Analysis of Soil Moisture Change Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Grassland on the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
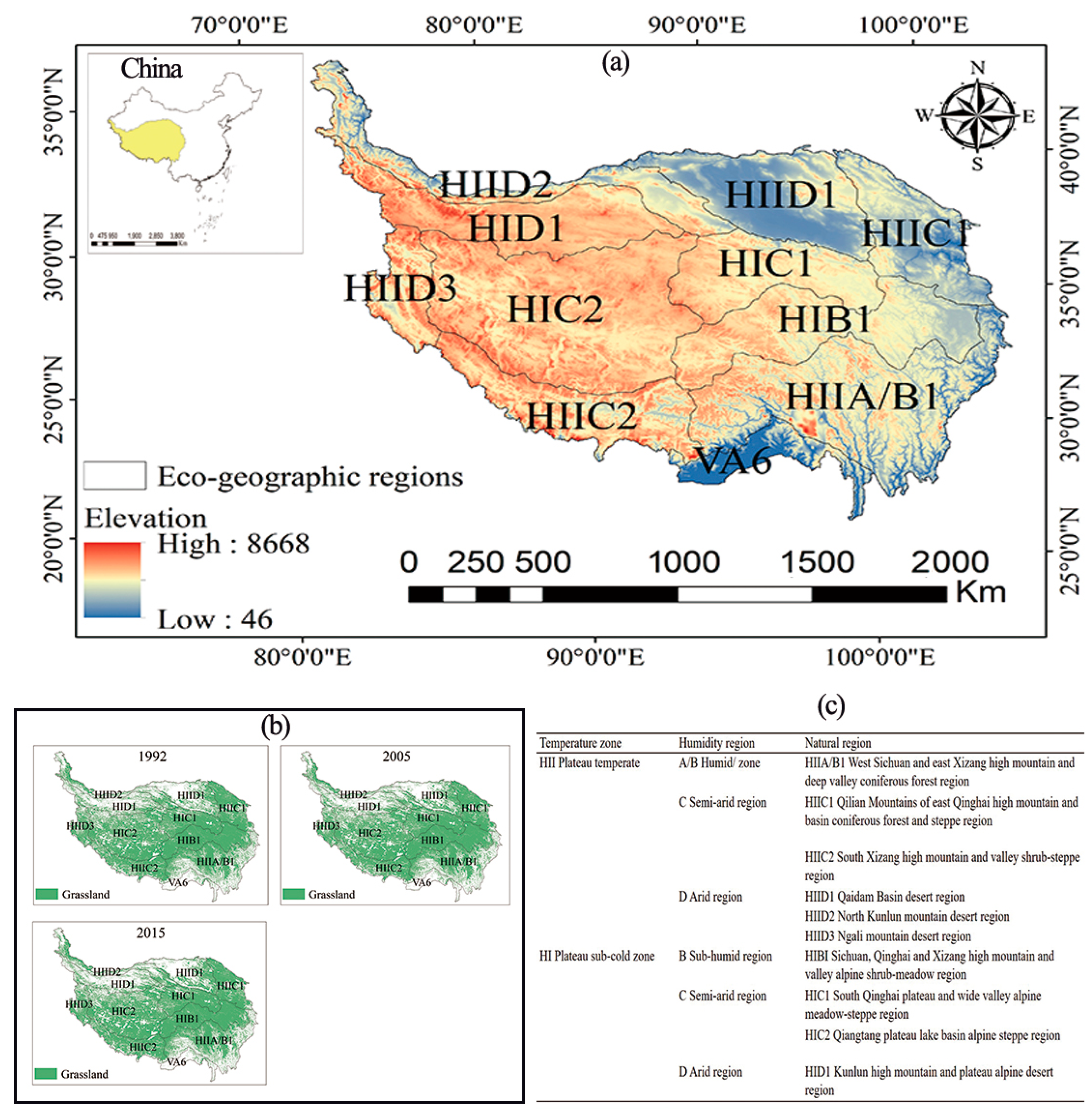
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
2.2.2. ERA5-Land Soil Moisture Data
2.2.3. Climate and Vegetation Data
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Pixel-By-Pixel Trend Analysis
2.3.2. Partial Correlation Analysis
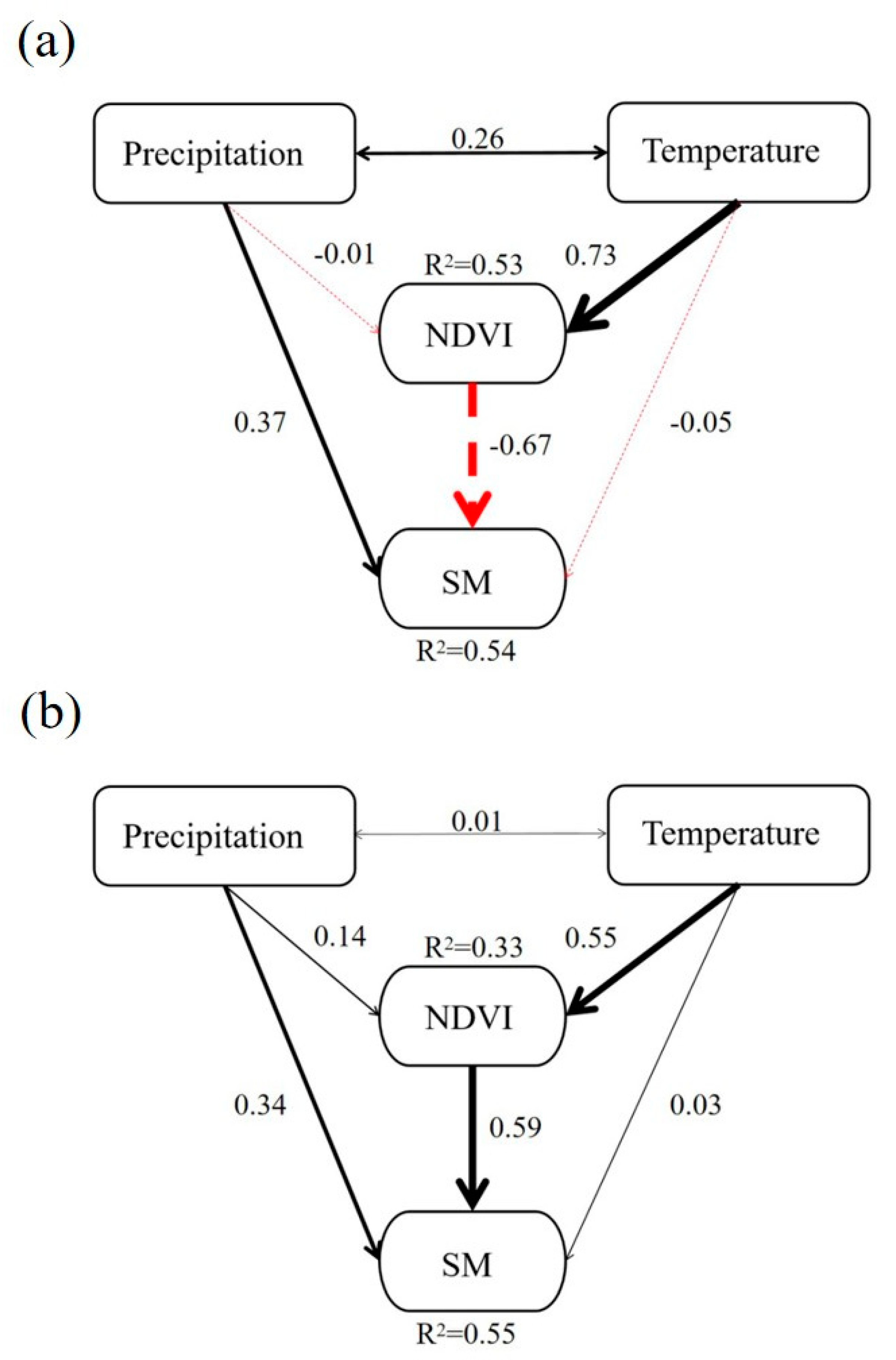
2.3.3. Structural Equation Model (SEM)
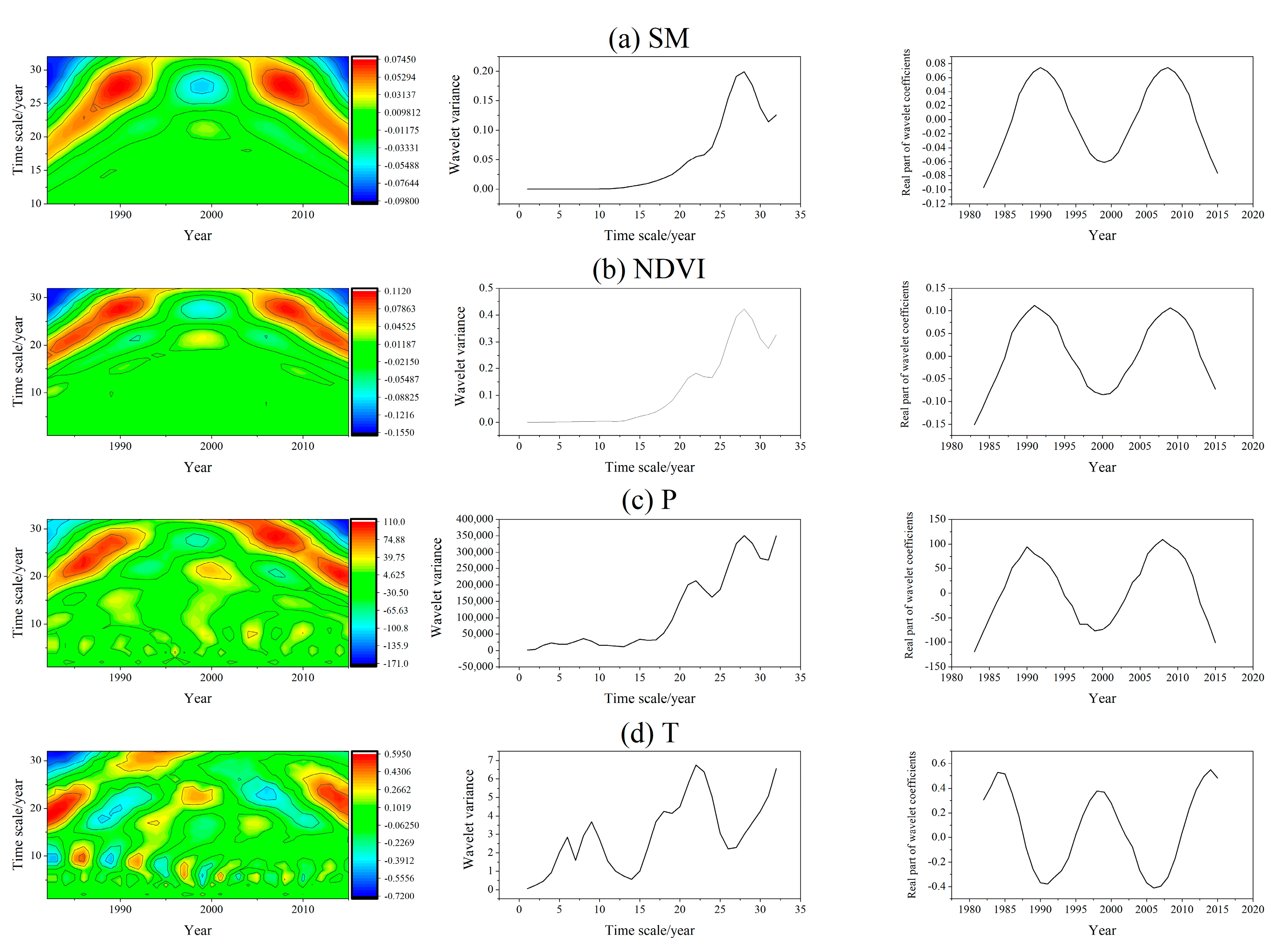
2.3.4. Wavelet Analysis
3. Results
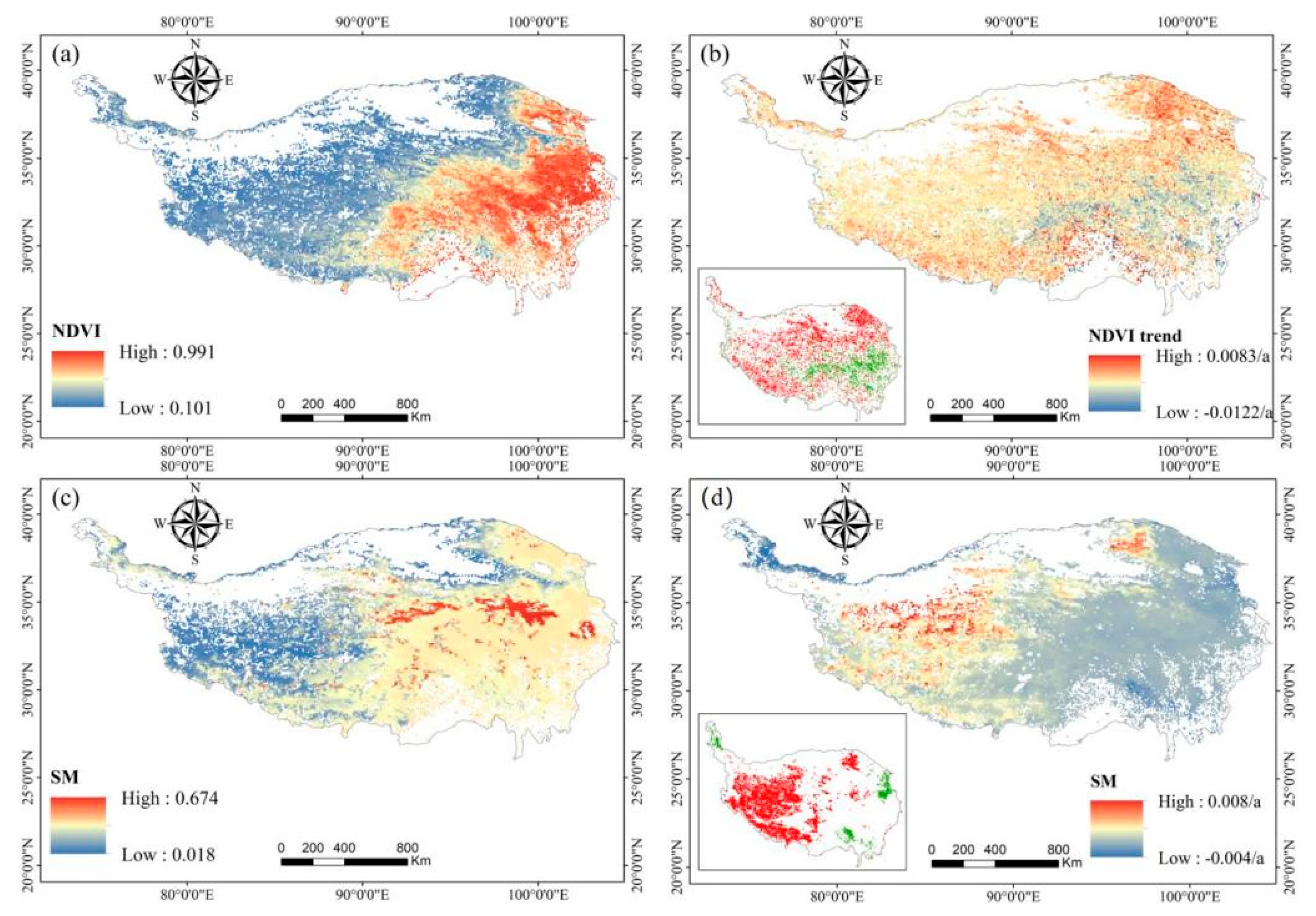
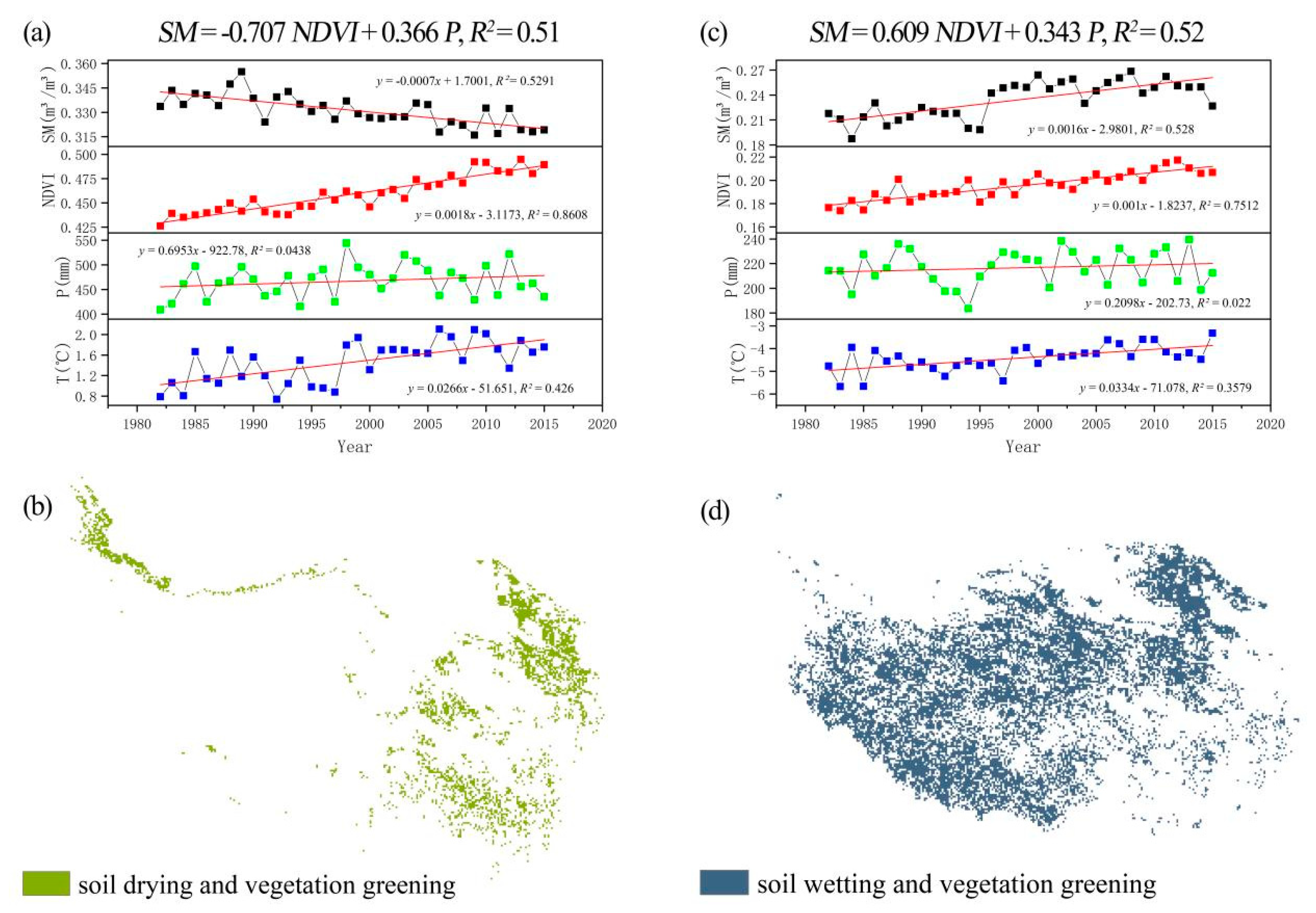
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Vegetation and Soil Moisture
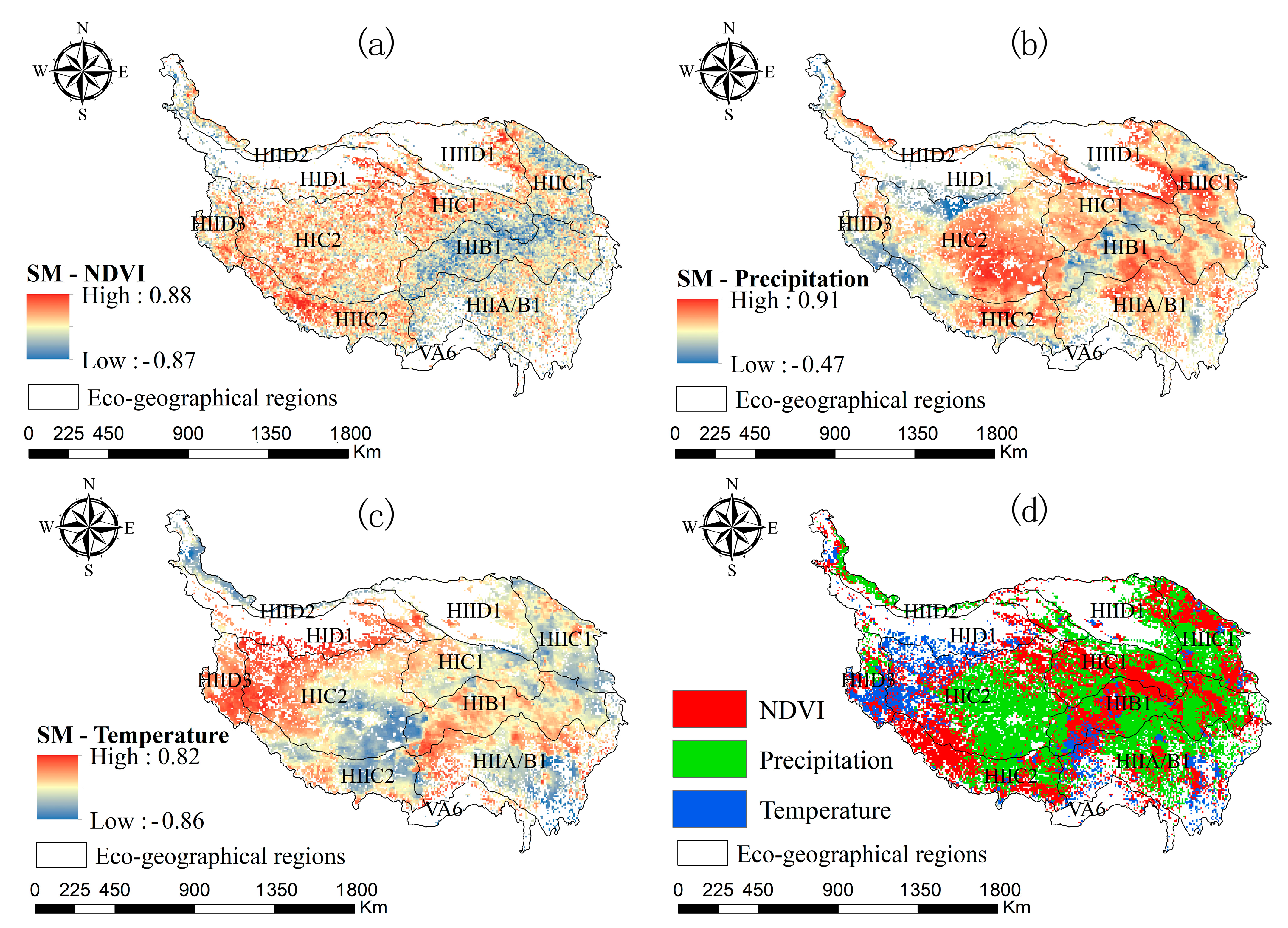
3.2. Influence of Vegetation and Climate on SM Changes
3.3. Analysis of the Causes of Soil Moisture Changes in Different Ecological Regions
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Moisture Characteristics and Attribution Analysis of the Tibetan Plateau
4.2. Cyclical Characteristics of SM and the Possibility of Future Changes
4.3. Influence of Vegetation Greening on SM Changes
4.4. Prospects for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, Y.P.; You, Q.L.; Wu, F.Y.; Pepin, N.; Kang, S.C. Surface mean temperature from the observational stations and multiple reanalyses over the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, R.R.; Keeling, C.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Jolly, W.M.; Piper, S.C.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B.; Running, S.W. Climate-driven increases in global terrestrial net primary production from 1982 to 1999. Science 2003, 300, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrall, B.; Pickering, C.M. Alpine vegetation in the context of climate change: A global review of past research and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.; Bagchi, S. Spatial patterns of long-term vegetation greening and browning are consistent across multiple scales: Implications for monitoring land degradation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2485–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009. Science 2010, 329, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liang, T.; Hou, F.; Xu, J.; Xue, P. Quantitative spatial analysis of vegetation dynamics and potential driving factors in a typical alpine region on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau using the Google Earth Engine. Catena 2021, 206, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zu, J.; Ding, M.; Paudel, B. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Vegetation Greenness Change and Associated Climatic and Anthropogenic Drivers on the Tibetan Plateau during 2000–2015. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.X. Variations and controlling factors of vegetation dynamics on the Qingzang Plateau of China over the recent 20 years. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zu, J.; Zhang, J. The Influences of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Dynamics in the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Water scarcity assessments in the past, present and future. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, J.S.; Seagar, R.; Smerdon, J.E.; Cook, B.I.; Williams, A.P.; Horton, R.M. Blue Water Trade-Offs With Vegetation in a CO2-Enriched Climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.M.; Fu, B.J.; Piao, S.L.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lü, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.R.; Liu, Y.F.; Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.L. Restoration of a hillslope grassland with an ecological grass species (Elymus tangutorum) favors rainfall interception and water infiltration and reduces soil loss on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2022, 219, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Shi, J.J.; Niu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.L. Effectiveness of mixed cultivated grasslands to reduce sediment concentration in runoff on hillslopes in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2022, 422, 115933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.L.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, G.L. Regulation of alpine meadow patch coverage on runoff and sediment under natural rainfall on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothoff, S.A.; Or, D.; Groeneveld, D.P.; Jones, S.B. The effect of vegetation on infiltration in shallow soils underlain by fissured bedrock. J. Hydrol. 1999, 218, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wei, X.H.; McNulty, S.G.; Vose, J.M. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2005, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.H.; Wang, S.J.; Bai, X.Y.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Chen, F.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Vegetation greening intensified soil drying in some semi-arid and arid areas of the world. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 292–293, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Q.; Long, D.; Hong, Y.; Gao, J.; Wan, W. Documentation of multifactorial relationships between precipitation and topography of the Tibetan Plateau using spaceborne precipitation radars. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zheng, D. Delineation of eco-geographic regional system of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2003, 13, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Q.; Kayumba, P.M. Evaluation of consistency among three NDVI products applied to High Mountain Asia in 2000–2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Luo, G.; Wu, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Variation trend of global soil moisture and its cause analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duveiller, G.; Hooker, J.; Cescatti, A. The mark of vegetation change on Earth’s surface energy balance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbach, T.; Luna, X. Inference for partial correlation when data are missing not at random. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2018, 141, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Zhou, R.L.; Ren, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wen, Z.M. Evaluating the dynamics of grassland net primary productivity in response to climate change in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Jiao, K.; Wu, S. Investigating the spatially heterogeneous relationships between climate factors and NDVI in China during 1982 to 2013. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.M.; Xue, Z.; Bagherzadeh, A.; Liu, M. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of NDVI and its response to climate on the Loess Plateau from 1985 to 2015. Catena 2021, 203, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Gerbing, D.W. Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychol. Bull. 1988, 103, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Latent variable path analysis in clinical research: A beginner’s tour guide. J. Clin. Psychol. 1991, 47, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, F.B.; Haghighi, A.T.; Riml, J.; Mathias Kondolf, G.; Kløve, B.; Marttila, H. A method for assessment of sub-daily flow alterations using wavelet analysis for regulated rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Sun, W. Relationship between the Formation of PM2.5 and Meteorological Factors in Northern China: The Periodic Characteristics of Wavelet Analysis. Adv. Meteorol. 2021, 2021, 9723676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, G. Periodic variations of rainfall, groundwater level and dissolved radon from the perspective of wavelet analysis: A case study in Tengchong, southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Ha, K.J. Prediction of dominant intraseasonal modes in the East Asian-western North Pacific summer monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, Q.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Sheng, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhao, L.; Jin, H.; Zou, D.; Wu, X. Characteristic, changes and impacts of permafrost on Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Effects of Air Temperature and Precipitation on Soil Moisture on the Tibetan Plateau during the 2015 Growing Season. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 4918945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Multi-depth evolution characteristics of soil moisture over the Tibetan Plateau in the past 70 years using reanalysis products. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 979853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.K.; Guo, X.W.; Lan, Y.T.; Fan, B.; Cao, G. Effects of Climatic Variability on Soil Water Content in an Alpine Kobresia Meadow, Northern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Water 2022, 14, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ma, W.; Luo, J. Drying–Wetting Changes of Surface Soil Moisture and the Influencing Factors in Permafrost Regions of the Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tang, H. Evidence of Warming and Wetting Climate over the Tibetan Plateau. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2010, 42, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xu, X.D.; Wang, P.J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, S.-J.; Wang, C.-Z.; Cai, W.-Y. The Warming and Wetting Ecological Environment Changes over the QinghaiTibetan Plateau and the Driving Effect of the Asian Summer Monsoon. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2022, 28, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, S.; Ding, Y. Active layer thickness variations on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau under the scenarios of climate change. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Du, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, L. Analysis of spatial distribution and multi-year trend of the remotely sensed soil moisture on the tibetan plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, B.; Yuan, W.P.; Guo, L.L.; Zhang, Y.F. Increasing interannual variability of global vegetation greenness. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Xu, G.C.; Li, P.; Li, Z.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Jia, L.; Cheng, Y.T.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhuang, S.H.; et al. Vegetation change and its relationship with climate factors and elevation on the Tibetan plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, D.L.; Shen, M.G.; Xu, X.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Huang, W.; YU, L.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Li, X.; et al. Contrasting Effects of Temperature and Precipitation on Vegetation Greenness along Elevation Gradients of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.D.; Zheng, C.; Liu, X.H.; Lu, Y.D.; Chen, Y.F.; Wei, Y.; Ma, Y.D. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change and human activities from 1982 to 2020: A case study in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Jia, X.X.; Jia, Y.H.; Shao, M.A.; Hu, W. Modeling long-term soil water dynamics in response to land-use change in a semi-arid area. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Akbar, R.; Konings, A.G.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D. The global distribution and dynamics of surface soil moisture. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhao, F.; Guan, Y. Quantifying spatiotemporal variations in soil moisture driven by vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez-Macho, G.; Fan, Y. Spatiotemporal origin of soil water taken up by vegetation. Nature 2021, 598, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
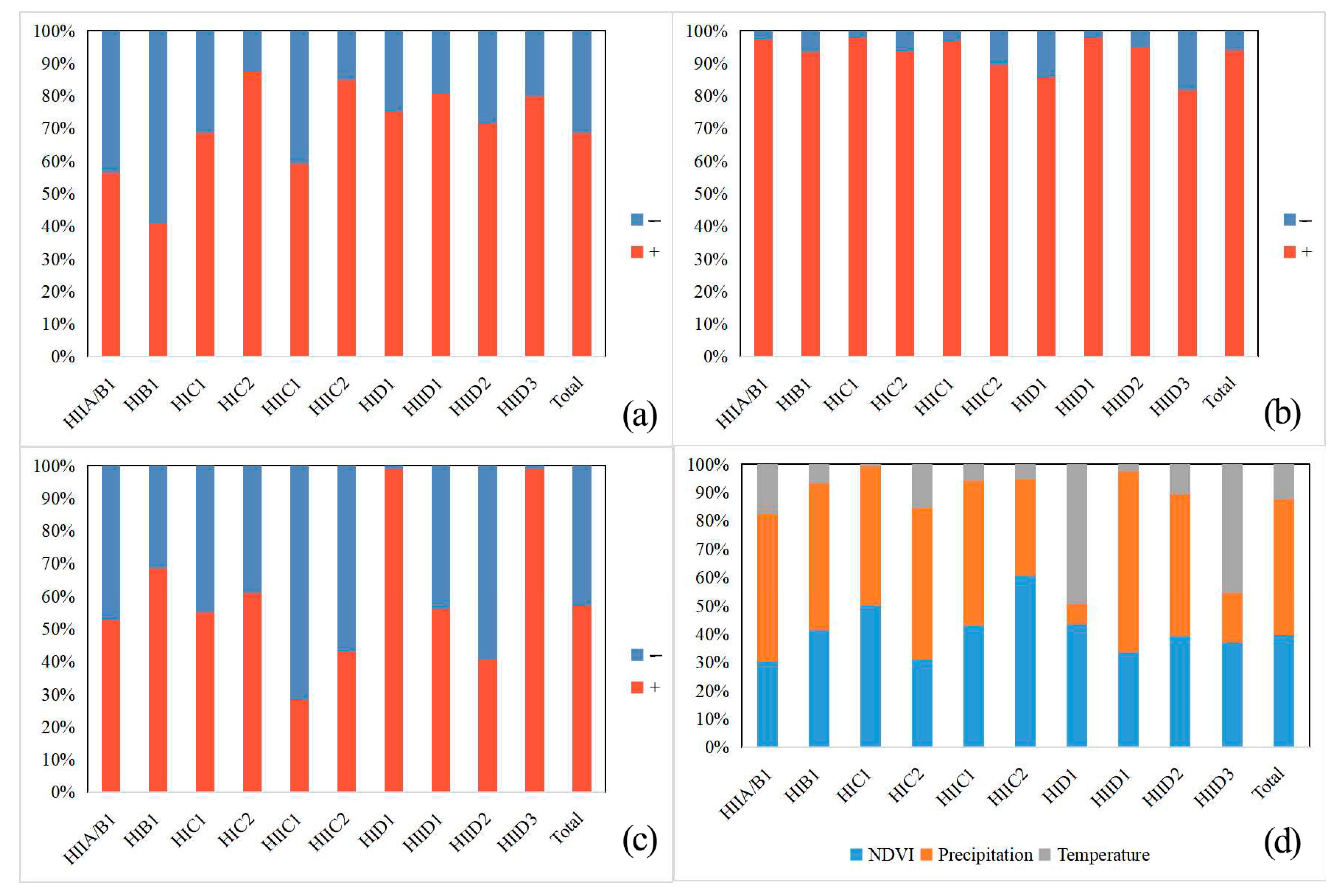

| Humid Regions | Arid Regions | |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | 35.68 | 41.29 |
| Precipitation | 52.09 | 46.09 |
| Temperature | 12.23 | 12.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, R.; Duan, G.; Wen, Z. Analysis of Soil Moisture Change Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020298
Wang L, Lu J, Zhou R, Duan G, Wen Z. Analysis of Soil Moisture Change Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(2):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020298
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Licheng, Jinxin Lu, Ronglei Zhou, Gaohui Duan, and Zhongming Wen. 2023. "Analysis of Soil Moisture Change Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Grassland on the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 15, no. 2: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020298
APA StyleWang, L., Lu, J., Zhou, R., Duan, G., & Wen, Z. (2023). Analysis of Soil Moisture Change Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 15(2), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15020298









