Abstract
Dune migration is one of the main processes in arid lands’ geomorphology and is important for the design of windbreaks and sand fixation projects and for the monitoring of desertification dynamics. We conducted long-term continuous positioning monitoring of barchan dunes using RTK equipment and wind regime monitoring in the Sanlongsha dune field, which is located in the northern part of China’s Kumtagh Desert. We analyzed the wind energy environment of the study area, the migration characteristics of different positions in the barchan dune, and dune shape changes during different periods. We found that (1) comparing the differences in migration distance and direction measured at six positions in the barchan, there existed variations in barchan migration across these positions. (2) The shape changes at the left horn, right horn, and windward slope of barchans were larger than at the center of the leeward toe and brink, so the estimates based on measurements at these four positions had a weaker fit with the resultant drift potential (RDP) and a greater difference from the resultant drift direction (RDD). (3) The shape of the leeward slope on the barchan did not change much during dune migration, so the center of the leeward toe and brink measurements were closer to the actual dune migration distance and direction. Thus, we recommend using the center of the leeward toe or brink as the optimal measurement points to monitor barchan dune migration. This study will provide a reference for the more accurate measurement of barchan dune migration.
1. Introduction
Barchans are crescent-shaped sand dunes and they are characterized by a clear and simple morphology; their dynamics have been widely studied in multiple dune fields worldwide [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Under strong unidirectional wind regimes, barchan dunes manifest significant geomorphic evolution and long-distance migration [8,9]. The interaction of the wind environment and surface sediments controls the dune migration rate and direction [10,11,12,13]. The accurate monitoring and prediction of the dune migration rate and direction is important in preventing wind erosion, combating desertification, and preserving arid ecosystems [14].
At present, researchers mainly monitor the migration of barchan dunes using the needle pin method [5,15,16], real-time kinematic (RTK) GPS surveys [15,17], aerial photography from unpiloted aerial vehicles (UAVs) [18], and remote sensing images [5,17,19,20,21]. In these studies, the average annual migration rates of barchan dunes range between 4.7 and 95.2 m/yr, and the migration directions are the same as the regional annual resultant drift direction (Table 1). The migration velocity of barchans increases with an increase in wind velocity and decreases exponentially with an increasing dune height [22,23,24]. In addition, barchans’ migration is affected by other factors, such as the dune shape, sand grain size, vegetation, precipitation, and topography, etc. [16,17,25]. The influencing factors are different in different regions, resulting in greatly different movement characteristics of barchan dunes in different regions.
Each method of measuring dune migration requires the selection of a geometric position that enables the objective and replicable computation of movement. Some researchers consider that the slip face base is a clearly defined feature, as it has clear edges and relatively stable geometry, so they select the center of the bottom of the dune’s leeward slope as the measurement point [5,12,17,19,25]. Some researchers believe that the dune’s crest permits the more accurate measurement of the best position of the dune, and they derive dune migration rates by measuring the distance between the crest’s position at two points in time [20]. Other researchers believe that the average migration distance calculated based on multiple positions on the dune can better represent dune migration and therefore use the average value of measurements at several positions to calculate the dune migration distance; these positions include the leeward toe, brink, left horn, right horn, and windward toe (Table 1). Finally, some researchers select a combination of different positions based on features that define the morphological differences among barchan dunes, such as the windward toe, left horn, right horn, and leeward toe [26,27]. It is not yet clear which method best reflects the migration distance and direction of barchan dunes.

Table 1.
Different measurement methods for monitoring of barchan dune migration.
Table 1.
Different measurement methods for monitoring of barchan dune migration.
| Region | Migration Rate (m/yr) | Direction (° from North) | Measuring Position | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nazca to Tanaca area, Southern Peru | 11 to 60 | 135 | LT | Gay (1999) [19] |
| Northern Alxa Plateau, Inner Mongolia, China | 5.3 | 92 to 136 | B | Yao et al. (2007) [20] |
| Navajo Nation, Southwestern U.S. | 39.7 | / | LT | Bogle et al. (2015) [17] |
| In-Salah, Central Algerian Sahara | 7 to 18 | 63 | LT | Boulghobra (2016) [12] |
| Qatar | 2.5 to 27.5 | 156.6 | LT | Michel et al. (2018) [25] |
| Central Hexi Corridor, China | 8 to 53 | 115.6 | (LT + WT + LH + RH)/4 | Zhang et al. (2018) [28] |
| Quruq Desert, China | 8.9 to 32.1 | 233 to 248 | (LT + B + WT + LH + RH)/5 | Yang et al. (2019) [24] |
| Qaidam Basin, China | 4.66 | / | (B + LH + RH)/3 | Li et al. (2021) [29] |
| Kumtagh Sand Sea, China | 7 to 95.2 | 186.6 to 210.8 | LT | Yang et al. (2021) [5] |
| Badain Jaran and Tengger Desert, China | 5.88 to 19.55 | 109 to 135 | (LT + B + WT + LH + RH)/5 | Zhang et al. (2022) [30] |
Notes: LH (left horn), RH (right horn), LT (center of the leeward toe), B (brink), WT (windward toe).
To understand the migration characteristics of different positions of barchan dunes and select a consistent and objective method to accurately measure dune migration, we designed the present study to perform long-term research on aeolian sand movement and dune geomorphology evolution. As a case study, we chose the Sanlongsha dune field, in the northern part of China’s Kumtagh Desert. The objectives of this study were (1) comparing the differences in the migration distance and direction measured at several positions in barchans; (2) understanding the variations in characteristics such as the size, height, and other parameters of the barchans during migration; (3) associating the barchans’ shape changes and movements with the local wind regime, in order to better understand the barchans’ migration process.
2. Study Area
The Sanlongsha dune field is located on the northern edge of the Kumtagh Desert in Northwestern China, between 40°30′N and 41°02′N and between 92°50′E and 93°16′E, covering an area of 2728 km2 (Figure 1). The typical aeolian landforms include barchans, barchanoid chains, linear dunes, climbing dunes, mega-ripples, gobis, and yardangs, among which the barchans and barchanoid chains are the dominant mobile dunes, with approximately 171 individual barchan dunes in the dune field [5]. In the study area, the annual mean temperature was 18.5 °C, with the highest and lowest monthly mean temperatures reaching approximately 32.3 °C in July and 0.4 °C in January, respectively. The annual precipitation averaged approximately 45.8 mm, and rain fell mainly in the spring and summer; this resulted is an extremely arid temperate continental climate. The annual average wind speed was approximately 4.2 m/s, and, during periods with a strong wind (from May to August), the monthly average wind speed was over 5 m/s, leading to strong sand movement [31]. The prevailing sand movement direction was from the north–northeast (NNE, 22.5°), followed by northeast (NE, 45°) and north (N, 0°or 360°) winds. Due to the harsh natural conditions, there were few plant species in this area and the vegetation cover was generally low, with a few plant communities distributed in some degraded wetlands and catchment areas [5].
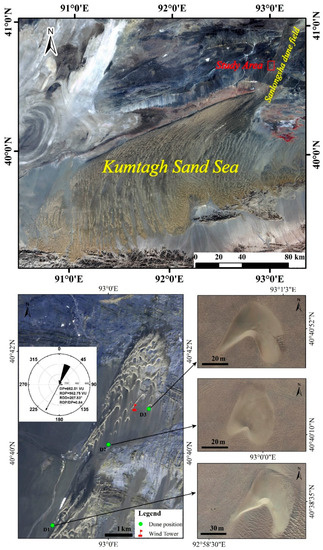
Figure 1.
Locations of the three barchan dunes (D1, D2, and D3) in the study area.
In this study, we selected three barchan dunes (D1, D2, and D3) in the middle of the Sanlongsha dune area for the topographic survey and simultaneous meteorological observations (Figure 1). The D1, D2, and D3 dunes differed significantly in size, shape, and development stages (Figure 2, Figures S2 and S3). The D1 dune was distributed on the mega-ripples and appeared recently after 2010. It was the largest one, with a height of 4.30 m, and had a slow migration rate (56.26 m/yr). The D2 dune was distributed on a flat gobi surface and was the smallest one, with a height of 1.82 m, and had a fast migration rate (81.36 m/yr). It appeared before 2010, became smaller with migration, evolved into a dome dune after June 2019, and finally disappeared in 2020. The D3 dune was distributed on a flat gobi surface and appeared at the latest time after 2015; it had a height of 2.96 m and a moderate migration rate (70.06 m/yr).

Figure 2.
Georectified historical satellite imagery of the change process of barchan dune D1 between 2011 and 2020.
3. Methods
We conducted morphological surveys of the barchan dunes using a real-time kinematic GPS receiver (GR-3, Topcon, Livermore, CA, USA) with 3D positioning accuracy of 5 mm (Figure 3b). We surveyed the three barchans (D1, D2, and D3) described in Section 2. From June 2018 to January 2020, we completed six field surveys for D1 and D2, and eight surveys for D3 (Table 2). Points were taken at a spatial interval of 0.3 to 0.5 m with less terrain relief (windward slope of barchan), while points were taken at a spatial interval of 0.1 to 0.2 m with significant terrain relief (leeward slope of barchan). Between 600 and 800 data points were sampled on a single dune for each field survey. The Kriging interpolation method was selected to perform spatial interpolation analysis on the surfaces of the barchans and to obtain a digital elevation model (DEM) at 0.15 m resolution.

Figure 3.
Field work photos. (a) Meteorological observation using a two-dimensional ultrasonic anemometer. (b) Morphological surveys of the barchan dunes using a RTK GPS receiver.

Table 2.
Dates of the field measurements for barchans D1, D2, and D3 and the morphological parameters of the three dunes on each date. Dune orientation was defined as the azimuth of line 5 in Figure 4.
We established three-dimensional models of the barchans using the RTK measurement results and then used existing methods of measuring barchan movement to estimate their migration distances and directions [17,20,27,31]. We selected six positions on the surface of the dune as measuring points (Figure 4): the left horn (LH), right horn (RH), center of the leeward toe (LT), brink (B), windward toe (WT), and windward middle (WM). The positions of LH and RH are obvious. To achieve the more consistent and objective determination of other positions, we used the following methods. LT represents the intersection point between a line drawn perpendicular to line 1, which connects LH with RH, and line 2, which represents the perpendicular distance from dotted line 1 toLT [17]. B represents the position of the intersection between the dune’s brink and dotted line 3, which is the highest point of the slip face [32,33,34]. WT is defined as the intersection point for the maximum distance of WT from line 3 along line 4, which is perpendicular to dotted line 3. WM is the midpoint of dotted line 5, which connects WT to B. We calculated the dune migration distance and direction based on measurements at all six positions, as well as the average migration distance for all six positions between consecutive measurement dates. In addition, we extracted 11 morphologic parameters for the three dunes in each survey: the bottom area, surface area, volume, height, perimeter, left horn length, right horn length, windward length, leeward length, width, and dune orientation (Figure 4, Table 2).
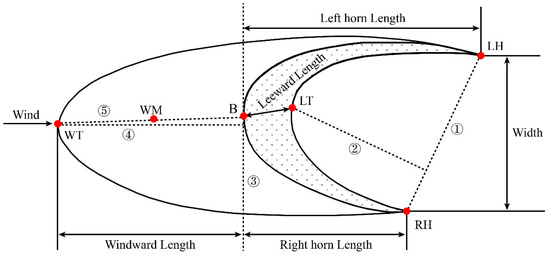
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of dune movement monitoring points and morphological parameters. Notes: The red dots represent the six measurement positions on the barchans, including LH, RH, LT, B, WM and WT. Numbers 1–5 represent the five dotted lines, among which ① represents the connecting line of RH and LH; ② represents the perpendicular distance from dotted line 1 to the LT; ③ is tangent to the brink line of the dune; ④ is perpendicular to dotted line 3 and intersects with WT; ⑤ is the connecting line with the positions of WT, WM and B.
Wind speeds and directions were recorded during each observation period using a WindSonic 2D ultrasonic anemometer (Gill Instruments, Lymington, UK) at a height 2 m above the ground (Figure 1 and Figure 3a). The distance from the anemometer to the D1, D2, and D3 dunes was 5.0, 1.5, and 0.5 km, respectively. The mean and maximum values for every 10-min period were recorded with a CR 1000 datalogger (Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, UT, USA). To determine the drift potential (DP), the wind speed at a height of 10 m must be calculated. According to the Karman–Prandtl velocity distribution law [1],
where uz is the wind speed at height z, u∗ is the shear velocity, k is von Karman’s constant (0.4), and z0 is the aerodynamic roughness length. Based on our measurement height (2 m), Equation (1), and the estimated value of z0, the wind speed at a height of 10 m (u10) could be calculated as follows [35]:
where u2 is the wind speed at a height of 2 m. Here, we used z0 = 0.00001 m, so the formula could be simplified as u10 = 1.13 × u2.
We analyzed the wind velocities and directions for winds above the threshold value for the entrainment of particles (12 knots, 6.2 m/s), as required by Fryberger and Dean [36], from June 2018 to January 2020. We also calculated the drift potential (DP), resultant drift potential (RDP), resultant drift direction (RDD), and directional variability index (RDP/DP) according to Fryberger and Dean [36] and Pearce and Walker [37].
4. Results
4.1. The Wind Energy Environment
Figure 5 is a sand rose showing the directional distribution of DP (in vector unit) and related parameters during each observation period. In the study area, the DP and RDP values ranged from 44 to 270 vector units (VU) and 37 to 240 VU, respectively. RDD ranged from 206° to 216°, indicating a dominant wind from the north–northeast throughout the year. DP and RDP were greatest from April to September, followed by September to November, and were lowest from November to April of the following year, indicating strong sand transport in the late spring, summer, and early autumn, and weak winds in other seasons. The RDP/DP values ranged from 0.80 to 0.89 and were greater than 0.86 from April to September, indicating that the wind direction variability was the lowest and the wind direction was the most stable in late spring, summer, and early autumn. In addition, from September 2018 to the following April, the RDP/DP values in the three periods were 0.80, 0.82, and 0.83, respectively, and were lower than in other periods in this year, indicating that the wind’s directional variability was larger, especially from September to November 2018, characterized by strong easterlies and high directional variability.
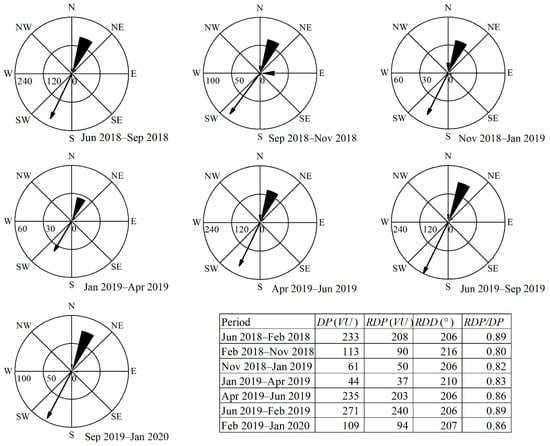
Figure 5.
Sand rose diagrams showing drift potential and related parameters for each of the seven observation periods in the study area. Abbreviations: DP, drift potential; VU, vector units; RDP, resultant drift potential; RDD, resultant drift direction; RDP/DP, directional variability index. The arrow length represents the RDP value, and the arrow direction indicates the RDD value.
4.2. Dune Migration at Different Positions
Figure 6, Figures S3 and S4 show the differences in the migration tracks for the three dunes at the six measurement positions. From June 2018 to January 2020, the mean migration distances and directions at the six positions of all measurements were 63.83 ± 5.51 m (mean ± standard deviation, SD) for D1 and 100.23 ± 14.51 m for D3 and 203.98° ± 3.64° for D1 and 205.50° ± 3.26° for D3, corresponding to a maximum difference in the six positions of 15.28 m and 8.57° for D1 and 32.70 m and 8.33°for D3, respectively. From June 2018 to June 2019, the mean migration distance and direction at the six positions for D2 were 74.00 ± 5.72 m and 205.71° ± 4.05°, with a maximum difference of 13.83 m and 11.33°, respectively. This indicates that the migration distance and direction of the three barchans varied across the six positions.
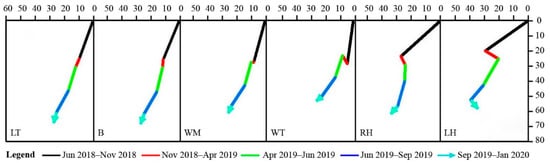
Figure 6.
Migration tracks of barchan dune D1 at six positions in five periods (defined in Table 2): LT, leeward toe; B, brink; WM, windward middle point; WT, windward toe; RH, right horn; LH, left horn. Note: The units of numbers in the figure are meters and the arrow represents the direction of dune migration.
Figure 7, Figures S5 and S6 show that the migration at the six positions differed greatly among several periods. For D1, the coefficients of variation (CV) for the migration distance and direction during the five periods were (in chronological order) 0.11, 0.45, 0.19, 0.10, and 0.27 for distance and 0.9, 0.37, 0.04, 0.04, and 0.16 for direction. The maximum value was observed from November to the following April and the minimum value was observed from June to September. For D2, the CV values for migration distance and direction during the five periods were 0.03, 0.19, 0.38, 0.49, and 0.15 for distance and 0.04, 0.04, 0.22, 0.31, and 0.02 for direction. The maximum value was observed from January to April, followed by November to January, and the minimum value was observed from June to September. For D3, the CV values of the migration distance and direction during the seven periods were 0.17, 0.29, 0.36, 0.51, 0.16, 0.19, and 0.13 for distance and 0.06, 0.09, 0.30, 0.20, 0.01, 0.02, and 0.01 for direction. The maximum value was observed from January to April, followed by November to the following January, with little difference in other periods. These results demonstrate that the barchans’ migration distances and directions varied significantly across different positions during the periods of weak winds from late autumn to early spring. However, during the periods of strong winds from late spring to early autumn, the migration distances and directions were relatively consistent across different positions.
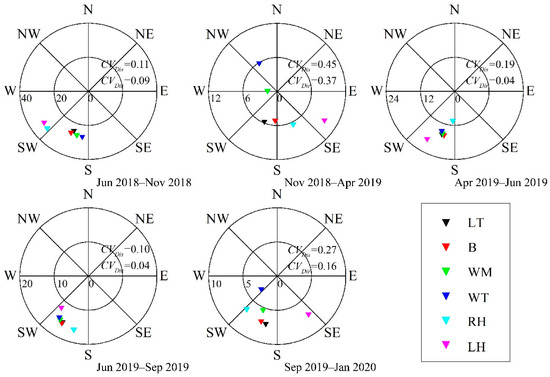
Figure 7.
Migration for barchan dune D1 at six positions among five periods. Notes: CVDis is the coefficient of variation of the dune migration distance at six positions in each period. CVDir is the coefficient of variation of the dune migration direction at six positions in each period.
We also conducted a pairwise comparison of the migration distance and direction at six positions (Figure 8, Figures S7 and S8) and found that the migration distance and direction measured at LT and B were the most consistent. Comparing the migration at LT with migration at the other five positions, for the three dunes, the ranges of values for the mean relative difference in the migration distance were 2.3 ± 2.0% to 2.8 ± 4.1% at B, 5.4 ± 8.6% to 14.9 ± 24.7% at WM, 7.6 ± 11.4% to 15.8 ± 17.4% at WT, 9.3 ± 7.5% to 16.9 ± 8.2% at LH, and 12.2 ± 9.1% to 20.1 ± 14.1% at RH. For the migration direction, the magnitude of the mean absolute difference was 1.50 ± 1.9° to 3.1 ± 3.8° at B, 3.0 ± 3.4° to 9.0 ± 14.9° at WM, 4.2 ± 5.4° to 24.2 ± 28.9° at WT, 7.8 ± 8.9° to 13.3 ± 7.3° at LH, and 7.6 ± 5.4° to 19.3 ± 14.7° at RH. For the pairwise comparison at the positions of B, WM, WT, LH, and RH, the migration distance and direction measured at B and WM for the three dunes were relatively consistent, in which the range of values of the mean relative difference in the migration distance was 3.8 ± 5.6% to 15.5 ± 19.0%, and that for the mean absolute difference in the migration direction was 1.6 ± 1.7° to 10.7 ± 19.2°. Therefore, these results suggest that the migration distance and direction of the three dunes were most consistent at LT and B, followed by B and WM.
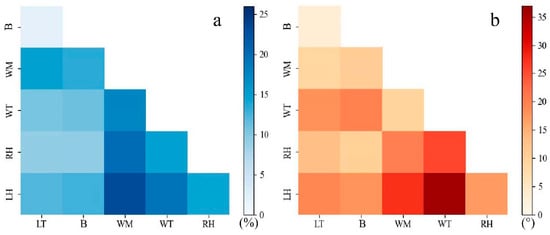
Figure 8.
The heat map of the pairwise comparison of the migration distance (a) and direction (b) at six positions for barchan dune D1.
4.3. Dune Shape Changes in Different Periods
Figure 9 shows the morphological changes of dunes D1, D2, and D3 at different times. Throughout the observation period, the maximum possible relative error (MPRE) ranged from 0.13 to 0.24 for the bottom area, 0.13 to 0.24 for the surface area, 0.06 to 0.44 for the volume, 0.07 to 0.21 for the height, and 0.03 to 0.20 for the perimeter, indicating that the dune size and height changed greatly during dune migration (Table 2). From June 2018 to June 2019, the maximum values of the bottom area, surface area, volume, height, and perimeter for dunes D1 and D2 occurred in April 2019; for dune D3, the maximum values of these parameters appeared in November 2018 and showed little change from November 2018 to the following April. Moreover, the heights of all three dunes decreased over time, implying that the three dunes shrank in size during their migration and exhibited a degradation trend.
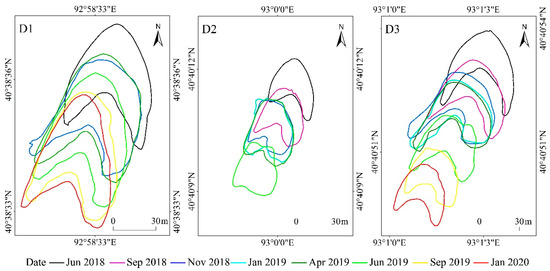
Figure 9.
Shape changes in the three dunes from June 2018 to January 2020.
Figure 10, Figures S9 and S10 are three-dimensional simulations of the morphologies of dunes D1, D2, and D3, respectively, at different dates. The MPRE and MAE values ranged from 0.18 to 0.55 and 6.87 to 13.59 m, respectively, for the left horn length; 0.12 to 0.42 and 4.37 to 8.61 m for the right horn length; 0.06 to 0.27 and 1.23 to 8.07 m for the windward length; 0.07 to 0.27 and 0.55 to 1.10 m for the leeward length; and 0.11 to 0.32 and 5.66 to 9.48 m for the dune width (Table 2). The maximum relative and absolute errors were large for the left horn length, right horn length, windward length, and dune width, whereas those for the leeward length were small. This indicates that the left horn, right horn, and windward slope of the dunes underwent significant shape changes during their migration, while the leeward slope remained relatively stable.
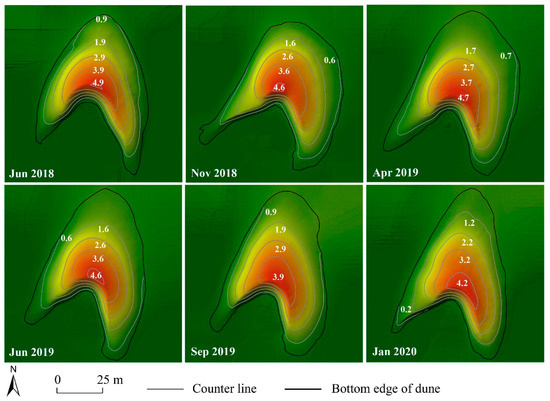
Figure 10.
Three-dimensional simulation of barchan dune D1 on six dates during migration to the southwest. Notes: The numbers beside the contour line indicate the absolute heights of the dunes. The color shades from green to red represent the dune height from low to high.
An interesting observation is that when the wind direction had a stronger component of winds from the east from June to November 2018, dunes D1, D2, and D3 migrated in a more clockwise direction by 7.61°, 11.78°, and 6.83°, respectively, and their right horns tilted towards the west. The length of the left horn for dunes D1, D2, and D3 continuously decreased, while the length of the right horn increased from June to November 2018 (Table 2, Figure 10, Figures S9 and S10). The windward lengths of dunes D1, D2, and D3 also increased by 9.79, 12.71, and 1.07 m, respectively, from November 2018 to April 2019. This indicates that the dune orientation, left horn, right horn, and windward slope changed during the dunes’ migration, especially during the period of high directional variability.
4.4. Relationships between the Wind Regime and Dune Migration
We fitted the relationship between the RDP and migration distance based on measurements at the six positions of the dunes in different survey periods, and we found a strong fit for all three dunes at positions LT (R2 from 0.93 to 0.98), B (R2 from 0.92 to 0.98), and WM (R2 from 0.91 to 0.97), but generally weaker relationships at WT (R2 from 0.89 to 0.96), LH (R2 from 0.62 to 0.99), and RH (R2 from 0.38 to 0.97) (Figure 11). The difference in the migration direction between the positions of LT and B was small for dunes D1, D2, and D3, with RDD ranging from 3.94 ± 3.40° to 7.97 ± 4.03° at LT and 6.06 ± 4.65° to 10.79 ± 8.23° at B, but the difference was larger (from 9.20 ± 6.92° to 49.11 ± 51.59°) at the positions WM, WT, LH, and RH (Table 3). The mean barchan migration distance and direction based on data from the six positions is likely to be less accurate than estimates based on data from the LT and B, with R2 from 0.90 to 0.95, and the difference between the migration directions and RDD from 5.24 ± 3.83° to 10.43 ± 9.03°. The fits between the dune migration distance based on measurements at positions LT and B and the RDP were stronger, and the migration direction was closer to the RDD.
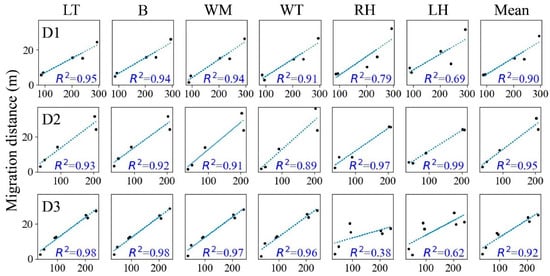
Figure 11.
Relationships between the resultant drift potential (RDP, in vector units (VU)) and the migration distance of dunes D1, D2, and D3 based on measurements at six positions on the dune: LT, leeward toe; B, brink; WM, windward middle point; WT, windward toe; RH, right horn; LH, left horn. All regressions were statistically significant at p < 0.05.

Table 3.
Differences in dune migration direction and resultant drift direction (RDD) based on measurements at six positions on the dune: LT, leeward toe; B, brink; WM, windward middle point; WT, windward toe; RH, right horn; LH, left horn.
5. Discussion
In this study, we found significant differences in dune migration distance and direction based on measurements at different positions (Figure 5, Figures S1 and S2), especially during periods with weaker winds in the winter. We also found that the dune shape changed greatly (Figure 9, Figures S7 and S8), and the calculated migration distance and direction differed greatly based on measurements at different positions, resulting in the inconsistent estimation of dune migration under the different measurement methods. Therefore, based on the measurement of a single position, the combination of several positions, and the mean of all positions, the selection of an optimal measurement method that can best reflect the migration of barchan dunes will improve our ability to compare research results from different regions, and this will be of great significance in deepening the relevant theories of dune migration.
The wind regime plays an important role in dune formation and evolution processes and is a dominant factor that controls dune mobility [8,17,36,38,39,40,41,42]. Most studies have reported that sand dunes migrate faster under stronger winds [12,24,27]. Bogle [17] and Yang [5] reported a strong linear increasing relationship between the dune migration distance and DP. Based on these previous findings, we also fitted the relationship between the RDP and migration distance based on measurements at the six positions (Figure 11) and calculated the difference between the migration directions and RDD (Table 3). We found that the fits between the dune migration distance based on measurements at positions LT and B and the RDP were stronger, and the migration direction was closer to the RDD. We thus conclude that these two positions are the optimal measurement points for barchan migration.
To support our proposal that the positions of LT and B are the optimal measuring points for dune migration, it is necessary to discuss dune shape changes. Due to the influences of the wind conditions and the sand supply, the dune shape undergoes significant changes during dune migration. In this study, the length and direction of the left horn and right horn changed greatly during the migration of dunes D1, D2, and D3, especially during the period of high directional variability (Figure 9, Figures S7 and S8). For example, when the wind direction included a stronger component of winds from the east, the left horn for the dunes faced the direction of the airflow; under the action of airflow acceleration, the left horn was continuously eroded and its length became shorter. In contrast, the right horn located in the area of airflow slowed down, where sand particles accumulated and its length increased [43]. Previous studies have also shown that during barchan migration, the left horn and right horn elongate obviously due to sand accumulation [20], and this increases the variation in the estimated dune migration distance and direction measured at LH and RH. For the windward slope, the weaker winter wind leads to sand grain accumulation at the WT position [16], and the windward slope increased significantly during the migration process for dunes D1, D2, and D3 from November to the following April (Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9). This process increased the variability in the barchan’s migration distance and direction based on measurements at the WT position, and it made the estimated distance and direction inconsistent with the real situation. The research of [34] showed that sand grains on the windward slope and at the brink fall on the leeward slope under the action of wind and form the leeward slope (i.e., the slip face). Because of the strong eddy current that develops in the backflow area in front of the leeward slope, sand grains do not escape the dune, and the barchan’s leeward slope remains relatively stable as the dune moves downwind. We also found that the shape of the leeward slope was relatively stable during the migration of the three dunes (Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9). Therefore, the barchans’ migration based on measurements at the center of the leeward toe and the brink is more consistent with the actual situation.
Our results showed that there were large variations in the estimated barchans’ migration distance and direction based on measurements at TW, LH, and RH. Although calculating the mean barchan migration distance and direction based on data from multiple positions can reduce the deviation of the estimate from actual values to some extent, the average value includes data from positions with high variation and is thus likely to be less accurate than estimates based on data from the LT and B positions, according to our fitting of the relationship between the migration distance and RDP (Figure 11) and the difference between the migration direction and RDD (Table 3). Given that measurement at multiple positions will add work without improving the estimation accuracy, we recommend not using average values based on multiple positions. Instead, to accurately measure the migration distance and direction for barchan dunes, we recommend measurements at the leeward toe or brink; however, since measurements based on these two positions tend to be highly consistent, it may be possible to average the two values to provide a more reliable estimation. Additional research (i.e., more fieldwork data) will be necessary to confirm whether this averaging is valuable.
6. Conclusions
Using RTK equipment, we performed long-term continuous positioning monitoring of barchan dunes and wind regime monitoring in the Sanlongsha dune field and analyzed the wind energy environment of the study area, the migration characteristics of different positions in the barchan dune, and dune shape changes during different periods. The main conclusions are as follows. (1) The measurements of the barchans’ migration distances and directions varied significantly depending on the position on the dune. There was relatively little variation between the measurements at the center of the leeward toe and brink of the barchan dune. (2) The barchans in our study area maintained their dune shape over time, but some of them changed significantly in winter when the wind direction varied significantly (RDP/DP). The left and right horns, the windward slope area, and the migration direction were affected by the low wind variability. (3) The barchan’s shape changes affected the estimated dune migration distance and direction. The estimates based on measurements at the left horn, right horn, windward toe, and windward middle had a weaker fit with the RDP and a greater difference from the RDD, indicating that averaging the estimates from several positions is not beneficial. (4) The shape of the leeward slope on the barchan does not change much during dune migration, so the center of the leeward toe and brink measurements are closer to the actual dune migration distance and direction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs15194728/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.X. and Z.Y.; methodology, X.X. and Z.Y.; investigation, X.X. and Z.Y.; writing—original draft, X.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.Y.; visualization, G.Q.; supervision, G.Q. and G.Z.; project administration, G.Q.; funding acquisition, G.Q. and G.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42071016), The Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (Qianke Jichu-ZK [2021]187), Digital Village Innovation Team of Higher Education Institutions in Guizhou Province (QianJiaoji [2023]076), Scientific Research Project of Higher Education Institutions of Guizhou Provincial Department of Education (Youth Project: QianJiaoij 249[2022] and 250[2022]), Reward and subsidy fund project of Guizhou Education University, Ministry of science and technology of the people’s Republic of China and National Natural Science Foundation of China (2023GZJB006).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Liang Fan for his hard work in the field. We also thank the Key Research Base of Humanities and Social Sciences, Education Department of Guizhou Province.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Methuen: London, UK, 1941; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- Baddock, M.C.; Livingstone, I.; Wiggs, G.F.S. The geomorphological significance of airflow patterns in transverse dune interdunes. Geomorphology 2007, 87, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Parteli, E.J.; Michaels, T.I.; Karam, D.B. The physics of wind-blown sand and dust. Rep. Prog. Phys. Phys. Soc. 2012, 75, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parteli, E.J.R.; Durán, O.; Bourke, M.C.; Tsoar, H.; Pöschel, T.; Herrmann, H. Origins of barchan dune asymmetry: Insights from numerical simulations. Aeolian Res. 2014, 12, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Qian, G.; Dong, Z.; Tian, M.; Lu, J. Migration of barchan dunes and factors that influence migration in the Sanlongsha dune field of the northern Kumtagh Sand Sea, China. Geomorphology 2021, 378, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Yang, Z.; Tian, M.; Dong, Z.; Liang, A.; Xing, X. From dome dune to barchan dune: Airflow structure changes measured with particle image velocimetry in a wind tunnel. Geomorphology 2021, 382, 107681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S. Mega-Yardangs: A Global Analysis. Geogr. Compass. 2006, 1, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N. Geomorphology of Desert Dunes; Routledge: London, UK, 1995; p. 290. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J. Long-term measurements of aeolian transport directional variations over a zibar surface in the northern Kumtagh Sand Sea. Geomorphology 2020, 371, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N. Variations in wind velocity and sand transport on the windward flanks of desert sand dunes. Sedimentology 1985, 32, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N. The Namib Sand Sea: Dune Forms, Processes and Sediments; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Boulghobra, N. Climatic data and satellite imagery for assessing the aeolian sand deposit and barchan migration, as a major risk sources in the region of In-Salah (Central Algerian Sahara). Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzolli, R.P.; Portz, L.C.; Bouzas, A.F.; Bitencourt, V.J.B.; Carrió, J.A. Contribution of Reverse Dune Migration to Stabilization of a Transgressive Coastal Dune Field at Lagoa do Peixe National Park Dune Field (South of Brazil). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koprowski, M.; Winchester, V.; Zielski, A. Tree reactions and dune movements: Slowinski National Park, Poland. Catena 2010, 81, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Muñoz-Pérez, J.J.; Román-Sierra, J.; Tsoar, H.; Rodríguez, I.; Gómez-Pina, G. Assessment of highly active dune mobility in the medium, short and very short term. Geomorphology 2011, 129, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbelrhiti, H. Initiation and early development of barchan dunes: A case study of the Moroccan Atlantic Sahara desert. Geomorphology 2012, 138, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogle, R.; Redsteer, M.H.; Vogel, J. Field measurement and analysis of climatic factors affecting dune mobility near Grand Falls on the Navajo Nation, southwestern United States. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Guo, J.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Cui, W. Monitoring and influencing factors of dune movement speed along the Yellow River using UAV technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 57–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gay, S.P. Observations regarding the movement of barchan sand dunes in the Nazca to Tanaca area of southern Peru. Geomorphology 1999, 27, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.Y.; Wang, T.; Han, Z.W.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhao, A.G. Migration of sand dunes on the northern Alxa Plateau, Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 70, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeesch, P.; Drake, N. Remotely sensed dune celerity and sand flux measurements of the world’s fastest barchans (Bodélé, Chad). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L24404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, H.J. The Barchans of Southern Peru. J. Geol. 1959, 67, 614–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery; Michael, C. Barchan migration on the Kuiseb River Delta, Namibia. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 1990, 72, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Shi, W.; Chen, G.; Shao, T.; Zeng, H. Migration of barchan dunes in the western Quruq Desert, northwestern China. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2019, 44, 2016–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, M.; Jean-Philippe, A.; Fran Ois, A.; Ewing, R.C.; Nathalie, V.; Essam, H. Comparing dune migration measured from remote sensing with sand flux prediction based on weather data and model, a test case in Qatar. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 497, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- El-Magd, I.A.; Hassan, O.; Arafat, S. Quantification of Sand Dune Movements in the South Western Part of Egypt, Using Remotely Sensed Data and GIS. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2013, 5, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.A.; Refaat, A.A.; Wahed, M.A. Morphologic characteristics and migration rate assessment of barchan dunes in the Southeastern Western Desert of Egypt. Geomorphology 2016, 257, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Hu, G.; Parteli, E.J.R. Migration and Morphology of Asymmetric Barchans in the Central Hexi Corridor of Northwest China. Geosciences 2018, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiao, J.; Cao, X.; Bai, L.; Chen, T.; Yan, X.; Qi, H. Spatial regionalization and response to morphological parameters of dune migration in the Qaidam Basin of China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 309–314. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Su, Z.; Liang, A.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y. Dune movement in the joint zone of the Badain Jaran Desert and Tengger Desert. J. Desert Res. 2022, 42, 82–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Qian, G.; Han, Z.; Dong, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J.; Liang, A.; Tian, M. Variation in grain-size characteristics as a function of wind direction and height in the Sanlongsha dune field of the northern Kumtagh Desert, China. Aeolian Res. 2019, 40, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parteli, E.J.R.; Schwämmle, V.; Herrmann, H.J.; Monteiro, L.H.U.; Maia, L.P. Profile measurement and simulation of a transverse dune field in the Lençóis Maranhenses. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddock, M.C.; Wiggs, G.F.S.; Livingstone, I. A field study of mean and turbulent flow characteristics upwind, over and downwind of barchan dunes. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2011, 36, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbelrhiti, H. Field evidence of appearance and disappearance of the brink line on barchans. Aeolian Res. 2015, 18, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenberg, O.; Yizhaq, H.; Tsoar, H.; Wenkart, R.; Karnieli, A.; Kok, J.F.; Katra, I. Megaripple flattening due to strong winds. Geomorphology 2011, 131, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryberger, S.G.; Dean, G. Dune Forms and Wind Regime; US Geological Survey and United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; pp. 137–169.
- Pearce, K.I.; Walker, I.J. Frequency and magnitude biases in the’Fryberger’model, with implications for characterizing geomorphically effective winds. Geomorphology 2005, 68, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.R.; Richmond, M.B.; Alpha, R.T. Storm-controlled oblique dunes of the Oregon coast. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1983, 94, 1450–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Yang, Z.; Luo, W.; Dong, Z.; Lu, J.; Tian, M. Morphological and sedimentary characteristics of dome dunes in the northeastern Qaidam Basin, China. Geomorphology 2020, 350, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, C.S. Bounding Surfaces in a Barchan Dune: Annual Cycles of Deposition? Seasonality or Erosion by Superimposed Bedforms? Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inmaculada, R.; David, G.; Tomás, M.; José, S.M.; Isabel, M.; Silvia, M.; Fernando, B.; Jordi, S.; Miguel, R.J.; Javier, G.F. Study and Evolution of the Dune Field of La Banya Spit in Ebro Delta (Spain) Using LiDAR Data and GPR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Development Environment and Evolution Patterns of Linear Dunes in the Qaidam Basin; Xi’an Jiaotong University Press: Xi’an, China, 2020; p. 165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pont, S.; Narteau, C.; Gao, X. Two modes for dune orientation. Geology 2014, 42, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).