Evaluating the Performance of the Greenbelt Policy in Beijing Using Multi-Source Long-Term Satellite Observations from 2000 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
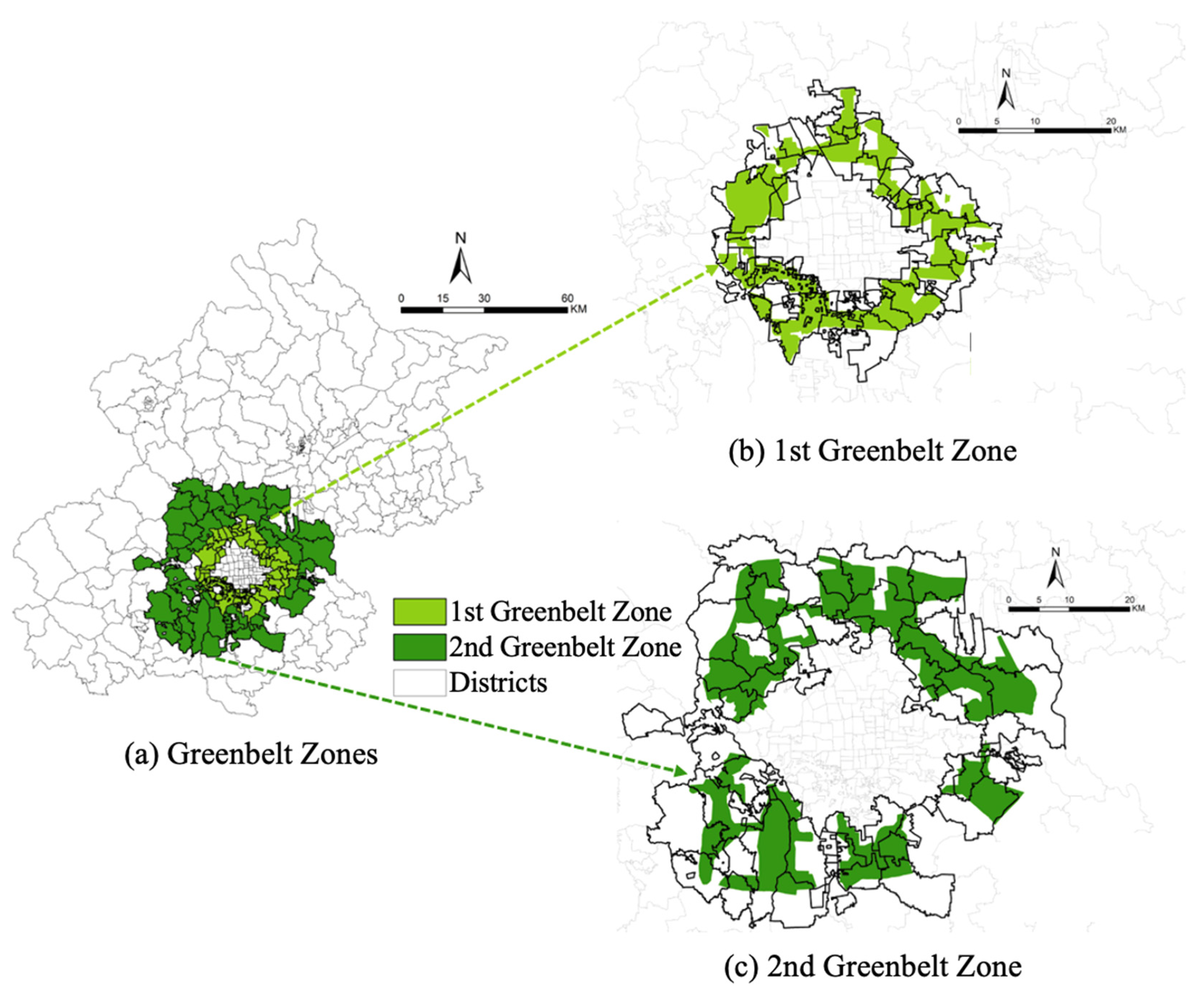
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. NDVI Data from MODIS
2.2.2. Land Surface Temperature Data from MODIS
2.2.3. Precipitation Dataset
2.2.4. Night-Light Composite Dataset
2.2.5. Population Density Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. MODIS Estimate of Long-Term Trends of NDVI Using Linear Regression Analysis
2.3.2. Evaluating the Greenbelt Policies Using Fixed Effects Regression
- (1)
- Fixed effects regression
- (2)
- Variable Selection
3. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Vegetation in Beijing over the Past 20 Years
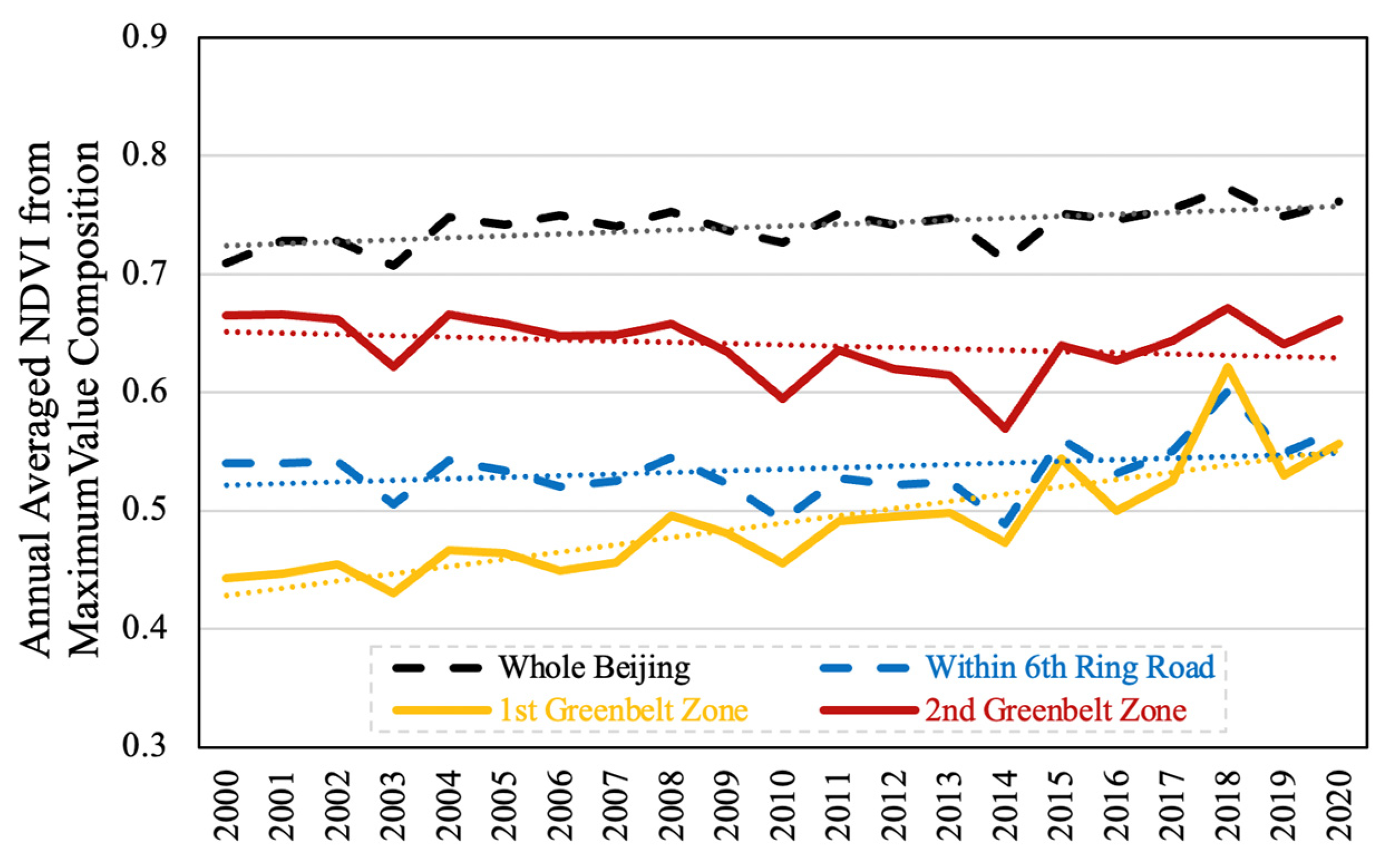
3.1. Interannual NDVI Variations
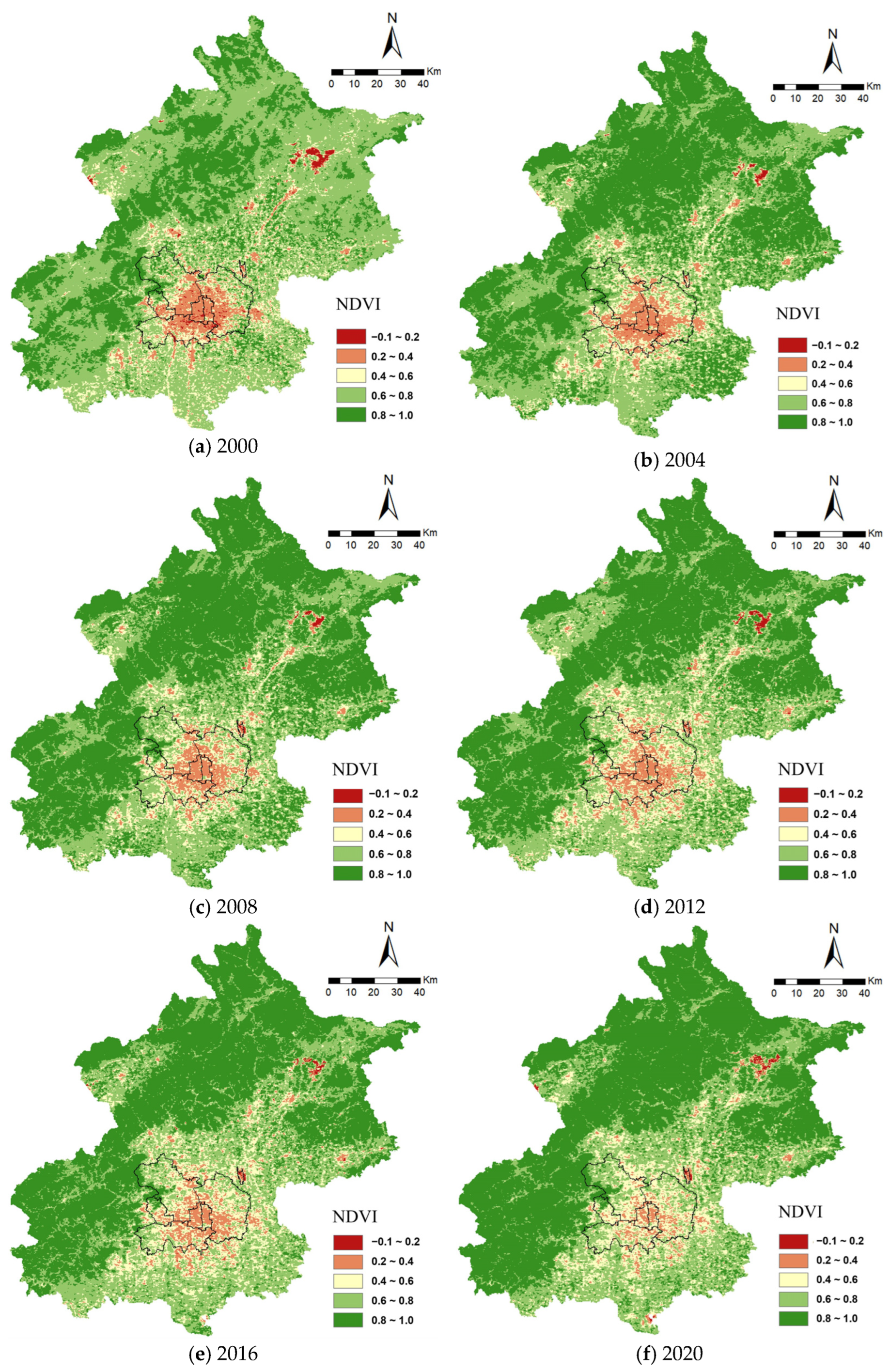
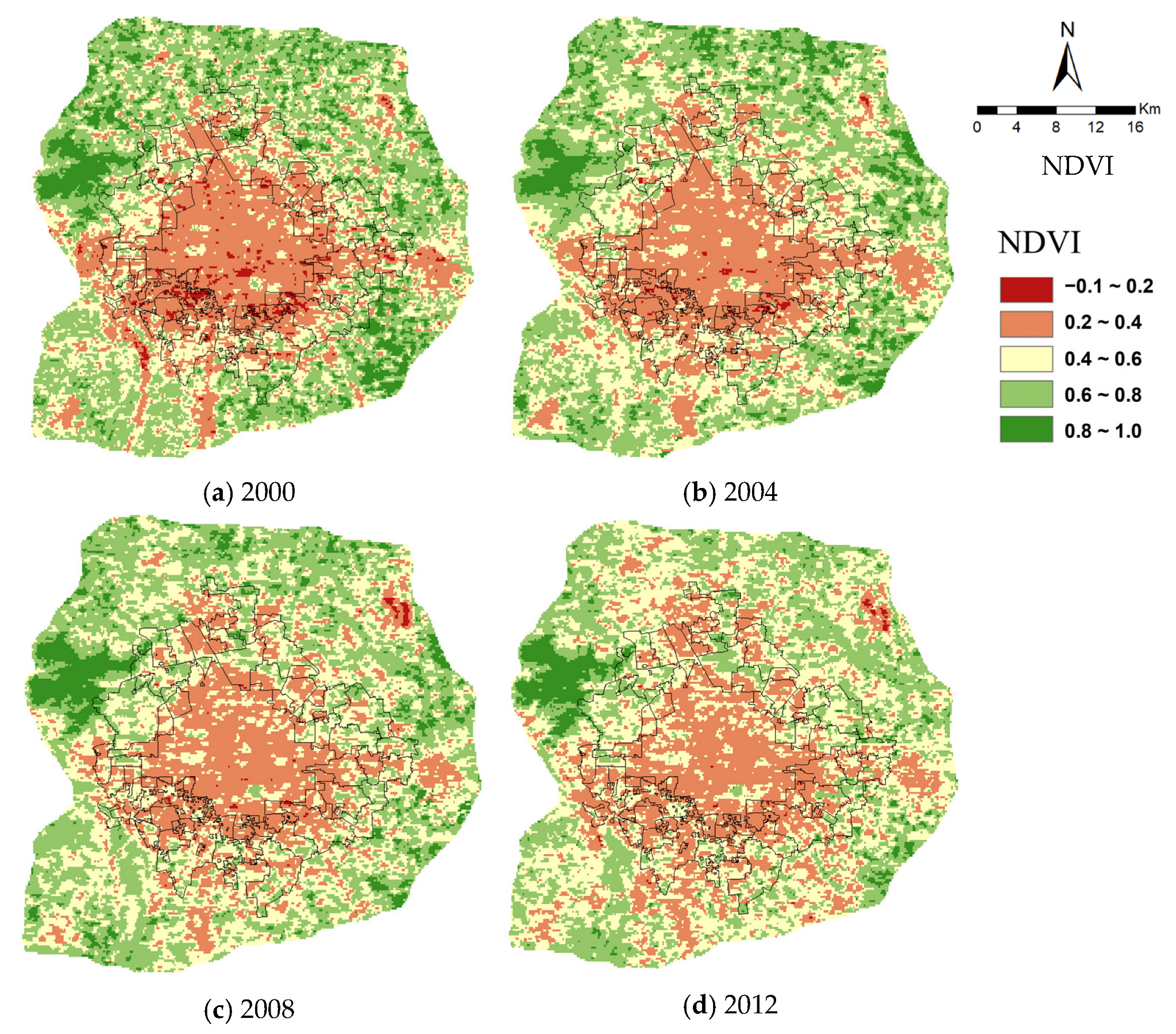
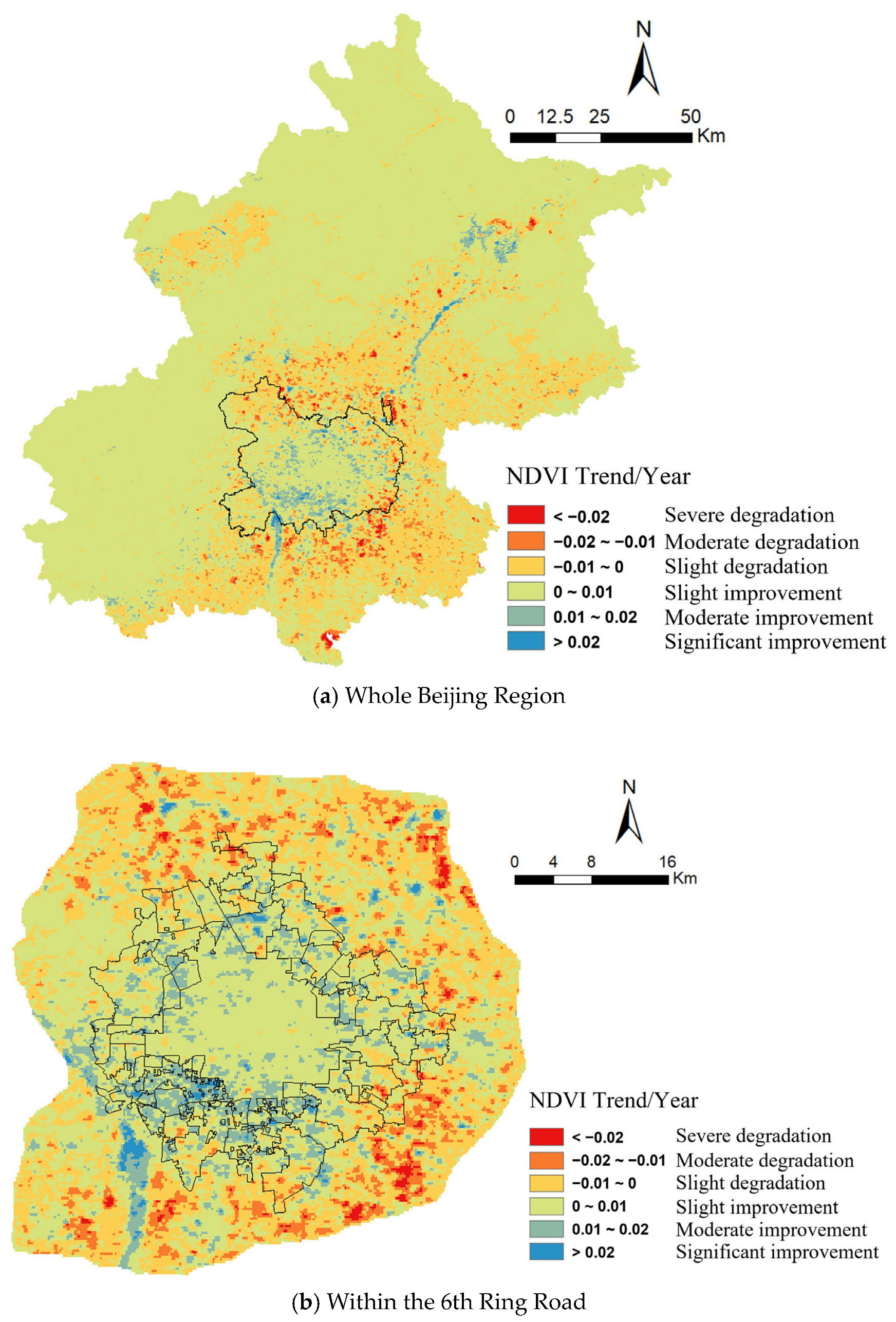
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Variations in NDVI in Beijing
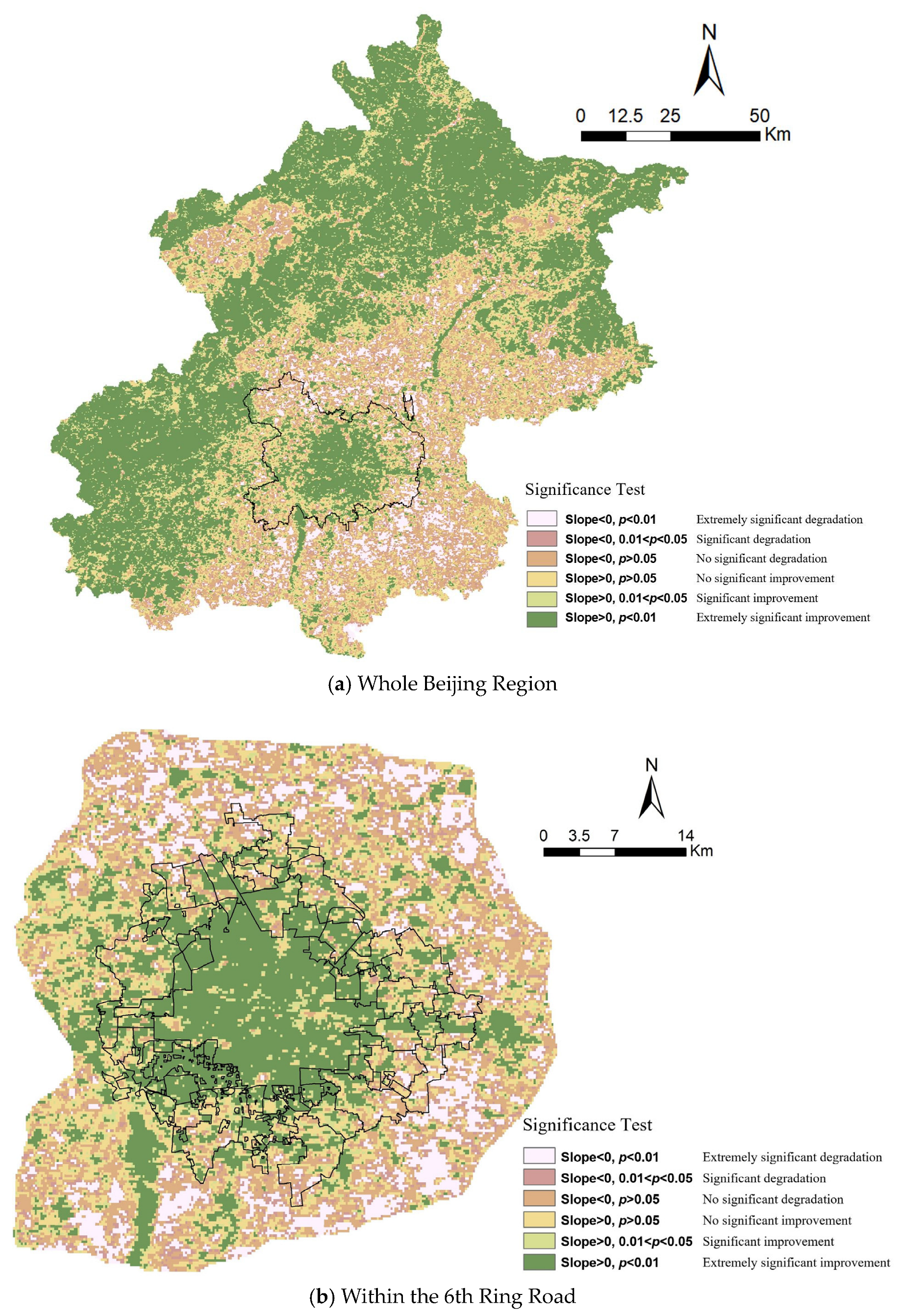
3.3. Temporal Trends of NDVI Change in Beijing from 2000 to 2020
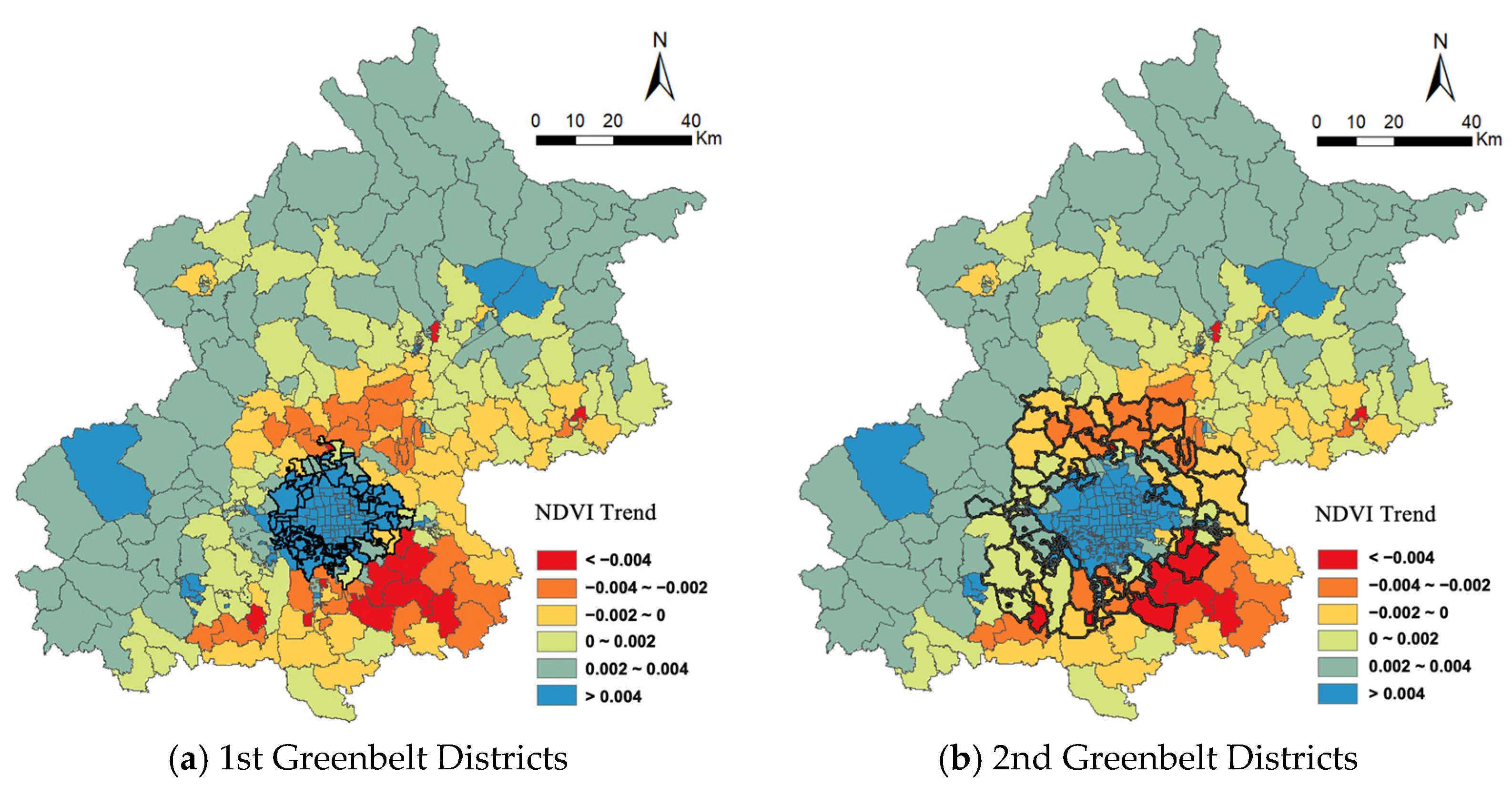
3.4. The Spatio-Temporal Variations of NDVI in Beijing at District Level
4. Quantitative Evaluation of the Performance of the Greenbelt Policies
4.1. Model Setting
4.2. Collinearity Test
4.3. Results from Fixed Effects Regression Model
4.4. Robustness Test for the Fixed Effects Regression Model Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Positive Outcomes from the Implementation of the 1st Greenbelt Policy
5.2. Mixed Outcomes from the Implementation of the 2nd Greenbelt Policy
5.3. Contribution of Other Related Factors in NDVI Changes in Beijing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y. Understanding urban plant phenology for sustainable cities and planet. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, R.; Paulussen, J.; Liu, X. Comprehensive concept planning of urban greening based on ecological principles: A case study in Beijing, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 72, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Crane, D.E.; Stevens, J.C. Air pollution removal by urban trees and shrubs in the United States. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J. Atmospheric carbon reduction by urban trees. J. Environ. Manag. 1993, 37, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenman, T.S.; Churkina, G.; Jariwala, S.P.; Kumar, P.; Lovasi, G.S.; Pataki, D.E.; Weinberger, K.R.; Whitlow, T.H. Urban trees, air quality, and asthma: An interdisciplinary review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 187, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Ma, L.; Huang, C. Factors affecting the use of urban green spaces for physical activities: Views of young urban residents in Beijing. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Jin, Y. What if Beijing had enforced the 1st or 2nd greenbelt?–Analyses from an economic perspective. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 182, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, J. The failure and success of greenbelt program in Beijing. Urban For. Urban Green. 2007, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Pan, M.; Huhe, T. Determinizing the contributions of human activities and climate change on greening in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yin, P.Y.; Li, X.C.; Niu, Q.D.; Wang, Y.X.; Cao, W.T.; Huang, J.X.; Chen, H.; Yao, X.C.; Yu, L.; et al. The divergent response of vegetation phenology to urbanization: A case study of Beijing city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Mapping the annual dynamics of land cover in Beijing from 2001 to 2020 using Landsat dense time series stack. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 185, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Clinton, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Gong, P.; Yang, J.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Mapping major land cover dynamics in Beijing using all Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, L.; Jing, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Guan, X. High-quality vegetation index product generation: A review of NDVI time series reconstruction techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreiras, J.M.B.; Pereira, J.M.C.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Stroppiana, D. Evaluation of compositing algorithms over the Brazilian Amazon using SPOT-4 VEGETATION data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 3427–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Lü, Y.; Harris, P.; Comber, A.; Wu, L. Peri-urbanization may vary with vegetation restoration: A large scale regional analysis. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 29, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z.; Li, S. The impacts of urbanization and climate change on urban vegetation dynamics in China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 54, 126764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, D.; Daeschner, S.; Hope, A.; Douglas, D.; Petersen, A.; Myneni, R.; Zhou, L.; Oechel, W. Variability of the seasonally integrated normalized difference vegetation index across the north slope of Alaska in the 1990s. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Pickett, S.T.; Li, W.; Han, L. The rapid but “invisible” changes in urban greenspace: A comparative study of nine Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Han, L. Understanding the dynamic of greenspace in the urbanized area of Beijing based on high resolution satellite images. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengston, D.N.; Youn, Y.C. Urban containment policies and the protection of natural areas: The case of Seoul’s greenbelt. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Chan, C.S.; Pei, T.; Wenting, Y.; Xin, Z. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and evolution mechanism of urban parks in Beijing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 64, 127265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ci, H.; Gu, X.; Gulakhmadov, A. Attribution of NDVI Dynamics over the Globe from 1982 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijing Municipal Government. No. 7 The Approval from Beijing Municipal Government on the Proposal from Beijing Municipal Commission Regarding Designation of the Greenbelt; Pub. L. No. Jingzhengfa (7); Beijing Municipal Government: Beijing, China, 1994.
- Beijing Municipal Government. No. 7 Opinions on Accelerating the Construction of Green Belt Areas in Beijing; Pub. L. No. Jingzhengfa (12); Beijing Municipal Government: Beijing, China, 2000.
- Beijing Municipal Government. No. 15 The Approavel from Beijing Municipal Government on the Proposal of Establishing the Second Greenbelt; Pub. L. No. Jingzhenghan (15); Beijing Municipal Government: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J.G. Urbanization alters spatiotemporal patterns of ecosystem primary production: A case study of the Phoenix metropolitan region, USA. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viovy, N.; Arino, O.; Belward, A.S. The best index slope extraction (BISE)—A method for reducing noise in NDVI time-series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, Y.; Sobrino, J.A.; Verhoef, W. Changes in land surface temperatures and NDVI values over Europe between 1982 and 1999. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnieli, A.; Agam, N.; Pinker, R.T.; Anderson, M.; Imhoff, M.L.; Gutman, G.G.; Panov, N.; Goldberg, A. Use of NDVI and land surface temperature for drought assessment: Merits and limitations. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.C.; Peterson, P.J.; Landsfeld, M.F.; Pedreros, D.H.; Verdin, J.P.; Rowland, J.D.; Romero, B.E.; Husak, G.J.; Michaelsen, J.C.; Verdin, A.P. A Quasi-Global Precipitation Time Series for Drought Monitoring; U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 832; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014; 4p. Available online: http://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/832/ (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, X.; Yao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Cai, W. Evaluation of CHIRPS and its application for drought monitoring over the Haihe River Basin, China. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, Z.; Chen, B.; Gong, P.; Fu, H.; Xu, B. A Prolonged Artificial Nighttime-light Dataset of China (1984–2020). National Tibetan Plateau Data Center 2021. Available online: https://cstr.cn/18406.11.Socioeco.tpdc.271202 (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- WorldPop (www.worldpop.org—School of Geography and Environmental Science, University of Southampton; Department of Geography and Geosciences, University of Louisville; Departement de Geographie, Universite de Namur) and Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN), Columbia University 2018. Global High Resolution Population Denominators Project—Funded by The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Available online: https://worldpop.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/WorldPop_Population_Density_1km/ImageServer (accessed on 1 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yao, F.; Li, W.; Si, M. VIIRS-based remote sensing estimation of ground-level PM2. 5 concentrations in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei: A spatiotemporal statistical model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J.M.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Elucidating the impact of temperature variability and extremes on cereal croplands through remote sensing. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, P.D. Fixed Effects Regression Models; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Xu, B. Olympic effects on reshaping urban greenspace of host cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 230, 104615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; van den Bosch, C.C.K.; Yang, J.; Devisscher, T.; Wirtz, Z.; Jia, L.; Duan, J.; Ma, L. Beijing’s 50 million new urban trees: Strategic governance for large-scale urban afforestation. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, J.A. Specification tests in econometrics. Econometrica 1978, 46, 1251–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, J.; John, R.; Joseph, S. Consistent response of vegetation dynamics to recent climate change in tropical mountain regions. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, Y. Trend analysis of vegetation dynamics in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | Data Sources | Time (Year) | Spatial Resolution | Links or References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | MOD13Q1 | 2000–2020 | 250 m | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod13q1v006 (accessed on 1 June 2023) |
| Land surface temperature | MOD11A1 | 2000–2020 | 1000 m | https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod11a1v006 (accessed on 1 June 2023) |
| Precipitation | CHIRPS | 2000–2020 | 5000 m | [34] |
| Population density | WorldPop | 2000–2020 | 1000 m | [37] |
| Night-light index | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | 2000–2020 | 100 m | [36] |
| Variables | Variable Names | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | NDVI | This indicates the coverage of district vegetation and the growth status of vegetation, with values ranging from −1 to 1. A larger value represents higher district vegetation coverage and better growth. |
| Key Explanatory Variable | 1st Greenbelt Policy | The 49 districts related to the 1st Greenbelt Policy during 2000–2020. |
| 2nd Greenbelt Policy | The 55 districts related to the 2nd Greenbelt Policy during 2004–2020. | |
| 2008 Summer Olympics | All 331 districts in Beijing during 2001–2008. | |
| Other Related Variables | Annual LST | The average surface temperature of each district in Beijing (unit: °C). |
| Annual Precipitation | The annual total precipitation for each district in Beijing (unit: millimeters). | |
| Population Density | The population density per square kilometer for each district in Beijing (unit: number per square kilometer). | |
| Night-Light Index | The normalized light intensity index of each district in Beijing. |
| Year | 2000 | 2004 | 2008 | 2012 | 2016 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | |||||||
| −0.1~0.2 | 0.64% | 0.20% | 0.15% | 0.24% | 0.17% | 0.20% | |
| 0.2~0.4 | 5.13% | 4.47% | 3.98% | 4.81% | 4.21% | 2.64% | |
| 0.4~0.6 | 10.95% | 9.11% | 9.76% | 12.28% | 13.04% | 12.23% | |
| 0.6~0.8 | 57.09% | 37.37% | 33.75% | 34.58% | 33.89% | 31.29% | |
| 0.8~1.0 | 26.18% | 48.85% | 52.35% | 48.09% | 48.70% | 53.64% | |
| Year | 2000 | 2004 | 2008 | 2012 | 2016 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | |||||||
| −0.1~0.2 | 1.82% | 0.46% | 0.30% | 0.20% | 0.28% | 0.20% | |
| 0.2~0.4 | 28.25% | 26.65% | 24.74% | 27.27% | 23.36% | 12.68% | |
| 0.4~0.6 | 26.61% | 31.84% | 35.06% | 40.17% | 41.94% | 45.81% | |
| 0.6~0.8 | 34.10% | 33.90% | 33.50% | 28.17% | 30.43% | 36.01% | |
| 0.8~1.0 | 9.23% | 7.15% | 6.40% | 4.19% | 3.99% | 5.30% | |
| Regions | Whole Beijing Region | Within the 6th Ring Road | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Categories | |||
| Severe degradation (trend < −0.02/year) | 0.28% | 1.05% | |
| Moderate degradation (−0.02/year < trend < −0.01/year) | 2.45% | 7.92% | |
| Slight degradation (−0.01/year < trend < −0.0/year) | 22.07% | 31.10% | |
| Slight improvement (0.0/year < trend < 0.01/year) | 72.67% | 48.71% | |
| Moderate improvement (0.01/year < trend < 0.02/year) | 2.35% | 10.34% | |
| Significant improvement (trend > −0.02/year) | 0.19% | 0.88% | |
| Regions | Whole Beijing Region | Within the 6th Ring Road | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI Trend | |||
| Extremely significant degradation | 5.56% | 12.70% | |
| Significant degradation | 3.32% | 5.74% | |
| No significant degradation | 15.06% | 21.28% | |
| No significant improvement | 18.89% | 22.38% | |
| Significant improvement | 8.68% | 7.73% | |
| Extremely significant improvement | 48.48% | 30.17% | |
| Variables | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Land Surface Temperature | 3.45 | 0.289920 |
| Annual Precipitation | 1.40 | 0.714479 |
| Population Density | 2.19 | 0.457112 |
| Night-Light Index | 3.45 | 0.289578 |
| 1st Greenbelt Policy | 1.17 | 0.858044 |
| 2nd Greenbelt Policy | 1.23 | 0.810510 |
| 2008 Summer Olympics | 1.36 | 0.733724 |
| Mean VIF | 2.04 |
| Variable Name | Model I | Model II | Model III |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Greenbelt Policy | 0.296 *** | 0.291 ** | |
| (19.09) | (19.96) | ||
| 2nd Greenbelt Policy | −0.021 *** | −0.026 *** | |
| (−3.63) | (−3.80) | ||
| 2008 Summer Olympics | 0.001 (0.17) | ||
| 2008 Summer Olympics and 1st Greenbelt Policy | −0.023 *** (−6.66) | ||
| 2008 Summer Olympics and 2nd Greenbelt Policy | 0.013 *** (3.02) | ||
| Annual LST | −0.190 *** | −0.178 *** | −0.184 *** |
| (−9.29) | (−8.88) | (−9.28) | |
| Annual Precipitation | 0.007 *** | 0.007 *** | 0.008 *** |
| (5.43) | (5.30) | (5.78) | |
| Population density | 0.012 *** | 0.011 *** | 0.011 *** |
| (14.88) | (14.70) | (15.19) | |
| Night-Light Index | −0.013 *** | −0.010 *** | −0.009 *** |
| (−4.80) | (−3.71) | (−3.18) | |
| Constant | 0.396 *** | 0.365 *** | 0.373 *** |
| (10.78) | (9.98) | (10.39) | |
| District | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 6951 | 6951 | 6951 |
| adj. R2 | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.976 |
| Variable Name | Model I | Model II | Model III |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Greenbelt Policy | 0.0831 *** | 0.080 ** | |
| (19.09) | (10.52) | ||
| 2nd Greenbelt Policy | −0.012 *** | −0.016 *** | |
| (−3.22) | (−3.68) | ||
| 2008 Summer Olympics | 0.029 *** (9.45) | ||
| 2008 Summer Olympics and 1st Greenbelt Policy | −0.015 *** (−5.84) | ||
| 2008 Summer Olympics and 2nd Greenbelt Policy | 0.009 *** (3.90) | ||
| Annual LST | −0.143 *** | −0.136 *** | −0.135 *** |
| (−10.57) | (−10.22) | (−10.06) | |
| Annual Precipitation | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** |
| (5.91) | (5.78) | (6.16) | |
| Population Density | 0.004 *** | 0.004 *** | 0.003 *** |
| (9.24) | (9.01) | (8.83) | |
| Night-Light Index | −0.006 *** | −0.004 *** | −0.004 *** |
| (−3.73) | (−2.83) | (−2.11) | |
| Constant | 0.363 *** | 0.346 *** | 0.343 *** |
| (15.58) | (15.02) | (14.81) | |
| District | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 6951 | 6951 | 6951 |
| adj. R2 | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.976 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, F.-Y.; Wang, C. Evaluating the Performance of the Greenbelt Policy in Beijing Using Multi-Source Long-Term Satellite Observations from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194766
Gong F-Y, Wang C. Evaluating the Performance of the Greenbelt Policy in Beijing Using Multi-Source Long-Term Satellite Observations from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194766
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Fang-Ying, and Chao Wang. 2023. "Evaluating the Performance of the Greenbelt Policy in Beijing Using Multi-Source Long-Term Satellite Observations from 2000 to 2020" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194766
APA StyleGong, F.-Y., & Wang, C. (2023). Evaluating the Performance of the Greenbelt Policy in Beijing Using Multi-Source Long-Term Satellite Observations from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194766







