.; Hunt, B. The CALIPSO Mission and Initial Results from CALIOP; SPIE6409: Goa, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Konsta, D.; Binietoglou, I.; Gkikas, A.; Solomos, S.; Marinou, E.; Proestakis, E.; Basart, S.; Garcia-Pando, C.P.; El-Askary, H.; Amiridis, V. Evaluation of the BSC-DREAM8b regional dust model using the 3D LIVAS-CALIPSO product. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 195, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Yang, B. Modeling the transport and radiative forcing of Taklimakan dust over the Tibetan Plateau: A case study in the summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Ding, A.; Fu, C. Dust-induced radiative feedbacks in north China: A dust storm episode modeling study using WRF-Chem. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over east Asian arid and semiarid regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Koren, I.; Rudich, Y. Effect of aerosol vertical distribution on aerosol-radiation interaction. A theoretical prospect. Heliyon 2015, 1, e00036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; di Sarra, A.; Di Iorio, T.; Fiocco, G. Influence of the vertical profile of Saharan dust on the visible direct radiative forcing. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2005, 93, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Schmid, B.; Bucholtz, A.; Bergstrom, R. Sensitivity of shortwave radiative flux density, forcing, and heating rate to the aerosol vertical profile. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D06209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.R.; Tafuro, A.M.; Kinne, S. Dust layer effects on the atmospheric radiative budget and heating rate profiles. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.T.; Heese, B.; McFarlane, S.A.; Chazette, P.; Jones, A.; Bellouin, N. Vertical distribution and radiative effects of mineral dust and biomass burning aerosol over West Africa during DABEX. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D00C12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.B.; Gu, Y.; Liou, K.N.; Meland, B. Dust vertical profile impact on global radiative forcing estimation using a coupled chemical-transport–radiative-transfer model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7097–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul Ricchiazzi, S.Y.; Gautier, C.; Sowle, D. SBDART: A Research and Teaching Software Tool for Plane-Parallel Radiative Transfer in the Earth’s Atmosphere. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Vaughan, M.; Liu, Z.; Lin, B.; Yang, P.; Littner, D.; Hunt, B.; Kuehn, R.; Huang, J.; Wu, D. The depolarization-attenuated backscatter relation: CALIPSO lidar measurements vs. theory. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 5327–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO mission and CALIOP data processing algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Jeong, M.-J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z. CALIPSO inferred most probable heights of global dust and smoke layers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5085–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackett, J.L.; Winker, D.M.; Getzewich, B.J.; Vaughan, M.A.; Young, S.A.; Kar, J. CALIPSO lidar level 3 aerosol profile product: Version 3 algorithm design. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4129–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds: The Software Package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Jian, B.; Huang, Z.; Yan, H. Climatology of Dust-Forced Radiative Heating Over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Surroundings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lee, K.-H.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Hao, W.-M. First observation-based estimates of cloud-free aerosol radiative forcing across China. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00K18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Jin, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B. Modeling dust sources, transport, and radiative effects at different altitudes over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1507–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Xie, L. Distribution and transport characteristics of dust aerosol over Tibetan Plateau and Taklimakan Desert in China using MERRA-2 and CALIPSO data. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Kumar, A.; Pratap, V.; Singh, A. Assessment of two intense dust storm characteristics over Indo–Gangetic basin and their radiative impacts: A case study. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; You, C. Tibetan Plateau Impacts on Global Dust Transport in the Upper Troposphere. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4745–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, K.N. An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Lin, C.; Gui, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y. Characterization of dust activation and their prevailing transport over East Asia based on multi-satellite observations. Atmos. Res. 2021, 265, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Chen, G.; Liu, T.; Lin, W.; Tu, J. Characterizing the transport pathways of Asian dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D17311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, K.; Evan, A.; Ralph, F. Evaluating the meteorological conditions associated with dusty atmospheric rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD035403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Luo, T.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, Z. Characteristics of Optical Properties and Heating Rates of Dust Aerosol over Taklimakan Desert and Tibetan Plateau in China Based on CALIPSO and SBDART. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030607
Xu X, Pan S, Luo T, Yang Y, Xiong Z. Characteristics of Optical Properties and Heating Rates of Dust Aerosol over Taklimakan Desert and Tibetan Plateau in China Based on CALIPSO and SBDART. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(3):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030607
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaofeng, Shixian Pan, Tianyang Luo, Yudi Yang, and Zixu Xiong. 2023. "Characteristics of Optical Properties and Heating Rates of Dust Aerosol over Taklimakan Desert and Tibetan Plateau in China Based on CALIPSO and SBDART" Remote Sensing 15, no. 3: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030607
APA StyleXu, X., Pan, S., Luo, T., Yang, Y., & Xiong, Z. (2023). Characteristics of Optical Properties and Heating Rates of Dust Aerosol over Taklimakan Desert and Tibetan Plateau in China Based on CALIPSO and SBDART. Remote Sensing, 15(3), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15030607



