A Semianalytical Algorithm for Estimating Water Transparency in Different Optical Water Types from MERIS Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
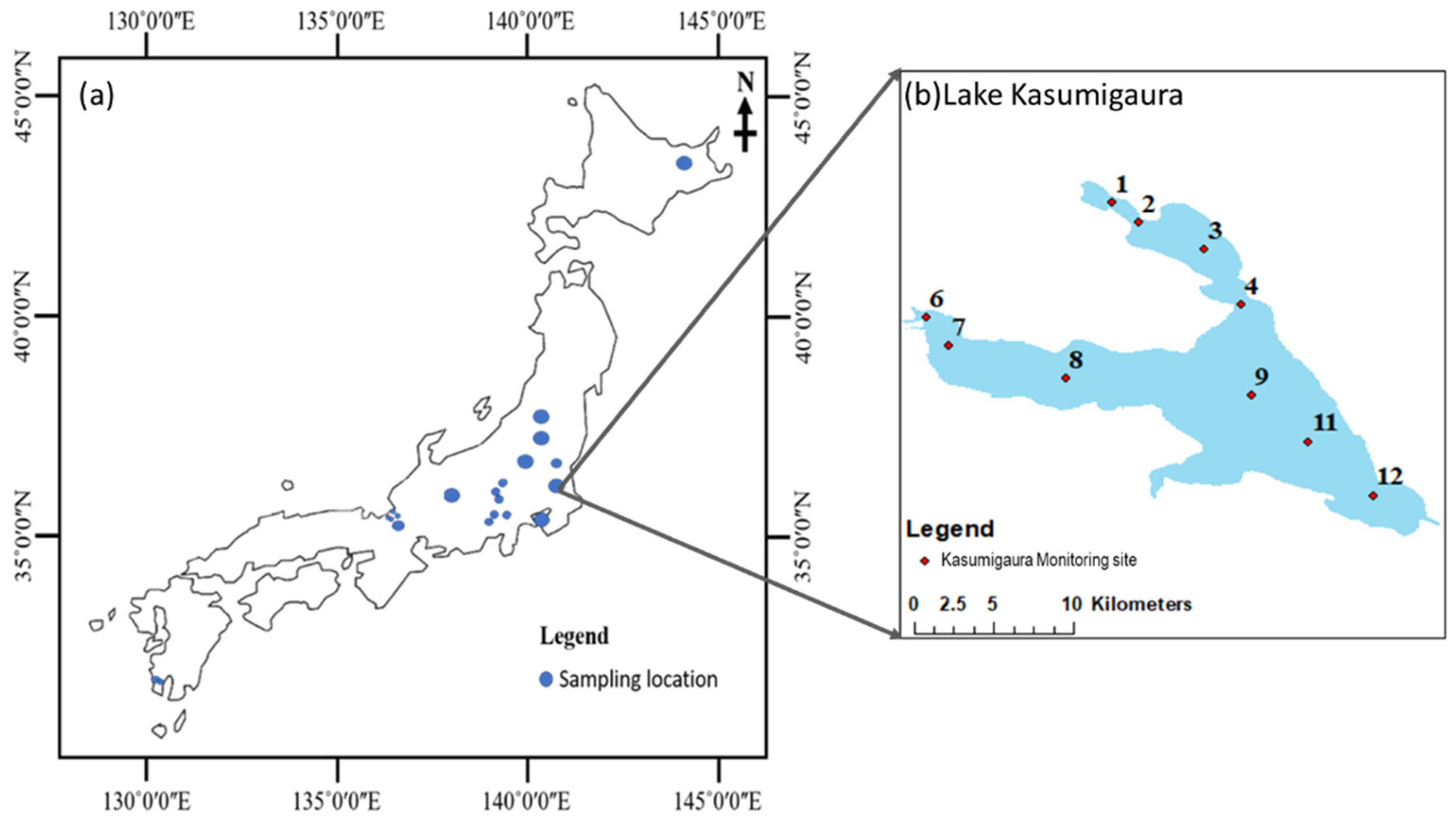
2.1.1. In Situ Data Collection
2.1.2. Synthetic Data Collection and Generation
2.1.3. Satellite Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Development of a Estimation Algorithm
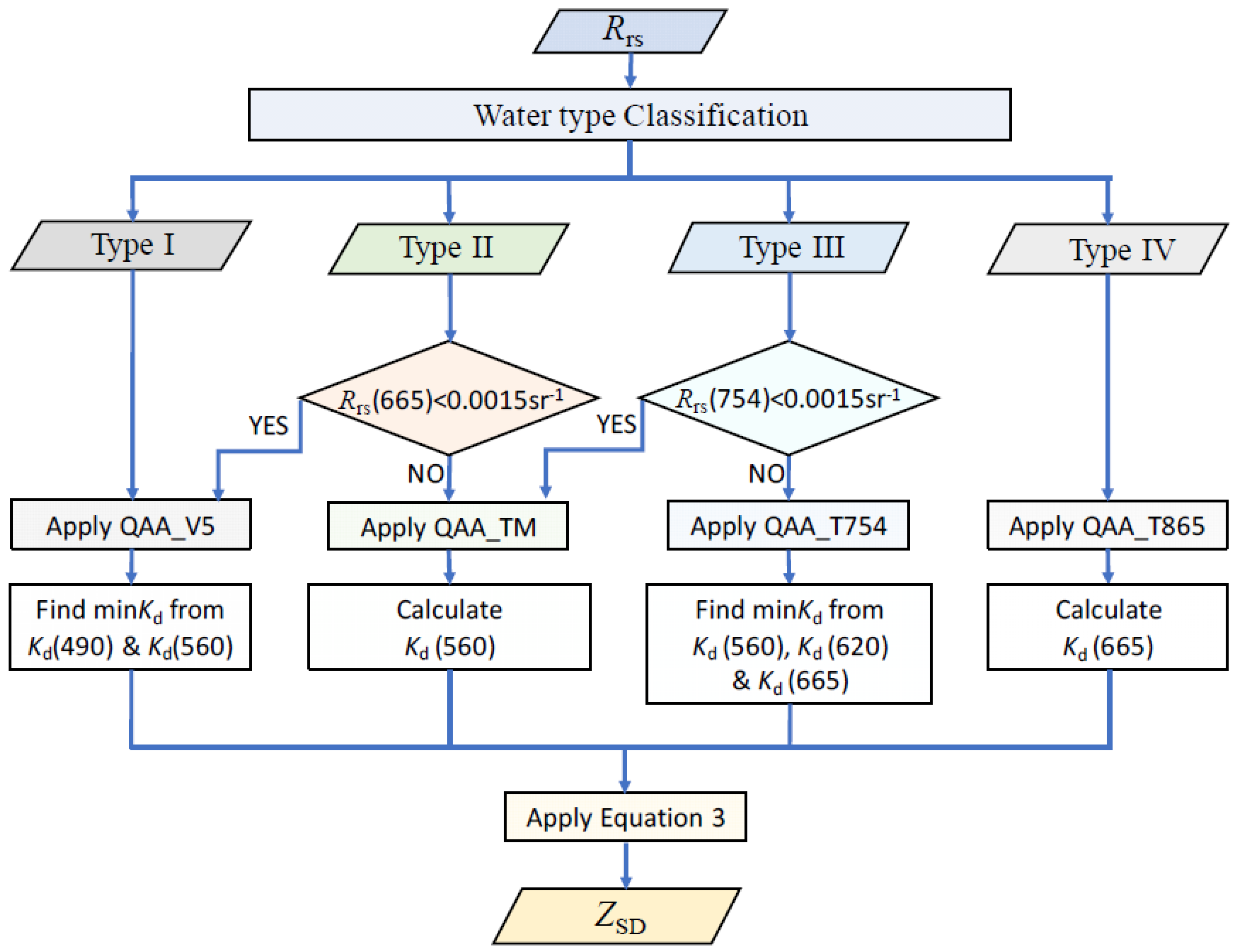
2.2.1. The Original Jiang19 Algorithm
2.2.2. Development of a New Estimation Algorithm
2.3. Accuracy Assessment
3. Results
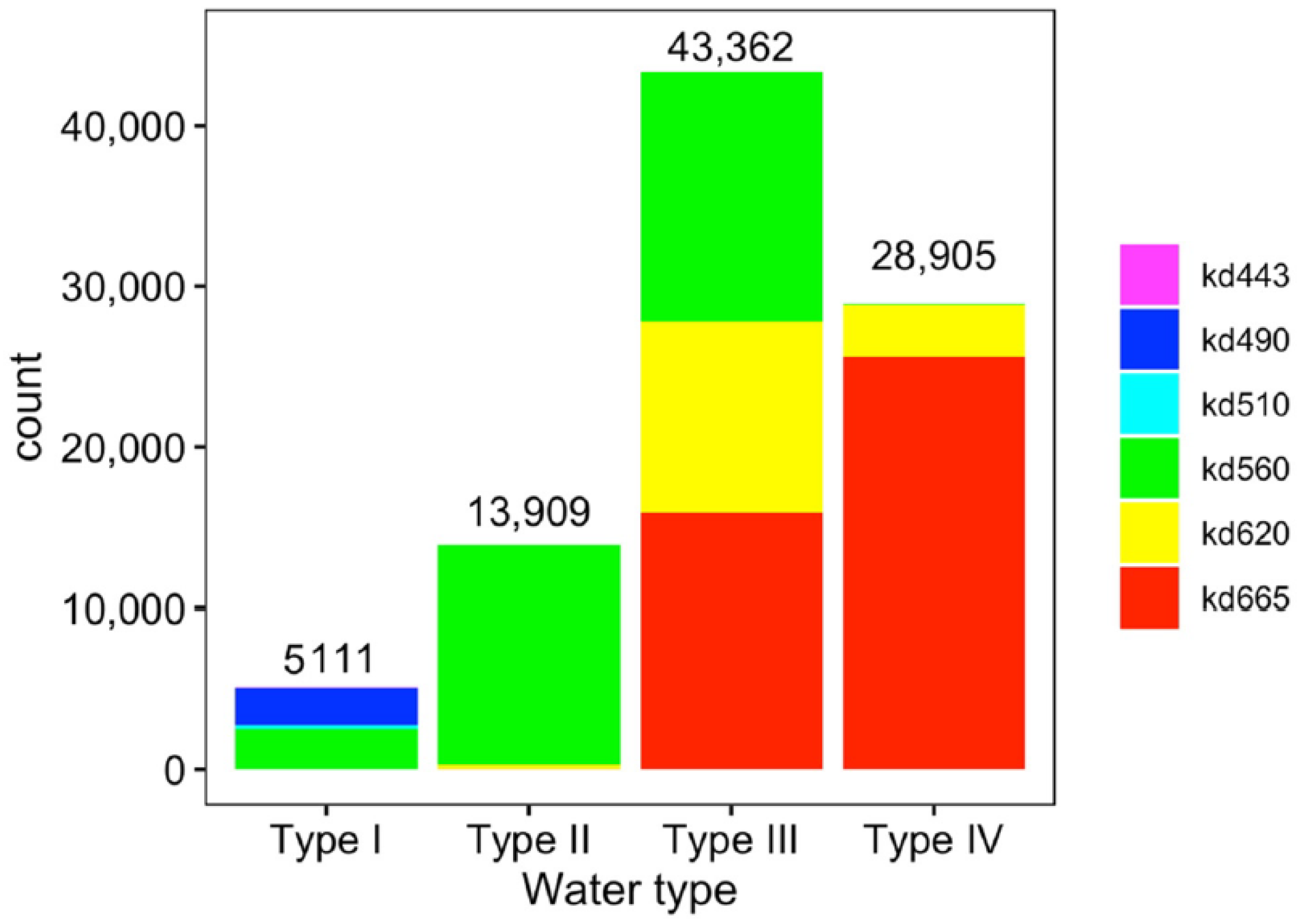
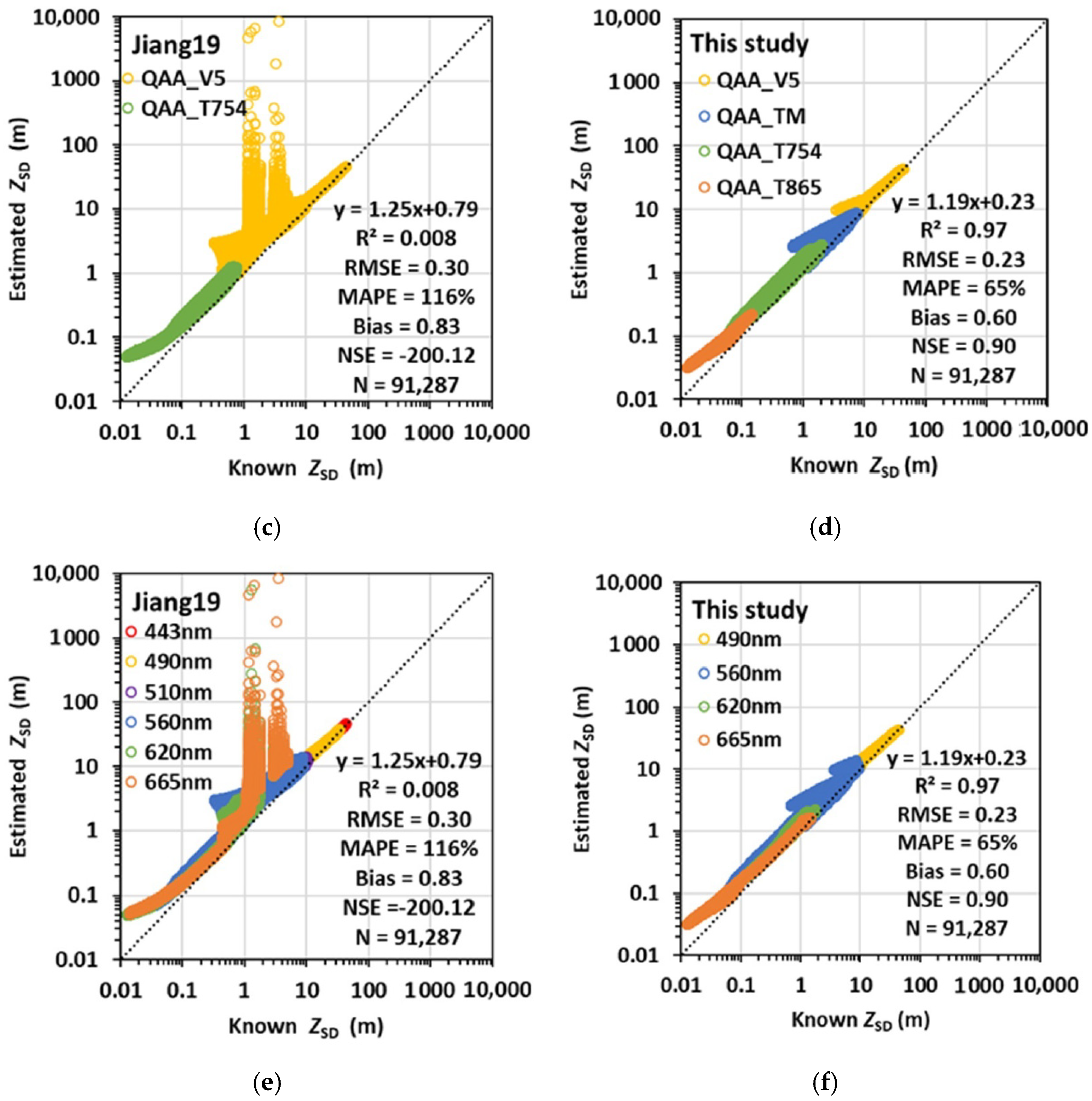
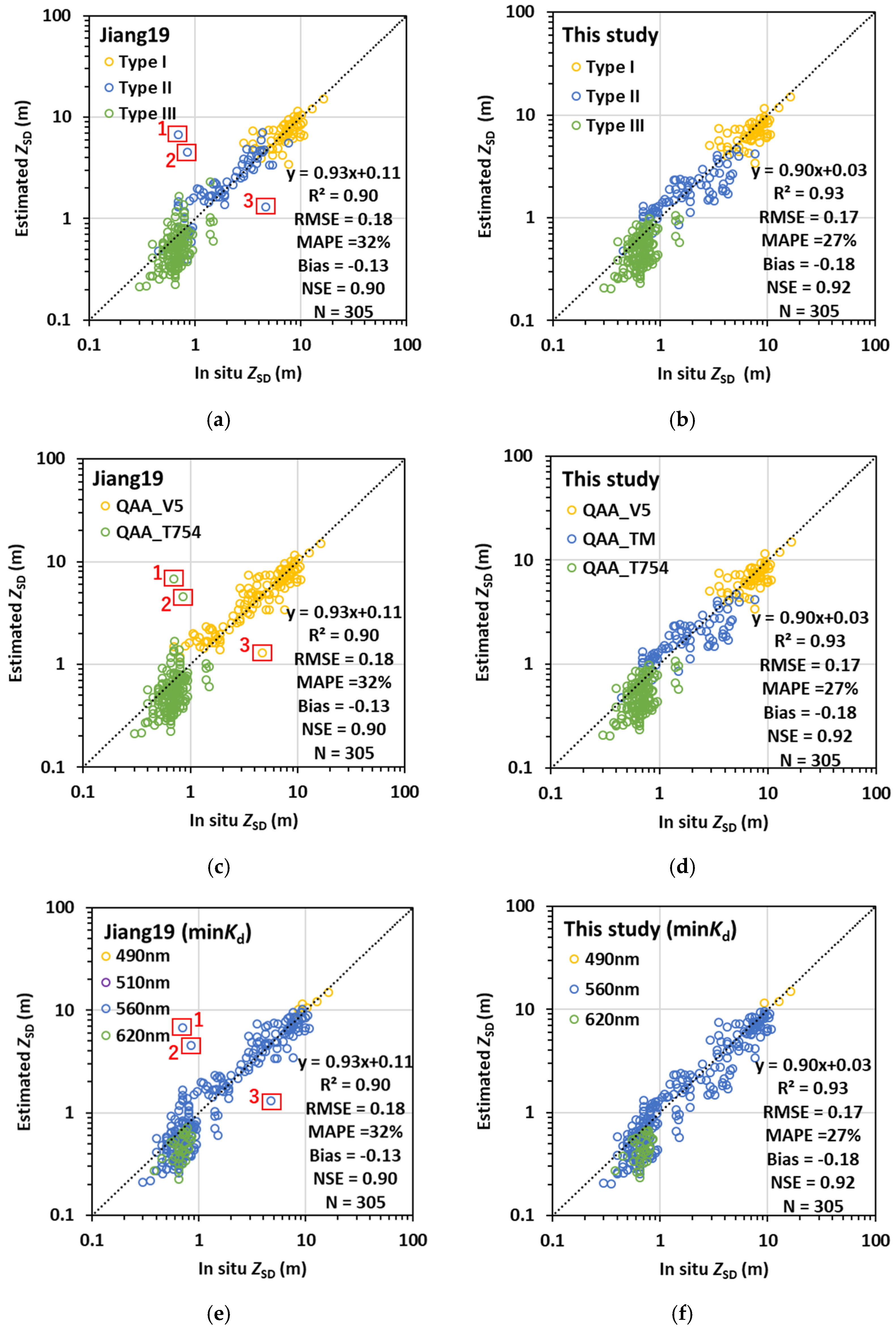
3.1. Validation Using Synthetic Datasets I and III
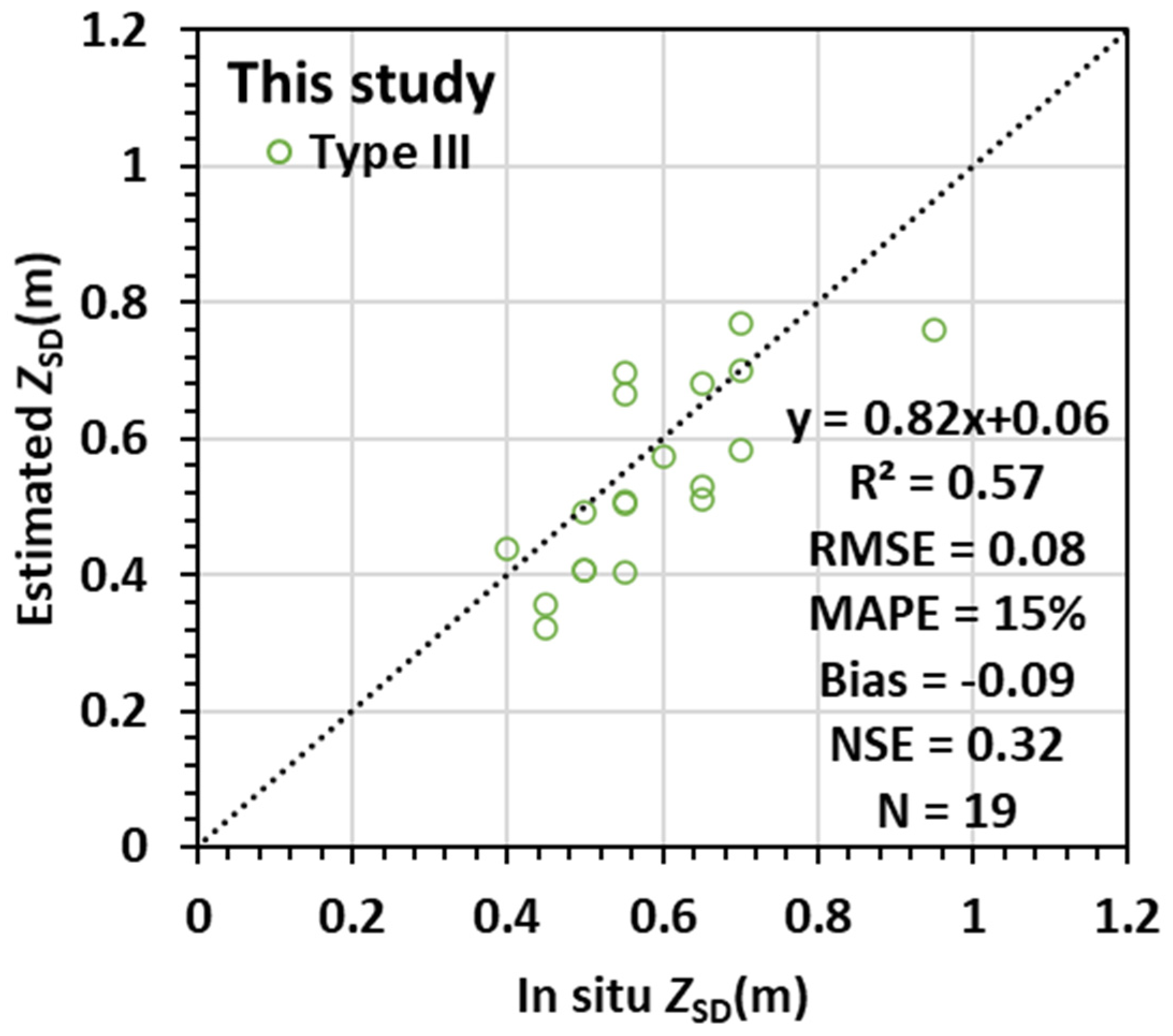
3.2. Validation Using In Situ Dataset
3.3. Validation Using MERIS Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swift, T.J.; Perez-Losada, J.; Schladow, S.G.; Reuter, J.E.; Jassby, A.D.; Goldman, C.R. Water clarity modeling in Lake Tahoe: Linking suspended matter characteristics to Secchi depth. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.; Babin, M.; Mangin, A.; Hembise, O. Estimation of light penetration, and horizontal and vertical visibility in oceanic and coastal waters from surface reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, C06003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Laamanen, M. Long-term changes in Secchi depth and the role of phytoplankton in explaining light attenuation in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 102–103, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukushima, T.; Matsushita, B.; Oyama, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Yang, W.; Terrel, M.; Kawamura, S.; Takegahara, A. Semi-analytical prediction of Secchi depth using remote-sensing reflectance for lakes with a wide range of turbidity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 780, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.; Alcântara, E.; Watanabe, F.; Imai, N. Retrieval of Secchi disk depth from a reservoir using a semi-analytical scheme. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Secchi Disk Depth Estimation from China’s New Generation of GF-5 Hyperspectral Observations Using a Semi-Analytical Scheme. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E.; Brezonik, P.L. A 20-year Landsat water clarity census of Minnesota’s 10,000 lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondie, A.; Mengistu, S.; Vijverberg, J.; Dejen, E. Seasonal variation in primary production of a large high altitude tropical lake (Lake Tana, Ethiopia): Effects of nutrient availability and water transparency. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Langeland, K.A.; Linda, S.B.; Haller, W.T. Relations between water transparency and maximum depth of macrophyte colonization in lakes. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 1985, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2 Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holland, R.E. Changes in Planktonic Diatoms and Water Transparency in Hatchery Bay, Bass Island Area, Western Lake Erie Since the Establishment of the Zebra Mussel. J. Great Lakes Res. 1993, 19, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, M.; Barry, J.; Mills, D.; Gowen, R.; Foden, J.; Sivyer, D.; Tett, P. Relationships between suspended particulate material, light attenuation and Secchi depth in UK marine waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, I.M.; Loftin, C.S.; Sader, S.A. High-frequency remote monitoring of large lakes with MODIS 500 m imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Gao, J.; Sun, D.; Tian, M. Monitoring Water Transparency in Shallow and Eutrophic Lake Waters Based on GOCI Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sòria-Perpinyà, X.; Pereira-Sandoval, M.; Ruiz-Verdú, A.; Soria, J.M.; Delegido, J.; Vicente, E.; Moreno, J.; Urrego, E.P. Monitoring water transparency of a hypertrophic lake (the Albufera of València) using multitemporal Sentinel-2 satellite images. Limnetica 2020, 39, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Song, J.; Han, J.; Ao, D. A novel index for assessing the water quality of urban landscape lakes based on water transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.; Babin, M.; Hembise, O.; Mangin, A.; Garnesson, P. Ocean transparency from space: Validation of algorithms estimating Secchi depth using MERIS, MODIS and SeaWiFS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2986–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Bilal, M. Variations of transparency derived from GOCI in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 12191–12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Lin, G. Deriving inherent optical properties from classical water color measurements: Forel-Ule index and Secchi disk depth. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 7642–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Setiawan, F.; Vundo, A. An improved algorithm for estimating the Secchi disk depth from remote sensing data based on the new underwater visibility theory. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vundo, A.; Matsushita, B.; Jiang, D.; Gondwe, M.; Hamzah, R.; Setiawan, F.; Fukushima, T. An Overall Evaluation of Water Transparency in Lake Malawi from MERIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duntley, S.Q. The Visibility of Submerged Objects; Visibility Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Scripps Institution of Oceanography: San Diego, CA, USA, 1952; Volume 74. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, D.G.; Roberts, E.M.; Hoguane, A.M.; Fall, K.A.; Massey, G.M.; Friedrichs, C.T. Secchi Disk Measurements in Turbid Water. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uudeberg, K.; Ansko, I.; Põru, G.; Ansper, A.; Reinart, A. Using Optical Water Types to Monitor Changes in Optically Complex Inland and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Lee, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, B.; Sun, Z. Remote Sensing of Secchi Depth in Highly Turbid Lake Waters and Its Application with MERIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Thompson, J.R.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; et al. Observations of water transparency in China’s lakes from space. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 92, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Lei, S.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Retrieval of Secchi Disk Depth in Turbid Lakes from GOCI Based on a New Semi-Analytical Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. Retrieval of Inherent Optical Properties for Turbid Inland Waters from Remote-Sensing Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3761–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Pahlevan, N.; Gurlin, D.; Lehmann, M.K.; Fichot, C.G.; Schalles, J.; Loisel, H.; Binding, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Remotely estimating total suspended solids concentration in clear to extremely turbid waters using a novel semi-analytical method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the remote-sensing reflectance from above-surface measurements. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Yang, W. A simple and effective method for removing residual reflected skylight in above-water remote sensing reflectance measurements. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 165, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIES. Lake Kasumigaura Database, National Institute for Environmental Studies, Japan. 2020. Available online: http://db.cger.nies.go.jp/gem/moni-e/inter/GEMS/database/kasumi/index.html. (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Gordon, H.R.; Brown, O.B.; Evans, R.H.; Brown, J.W.; Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S.; Clark, D.K. A Semianalytic Radiance Model of Ocean Color. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.-P.; Du, K.; Arnone, R. A model for the diffuse attenuation coefficient of downwelling irradiance. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2005, 110, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Hu, C.; Shang, S.; Du, K.; Lewis, M.; Arnone, R.; Brewin, R. Penetration of UV-visible solar radiation in the global oceans: Insights from ocean color remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 4241–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L. Scattering by pure seawater at high salinity. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 12685–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters. I. A semianalytical model. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 6329–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Borstad, G.; Brown, L. Detection of intense plankton blooms using the 709 nm band of the MERIS imaging spectrometer. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. Application of a Semianalytical Algorithm to Remotely Estimate Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient in Turbid Inland Waters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtarelli, V.P.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Maciel, D.A.; Júnior, R.F.; Carlos, F.M.; Novo, E.D.M.; Curtarelli, M.; Silva, E. Diffuse Attenuation of Clear Water Tropical Reservoir: A Remote Sensing Semi-Analytical Approach. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.D.; D’Sa, E.J. An estuarine-tuned quasi-analytical algorithm (QAA-V): Assessment and application to satellite estimates of SPM in Galveston Bay following Hurricane Harvey. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 4065–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, C.; Alcântara, E.; Bernardo, N.; Kampel, M. An assessment of semi-analytical models based on the absorption coefficient in retrieving the chlorophyll-a concentration from a reservoir. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhou, W.; Cao, W.; Wang, G.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zeng, K.; et al. Evaluating semi-analytical algorithms for estimating inherent optical properties in the South China Sea. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13155–13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R. Update of the Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA_v6); International Ocean Colour Coordnating Group—IOCCG: Monterey, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Reinart, A.; Herlevi, A.; Arst, H.; Sipelgas, L. Preliminary optical classification of lakes and coastal waters in Estonia and south Finland. J. Sea Res. 2003, 49, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.S.; Dowell, M.D.; Bradt, S.; Verdu, A.R. An optical water type framework for selecting and blending retrievals from bio-optical algorithms in lakes and coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsushita, B.; Yang, W.; Yu, G.; Oyama, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. A hybrid algorithm for estimating the chlorophyll-a concentration across different trophic states in Asian inland waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spyrakos, E.; O’Donnell, R.; Hunter, P.D.; Miller, C.; Scott, M.; Simis, S.G.H.; Neil, C.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Binding, C.E.; Bradt, S.; et al. Optical types of inland and coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 846–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, S.V.; Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Binding, C.; Schalles, J.; Loisel, H.; Gurlin, D.; Greb, S.; Alikas, K.; Randla, M.; et al. Robust algorithm for estimating total suspended solids (TSS) in inland and nearshore coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Synthetic Dataset | I (Jiang et al. [31]) | II (This Study) | III (This Study) | Total Number of Data | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | (0.01–44.68 m) | 91,287 | Algorithm Validation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Msusa, A.D.; Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B. A Semianalytical Algorithm for Estimating Water Transparency in Different Optical Water Types from MERIS Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040868
Msusa AD, Jiang D, Matsushita B. A Semianalytical Algorithm for Estimating Water Transparency in Different Optical Water Types from MERIS Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040868
Chicago/Turabian StyleMsusa, Anastazia Daniel, Dalin Jiang, and Bunkei Matsushita. 2022. "A Semianalytical Algorithm for Estimating Water Transparency in Different Optical Water Types from MERIS Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040868
APA StyleMsusa, A. D., Jiang, D., & Matsushita, B. (2022). A Semianalytical Algorithm for Estimating Water Transparency in Different Optical Water Types from MERIS Data. Remote Sensing, 14(4), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040868







