Abstract
Turbulence is ubiquitous in the planetary boundary layer (PBL), which is of great importance to the prediction of weather and air quality. Nevertheless, the profiles of turbulence in the whole PBL as observed by radar wind profilers (RWPs) are rarely reported. In this communication, the purpose was to investigate the vertical structures of turbulence dissipation rate (ε) obtained from the Doppler spectrum width measurements from two RWPs at plateau (Zhangbei) and plain (Baoding) stations in the North China Plain for the year 2021, and to tease out the underlying mechanism for the difference of ε between Zhangbei and Baoding. Under clear-sky conditions, the annual mean value of ε in the PBL over the plateau station was found to be higher than that over the plain station throughout the daytime from 0900 to 1700 local standard time. The magnitude of ε at both stations showed significant seasonal variation, with the strongest ε in summer but the weakest in winter. If a larger difference between the 2 m air temperature and surface temperature (Ta−Ts), as a surrogate of sensible heat flux, is observed, the turbulence intensity tends to become stronger. The influence of vertical wind shear on turbulence was also analyzed. Comparison analyses showed that the plateau station of Zhangbei was characterized by larger sensible heat flux and stronger wind shear compared with the plain station of Baoding. This may account for the more intense ε within the PBL of Zhangbei. Moreover, the magnitude of ε in the PBL was positively correlated with the values of both Ta−Ts and vertical wind shear. The findings highlight the urgent need to characterize the vertical turbulence structure in the PBL over a variety of surfaces in China.
1. Introduction
The planetary boundary layer (PBL) is the lowermost layer of the troposphere adjacent to the Earth’s surface, in which the moisture, heat, momentum, and air mass are dramatically and frequently exchanged between the atmosphere and the surface [1,2,3]. The exchange is largely determined or governed by the turbulence in the PBL, particularly under stable or neutral conditions [4,5]. Moreover, the turbulence in the atmosphere is often generated thermally through convection-related instability, or mechanically through Kelvin–Helmholtz billows, the reversal or disruption of gravity waves, and inertial gravity waves [6,7,8,9].
The changes in meteorological variables and air pollution near the surface can be rapidly conveyed over the entire PBL by chaotic turbulent eddies on a time scale of one hour or less [4,10]. The turbulence in the PBL can alter the process of new particle formation, thereby affecting the development of clouds and precipitation [11]. The pioneer work in [11] is a great step forward to fully answer the question of “Can we understand clouds without turbulence” posed by Bodenschatz et al. in the year 2010 [12]. Nevertheless, the turbulence measurements used in Wu et al. [11] are mostly limited to the ground level. Turbulence-resolving model simulation studies show that the turbulent eddies, along with convection, can dramatically affect the microphysical properties of clouds by transporting water vapor and heat to the PBL top and beyond, thereby altering the onset and development of precipitation [13].
Turbulent mixing is recognized to tremendously affect the concentration of atmospheric pollutants. Zhang et al. [14] derived the vertical wind shear up to 3 km above ground level (AGL) as observed by one radar wind profiler (RWP) in Beijing and their results showed that weak wind shear in the PBL (weak turbulence and dispersion condition) corresponded to severe atmospheric pollution. This highlights the clear need to characterize the turbulence profile in the PBL to better understand the evolution of atmospheric pollution. In addition, previous intensive efforts have elucidated the close link between aviation safety and encountered turbulence. Around the jet stream, clear air turbulence caused by strong wind shear is one of the main driving forces for aviation accidents of passenger airliners [9,15,16]. Moreover, the continuous turbulence observations in the PBL from an RWP are of great significance for accurately nowcasting the onset of precipitation [17].
Nevertheless, our knowledge concerning atmosphere turbulence remains limited, given its multiple scales, rapid variation, and chaotic nature [18]. The measurements of key parameters used to characterize the turbulence properties from a variety of instruments to some extent help us fill the knowledge gap. Among others, turbulent dissipation rate (ε), an integral parameter to characterize turbulent eddies, is generally used to indicate the rate at which the energy cascades into smaller and smaller eddies until the energy is converted to heat at the Kolmogorov scale [19]. ε is an important parameter that is generally used to determine the transfer rates or mixing level of mass, heat and momentum between the surface layer and its overlying atmosphere. This parameter can be derived from high- or ultra-high-frequency Doppler Lidar [20,21], sonde observations [22,23,24,25], radar wind profilers (RWPs) [3], and tower-based sonic anemometers [26,27]. For instance, Harvey et al. [28] proposed a method to identify specific atmospheric boundary layer types based on the ε measurements from Doppler lidar. The PBL turbulence is generally thought to be greater that [29]. Compared with the profile of ε from Doppler lidar that is reliable under clear sky conditions, RWPs can characterize the fine ε profile even under cloudy conditions. Moreover, the Thorpe analysis method has been widely used to determine ε in the atmosphere using high-vertical-resolution sonde data, which is typically limited to a height above 3 km AGL [25,30,31,32,33]. These turbulence profiling measurements can not only characterize the fine structure of PBL, but also provide an observational benchmark for a variety of research, including air quality, aviation safety, weather, climate, and climate change [2,34].
The North China Plain is one of the main economic zones in China, in which rapid urbanization and high atmospheric pollutant emissions have been seen in recent years. Although Solanki et al. [3] has revealed the fine PBL structure in Beijing by retrieving ε using a one-year record of RWP measurements, the PBL structures on the regional scale remain unclear. As shown in Figure 1, two RWP stations at Baoding (plain area) and Zhangbei (plateau area), part of the RWP network of China [35], provide us another unique opportunity to check the variation of PBL structure over different terrain. Therefore, the objectives of this study were twofold: (1) what is the difference in turbulent dissipation rate profile between plain and plateau areas, and (2) what are the influential factors and relevant underlying mechanisms. The following parts of this paper will proceed as follows: The RWP measurements and analysis methods are described in Section 2. In Section 3, observational analysis will be conducted on the turbulence dissipation rate difference between the Baoding and Zhangbei stations, and the potential influential factors and mechanisms are also discussed. Finally, the main conclusions are given in Section 4.
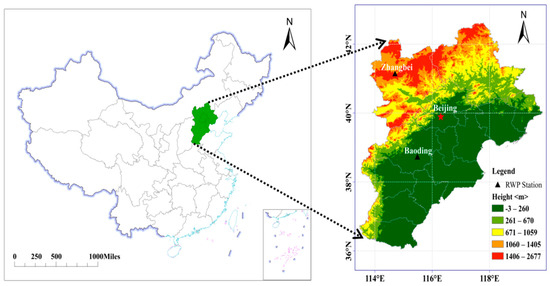
Figure 1.
Topographical map of the North China Plain, where Baoding (plain station) and Zhangbei (plateau station) are marked in black triangles. Both weather stations are deployed with radar wind profilers.
2. Meteorological Observations and Methods
2.1. RWP and Surface Meteorological Measurements
An incoherent RWP is a ground-based remote sensing instrument, which can detect the vertical profile of wind and spectrum width by measuring the turbulence of air masses. The working frequency of an RWP is 1360 MHz, and here the low detection mode was used, which has a temporal resolution of 6 min and a vertical resolution of 120 m. The detection height of the RWPs at Baoding and Zhangbei range from 150 to 3630 m. The RWP at Baoding (38.73°N, 115.48°E) is located in the core area of the North China Plain, whereas the RWP at Zhangbei (41.15°N, 114.7°E) is mainly located over the Mongolian Plateau with a mean elevation of about 2000 m, which are shown in Figure 1. The RWP observational network in China is designed primarily for providing continuous wind profiles in the PBL and the lower troposphere, sampling the atmosphere at 6 min intervals with a vertical resolution of 60 m or 120 m [36]. In this present study, one-year's (2021) worth of RWP power spectrum width measurements have been gleaned to characterize the turbulent structures of the lower troposphere over Baoding and Zhangbei. Given the large noise due to the presence of clouds and precipitating particles [36], all the samples from both RWP stations used in study were obtained in clear-air weather conditions which were sampled at 6 min intervals with a vertical resolution of 60 m, unless noted otherwise.
The original spectrum width data from the RWPs were acquired from the National Meteorological Information Center (NMIC) of the China Meteorological Administration (CMA), which have undergone strict quality control procedures. As such, the spectrum width measurements can be used to distinguish the discrepancy of ε between Baoding and Zhangbei. For example, if more than 20% of the RWP measurements are missing below 2 km AGL, this is deemed as no valid observation and thus the entire profile is discarded. Given the fact that inertia oscillations and super-geostrophic winds tend to frequently occur at night [37], it remains a challenge to tease out the complex causal factors accounting for the profile of ε and its evolution in the lower troposphere. Our study was limited to the daytime ranging from 0900 to 1700 local standard time (LST) at Baoding and Zhangbei. On top of that, given the fact that the radar signals are dramatically weakened by the hydrometers in the presence of precipitation, all the Doppler spectrum width and wind measurements analyzed here were obtained during time periods with no rain, which were screened out based on hourly rain gauge measurements at Baoding and Zhangbei.
In addition, the surface temperature at 0 cm (Ts) and air temperature at 2 m (Ta) at 1 min intervals were measured at both RWP stations, from which 6 min averages were further taken to match the RWP measurements. All the above-mentioned meteorological observations have undergone strict data quality control procedures implemented by the National Meteorological Information Center.
2.2. Retrieval of ε
Here, we used the spectrum broadening method to determine the profile of ε, which requires the input from the tilted beam Doppler spectrum width measurement of the RWPs [38]. The measurement of the Doppler spectral width () of an RWP is expressed as the spatio-temporal variations in the radial velocity within the volume of the radar resolution; it includes both turbulent () and non-turbulent spectra width contributions. The non-turbulent process mainly includes beam broadening (), shear broadening (σ_shear), broadening caused by data processing, instantaneous pollution, and residual noise of spectral width. Through extracting the after removing the influence of these non-turbulent process to implement the corrections on the , we can estimate the profiles of the ε. The turbulent spectral width is calculated as follows:
where the beam broadening factor, shear broadening factor, and broadening caused by data processing can be quantified as follows:
where = , V_h is the horizontal wind speed, and is the one-way half-power beam width of RWP. is the off-zenith angle and Δz is the vertical resolution of the RWP in Equation (3), and the shear broadening component of the spectral width is the result of the vertical gradient of horizontal wind [39]. According to the specification of the RWP, the contribution of radar signal processing can be regarded as equal to 4% of the square of the observed spectrum width (Equation (4)).
The pollution factor due to the transience of atmospheric motion is an outcome of changes in wind flow during the beam dwell time and is determined by the number of incoherent integrations of the spectrum [40]. According to the RWP observations used in this paper, instantaneous pollution and residual noise of spectral width are ignored. Because we only studied complete turbulence in the PBL under clear-sky conditions, other influences such as specular reflection, the widening effect of gravity waves, or the propagation of the falling velocity of raindrops, etc., were omitted. For the estimation of ε, only the positive value of can be considered, and the negative value of may be related to negligible small-scale turbulences [41].
By assuming a homogeneous and isotropic nature for the atmospheric turbulence, ε can be expressed as follows:
where A refers to the empirical Kolmogorov constant in the inertia subregion of the velocity spectrum and 1.6 is used here for subsequent calculations by following the method proposed by Solanki et al. [3]. The term J can be derived based on the following equation:
where Γ is the Gamma function, and the double integral is evaluated between 0 and π/2 in spherical coordinates and is computed iteratively for each height interval of 60 m. The parameter represents the radius of the pulse volume. , where Ω denotes the proportionality constant that equals for an infinite response of the receiver.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Climatology of ε Profile at Plateau and Plain Stations
The diurnal variations of the PBL structure and process can be well described using the ε profiles as retrieved by the RWPs. Figure 2 shows the annual averaged profiles of ε below 3 km AGL under clear-sky conditions using the RWP measurements at Baoding and Zhangbei during the daytime (0900 LST–1700 LST) in the year 2021.
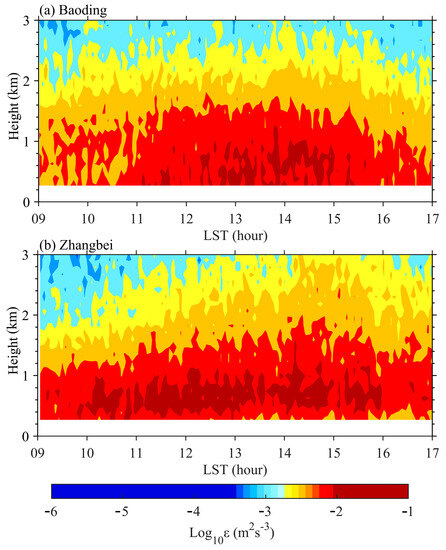
Figure 2.
Temporal variation of the annual mean profile of turbulent dissipation rate (color shading) during daytime from 0900 LST to 1700 LST for the whole year of 2021, as calculated from the RWPs at the plain station of Baoding and the plateau station of Zhangbei.
The ε exhibits significant dependence on height during the daytime over the two stations. A pronounced spatial gradient can be observed, decreasing gradually from the ground surface up to 3 km AGL. Most of the ε values within the 3 km at Baoding varied from to , which are consistent with those reported for the similar lower tropospheric region in other cities [3,39]. By comparison, a much stronger ε was observed at Zhangbei, most of which varied from to on average within 1 km AGL. This phenomenon begins at 1000 LST and lasts until 1600 LST. This suggests that the turbulent activity in the PBL at the plateau station is obviously stronger than that in the plain station. More intense turbulence found in the PBL over the plateau station could be likely due to the mountain wave breaking over complex terrain at Zhangbei [42,43,44,45].
Also, the lower air density in the plateau tends to produce a strong buoyancy effect in the PBL, thereby inducing more severe turbulence. It is widely reported that thermally induced buoyancy is usually the main source of turbulence mixing in the PBL during the daytime [46]. The development of the PBL mainly depends on surface solar heating under clear-sky conditions. After sunrise, especially during 0900 LST–1100 LST, the ground warms up after receiving solar radiation; thermal bubbles rising from the surface tend to make the lower part of PBL turbulent, and the turbulence intensity is constantly enhanced under the effect of buoyancy. After sunset, the ground gradually cools, and the turbulence intensity gradually weakens.
Figure 3 shows that the diurnal variation of the ε profile within 3 km AGL at Baoding in the daytime under clear-sky conditions for the four seasons. Overall, the PBL in boreal summer reached much higher compared with that in boreal winter, given the strong turbulence (greater than ) observed at a height as high as 1 km in summer. Intense turbulence can be seen in the late afternoon (1500 LST–1700 LST) of summer in the altitude range between 1 and 2 km, which cannot be seen in other seasons at the same station of Baoding.
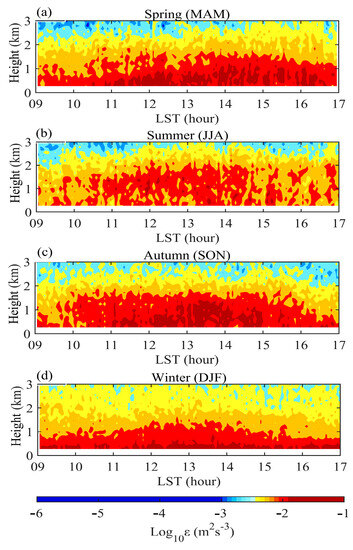
Figure 3.
The same as Figure 2, but for the temporal variation of seasonal mean profile of turbulent dissipation rate at Baoding station: spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d).
Over the plateau station, the strongest variation in magnitude of ε throughout the day and the vertical direction was found in both spring and summer, whereas the weakest ε was observed in winter (Figure 4). Overall, more intense turbulence was observed in summer for the lowest 1 km of the atmosphere at the plateau station of Zhangbei than at the plain station of Baoding. This strong turbulence in summer over plateau station could be likely caused by the stronger solar radiation on the plateau and the greater sensible heat flux on the ground [47]. The diurnal variation trend showed similar changes at both stations in the spring. In winter, the ε with a magnitude greater than was mostly confined to below 0.8 km AGL. Interestingly, the magnitude of ε remained much weaker in the altitude above 0.8 AGL and did not show conspicuous diurnal variations in winter at both the plain and plateau stations. This agrees well with the results reported for the lowest tropospheric region in previous observational studies [3,15].
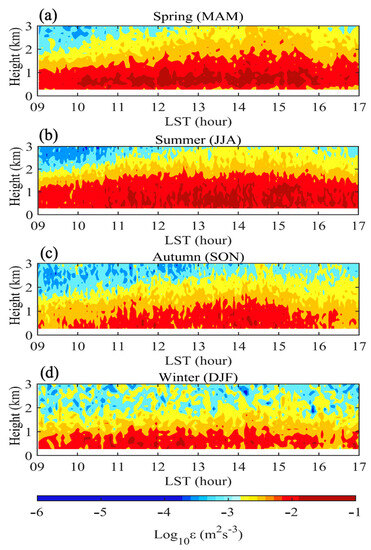
Figure 4.
The same as Figure 2, but for the temporal variation of seasonal mean profile of turbulent dissipation rate at Zhangbei station: spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d).
3.2. Potential Factors Influencing ε
3.2.1. Influence of Sensible Heat Flux on ε
Near-surface turbulent sensible heat flux is one of the main energy sources driving air motion in the PBL [48,49,50]. The prevailing view is that the turbulence intensity in the lowest part of the PBL is largely determined by the buoyancy that is closely linked to sensible heat flux and by the frictional forces on the surface wind that is associated with the damping effect of viscosity [51,52,53,54]. Coincidently, the difference between Ta and Ts has been used to indicate the variation characteristics of near-surface sensible heat flux [55]. Therefore, the difference between 2 m air temperature and surface temperature (Ta−Ts), as a surrogate of near-surface sensible heat flux, is used here to characterize the potential underlying thermodynamic causes for the diurnal change in ε vertical structure at both the plain and plateau stations.
Figure 5 shows the probability distribution and accumulated probability distribution of Ta−Ts at Zhangbei and Baoding. To better reveal the potential impact of Ta−Ts, all these samples in Figure 5 were divided into three same-size bins. At Baoding, the top tercile of Ta−Ts (greater than −0.3 °C) is referred to as (Ta−Ts)high, and the bottom tercile (less than −2.8 °C) is referred to as (Ta−Ts)low. By comparison, (Ta−Ts)low at Zhangbei represents those samples with values less than −5.0 °C, and (Ta−Ts)high represents those samples with values greater than −0.4 °C. Notably, the value of Ta−Ts at Zhangbei station was much higher than that at Baoding station. Meanwhile, the 90th percentile of Ta−Ts at Zhangbei was 3.4 °C higher than that at Baoding station. This provides circumstantial evidence that the plateau station of Zhangbei tends to have larger sensible heat flux, thereby producing stronger turbulence in the PBL, as shown in Figure 2.
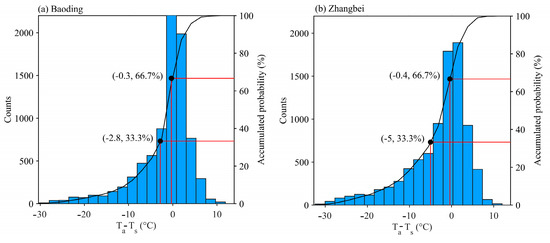
Figure 5.
Probability distribution (blue bar) and accumulated probability distribution (solid line) of the difference between 2 m air temperature and surface temperature (Ta−Ts) at Baoding (a) and Zhangbei (b).
Figure 6 shows the vertical structures of annual mean ε profiles stratified by (Ta−Ts)high and (Ta−Ts)low during the daytime for the year of 2021 at Baoding and Zhangbei. Overall, the higher the Ta−Ts, the greater magnitude of the ε value at both stations, irrespective of the altitude. This suggests that the vertical structure of ε is closely related to Ta−Ts. Also noteworthy is that the PBL (particularly below 1 km) was characterized by much higher ε values at Zhangbei compared with those at Baoding no matter how the value of Ta−Ts is stratified. Above 1 km, ε tended to decrease with the altitude at both stations. The decrease in ε with altitude could be associated with the changes in the dominant source of turbulence above the PBL, along with the diminishing size of turbulent eddies.
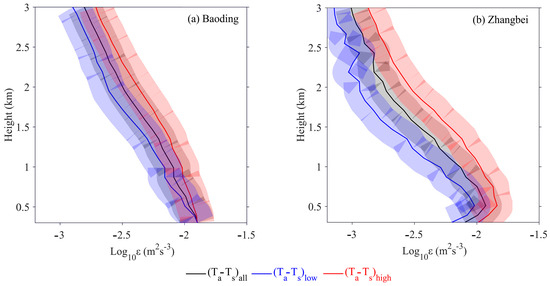
Figure 6.
Vertical distribution of the annual mean turbulent dissipation rate stratified by the difference between 2 m air temperature and surface temperature (Ta−Ts) during the daytime for the year 2021 at Baoding (a) and Zhangbei (b). All the samples are divided into three same-size bins. Note that the turbulent dissipation rate profiles for the top tercile, i.e., (Ta−Ts)high, and bottom tercile, i.e., (Ta−Ts)low, along with all samples, i.e., (Ta−Ts)all are shown. Also marked is one standard deviation.
The average magnitude of ε above 1 km varied between and at Baoding, and the variation range of ε at Zhangbei seemed much larger, lying between and . This is basically consistent with the findings over plateau regions in previous studies. Simultaneously, larger Ta−Ts values can be observed at the plateau station of Zhangbei throughout the whole daytime, compared to those at the plain station of Baoding (Figure 7).
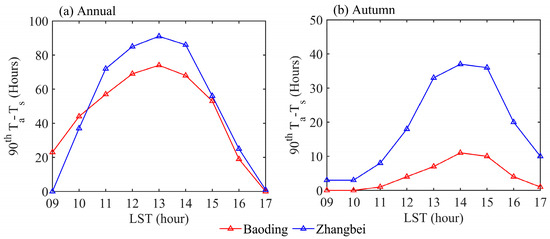
Figure 7.
Temporal variation of the 90th percentile of the difference between 2 m air temperature and surface temperature (Ta−Ts) during daytime from 0900 LST to 1700 LST at Baoding (red solid line) and Zhangbei (blue solid line).
3.2.2. Influence of Vertical Wind Shear on ε
Besides the sensible heat flux, wind shear is another important influential factor that affects the variation in ε. It is generally assumed that the turbulence in the free atmosphere is more susceptible to changes in the wind, whereas the turbulence in the PBL is affected by the mechanical friction between the atmosphere and the ground, and by wind shear [52,53]. Given the finding that the large value of ε is mostly concentrated below 1 km (Figure 2), we examined the impact of wind shear below 1 km and within the height range of 1–3 km on ε.
Figure 8 illustrates that ε was positively correlated with vertical wind shear at the Baoding and Zhangbei stations throughout the whole altitude range of 0–3 km. Interestingly, the vertical wind shear occurring below 1 km was much greater than that in the altitude range of 1–3 km. The value of vertical wind shear at the plateau station was stronger than that at the plain station, indicating that the vertical structure of turbulence over the plateau region is more susceptible to large wind shear.
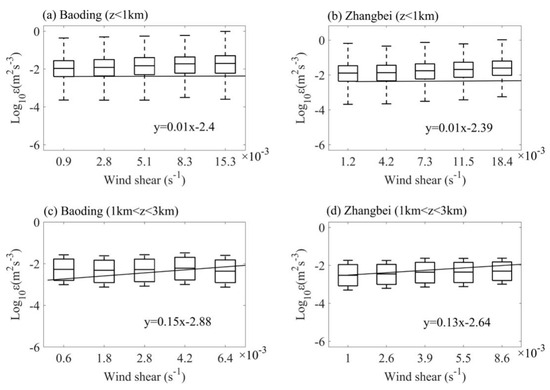
Figure 8.
Turbulent dissipation rate (ε) at the height range lower than 1 km (a,b) and the height range between 1 km and 3 km (c,d) as a function of vertical wind shear at Baoding (a,c) and Zhangbei (b,d). All samples are evenly divided into five same-size bins, and the regression linear equation is shown in each panel as well.
A closer look at Figure 8 reveals that the slope of the linear regression equation for ε versus wind shear in the altitude range between 1 and 3 km was steeper than that for the height below 1 km, despite its relatively low value. This indicates that the vertical wind shear in the height range of 1–3 km tends to be more correlated with intense turbulence than in the height below 1 km. The large magnitude of ε in the lower troposphere may be related to the breaking of Kelvin–Helmholtz waves in the elevated shear layer [56,57]. A large portion of clear-air turbulence events can be explained by the Kelvin–Helmholtz instability, which frequently occurs above or below a strong jet stream accompanied by an upper-level front [58]. Strong vertical wind shear around the jet stream increases the denominator of the formula used to calculate the Richardson number (Ri), which in turn decreases Ri until it reaches a critical value (below 0.25), resulting in the generation of turbulence [59,60]. This means that the shear-driven turbulence is an important mechanism for the turbulence generation between the PBL top and the free atmosphere at both the plain and plateau stations of the North China Plain.
3.2.3. Joint Influence of Vertical Wind Shear and Sensible Heat Flux on ε
The values of ε throughout the PBL during the daytime of autumn at Zhangbei exhibited much larger magnitudes than those at Baoding (Figure 3c and Figure 4c). This is in sharp contrast to the annual averaged ε (Figure 2). To illustrate the underlying causes, we further calculated the 2D joint probability distributions of wind shear and Ta−Ts versus ε at both stations.
Overall, the joint impact of wind shear and sensible heat flux on ε in the PBL at Baoding and Zhangbei seemed very complicated, irrespective of annual and seasonal averages (Figure 9). In autumn, strong turbulence at Baoding generally occurred under conditions of high vertical wind shear (Figure 9a). Interestingly, Figure 9c shows that the strong turbulence at Baoding tended to occur under conditions of low values of Ta−Ts (large sensible heat flux). This suggests that vertical wind shear, rather than sensible heat flux, accounts for much of the intense turbulence observed in the PBL at Baoding. By comparison, a much weaker turbulence was observed at Zhangbei in autumn, and intense turbulence tended to occur when the vertical wind shear was much lower. In terms of the annual mean ε at Zhangbei, intense turbulence often occurred when the vertical wind shear was weak whereas the sensible heat flux was small (Figure 9d).
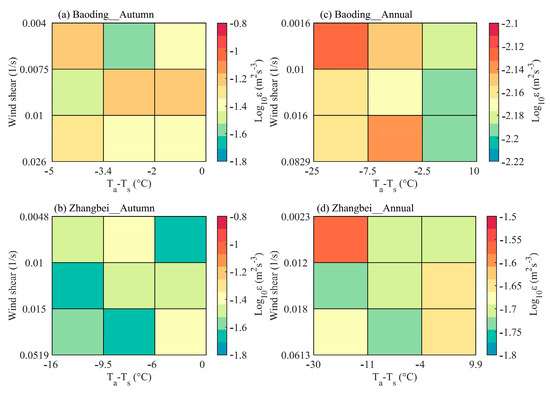
Figure 9.
Joint dependence of (a,b) autumn mean turbulent dissipation rate (ε) and (c,d) annual mean ε in the PBL at (a,b) Baoding and (c,d) Zhangbei on vertical wind shear and the difference between 2 m air temperature and surface temperature (Ta−Ts).
4. Concluding Remarks
One-year (2021) of Doppler spectral width measurements from two radar wind profilers (RWPs) have been utilized to make a comparison analysis concerning the spatio-temporal variation of turbulence dissipation rate (ε) profiles in the lower troposphere at plateau (Zhangbei) and plain (Baoding) stations over the North China Plain. The results show that the value of ε over both stations had a more obvious diurnal process under the influence of sensible heat in the daytime, and turbulence was stronger over the plateau than over the plain, especially the strong turbulence observed in the PBL. This may be due to the more intense radiation received by the plateau surface, or the influence of deeper mixed layers that are affected by the complex underlying surface. It was found that ε at the plain and plateau stations showed significant seasonal variations. Overall, the magnitude of ε was strongest in summer and weakest in winter in both areas. The increase in ε in autumn may be due to the increase in the number of LLJ, which leads to an increase in vertical wind shear, or the influence of a coupled Kelvin–Helmholtz vortex below the bottom of LLJ in the residual layer [43].
Moreover, the potential influences of sensible heat flux (represented by the difference between 2 m air temperature and surface temperature, namely Ta−Ts) and vertical wind shear on the magnitude of ε were investigated. A larger Ta−Ts was generally accompanied by more intense turbulence, and the vertical structure of ε over the plateau station was affected more obviously by the sensible heat flux. In particular, the ε profiles in the PBL in the plateau station were more complicated, owing to the joint influence of terrain, circulation, temperature, humidity, etc. Meanwhile, the vertical wind shear was positively correlated with ε within the height range of 1–3 km AGL.
However, ε is often found to be extremely intermittent and to change dramatically in short time intervals [61]. Therefore, in the future, the continuous measurements of turbulence characteristics are warranted over different surfaces within the lowermost 3 km based on the RWP network measurements across China, which will pave the way for the development of improved parameterization schemes in the future. This will, in turn, help improve our understanding of the contrasting turbulent structures in the PBL over the plains and plateaus.
Author Contributions
Methodology, R.Y., L.L., D.M. and J.G.; Conceptualization, L.L. and J.G.; software, R.Y.; Validation, J.G., W.D. and L.L.; Formal analysis, R.Y.; Investigation, R.Y., D.M., N.L., J.G., Z.L., Y.S., G.Z., W.D. and L.L.; Resources, J.G.; Data curation, R.Y. and L.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, R.Y., L.L., N.L. and J.G.; Writing—review and editing, R.Y., D.M., L.L., W.D., Y.S., Z.L., G.Z., N.L., J.F. and J.G.; Visualization, R.Y.; Supervision, J.G. and L.L.; Funding acquisition, J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant U2142209, the Youth Cross Team Scientific Research Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences under grant JCTD-2021-10, and the Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences under grant 2021KJ008.
Data Availability Statement
The turbulence dissipation rate and velocity spectrum data that are estimated from radar wind profilers at Baoding and Zhangbei in 2021 are publicly available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7922799 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Hebei Meteorological Services for providing surface meteorological measurements and the observations of the radar wind profilers at Baoding and Zhangbei.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cimini, D.; Haeffelin, M.; Kotthaus, S.; Löhnert, U.; Martinet, P.; O’connor, E.; Walden, C.; Coen, M.C.; Preissler, J. Towards the profiling of the atmospheric boundary layer at European scale—Introducing the COST Action PROBE. Bull. Atmos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.; Piepmeier, J.R.; Nehrir, A.R.; Ao, C.O.; Chen, S.S.; Clayson, C.A.; Fridlind, A.M.; Lebsock, M.; McCarty, W.; Salmun, H.; et al. Toward a Global Planetary Boundary Layer Observing System: The NASA PBL Incubation Study Team Report; NASA PBL Incubation Study Team: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; 134p.
- Solanki, R.; Guo, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Tong, B.; Li, J. Elucidating the atmospheric boundary layer turbulence by combining UHF radar wind profiler and radiosonde measurements over urban area of Beijing. Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Lv, Y. Assessing the Surface-Layer Stability over China Using Long-Term Wind-Tower Network Observations. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2021, 180, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, J.W. Numerical Investigation of Neutral and Unstable Planetary Boundary Layers. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeng, C.-H.; Sullivan, P.P. A Comparison of Shear- and Buoyancy-Driven Planetary Boundary Layer Flows. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 999–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.S.; Ghosh, A.K.; Satheesan, K.; Jain, A.R.; Uma, K.N. Characteristics of atmospheric turbulence in terms of background atmospheric parameters inferred using MST radar at Gadanki (13.5°N, 79.2°E). Radio Sci. 2010, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, R.D.; Trier, S.B.; Lane, T.P.; Doyle, J.D. Sources and dynamics of turbulence in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere: A review. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.M.; Hobbs, P.V. Atmospheric Science an Introductory Survey, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Deigo, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Luo, K.; Wang, Y.; Yan, P.; Hu, F.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Y.; Shang, D.; et al. The impact of the atmospheric turbulence-development tendency on new particle formation: A common finding on three continents. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 8, nwaa157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenschatz, E.; Malinowski, S.P.; Shaw, R.A.; Stratmann, F. Can we understand clouds without turbulence? Science 2010, 327, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuijens, L.; Siebesma, A.P. Boundary Layer Clouds and Convection over Subtropical Oceans in our Current and in a Warmer Climate. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2019, 5, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yim, S.H. Vertical Wind Shear Modulates Particulate Matter Pollutions: A Perspective from Radar Wind Profiler Observations in Beijing, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Chun, H.-Y. Statistics and Possible Sources of Aviation Turbulence over South Korea. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gultepe, I.; Sharman, R.; Williams, P.D.; Zhou, B.; Ellrod, G.; Minnis, P.; Trier, S.; Griffin, S.; Yum, S.S.; Gharabaghi, B.; et al. A Review of High Impact Weather for Aviation Meteorology. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 1869–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, D.; Yun, Y. Vertical divergence profiles as detected by two wind-profiler mesonets over East China: Implications for nowcasting convective storms. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2023, 149, 1629–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, J.R. The atmospheric boundary layer. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 89–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, S.A. Radar Measurements of Turbulent Eddy Dissipation Rate in the Troposphere: A Comparison of Techniques. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1995, 12, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Luce, H.; Hashiguchi, H.; Nishi, N.; Yabuki, Y. Energetics of persistent turbulent layers underneath mid-level clouds estimated from concurrent radar and radiosonde data. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2014, 118, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.A.; Thomas, L. Complementary criteria for identifying regions of intense atmospheric turbulenc e using lower VHF radar. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 1998, 60, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frehlich, R.; Meillier, Y.; Jensen, M.L.; Balsley, B. Turbulence measurements with the CIRES tethered liftin g system during CASES-99: Calibration and spectral analysis of temperature and velocity. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayson, C.A.; Kantha, L. On Turbulence and Mixing in the Free Atmosphere Inferred from High-Resolution Soundings. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2008, 25, 833–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsley, B.B.; Svensson, G.; Tjernström, M. On the Scale-dependence of the Gradient Richardson Number in the Residual Layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2008, 127, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. Turbulence and mixing in a Scottish Loch. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1977, 286, 125–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimal, J. Sonic anemometer measurement of atmospheric turbulence. In Proceedings of the Dynamic Flow Conference 1978 on Dynamic Measurements in Unsteady Flows; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 551–565. [Google Scholar]
- Barthlott, C.; Fiedler, F. Turbulence Structure in the Wake Region of a Meteorological Tower. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2003, 108, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.J.; Hogan, R.J.; Dacre, H.F. A method to diagnose boundary-layer type using Doppler lidar. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 139, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borque, P.; Luke, E.; Kollias, P. On the unified estimation of turbulence eddy dissipation rate using Doppler cloud radars and lidars: Radar and lidar turbulence estimation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5972–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheesan, K.; Krishna Murthy, B.V. Turbulence parameters in the tropical troposphere and lower stratosphere. J. Gephys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, ACL-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Chun, H.; Wilson, R.; Geller, M.A. Characteristics of Atmospheric Turbulence Retrieved From High Vertical-Resolution Radiosonde Data in the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7553–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.D.; Huang, C.M.; Huang, K.M.; Gong, Y.; Gan, Q.; Zhang, Y.H. Statistical Study of Atmospheric Turbulence by Thorpe Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric turbulence over China estimated using operational high-resolution soundings. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMone, M.A.; Angevine, W.M.; Bretherton, C.S.; Chen, F.; Dudhia, J.; Fedorovich, E.; Katsaros, K.B.; Lenschow, D.H.; Mahrt, L.; Patton, E.G.; et al. 100 Years of Progress in Boundary Layer Meteorology. Meteorol. Monogr. 2019, 59, 9.1–9.85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, J.; Gong, W.; Shi, Y.; Jin, S. Boundary Layer Height as Estimated from Radar Wind Profilers in Four Cities in China: Relative Contributions from Aerosols and Surface Features. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, J.; Gong, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y. Characteristics and performance of wind profiles as observed by the radar wind profiler network of China. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4589–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Xian, T.; Li, N.; Meng, D.; Li, H.; Cheng, W. Investigation of low-level supergeostrophic wind and Ekman spiral as observed by a radar wind profiler in Beijing. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1195750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby-Koaly, S.; Campistron, B.; Bernard, S.; Bénech, B.; Girard-Ardhuin, F.; Dessens, J.; Dupont, E.; Carissimo, B. Turbulent dissipation rate in the boundary layer via UHF wind profiler Doppler spectral width measurements. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2002, 103, 361–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukao, S.; Hamazu, K. Radar Observations of the Clear Atmosphere, Radar for Meteorological and Atmospheric Observations; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Kumar, K.K.; Sivakumar, V.; Ghosh, A.; Jain, A.; Reddy, K.K. Diurnal and seasonal variability of TKE dissipation rate in the ABL over a tropical station using UHF wind profiler. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, W.K. Two years of continuous measurements of turbulence parameters in the upper mesosphere and lower thermosphere made with a 2-MHz radar. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Bian, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Suolongduoji; et al. A comprehensive physical pattern of land-air dynamic and thermal structure on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowski, P.; Richardson, Y. Mesoscale Meteorology in Midlatitudes; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; 407p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenger, H.; Wilson, R.; Davison, J.L.; Duvel, J.P.; Xu, W.; Lott, F.; Katsumata, M. Tropospheric Turbulence over the Tropical Open Ocean: Role of Gravity Waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 1249–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Giorgetta, M.A.; Guo, J. The daytime trapped lee wave pattern and evolution induced by two small-scale mountains of different heights. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 148, 1300–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. Boundary Layer Climates, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1992; 464p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Sun, J.; Lenschow, D.H.; et al. Analysis of land surface parameters and turbulence characteristics over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9540–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.S.; Masahide, K. Studies of the interannual variability of springtime Eurasian surface air temperature. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.-T.; Huang, R.-H. Interdecadal variability of summer rainfall in Northwest China and its possible causes. Int. J. Clim. 2010, 30, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yun, Y.; Solanki, R.; Hu, N.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Su, J.; et al. The near-surface turbulent kinetic energy characteristics under the different convection regimes at four towers with contrasting underlying surfaces. Atmos. Res. 2022, 270, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanady, G.T. The Free Surface Turbulent Shear layer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1984, 14, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Brewer, W.A. Turbulent Velocity-Variance Profiles in the Stable Boundary Layer Generated by a Nocturnal Low-Level Jet. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2700–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuononen, M.; O’Connor, E.J.; Sinclair, V.A.; Vakkari, V. Low-level jets over Utö, Finland, based on Doppler lidar observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 2577–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, T.; Salazar, D.M.; Miozzi, M. Skin friction and surface optical flow in viscous flows. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 067101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, Q. The spatiotemporal characteristics and long-term trends of surface-air temperatures difference in China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2019, 15, 374–384. [Google Scholar]
- Grasmick, C.; Geerts, B. Detailed Dual-Doppler Structure of Kelvin–Helmholtz Waves from an Airborne Profiling Radar over Complex Terrain. Part I: Dynamic Structure. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 1761–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Impact of elevated Kelvin–Helmholtz billows on the atmospheric boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 78, 3983–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellrod, G.P.; Knapp, D.I. An Objective Clear-Air Turbulence Forecasting Technique: Verification and Operational Use. Weather. Forecast. 1992, 7, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, J.A.; Panofsky, H.A. Clear Air Turbulence: A Mystery May Be Unfolding. Science 1970, 167, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Shao, J. Inertia-gravity wave energy and instability drive turbulence: Evidence from a near-global high-resolution radiosonde dataset. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 2927–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, W.K. Measurement of turbulent energy dissipation rates in the middle atmosphere by radar techniques: A review. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1403–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).