Effect of ENSO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the WACCM4 Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Observational Data
2.2. WACCM 4 Numerical-Simulation Experiment
2.3. Methods
3. Connection between ENSO and the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau
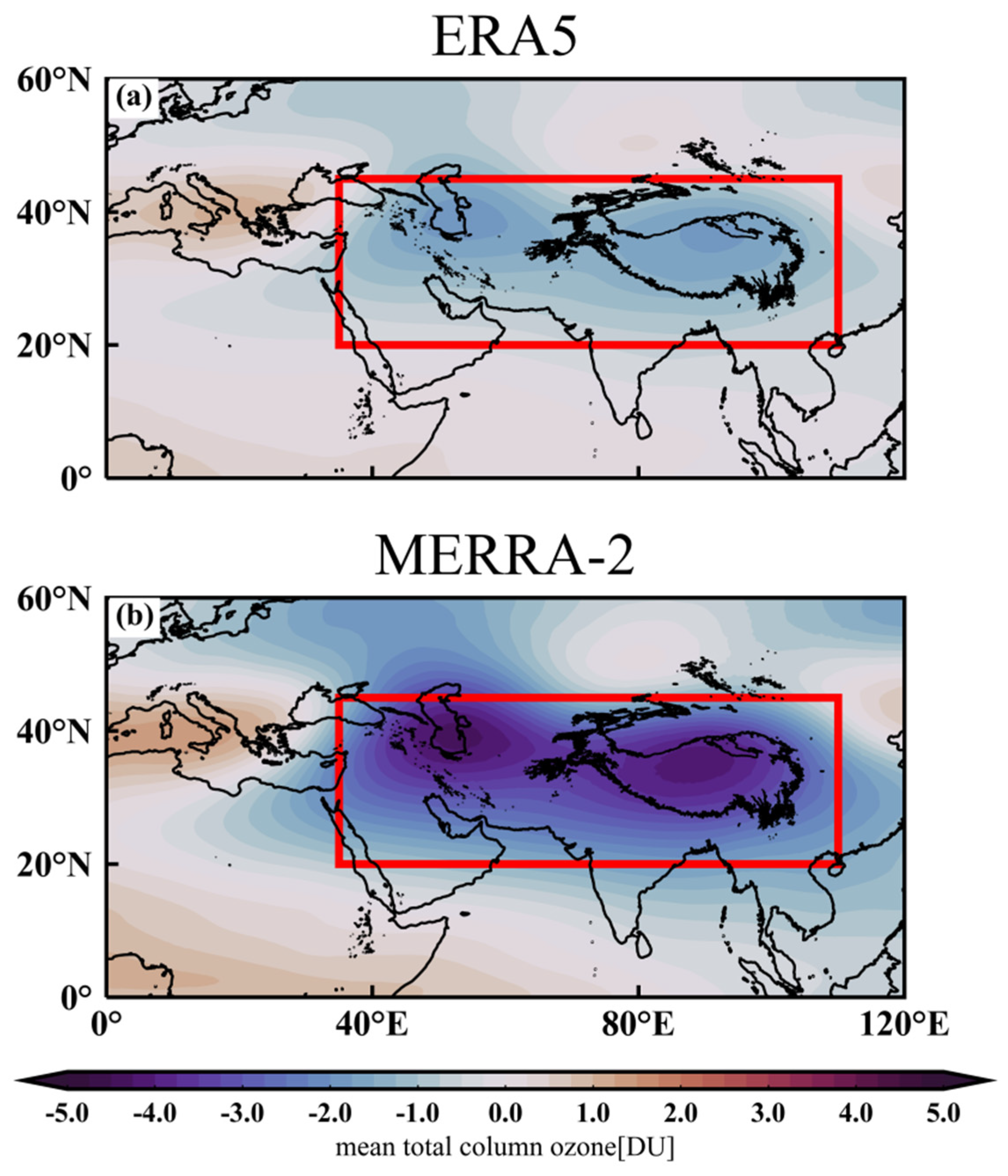
3.1. Spatiotemporal-Distribution Characteristics of the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau
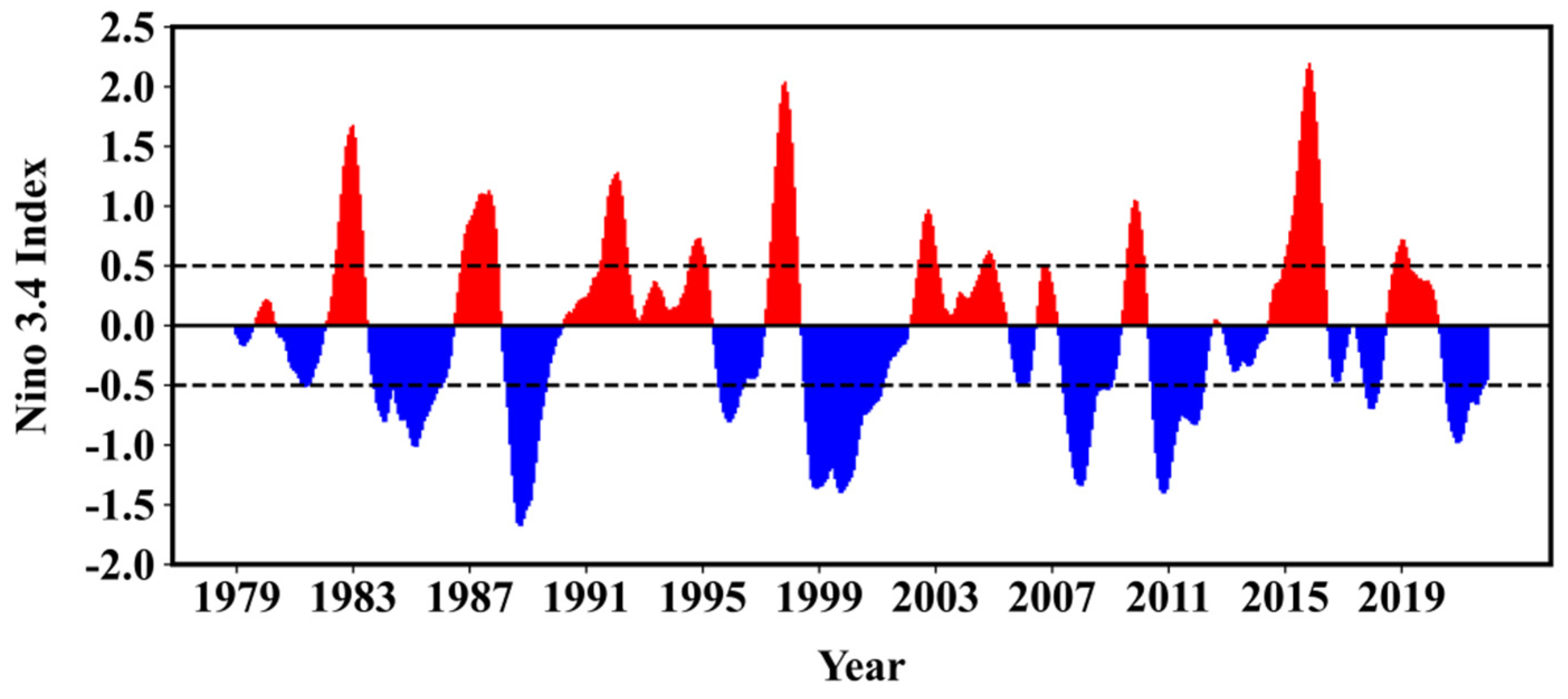
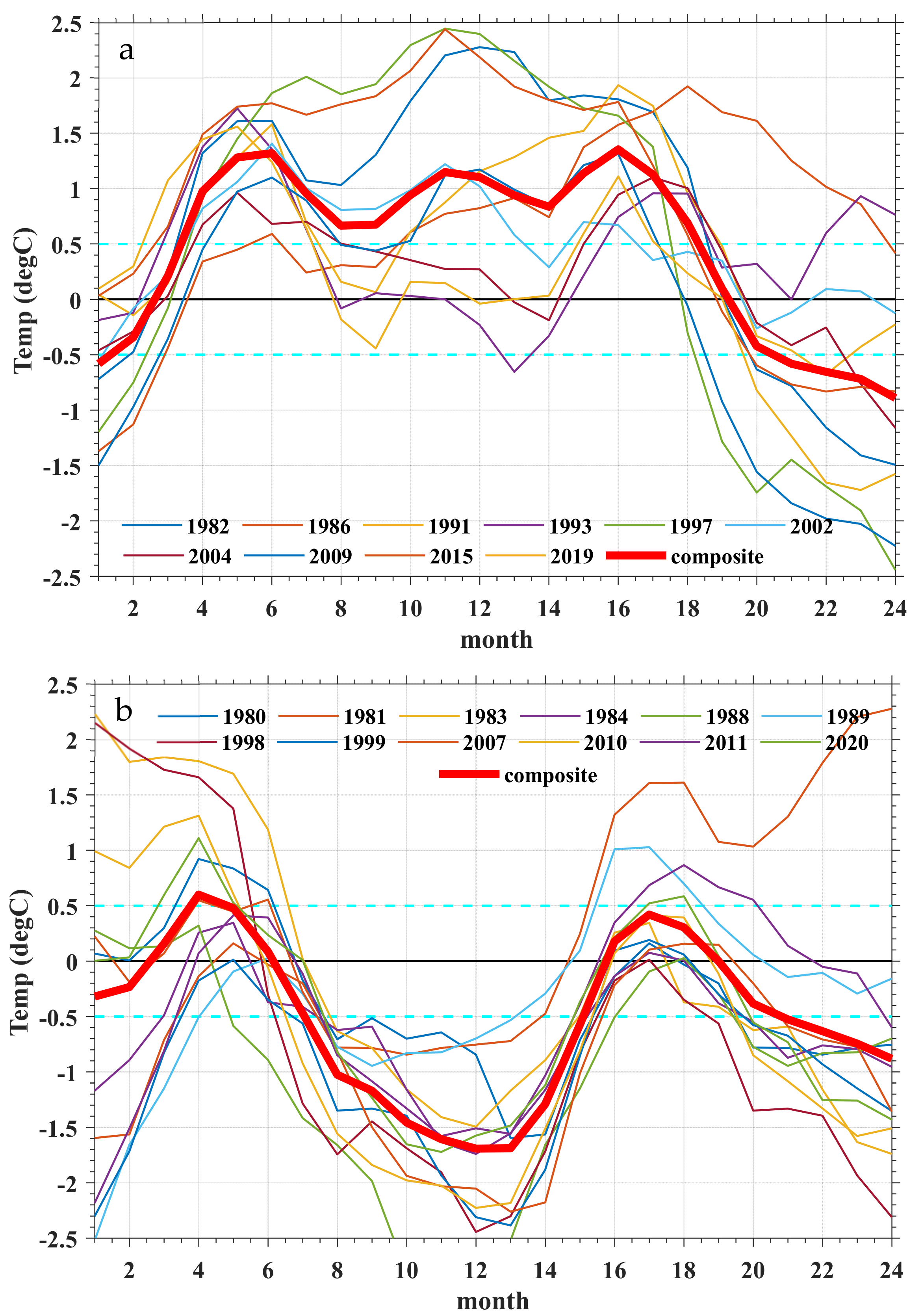
3.2. Relationship of ENSO with the Ozone over the Tibetan Plateau
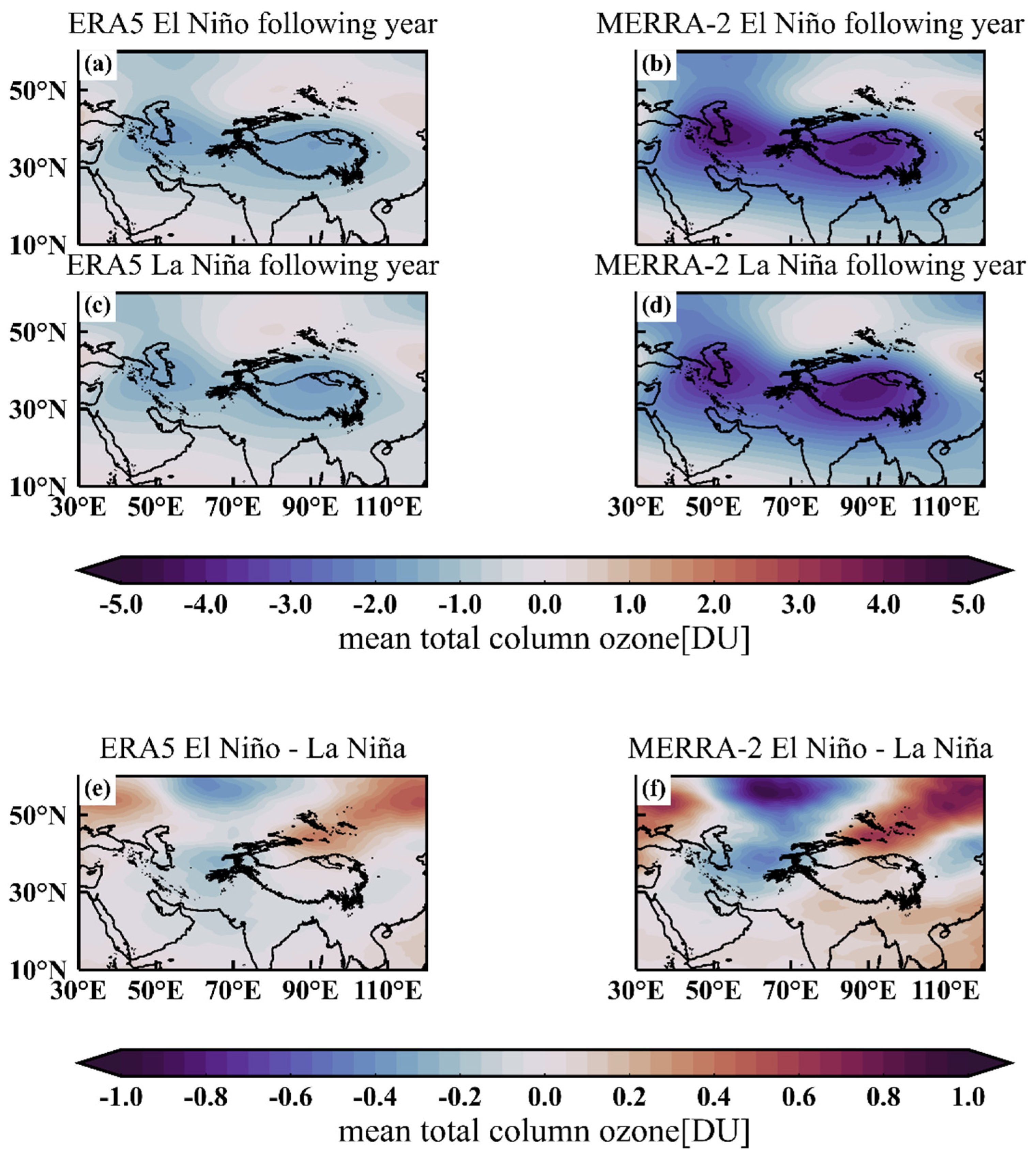
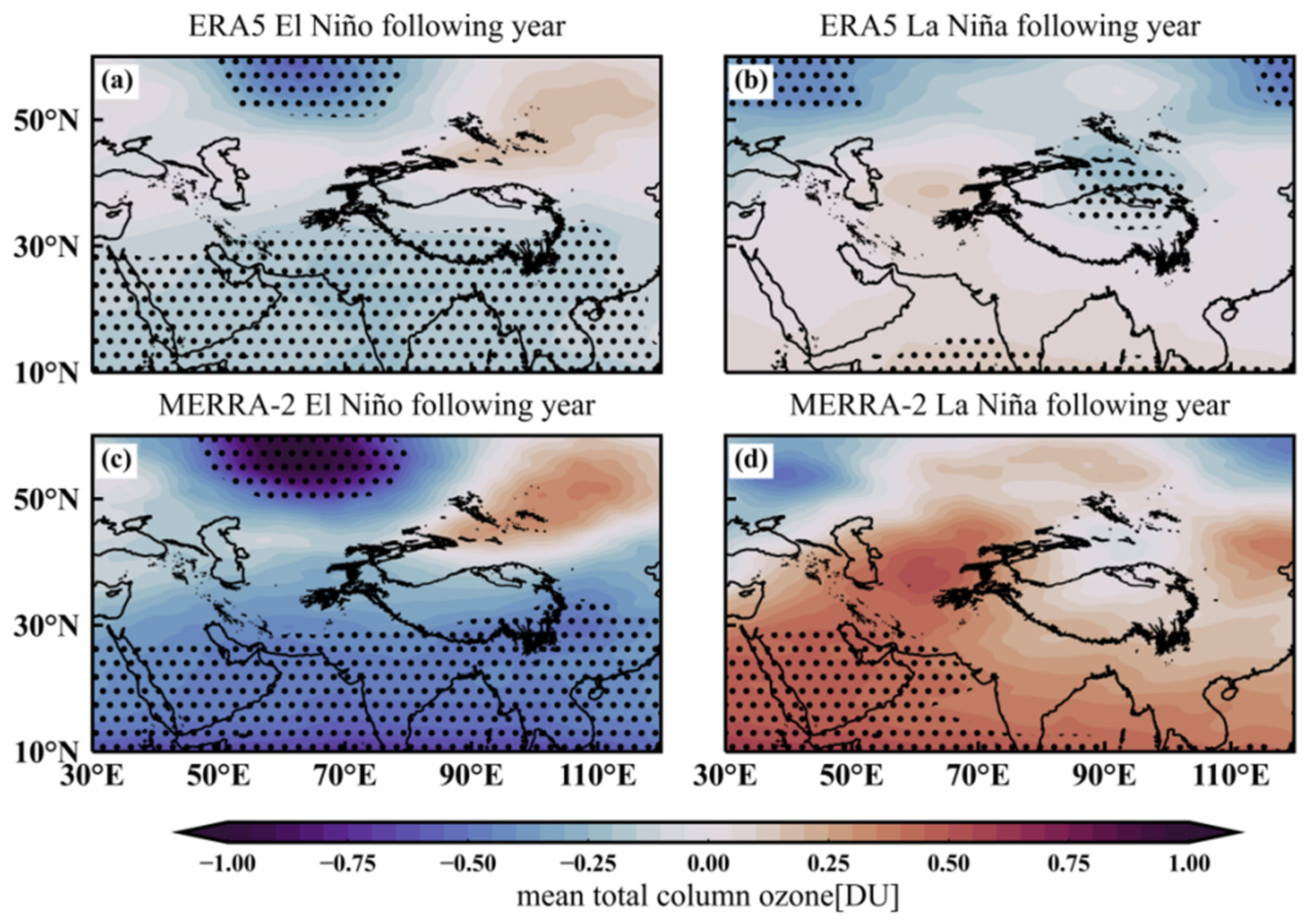
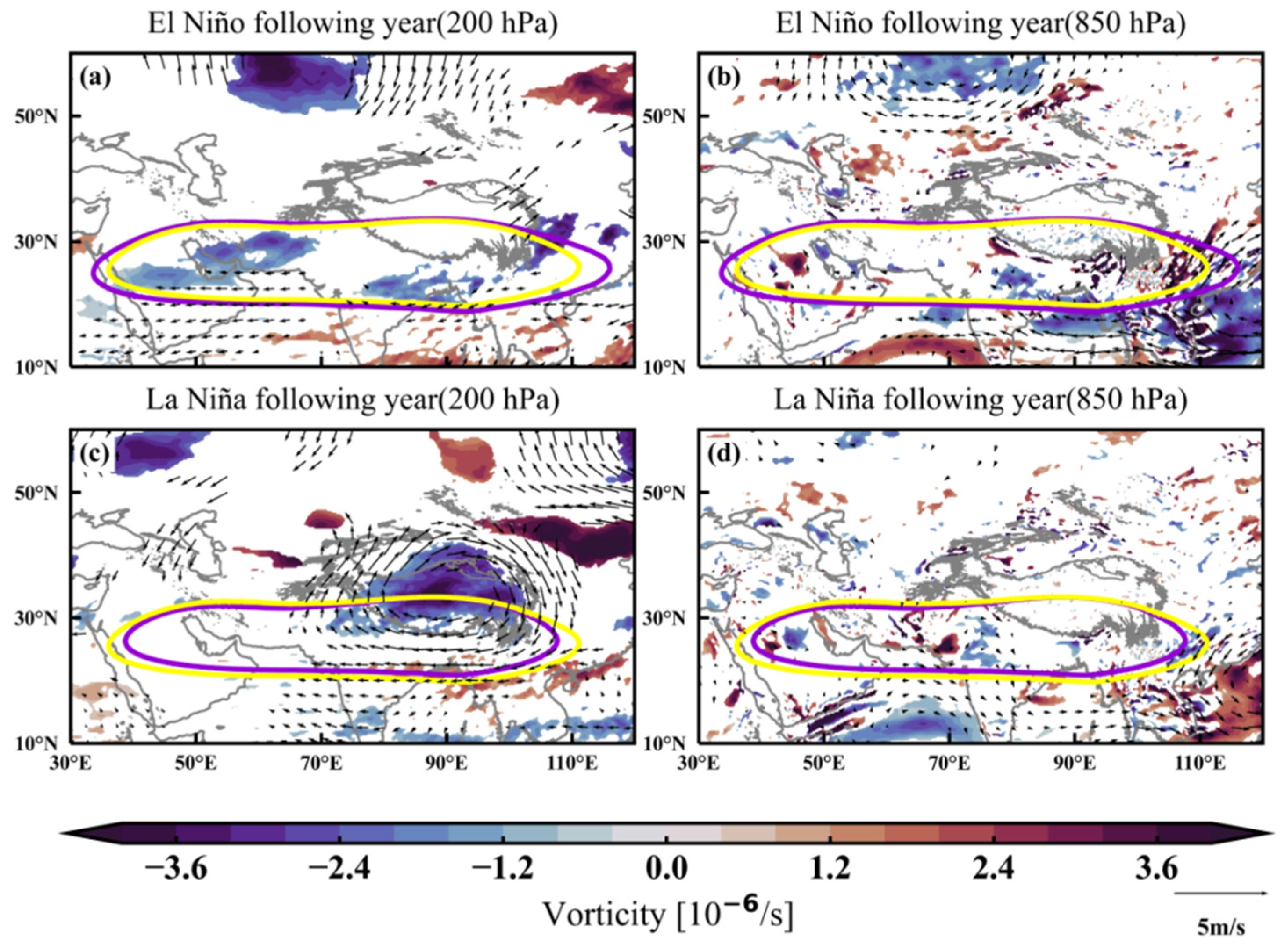
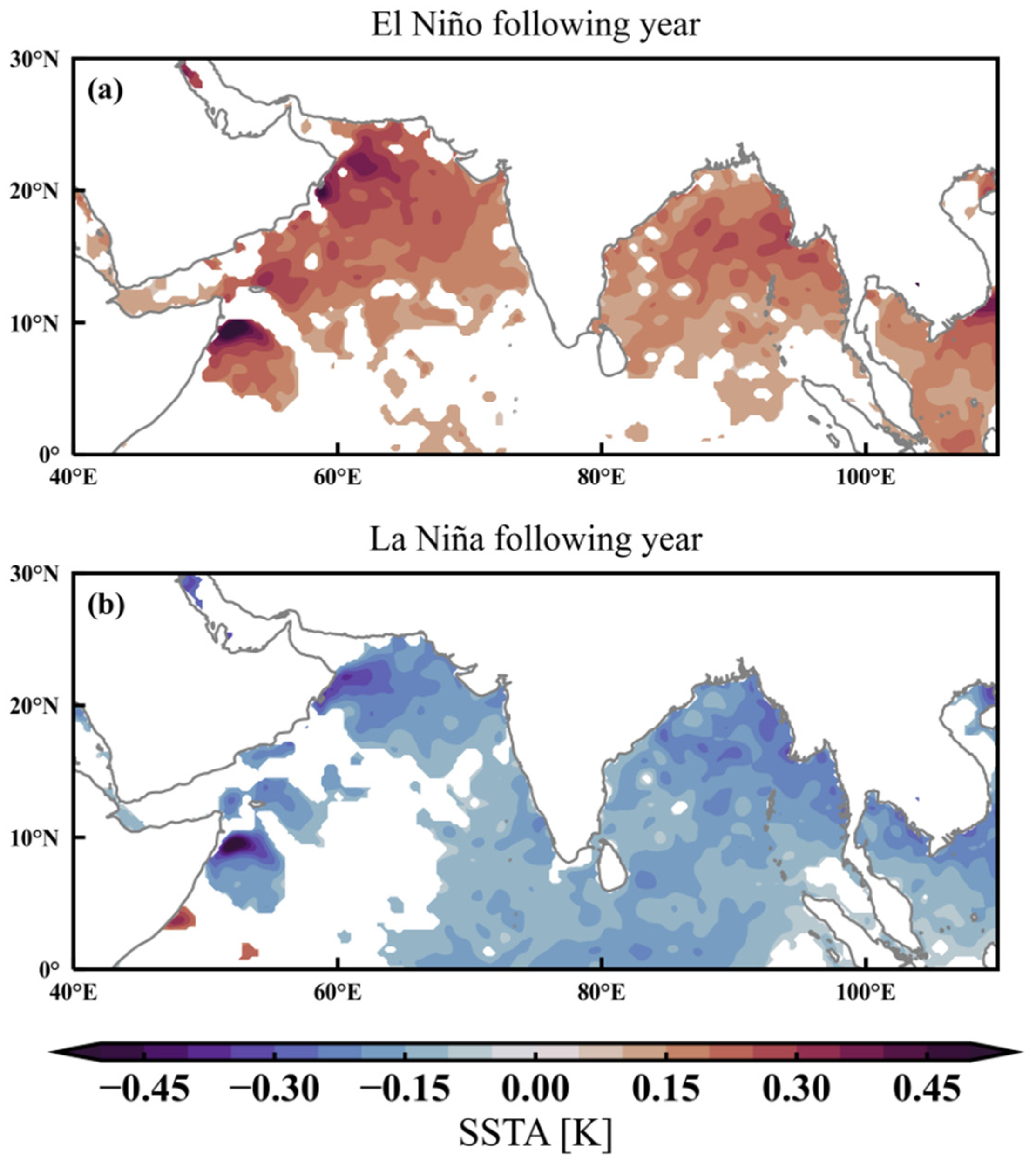
4. Analysis of the Effect of ENSO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau
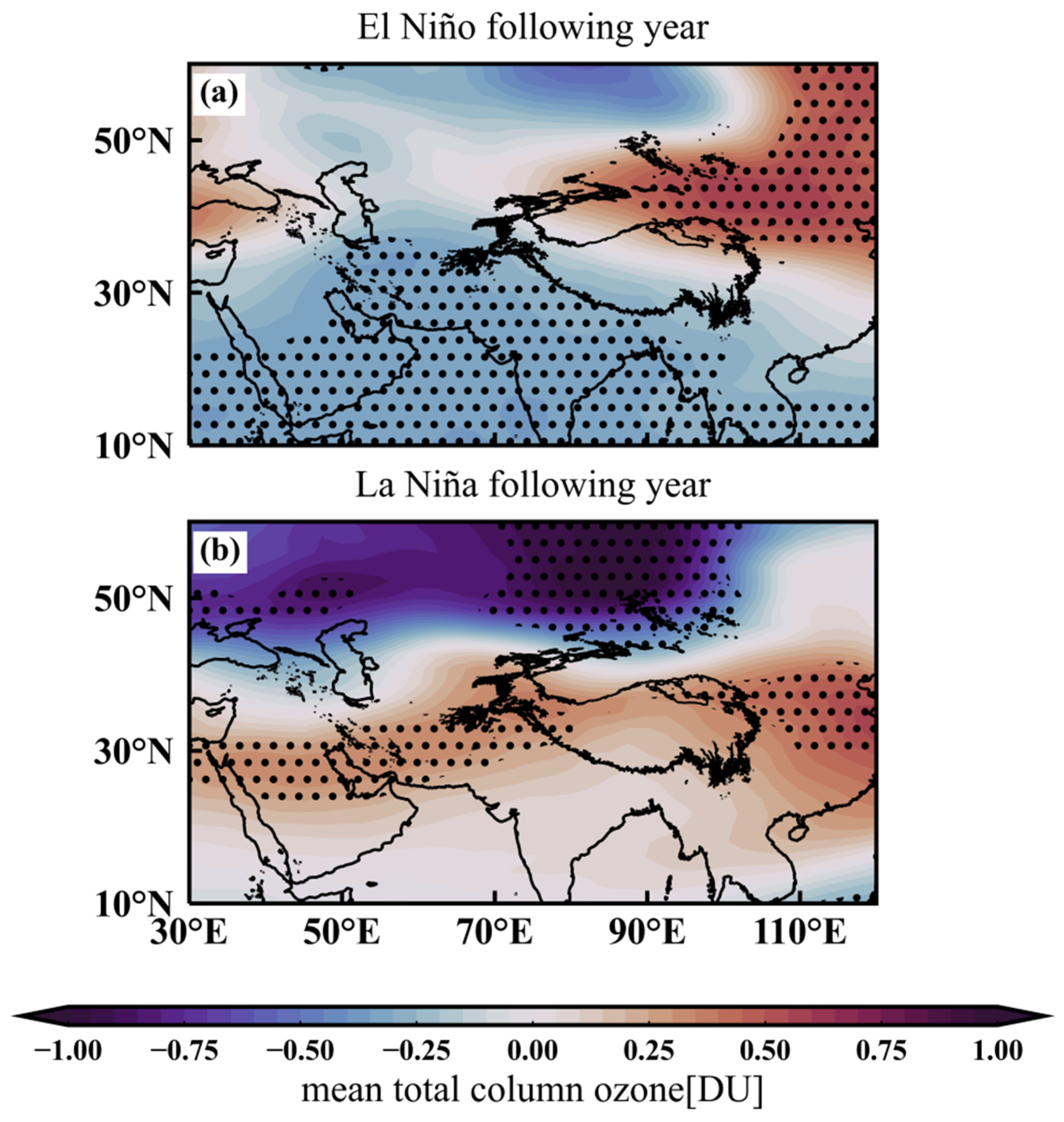
5. Simulated ENSO Effects on the Ozone over the Tibetan Plateau
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de F. Forster, P.M.; Shine, K.P. Radiative forcing and temperature trends from stratospheric ozone changes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 10841–10855. [Google Scholar]
- Haigh, J.D. The role of stratospheric ozone in modulating the solar radiative forcing of climate. Nature 1994, 370, 544–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidston, J.; Scaife, A.A.; Hardiman, S.C.; Mitchell, D.M.; Butchart, N.; Baldwin, M.P.; Gray, L.J. Stratospheric influence on tropospheric jet streams, storm tracks and surface weather. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Cobb, J.B. Coherent variations of monthly mean total ozone and lower stratospheric temperature. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 5433–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Tian, W.; Chipperfield, M.P. Radiative effect of ozone change on stratosphere-troposphere exchange. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D00B09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.G.; Holton, J.R.; Leovy, C.B. Middle Atmosphere Dynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bian, J.; Zhao, C. Stratospheric ozone loss-induced cloud effects lead to less surface ultraviolet radiation over the Siberian Arctic in spring. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 084057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; He, M.; Feng, Y. Observations of Inertia Gravity Waves in the Western Pacific and Their Characteristic in the 2015/2016 Quasi-biennial Oscillation Disruption. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD037208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; Tian, T. Spectral Analysis of Gravity Waves in the Martian Thermosphere during Low Solar Activity Based on MAVEN/NGIMS Observations. Astrophys. J. 2022, 938, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, Q.; Sheng, Z.; He, M.; He, Y.; Zuo, X.; He, Z.; Qin, Z.; Wu, G. Observation based climatology Martian atmospheric waves perturbation Datasets. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, R.; Guan, Z.; Yang, Q.; Hu, M. Precursory Signals in the Stratospheric Meridional Mass Circulation for Mid-Latitude Cold Air Outbreak Events of High and Low Sub-Seasonal Predictability. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD036814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; Ge, W.; Zhao, X.; He, M. Atmospheric Disturbance Characteristics in the Lower-middle Stratosphere Inferred from Observations by the Round-Trip Intelligent Sounding System (RTISS) in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, X.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; He, M. Statistical Characteristics of Inertial Gravity Waves Over a Tropical Station in the Western Pacific Based on High-Resolution GPS Radiosonde Soundings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD034719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, J.; Cai, W. Characteristics and mechanism of troposphere-to-stratosphere transport dominated by a mesoscale convective complex in Southwest China. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 45, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jin, X.; Shi, C.; Chen, D. The Troposphere-to-Stratosphere Transport Caused by a Rossby Wave Breaking Event over the Tibetan Plateau in Mid-March 2006. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Polvani, L.; Wu, F.; Kinnison, D.E.; Zou, C.Z.; Mears, C. Troposphere-stratosphere temperature trends derived from satellite data compared with ensemble simulations from WACCM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 9651–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y. On the climate impacts of upper tropospheric and lower stratospheric ozone. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Xie, F.; Sang, W.; Guo, D.; Chipperfield, M.; Feng, W.; Hu, D. Zonally asymmetric trends of winter total column ozone in the northern middle latitudes. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 4483–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monforte, P.; Ragusa, M.A. Temperature trend analysis and investigation on a case of variability climate. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Bateni, S.M.; Jun, C. Global surface temperature: A new insight. Climate 2021, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.A.; Bladé, I.; Newman, M.; Lanzante, J.R.; Lau, N.-C.; Scott, J.D. The atmospheric bridge: The influence of ENSO teleconnections on air–sea interaction over the global oceans. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2205–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Yang, S. Lessened response of boreal winter stratospheric polar vortex to El Niño in recent decades. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Li, J.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Shu, J. The impacts of two types of El Niño on global ozone variations in the last three decades. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Garcia, R.R.; Calvo, N.; Marsh, D. ENSO influence on zonal mean temperature and ozone in the tropical lower stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L15822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerefos, C.S.; Bais, A.F.; Ziomas, I.C.; Bojkov, R.D. On the relative importance of quasi-biennial oscillation and El Nino/Southern Oscillation in the revised Dobson total ozone records. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 10135–10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, A.; Proffitt, M.; VanZandt, T.; Lamarque, J.F. Modulation of tropospheric ozone by a propagating gravity wave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 26605–26613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Cai, H.; Yi, M.; Guo, J. The impact of the ENSO cycle on the stratospheric aerosol distribution. Chin. J. Geophys. 2011, 54, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Barca, S.; Calvo, N.; Abalos, M. Driving mechanisms for the ENSO impact on stratospheric ozone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2022, 22, 15729–15745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamelin, B.L.; Carvalho, L.; Kayano, M. The combined influence of ENSO and PDO on the spring UTLS ozone variability in South America. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1539–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, M. Independent and joint influences of eastern Pacific El Niño–southern oscillation and quasi-biennial oscillation on Northern Hemispheric stratospheric ozone. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 5289–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, F.; Wang, F. The influence of ENSO on northern midlatitude ozone during the winter to spring transition. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 4774–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Luo, C.; Li, W.; Shi, J. Variation of total ozone over China and low value center over Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1995, 15, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; King, G.; Chen, H.; Qi, D.; Lu, D.; Zhou, X. The tiny ozone hole appeared over the Tibetan Plateau in December 2003. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 606–609. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, P. The dynamic effects of the South Asian high on the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 70, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Yan, R.; Chen, H.; Lü, D.; Massie, S.T. Formation of the summertime ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau: The Asian summer monsoon and air column variations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Su, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Z. Evaluation of the trend uncertainty in summer ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau in three reanalysis datasets. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; He, J. Mechanism of formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau in summer—Transport and chemical process of ozone. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, X. A possible effect of heterogeneous reactions on the formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2010, 68, 836–846. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Feng, W.; Dhomse, S.S.; Pope, R.J.; Li, F.; Guo, D. Analysis and attribution of total column ozone changes over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8627–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Chongping, J.; Libo, Z.; Wei, W.; Yongxiao, J. ENSO signal in total ozone over Tibet. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, W.; Xie, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, J.; Tian, H. Influence of the El Niño Southern Oscillation on the total ozone column and clear-sky ultraviolet radiation over China. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 120, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, S. lmpact of the ENSO cycle on the stratospheric ozone distribution over east Asia. Plateau Meteorol. 2017, 36, 865–874. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, C.; Fadnavis, S.; Sabin, T. The stratospheric ozone rich cold intrusion during El-Niño over the Indian region: Implication during the Indian summer monsoon. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, E233–E248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Shi, C.; Guo, D.; Xu, J. Attribution of the Principal Components of the Summertime Ozone Valley in the Upper Troposphere and Lower Stratosphere. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Tian, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Lu, J. Increase in Lower Stratospheric Water Vapor in the Past 100 Years Related to Tropical Atlantic Warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hong, J.; Shangguan, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, S. Zonally asymmetric influences of the quasi-biennial oscillation on stratospheric ozone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 13695–13711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.; Marsh, D.; Kinnison, D.; Boville, B.; Sassi, F. Simulation of secular trends in the middle atmosphere, 1950–2003. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D09301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D.R.; Mills, M.J.; Kinnison, D.E.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Calvo, N.; Polvani, L.M. Climate change from 1850 to 2005 simulated in CESM1 (WACCM). J. Clim. 2013, 26, 7372–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Guo, D. Combined Effects of the ENSO and the QBO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, Y. Ozone variations over the tibetan and lranian plateaus and their relationship with the south asia high. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. China 2005, 35, 899–908. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Liu, p.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Impacts of the sea surface temperature anomaly in theindian ocean on the subtropical anticycloneover the western pacific—Two-stage thermal adaptation in the atmosphere. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2000, 58, 513–522. [Google Scholar]

| Trial | Simulation Period | Simulation Process |
|---|---|---|
| E1 | 1955–2005 | The SSTA force was applied at 5°S–5°N, 190°E–120°W. The normal-year SSTAs are given for the first 5 years as the spin-up. Next, the SSTA of the composite El Niño events was added for every five years. For the composite El Niño covering 5 years, we used the monthly SSTAs to predict the months with SSTA > 0.5 °C (<0.5 °C), and the monthly SSTAs for other months were synthesized in the normal years for the first 2 years. For the last 3 years, normal SSTA forcing was used. A total of nine observations of the composite El Niño events were added to the SSTA. |
| E2 | 1955–2005 | Similar to E1, with the addition of the observed composite SSTA of La Niña events. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Wan, L.; Chen, P.; Guo, D.; Chang, S.; Yang, C. Effect of ENSO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the WACCM4 Model. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020525
Li Y, Xu F, Wan L, Chen P, Guo D, Chang S, Yang C. Effect of ENSO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the WACCM4 Model. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020525
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yongchi, Feng Xu, Lingfeng Wan, Peng Chen, Dong Guo, Shujie Chang, and Chen Yang. 2023. "Effect of ENSO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the WACCM4 Model" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020525
APA StyleLi, Y., Xu, F., Wan, L., Chen, P., Guo, D., Chang, S., & Yang, C. (2023). Effect of ENSO on the Ozone Valley over the Tibetan Plateau Based on the WACCM4 Model. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020525








