Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days in the Taklimakan Desert, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
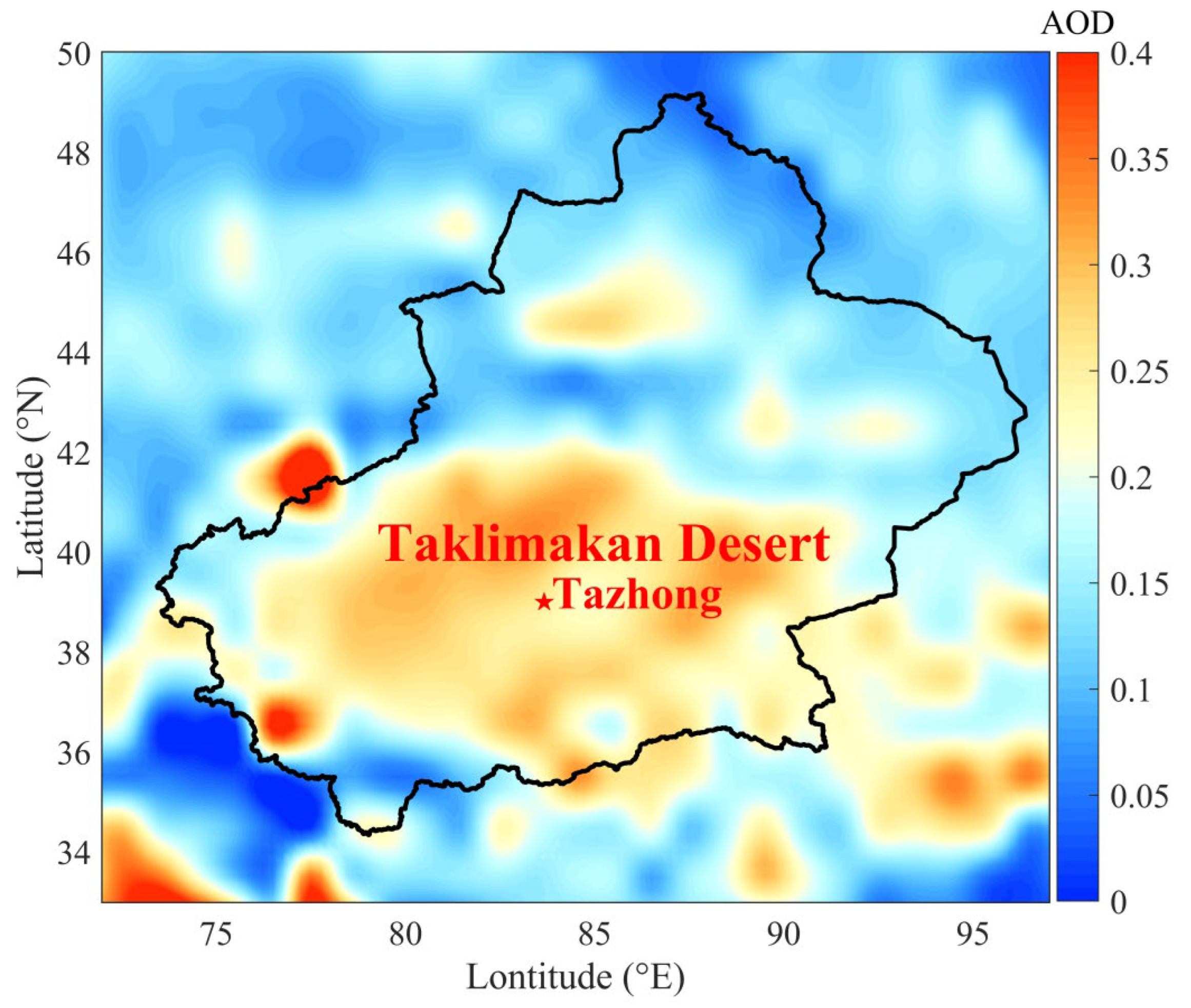
2.1. Experimental Site and Data
2.2. Threshold Velocity for Saltation Activity
3. Results
3.1. Daily Examples
3.2. Atmospheric and Soil Conditions on Non-Dust Days
3.3. Threshold Velocity for Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days
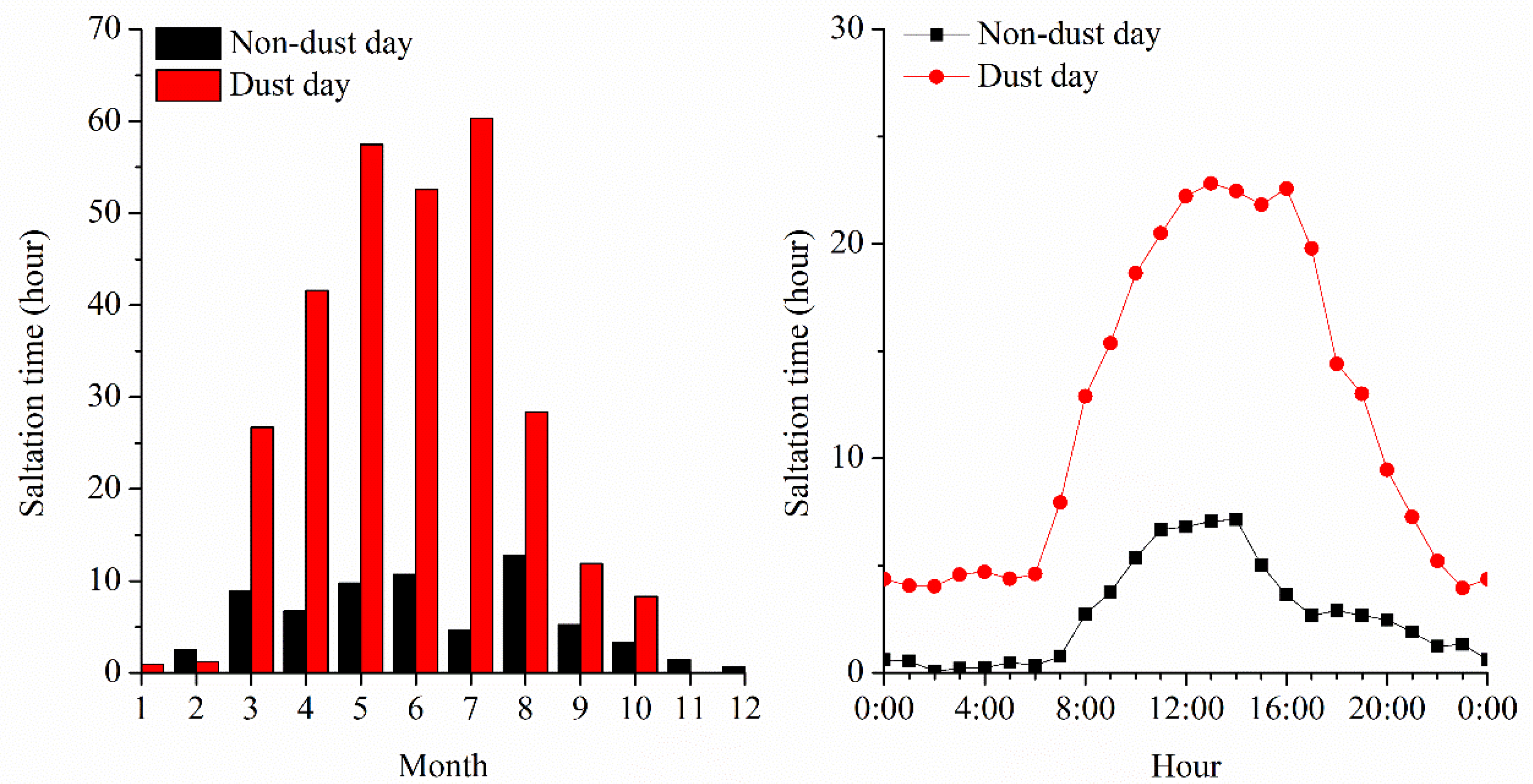
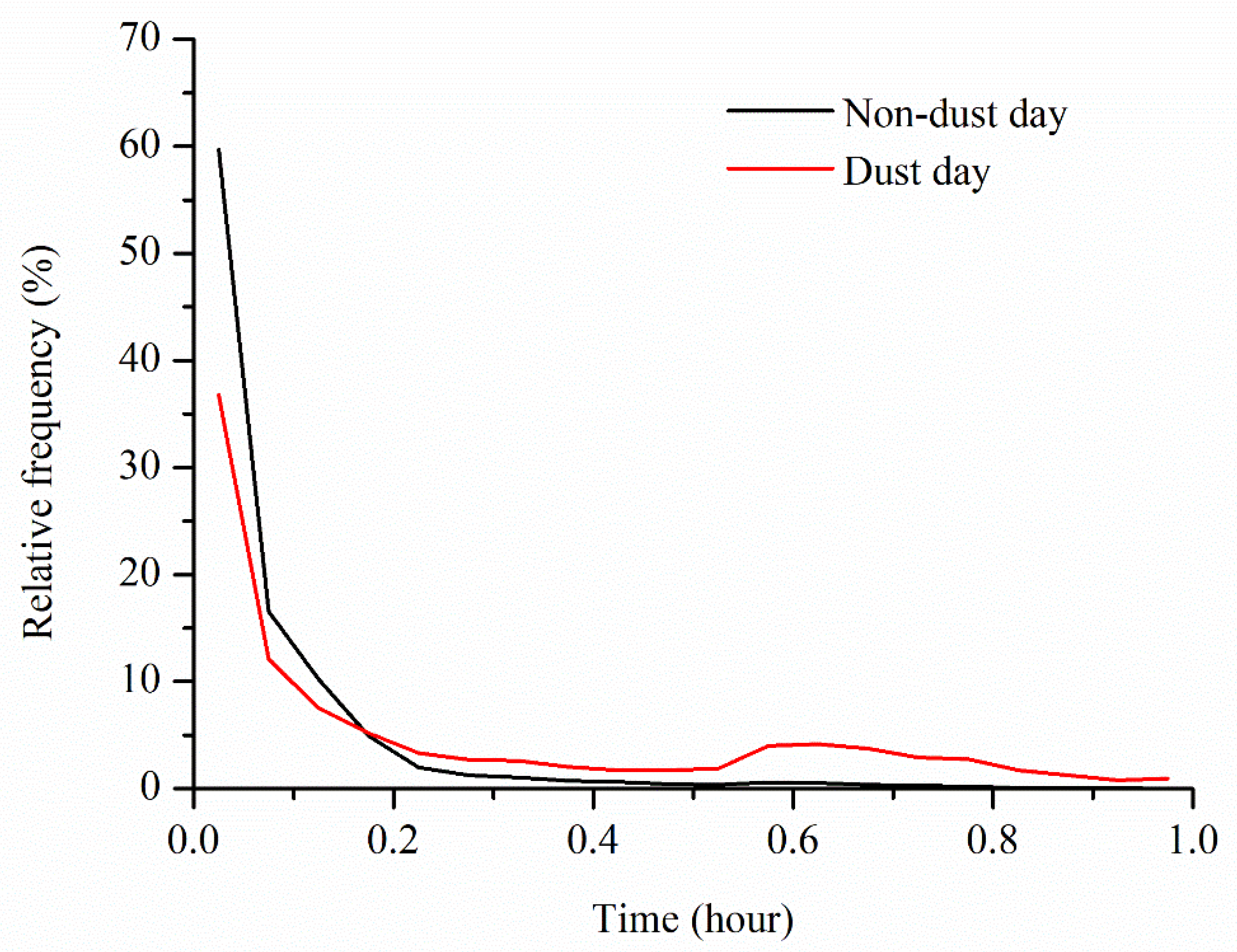
3.4. Saltation Time during Non-Dust Days
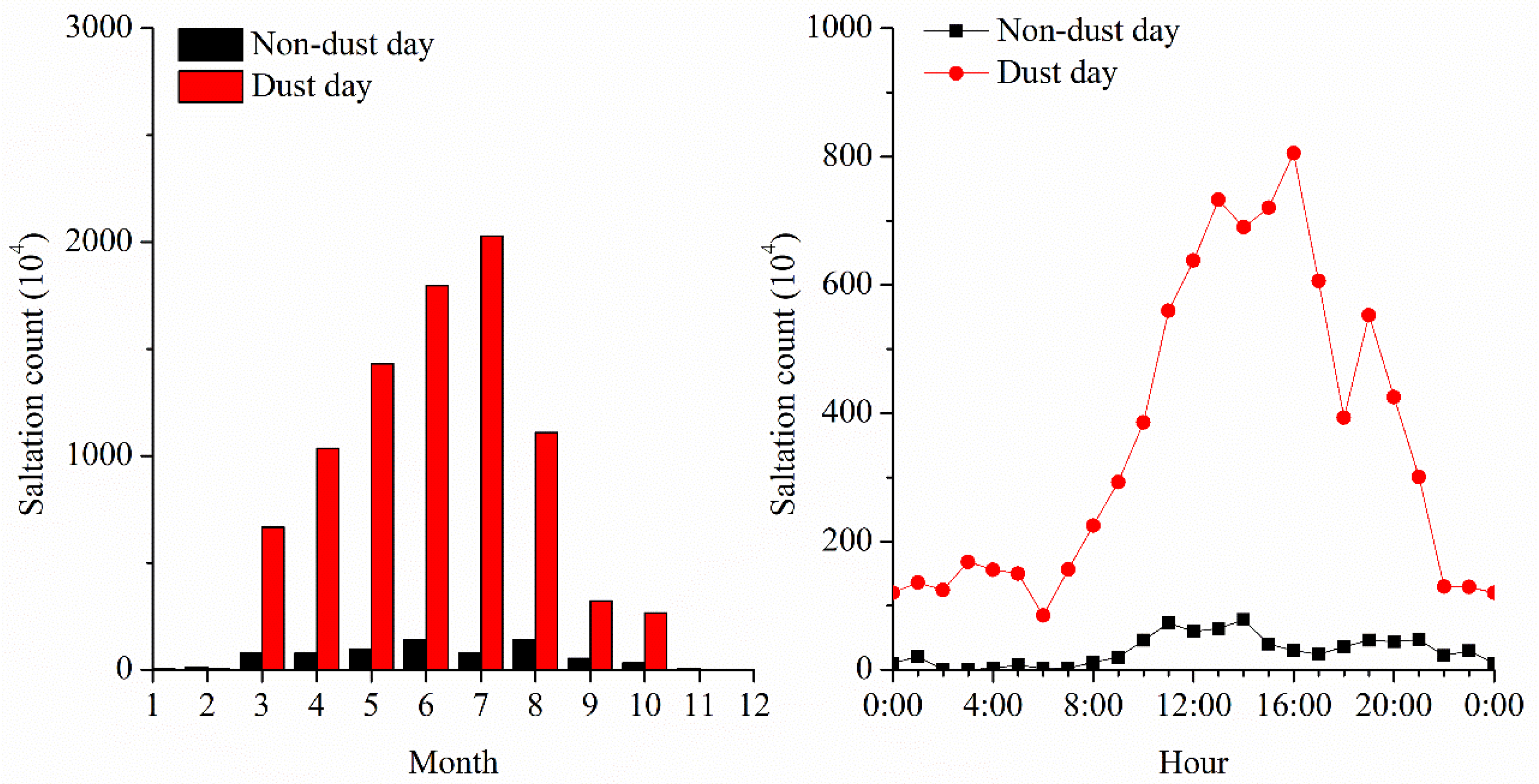
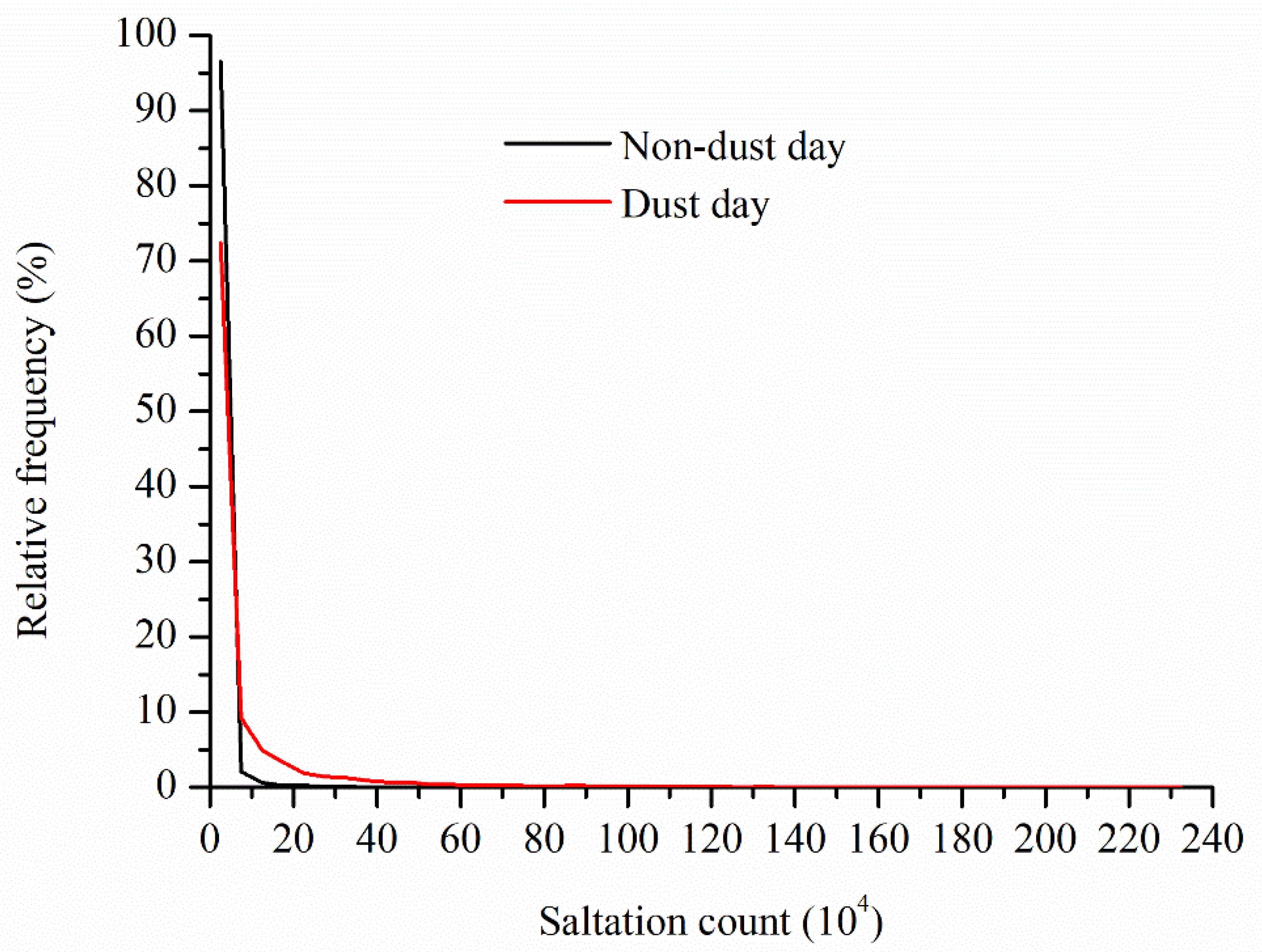
3.5. Saltation Count on Non-Dust Days
4. Discussions
4.1. Atmospheric/Soil Conditions and Threshold Velocities on Non-Dust Days
4.2. Wind Speed Conditions and Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days
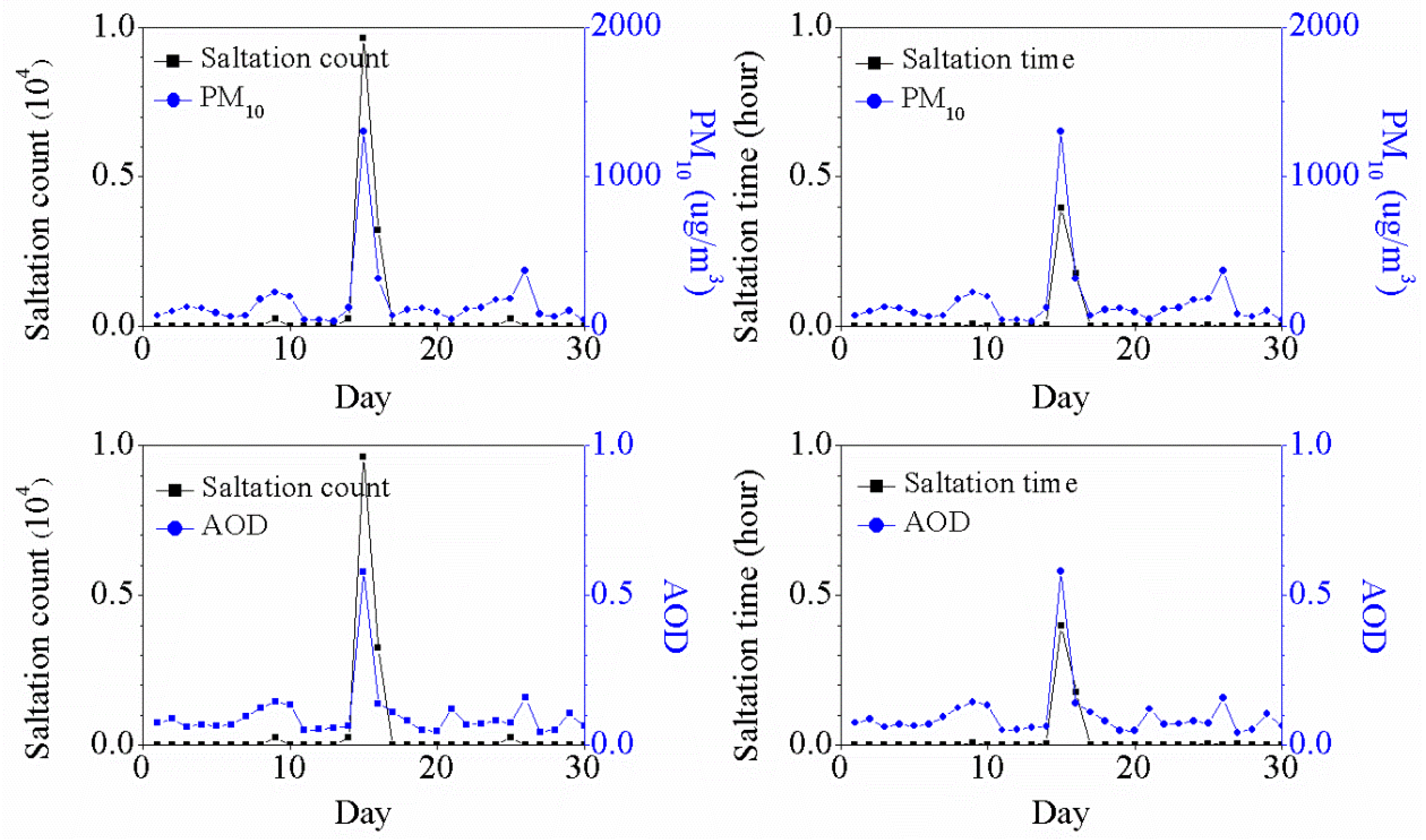
4.3. Saltation Activity and Dust Aerosols on Non-Dust Days
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; William Morrow & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1941; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chepil, W.S. Dynamics of wind erosion: I. Nature of movement of soil by wind. Soil Sci. 1945, 60, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.P. Physics and Modeling of Wind Erosion; Kluwer Academic Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 149–206. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, K.F.; Hotta, S. Wind erosion from cropland in the USA: A review of problems, solutions and prospects. Geoderma 2004, 121, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 12, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Desert dust hazards: A global review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Q.; Li, S.; Webb, N.P.; Zuo, X.A.; Liu, X.Y. Soil organic carbon (SOC) enrichment in aeolian sediments and SOC loss by dust emission in the desert steppe, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillette, D.A. Fine particulate emissions due to wind erosion. Trans. ASAE 1977, 20, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, D.A. Production of dust that may be carried great distances. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 1981, 186, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.P.; Raupach, M.R.; Findlater, P.A. The effect of saltation bombardment on the entrainment of dust by wind. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 12719–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzamostafa, N.; Hagen, L.J.; Stone, L.R.; Skidmore, E.L. Soil aggregate and texture effects on suspension components from wind erosion. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.P. A model for mineral dust emission. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 20239–20254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, T.T.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.S.; Cai, X.U.; Song, Y. Comparison of two different dust emission mechanisms over the Horqin Sandy Land area: Aerosols contribution and size distributions. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 176, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarko, J.; Kucharski, M.; Li, H.L.; Li, H.R. PM2.5 and PM10 emissions by breakage during saltation of agricultural soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. Desert Dust in the Global System; Springer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- McTainsh, G.; Strong, C. The role of aeolian dust in ecosystems. Geomorphology 2007, 89, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Teigell, P.N.; Valladares, B.; Griffin, G.W. The global dispersion of pathogenic microorganisms by dust storms and its relevance to agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2014, 127, 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Goudie, A.S. Desert dust and human health disorders. Environ. Int. 2014, 63, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, C.J.; Michael, S.; Maria, A.L.C.; Albert, A.; Adolfo, C.; Maria, P.Z.; Alejandro, R.G.; Constantino, M.P. Aerosol radiative impact during the summer 2019 heatwave produced partly by an inter-continental Saharan dust outbreak Part 1: Short-wave dust direct radiative effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6455–6479. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, R.P. Saltation of uniform grains in air. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 20, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.R. Soil transport by winds on Mars. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 1979, 84, 4643–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.B.; Qian, G.Q.; Luo, W.Y.; Wang, H.T. Analysis of the mass flux profiles of an aeolian saltating cloud. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111, D16111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockton, P.; Gillette, D. Field measurement of the sheltering effect of vegetation on erodible land surfaces. Land Degrad. Dev. 1990, 2, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. Intermittent saltation. Sedimentology 1997, 44, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, A.C. Evaluation of saltation flux impact responders (Safires) for measuring instantaneous aeolian sand transport intensity. Geomorphology 2004, 59, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, K. New method for estimation of aeolian sand transport rate using ceramic sand flux sensor (UD-101). Sensors 2009, 9, 9058–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, D.J.; Li, B.; Farrell, E.J.; Ellis, J.T.; Cox, W.D.; Maia, L.P.; Sousa, P.H. Measuring aeolian saltation: A comparison of sensors. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 59, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raygosa-Barahona, R.; Ruiz-Martinez, G.; Marino-Tapia, I.; Heyser-Ojeda, E. Design and initial testing of a piezoelectric sensor to quantify aeolian sand transport. Aeolian Res. 2016, 22, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Winter, W.; Van Dam, D.; Delbecque, N.; Verdoodt, A.; Ruessink, B.; Sterk, G. Measuring high spatiotemporal variability in saltation intensity using a low-cost Saltation Detection System: Wind tunnel and field experiments. Aeolian Res. 2018, 31, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, W.; Vanden Abeele, G. Wind borne particle measurements with acoustic sensors. Soil Technol. 1991, 4, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.T.; Sherman, D.J.; Farrell, E.J.; Li, B. Temporal and spatial variability of aeolian sand transport: Implications for field measurements. Aeolian Res. 2012, 3, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Goossens, D.; Riksen, M.J. Evaluating the SandFlow, an acoustic sediment transport sensor. Aeolian Res. 2020, 42, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Yamada, Y.; Ishizuka, M.; Ishimaru, T.; Gao, W.; Zeng, F.J. Measurement of saltation process over gobi and sand dunes in the Taklimakan desert, China, with newly developed sand particle counter. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2005, 110, D18S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.; Bauer, B.; Walker, I.; Hesp, P.; Ollerhead, J.; Delgado-Fernandez, I. Instantaneous and mean aeolian sediment transport rate on beaches: An intercomparison of measurements from two sensor types. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 56, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz, C.H.; Barchyn, T.E. Laboratory and field performance of a laser particle counter for measuring aeolian sand transport. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2011, 116, F01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chapman, C.; Walker, I.J.; Hesp, P.A.; Bauer, B.O.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.; Ollerhead, J. Reynolds stress and sand transport over a foredune. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2013, 38, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.L.; Kok, J.F.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Barchyn, T.E.; Chamecki, M.; Ellis, J.T. High-frequency measurements of aeolian saltation flux: Field-based methodology and applications. Aeolian Res. 2018, 30, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.L.; Ning, Q.Q.; Yu, Y.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Meldaua, L.F.; Liu, J.H. A laser sheet sensor (LASS) for wind-blown sand flux measurement. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.H.; An, Z.S.; Zhang, K.C.; Qu, J.J.; Han, Q.J.; Wang, J.Z. Intermittent aeolian saltation over a Gobi surface: Threshold, saltation layer height, and high-frequency variability. J. Geophys. Res.-Eaerth Surf. 2020, 125, e2019JF005329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.S. Soil moisture effects on sand saltation and dust emission observed over the Horqin Sandy land area in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deoro, L.A.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Threshold wind velocity as an index of soil susceptibility to wind erosion under variable climatic conditions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2009, 20, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchyn, T.E.; Hugenholtz, C.H. Winter variability of aeolian sediment transport threshold on a cold-climate dune. Geomorphology 2012, 177–178, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Mamtimin, A.; He, Q.; Liu, X.C.; Huo, W. Observation of saltation activity at Tazhong area in Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Arid. Land 2013, 5, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.E. Detecting patterns of aeolian transport direction. J. Arid. Environ. 2014, 107, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, X.H.; Shen, S.H.; Yang, F.; He, Q.; Mamtimin, A.; Huo, W.; Liu, X.C. Spatial and temporal variations of blowing dust events in the Taklimakan Desert. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 125, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensit Company. Technical Description for the New Model H11-LIN; Sensit Company: Readlands, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.H.; He, Q.; Mamtimin, A.; Huo, W.; Liu, X.H.; Trake, M. A field experiment on dust emission by wind erosion in the Taklimakan Desert. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Weather Bureau of China. Criterion of Surface Meteorological Observation; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1979; pp. 33–34.
- Stout, J.E. A method for establishing the critical threshold for aeolian transport in the field. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2004, 29, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; He, Q.; Mamtimin, A.; Yang, F.; Huo, W.; Liu, X.C.; Zhao, T.L.; Shen, S.H. Threshold velocity for saltation activity in the Taklimakan Desert. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 4459–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Niu, B.C.; Qu, J.J. Large scale sand saltation over hard surface: A controlled experiment in still air. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, H.T. Intermittency of aeolian saltation. Eur. Phys. J. 2014, 37, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhao, J.F.; Nagashima, H. The distribution of sandstorms in the Taklimakan Desert. J. Arid. Land Study 1996, 1, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.H. Observation and Parameterization on Dust Emission over the Taklimakan Desert. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.N.; Dong, Z.B.; Yang, Z.T.; Han, Z.W.; Zhang, J.K.; Zhang, M.L. Threshold velocities of sand-driving wind in the Taklimakan Desert. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1995, 50, 360–367. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, M.C. Effects of temperature and humidity upon the entrainment of sedimentary particles by wind. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2003, 108, 61–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Deoro, L.A. A field-scale analysis of the dependence of wind erosion threshold velocity on air humidity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L21404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankey, J.B.; Germino, M.J.; Glenn, N.F. Relationships of post-fire aeolian transport to soil and atmospheric conditions. Aeolian Res. 2009, 1, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Yang, F.; Zhou, C.L.; Mamtimin, A.; Huo, W.; He, Q. Improved parameterization for effect of soil moisture on threshold friction velocity for saltation activity based on observations in the Taklimakan Desert. Geoderma 2020, 369, 114322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhao, T.L.; He, Q.; Yang, X.H.; Mamtimin, A.; Yang, F.; Zhou, C.L.; Huo, W.; Wang, M.Z.; Pan, H.L.; et al. Climatic characteristics of floating dust and persistent floating dust over the Tarim basin in the recent 30 years. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2022, 80, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.G.; Chen, S.Y.; Huang, J.P.; Wu, D.Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, G.L.; Ma, X.J.; Chen, Z.Q.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X.H. Influence of dynamic and thermal forcing on the meridional transport of Taklimakan Desert dust in spring and summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Weather | Temperature (°C) | Vapor Pressure (kPa) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Soil Moisture (m3/m3) | Saltation Time (h) | Saltation Count (104) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 08–09 | Dust days | 23.2 | 6.7 | 3.9 | 0.021 | 311.63 | 10,539.5 |
| Non-dust days | 10.3 | 3.3 | 1.4 | 0.019 | 79.88 | 858.3 | |
| 09–10 | Dust days | 19.4 | 4.7 | 3.1 | 0.020 | 270.61 | 6821.5 |
| Non-dust days | 9.4 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.018 | 53.68 | 574.8 |
| Saltation Time (h) | Saltation Count (104) | |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly wind speed (m/s) | 0.81 | 0.91 |
| Diurnal wind speed (m/s) | 0.94 | 0.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Zhou, C.; Yang, F.; Meng, L.; Huo, W.; Mamtimin, A.; He, Q. Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days in the Taklimakan Desert, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092099
Yang X, Zhou C, Yang F, Meng L, Huo W, Mamtimin A, He Q. Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days in the Taklimakan Desert, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(9):2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092099
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xinghua, Chenglong Zhou, Fan Yang, Lu Meng, Wen Huo, Ali Mamtimin, and Qing He. 2022. "Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days in the Taklimakan Desert, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 9: 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092099
APA StyleYang, X., Zhou, C., Yang, F., Meng, L., Huo, W., Mamtimin, A., & He, Q. (2022). Saltation Activity on Non-Dust Days in the Taklimakan Desert, China. Remote Sensing, 14(9), 2099. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14092099









