Geometric Primitive-Guided UAV Path Planning for High-Quality Image-Based Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We pioneer the preprocessing method of planar segmentation and primitive extraction to divide the reconstructed scene into independent geometric primitives, and we simplify the viewpoint optimization of the whole scene to the reconstructable optimization problem of each independent primitive.
- We establish two mathematical models from the traditional aerial photogrammetry to measure the reconstructability of polygon and line primitives, based on which suitable overlap ratios are calculated to quickly generate an initial set of viewpoints for approximating the global optimum.
- We construct an objective function that satisfies submodularity to accelerate the iterative selection of optimal viewpoints for the point primitives by measuring the expected gain instead of the actual reward.
2. Related Works
2.1. Priori Geometry Proxy
2.2. Viewpoint Optimization
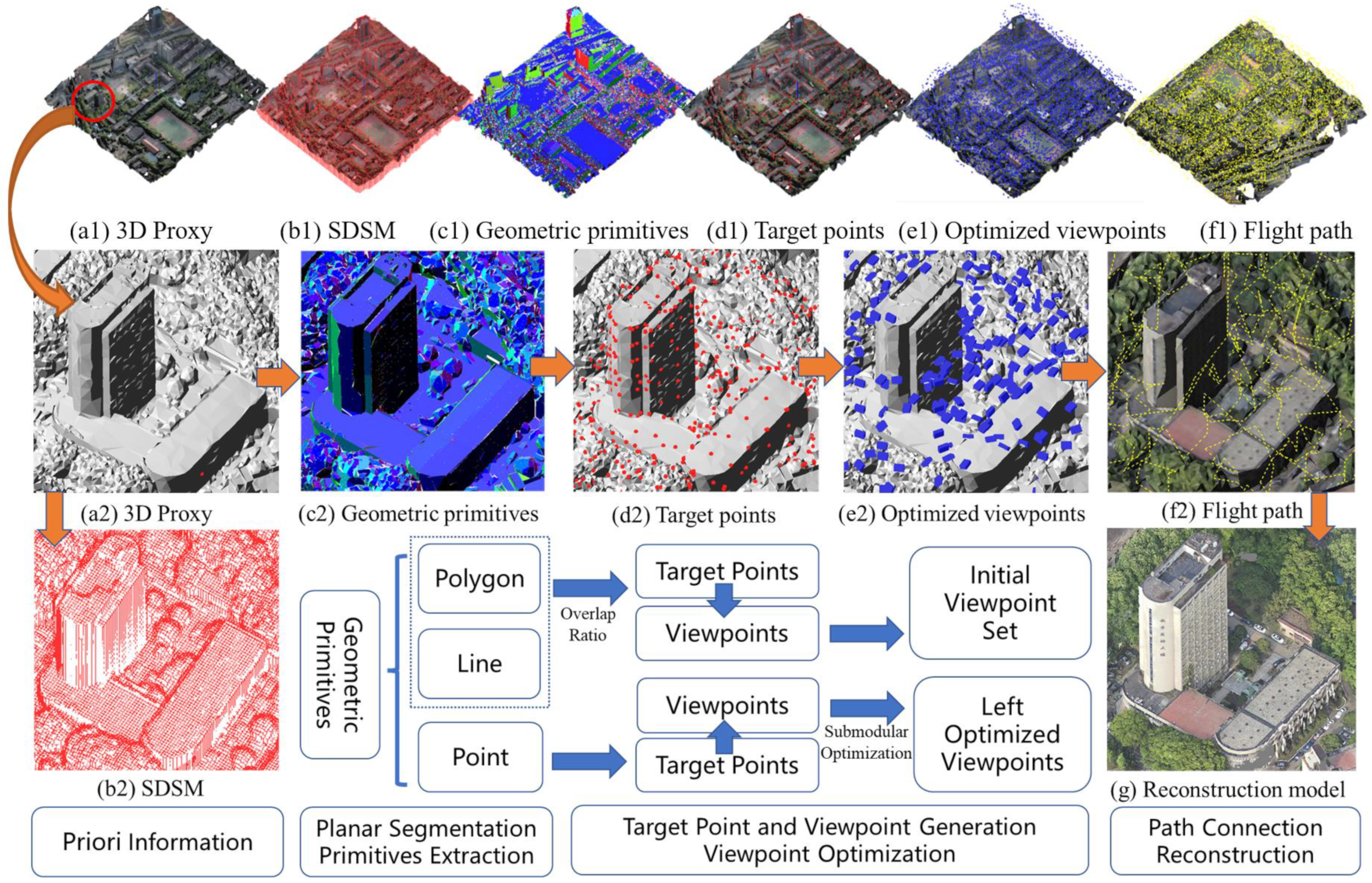
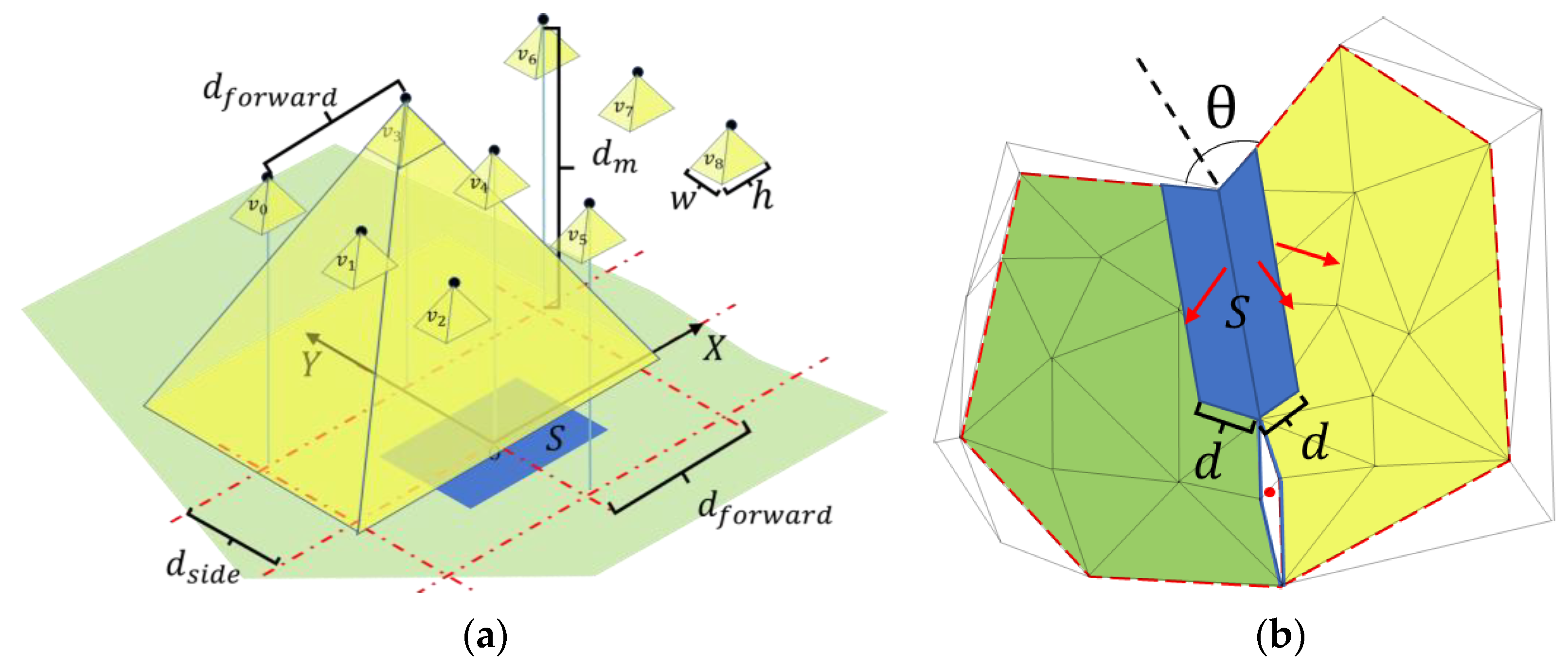
3. Methodology
3.1. Priori Information and Pre-Processing
3.1.1. Geometric Proxy Preparation
3.1.2. SDSM Generation
3.1.3. Geometric Primitives Extraction
3.2. Primitive-Guided Viewpoint Generation and Optimization
3.2.1. Sample on Primitives
- Viewpoint Generation and Adjustment.
- Reconstruction Heuristics
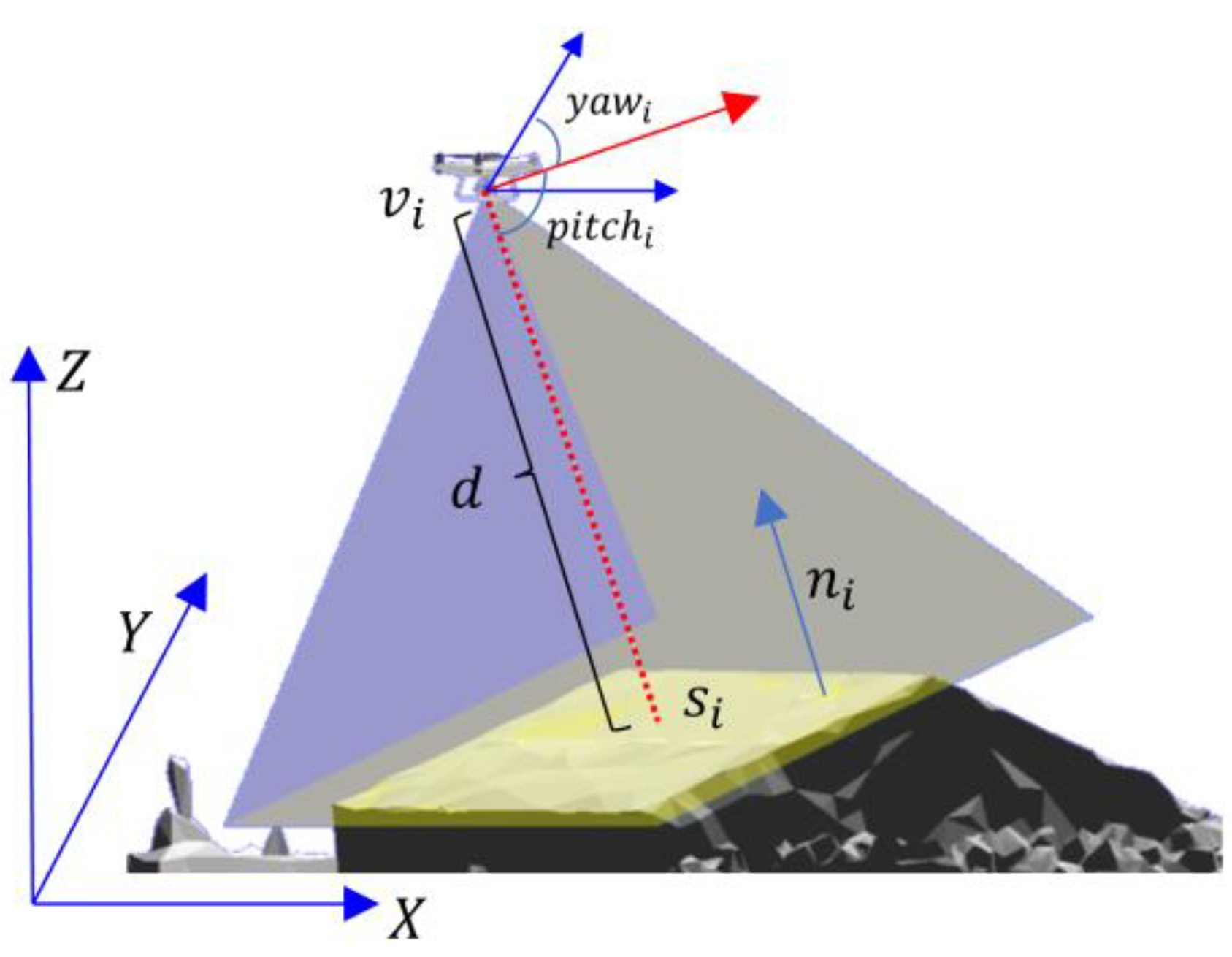
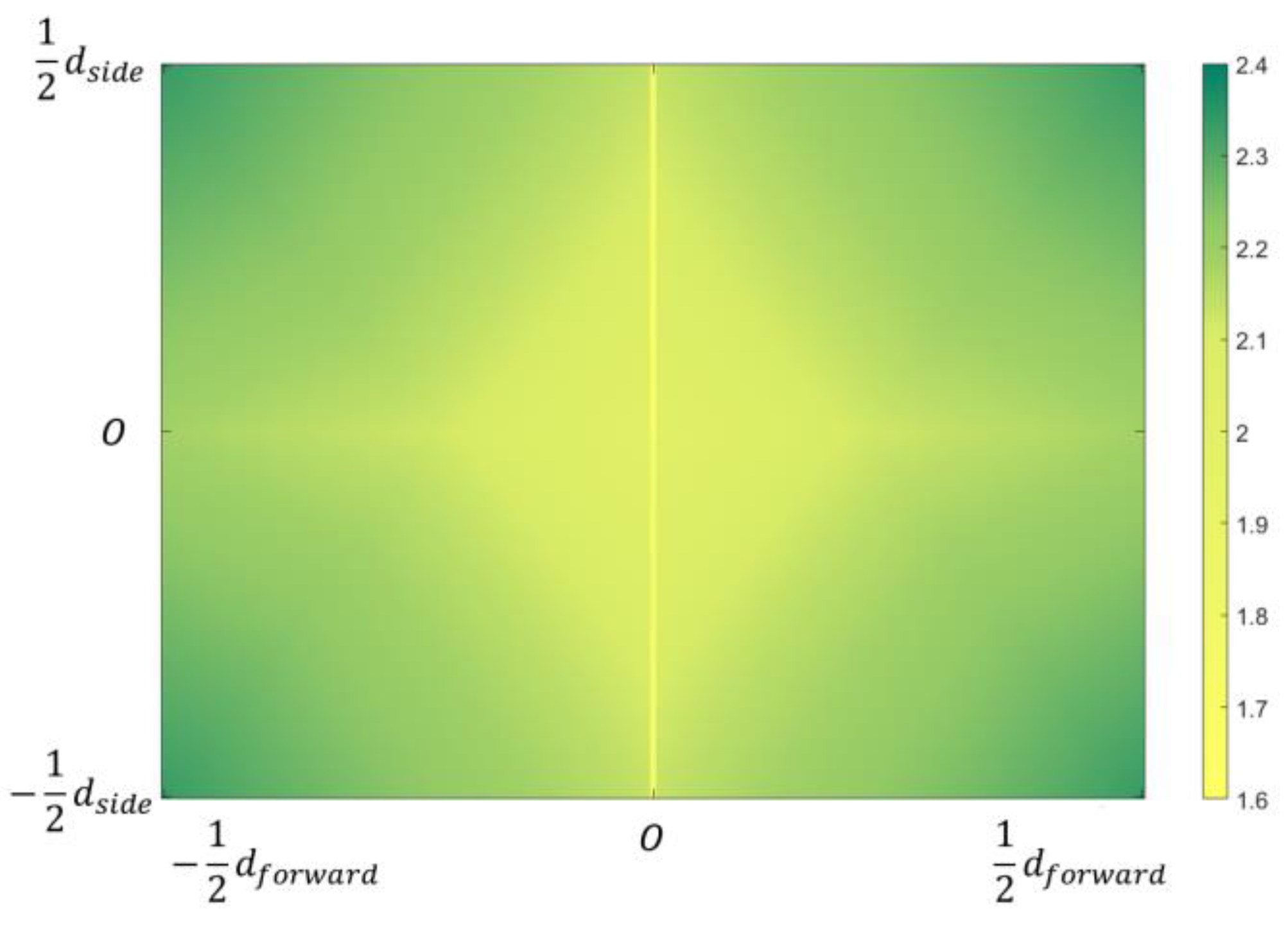
3.2.2. Optimization Objective Function
3.2.3. Initial Optimal Set for Polygon and Line Primitives
3.2.4. Submodular Optimization for Point Primitives
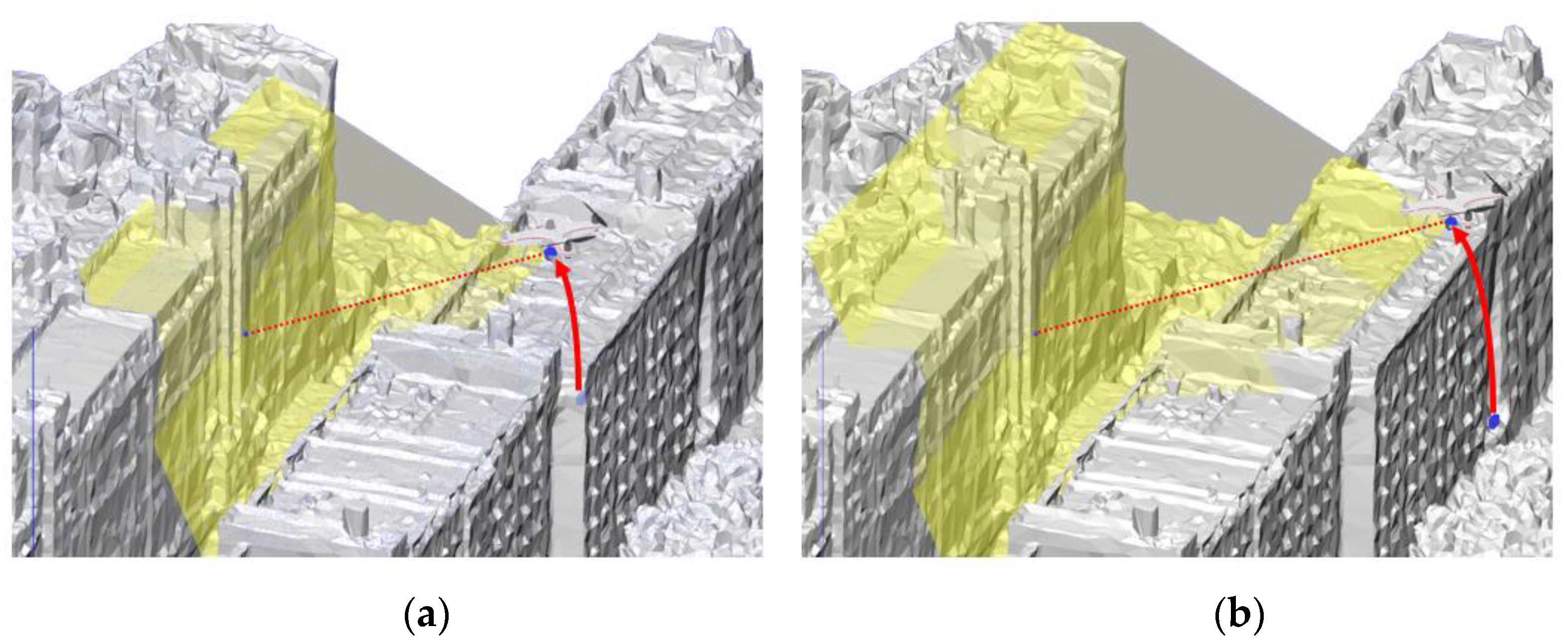
3.3. Shortest Path Connection
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Measures
4.2. Self-Evaluation
4.2.1. Impact of Different Detailed Proxy
4.2.2. Impact of Overlap Ratio
4.2.3. Effectiveness of Submodular Formulation
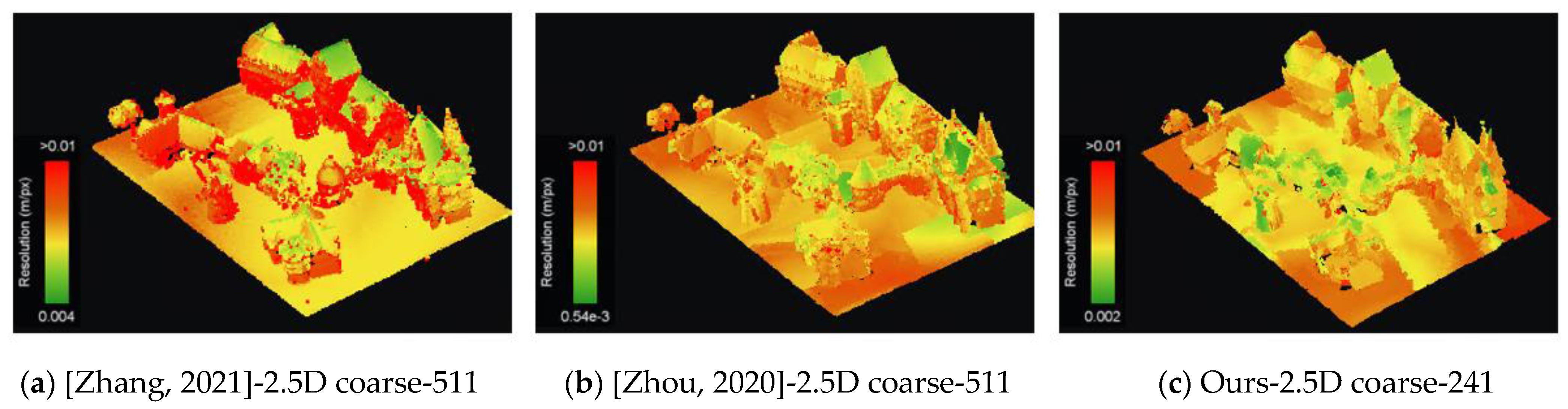
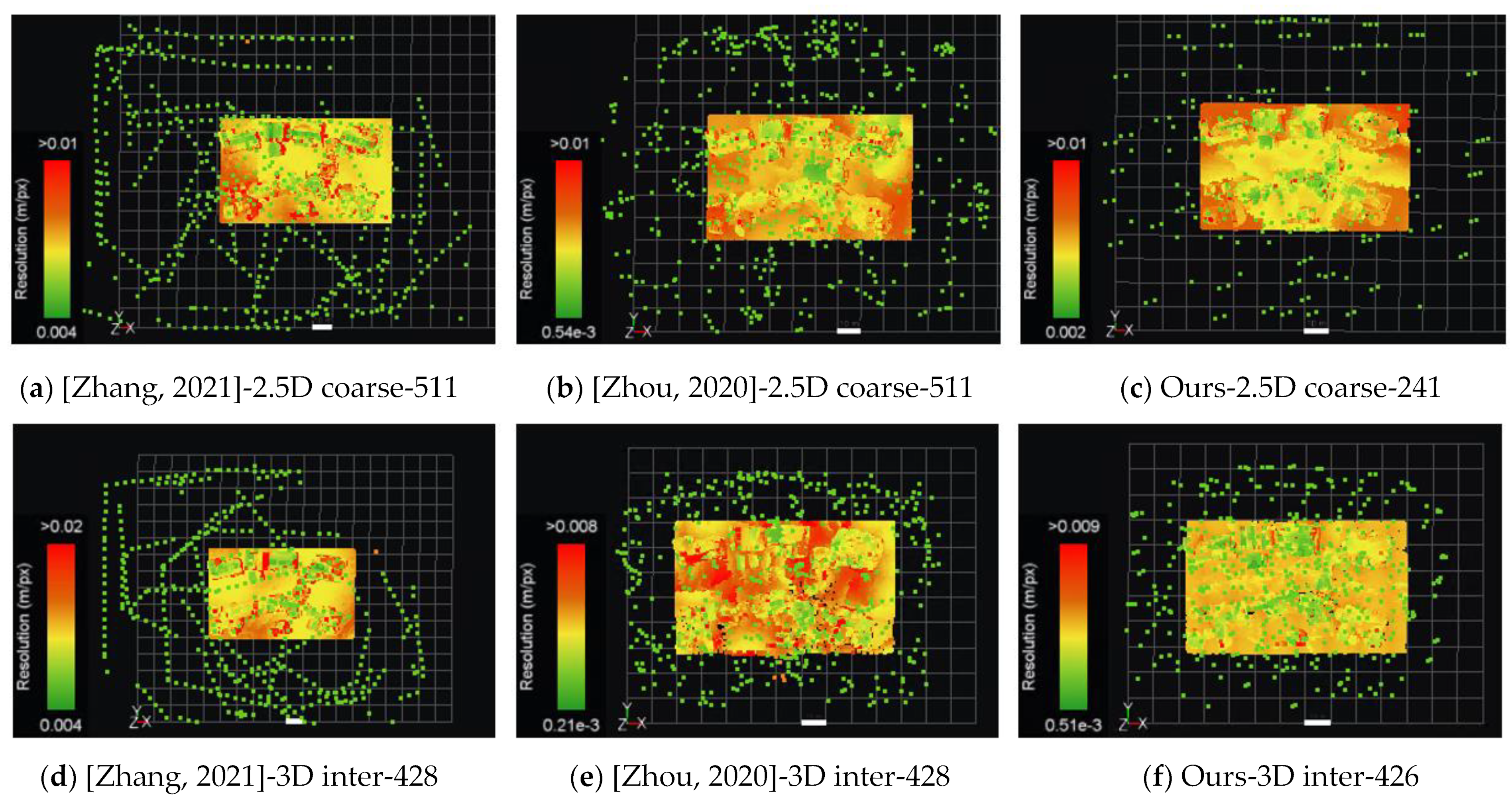
4.3. Comparison to State of the Art
- Comparison with [20]
4.4. Field Test
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aharchi, M.; Ait Kbir, M. A Review on 3D Reconstruction Techniques from 2D Images. In Innovations in Smart Cities Applications, 3rd ed.; Ben Ahmed, M., Boudhir, A.A., Santos, D., El Aroussi, M., Karas, İ.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 510–522. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, S. A Review of 3D Reconstruction Techniques in Civil Engineering and Their Applications. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 37, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reu, J.; De Smedt, P.; Herremans, D.; Van Meirvenne, M.; Laloo, P.; De Clercq, W. On Introducing an Image-Based 3D Reconstruction Method in Archaeological Excavation Practice. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Hernández, C. Multi-View Stereo: A Tutorial. Found. Trends® Comput. Graph. Vis. 2015, 9, 1–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.F.; Hambrey, M.J.; Reynolds, J.M. ‘Structure-from-Motion’ Photogrammetry: A Low-Cost, Effective Tool for Geoscience Applications. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Zheng, E.; Frahm, J.-M.; Pollefeys, M. Pixelwise View Selection for Unstructured Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 501–518. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, S.M.; Curless, B.; Diebel, J.; Scharstein, D.; Szeliski, R. A Comparison and Evaluation of Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 1, pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Snavely, N.; Seitz, S.M.; Szeliski, R. Photo Tourism: Exploring Photo Collections in 3D. ACM Trans. Graph. 2006, 25, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. MVSNet: Depth Inference for Unstructured Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 785–801. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Shen, T.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. Recurrent MVSNet for High-Resolution Multi-View Stereo Depth Inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 5525–5534. [Google Scholar]
- Goesele, M.; Snavely, N.; Curless, B.; Hoppe, H.; Seitz, S.M. Multi-View Stereo for Community Photo Collections. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hornung, A.; Zeng, B.; Kobbelt, L. Image Selection for Improved Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, Alaska, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, H.; Dai, F.; Lourakis, M. Automated As-Built 3D Reconstruction of Civil Infrastructure Using Computer Vision: Achievements, Opportunities, and Challenges. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, P.; Xi, K.; Chen, L.; Junior, J. An object-oriented uav 3d path planning method applied in cultural heritage documentation. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, V-1–2022, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, B.; Nießner, M.; Hilliges, O. Plan3D: Viewpoint and Trajectory Optimization for Aerial Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Truong, A.; Sinha, S.; Kapoor, A.; Hanrahan, P.; Joshi, N. Submodular Trajectory Optimization for Aerial 3D Scanning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5334–5343. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, T.; Körner, M.; Fraundorfer, F. Automatic and Semantically-Aware 3D UAV Flight Planning for Image-Based 3D Reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hailes, S.; Julier, S.; Liu, M. UAV-Based SLAM and 3D Reconstruction System. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Macau, China, 5–8 December 2017; pp. 2496–2501. [Google Scholar]
- Nex, F.; Remondino, F. UAV for 3D Mapping Applications: A Review. Appl. Geomat. 2014, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Moehrle, N.; Goesele, M.; Heidrich, W. Aerial Path Planning for Urban Scene Reconstruction: A Continuous Optimization Method and Benchmark. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboudi, M.; Homaei, M.; Song, S.; Malihi, S.; Saadatseresht, M.; Gerke, M. A Review on Viewpoints and Path-Planning for UAV-Based 3D Reconstruction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.03716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, B.; Dey, D.; Sinha, S.N.; Kapoor, A.; Joshi, N.; Hilliges, O. Learn-to-Score: Efficient 3D Scene Exploration by Predicting View Utility. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Q.; Wu, J.; Pan, J.; Zhou, B. Real-Time UAV Path Planning for Autonomous Urban Scene Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 1156–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, R.; Xie, K.; Gong, M.; Huang, H. Aerial Path Planning for Online Real-Time Exploration and Offline High-Quality Reconstruction of Large-Scale Urban Scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. 2021, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, E.; Stachniss, C. Effective Exploration for MAVs Based on the Expected Information Gain. Drones 2018, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, W.; Long, P.; Huang, H.; Cohen-Or, D.; Gong, M.; Deussen, O.; Chen, B. Quality-Driven Poisson-Guided Autoscanning. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 33, 203:1–203:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Huang, H.; Su, H.; Cohen-Or, D.; Chen, B. 3D Attention-Driven Depth Acquisition for Object Identification. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 238:1–238:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Kim, D.; Jo, S. Online Coverage and Inspection Planning for 3D Modeling. Auton. Robot. 2020, 44, 1431–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, L.; Pantic, M.; Khanna, R.; Ott, L.; Siegwart, R.; Nieto, J. An Efficient Sampling-Based Method for Online Informative Path Planning in Unknown Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Xie, K.; Fu, C.-W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H. Continuous Aerial Path Planning for 3D Urban Scene Reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2021, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, K.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, M.; Huang, H. Offsite Aerial Path Planning for Efficient Urban Scene Reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2020, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Xia, E.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z. Sampling-Based Path Planning for High-Quality Aerial 3D Reconstruction of Urban Scenes. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, F.; Li, Z. A Multi-UAV Cooperative Route Planning Methodology for 3D Fine-Resolution Building Model Reconstruction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Hu, Y.; Xie, K.; Fu, C.-W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H. Learning Reconstructability for Drone Aerial Path Planning. ACM Trans. Graph. 2022, 41, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Yu, W.; Jiang, S. Optimized Views Photogrammetry: Precision Analysis and a Large-Scale Case Study in Qingdao. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1144–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, C.; Wendel, A.; Zollmann, S.; Pirker, K.; Irschara, A.; Bischof, H.; Kluckner, S. Photogrammetric Camera Network Design for Micro Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision Winter Workshop, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2012; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzas, V.; Ledoux, H.; Nan, L. Structure-Aware Building Mesh Polygonization. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, J.; Atkins, E. Polylidar—Polygons From Triangular Meshes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4634–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, J.; Atkins, E. Polylidar3D-Fast Polygon Extraction from 3D Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the Reduction of the Number of Points Required to Represent a Digitized Line or Its Caricature. Cartographica 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, J.; Snoeyink, J. Speeding Up the Douglas-Peucker Line-Simplification Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Spatial Data Handling, Charleston, SC, USA, 3–7 August 1992; pp. 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Isler, V. Adaptive View Planning for Aerial 3D Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 2981–2987. [Google Scholar]
- Abeywickrama, H.V.; Jayawickrama, B.A.; He, Y.; Dutkiewicz, E. Comprehensive Energy Consumption Model for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Based on Empirical Studies of Battery Performance. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 58383–58394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibbotuwawa, A.; Nielsen, P.; Zbigniew, B.; Bocewicz, G. Energy Consumption in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: A Review of Energy Consumption Models and Their Relation to the UAV Routing. In Information Systems Architecture and Technology, Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Information Systems Architecture and Technology—ISAT 2018, Nysa, Polska, 16–18 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Gambardella, L.M. Ant Colony System: A Cooperative Learning Approach to the Traveling Salesman Problem. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinderowicz, R. The GPU-Based Parallel Ant Colony System. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2016, 98, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Xie, K.; Huang, H. Capturing, Reconstructing, and Simulating: The UrbanScene3D Dataset. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Vose, M.D. A Linear Algorithm for Generating Random Numbers with a given Distribution. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 1991, 17, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Scene | Proxy | #Imgs | Precision | Recall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m ↑% | 90% ↓m | 0.1 m ↑% | 90% ↓m | |||
| Town 0.7 cm 53% | 2.5D Box | 183 | 91.47 | 0.066 | 70.51 | 0.806 |
| 2.5D Coarse | 220 | 93.04 | 0.056 | 71.07 | 0.778 | |
| 3D Inter | 242 | 94.00 | 0.053 | 71.31 | 0.769 | |
| School 0.7 cm 53% | 2.5D Box | 198 | 67.83 | 30.103 | 44.27 | 2.308 |
| 2.5D Coarse | 220 | 85.79 | 0.212 | 46.47 | 2.041 | |
| 3D Inter | 379 | 85.63 | 0.253 | 50.53 | 1.663 | |
| Overlap Ratio | #Imgs | Reconstructable Percent ↑% | Precision | Recall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m ↑% | 90% ↓m | 0.1 m ↑% | 90% ↓m | |||
| 45–45% | 66 | 64.8 | aerial triangulation failed | |||
| 53–53% | 76 | 94.4 | 93.50 | 0.060 | 79.54 | 0.296 |
| 56–56% | 79 | 96.8 | 94.51 | 0.055 | 80.53 | 0.257 |
| 60–60% | 86 | 99.1 | 93.76 | 0.055 | 81.07 | 0.174 |
| 66–66% | 97 | 99.6 | 94.33 | 0.052 | 81.18 | 0.211 |
| 66–33% | 80 | 89.0 | 92.01 | 0.068 | 78.28 | 0.307 |
| 66–8% | 59 | 73.7 | aerial triangulation failed | |||
| Scene | Optimization End | #Images | Reconstructable Percent ↑% | EH | ΔH | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m ↑% | 90% ↓m | ||||||
| Town Inter 0.7 cm | Φ | 236 | 98.30 | 70.62 | 0.782 | ||
| convergence | 242 | 98.90 | 3532.52 | 36.63 | 71.31 | 0.769 | |
| Φ + 15 | 251 | 98.96 | −486.44 | 2.20 | 71.34 | 0.765 | |
| Φ + 30 | 266 | 99.01 | −1835.38 | 2.65 | 71.32 | 0.772 | |
| Φ + 50 | 286 | 99.01 | −3377.84 | 0.02 | 71.48 | 0.752 | |
| School Inter 0.7 cm | Φ | 359 | 97.29 | 49.36 | 1.768 | ||
| Φ + 15 | 374 | 99.60 | 8071.96 | 120.32 | 50.27 | 1.669 | |
| convergence | 379 | 99.67 | 160.64 | 11.48 | 50.53 | 1.663 | |
| Φ + 30 | 389 | 99.73 | −283.32 | 1.6 | 50.67 | 1.637 | |
| Φ + 50 | 409 | 99.74 | −1425.27 | 0 | 50.79 | 1.630 | |
| Scene | Method | #Plan ↓mins | #Imgs | Length ↓m | Time ↓s | Energy ↓J | RMSE ↓mm | GSD ↓mm | Precision | LComp | GComp | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% ↓m | 95% ↓m | 0.05 m ↑% | 0.075 m ↑% | 0.50 m ↑% | 0.75 m ↑% | |||||||||
| UK | [20] | 7.93 | 923 | 7819 | 6795 | 58,162 | 5.70 | 13.72 | 0.04 | 0.069 | 35.99 | 38.25 | 69.20 | 73.21 |
| Ours-53% | 1.45 | 479 | 6923 | 2962 | 25,924 | 5.47 | 13.57 | 0.039 | 0.060 | 37.35 | 39.46 | 69.31 | 73.26 | |
| NY | [20] | 4.12 | 433 | 2807 | 2960 | 25,258 | 4.20 | 9.86 | 0.064 | 0.218 | 45.09 | 48.89 | 83.61 | 85.57 |
| Ours-53% | 0.75 | 234 | 2639 | 1189 | 10,366 | 4.57 | 10.17 | 0.045 | 0.247 | 44.98 | 48.49 | 83.99 | 85.88 | |
| GOTH | [20] | 5.52 | 588 | 4213 | 4206 | 35,917 | 4.50 | 12.02 | 0.034 | 0.084 | 52.83 | 56.69 | 84.77 | 88.77 |
| Ours-53% | 0.92 | 334 | 4558 | 1927 | 16,870 | 5.34 | 12.04 | 0.039 | 0.191 | 52.54 | 56.35 | 85.09 | 89.42 | |
| Proxy | Method | #Imgs | Length | Time | Energy | RMSE | GSD | Precision | Recall | F-Score | Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m | 90% | 0.1 m | 90% | ||||||||||
| ↓m | ↓s | ↓J | ↓mm | ↓mm | ↑% | ↓m | ↑% | ↓m | ↑% | ||||
| 2.5D Coarse (School) | [30]-high | 570 | 4485 | 2120 | 18,504 | 6.05 | 12.86 | 82.62 | 0.316 | 48.20 | 1.814 | 60.89 | 1 |
| [30]-low | 330 | 4294 | 1587 | 14,013 | 5.97 | 11.98 | 82.96 | 0.325 | 46.64 | 1.893 | 59.71 | 2 | |
| Ours-53%-0.7 | 220 | 3404 | 1300 | 11,434 | 3.68 | 8.13 | 85.79 | 0.212 | 46.47 | 2.041 | 60.29 | 3 | |
| 3D Inter (School) | [30]-high | 570 | 4521 | 2105 | 18,385 | 8.73 | 15.70 | 78.74 | 0.525 | 48.43 | 1.678 | 59.97 | 4 |
| [30]-low | 330 | 4239 | 1560 | 13,776 | 8.70 | 15.96 | 79.95 | 0.413 | 46.81 | 1.853 | 59.05 | 5 | |
| Ours-53%-0.8 | 328 | 4238 | 1545 | 13,474 | 3.71 | 8.03 | 86.55 | 0.191 | 50.37 | 1.710 | 63.68 | 6 | |
| 2.5D Coarse (Town) | [30]-high | 511 | 3638 | 1840 | 16,024 | 5.44 | 12.52 | 90.11 | 0.097 | 69.32 | 0.805 | 78.36 | 7 |
| [30]-low | 217 | 3457 | 1197 | 10,608 | 6.08 | 12.76 | 90.09 | 0.098 | 68.50 | 0.841 | 77.83 | 8 | |
| Ours-53%-0.7 | 220 | 2860 | 1085 | 9540 | 3.87 | 8.51 | 93.04 | 0.056 | 71.07 | 0.778 | 80.58 | 9 | |
| 3D Inter (Town) | [30]-high | 428 | 3502 | 1641 | 14,331 | 5.66 | 12.65 | 89.76 | 0.106 | 68.95 | 0.825 | 77.99 | 10 |
| [30]-low | 258 | 3115 | 1212 | 10,683 | 6.04 | 12.87 | 89.75 | 0.106 | 68.85 | 0.800 | 77.92 | 11 | |
| Ours-53%-0.7 | 242 | 2626 | 1098 | 9615 | 3.50 | 7.32 | 94.00 | 0.053 | 71.31 | 0.769 | 81.10 | 12 | |
| Proxy | Method | #Imgs | RMSE | GSD | Precision | Recall | F-Score | Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m | 90% | 0.1 m | 90% | |||||||
| ↓mm | ↓mm | ↑% | ↓m | ↑% | ↓m | ↑% | ||||
| 2.5D Coarse (School) | [31]-high | 570 | 4.18 | 9.16 | 83.97 | 0.304 | 51.2 | 1.602 | 63.61 | 1 |
| [31]-low | 330 | 4.24 | 8.68 | 86.85 | 0.179 | 48.46 | 1.963 | 62.21 | 2 | |
| Ours-60%-0.7 | 272 | 3.72 | 8.15 | 85.69 | 0.226 | 49.39 | 1.744 | 62.67 | 3 | |
| 3D Inter (School) | [31]-high | 595 | 3.79 | 8.03 | 15.39 | 1.819 | 9.86 | 2.136 | 12.02 | 4 |
| [31]-low | 342 | 3.99 | 8.26 | 87.14 | 0.157 | 48.2 | 1.992 | 62.07 | 5 | |
| Ours-60%-0.7 | 400 | 3.15 | 7.02 | 87.50 | 0.163 | 50.52 | 1.639 | 64.06 | 6 | |
| 2.5D Coarse (Town) | [31]-high | 511 | 4.02 | 8.77 | 92.01 | 0.061 | 72.02 | 0.721 | 80.80 | 7 |
| [31]-low | 217 | 4.36 | 8.61 | 92.74 | 0.059 | 70.77 | 0.763 | 80.28 | 8 | |
| Ours-60%-0.7 | 241 | 3.81 | 8.56 | 92.85 | 0.057 | 71.70 | 0.747 | 80.92 | 9 | |
| 3D Inter (Town) | [31]-high | 428 | 2.78 | 4.48 | 95.29 | 0.050 | 72.02 | 0.727 | 82.04 | 10 |
| [31]-low | 259 | 2.46 | 4.11 | 84.32 | 2.07 | 66.75 | 0.926 | 74.51 | 11 | |
| Ours-60%-0.45 | 426 | 2.33 | 4.79 | 94.90 | 0.050 | 73.28 | 0.700 | 82.70 | 12 | |
| Scene | Method | #Imgs | GSD | Precision | Recall | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m | 0.5 m | 0.1 m | 0.5 m | ||||
| mm | ↑% | ↑% | ↑% | ↑% | |||
| Museum | Oblique-1.2 cm | 270 | 15.23 | 50.43 | 70.46 | 54.56 | 72.24 |
| Ours-0.6 cm | 274 | 6.15 | 62.75 | 79.16 | 70.52 | 91.64 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Ji, Z.; You, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, K.; Lin, S.; Huang, X. Geometric Primitive-Guided UAV Path Planning for High-Quality Image-Based Reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102632
Zhou H, Ji Z, You X, Liu Y, Chen L, Zhao K, Lin S, Huang X. Geometric Primitive-Guided UAV Path Planning for High-Quality Image-Based Reconstruction. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102632
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hao, Zheng Ji, Xiangyu You, Yuchen Liu, Lingfeng Chen, Kun Zhao, Shan Lin, and Xiangxiang Huang. 2023. "Geometric Primitive-Guided UAV Path Planning for High-Quality Image-Based Reconstruction" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102632
APA StyleZhou, H., Ji, Z., You, X., Liu, Y., Chen, L., Zhao, K., Lin, S., & Huang, X. (2023). Geometric Primitive-Guided UAV Path Planning for High-Quality Image-Based Reconstruction. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102632