A Calibration Method for Large-Footprint Full-Waveform Airborne Laser Altimeter without a Calibration Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
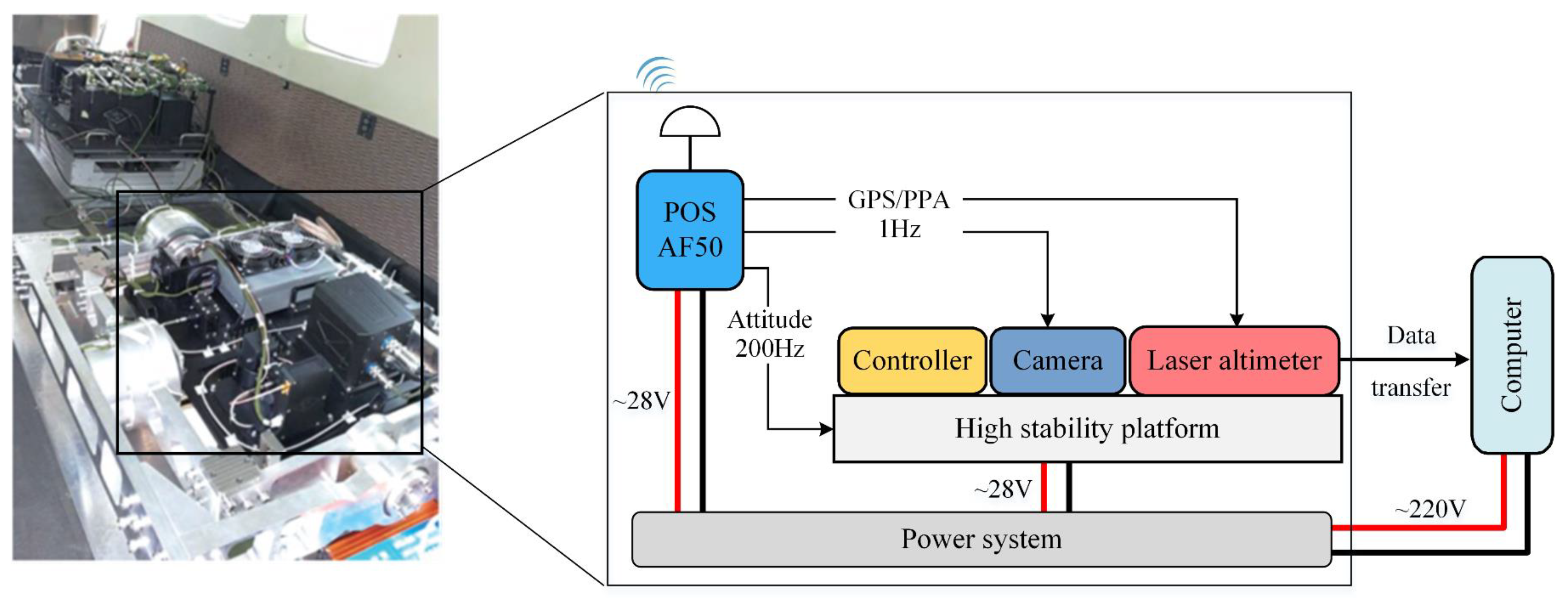
2. The Airborne Large-Footprint Laser Altimeter System
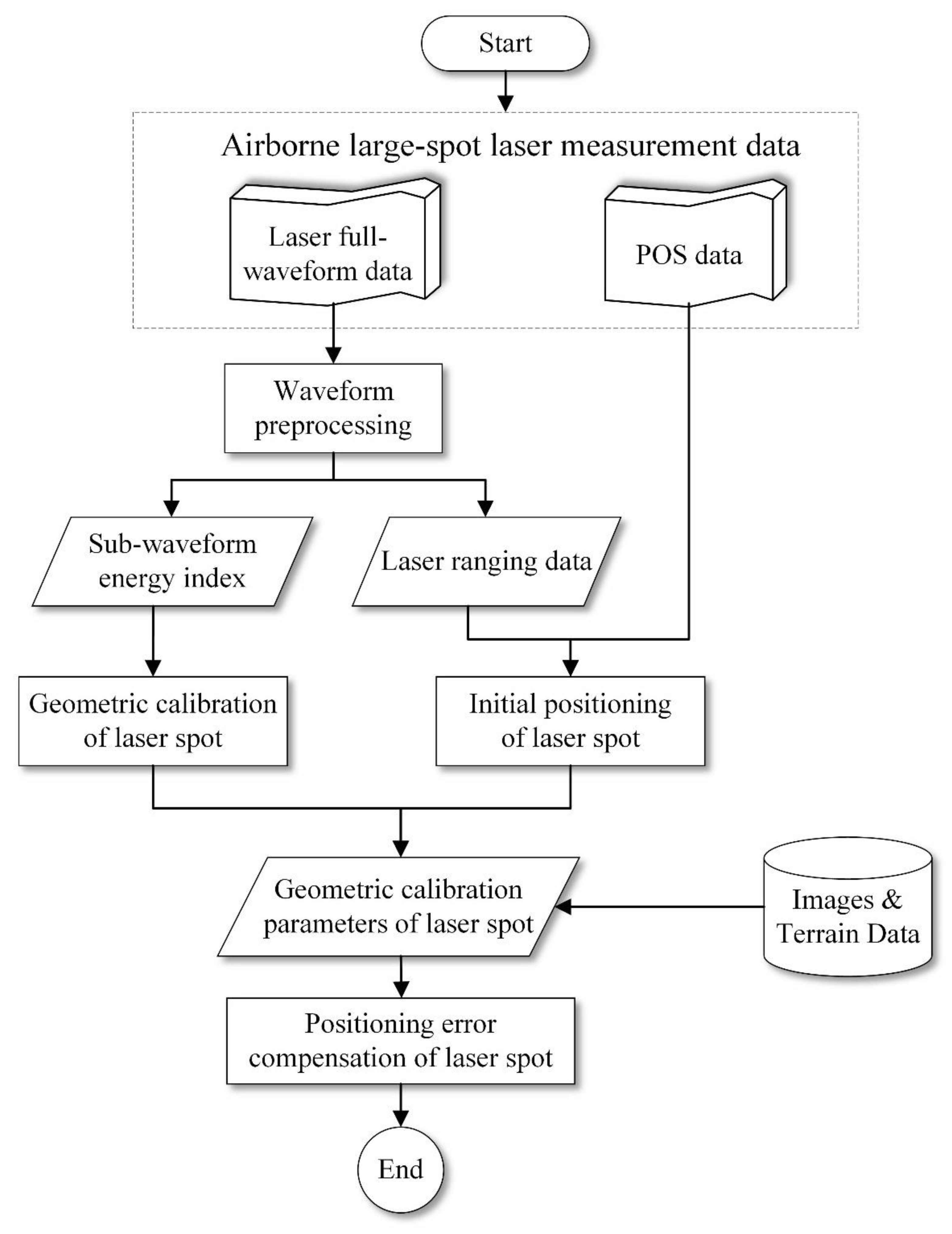
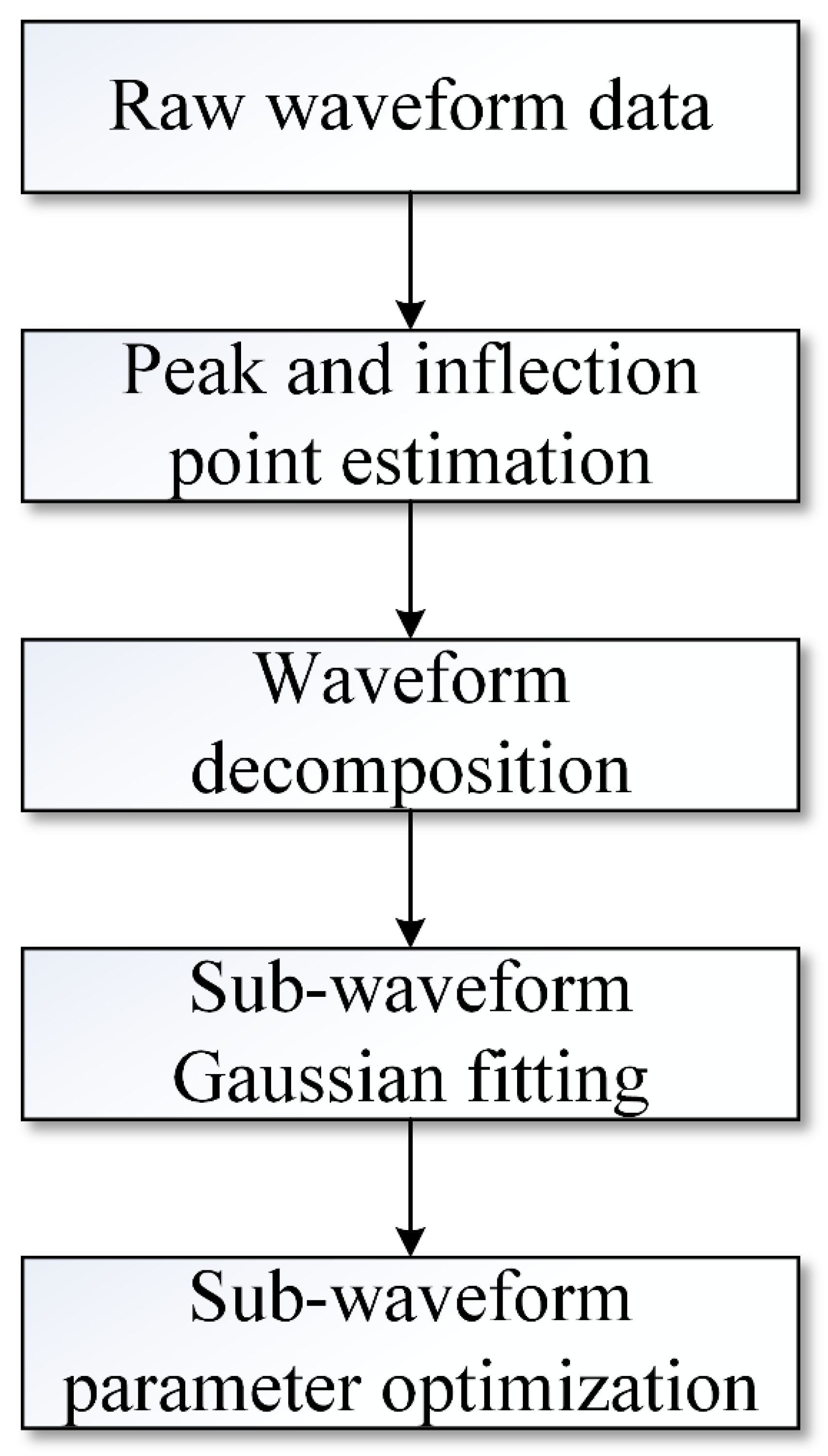
3. Methods
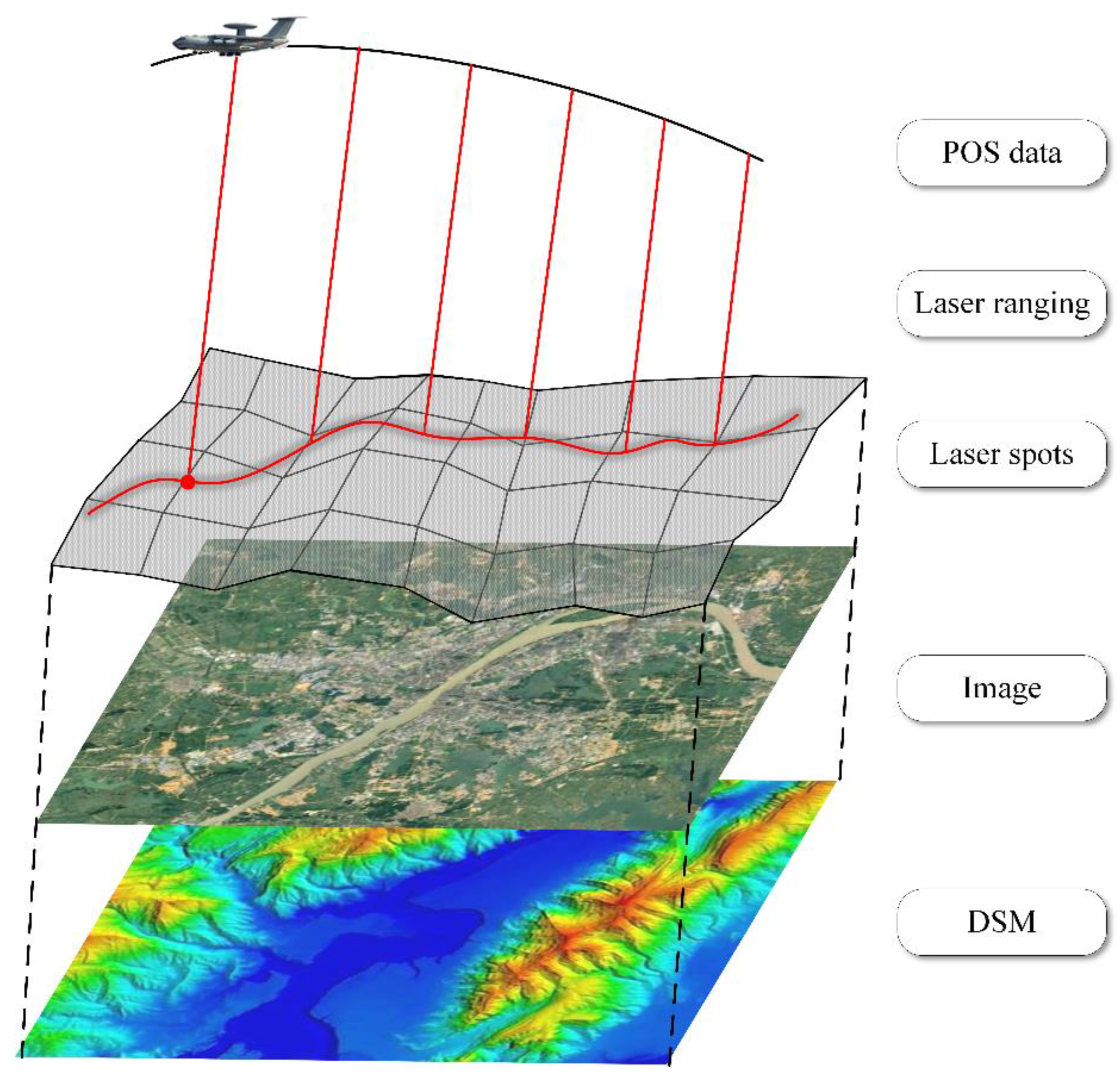
3.1. Geometric Positioning of the Laser Spot
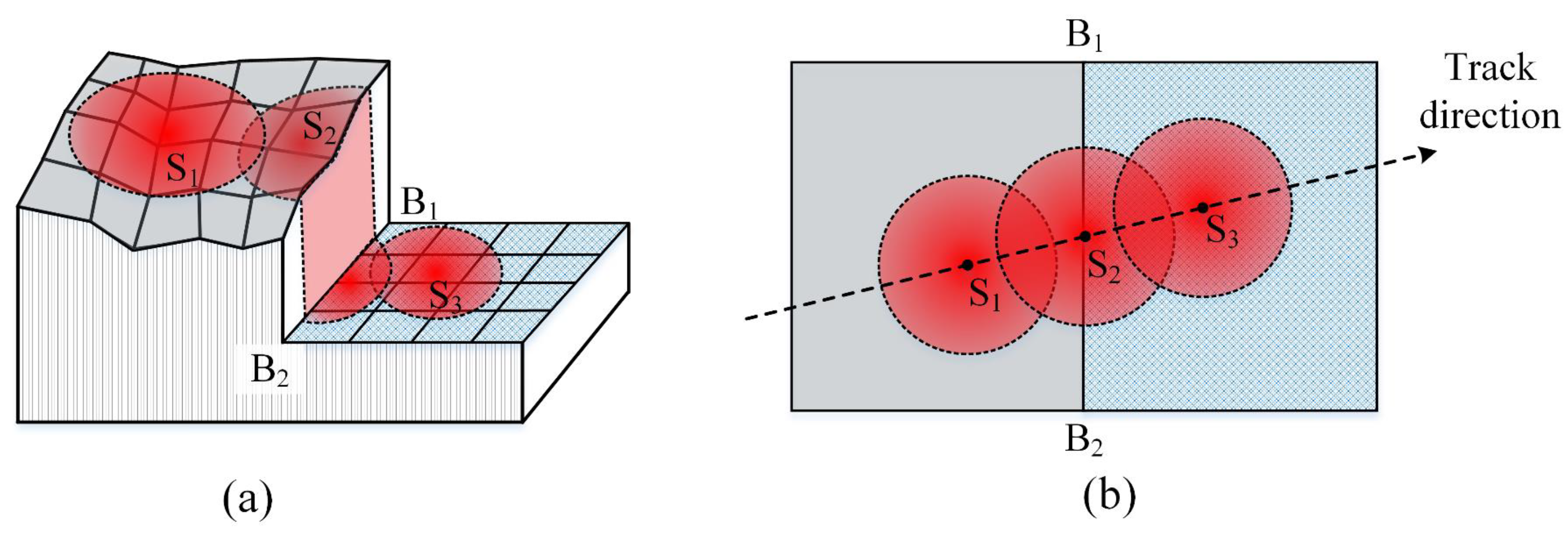
3.2. Calibration of the Laser Spot
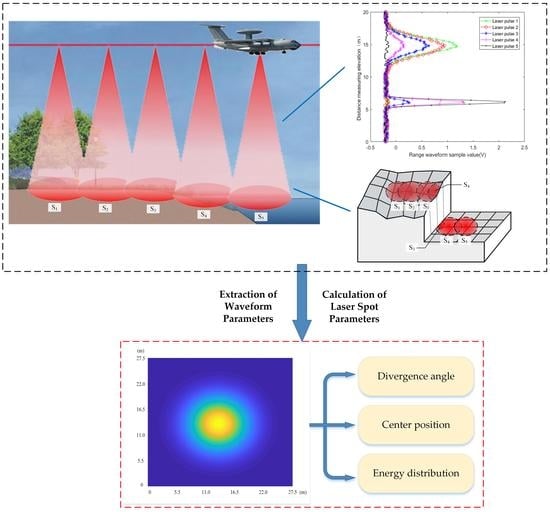
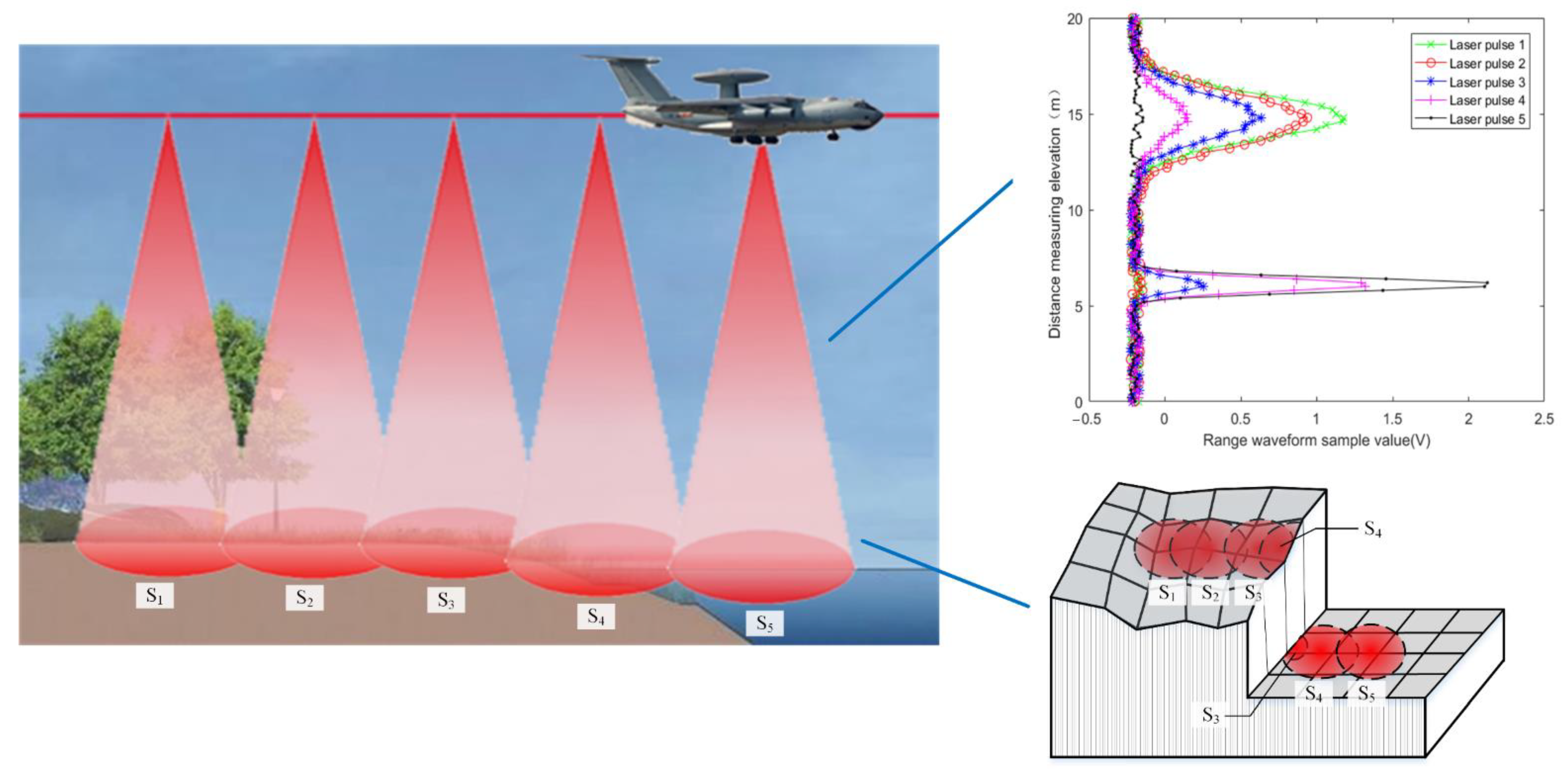
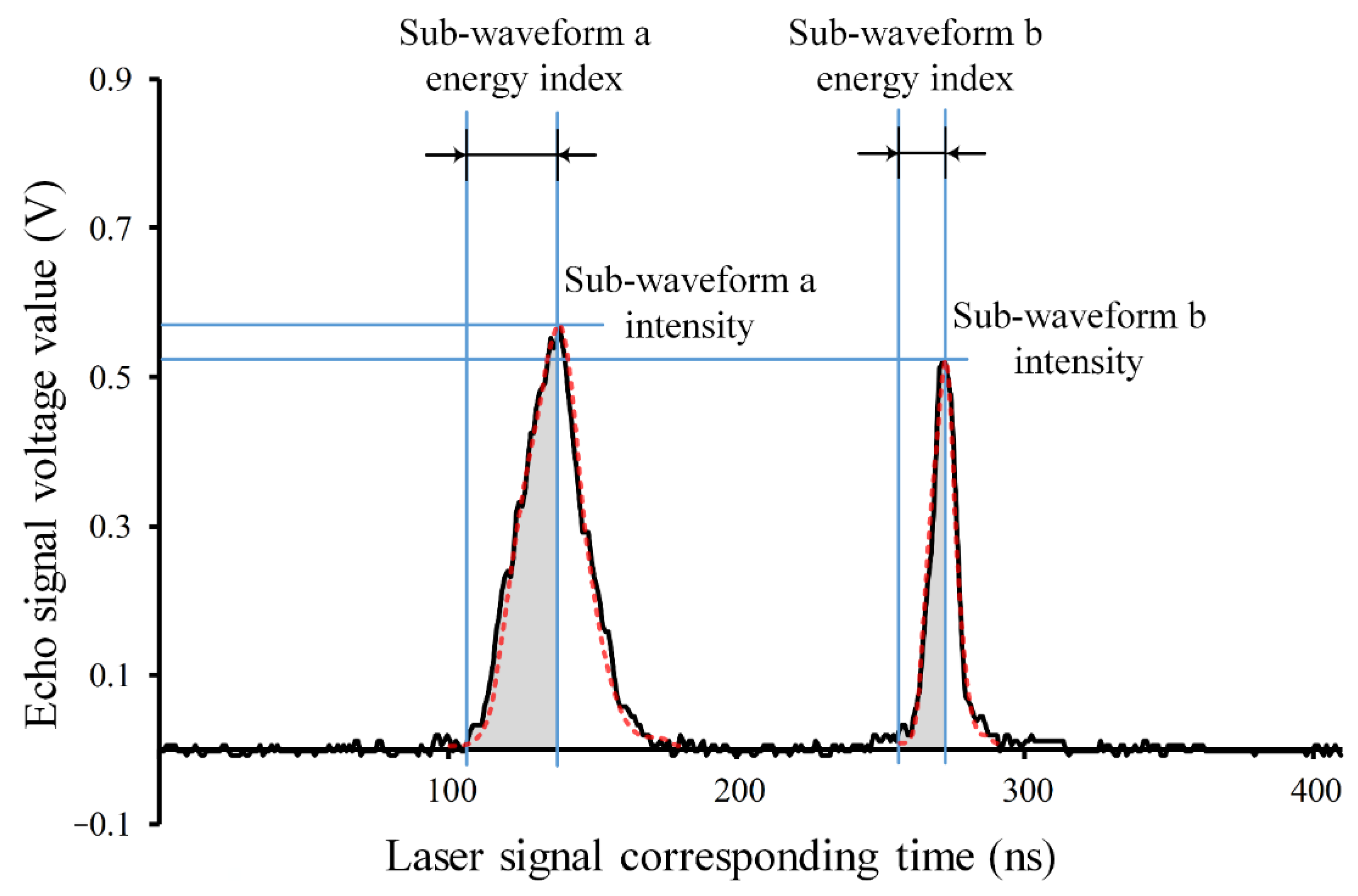
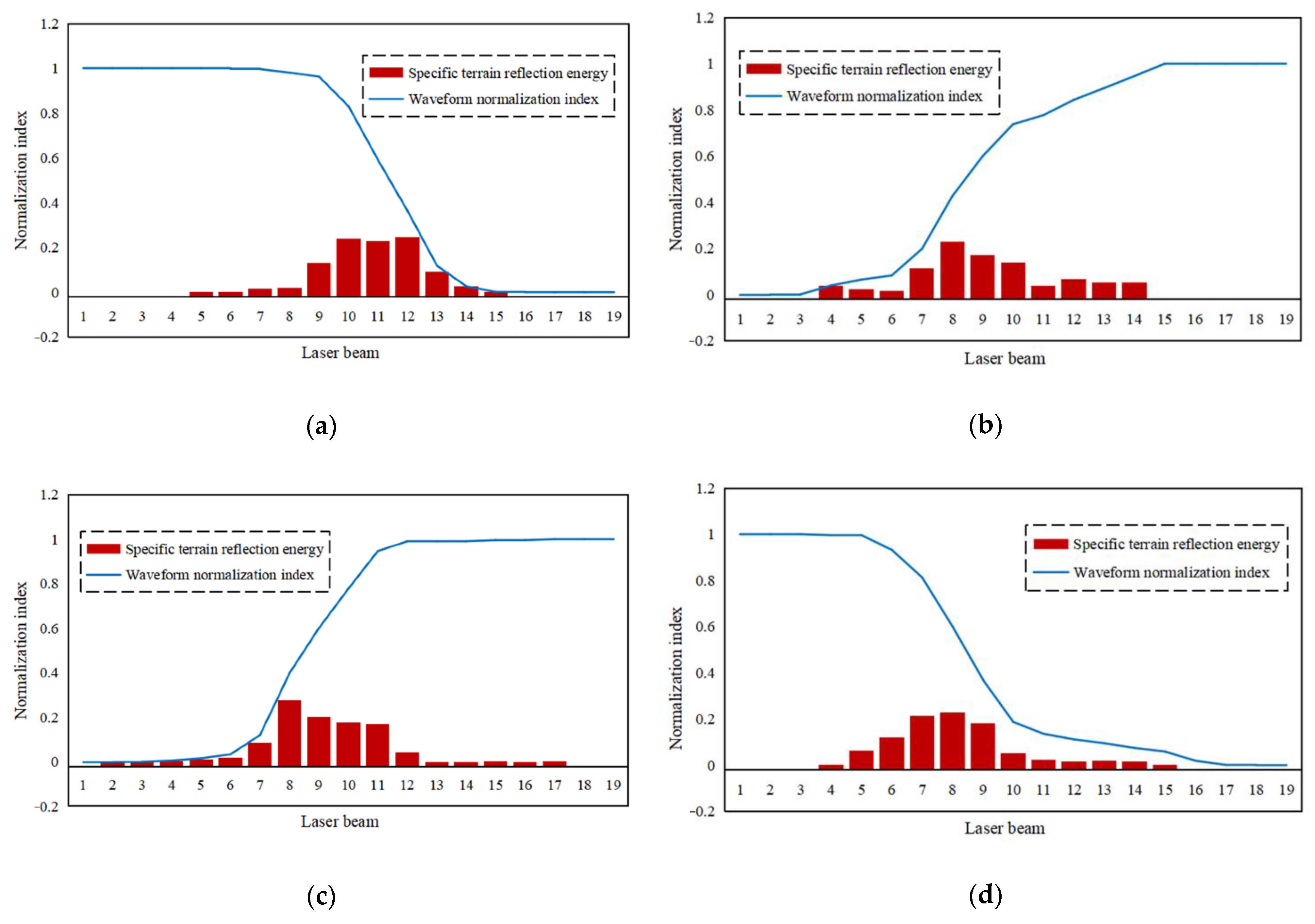
3.3. Extraction of Waveform Parameters
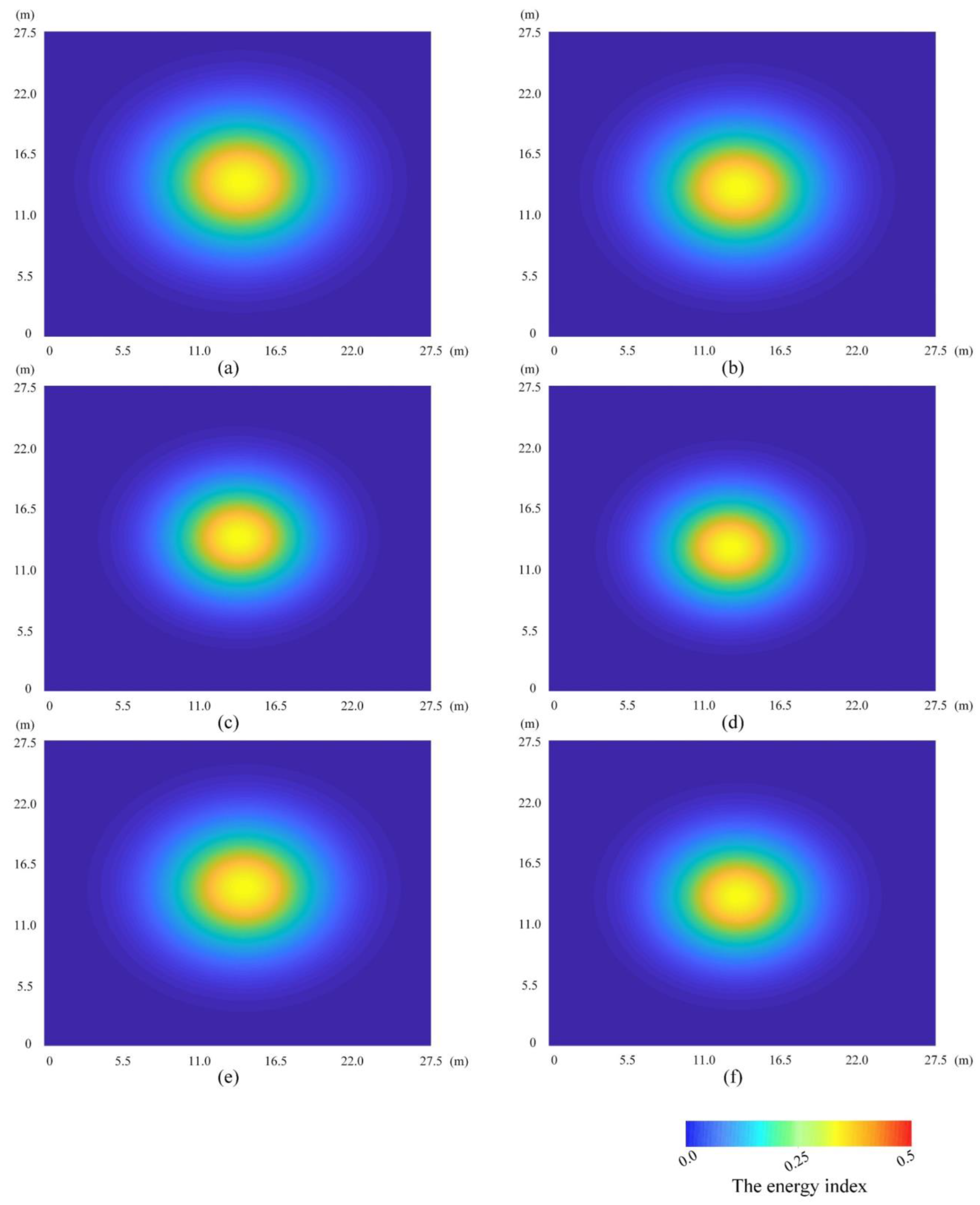
3.4. Calculation of Laser Spot Parameters
4. Results
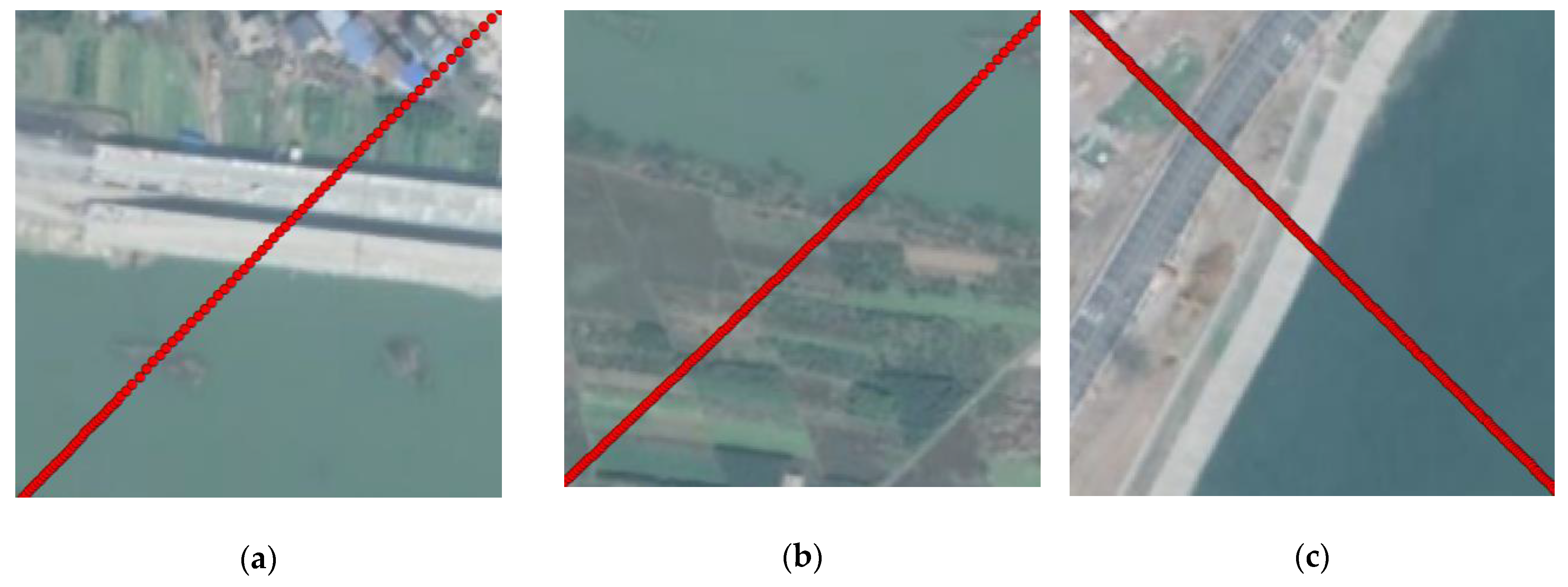
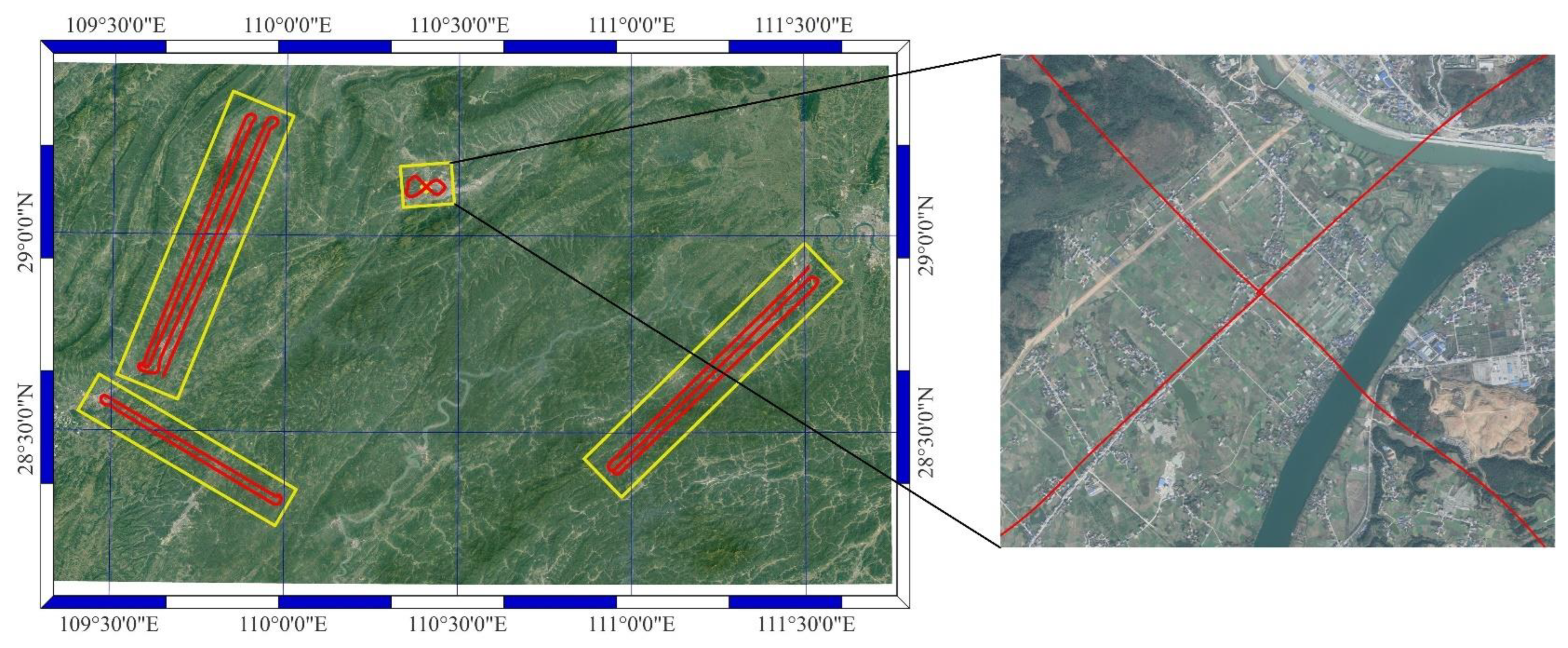
4.1. Data
4.2. Experiments and Results
4.3. Accuracy Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The geometric parameter calibration of the large-footprint laser altimeter can be achieved in the area of the step surface, complementing the laser calibration field. It greatly improves the efficiency of the on-orbit calibration for the laser altimeter and provides a reference for the inversion of vegetation height with the laser measurement data;
- The feasibility of the method in this paper was verified by experiments of airborne large-footprint laser altimetry. The divergence angle of the laser beam obtained from the six experimental areas was slightly smaller than the design parameter, and the consistency of the energy distribution from each laser spot reached 92.67%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Fan, C.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, S. Using ICESAT altimeter data to determine the Antarctic ice sheet elevation model. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2008, 33, 226–228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.; Mountrakis, G. An accurate and computationally efficient algorithm for ground peak identification in large footprint waveform LiDAR data. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 95, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Wang, C.; Xi, X.; Li, G.; Luo, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhu, X. Exploring the influence of various factors on slope estimation using large-footprint LiDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6611–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, L.; Niemann, K.; Wulder, M. Estimating forest canopy height and terrain relief from GLAS waveform metrics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Gong, P.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Li, W. Forest canopy height extraction in rugged areas with ICESAT/GLAS data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 4650–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, I.; Baghdadi, N.; Bailly, J.-S.; Barbier, N.; Gond, V.; El Hajj, M.; Fabre, F.; Bourgine, B. Canopy height estimation in French Guiana with LiDAR ICESat/GLAS data using principal component analysis and random forest regressions. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11883–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Pang, Y. Review on forest parameters inversion using LiDAR. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, W.; Sun, G.; Chi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Z. Slope-adaptive waveform metrics of large footprint lidar for estimation of forest aboveground biomass. Remote Sens.Environ. 2019, 224, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, B.E.; Zwally, H.J.; Shuman, C.A.; Hancock, D.; DiMarzio, J.P. Overview of the ICESat mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L21S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Zwally, H.J.; Sun, X. ICESat measurement of Greenland ice sheet surface slope and roughness. Ann. Glaciol. 2005, 42, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A.C.; DiMarzio, J.P.; Zwally, H.J. Precision and accuracy of satellite radar and laser altimeter data over the continental ice sheets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansma, P.; Mattioli, G.; Matias, A. Slicer laser altimetry in the eastern Caribbean. Surv. Geophys. 2001, 22, 561–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Kennedy, R.E.; Choi, S.; Wu, J.; Lefsky, M.A.; Bi, J.; Mantooth, J.A.; Myneni, R.B.; Knyazikhin, Y. Application of physically-based slope correction for maximum forest canopy height estimation using waveform lidar across different footprint sizes and locations: Tests on LVIS and GLAS. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6566–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, K.; Xu, L. Within-footprint roughness measurements using ICESat/GLAS waveform and LVIS elevation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2016, 27, 125012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncanson, L.; Neuenschwander, A.; Hancock, S.; Thomas, N.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Simard, M.; Silva, C.A.; Armston, J.; Luthcke, S.B.; Hofton, M. Biomass estimation from simulated GEDI, ICESat-2 and NISAR across environmental gradients in Sonoma County, California. Remote Sens.Environ. 2020, 242, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.; Duncanson, L.; Hancock, S.; Neuenschwander, A.; Thomas, N.; Hofton, M.; Fatoyinbo, L.; Simard, M.; Marshak, C.Z.; Armston, J. Fusing simulated GEDI, ICESat-2 and NISAR data for regional aboveground biomass mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Guo, J.; Tang, X.; Ye, F.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xue, Y. Preliminary quality analysis of GF-7 satellite laser altimeter full waveform data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 43, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, J.; Liu, R.; Huang, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhen, Y.; Tang, H.; Dou, X. Overview of the GF-7 laser altimeter system mission. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2019EA000777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, G.; Liu, R.; Zhao, C.; Dai, J.; Jin, T.; Mo, F.; Zhen, Y.; Xi, S.; Tang, H. Design and data processing of China’s first spaceborne laser altimeter system for earth observation: GaoFen-7. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Fan, X. Rigorous Sensor Model of Gaofen-7 Satellite Laser Altimeter Based on Coupled Footprint Camera. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, X.; MAO, Y.; MO, F. Overall Design of Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Inventory Satellite. Spa. Rec. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Design of Laser Transmitter for Terrestrial Ecosystem Carbon Inventory Satellite’s Multi-beam LiDAR. Spacecr. Rec. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Gao, X.; Pan, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Design and application of forest detecting based on airborne large-footprint LiDAR system. For. Res. Manag. 2018, 4, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, F.; Sun, Z.; Lister, A.; Gao, X.; Li, W.; Peng, D. The laser vegetation detecting sensor: A full waveform, large-footprint, airborne laser altimeter for monitoring forest resources. Sensors 2019, 19, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X. Waveform Processing and Accuracy Verification of Airborne Large-Footprint LiDAR System. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, F.; Gao, X.; Gao, J.; Hu, Y. Estimation of Forest Canopy Height Based on Large-Footprint Airborne LiDAR Data. For. Res. Manag. 2020, 3, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, J.; Fu, X.; Mo, F.; Li, S.; Dou, X. ZY3-02 laser altimeter on-orbit geometrical calibration and test. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 714–723. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Xie, J.; Mo, F.; Dou, X.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Huang, G.; Fu, X.; Liu, R. GF-7 dual-beam laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration and test verification. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2021, 50, 384–395. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Cui, C.; Gao, J.; Yu, J.; Cai, L.; Wu, F. Calibration and Validation of National Forest and Grassland Inventory Airborne Large-Footprint LiDAR. For. Res. Manag. 2021, 2, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xie, J.; Mo, F.; Zhu, G.; Dou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Ouyang, S. Footprint location prediction method of ZY3-02 altimeter. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 866–873. [Google Scholar]
- ZHANG, G.; LI, S.; HUANG, W.; LI, D. Geometric calibration and validation of ZY3-02 satellite laser altimeter system. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2017, 42, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar]
- YUE, C.; SUN, S.; HE, H. A Positioning Method in Footprint of Space-Borne Laser Altimeter. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 44, 586–592. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y. Geometric calibration of satellite laser altimeters based on waveform matching. Photogramm. Rec. 2021, 36, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Equipment | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Laser altimeter | Laser wavelength | 1064 nm |
| Pulse energy | 2 mJ | |
| Divergence angle | 5 mrad | |
| FWHM | 2.0~3.0 ns | |
| Pulse repetition rate | 40 Hz | |
| Telescope | Diameter | 100 mm |
| FOV | 6 mrad | |
| Electronic system | Sampling frequency | 1.0 GHz |
| Flight Altitude | Flight Speed | Spot Diameter | Adjacent Spot Centers Spacing |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 km | 110 m/s | 15 m | ~2.75 m |
| Experimental Areas | Flight Altitude (m) | Angle ε (°) | Adjacent Spot Centers Spacing (m) | Fitting Spot Diameter (m) | Divergence Angle (mRad) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aera_01 | 3043.35 | 59.64 | 2.73 | 12.98 | 5.06 |
| Aera_02 | 3043.95 | 52.69 | 1.83 | 12.33 | 4.81 |
| Aera_03 | 3040.65 | 74.98 | 1.88 | 10.98 | 4.29 |
| Aera_04 | 3046.51 | 70.23 | 2.07 | 10.58 | 4.12 |
| Aera_05 | 3002.55 | 82.71 | 1.58 | 12.22 | 4.83 |
| Aera_06 | 2956.05 | 86.11 | 1.76 | 11.21 | 4.51 |
| Spot Matrix Consistency | Aera_01 | Aera_02 | Aera_03 | Aera_04 | Aera_05 | Aera_06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aera_01 | 100% | 89.50% | 98.52% | 84.88% | 99.94% | 89.13% |
| Aera_02 | 90.50% | 100% | 91.84% | 95.82% | 90.55% | 99.66% |
| Aera_03 | 98.55% | 91.11% | 100% | 86.56% | 98.60% | 90.74% |
| Aera_04 | 86.87% | 95.99% | 88.15% | 100% | 86.92% | 96.31% |
| Aera_05 | 99.94% | 89.56% | 98.58% | 84.95% | 100% | 89.19% |
| Aera_06 | 90.20% | 99.67% | 91.53% | 96.17% | 90.25% | 100% |
| Spot Matrix Consistency | Aera_01 | Aera_02 | Aera_03 | Aera_04 | Aera_05 | Aera_06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured spot in the labora-tory | 94.34% | 95.75% | 95.74% | 91.39% | 94.40% | 95.40% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Yu, Q.; Fu, A.; Zhang, G. A Calibration Method for Large-Footprint Full-Waveform Airborne Laser Altimeter without a Calibration Field. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112789
Li S, Yu Q, Fu A, Zhang G. A Calibration Method for Large-Footprint Full-Waveform Airborne Laser Altimeter without a Calibration Field. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112789
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shaoning, Qifan Yu, Anmin Fu, and Guo Zhang. 2023. "A Calibration Method for Large-Footprint Full-Waveform Airborne Laser Altimeter without a Calibration Field" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112789
APA StyleLi, S., Yu, Q., Fu, A., & Zhang, G. (2023). A Calibration Method for Large-Footprint Full-Waveform Airborne Laser Altimeter without a Calibration Field. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112789