Removing Prior Information from Remotely Sensed Atmospheric Profiles by Wiener Deconvolution Based on the Complete Data Fusion Framework
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Demonstrative Application
3.1. Settings
3.2. Simulated Data
3.3. Real Observations
3.4. Retrieval Averaging
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodgers, C.D. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- von Clarmann, T.; Grabowski, U. Elimination of hidden a priori information from remotely sensed profile data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppens, A.; Compernolle, S.; Verhoelst, T.; Hubert, D.; Lambert, J.C. Harmonization and comparison of vertically resolved atmospheric state observations: Methods, effects, and uncertainty budget. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4379–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccherini, S.; Carli, B.; Raspollini, P. The average of atmospheric vertical profiles. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 24808–24816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Clarmann, T.; Glatthor, N. The application of mean averaging kernels to mean trace gas distributions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5155–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccherini, S.; Carli, B.; Raspollini, P. Equivalence of data fusion and simultaneous retrieval. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 8476–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccherini, S.; Carli, B.; Tirelli, C.; Zoppetti, N.; Del Bianco, S.; Cortesi, U.; Kujanpää, J.; Dragani, R. Importance of interpolation and coincidence errors in data fusion. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiener, N. Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Langerock, B.; De Mazière, M.; Hendrick, F.; Vigouroux, C.; Desmet, F.; Dils, B.; Niemeijer, S. Description of algorithms for co-locating and comparing gridded model data with remote-sensing observations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cortesi, U.; Ceccherini, S.; Del Bianco, S.; Gai, M.; Tirelli, C.; Zoppetti, N.; Barbara, F.; Bonazountas, M.; Argyridis, A.; Bós, A.; et al. Advanced Ultraviolet Radiation and Ozone Retrieval for Applications (AURORA): A Project Overview. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, O.E.; Schneider, M.; Sepúlveda, E.; Hase, F.; Blumenstock, T.; Cuevas, E.; Ramos, R.; Gross, J.; Barthlott, S.; Röhling, A.N.; et al. Twenty years of ground-based NDACC FTIR spectrometry at Izaña Observator—Overview and long-term comparison to other techniques. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021, 2021, 15519–15554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtmans, D.; Coheur, P.F.; Wespes, C.; Clarisse, L.; Scharf, O.; Clerbaux, C.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; George, M.; Turquety, S. FORLI radiative transfer and retrieval code for IASI. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2012, 113, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, G.M.; Siddans, R.; Kerridge, B.J.; Latter, B.G.; Richards, N.A.D. Tropospheric ozone and ozone profiles retrieved from GOME-2 and their validation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raspollini, P.; Piro, A.; Hubert, D.; Keppens, A.; Lambert, J.C.; Wetzel, G.; Moore, D.; Ceccherini, S.; Gai, M.; Barbara, F.; et al. ENVIromental SATellite (ENVISAT) Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS) ESA Level 2 Version 8.22 Products—Product Quality Readme File; Technical Report; ESA: Paris, France, 2020; Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/37627/README_V8_issue_1.0_20201221.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Fischer, H.; Birk, M.; Blom, C.; Carli, B.; Carlotti, M.; von Clarmann, T.; Delbouille, L.; Dudhia, A.; Ehhalt, D.; Endemann, M.; et al. MIPAS: An instrument for atmospheric and climate research. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2151–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppens, A.; Lambert, J.C.; Granville, J.; Hubert, D.; Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Latter, B.; Kerridge, B.; Siddans, R.; Boynard, A.; et al. Quality assessment of the Ozone_cci Climate Research Data Package (release 2017)—Part 2: Ground-based validation of nadir ozone profile data products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 3769–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, M.; Blumenstock, T.; Hase, F.; Höpfner, M.; Cuevas, E.; Redondas, A.; Sancho, J. Ozone profiles and total column amounts derived at Izaña, Tenerife Island, from FTIR solar absorption spectra, and its validation by an intercomparison to ECC-sonde and Brewer spectrometer measurements. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2005, 91, 245–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, A.; Cooper, O.R.; Ancellet, G.; Barret, B.; Boynard, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F.; Cuesta, J.; Cuevas, E.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day distribution and trends of tropospheric ozone relevant to climate and global atmospheric chemistry model evaluation. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2018, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

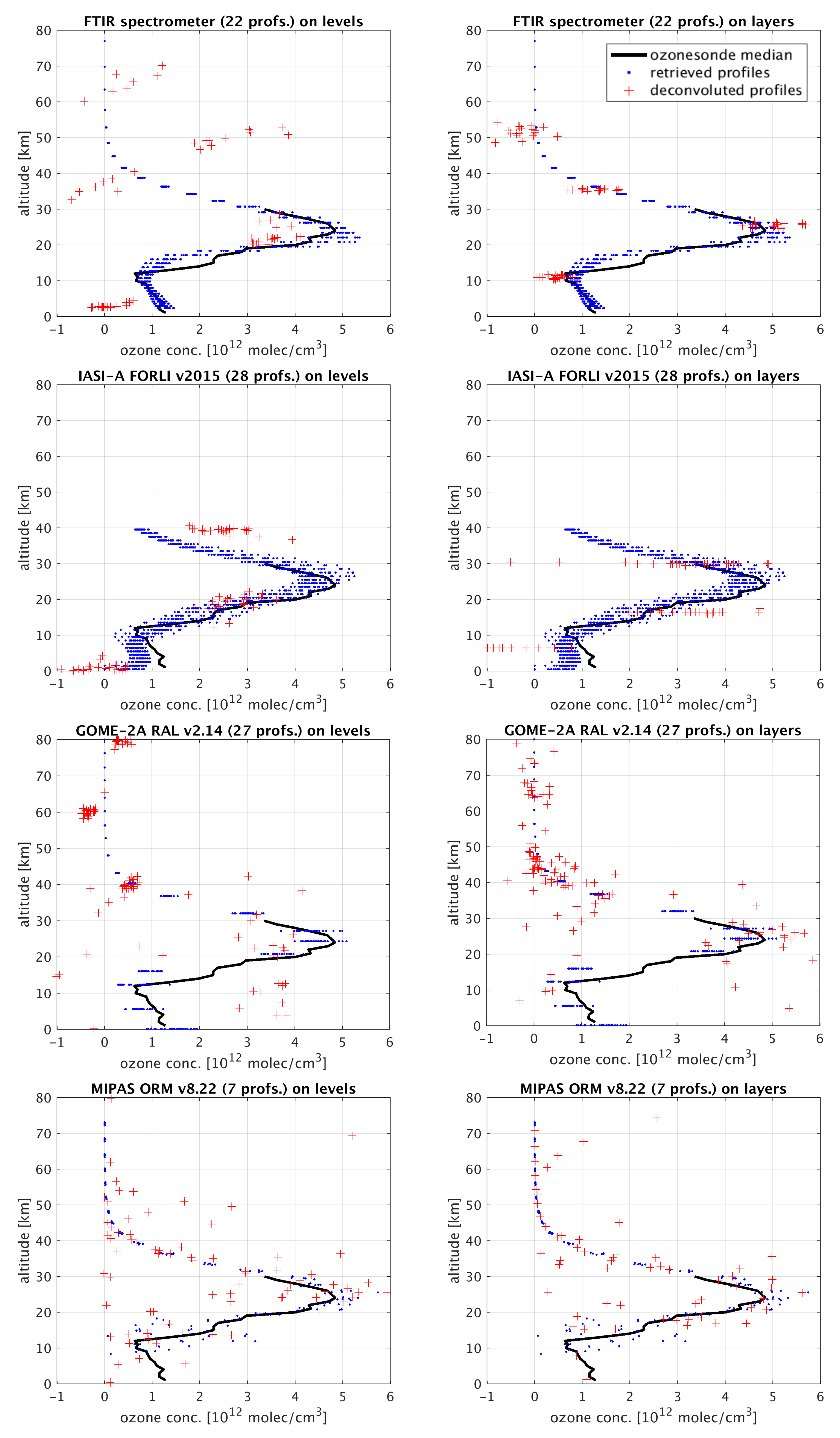
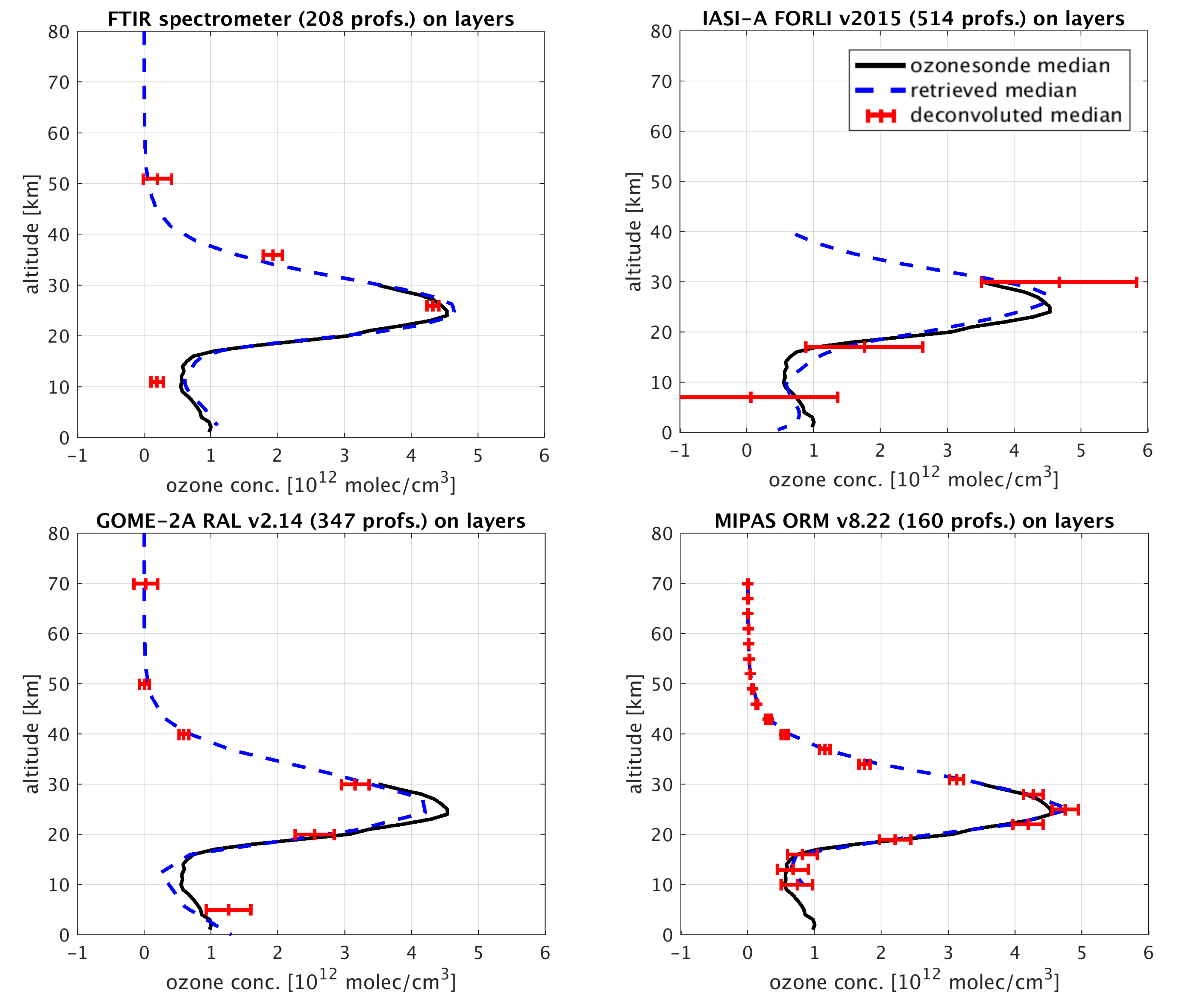
| Levels | Layers | |
|---|---|---|
| / | ||
| Data Source | Data Version | Coinc. | Profs. | Avg. d | Avg. e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S5 UVNS sim. UV | AURORA [10] | 50 | 67 | 6.5 | 0.1–0.1 |
| IASI-NG sim. TIR | AURORA [10] | 50 | 46 | 5.0 | 0.1–0.1 |
| FTIR spectrometer | NDACC [11] | / | 22 | 4.2 | 0.4–0.1 |
| IASI on Metop-A | FORLI v2015 [12] | 30 | 28 | 3.4 | 0.2–0.2 |
| GOME-2 on Metop-A | RAL v2.14 [13] | 100 | 27 | 5.6 | 0.2–0.6 |
| MIPAS on Envisat | ORM v8.22 [14] | 500 | 7 | 23.2 | 0.1–0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keppens, A.; Compernolle, S.; Hubert, D.; Verhoelst, T.; Granville, J.; Lambert, J.-C. Removing Prior Information from Remotely Sensed Atmospheric Profiles by Wiener Deconvolution Based on the Complete Data Fusion Framework. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092197
Keppens A, Compernolle S, Hubert D, Verhoelst T, Granville J, Lambert J-C. Removing Prior Information from Remotely Sensed Atmospheric Profiles by Wiener Deconvolution Based on the Complete Data Fusion Framework. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092197
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeppens, Arno, Steven Compernolle, Daan Hubert, Tijl Verhoelst, José Granville, and Jean-Christopher Lambert. 2022. "Removing Prior Information from Remotely Sensed Atmospheric Profiles by Wiener Deconvolution Based on the Complete Data Fusion Framework" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092197
APA StyleKeppens, A., Compernolle, S., Hubert, D., Verhoelst, T., Granville, J., & Lambert, J.-C. (2022). Removing Prior Information from Remotely Sensed Atmospheric Profiles by Wiener Deconvolution Based on the Complete Data Fusion Framework. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092197







