A Method to Suppress Interferences Based on Secondary Compensation with QPC-FDA-MIMO Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Compared with the traditional FDA-MIMO radar, DOFs are extended to the joint Doppler transmit–receive domain, resulting in suppressing the multiple false targets in the identical pulse with the true one.
- Based on the QPC technique, the mainlobe deceptive interference and sidelobe barrage jammer are suppressed in FDA-MIMO radar.
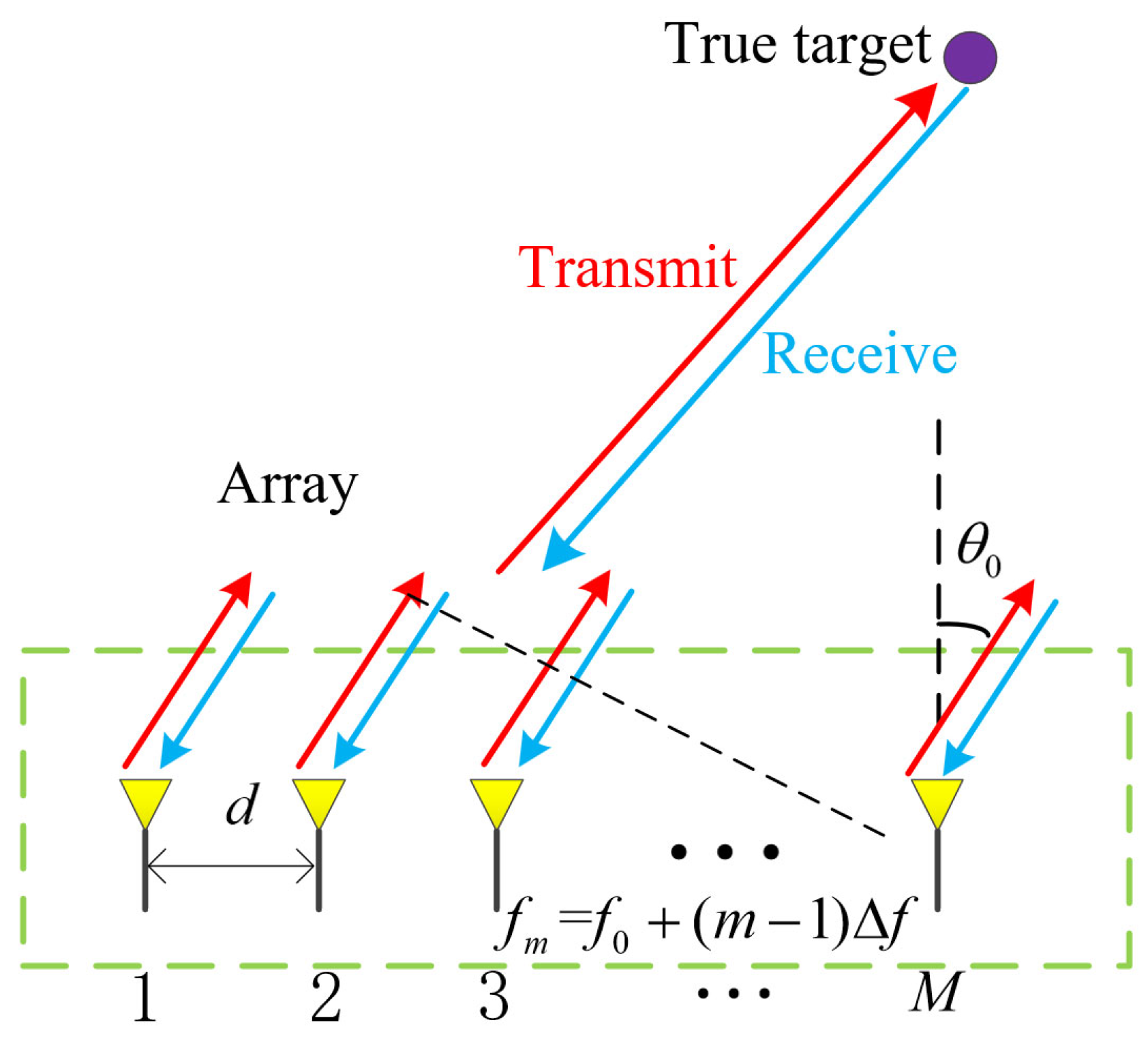
2. FDA-MIMO Radar Signal Model
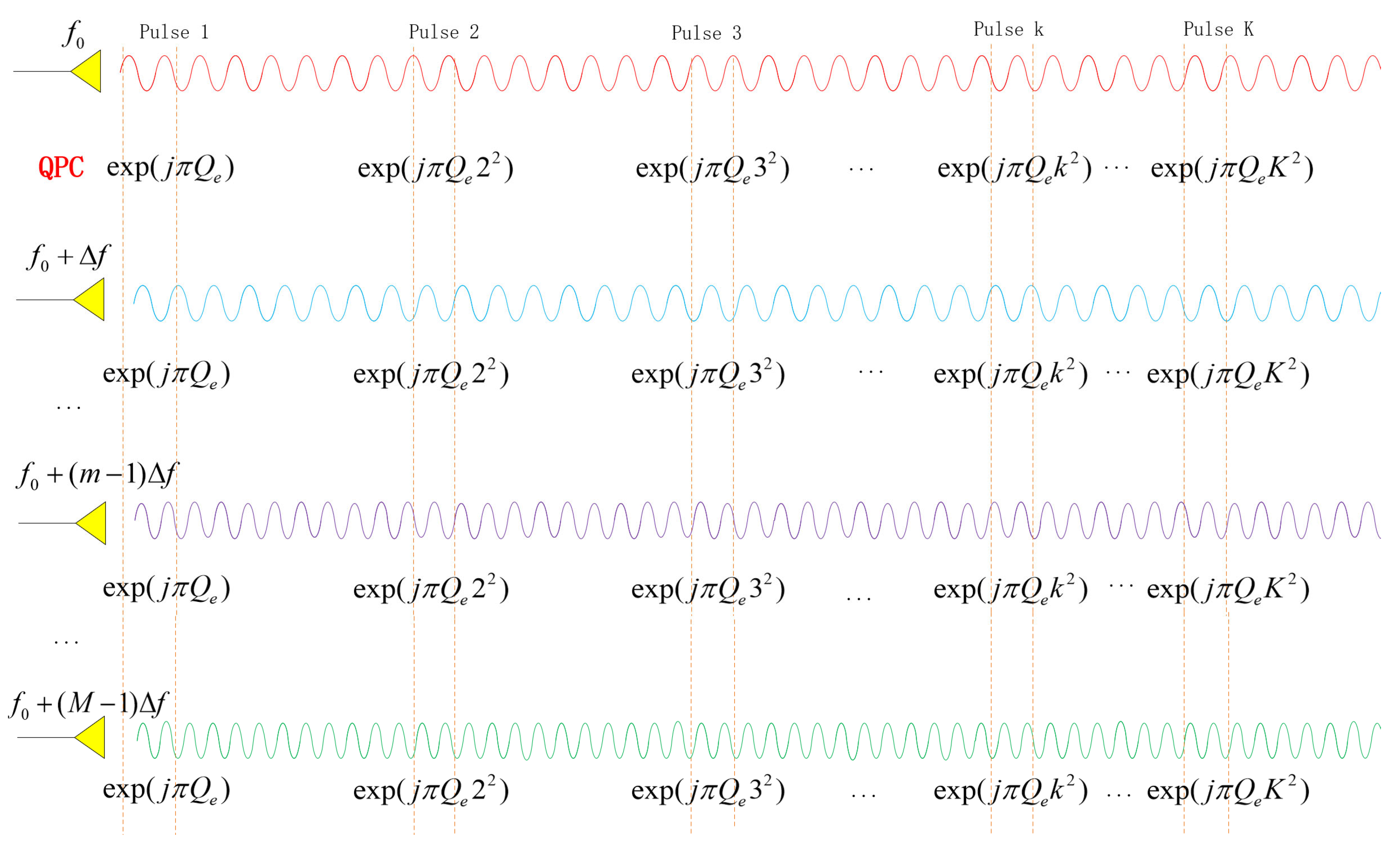
2.1. Transmit Signal Model
2.2. Receive Signal Model
- is the transmit steering vector after modulation.
- represents the transmit steering vector after demodulation.
- represents the complex echo coefficient.
- represents the normalized Doppler shift frequency.
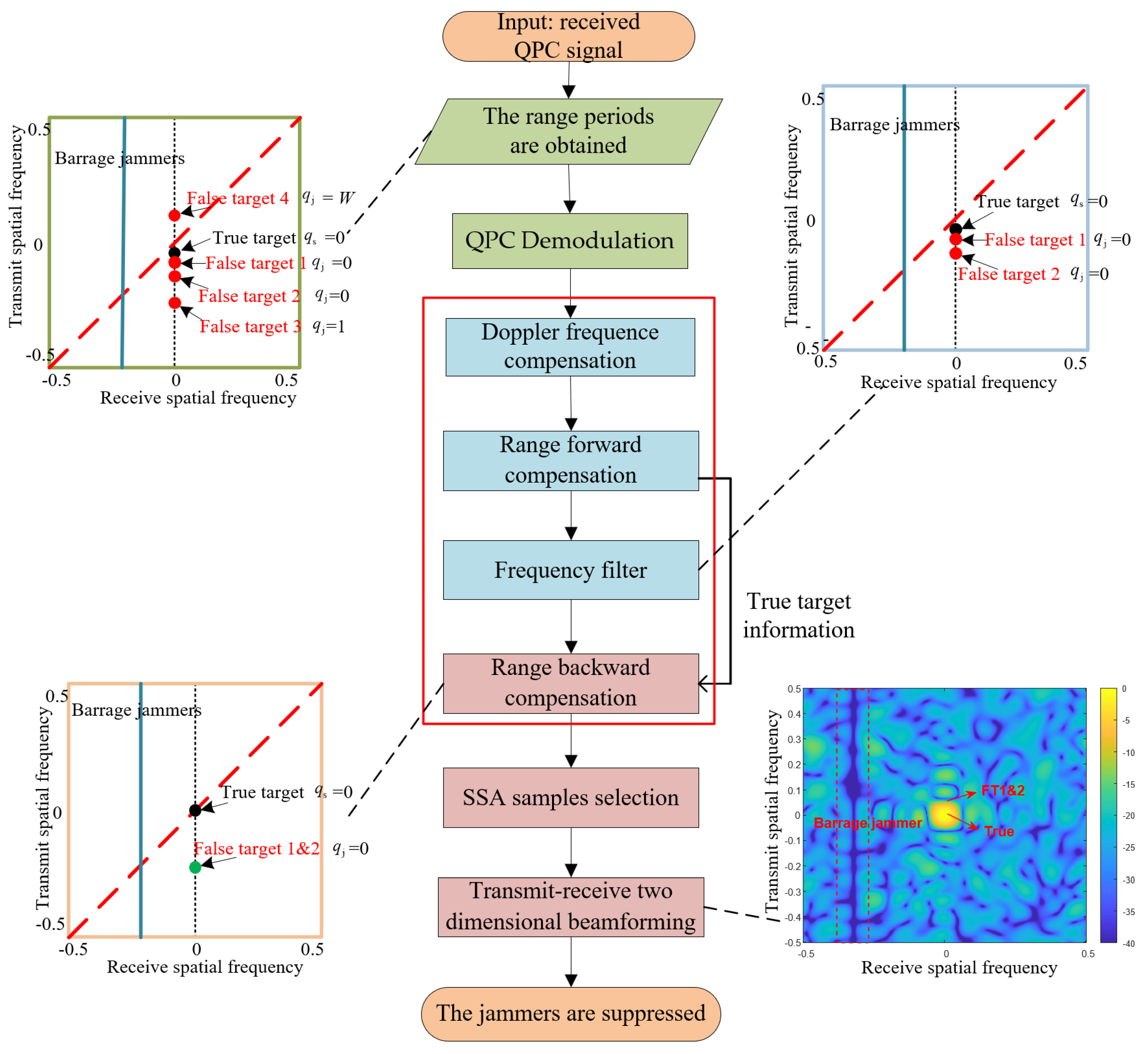
3. Principle of Interference Suppression in QPC–FDA-MIMO
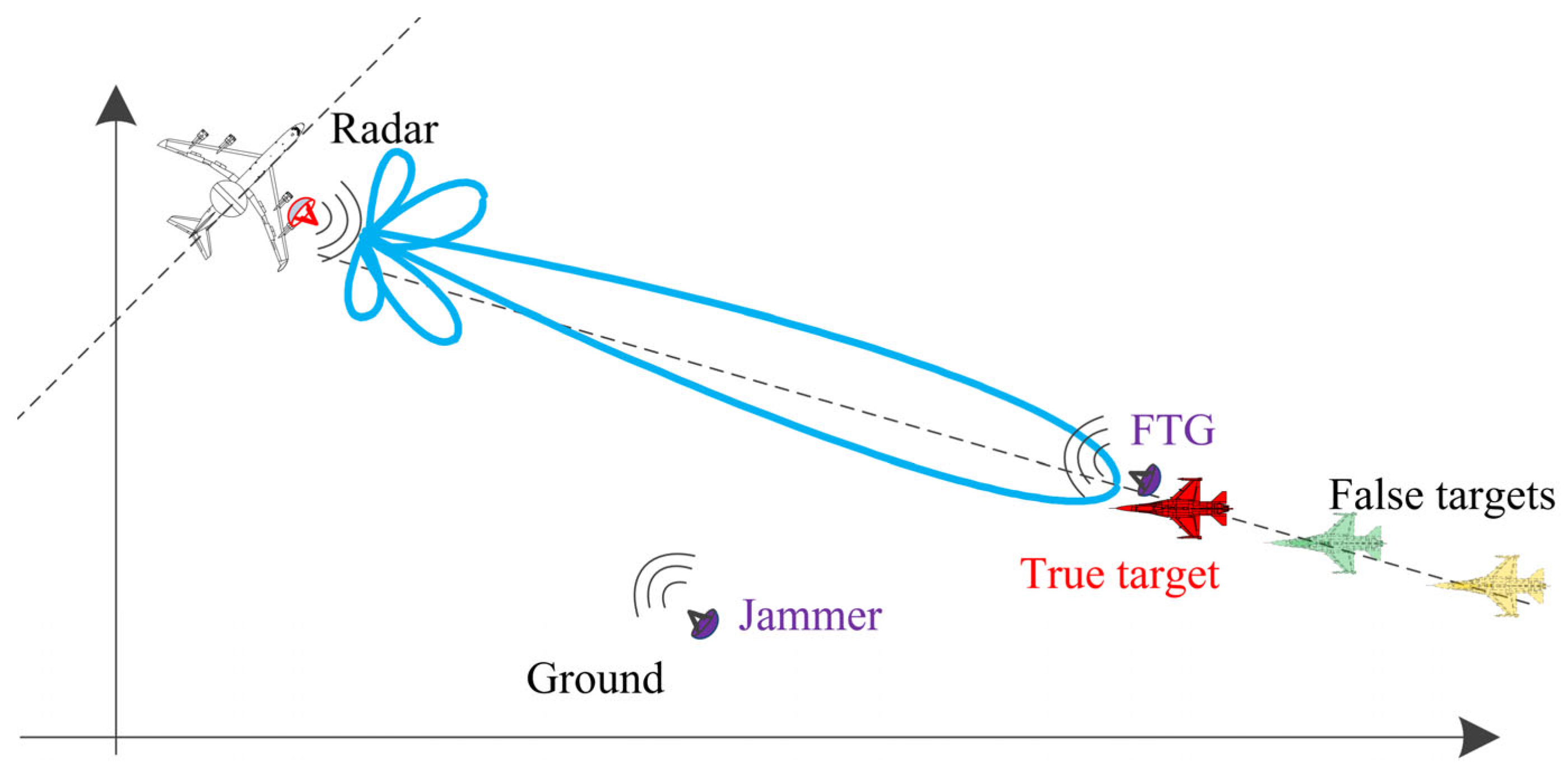
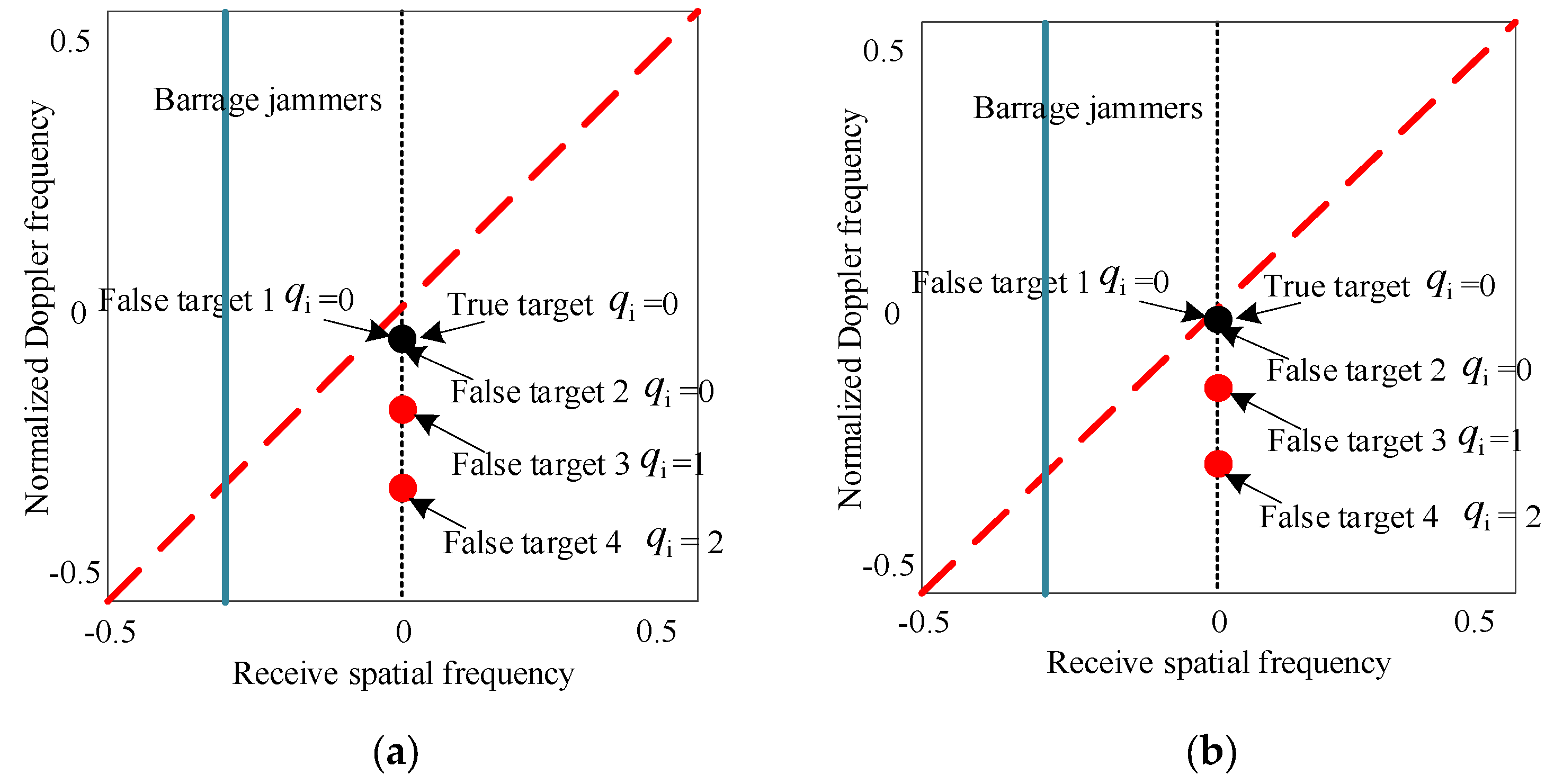
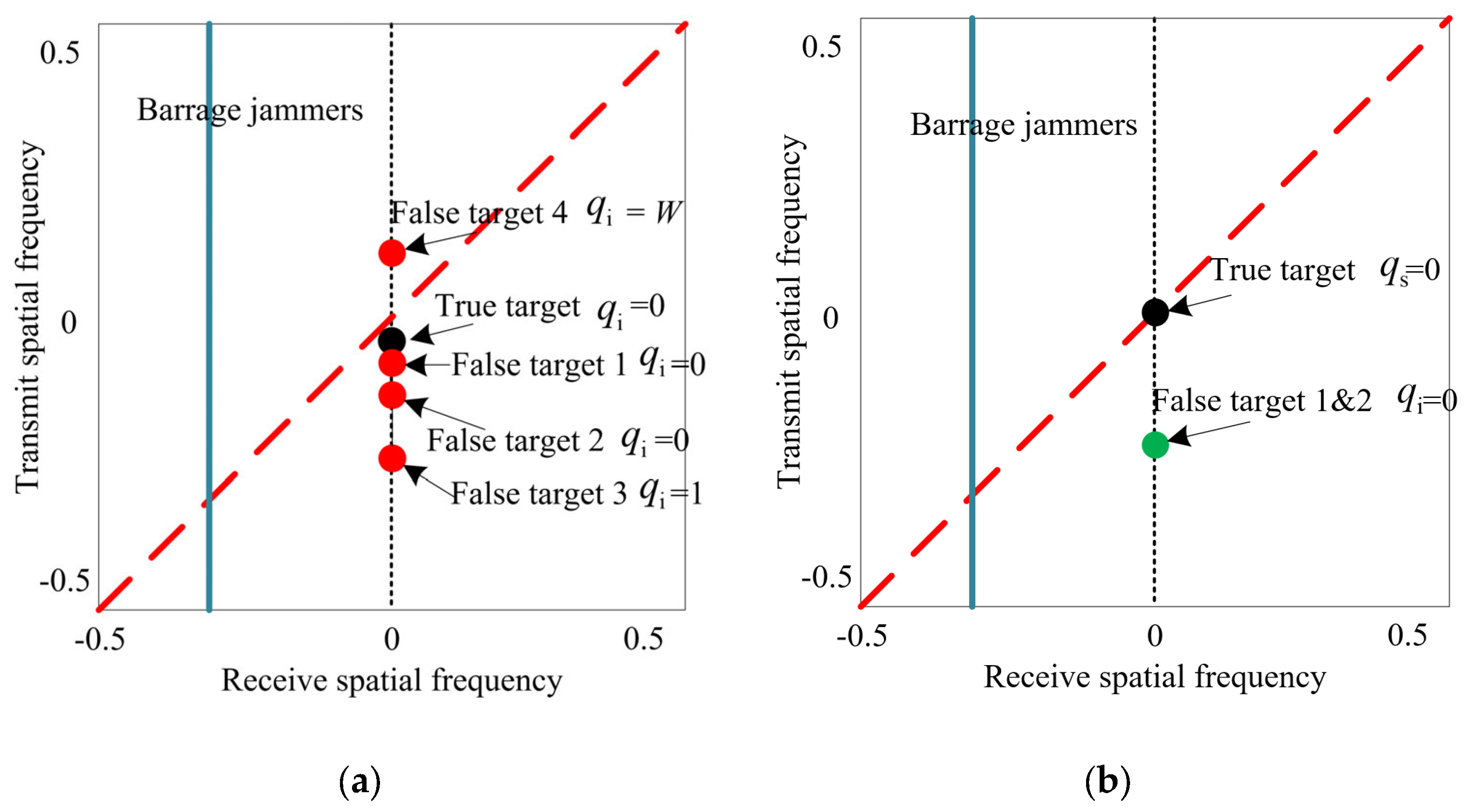
3.1. Generation of Barrage Jammer and Mainlobe Deceptive False Targets
- (1)
- Condition 1: The false target 1 is generated behind the true target with the identical transmit pulse and receive pulse, which locate in range ambiguity 1, i.e., .
- (2)
- Condition 2: The false target 2 is generated ahead of the true target, where both are located in the same receive pulse and come from different transmit pulses, i.e., the false 2 target corresponds to the previous transmit pulse, i.e., , where is the delayed pulse number difference.
- (3)
- Condition 3: The false target 3 and the true target are generated in the same range bin, where both are located in the same receive pulse and come from different transmit pulses, i.e.,
- represents the complex echo coefficient of the -th false target.
- represents the normalized Doppler shift frequency of the -th false target and represents the normalized Doppler frequency of the -th false target.
- represents the transmit steering vector, which is in the form of
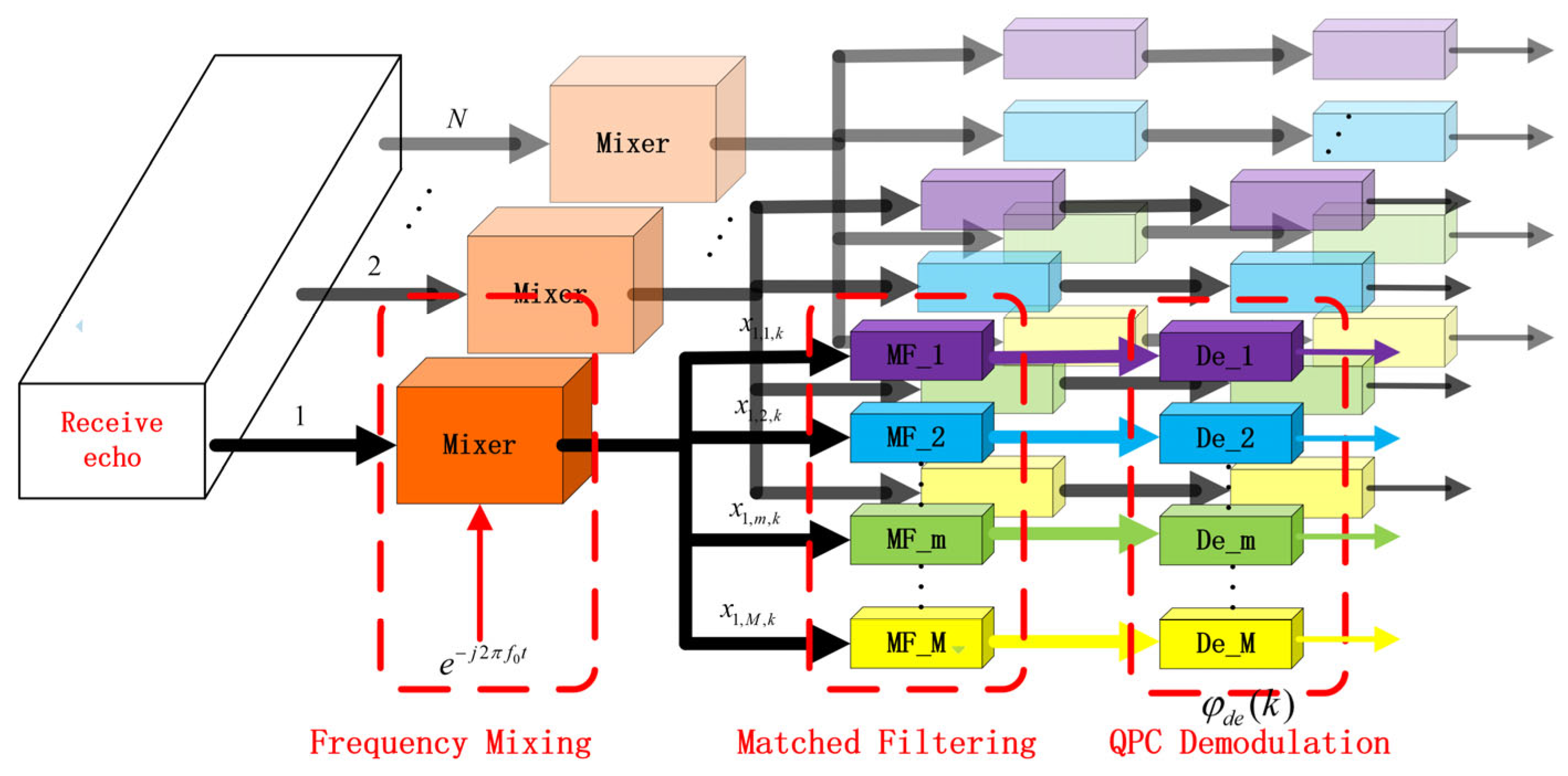
3.2. Suppression Based on Doppler Frequency Compensation
3.2.1. Distinguishing the Targets in Doppler Domain
3.2.2. Suppression in Doppler Domain
3.3. Suppression Based on Principle Range Frequency Compensation
3.3.1. Distinguishing the Targets in Spatial Domain
3.3.2. Samples Selection Based on Singular Spectrum Analysis
3.3.3. Adaptive Beamforming Based on Distance–Angle Two-dimensional Approach
| Algorithm 1: Secondary Compensation anti-interference method |
| Input: |
| Output: |
| Step 1. Construct the signal model in Equation (1) with and . |
| Step 2. Construct QPC vector in Equation (5) and demodulation vector according to Equation (16). |
| Step 3. Obtain the residual vectors after matched filtering and QPC demodulation according to Equation (17). |
| Step 4. Obtain output after Doppler frequency compensation according to Equation (26). |
| Step 5. Construct Frequency filter according to Equation (31). |
| Step 6. Obtain output after principle range frequency compensation according to Equation (38). |
| Step 7. Obtain the interference plus noise covariance matrix after SSA samples selection according to Equation (42). |
| Step 8. Obtain the weight vector via transmit-receive two dimensional beamforming according to Equation (45) |
| Step 9. Calculate output according to Equation (46) |
4. Simulations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, F.; Cao, S. Automotive radar interference mitigation using adaptive noise canceller. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3747–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Nguyen, B.V.; Song, I.; Kim, K. Design of anti-Jamming waveforms for time-hopping spread spectrum systems in tone jamming environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wen, C.; Li, J.; Xia, X.G.; Hong, W. An Efficient Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation Algorithm in Real Synthetic Aperture Radar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wen, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, W. HRWS SAR Narrowband Interference Mitigation Using Low-Rank Recovery and Image-Domain Sparse Regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Q.; So, H.C.; Farina, A. An Overview on Time/Frequency Modulated Array Processing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 228–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salehi, A.; Qureshi, I.; Malik, A.; Khan, Z.; Khan, W. Throughput enhancement for dual-function radar-embedded communications using two generalized sidelobe cancellers. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 91390–91398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ye, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Z.; An, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, J. Bistatic SAR clutter-ridge matched STAP method for nonstationary clutter suppression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, S.; Yong, G. TDOA estimation of dual-satellites interference localization based on blind separation. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2019, 30, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cui, G.; Kong, L. Main lobe jamming suppression for distributed radar via joint blind source separation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, R.; Shen, B. Adaptive Beamforming Design of Planar Arrays Based on Bayesian Compressive Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5185–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Lan, T.; Han, B.; Sun, H.; Yu, Z. Radar main-lobe jamming suppression and identification based on robust whitening Blind Source Separation and Convolutional Neural Networks. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2022, 16, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tous, H.; Barhumi, I.; Al-Dhahir, N. Narrow-Band Interference Mitigation Using Compressive Sensing for AF-OFDM Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 6146–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, H. High-fidelity SAR intermittent sampling deceptive jamming suppression using azimuth phase coding. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Thompson, J.; Huang, X.; Jin, T.; Zhou, Z. Random-frequency SAR imaging based on compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, B.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Xing, M.; Hong, W. Sparse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging from Compressed Sensing and Machine Learning: Theories, Applications and Trends. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 32–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, L.M.; Zhang, J.A.; Nguyen, D.N.; Huang, X.; Kekirigoda, A.; Hui, K.P. Suppression of Multiple Spatially Correlated Jammers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10489–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Zhan, L.; Lindsey, A. Subspace array processing for the suppression of FM jamming in GPS receivers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Zhu, S.; So, H.C. Mainlobe Deceptive Jammer Suppression in SF-RDA Radar: Joint Transmit-Receive Processing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 12602–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, H. Game Theory Design for Deceptive Jamming Suppression in Polarization MIMO Radar. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 114191–114202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, K. An Advanced Scheme for Range Ambiguity Suppression of Spaceborne SAR Based on Blind Source Separation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5230112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Dong, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X.; Liao, G.; Xu, H.; Sun, S. A Coherent integration method for moving target detection using frequency agile radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, G.C.; Xing, M.D. Range-Doppler reconstruction for frequency agile and PRF-jittering radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, T.; Long, T.; Sarkar, T.K. Mainlobe interference suppression based on eigen-projection processing and covariance matrix reconstruction. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H. Covariance matrix reconstruction with interference steering vector and power estimation for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 8495–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; He, Z. Mainlobe interference suppression with eigen-projection algorithm and similarity constraints. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S. Main-Lobe Jamming Suppression Method of using Spatial Polarization Characteristics of Antennas. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, P.; Baker, C.; Griffiths, H. Frequency diverse MIMO techniques for radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; So, H.C. Beampattern Synthesis Based on Novel Receive Delay Array for Mainlobe Interference Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2023, 71, 4470–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Wang, W.-Q.; Nusenu, S.Y. Adaptive Transmit Array Sidelobe Control Using FDA-MIMO for Tracking in Joint Radar-Communications. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 97, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, G.; Lan, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Suppression of Mainlobe Jammers with Quadratic Element Pulse Coding in MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Liao, G. Range Ambiguous Clutter Suppression for Airborne FDA-STAP Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Zhu, S.; Huang, L.; So, H.C. Joint Range and Angle Estimation Using MIMO Radar with Frequency Diverse Array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 3396–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; So, H.; Farina, A. FDA-MIMO Signal Processing for Mainlobe Jammer Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2019 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), A Coruna, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Huang, Y.; Peng, J.; Wu, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Y. Slow-time FDA-MIMO technique with application to STAP radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, W.-Q.; Li, F.; So, H.C. Sparsity-aware transmit beamspace design for FDA-MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2018, 144, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Lan, L. Mainlobe Deceptive Jammer Suppression Based on Quadratic Phase Coding in FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Huang, Y. MIMO Radar Beampattern Design Via PSL/ISL Optimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3955–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Wang, W.-Q.; Wali, S.; Nusenu, S.Y. Transmit beamspace design for FDA–MIMO radar with alternating direction method of multipliers. Signal Process. 2021, 180, 107832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Zhu, S.; So, H.C. Deceptive jamming suppression with frequency diverse MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2015, 113, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, G.; So, H.C. Resolving Range Ambiguity via Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Radar With Element-Pulse Coding. IEEE Trans. Signal Process 2020, 68, 2770–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S. Mainlobe deceptive jammer suppression using element-pulse coding with MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2021, 182, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. Enhanced Three-Dimensional Joint Domain Localized STAP for Airborne FDA-MIMO Radar under Dense False-Target Jamming Scenario. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 4154–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, B.; Wang, C.; Gong, J.; Tan, M. Robust adaptive beamforming via improved worst-case performance optimization algorithm based on FDA-MIMO. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 33, 725–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Huang, L. An Adaptive Range-Angle-Doppler Processing Approach for FDA-MIMO Radar Using Three-Dimensional Localization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 11, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Marino, A.; Aubry, A.; De Maio, A.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. GLRT-Based Adaptive Target Detection in FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Ding, Z.; So, H.C. Target localization with jammer removal using frequency diverse array. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 11685–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Xu, J.; Liao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Fioranelli, F.; So, H.C. Suppression of Mainbeam Deceptive Jammer with FDA-MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 11584–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

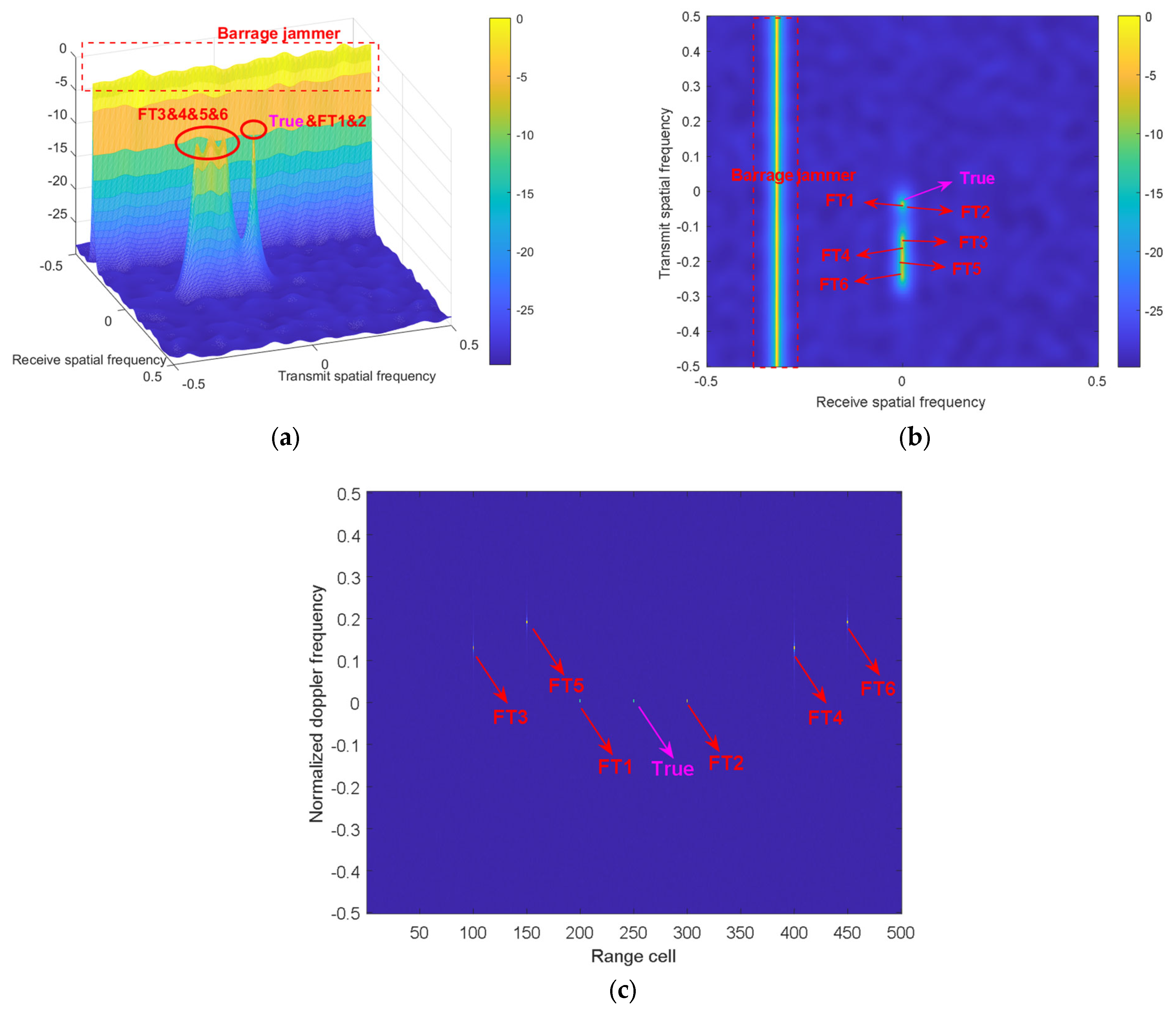
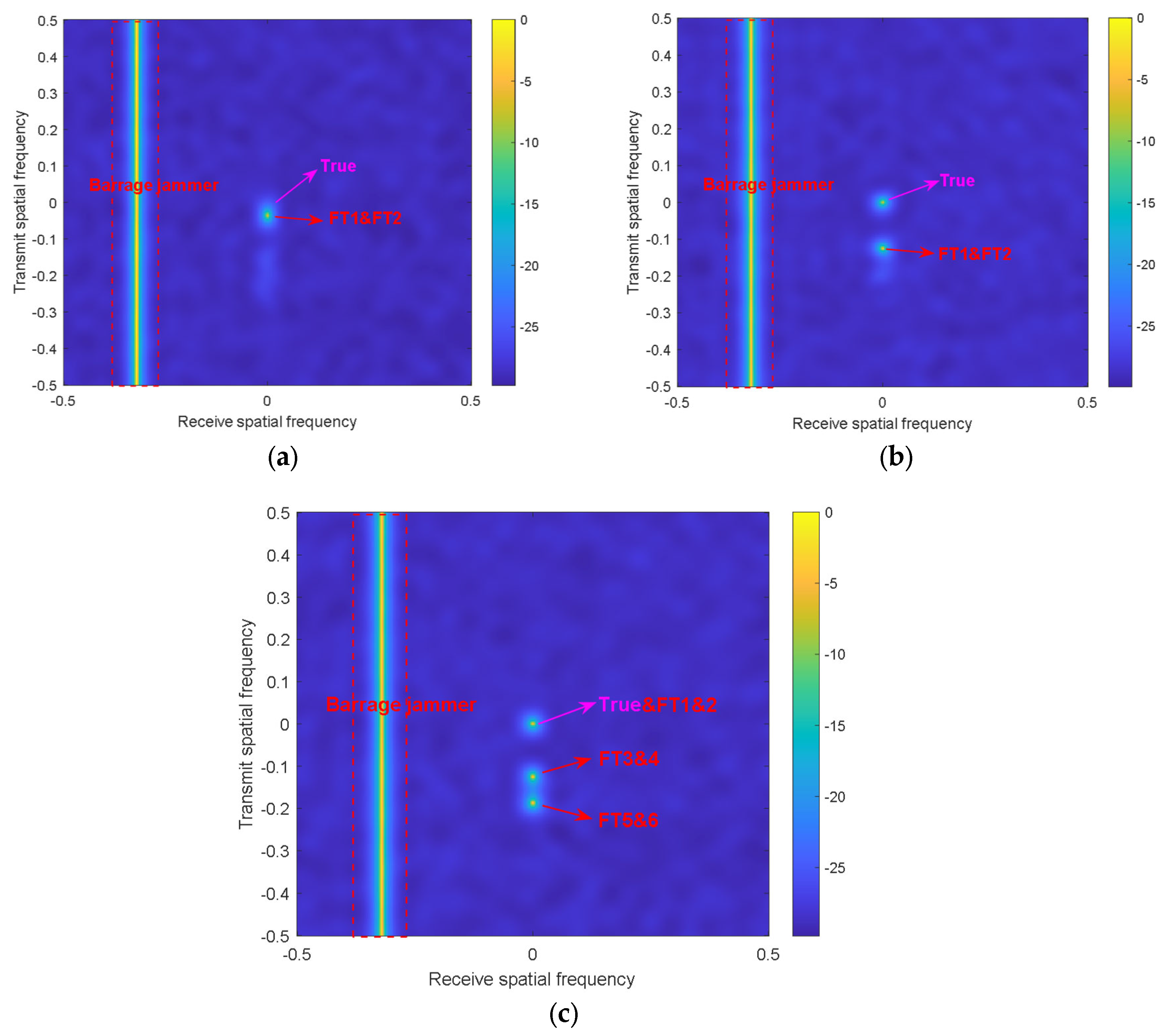

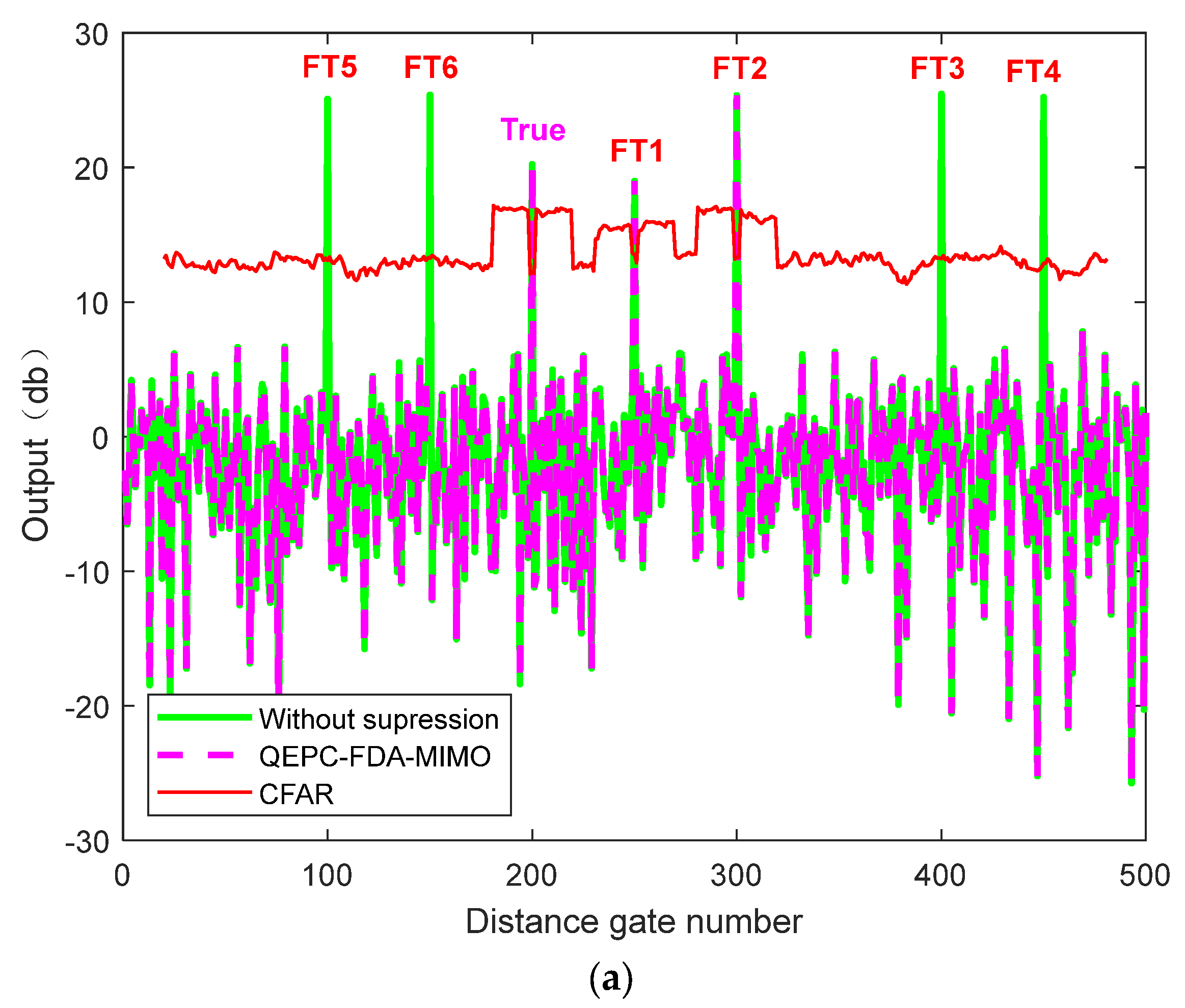


| True Target | FT 1 | FT 2 | FT 3 | FT 4 | FT 5 | FT 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle (°) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Range(km) | 9 | 11.25 | 13.5 | 49.5 | 63 | 74.25 | 87.75 |
| Range bin | 200 | 250 | 300 | 100 | 400 | 150 | 450 |
| Time delay (ms) | 0 | 0.015 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.435 | 0.525 |
| Velocity (m/s) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| SNR (dB) | 20 | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ |
| JNR (dB) | \ | 20 | 25 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Delayed pulse | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lan, L. A Method to Suppress Interferences Based on Secondary Compensation with QPC-FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4711. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194711
Zhang Y, Liao G, Xu J, Zhang X, Lan L. A Method to Suppress Interferences Based on Secondary Compensation with QPC-FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(19):4711. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194711
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiqun, Guisheng Liao, Jingwei Xu, Xuepan Zhang, and Lan Lan. 2023. "A Method to Suppress Interferences Based on Secondary Compensation with QPC-FDA-MIMO Radar" Remote Sensing 15, no. 19: 4711. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194711
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liao, G., Xu, J., Zhang, X., & Lan, L. (2023). A Method to Suppress Interferences Based on Secondary Compensation with QPC-FDA-MIMO Radar. Remote Sensing, 15(19), 4711. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15194711








