Assessment and Data Fusion of Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimation Products over Ungauged Areas Based on Triple Collocation without In Situ Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
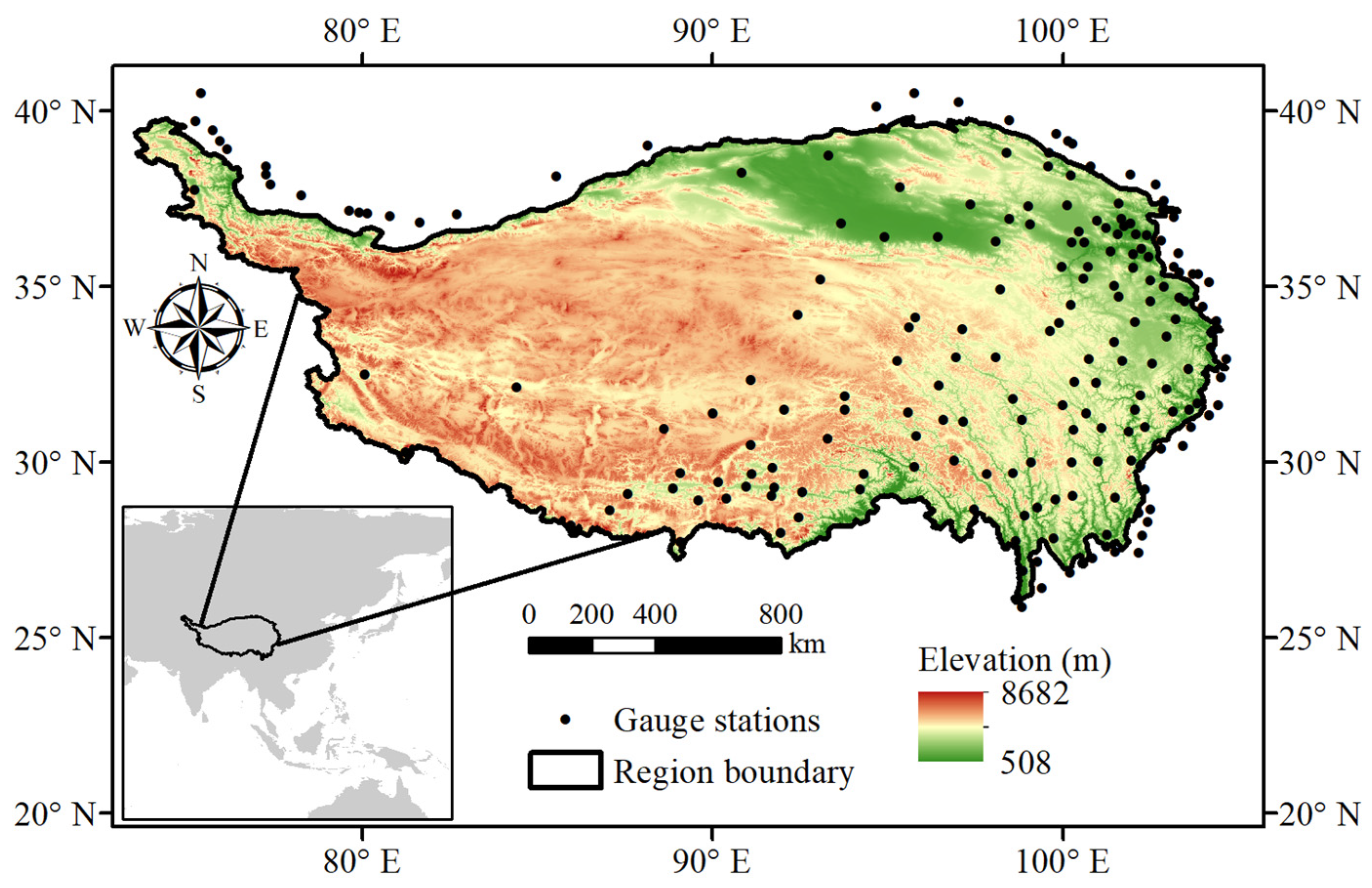
2.1. Tibetan Plateau
2.2. Gauge Observations
2.3. Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimation Products
- 1.
- IMERG
- 2.
- PDIR
- 3.
- CMORPH
2.4. Other Gridded Precipitation Products
- 1.
- ERA5
- 2.
- SM2RAIN-ASCAT
3. Methods
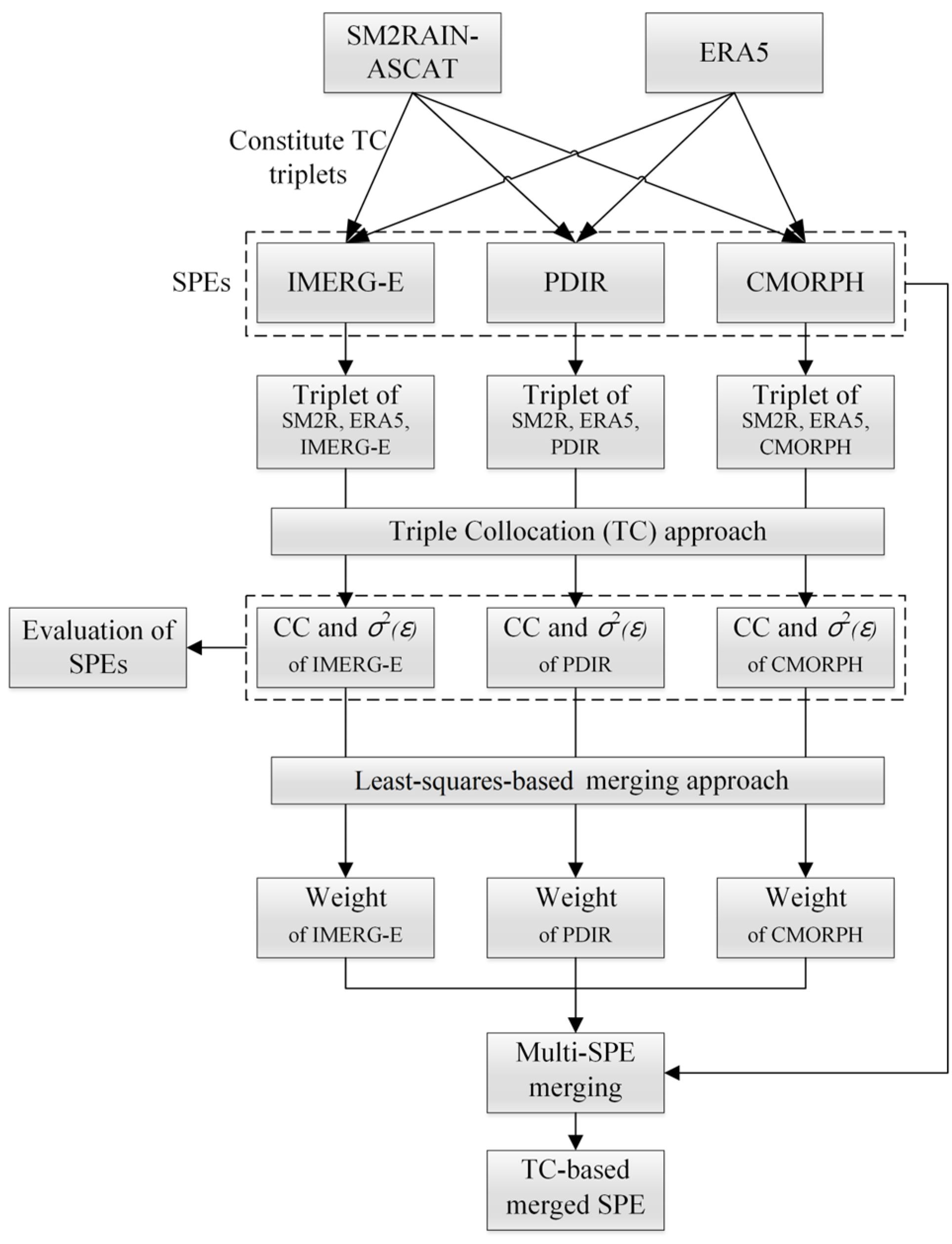
3.1. The Triple Collocation (TC) Approach
3.2. TC-Based Merging Approach
3.3. Assessment Metrics
4. Results
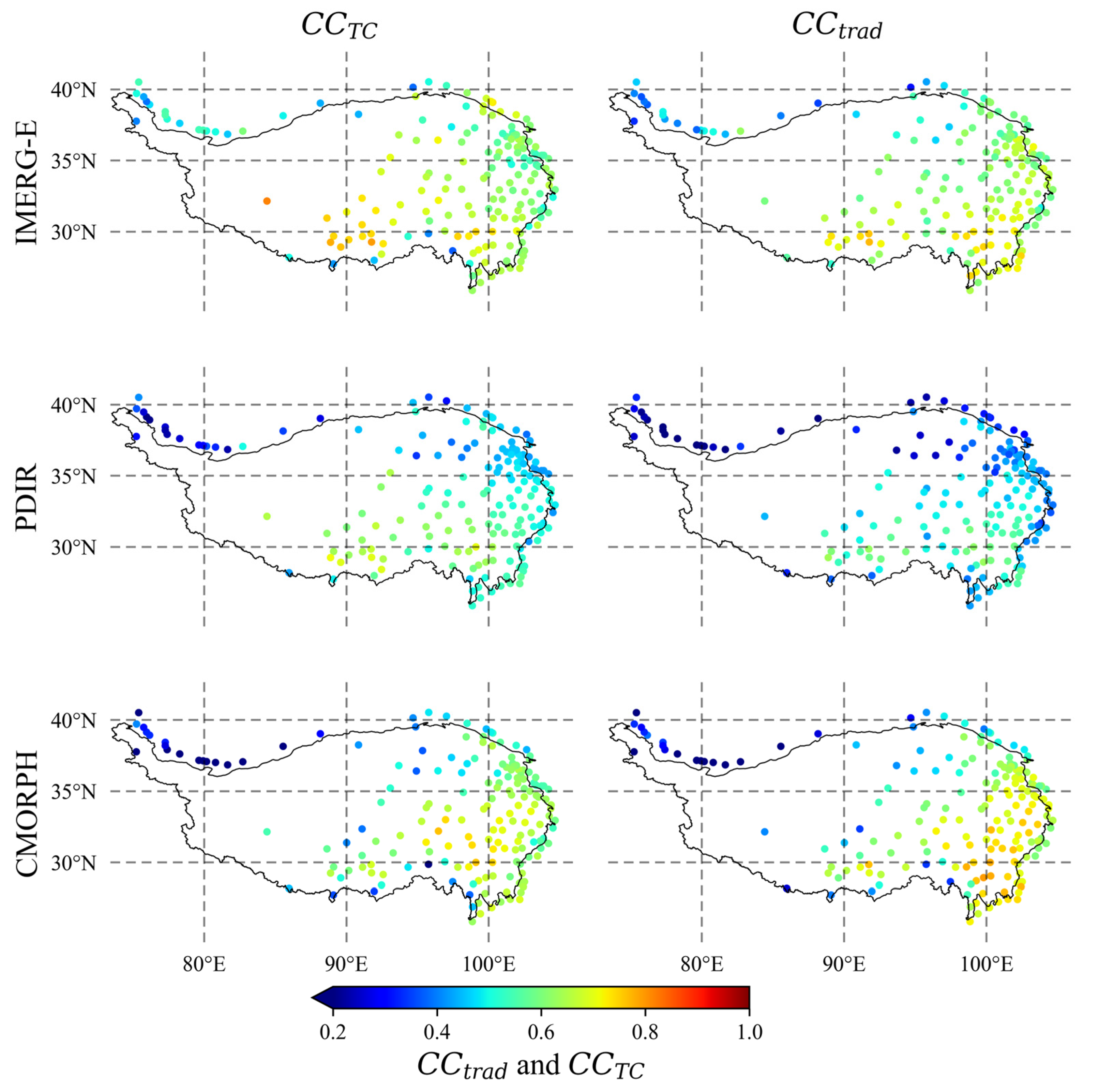
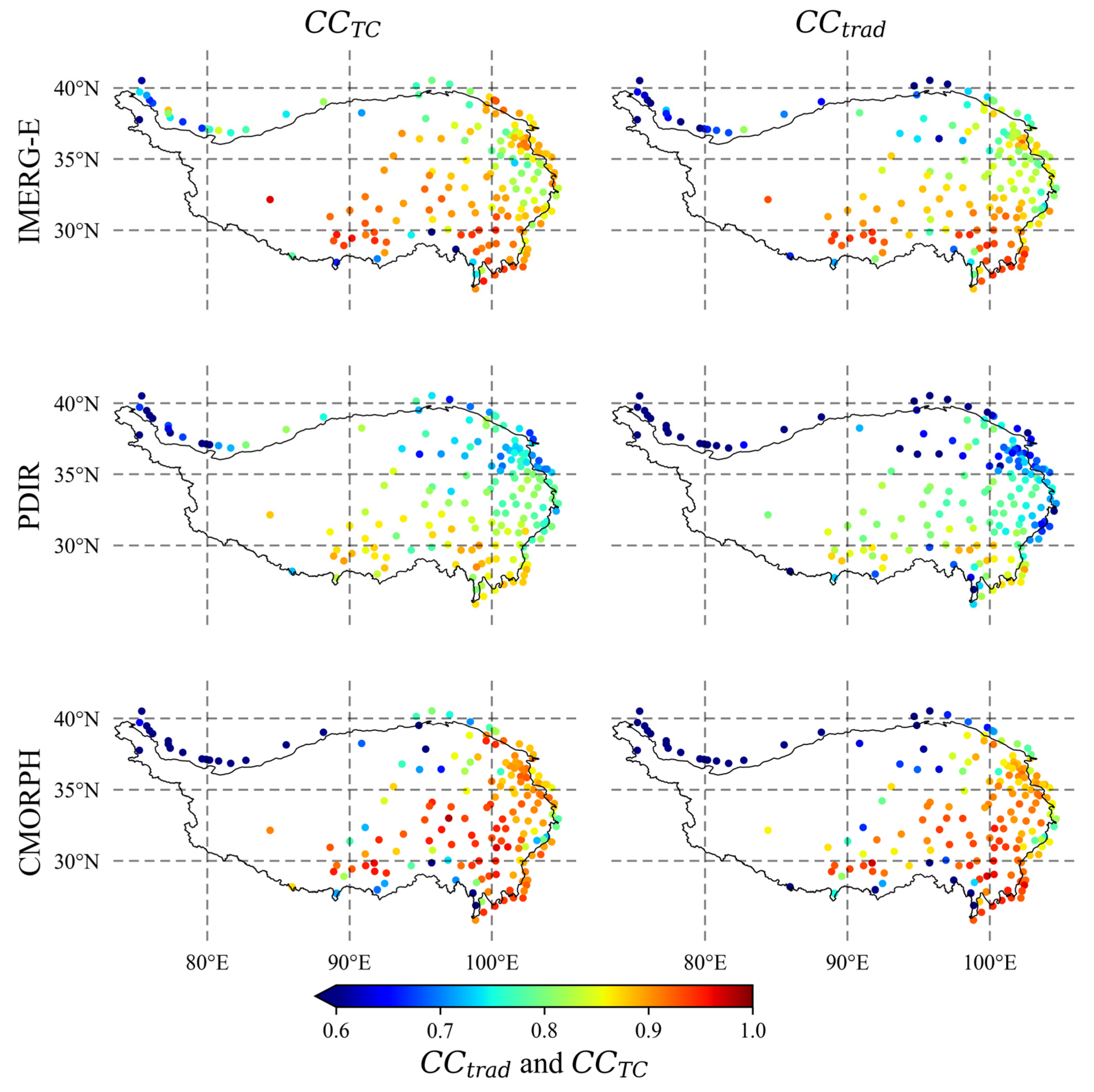
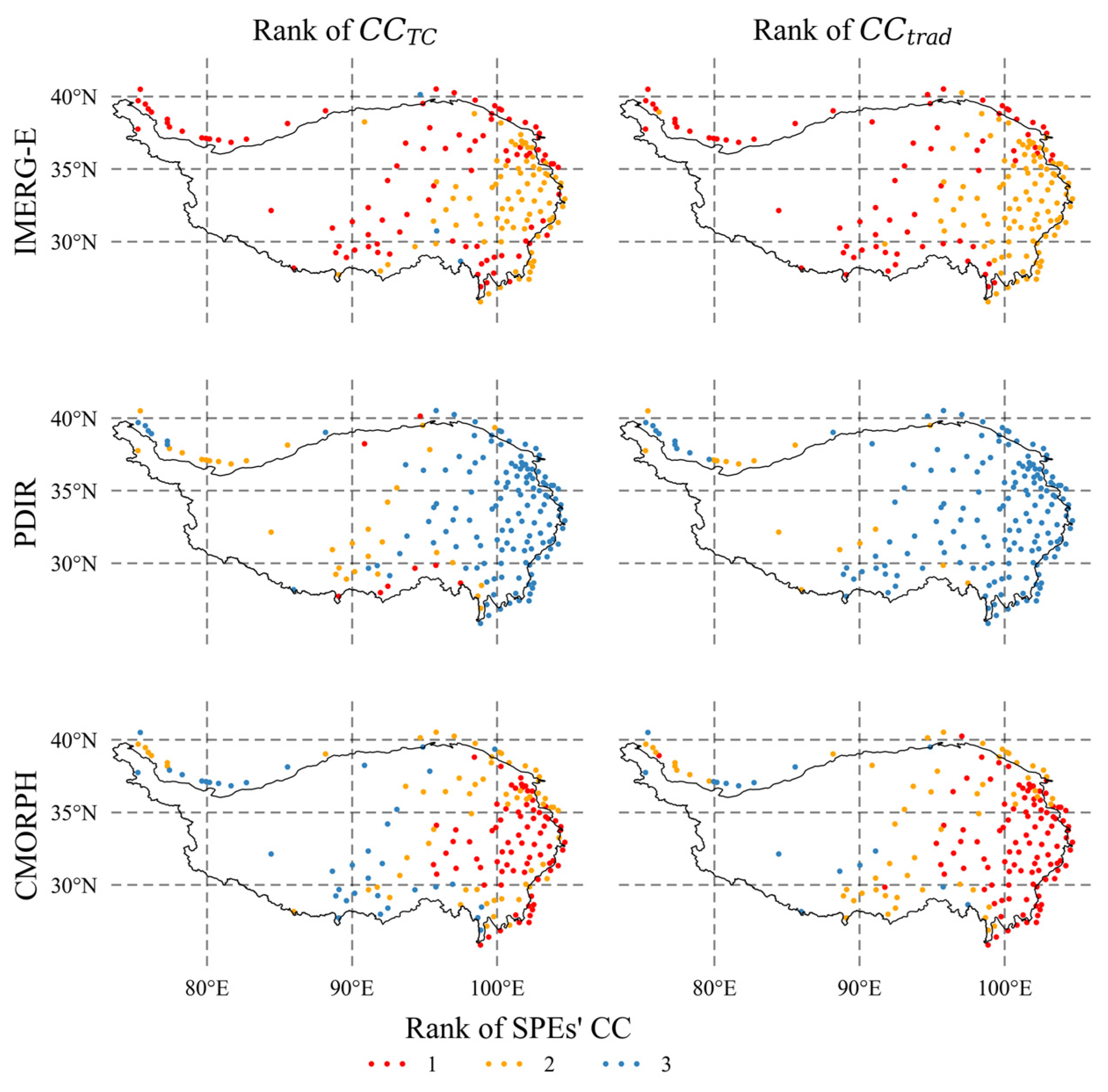
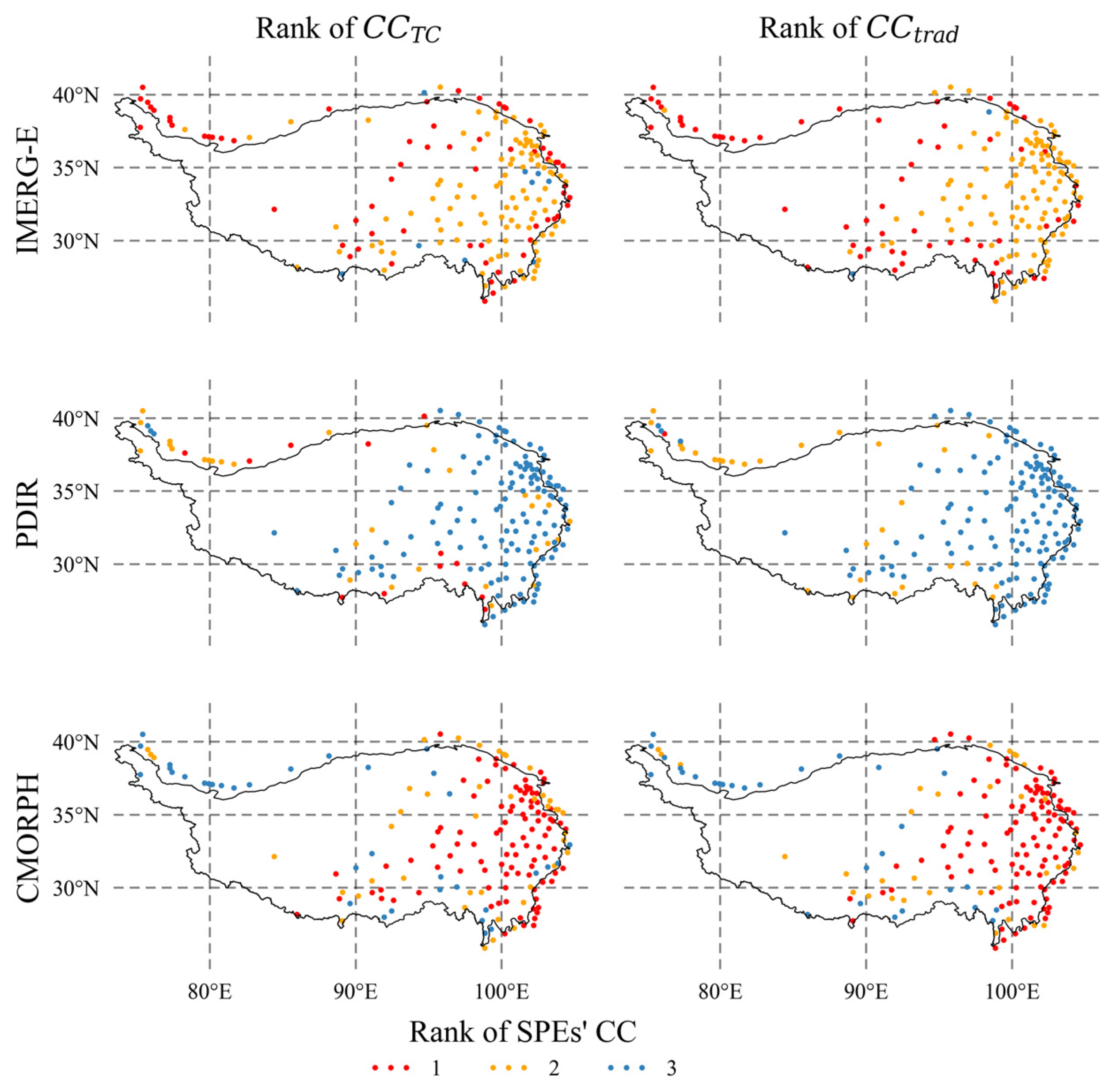
4.1. Validation of the TC Assessment Approach
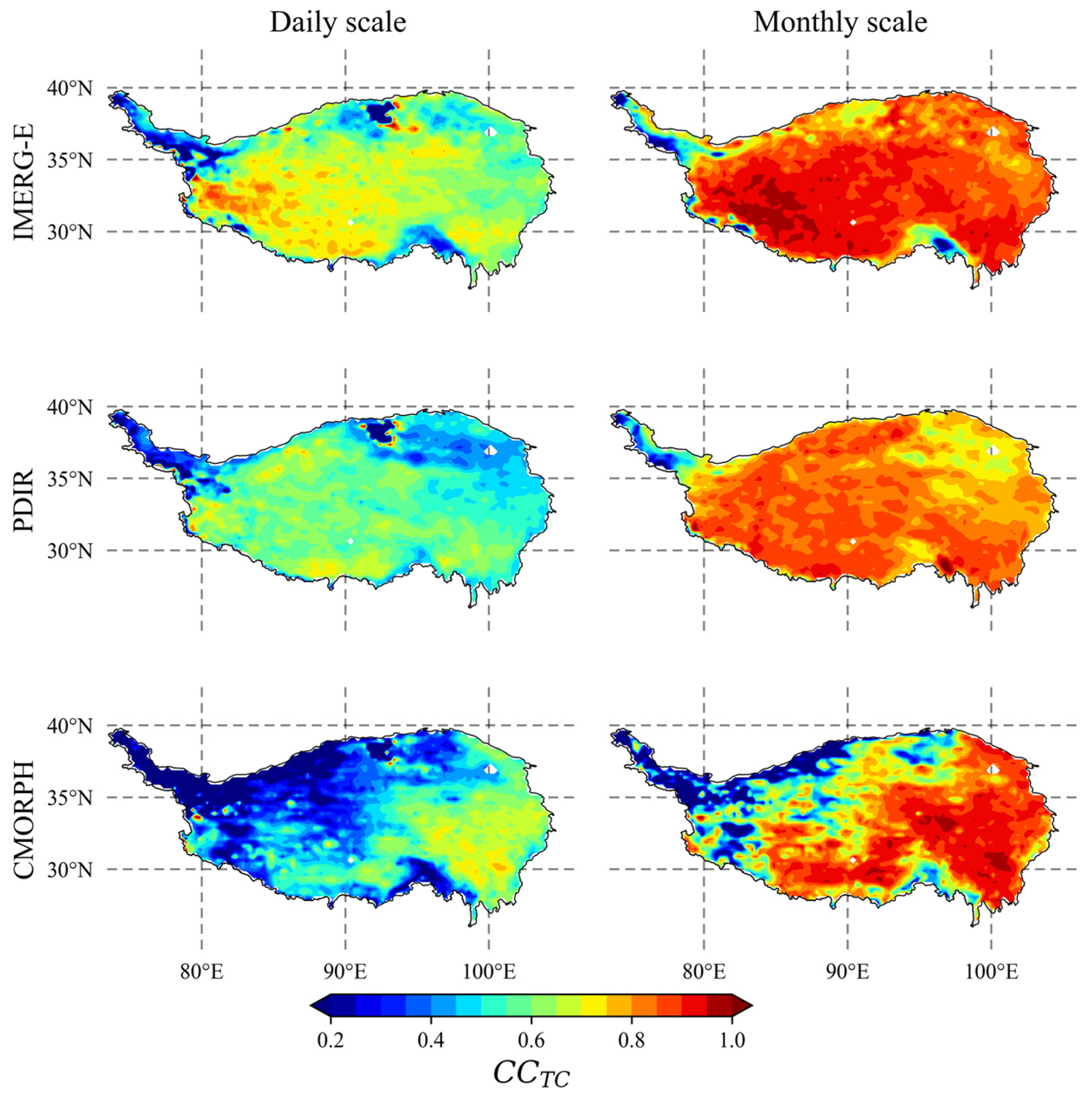
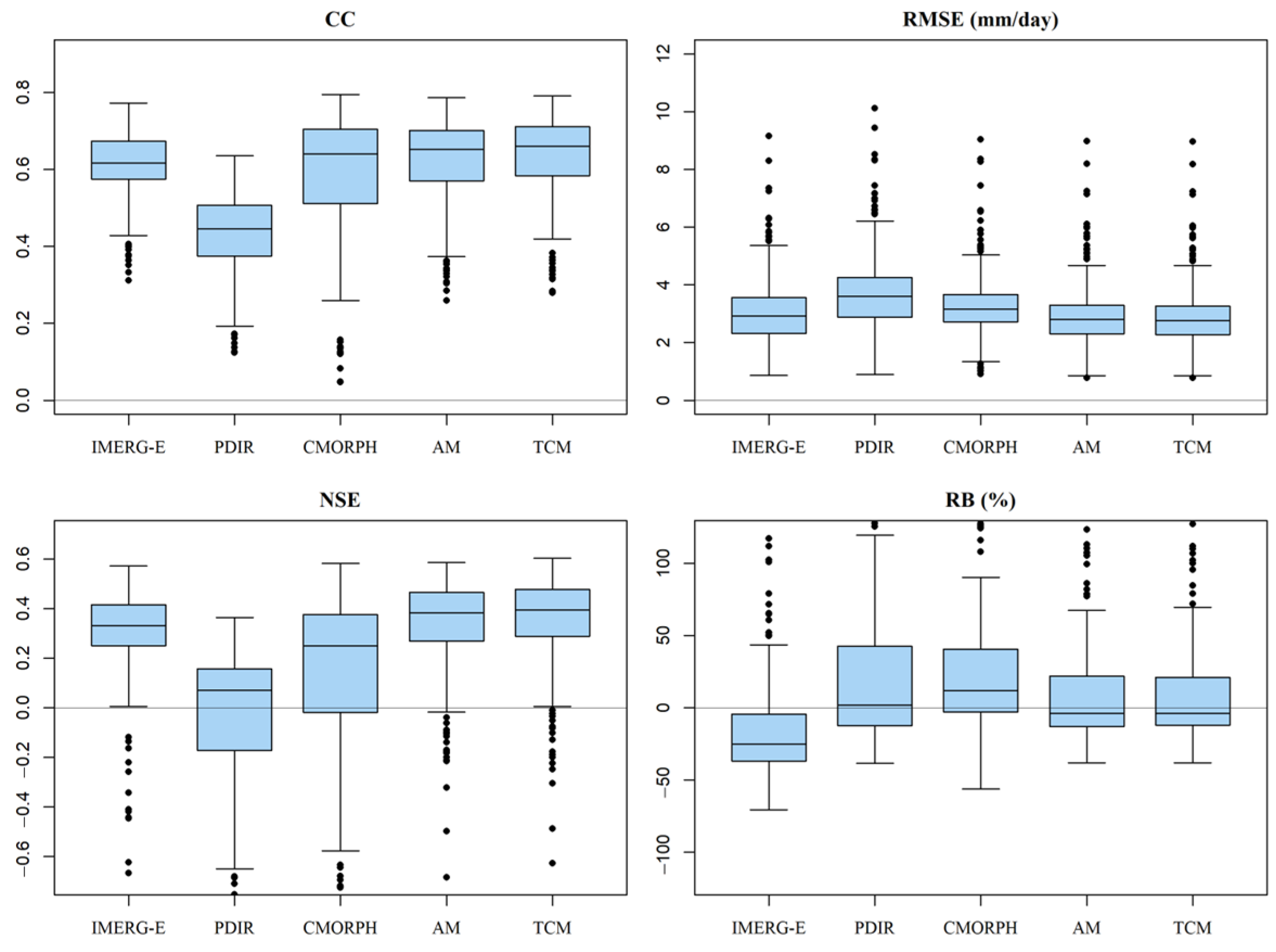
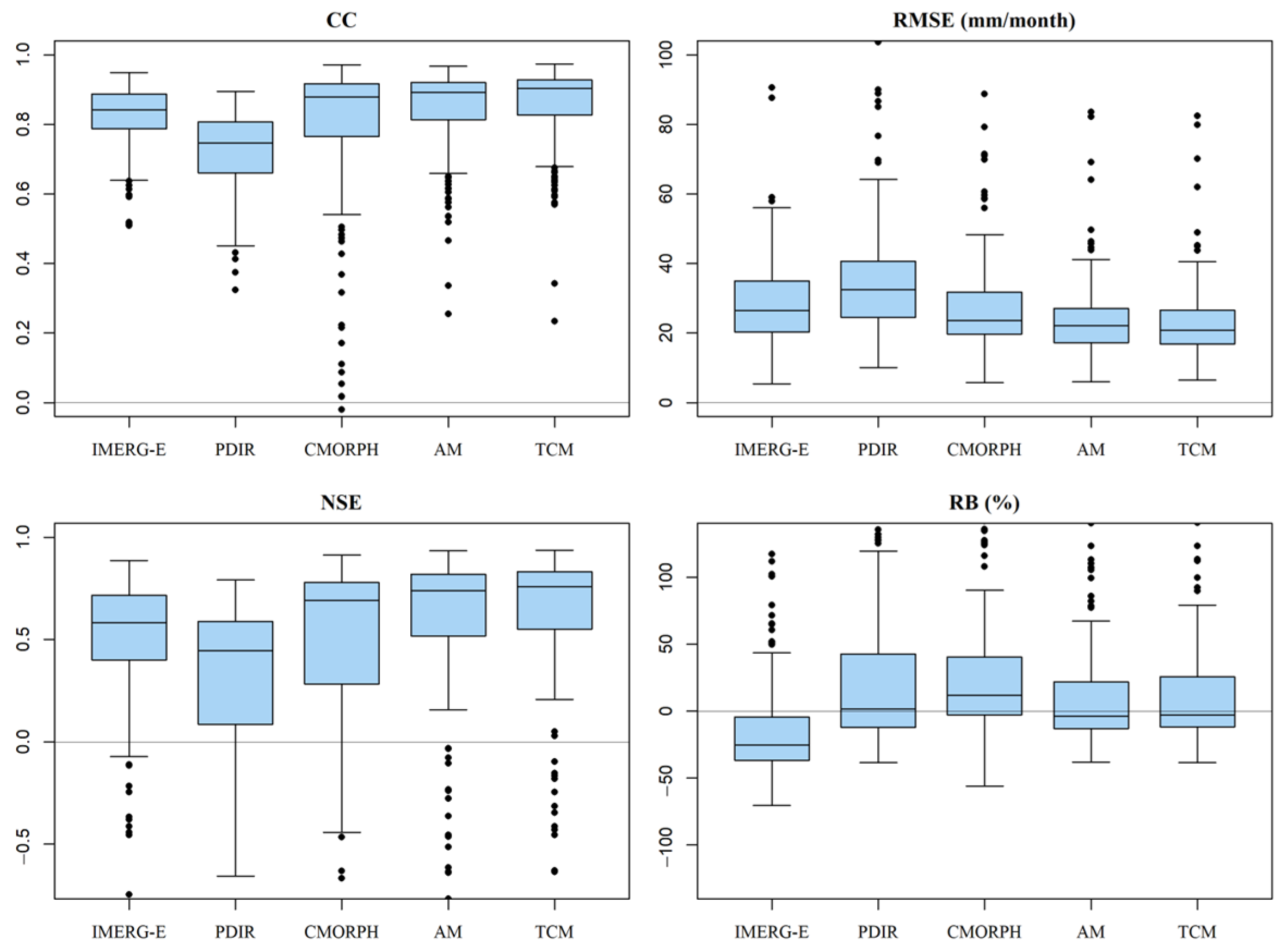
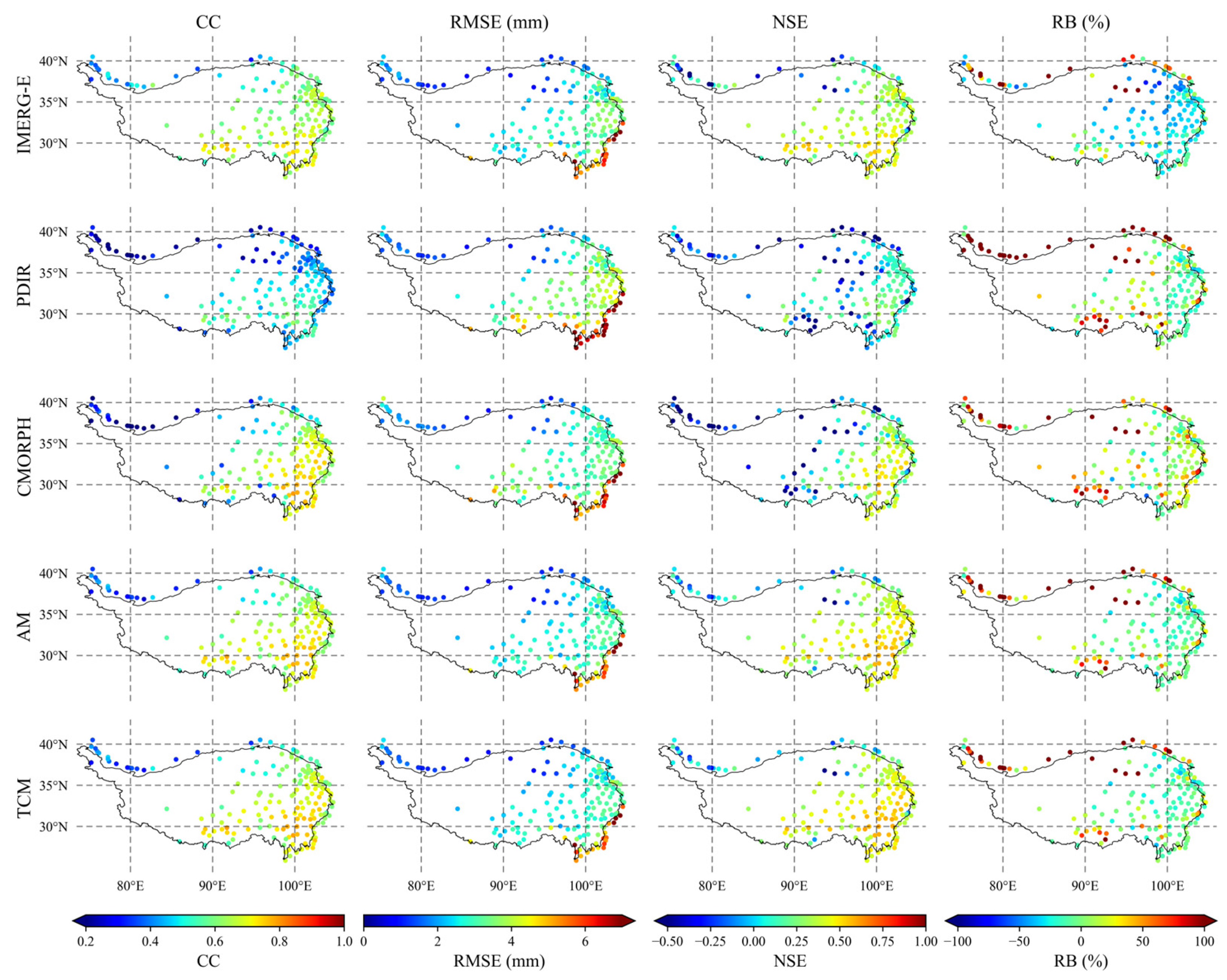
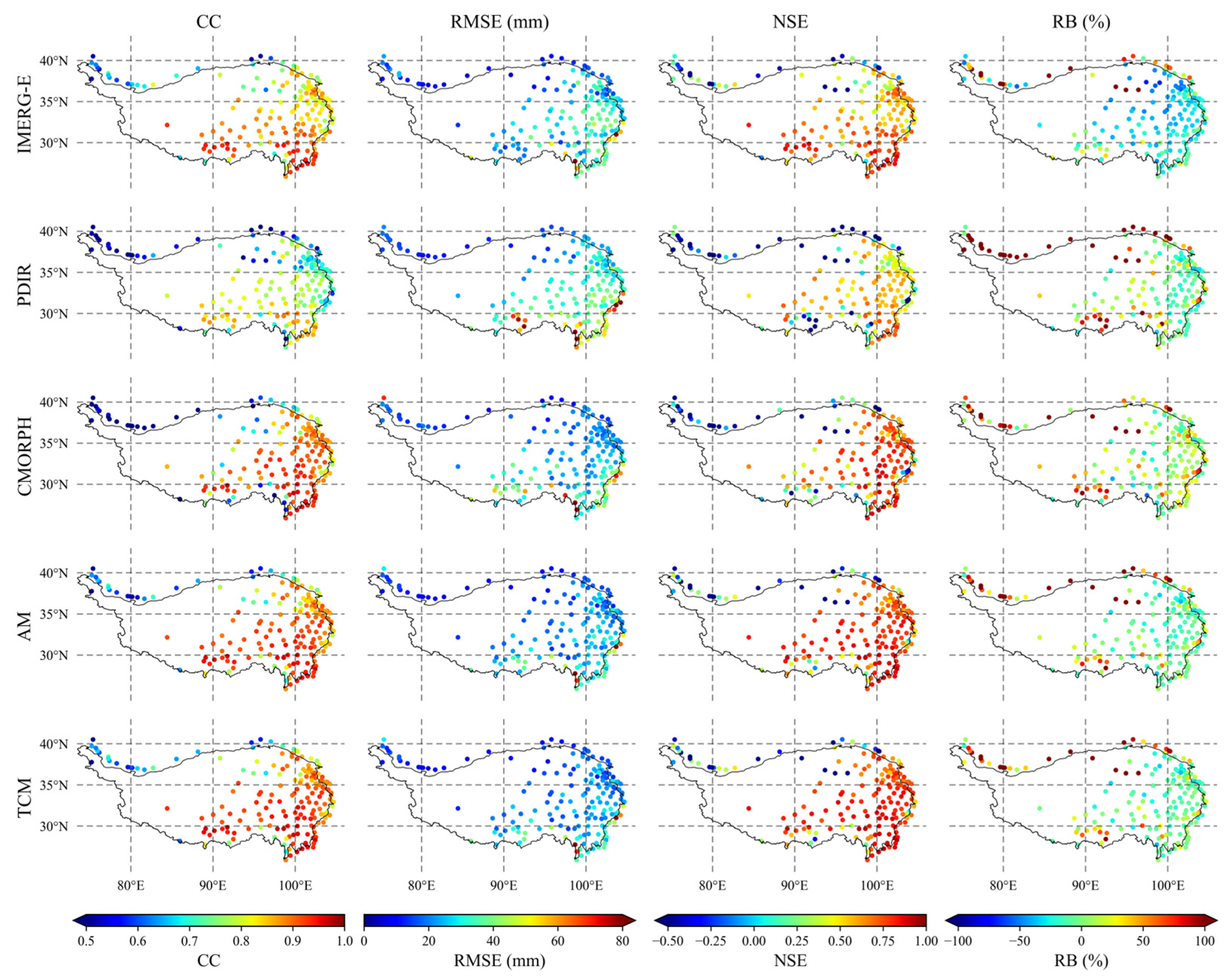
4.2. Performance of the TC Approach
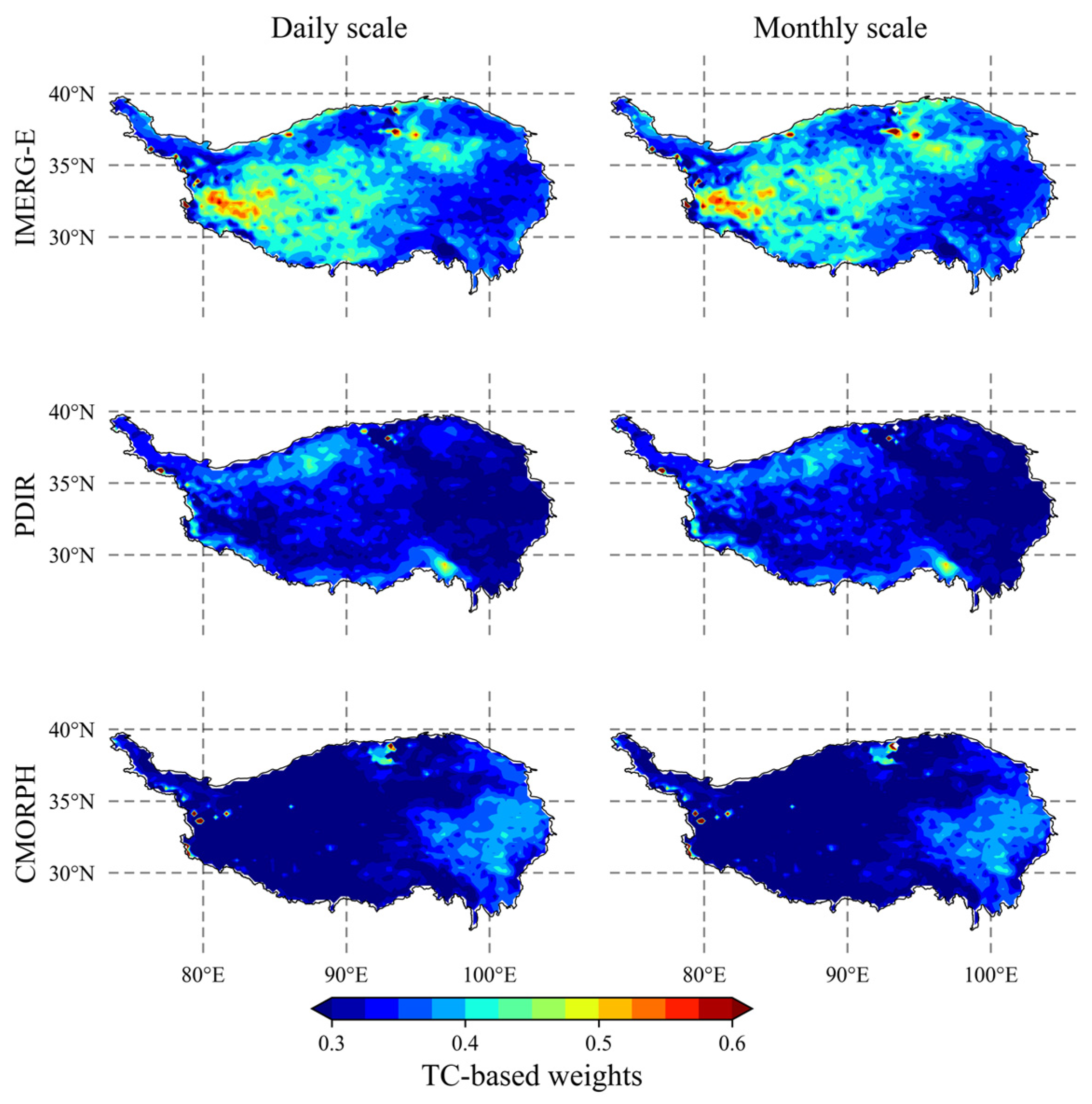
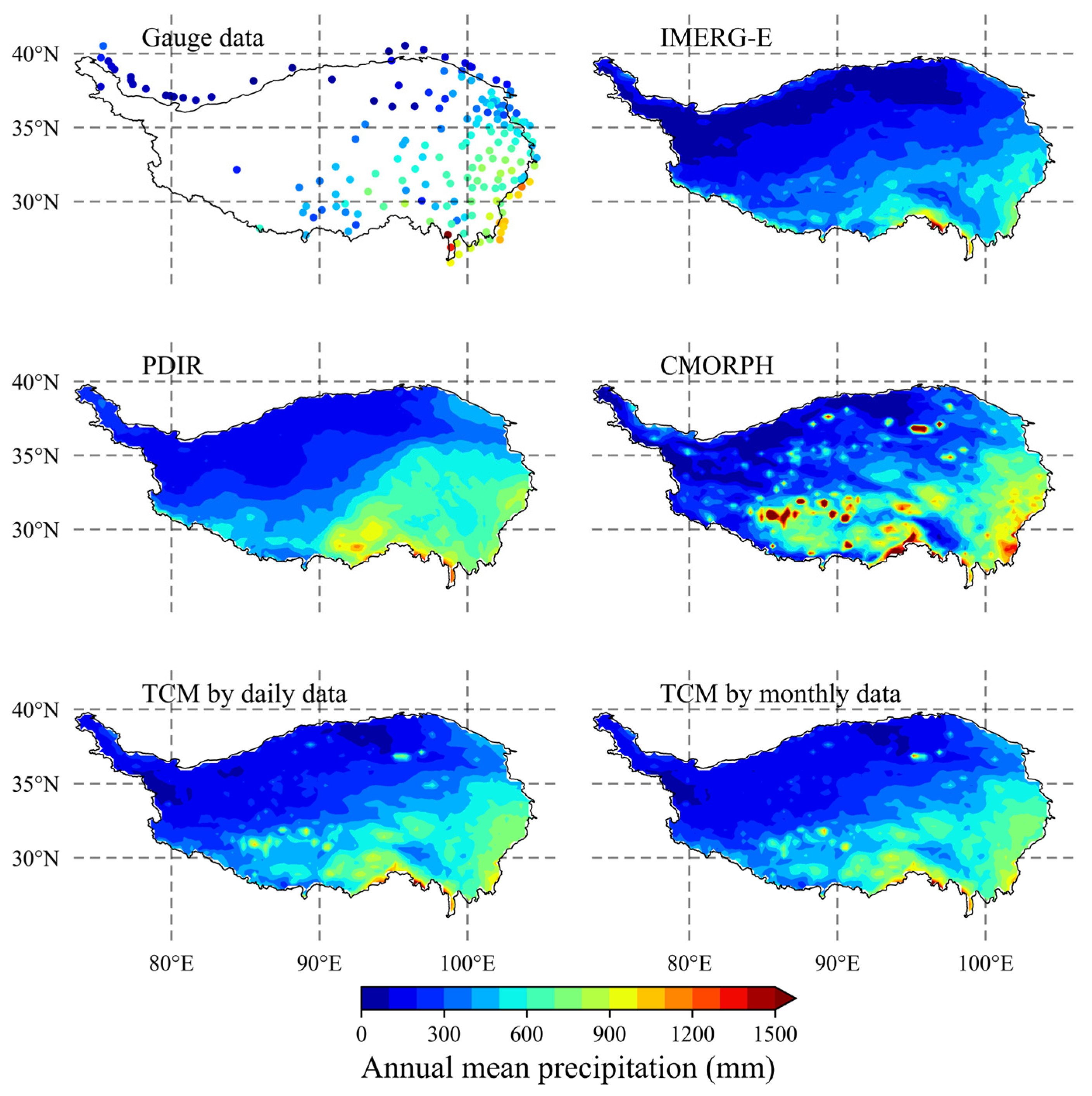
4.3. Data Fusion of SPEs Based on the TC Approach
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Li, X.; Long, D.; Scanlon, B.R.; Mann, M.E.; Li, X.; Tian, F.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G. Climate change threatens terrestrial water storage over the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Ma, Z.; Hong, Y. Have satellite precipitation products improved over last two decades? A comprehensive comparison of GPM IMERG with nine satellite and reanalysis datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, P. Blending long-term satellite-based precipitation data with gauge observations for drought monitoring: Considering effects of different gauge densities. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 124007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, G.; Yao, Y.; Long, D.; Li, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, R. Performance of Optimally Merged Multisatellite Precipitation Products Using the Dynamic Bayesian Model Averaging Scheme over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 814–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Lai, C. Evaluation and hydrologic validation of TMPA satellite precipitation product downstream of the Pearl River Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4169–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Farhan, S.B. Precipitation bias variability versus various gauges under different climatic conditions over the Third Pole Environment (TPE) region. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation ofsatellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A Method that Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive Microwave and Infrared Data at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J.; et al. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission (IMERG); Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C.D., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Z. Triple collocation-based error estimation and data fusion of global gridded precipitation products over the Yangtze River basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P.A. Global Precipitation: A 17-Year Monthly Analysis Based on Gauge Observations, Satellite Estimates, and Numerical Model Outputs. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, H.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y. A two-stage blending approach for merging multiple satellite precipitation estimates and rain gauge observations: An experiment in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, G. A spatiotemporal deep fusion model for merging satellite and gauge precipitation in China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Lai, C.; Chen, X. Evaluation of TMPA 3B42-V7 Product on Extreme Precipitation Estimates. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shen, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, P. Applicability of long-term satellite-based precipitation products for drought indices considering global warming. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Zhong, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Lian, Y. Monitoring hydrological drought using long-term satellite-based precipitation data. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Five Satellite-Based Precipitation Products in Two Gauge-Scarce Basins on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhong, R.; Lai, C.; Chen, J. Evaluation of the GPM IMERG satellite-based precipitation products and the hydrological utility. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, G.; Long, D.Y.B.; Zhong, L.W.W.; Hong, Y. Similarity and Error Intercomparison of the GPM and Its Predecessor-TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis Using the Best Available Hourly Gauge Network over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over Mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Gourley, J.J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W07542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, Y. Merging multiple satellite-based precipitation products and gauge observations using a novel double machine learning approach. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xiong, L.; Ma, Q.; Kim, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, C. Improving daily spatial precipitation estimates by merging gauge observation with multiple satellite-based precipitation products based on the geographically weighted ridge regression method. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Vogelzang, J.; Konings, A.G.; Entekhabi, D.; Piles, M.; Stoffelen, A. Extended triple collocation: Estimating errors and correlation coefficients with respect to an unknown target. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6229–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffelen, A. Toward the true near-surface wind speed: Error modeling and calibration using triple collocation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 7755–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Crow, W.T.; Bindlish, R.; Colliander, A.; Burgin, M.S.; Asanuma, J.; Aida, K. Global-scale evaluation of SMAP, SMOS and ASCAT soil moisture products using triple collocation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chai, L.; Crow, W.; Dong, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S. The reliability of categorical triple collocation for evaluating soil freeze/thaw datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 281, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Park, J. The use of triple collocation approach to merge satellite- and model-based terrestrial water storage for flood potential analysis. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, G.; Hong, Y. Cross-evaluation of ground-based, multi-satellite and reanalysis precipitation products: Applicability of the Triple Collocation method across Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemohammad, S.H.; McColl, K.A.; Konings, A.G.; Entekhabi, D.; Stoffelen, A. Characterization of precipitation product errors across the United States using multiplicative triple collocation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 3489–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bai, X.; Wu, X.; Lai, C.; Zhang, Z. Spatially continuous assessment of satellite-based precipitation products using triple collocation approach and discrete gauge observations via geographically weighted regression. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Tang, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, M. The potential and uncertainty of triple collocation in assessing satellite precipitation products in Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2021, 252, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Li, H.; Hou, E.; Song, S.; Lai, C. Assessment and Hydrological Validation of Merged Near-Real-Time Satellite Precipitation Estimates Based on the Gauge-Free Triple Collocation Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, C.; Crow, W.; Brocca, L. An assessment of the performance of global rainfall estimates without ground-based observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4347–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, P.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. Assessing the accuracy and drought utility of long-term satellite-based precipitation estimation products using the triple collocation approach. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Filippucci, P.; Hahn, S.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Schüller, L.; Bojkov, B.; Wagner, W. SM2RAIN–ASCAT (2007–2018): Global daily satellite rainfall data from ASCAT soil moisture observations. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1583–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.T.; Crow, W.T.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C. An objective methodology for merging satellite-and model-based soil moisture products. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Lei, F.; Wei, L. Triple Collocation Based Multi-Source Precipitation Merging. Front. Water. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Tang, G.; Behrangi, A.; Wang, T.; Tan, X.; Ma, Z.; Xiong, W. Precipitation Merging Based on the Triple Collocation Method Across Mainland China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. 2021, 59, 3161–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zuo, Z.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, D.; Liang, Q. Linkage of the surface air temperature over Tibetan Plateau and Northeast hemisphere in winter at interannual timescale. Atmos. Res. 2022, 274, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Zhao, T.; Chen, X. Evaluating the tradeoff between hydropower benefit and ecological interest under climate change: How will the water-energy-ecosystem nexus evolve in the upper Mekong basin? Energy 2021, 237, 121518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Shum, C.; Bolch, T.; Yi, S.; Allen, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Response of Tibetan Plateau lakes to climate change: Trends, patterns, and mechanisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103269. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Global Planet. Change 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.; Shearer, E.J.; Ombadi, M.; Gorooh, V.A.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Logan, W.S.; Ralph, M. PERSIANN Dynamic Infrared–Rain Rate Model (PDIR) for High-Resolution, Real-Time Satellite Precipitation Estimation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E286–E302. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X. Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Imagery Using an Artificial Neural Network Cloud Classification System. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Melone, F.; Wagner, W. A new method for rainfall estimation through soil moisture observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Moramarco, T.; Hahn, S.; Hasenauer, S.; Kidd, R.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W.; Levizzani, V. Soil as a natural rain gauge: Estimating global rainfall from satellite soil moisture data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5128–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, T. Predictive performance of ensemble hydroclimatic forecasts: Verification metrics, diagnostic plots and forecast attributes. WIREs Water 2022, 9, e1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Lü, H.T.; Crow, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, J. Evaluation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from IMERG V04A and V03D, CMORPH and TMPA with Gauged Rainfall in Three Climatologic Zones in China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. Evaluation and Hydrological Utility of the Latest GPM IMERG V5 and GSMaP V7 Precipitation Products over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Ao, T.; Li, X. Comprehensive evaluation of satellite and reanalysis precipitation products over the eastern Tibetan plateau characterized by a high diversity of topographies. Atmos. Res. 2021, 259, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Schepen, A.; Robertson, D.E. Merging Seasonal Rainfall Forecasts from Multiple Statistical Models through Bayesian Model Averaging. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 5524–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez-Villanueva, O.M.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Beck, H.E.; McNamara, I.; Ribbe, L.; Nauditt, A.; Birkel, C.; Verbist, K.; Giraldo-Osorio, J.D.; Xuan Thinh, N. RF-MEP: A novel Random Forest method for merging gridded precipitation products and ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111606. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tuo, Y.; Chiogna, G.; Disse, M. Evaluation of eight high spatial resolution gridded precipitation products in Adige Basin (Italy) at multiple temporal and spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1536–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Metric | Equation * | Perfect Score |
|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient (CC) | 1 | |
| Root mean square error (RMSE) | 0 | |
| Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) | 1 | |
| Relative bias (RB) | 0 |
| Time Scale | Metrics | IMERG-E | PDIR | CMORPH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | 0.612 | 0.499 | 0.555 | |
| 0.609 | 0.429 | 0.586 | ||
| 0.677 | 0.873 | 0.938 | ||
| Monthly | 0.852 | 0.779 | 0.807 | |
| 0.823 | 0.719 | 0.790 | ||
| 0.738 | 0.812 | 0.955 |
| SPEs | Daily | Monthly | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | RMSE (mm) | NSE | RB (%) | CC | RMSE (mm) | NSE | RB (%) | |
| IMERG-E | 0.640 | 3.39 | 0.378 | −23.4 | 0.855 | 30.77 | 0.701 | −23.4 |
| PDIR | 0.470 | 4.08 | 0.098 | 4.9 | 0.756 | 38.11 | 0.541 | 4.9 |
| CMORPH | 0.652 | 3.61 | 0.293 | 12.3 | 0.864 | 30.50 | 0.706 | 12.3 |
| AM | 0.667 | 3.24 | 0.432 | −2.1 | 0.884 | 26.34 | 0.781 | −2.1 |
| TCM | 0.674 | 3.21 | 0.442 | −2.4 | 0.891 | 25.50 | 0.794 | −1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Zhu, J.; Lai, C. Assessment and Data Fusion of Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimation Products over Ungauged Areas Based on Triple Collocation without In Situ Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174210
Wu X, Zhu J, Lai C. Assessment and Data Fusion of Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimation Products over Ungauged Areas Based on Triple Collocation without In Situ Observations. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(17):4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174210
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiaoqing, Jialiang Zhu, and Chengguang Lai. 2023. "Assessment and Data Fusion of Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimation Products over Ungauged Areas Based on Triple Collocation without In Situ Observations" Remote Sensing 15, no. 17: 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174210
APA StyleWu, X., Zhu, J., & Lai, C. (2023). Assessment and Data Fusion of Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimation Products over Ungauged Areas Based on Triple Collocation without In Situ Observations. Remote Sensing, 15(17), 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15174210





