Investigating the Influence of Water Vapor on Heavy Rainfall Events in the Southern Korean Peninsula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
3. Results
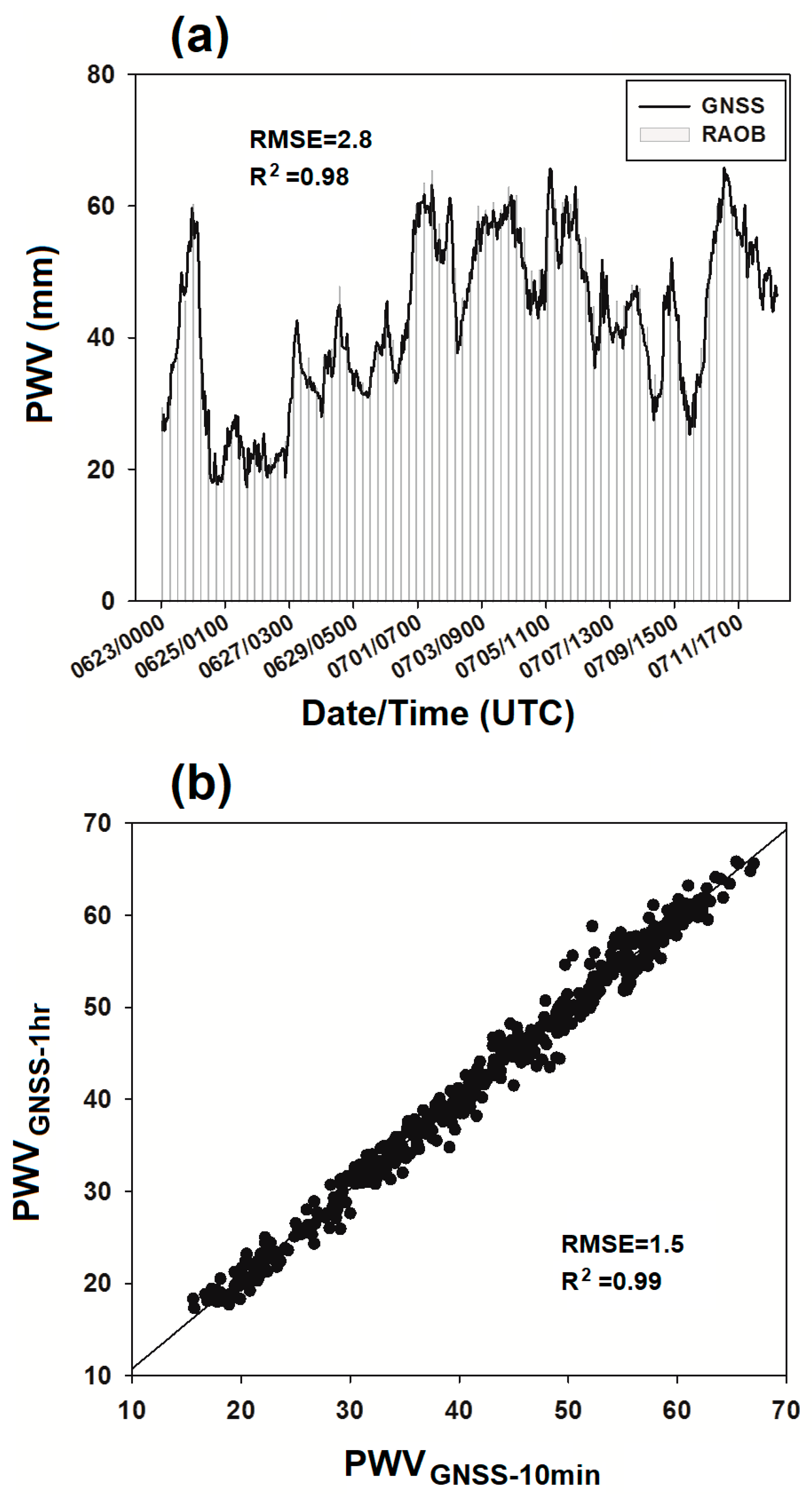
3.1. Data Validation
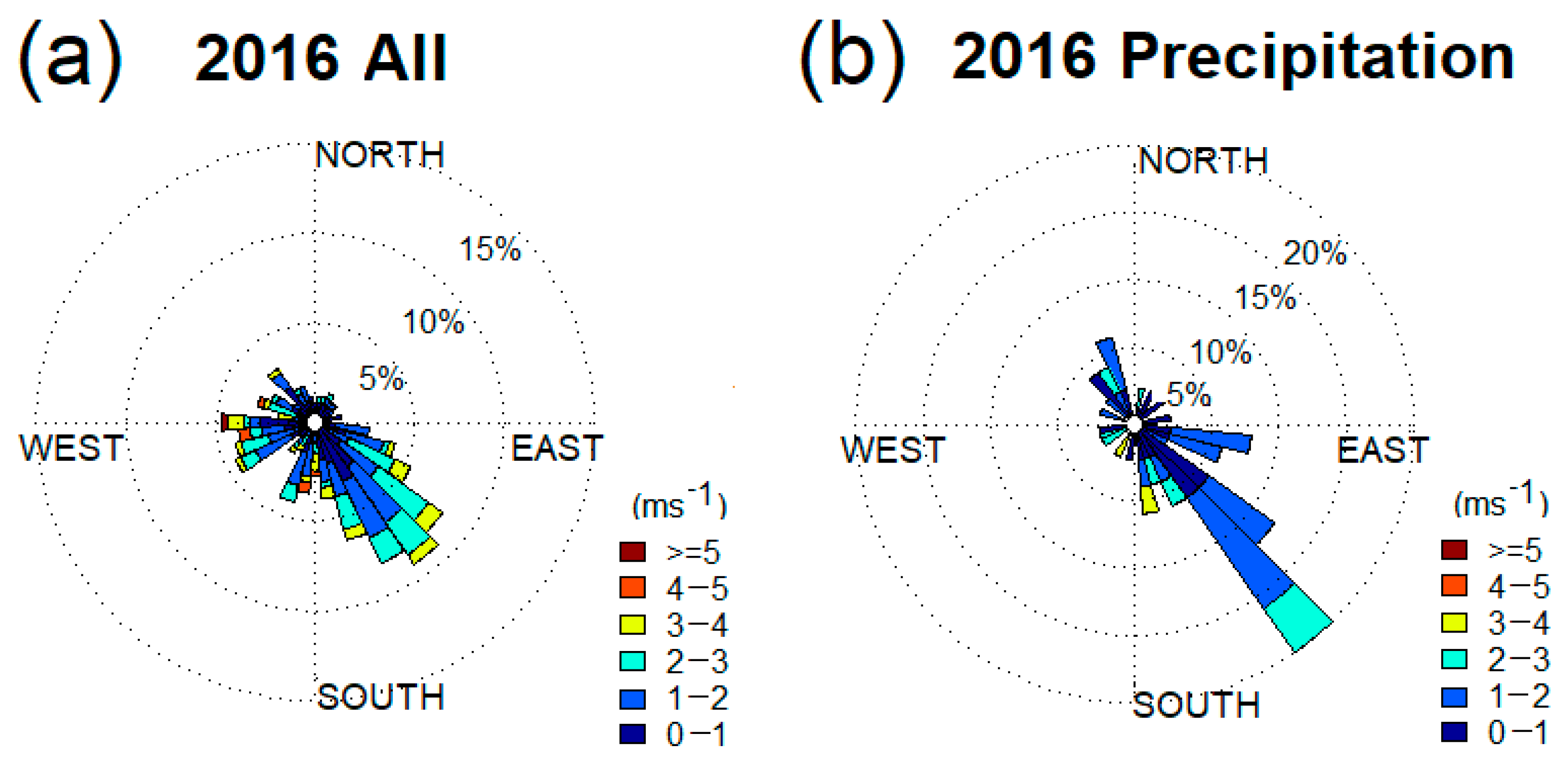
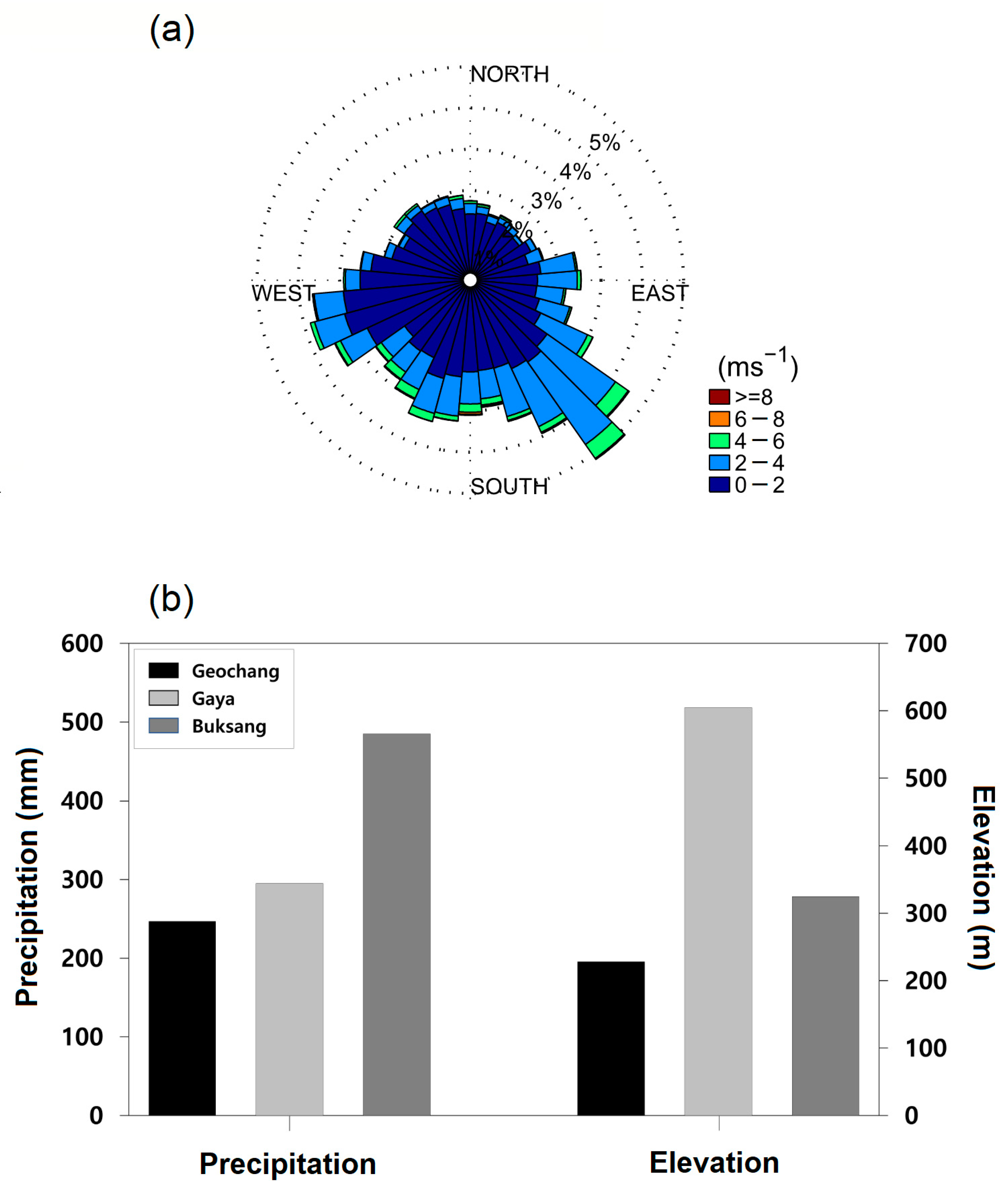
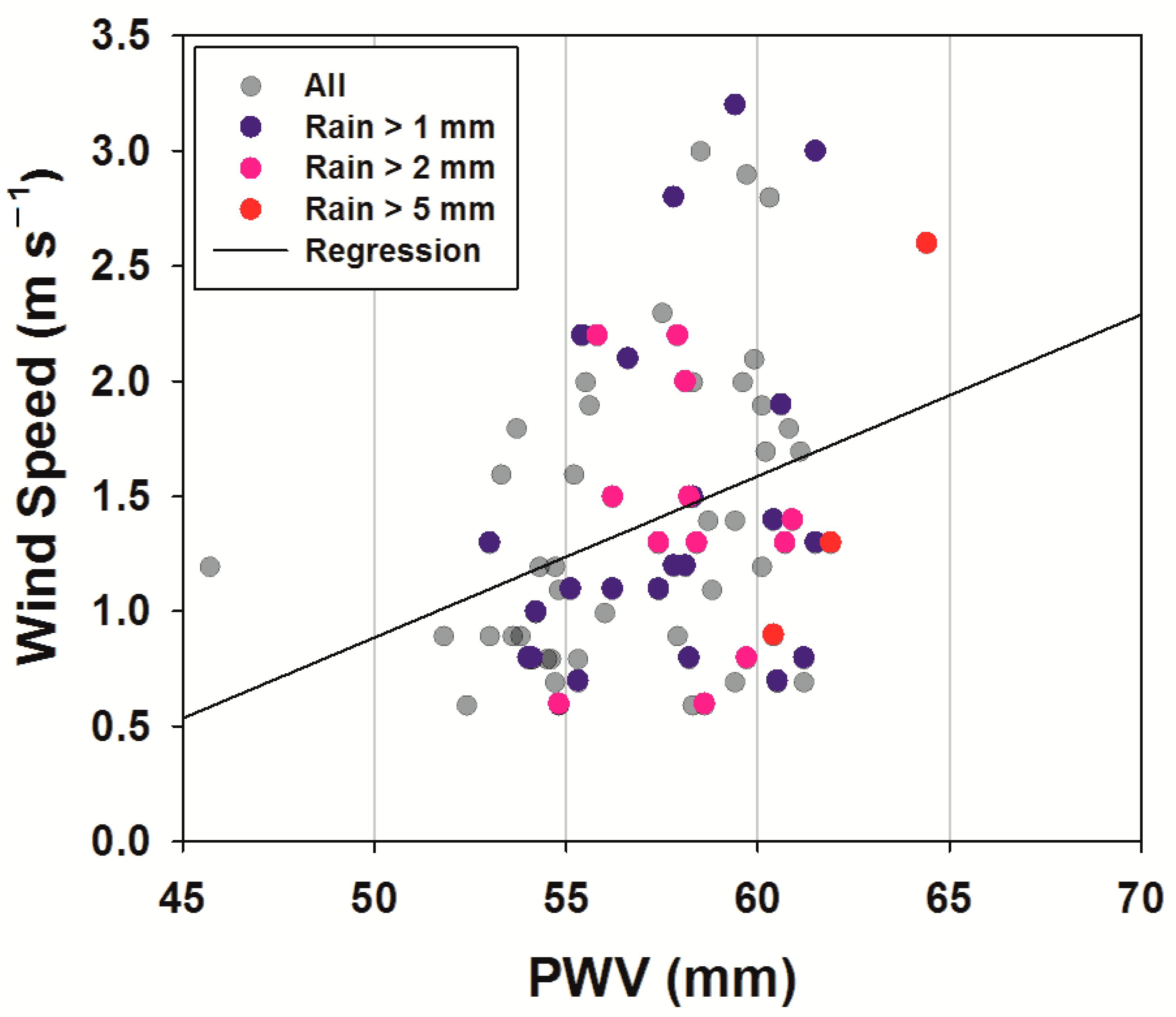
3.2. Wind Rose Analysis
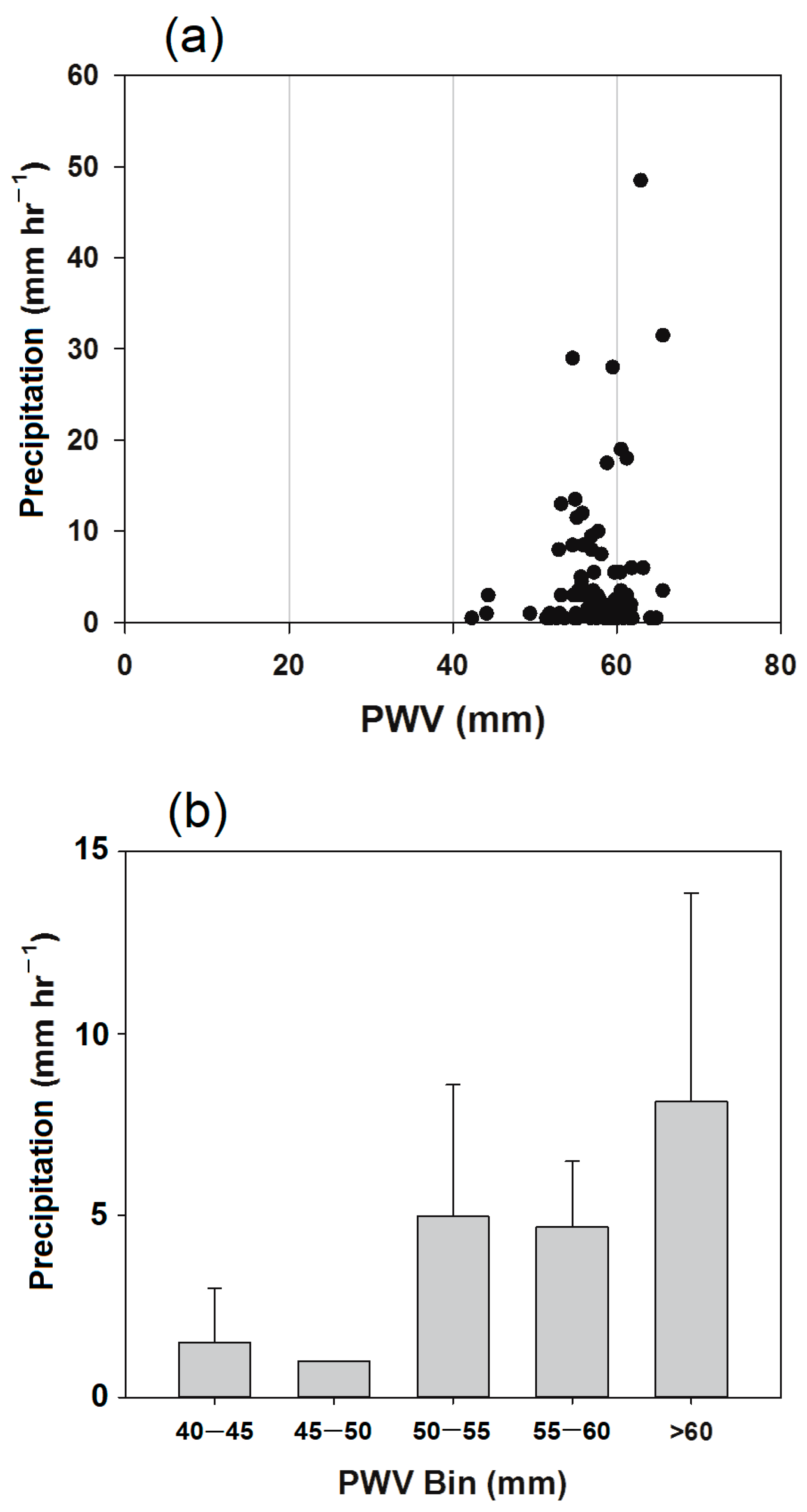
3.3. Relationship between GNSS-PWV and Precipitation
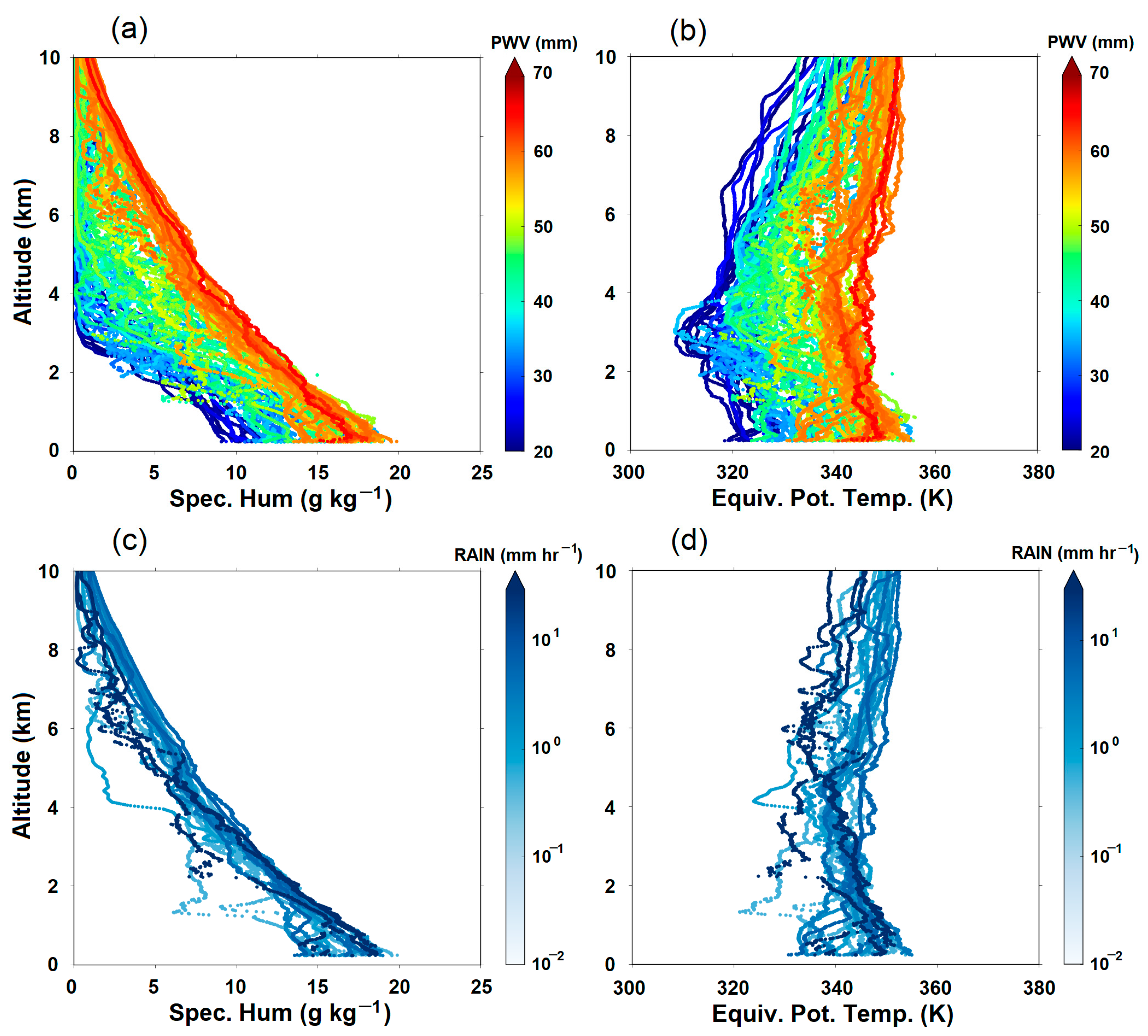
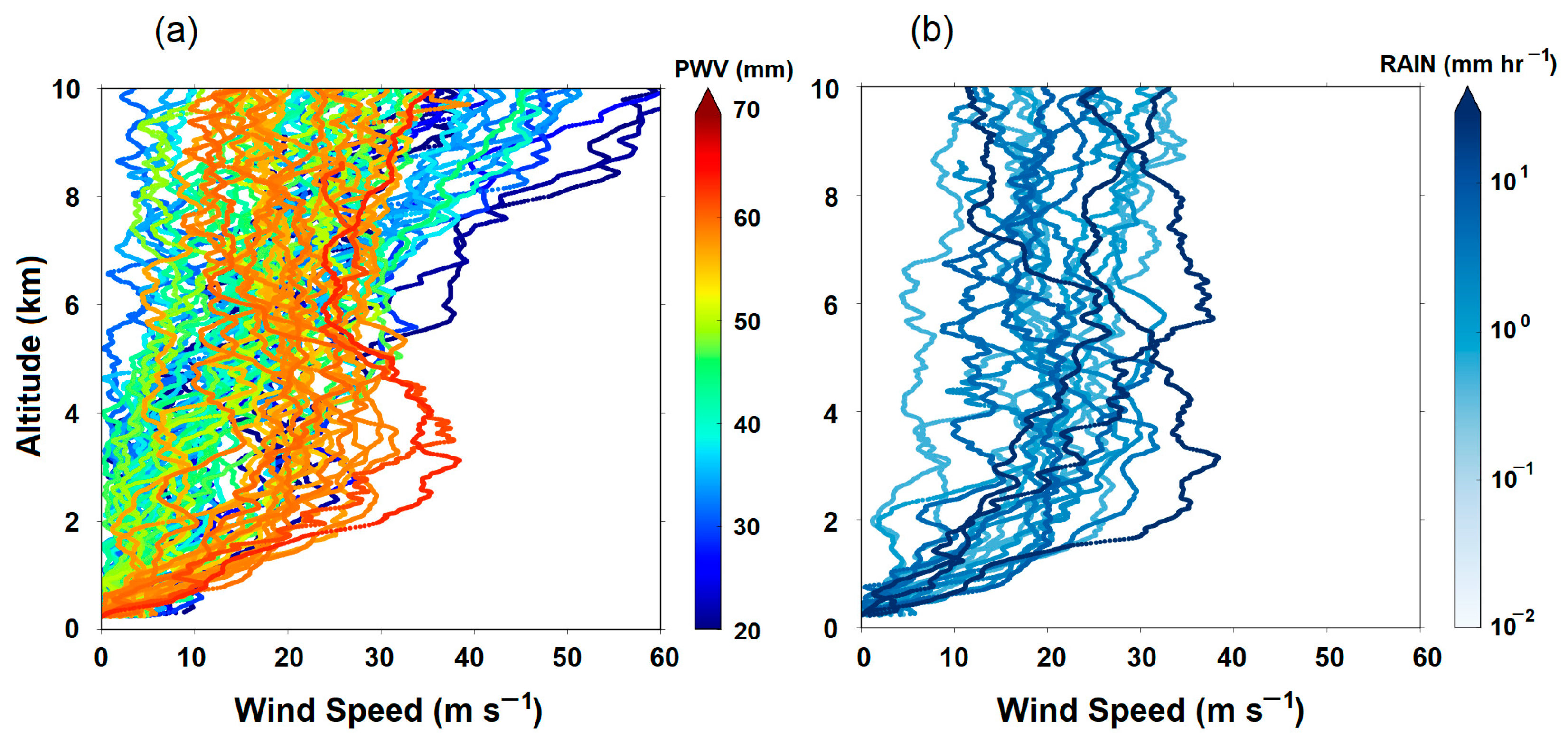
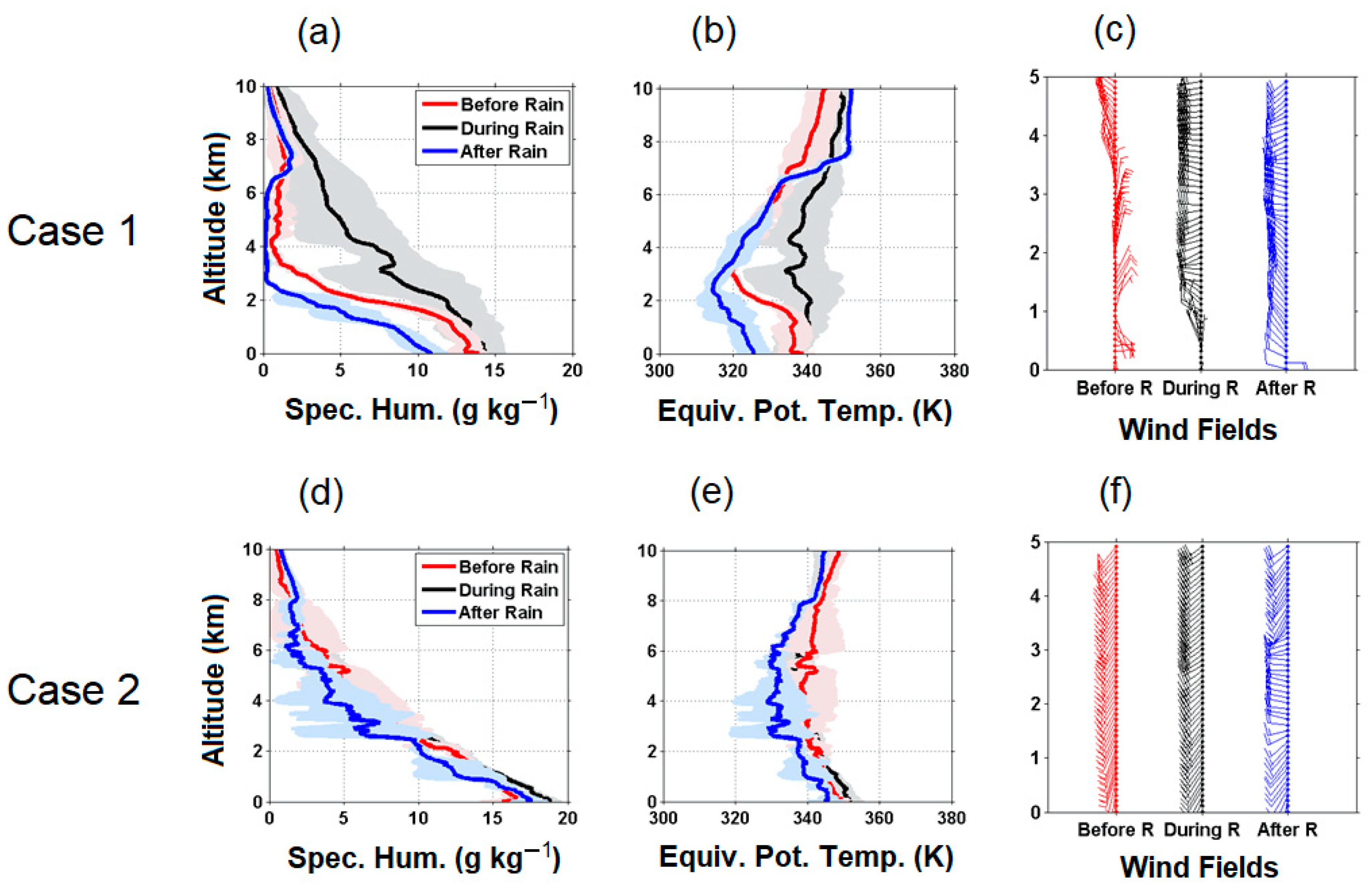
3.4. Vertical Profiles of Moisture and Wind Speed
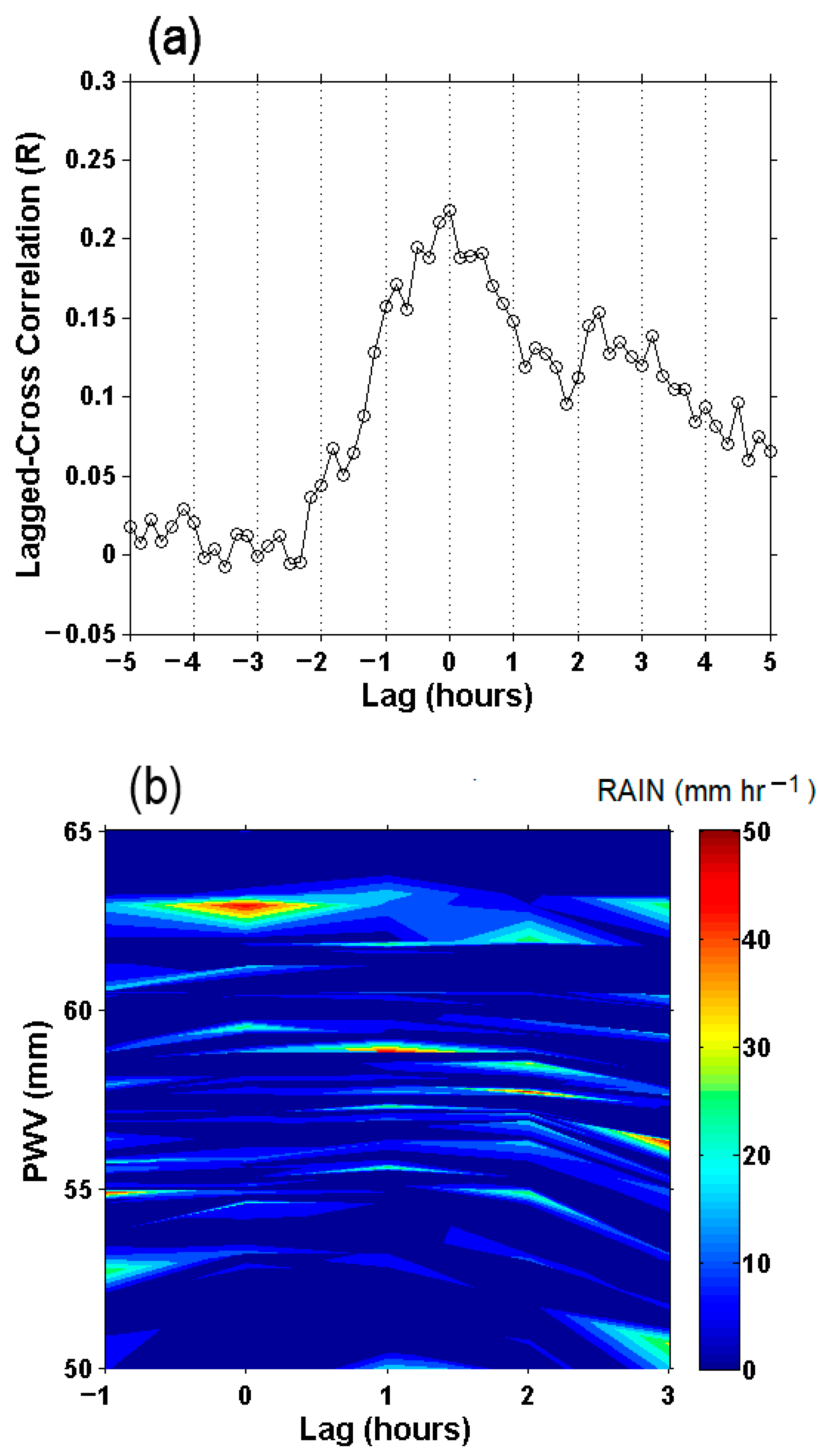
3.5. Precipitation Cross-Correlation Analysis
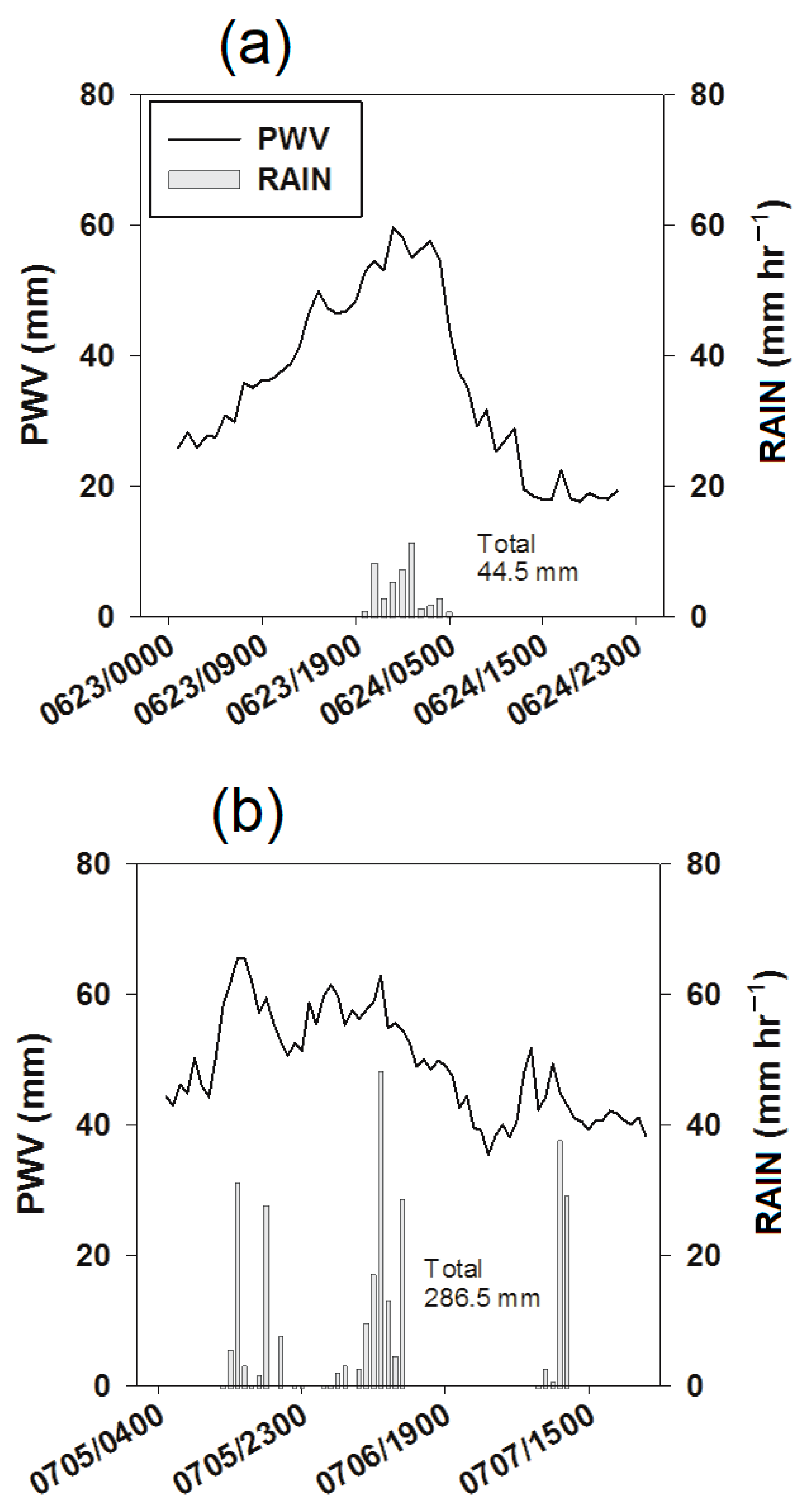
4. Cases of Heavy Rainfall
4.1. Synoptic Characteristics
4.2. Detailed Observational Structures
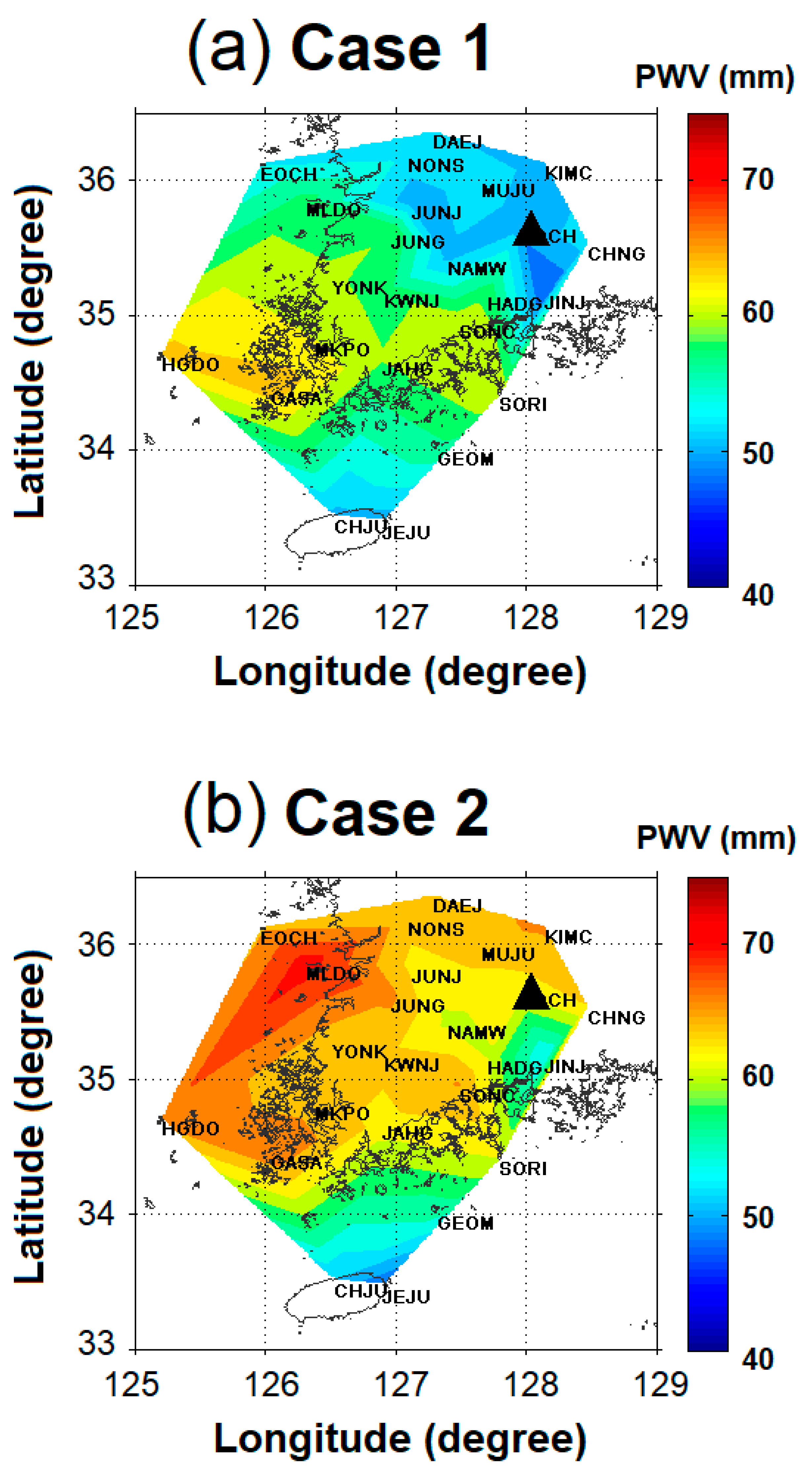
4.3. PWV Plumes in the Ground GNSS Database
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Stations | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | H 1 (m) | Receiver/Antenna |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KIMC | 36.137 | 128.142 | 94.652 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| GOCH | 35.668 | 127.943 | 217.203 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| CHNG | 35.533 | 128.478 | 61.753 | Leica GR50/LEIAR25.R4 |
| MUJU | 36.003 | 127.661 | 230.189 | Leica GR50/LEIAR25.R4 |
| DAEJ | 36.363 | 127.291 | 116.840 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| NONS | 36.186 | 127.099 | 50.684 | Trimble NetR5/TRM59800.00 |
| EOCH | 36.125 | 125.968 | 88.945 | Trimble NetR9/ChokeRing |
| MLDO | 35.858 | 126.315 | 75.290 | Trimble NetR9/ChokeRing |
| JUNJ | 35.843 | 127.135 | 77.148 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| JINJ | 35.173 | 128.050 | 122.001 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| JUNG | 35.623 | 126.974 | 141.387 | Leica GR50/LEIAR25.R4 |
| NAMW | 35.423 | 127.396 | 179.845 | Leica GR50/LEIAR25.R4 |
| HADG | 35.162 | 127.709 | 76.592 | Trimble Alloy/TRM59800.00 |
| KWNJ | 35.178 | 126.910 | 71.626 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| YONK | 35.279 | 126.516 | 100.002 | Leica GR50/LEIAR25.R4 |
| MKPO | 34.817 | 126.381 | 64.380 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| JANG | 34.675 | 126.900 | 116.773 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| HGDO | 34.711 | 125.204 | 112.025 | Trimble NetR9/ChokeRing |
| GASA | 34.461 | 126.043 | 84.502 | Trimble NetR9/L1/L2 |
| GEOM | 34.008 | 127.322 | 95.421 | Trimble NetR9/ChokeRing |
| SORI | 34.412 | 127.801 | 114.177 | Trimble NetR9/ChokeRing |
| CHJU | 33.514 | 126.530 | 50.337 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| JEJU | 33.468 | 126.905 | 430.203 | Trimble NetR9/TRM59800.00 |
| SONC | 34.957 | 127.486 | 43.617 | Leica GR50/LEIAR25.R4 |
References
- Kim, D.-K.; Chun, H.-Y. A numerical study of the orographic effects associated with a heavy rainfall event. J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2000, 36, 441–454, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson, E.C.; Richard, E.R.; Rosset, R.; Smith, D.R. The numerical simulation of clouds, rain, and airflow over the Vosges and Black Forest mountains: A meso-β model with parameterized microphysics. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1985, 114, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Lee, H.W.; Jung, W.-S. The effects of low-level jet and topography on heavy rainfall near Mt. Jirisan. J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2003, 39, 441–458, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ryu, C.-S. Numerical studies on the relation between low-level jet and heavy rainfall. Proc. Spring Meet. Korean Earth Sci. Soc. 2004, 1, 118–120. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-W.; Hong, S.-Y. A numerical simulation study of orographic effects for a heavy rainfall event over Korea using the WRF model. J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2006, 16, 319–332, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.-K.; Eom, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, J.-B. High-resolution summer rainfall prediction in the JHWC real-time WRF system. Asia-Pacific J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 46, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hann, S. National/Regional Operational Procedures of GPS Water Vapour Networks and Agreed International Procedures; KNMI: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, D. The role of water vapour in the atmosphere. A short overview from a climate modeller’s point of view. Phys. Chem. Earth 2001, 26, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Kouba, J.; Schutz, B.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-J. Monitoring precipitable water vapor in real-time using global navigation satellite systems. J. Geodesy 2013, 87, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.R.; Penna, N.T.; Clarke, P.J.; Webster, S.; Martin, I.; Bennitt, G.V. Kinematic GNSS estimation of zenith wet delay over a range of altitudes. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Yuter, S.E.; Neiman, P.J.; Kingsmill, D.E. Water vapor fluxes and orographic precipitation over northern California associated with a landfalling atmospheric river. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2010, 138, 74–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, R.A.; Kingsmill, D.E. Orographic precipitation forcing along the coast of northern California during a landfalling winter storm. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2015, 143, 3570–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maussion, F.; Scherer, D.; Mölg, T.; Collier, E.; Curio, J.; Finkelnburg, R. Precipitation Seasonality and variability over the Tibetan Plateau as resolved by the High Asia Reanalysis. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1910–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dai, W.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Kuang, C.; Ao, M. Constructing a precipitable water vapor map from regional GNSS network observations without collocated meteorological data for weather forecasting. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5153–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.-P.; Yin, Y.-T.; Zhang, L.-F.; Wang, J.-N.; Zhang, M.-Y. Comparison analysis of total precipitable water of satellite-borne microwave radiometer retrievals and island radiosondes. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y. Comprehensive precipitable water vapor retrieval and application platform based on various water vapor detection technique. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billault-Roux, A.-C.; Berne, A. Integrated water vapor and liquid water path retrieval using a single-channel radiometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 2749–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walbröl, A.; Crewell, S.; Engelmann, R.; Orlandi, E.; Griesche, H.; Radenz, M.; Hofer, J.; Althausen, D.; Maturilli, M.; Ebell, K. Atmospheric temperature, water vapour and liquid water path from two microwave radiometers during MOSAiC. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antuña-Marrero, J.C.; Román, R.; Cachorro, V.E.; Mateos, D.; Toledano, C.; Calle, A.; Antuña-Sánchez, J.C.; Vaquero-Martínez, J.; Antón, M.; de Frutos Baraja, Á.M. Integrated water vapor over the Arctic: Comparison between radiosondes and sun photometer observations. Atmos. Res. 2022, 270, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, V.; Riley, S.; Minschwaner, K. Atmospheric precipitable water vapor and its correlation with clear-sky infrared temperature observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2022, 15, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, A.; Li, W.; Fu, E.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Z. An improved method for rainfall forecast based on GNSS-PWV. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Mo, Z.; Xie, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Kang, C.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal characteristics of GNSS-derived precipitable water vapor during heavy rainfall events in Guilin, China. Satell. Navig. 2022, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Choy, S.; Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, K.; Li, L.; Fu, E.; et al. Detecting heavy rainfall using anomaly-based percentile thresholds of predictors derived from GNSS-PWV. Atmos. Res. 2022, 265, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-D. Effects of regional warming due to urbanization on daytime local circulations in a complex basin of the Daegu metropolitan area, Korea. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Hugentobler, U.; Fridez, P.; Meindl, M. Bernese GPS Software, version 5.0; Astronomical Institute, University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Niell, A.E. Global mapping functions for the atmosphere delay at radio wavelengths. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 3227–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging of satellites. In The Use of Artificial Satellites for Geodesy; Geophysical Monograph Series; Henriksen, S.W., Mancini, A., Chovitz, B.H., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; Volume 15, pp. 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, inertial, and multi-sensor integrated navigation systems. Artech House 2007, 64, 161–277. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.L.; Herring, T.A.; Shapiro, I.I.; Gogers, A.E.E.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.; Park, K.D.; Heo, B.H. Comparisons of a local mean temperature equation for GPS-based precipitable water vapor over the Korean Peninsula. J. Astron. Space Sci. 2008, 25, 425–434, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson Correlation Coefficient. In Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, D. The computation of equivalent potential temperature. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1980, 108, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-E.; Yoo, S.-M.; Yoon, H.S.; Chung, J.-K.; Cho, J. Performance analysis of mapping functions and mean temperature equations for GNSS precipitable water vapor in the Korean Peninsula. J. Position. Navig. Timing 2016, 5, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, E.C.; Richard, E.R.; Rosset, R.; Smith, D.R. The statistical relationship between upslope flow and rainfall in California’s coastal mountains: Observations during CALJET. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2002, 130, 1468–1492. [Google Scholar]
- Holloway, C.E.; Neelin, J.D. Moisture vertical structure, column water vapor, and tropical deep convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1665–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.E.; Neelin, J.D. Temporal relations of column water vapor and tropical precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidema, P.; Torri, G.; Muller, C.; Chandra, A. A survey of precipitation-induced atmospheric cold pools over oceans and their interactions with the larger-scale environment. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 38, 1283–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, A.M. Organization of tropical convection in low vertical wind shears: The role of water vapor. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, S.H.; Beau, I.; Bechtold, P.; Grandpeix, J.-Y.; Piriou, J.-M.; Redelsperger, J.-L.; Soares, P.M.M. Sensitivity of moist convection to environmental humidity. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2004, 130, 3055–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, D.-I.; Wang, C.-C. Impact of the cold pool on mesoscale convective system–Produced extreme rainfall over southeastern South Korea: 7 July 2009. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2016, 144, 3985–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Werl, B.; Schuh, H. Troposphere mapping functions for GPS and very long baseline interferometry from European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts operational analysis data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.B.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, R.M.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Persson, P.O.G. Coastal orographic rainfall processes observed by radar during the California LandFalling Jets Experiment. J. Hydrometeor. 2003, 4, 264–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, F.M.; Rotunno, R. Dropsonde observations in low-level jets over the northeastern Pacific Ocean from CALJET-1998 and PACJET-2001: Mean vertical profile and atmospheric river characteristics. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2005, 133, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M.; White, A.B.; Lundquist, J.D.; Dettinger, M.D. Meteorological characteristics and overland precipitation impacts of atmospheric rivers affecting the west coast of North America based on eight years of SSM/I satellite observations. J. Hydrometeor. 2008, 9, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
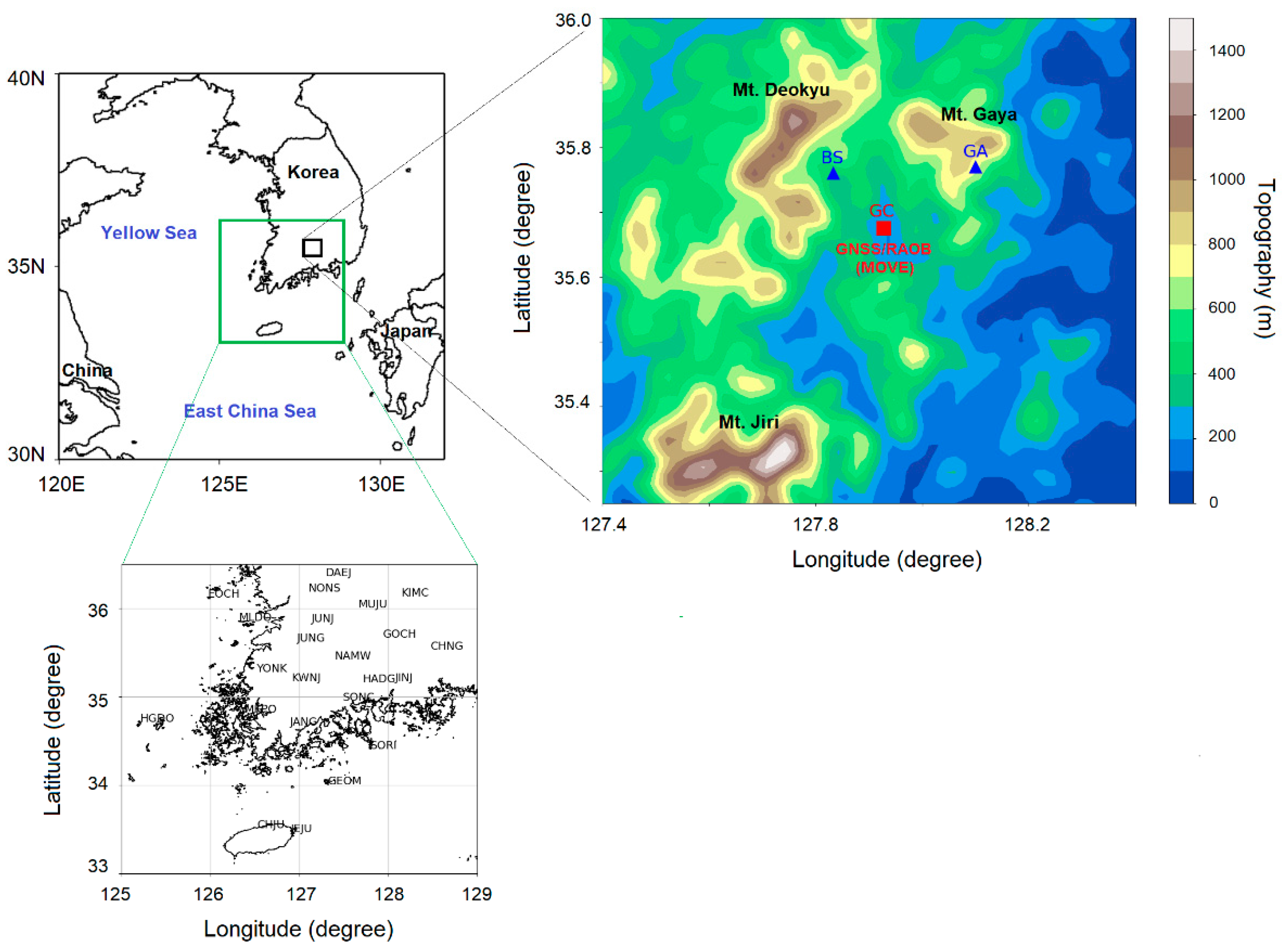


| Variables (Intervals) | Instruments (Site) | Manufacture (Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical profile (6 h) | Rawinsonde (GC; MOVE 1) | GRAW, Germany (DFM-09) |
| Precipitable water vapor (1 h, 10 min) | Global navigation satellite system (GC; MOVE) | Trimble, US (NetR9) |
| Precipitation amounts (1 min) | Weighting precipitation gauge (GC, BS, GA 2) | Wellbian system, South Korea (WPG-A1) |
| Wind speed and direction (1 min) | Anemometer (GC) | R. M. Young, US (05018) |
| GNSS1h vs. RAOB 1 | GNSS10min vs. RAOB | GNSS10min vs. GNSS1h | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 77 | 77 | 480 |
| Slope 2 | 1.01 | 1.00 | 0.98 |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| RMSE 3 (mm) | 2.8 | 3.4 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-J.; Jee, J.-B.; Lim, B. Investigating the Influence of Water Vapor on Heavy Rainfall Events in the Southern Korean Peninsula. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020340
Kim Y-J, Jee J-B, Lim B. Investigating the Influence of Water Vapor on Heavy Rainfall Events in the Southern Korean Peninsula. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020340
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yoo-Jun, Joon-Bum Jee, and Byunghwan Lim. 2023. "Investigating the Influence of Water Vapor on Heavy Rainfall Events in the Southern Korean Peninsula" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020340
APA StyleKim, Y.-J., Jee, J.-B., & Lim, B. (2023). Investigating the Influence of Water Vapor on Heavy Rainfall Events in the Southern Korean Peninsula. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020340







