CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport
Abstract
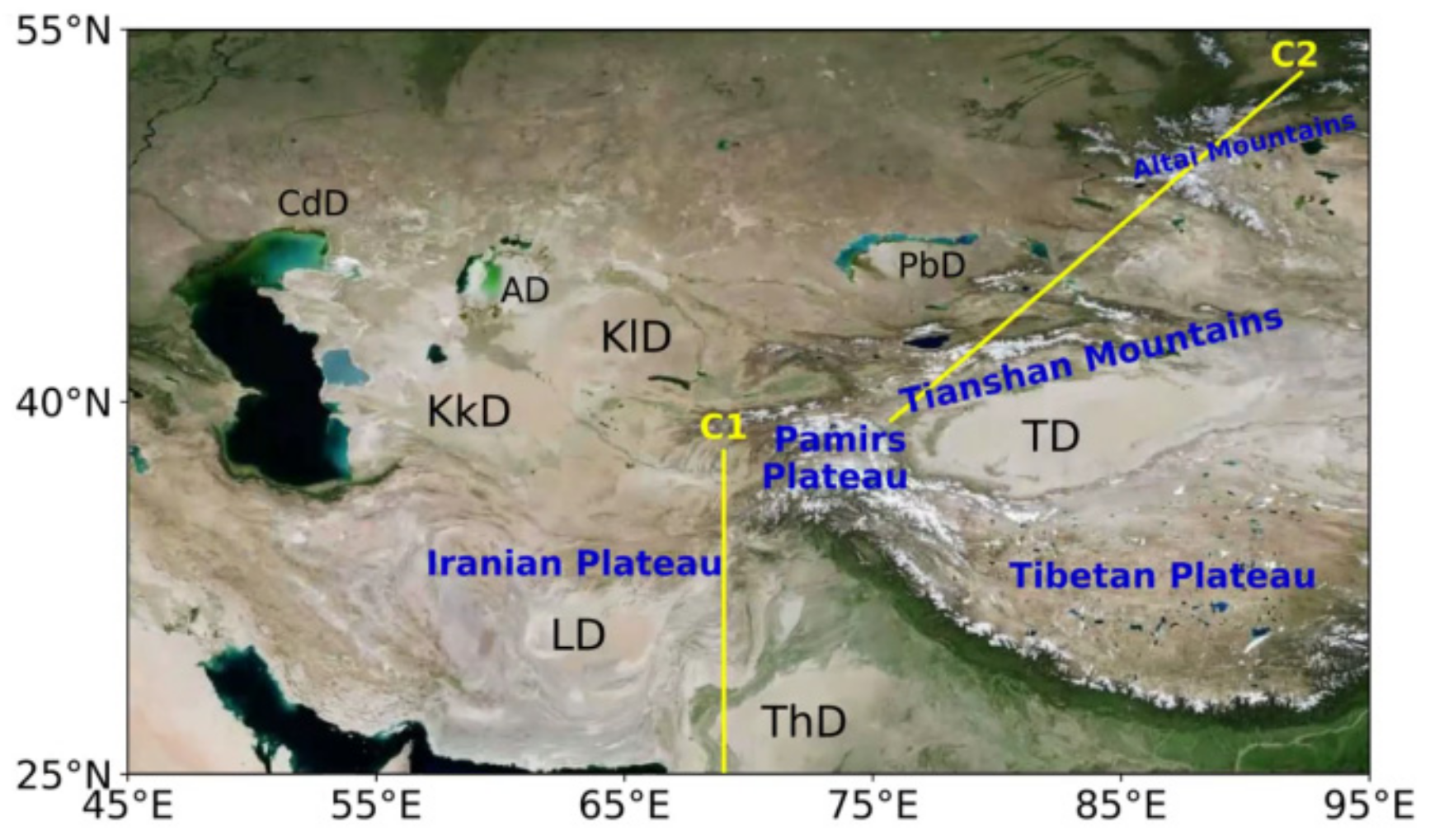
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. CALIOP and MODIS Data
2.2. MERRA-2 Data
2.3. Estimates of Dust Transport Flux and Downstream Contribution
3. Results
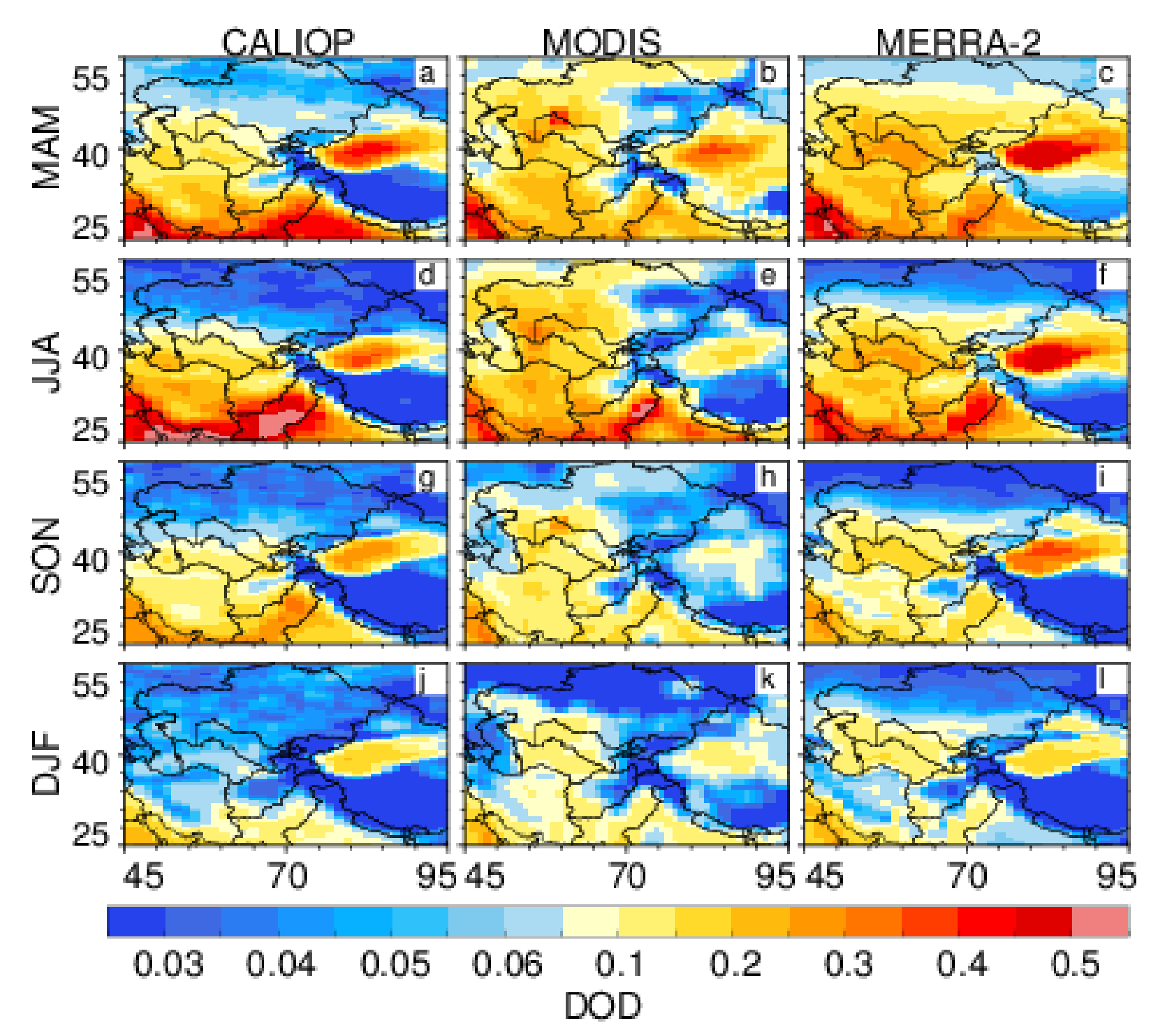
3.1. Climatology of Central Asian Dust
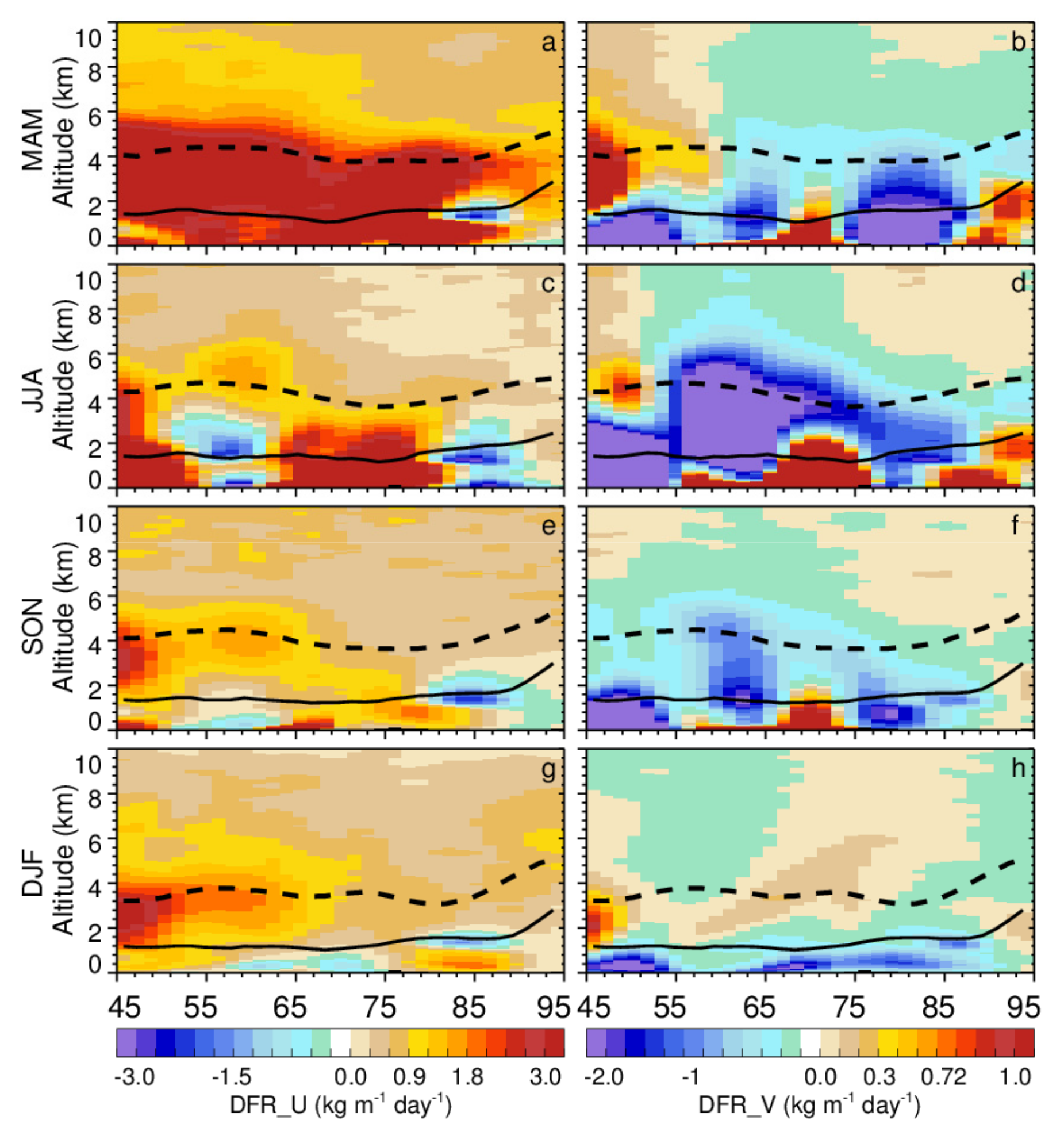
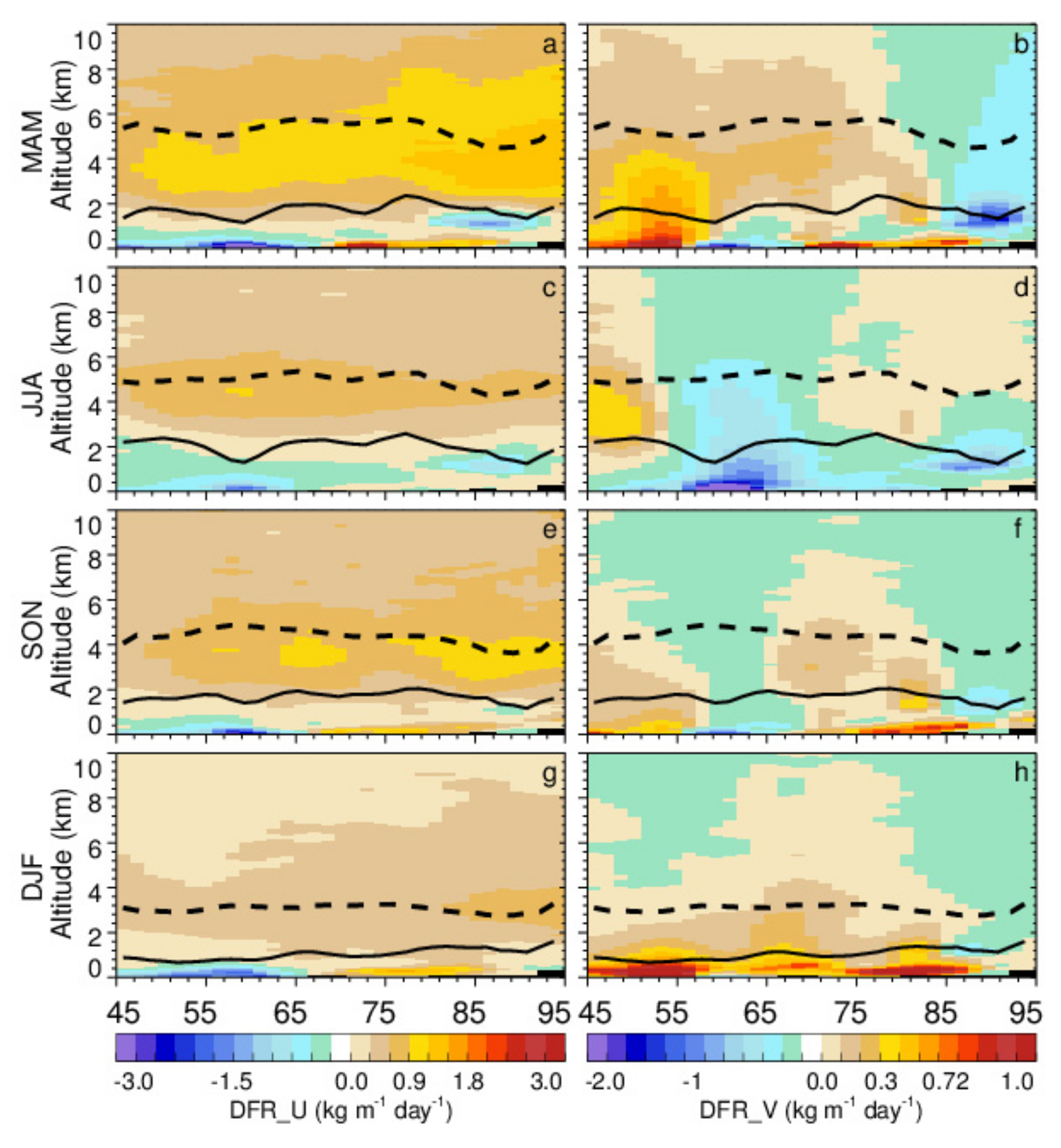
3.2. Climatology of Central Asian Dust Transport
3.2.1. Horizontal Distribution
3.2.2. Vertical Distribution
3.3. Downstream Contribution of Central Asian Dust
4. Discussion
4.1. Uncertainties of Central Asian Dust Transport
4.2. Potential Applications of Dust Transport Flux
5. Conclusions
- -
- The distribution of Central Asian dust DOD exhibits obvious spatial and temporal variability. The DOD of southern Central Asia is larger than that of the northern region throughout the year. Additionally, peak DOD appears in spring and summer, while a trough occurs in winter.
- -
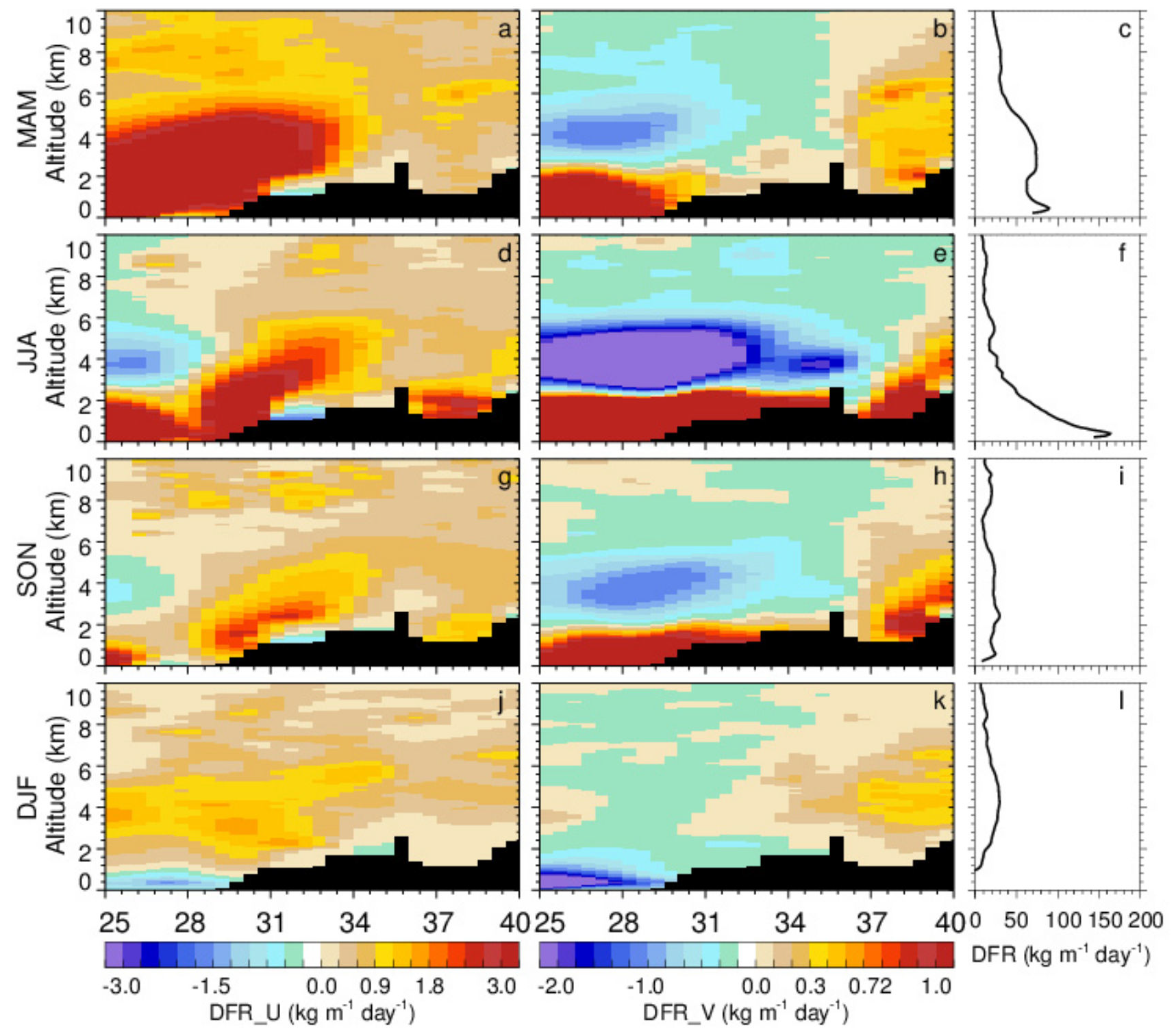
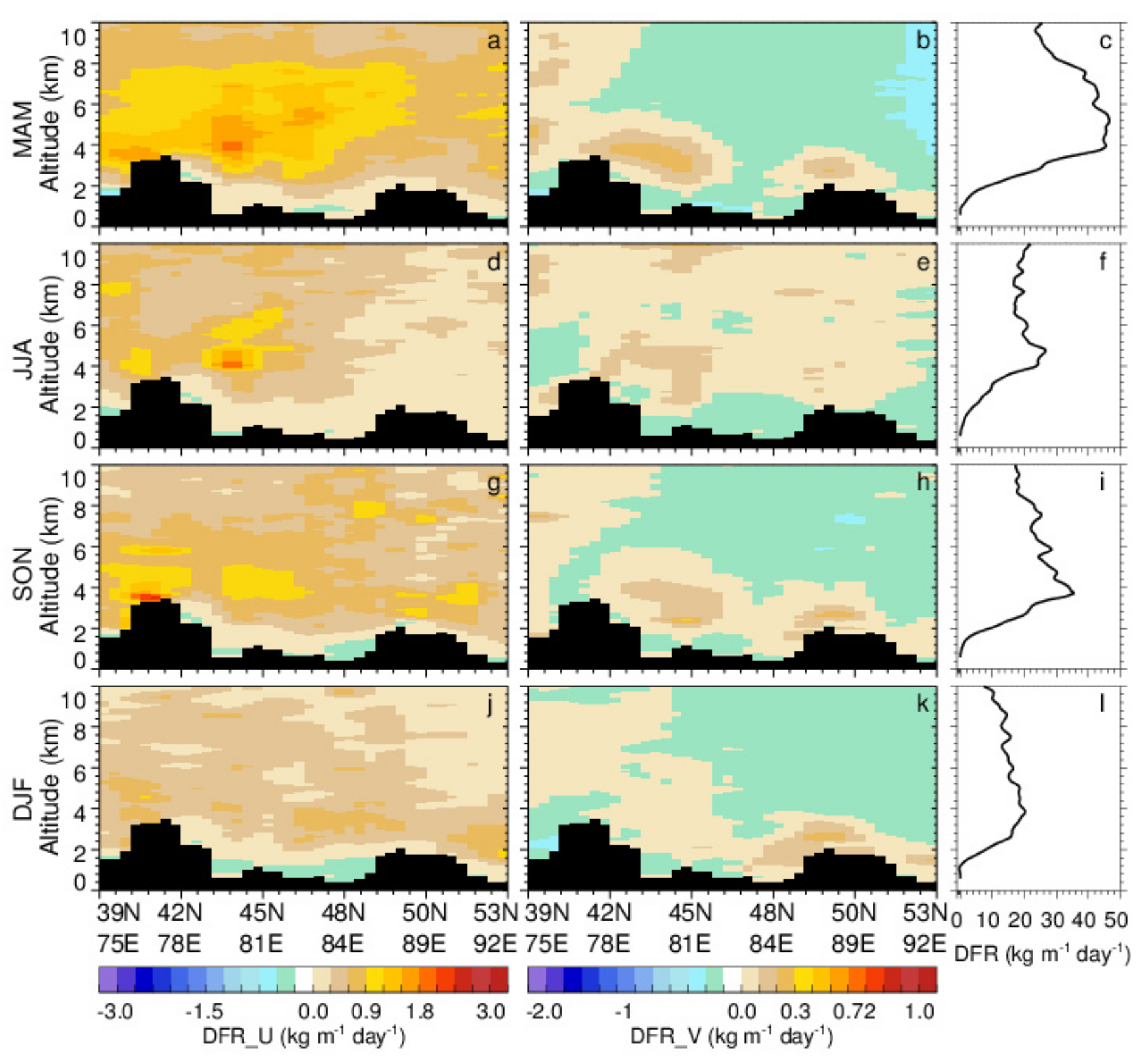
- Central Asian dust can be transported to East and South Asia, with a significant seasonal fluctuation. The dust transport activity is the strongest in spring and the weakest in winter. The Central Asian dust mainly shifts southward in summer due to the South Asian summer monsoon, while it has an obvious tendency of moving eastward in other seasons under the control of the westerly jet.
- -
- The transport of Central Asian dust across the Pamir Plateau to the Tibetan Plateau is also non-negligible, especially in spring, with a DFR of 150 kg m−1 day−1, and in summer, with a DFR of 90 kg m−1 day−1.
- -
- Despite the consistent distribution pattern between the CALIOP observation and MERRA-2 reanalysis for both DOD and DFR, their magnitudes are different. Compared to CALIOP DOD, MERRA-2 DOD is larger over the Central Asian dust source regions and their surrounding areas, especially in Kazakhstan, while it is smaller in remote regions (i.e., Pakistan and the Indian peninsula). However, the MERRA-2 can underestimate the DFR in all regions throughout the year. This could be due to the set scheme of dependence on dust size, dust emission, and deposition in the MERRA-2 models.
- -
- Based on CALIOP observations, the annual downstream contribution of Central Asian to South Asia is the largest, with a value of 164.01 Tg (accounting about 68% of the total contribution from Central Asia), while the contribution to East Asia is only 78.36 Tg. However, these contributions estimated from MERRA-2 are 58.52 Tg and 78.36 Tg, which are only 0.36 and 0.84 times that of CALIOP, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xi, X.; Sokolik, I.N. Dust interannual variability and trend in Central Asia from 2000 to 2014 and their climatic linkages. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12175–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H. Temporal variation of dust emissions in dust sources over Central Asia in recent decades and the climate linkages. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 222, 117176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, F.; Yang, S.; Xia, N.; Ariken, M. Exploring the spatial-temporal characteristics of the aerosol optical depth (AOD) in Central Asia based on the moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; Derose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yao, T.; Xu, B.; Tian, L.; Li, Z.; Duan, K. Seasonal variations of dust record in the Muztagata ice cores. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 2506–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Edwards, R.; Wu, L.; Zhou, P. Temporal characteristics of mineral dust particles in precipitation of Urumqi River Valley in Tian Shan, China: A comparison of alpine site and rural site. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Gao, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, W. Concentration and composition of dust particles in surface snow at Urumqi Glacier No. 1, Eastern Tien Shan. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 74, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobakht, M.; Shahgedanova, M.; White, K. New Inventory of Dust Emission Sources in Central Asia and Northwestern China Derived from MODIS Imagery Using Dust Enhancement Technique. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Gong, S.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Lu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ke, H.; Zhang, H. Impacts of long-range transports from Central and South Asia on winter surface PM2.5 concentrations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, D.; Wu, G. Saline dust storms and their ecological impacts in arid regions. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sternberg, T.; Edwards, M. Desert Dust and Health: A Central Asian Review and Steppe Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Abuduwaili, J.; Samat, A.; Ma, L. A review on the research of modern aeolian dust in Central Asia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A Satellite View of Aerosols in the Climate System. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, R.; Nishizawa, T.; Aoyagi, T. Vertical profiles of aerosol optical properties and the solar heating rate estimated by combining sky radiometer and lidar measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 3223–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoj, V.; Rasch, P.J.; Wang, H.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ma, P.-L.; Landu, K.; Singh, B. Short-term modulation of Indian summer monsoon rainfall by West Asian dust. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Lin, C.; Gui, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, Y. Characterization of dust activation and their prevailing transport over East Asia based on multi-satellite observations. Atmos. Res. 2021, 265, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunari, T.J.; Koster, R.D.; Lau, W.K.M.; Kim, K. Impact of snow darkening via dust, black carbon, and organic carbon on boreal spring climate in the Earth system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5485–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Lei, J.; Sha, Y.; Liu, X. Snow-darkening versus direct radiative effects of mineral dust aerosol on the Indian summer monsoon onset: Role of temperature change over dust sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1605–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Jian, B.; Huang, Z.; Yan, H. Climatology of Dust-Forced Radiative Heating Over the Tibetan Plateau and Its Surroundings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Kang, S.; Sprenger, M.; Tao, S.; Du, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Meng, W. Effects of black carbon and mineral dust on glacial melting on the Muz Taw glacier, Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Fan, K. Simulation of dust aerosol radiative feedback using the Global Transport Model of Dust: 1. Dust cycle and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J.; Galayeva, O.; Semenov, O.; Bazarbayeva, T. Aeolian transportation of sand and dust in the Aral Sea region. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opp, C.; Groll, M.; Aslanov, I.; Lotz, T.; Vereshagina, N. Aeolian dust deposition in the southern Aral Sea region (Uzbekistan): Ground-based monitoring results from the LUCA project. Quat. Int. 2017, 429, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, H.; Gu, W.; Gao, J.; Jian, X.; Shi, G.; Zhu, B.; Xie, L.; Guo, L.; Gao, X.; et al. Hygroscopic Properties of Saline Mineral Dust From Different Regions in China: Geographical Variations, Compositional Dependence, and Atmospheric Implications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 10844–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Claiborn, C.; Lei, J.-Q.; Vaughan, J.; Wu, S.-X.; Li, S.-Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.-D.; Huang, S.-Y.; et al. Aeolian dust in Central Asia: Spatial distribution and temporal variability. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 238, 117734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machalett, B.; Oches, E.A.; Frechen, M.; Zöller, L.; Hambach, U.; Mavlyanova, N.G.; Marković, S.B.; Endlicher, W. Aeolian dust dynamics in central Asia during the Pleistocene: Driven by the long-term migration, seasonality, and permanency of the Asiatic polar front. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008, 9, Q08Q09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Chu, A.; Levy, R.; Remer, L.; Kaufman, Y.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Ginoux, P.; Gao, Q.X. Aerosol distribution in the Northern Hemisphere during ACE-Asia: Results from global model, satellite observations, and Sun photometer meas-urements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Gu, X.F.; Xu, H.; Yu, T.; Zheng, F.J. Assessment of OMI near-UV aerosol optical depth over Central and East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rupakheti, D.; Rupakheti, M.; Yin, X.F.; Hofer, J.; Rai, M.; Hu, Y.L.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Kang, S.C. Modifications in aerosol physical, optical and radiative properties during heavy aerosol events over Dushanbe, Central Asia. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, J.; Althausen, D.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Makhmudov, A.N.; Nazarov, B.I.; Schettler, G.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H.; Fomba, K.W.; Mueller, K.; et al. Long-term profiling of mineral dust and pollution aerosol with multiwavelength polarization Raman lidar at the Central Asian site of Dushanbe, Tajikistan: Case studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14559–14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ming, J. Aerosol Optical Properties Measured Using a PAX in Central Asia from 2016 to 2019 and the Climatic and Environmental Outlooks. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Sepehr, A. Statistical evaluation of the dust events at selected stations in Southwest Asia: From the Caspian Sea to the Arabian Sea. Catena 2018, 165, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issanova, G.; Abuduwaili, J.; Kaldybayev, A.; Semenov, O.; Dedova, T. Dust Storms in Kazakhstan: Frequency and Division. J. Geol. Soc. India 2015, 85, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Orlovsky, L. Dust storms in Central Asia: Spatial and temporal variations. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 85, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.-P.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.R.; et al. The CALIPSO Automated Aerosol Classification and Lidar Ratio Selection Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Kar, J.; Zeng, S.; Tackett, J.; Vaughan, M.; Avery, M.; Pelon, J.; Getzewich, B.; Lee, K.-P.; Magill, B.; et al. Discriminating between clouds and aerosols in the CALIOP version 4.1 data products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 703–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.Y.; Chiba, M. A numerical study of the contributions of dust source regions to the global dust budget. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davitashvili, T.; Samkharadze, I. Study of Aeolian transfer of mineral dust from deserts to the territory of Georgia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Dong, C.H. A review on East Asian dust storm climate, modelling and monitoring. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G. Sensitivity of simulating a dust storm over Central Asia to different dust schemes using the WRF-Chem model. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 207, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, M.; Shao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Ishizuka, M.; Mikami, M.; Leys, J.F. Further development of a parameterization for convective turbulent dust emission and evaluation based on field observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 10441–10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, I.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Ginoux, P.; Fan, S. Dust transport and deposition observed from the Terra-Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) spacecraft over the Atlantic ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Chin, M.; Bian, H.; Yuan, T.; Prospero, J.; Omar, A.H.; Remer, L.A.; Winker, D.M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Quantification of trans-Atlantic dust transport from seven-year (2007–2013) record of CALIPSO lidar measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 159, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tan, Q.; Chin, M.; Remer, L.A.; Kahn, R.A.; Bian, H.; Kim, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Omar, A.H.; et al. Estimates of African Dust Deposition Along the Trans-Atlantic Transit Using the Decadelong Record of Aerosol Measurements from CALIOP, MODIS, MISR, and IASI. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7975–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebiyi, A.A.; Kok, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Ito, A.; Ridley, D.A.; Nabat, P.; Zhao, C. Dust Constraints from joint Observational-Modelling-experiMental analysis (DustCOMM): Comparison with measurements and model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 829–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kok, J.F.; Adebiyi, A.A.; Albani, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Checa-Garcia, R.; Chin, M.; Colarco, P.R.; Hamilton, D.S.; Huang, Y.; Ito, A.; et al. Contribution of the world’s main dust source regions to the global cycle of desert dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 8169–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, T.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Jian, B.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J. New insights into the Asian dust cycle derived from CALIPSO lidar measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 272, 112906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Zhou, T.; Dong, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S.; Bi, J.; Shi, J. Investigation of aerosol absorption with dual-polarization lidar observations. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 7028–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Ginoux, P.; Shen, J. Global dust optical depth climatology derived from CALIOP and MODIS aerosol retrievals on decadal timescales: Regional and interannual variability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 13369–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Tan, Q.; Chin, M.; Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Smith, S.J.; Yuan, T.; Shi, Y. Interannual variability and trends of combustion aerosol and dust in major continental outflows revealed by MODIS retrievals and CAM5 simulations during 2003-2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Ignatov, A.; Zhou, X. Exploring MERRA-2 global meteorological and aerosol reanalyses for improved SST retrieval. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Liu, D.; Kumar, K.R.; Wang, M.; Devi, N.L. Global distribution of maritime low clouds with an emphasis on different aerosol types and meteorological parameters inferred from multi-satellite and reanalysis data during 2007–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 246, 118082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Che, H.; Gui, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Can MERRA-2 Reanalysis Data Reproduce the Three-Dimensional Evolution Characteristics of a Typical Dust Process in East Asia? A Case Study of the Dust Event in May 2017. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousefi, R.; Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Shaheen, A. Long-term aerosol optical depth trend over Iran and identification of dominant aerosol types. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchard, V.; Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.R.; Govindaraju, R.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Ziemba, L.D.; et al. The MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis, 1980 Onward. Part II: Evaluation and Case Studies. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6851–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yin, Z.; An, Z. Global Impact of ENSO on Dust Activities with Emphasis on the Key Region from the Arabian Peninsula to Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Chen, X.; Mamadjanov, Y.; Tan, L. Atmospheric dust dynamics in southern Central Asia: Implications for buildup of Tajikistan loess sediments. Atmos. Res. 2019, 229, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, D. Temporal Variability and Potential Diffusion Characteristics of Dust Aerosol Originating from the Aral Sea Basin, Central Asia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, M.; Opp, C.; Aslanov, I. Spatial and temporal distribution of the dust deposition in Central Asia-results from a long term monitoring program. Aeolian Res. 2012, 9, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Contreras, R.; Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Christopher, S. A study of 15-year aerosol optical thickness and direct shortwave aerosol radiative effect trends using MODIS, MISR, CALIOP and CERES. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13849–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Sturman, A.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Alizadeh-Choobari, O.; Sturman, A.; Zawar-Reza, P. A global satellite view of the seasonal distribution of mineral dust and its correlation with atmospheric circulation. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2014, 68, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Winker, D.; Trepte, C. A height resolved global view of dust aerosols from the first year CALIPSO lidar measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atoms. 2008, 113, D16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestakis, E.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Solomos, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Chimot, J.; Che, H.; Alexandri, G.; Binietoglou, I.; et al. Nine-year spatial and temporal evolution of desert dust aerosols over South and East Asia as revealed by CALIOP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1337–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Sawyer, V.; Shi, Y.; Colarco, P.R.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Wang, Y.; Remer, L.A. Exploring systematic offsets between aerosol products from the two MODIS sensors. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4073–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uno, I.; Eguchi, K.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Uematsu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Asian dust transported one full circuit around the globe. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Eguchi, K.; Yumimoto, K.; Liu, Z.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N.; Shimizu, A.; Takemura, T. Large Asian dust layers continuously reached North America in April 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7333–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, A. Seasonal and interannual variations of atmospheric dust aerosols in mid and low latitudes of Asia-A comparative study. Atmos. Res. 2020, 244, 105036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tang, J.; Sun, M.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Han, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Identifying a transport mechanism of dust aerosols over South Asia to the Tibetan Plateau: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 758, 143714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Yang, K.; Darmenov, A.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; et al. Understanding processes that control dust spatial distributions with global climate models and satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13835–13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Chin, M.; Yu, H.; Diehl, T.; Tan, Q.; Kahn, R.A.; Tsigaridis, K.; Bauer, S.E.; Takemura, T.; Pozzoli, L.; et al. Sources, sinks, and transatlantic transport of North African dust aerosol: A multimodel analysis and comparison with remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 6259–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Tackett, J.L.; Giles, D.; Kar, J.; Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Trepte, C.R. CALIOP and AERONET aerosol optical depth comparisons: One size fits none. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4748–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denjean, C.; Bourrianne, T.; Burnet, F.; Mallet, M.; Maury, N.; Colomb, A.; Dominutti, P.; Brito, J.; Dupuy, R.; Sellegri, K.; et al. Overview of aerosol optical properties over southern West Africa from DACCIWA aircraft measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4735–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Hua, W.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J.; Xie, H. Profiling Dust Mass Concentration in Northwest China Using a Joint Lidar and Sun-Photometer Setting. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dousari, A.M.; Al-Awadhi, J. Dust fallout in northern Kuwait, major sources and characteristics. Kuwait J. Sci. 2012, 39, 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, S.L.; Clarke, M.L.; Elatrash, M.S. Field measurements of desert dust deposition in Libya. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3881–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Brabander, D.J.; Panek, L.A.; Besancon, J.R. Enrichment of potentially toxic elements in the fine fraction of soils from Iraq and Kuwait. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3545–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.-M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s Rapid Warming Accompanies Cryospheric Melt and Water Cycle Intensification and Interactions between Monsoon and Environment: Multidisciplinary Approach with Observations, Modeling, and Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | Annual | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | CALIOP | 55.59 | 69.03 | 26.08 | 13.31 | 164.01 |
| MERRA-2 | 24.10 | 20.77 | 5.94 | 7.71 | 58.52 | |
| C2 | CALIOP | 30.84 | 16.70 | 19.48 | 11.34 | 78.36 |
| MERRA-2 | 29.31 | 16.05 | 11.63 | 9.18 | 66.17 |
| MAM | JJA | SON | DJF | Annual | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 14.26 (25.7%) | 17.93 (26.0%) | 6.57 (25.7%) | 3.38 (25.2%) | 42.14 (25.7%) |
| C2 | 6.89 (22.3%) | 3.92 (23.5%) | 4.33 (22.2%) | 2.61 (23.0%) | 17.75 (22.7%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Wang, T.; Tan, R.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; He, S.; Dong, Y.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J. CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061416
Han Y, Wang T, Tan R, Tang J, Wang C, He S, Dong Y, Huang Z, Bi J. CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(6):1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061416
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Ying, Tianhe Wang, Ruiqi Tan, Jingyi Tang, Chengyun Wang, Shanjuan He, Yuanzhu Dong, Zhongwei Huang, and Jianrong Bi. 2022. "CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport" Remote Sensing 14, no. 6: 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061416
APA StyleHan, Y., Wang, T., Tan, R., Tang, J., Wang, C., He, S., Dong, Y., Huang, Z., & Bi, J. (2022). CALIOP-Based Quantification of Central Asian Dust Transport. Remote Sensing, 14(6), 1416. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14061416








