Abstract
In this study, we proposed a region of interest (ROI) compression algorithm under the deep learning self-encoder framework to improve the reconstruction performance of the image and reduce the distortion of the ROI. First, we adopted a remote sensing image cloud detection algorithm for detecting important targets in images, that is, separating the remote sensing background from important regions in remote sensing images and then determining the target regions because most traditional ROI-based image compression algorithms utilize the manual labeling of the ROI to achieve region separation in images. We designed a multiscale ROI self-coding network from coarse to fine with a hierarchical super priority layer to synthesize images to reduce the spatial redundancy more effectively, thus greatly improving the distortion rate performance of image compression. By using a spatial attention mechanism for the ROI in the image compression network, we achieved better compression performance.
1. Introduction
Multimedia data [1] play a vital role in our daily lives. With the continuous innovations in the parallel computing capability of hardware devices such as GPU [2], the field of artificial intelligence has witnessed immense progress. Image processing technology based on deep learning (DL) [3] has also become an important method of multimedia data processing. Compression technology is one of the essential technologies in image transmission and processing. In the 5G era, people have higher requirements for the quality of multimedia data (images, videos, audio, etc.); thus, multimedia processing technology needs to be continuously innovated. Traditional image compression technology [4] cannot meet people’s requirements in the current application environment; thus, extensive research has been conducted on DL image compression algorithms for high-quality image compression tasks.
People can obtain optical remote sensing data with different resolutions through various satellites, and these image data can be widely used in Earth observation tasks, such as disaster monitoring, resource detection, etc. However, whether it concerns weather prediction from the distribution of clouds or the better differential compression of feature information to improve the transmission efficiency and utilization of images, high-performance semantic segmentation algorithms need to be designed to perform cloud detection on remote sensing images [5]. The cloud detection task is a binary classification of each pixel of the image, which represents the location of the cloud region. Meanwhile, in order to further improve the efficiency of image transmission and obtain finer and more valuable feature information with less bandwidth resources, a multilayer super-priori image compression algorithm based on a multiscale ROI attention mechanism is proposed. Remote sensing images include cloud and noncloud areas.
The image compression technology based on the region of interest (ROI) can better adapt to people’s visual needs [6]. When target individuals are present in the image, different compression strategies are adopted in different regions to achieve a high compression efficiency and good visual reconstruction effect. However, in remote sensing images, the details are richer than those in ordinary images, and achieving a good compression performance is challenging when the wireless channel [7] environment is relatively limited. Therefore, in this study, to improve the human visual experience of compressed and reconstructed images, differential compression was performed on the ROI [8] and the background region. Since the noncloud area in the remote sensing image is the area we focus on, the ROI compression can pay more attention to the noncloud area. From this point, we propose a ROI-based image compression method.
The ROI binary map used in our designed network is based on the cloud detection algorithm which is used to detect cloud pixels in Gaofen-1 WFV images. In this method, a deep network is used to learn multiscale global features, combining high-level semantic information obtained during the feature learning process with low-level spatial information to classify images into cloud and noncloud regions. The cloud detection algorithm can obtain the binarized mask image we compressed in the multiscale region of interest image.
The contribution of this paper is as follows:
- A multiscale ROI spatial attention module was designed for the image compression network.
- A multiscale interest autocoding network with hierarchical super-priority layers was designed to comprehensively analyze the image and more effectively reduce spatial redundancy, thus greatly improving the rate distortion performance of image compression and achieving a superior compression performance in the ROI by using a spatial attention mechanism for the ROI in the image compression network.
2. Related Work
Image Compression Network Structure Based on Super-Prior Architecture
Degree-learning image compression networks utilize autoencoders that learn an invertible mapping from pixels to quantized latent representations by using the analytical transformations A and S [9,10] to map the image to a potential feature representation. Then, the potential features are decoded using the obtained feature representation and the original image is obtained. The analytical transformation and generalized divisive normalization layer (GDN) [9,11] greatly reduce the spatial redundancy between pixels, thus facilitating the probabilistic modeling of potential representations; however, due to the limited ability to perceive the context, the contextual relevance of potential features [12] is ignored. The joint distribution [13,14,15] representing the latent feature is approximated in an adaptive manner as :
where denotes the random variables representing the elements of context encoding and decoding and are used to calculate the prior representation of the current pixel. Equation (1) is an approximate representation of the joint distribution considering the nearest top m prior probability distributions.
However, in the case of long-term dependencies between variables, this approximate relationship is very inaccurate. Therefore, during image compression, there is a trade-off in choosing an appropriate value of m to obtain an accurate probability distribution estimate. If the m value is too large, excellent modeling performance is obtained; however, the complexity of the probability estimation model increases greatly, which poses a challenge to the computing power of the device and is thus challenging to apply in practice. Furthermore, based on the dependency relationship of a single pixel, the probability distribution must be estimated separately. Only the previous point can be obtained before the information of the current point can be obtained; this increases the training time of the model [16,17,18].
Currently, to address the aforementioned limitations and construct an effective and efficient compression framework, efficient compression is performed using the superior latent representation of the image. The codec module is combined with an entropy model to obtain the probability distribution prior to the potential representation and can be used with standard arithmetic coding algorithms to produce compressed bit streams. As shown in Figure 1, the input image is passed through the main encoder to obtain the output y (i.e., the potential feature representation is obtained), which is then quantized to obtain the output . The super-prior network performs scale capturing on and models each point of the potential representation as a Gaussian distribution with mean 0 and variance , as shown in Equation (2) [19,20].
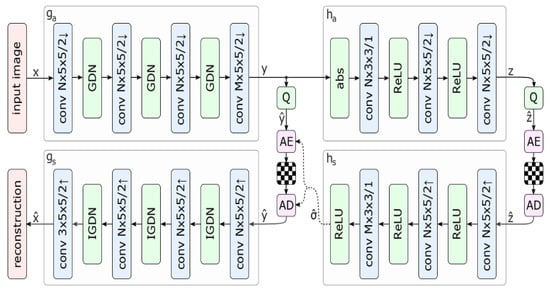
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the image compression network structure based on super-priori architecture [9].
Some previous studies have modeled the overall potential features by using an entropy model for all feature elements in the inference stage; however, the super-prior architecture models each feature point independently by constructing an entropy model [21] of the feature values to obtain each point of the potential feature representation for code rate estimation [22] and entropy coding [23]. Because the arithmetic encoder requires the occurrence probability and cumulative probability distribution of the elements in the coding and decoding stages, this information is compressed into the codestream file and then transmitted to the decoding side for proper entropy decoding. Then, the entropy decoding result is inputted into the main decoding end to obtain the final reconstructed image. The overall rate distortion function [24] is used as the loss function [25] of the network to optimize the parameters of the whole network.
In existing DL-based image compression methods, the entropy model used for compressing the potential representation is represented as a joint distribution or even a fully decomposed probability distribution. The probability distribution of the potential representation is unknown, and it is assumed that the parameters of the entropy model fit the real data distribution well. The more accurately the entropy model estimates the potential representation, the closer it is to the theoretical entropy value. Assume two probability distributions P and Q in a sample set, where P is the true distribution and Q is the untrue distribution. According to Shannon’s law, the expectation formula for the coding length required to represent a sample according to the true distribution P can be expressed as follows:
If the wrong distribution Q is used to represent the average code length from the true distribution P, the minimum average code length that can be achieved by the encoder and decoder pairs by using their shared entropy models can be obtained using the Shannon cross-entropy [26] between the two distributions:
The model is an end-to-end optimization model; thus, by balancing the code rate and distortion, the total expected coding length can be minimized as follows:
where D represents the distortion between the reconstructed image and the original image, and R represents the compression bit rate of the overall frame.
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Motivation
The context dependencies captured by the context model are modeled as higher-level potential representations. The algorithms used for super-prior potential representations are parallelized to capture a larger range of spatial dependencies. The cross-entropy value of the two divisions is minimized when the estimated distribution of the model is equal to the actual probability distribution. However, when the actual distribution of the potential representation contains statistical dependencies, using a fully decomposed entropy model leads to nonoptimal compression performance. Therefore, Peking University proposed constructing a coarse-to-fine multilayer variational autoencoder hyperprior network [27], subsequently referred to as CFHPM [28], and used it to learn the potential representation distribution of the entropy model. However, this algorithm overlays a multilayer hyperprior probability estimation network of potential representations to achieve coarse-to-fine abstraction modeling to approximate the decomposition of the conditional entropy model through training.
The latent variables of the aforementioned single-layer hyper-prior network are spatially redundant, resulting in redundant information being repeatedly encoded—thus, increasing the codeword consumption; moreover, there is insufficient information describing the image at the decoding end due to the presence of redundant information, resulting in the inability to reconstruct a better-quality image. Thus, the redundant information in the latent variables must be eliminated to save code words and help the encoder learn more information with differences from the input image. Therefore, the hyper-priori network first compresses the latent representation into , transmits it to the hyper-priori decoder by performing the quantized entropy coding of , and learns the modeling parameters of the latent representation y by decoding it in the hyper-priori decoder. After obtaining the modeling distribution of the potential representation y through the super-priori network, the compressed stream file is obtained by modeling and entropy coding the quantized , and is obtained by entropy decoding, which further reduces the bit rate and improves the rate distortion performance of the codec.
We constructed a coarse-to-fine algorithmic structure by using multilayer hyperanalytical and hypersynthetic transformation to eliminate as much image redundancy as possible and reduce the spatial dependencies between pixels. The input image X is analytically transformed into the hidden layer representation Y followed by rounded quantization. The probabilistic prediction network is used to construct an entropy model to estimate the likelihood probability by computing through Y. Similar to the aforementioned super-prior model, the conditional distribution of each element in the feature representation is assumed to satisfy the Gaussian distribution m with mean and variance . Because the hidden layer representation has been rounded to the discrete form, the likelihood of the hidden layer representation can be calculated as follows:
where represents the cumulative distribution function of the standard positive terminus distribution, and and are predicted from Y. The multilayer super-prior structure is constructed by recompressing the redundant Y and predicting the distribution of Y from Z. This process is the same as that used for predicting X from Y. Because Z removes as much spatial dependence as possible between the features, the likelihood of each element of Z can be calculated as follows:
where is the optimized parameter used for obtaining a more accurate estimate of the distribution of Y. Each channel in the hidden layer shares the same , whereas the of different channels are independent of each other.
To model images from coarse to fine, more information must be retained while applying increasingly complex synthetic analytical transformations on larger-resolution feature maps. The spatial correlation between potential hidden layer representations has been greatly reduced compared to normal images; however, the convolution of large convolution kernels relies on local correlation under the sensory field. Moreover, the supertransformation analysis module developed in previous studies uses a stepwise convolution operation and ReLU activation; stepwise convolution is used to achieve the downsampling of the feature layer and ReLU is used to deactivate neurons with negative values. Because the number of convolutional layers must be gradually deepened to ensure that the hidden layer features can be decomposed gradually, the existing supertransformation module leads to excessive information loss.
To facilitate the multilayer structure to retain the coarse-to-fine analytical transformation features, the analytical transformation module is structured as shown in Table 1 [28]. The module eliminates the use of convolution under a large convolution kernel for feature extraction and uses a relatively small convolution kernel in the first layer, thereby eliminating the activation of the nonlinear activation function and performs a 1 × 1 convolution operation in the remaining convolution layers. The first layer in the network increases the dimensionality of the original feature representation, and combined with the nonlinear layers in the subsequent network layers, not only preserves the information of the original features but also provides the network with the ability to perform nonlinear modeling.

Table 1.
Hyper analysis transform.
In addition, the proposed algorithm reshapes the potential feature representation tensor by the spatial depth transformation operation so that spatially adjacent elements are scattered at the same locations in different dimensions. In this manner, the next 1 × 1 convolution operation can be performed in a nonlinear manner, thereby reducing spatial redundancy. In the final layer of the module, the network performs channel compression on the features to make the feature representation more efficient. The synthetic transformation module is designed as a symmetric module to generate the reconstructed feature maps. The structure of the transformation module is shown in Table 2 [28].

Table 2.
Hyper synthesis transform.
During decoding, to better reconstruct the image, the decoder must fully utilize the information provided in the codestream. The proposed algorithm uses the output features of the super-priority module as edge information and aggregates the multiscale feature information of each layer obtained from the multilayer super-priority module. As shown in Figure 2 [28], the information aggregation subnet is mainly used to realize the reconstruction in the image compression process. The decoding network upsamples the main super-priori potential feature representation and the smaller-scale higher-order features to half the resolution of the original image and then performs feature fusion by connecting the two feature layers, and the fused image is processed by the residual block and upsampled back to the scale of the decoded image.
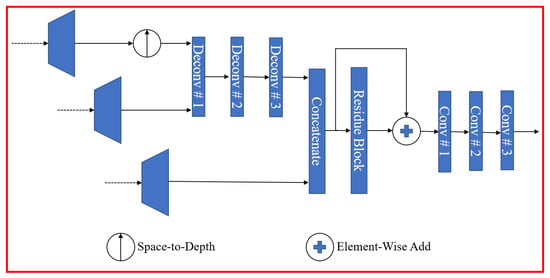
Figure 2.
Information Aggregation Decoding Subnet.
By fusing the feature representation of the backbone codec network and the super-priority feature representation, the information at different scales is effectively utilized and the feature representation is constrained to help the recovery of the decoded image. The higher-order feature representation provides better global information due to its higher perceptual field, whereas the other feature representation retains the detailed information contained in the image. The fusion process is performed at a lower spatial resolution to prevent high computational complexity, improve the efficiency of the network, and avoid network overfitting. After feature fusion, the network uses a residual block and a superimposed convolutional layer to map the features back to the dimension of the original image, and thus the decoded reconstruction of the image is realized.
In this study, CABAC [29] arithmetic coding was used for entropy coding because it is widely used in the H.264/AVC standard for entropy coding. CABAC arithmetic coding consists of three steps: binarization, context modeling, and binary arithmetic coding and can adaptively adjust the probability model according to the input; thus, CABAC is a coding method with high efficiency and excellent real-time performance.
3.2. The Attention Module Based on the Region of Interest
When performing arithmetic coding by using the entropy codec, the network uses the quantized potential feature representation as the symbol to be encoded for probability estimation. For the innermost layer with the smallest scale, a simple entropy model structure is used to model the Gaussian distribution with zero mean by using the variance of each channel to determine the distribution. For the remaining layers, a complex Gaussian distribution is estimated for each element. As shown in Figure 3 [28], this module has a predictive self-network with more suitable sampling regions to make fuller use of the super-priority features. The decoded super-prior features are taken as the input and a window region of size 5 × 5 is sampled centered on the location to be predicted. Each sampling block uses a multilayer convolutional subnetwork to estimate the probabilities. In the last layer of the subnetwork, the sampled blocks are tiled into a vector and the feature vector is mapped to a vector with mean and variance at the current location by using a fully connected layer with a convolution kernel that is used for the local convolution of all spatial locations. Thus, the distribution estimation is performed by densely sampling the super-prior feature representation, thereby preventing information loss during the convolution operation.
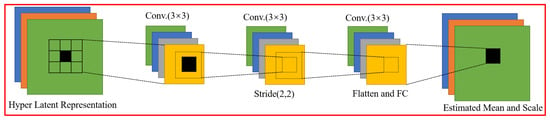
Figure 3.
Estimation Subnetwork.
The proposed algorithm serves as the basis of the image compression network structure, and the salient target cloud regions detected by the semantic segmentation network are introduced into the image compression network as the ROI. However, this base network does not focus on noncloud regions, thus, we designed a multiscale ROI attention module to implement the image compression algorithm based on the multiscale ROI attention module to enhance the noncloud regions in the original image at different scales and achieve a better reconstruction performance of the ROI. The structure of the attention module based on the ROI is illustrated in Figure 4. Multiscale refers to feature maps of different scales, and different features can be observed at different scales. In neural networks, multiscale can be embodied as scaling the output feature maps of different convolutional layers to a uniform size, so that it contains both global overall information and local detail information. Therefore, we pass the input graph through the ROI module twice to realize the information of the feature map at different scales.
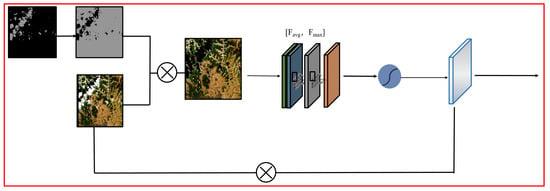
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the structure of the attention module based on the region of interest.
3.3. Framework
The output of the salient region detection network is a binary mask; the mask values of cloud and noncloud regions are 1 and 0, respectively, as is shown in Figure 5. The binary ROI representing the feature regions of remote sensing images is obtained by inverting the binary mask, and the noncloud regions in the original image are extracted by multiplying the binary ROI with the original image. Then, the spatial attention mechanism is applied to the feature images with the noncloud regions to learn the normalized weights of the spatial location information of the image, and the weights are multiplied with the original image to be compressed to obtain the image information after the enhancement of spatial location information. For the better image compression of the full image, in this study, the enhanced image was not used as the input of the compression network; instead, the output of the multiscale ROI attention module was added to the original image to achieve image enhancement and obtain spatial information. Therefore, in this study, an image compression network based on the multiscale ROI attention module (subsequently referred to as MROI-CFHPM in the paper) was constructed to achieve ROI-guided image compression under multiscale constraints. The structure of the proposed network is shown in Figure 6.
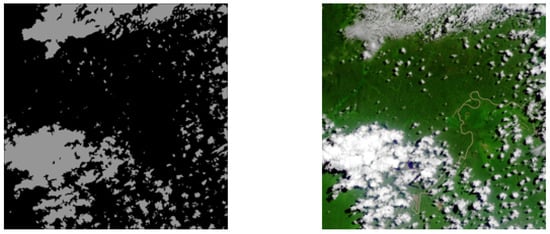
Figure 5.
The (left) image is the region of interest image obtained by the cloud detection network [5], and the (right) image is the original color image.
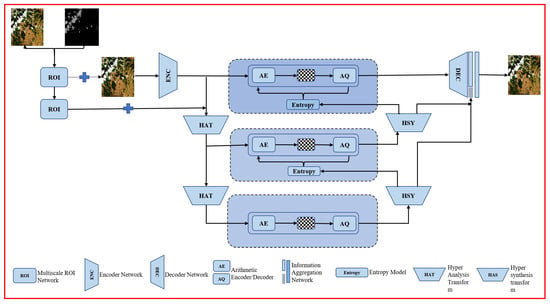
Figure 6.
Image compression network structure based on multiscale region of interest attention module.
In the DL-based image compression methods, the compression network must be trained end-to-end, and backpropagation must be employed when the quantization operation solves the gradient to zero or the derivative cannot be obtained. Thus, the training and testing processes require different quantization methods. During training, variables such as uniform noise are added, and the quantization backpropagation gradient is modified. However, in the case of no backpropagation, only the rounding operation must be performed on the quantized variables (i.e., nearest-neighbor quantization) to convert them to a finite value domain.
(1) Adding uniform noise: The method of adding uniform noise was first used by Balle, as shown in Equation (8). Quantization can be achieved by adding uniform noise obeying or the variable during training.
(2) Modifying the quantization backpropagation gradient: modifying the quantization backpropagation gradient is an engineering approach employed to directly quantify the nearest neighbors of the variables during training and ensures the overall end-to-end training of the model. Generally, the backpropagation gradient is set as 1 to ensure high quantization accuracy during forward propagation during training so that the training and testing yield consistent results.
Cheng demonstrated that different quantization methods have a negligible effect on the compression performance of the model after training; thus, in the current study, uniform noise was added as the simulation of quantization noise during training.
4. Experimental Results
The experiments were conducted on four 2080 Ti NVIDIA graphics cards. Python 3.7 and the DL PyTorch package were used for modeling. In the following subsections, the performance and experimental results are discussed.
4.1. Performance
We compared the performance of the proposed method with that of CFHPM and the conventional image compression standard JPEG2000. To evaluate the distortion of the compressed image and the distortion of the ROI, this section uses the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) as the evaluation index, and the image depth bpp is used to evaluate the compression ratio. The larger the PSNR, the lower the distortion between the reconstructed image and the original image, and the better the image quality. The PSNR and MSE are calculated as follows:
where MSE is the mean square error between the original image and the processed image, x is the original image, and y is the compressed and decompressed image.
4.2. The Dataset
We used the Landsat dataset, which is the collective name for the eight satellites launched by the United States since 1972. The number of training datasets required for the compression task is not as high as that required for the semantic segmentation task. To subjectively compare the reconstruction and detail loss after image compression and decompression, we used Landsat visible light remote sensing images as the dataset. Images from the Landsat-8 OLI/TIRS satellite were used. The Landsat-8 satellite has two image acquisition payloads: the Land Imager and the Thermal Infrared Sensor. Bands 1–9 are the data acquired by the OLI sensor in the bandwidth of 0.43–229 mm. Bands 10 and 11 are the data acquired by the TIRS sensor in the bandwidth of 10.60–1251 mm.
The dataset has a resolution of 1000 × 1000. These data are divided into seven categories: shadows, surface shadows, water, snow and ice, land, clouds, and inundated areas.
4.3. Experimental Environment and Parameter Settings
For network training, the Adam [30] optimizer was used, and the initial learning rate was set as . The training of the network was divided into three stages [31]. In the first stage, the analytical transformation module and synthetic transformation module of the main network were pretrained to achieve good initial image reconstruction. The main analytical and synthetic transformation modules were pretrained using a single-layer super-prior probability estimation model. In the second stage, the second layer of super-prior estimation network was randomly initialized, and the model was trained end-to-end. In the third stage, the last layer of the original final synthetic transformation module was replaced with the information aggregation subnetwork, and the entire network was trained jointly [32]. In the forward propagation of training and inference for the analytical transformation module and synthetic transformation module of the subnetwork, quantization was performed by direct rounding. To estimate the distribution of the latent feature representation during training, uniform noise [33] was added to the original latent feature representation. During backpropagation, the gradient was set as 1 to facilitate backpropagation [34].
The sum of the cross-entropy [35] of each layer was used as the R in the loss function during training, and different models were trained using different values to evaluate the performance of the code rate distortion at different code rates. The code-rate control [36] was achieved by selecting different values of in the loss function during the training process.
4.4. Results
In Figure 7 and Figure 8, we show the visual results in the test dataset under different bpp to evaluate the visual quality of the reconstructed images. As shown in Figure 8d,f, JPEG2000 loses a lot of high-frequency information compared to MROI-CFHPM, because JPEG2000 has aliasing and ringing effects, which greatly damage the visual quality. From the red boxes in Figure 7 and Figure 8, it can be seen that the image compressed by JPEG2000 has problems such as blurring, color distortion, and loss of detail. The CFHPM and MROI-CFHPM algorithms reduce the loss of details to a certain extent, and the edges of objects are relatively clear. The texture details of remote sensing images are very complex, which brings great difficulty to the image compression algorithm; however, it can be seen from Figure 8a–c that the MROI-CFHPM algorithm restores the ground information more clearly. Figure 8d–f includes man-made objects; from the perspective of regular lines, the proposed algorithm shows better reconstruction results for the images of such regular objects.

Figure 7.
Comparison of Subjective Performance of Different Compression Algorithms on the Landsat Image Test Set with bpp = 0.42.
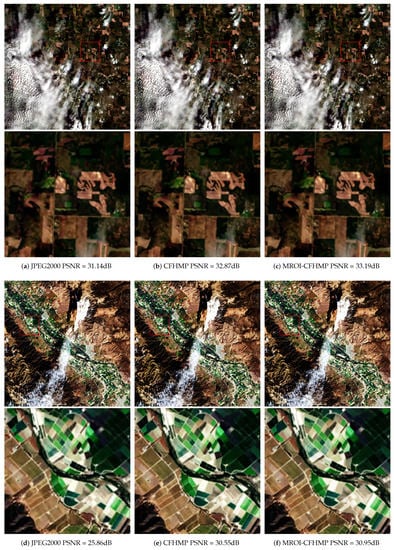
Figure 8.
Comparison of Subjective Performance of Different Compression Algorithms on the Landsat Image Test Set with bpp = 1.36.
Figure 9 shows the transformation of PSNR at different bpp values; the PSNR represents the full-picture PSNR. We studied the effectiveness of the proposed multilayer subnetwork [37] of interest. We set the original two-layer hyperprior (Balle et al. 2018) model as the baseline method and compared CFHPM with the traditional compression algorithm JPEG2000. The results revealed that the image compression network guided by CFHPM improved the image compression performance compared with the traditional JPEG2000 algorithm but could not perform differentiated compression for different types of terrain coverage. If raw synthetic and analytical transformations are employed, constructing a multilayered hyperprior network is difficult. In this case, the extra superlayer fails to capture additional useful information to model the probability distribution of the upper layer. This may be due to the loss of information during forward propagation, the use of the ReLU activation function, and large convolution kernels. The use of the proposed signal-preserving super-prior layers and the corresponding additional super-prior layer yielded significant improvements to the R-D performance. Figure 10 shows the calculated PSNR values of the ROI. By comparing Figure 9 and Figure 10, it can be concluded that the MROI-CFHPM designed in this study can target the ROI region and can achieve better compression performance; moreover, MROI-CFHPM can employ a higher bit rate in ROI compression, reduce the concern on noncloud areas, and achieve excellent ROI compression. Figure 11 shows the relationship between the compression multiplier and bpp, and it can be seen that the compression multiplier decreases with increasing bpp. A high compression multiplier can be obtained at low bpp.
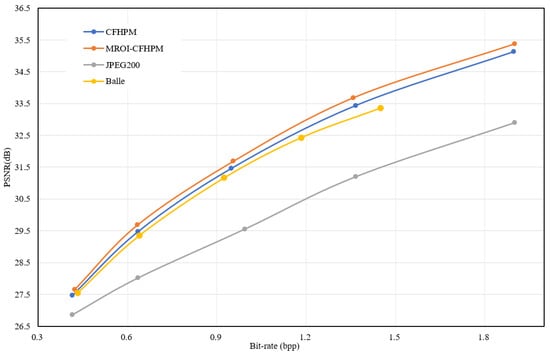
Figure 9.
Rate–distortion curves of our proposed MROI-CFHPM against the JPEG2000, CFHPM, and Balle. This PSNR is for the entire image, including noncloud and cloud regions.
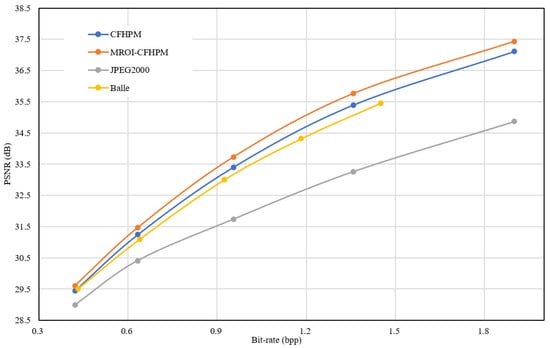
Figure 10.
Rate–distortion curves of our proposed MROI-CFHPM against the JPEG2000, CFHPM, and Balle. This PSNR only includes noncloud regions.
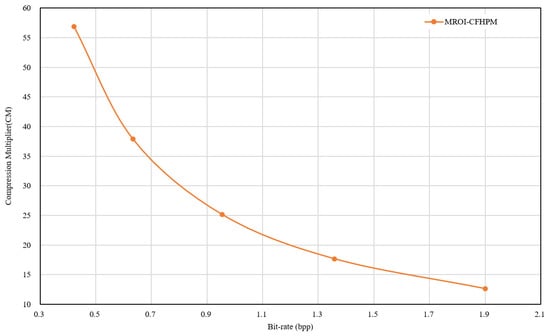
Figure 11.
Changes in compression factor at a different bit-rate.
5. Discussion
From the experimental results, our designed multiscale interest network puts more attention on noncloud regions, so the PSNR of noncloud regions in the whole recovered image is significantly improved, and the PSNR of cloud regions is reduced because there is no attention on cloud regions. Furthermore, we can see from the detail subjective map that the texture quality of the recovered high-frequency information detail for the noncloud region is highly improved compared with JPEG2000, because the multiscale region of interest network will mainly focus on the noncloud region, so we can obtain this experimental result.
Whilst we will further conduct further research on multiscale regions of interest, in this paper, the ROI of noncloud regions were treated the same, and in the future, we will study how to perform further feature extraction on regions of interest, i.e., further subdividing ROI regions to improve the quality of recovered images. Due to the further segmentation of ROI, the image coding can be divided into two layers, a base layer and an attention-guided refinement layer, which is different from the existing image compression methods that spend extra bits on all pixels of ROI on average, a work we are currently undertaking.
6. Conclusions
In this study, an image compression algorithm was designed for multilayer super-prior probability estimation. In addition, a multiscale ROI spatial attention mechanism module was designed to enhance the feature extraction ability of the network in the ROI and improve the overall image compression performance. The proposed algorithm can employ a higher bit rate to effectively compress the ROI and improve the effect of image compression through the accurate key information enhancement mechanism. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm was experimentally evaluated, and the performance was objectively and subjectively compared with the traditional algorithms (CFHPM and JPEG2000). The experimental results revealed that MROI-CFHPM is superior to CFHPM and JPEG2000.
An end-to-end multiscale attention of interest self-coding network is designed to reduce spatial redundancy, thus greatly improving the rate distortion performance [38] of image compression. In addition, the better compression performance of the ROI was achieved using the spatial attention mechanism for the ROI in the image compression network.
The designed ROI image compression algorithm was trained and tested on the Landsat-8 satellite image dataset, and its performance was compared with that of the traditional image compression algorithm and the DL image compression algorithm without the attention mechanism. To conclude, the differential compression of the ROI can be achieved using MROI-CFHPM, and the compression performance of the overall image can be greatly improved.
The multiscale spatial interest attention mechanism module, which enhances the feature extraction capability of the network for the region of interest, not only achieves the improvement of the overall image compression performance, but also enables the code rate to be utilized more for the compression of the region of interest, and improves the image compression effect through the precise key information enhancement mechanism. The experimental results show that, compared with the existing methods, the algorithm is superior in performance and has a strong application value.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z. and S.Z.; methodology, J.Z. and S.Z.; software, J.Z., H.W., Y.L. and R.L.; writing–original draft preparation, H.W., Y.L. and R.L.; writing–review and editing, J.Z. and S.Z.; supervision, Y.L. and R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Wuhu and Xidian University special fund for industry–university-research cooperation (Project No.: XWYCXY-012021019) and the General project of key R&D Plan of Shaanxi Province (Project No.: 2022GY-060).
Data Availability Statement
The processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| CFHPM | Coarse-to-Fine Hyper-Prior Modeling for Learned Image Compression |
| MROI-CFHPM | Multiscale Region of Interest Coarse-to-Fine Hyper-Prior Modeling for Learned Image Compression |
References
- Sundararaj, V.; Selvi, M. Opposition grasshopper optimizer based multimedia data distribution using user evaluation strategy. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 29875–29891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, O.; Subramaniyan, S.; Chinthalaa, R.; Andrade, J.; Cavallaro, J.R.; Nandy, S.K.; Silva, V.; Zhang, X.; Purnaprajna, M.; Falcao, G. A Survey on High-Throughput Non-Binary LDPC Decoders: ASIC, FPGA, and GPU Architectures. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 24, 524–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Abbas, K. A survey on deep learning and its applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi, T.; Khelifi, F.; Kacha, A. An efficient JPEG-2000 based multimodal compression scheme. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 21241–21260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y. Deep network based on up and down blocks using wavelet transform and successive multi-scale spatial attention for cloud detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 261, 112483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, P.D.; Holz, J.A.; Giudice, N.A. Fully autonomous vehicles for people with visual impairment: Policy, accessibility, and future directions. ACM Trans. Access. Comput. (TACCESS) 2021, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Huang, X.; Bovolo, F.; Li, J.; Ke, X.; Zhang, A.; Benediktsson, J.A. Change detection from very-high-spatial-resolution optical remote sensing images: Methods, applications, and future directions. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Mag. 2021, 9, 68–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poldrack, R.A. Region of interest analysis for fMRI. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2007, 2, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballé, J.; Minnen, D.; Singh, S.; Hwang, S.J.; Johnston, N. Variational image compression with a scale hyperprior. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.01436. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Cho, S.; Beack, S.K. Context-adaptive entropy model for end-to-end optimized image compression. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10452. [Google Scholar]
- Ballé, J.; Laparra, V.; Simoncelli, E.P. End-to-end optimized image compression. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01704. [Google Scholar]
- Minnen, D.; Ballé, J.; Toderici, G.D. Joint autoregressive and hierarchical priors for learned image compression. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sklar, A. Random variables, joint distribution functions, and copulas. Kybernetika 1973, 9, 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Wang, J.; Ding, G.; Sun, J.; Yu, P.S. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 2200–2207. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, J.W.; Laird, N.M. Mixture models for the joint distribution of repeated measures and event times. Stat. Med. 1997, 16, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Edo, I.; Zadeh, A.H.; Awad, O.M.; Pekhimenko, G.; Albericio, J.; Moshovos, A. Tensordash: Exploiting sparsity to accelerate deep neural network training. In Proceedings of the 2020 53rd Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 781–795. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Li, M.; Jin, L. Data normalization to accelerate training for linear neural net to predict tropical cyclone tracks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 931629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Ni, L.M.; Zhang, L. Dn-detr: Accelerate detr training by introducing query denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 13619–13627. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, N.R. Statistical analysis based on a certain multivariate complex Gaussian distribution (an introduction). Ann. Math. Stat. 1963, 34, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Buyya, R. Gaussian distribution-based machine learning scheme for anomaly detection in healthcare sensor cloud. Int. J. Cloud Appl. Comput. (IJCAC) 2021, 11, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Shokrieh, M.; Jamali, M.; Mahmoudi, A.; Fazlali, B. Damage-entropy model for fatigue life evaluation of off-axis unidirectional composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 270, 114100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feutrill, A.; Roughan, M. A Review of Shannon and Differential Entropy Rate Estimation. Entropy 2021, 23, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, H.; Coban, M.; Karczewicz, M.; Chuang, T.D.; Bossen, F.; Alshin, A.; Lainema, J.; Helmrich, C.R.; Wiegand, T. Quantization and entropy coding in the versatile video coding (VVC) standard. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 3891–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyner, A.; Ziv, J. The rate-distortion function for source coding with side information at the decoder. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1976, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Cho, D.; Min, J.; Lee, K.M. Meta-Learning with Task-Adaptive Loss Function for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 9465–9474. [Google Scholar]
- Yi-de, M.; Qing, L.; Zhi-Bai, Q. Automated image segmentation using improved PCNN model based on cross-entropy. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Intelligent Multimedia, Video and Speech Processing, Hong Kong, China, 20–22 October 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 743–746. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczak, J.; Welling, M. VAE with a VampPrior. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Las Palmas, Spain, 9–11 April 2018; PMLR: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1214–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Coarse-to-fine hyper-prior modeling for learned image compression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11013–11020. [Google Scholar]
- Sze, V.; Budagavi, M. High throughput CABAC entropy coding in HEVC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2012, 22, 1778–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Abandah, G.A.; Suyyagh, A.E.; Abdel-Majeed, M.R. Transfer learning and multi-phase training for accurate diacritization of arabic poetry. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 3744–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritz, P.J.; Ma, L.; Leung, K.K. Jointly-Trained State-Action Embedding for Efficient Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2021 Conference, Vienna, Austria, 3–7 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lisi, M.A.; Peiyu, H.E.; Ao, C.U.I.; Weichuang, Y.U. Adaptive Beamforming Method Based on MISC Array in Non-uniform Noise. J. Signal Process. 2022, 38, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Solis, F.; Reyes, B.T.; Morero, D.A.; Hueda, M.R. Design and Experimental Verification of a Novel Error-Backpropagation-Based Background Calibration for Time Interleaved ADC in Digital Communication Receivers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.04806. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu-Lin, L.I.; Jia-Feng, H.E. Vehicles Detection Based on Three-frame-difference Method and Cross-entropy Threshold Method. Comput. Eng. 2011, 37, 172–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, L.I. FFT-based coding algorithm with accurate rate control for space-borne SAR complex images. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 13, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Q.; Yan, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S. Single Image Rain Removal Using Image Decomposition and a Dense Network. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2019, 6, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Ji, R.; Chao, C.; Huang, F. ESPACE: Accelerating convolutional neural networks via eliminating spatial and channel redundancy. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).