Abstract
Accurate knowledge of snow cover extent, depth (SD), and water equivalent is essential for studying the global water cycle, climate, and energy–mass exchange in the Earth–atmosphere system, as well as for water resources management. Ratio between SAR cross- and co-polarization backscattering () was used to monitor SD during snowy months in mountain areas; however, published results refer to short periods and show lack of correlation during non-snowy months. We analyze Sentinel-1A images from a study area in Central Pyrenees to generate and investigate (i) time series of spatial dispersion, (ii) spatial distribution of pixelwise temporal standard deviation, and (iii) fundamental modes of evolution by non-negative matrix factorization. The spatial dispersion evolution and the first mode are highly correlated (correlation coefficients larger than 0.9) to SD evolution during the whole seven-year-long period, including snowy and non-snowy months. The local incidence angle strongly affects how accurately locally follows the first mode; thus, areas where it predominates are orbit-dependent. When combining ascending- and descending-orbit images in a single data matrix, the first mode becomes predominant almost everywhere snow pack persists during winter. Capability of our approach to reproduce SD evolution makes it a very effective tool.
1. Introduction
Snow cover plays a crucial role in several important Earth phenomena, from water resources to climate change, e.g., because of surface albedo. Accurate knowledge of snow cover extent (SCE) and snowpack parameters—snow density, snow depth SD and snow water equivalent SWE, i.e., the amount of water contained in the snowpack—is essential for studying the global water cycle, climate, and the energy–mass exchange in the Earth–atmosphere system, as well as for water resources management.
Unfortunately, morphology and condition variability in mountain regions often make SCE, SD and SWE ground measurements (where they are carried out) partially representative of the surrounding areas; moreover, high elevations and inaccessible and remote places are seldom equipped with instrumentation. These disadvantages are partly overcome by space-borne remote sensing, which is a powerful snow monitoring technique with a resolution of tens of meters as for both optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) sensors. Even if optical products are easier to use than SAR ones, nevertheless, clouds and illumination conditions can severely limit their applicability.
Reliable snow cover estimation from SAR backscattering dates back to about 30 years (e.g., [1] and references therein), following the possibility to use repeat-pass multi-temporal observations. Different missions are equipped with L- (15–30 cm), C- (3.8–7.5 cm) and X- (2.4–3.8 cm) band sensors and can provide even SAR time series; the snowpack is nearly invisible in L–band data, X–band data have the highest sensitivity, but C–band SAR data are also suitable and most–used for snow detection (e.g., [2]).
Different approaches have been developed to sense SCE, SD, and SWE from SAR data (e.g., [3,4,5]; for a review, e.g., [6]). As for SCE, backscattering–based methods were the first to be implemented, but also interferometric and polarimetric methods are well developed. Backscattering indicators relying on different ad hoc thresholds have proven effective in terms of a true/false—i.e., snow presence or absence—binary result; indicators based on interferometric analyses rely on the choice of an appropriate coherence threshold; indicators based on decomposition methods from polarimetric SAR techniques rely on machine learning classification trained by external SCE results, seasonal parameters’ difference before thresholding, or direct thresholding (for a review, see, e.g., [1]).
Spatial resolution of recent SAR missions (e.g., C-band Sentinel-1, pixel size down to less than 5 m in Stripmap mode, which is used to image small islands and in exceptional cases only [7], and about 5 × 20 m in Interferometric Wide (IW) swath mode [8]) is fully spatially adequate for sensing SCE, while temporal resolution is still insufficient to detect day-lasting dynamic phenomena (e.g., sudden SCE changes because of snow melt). SD and SWE are not directly obtained from SAR data; their retrieval requires inversions or empirical models. Signatures of polarimetric SAR backscattering over snow have been used to retrieve SD; in particular, ratio between cross- and co-polarization backscattering depends on SD and, with respect to mere backscattering, can reduce the impacts of ground, vegetation, and surface geometry (e.g., see details in [2] about Sentinel-1 expected backscattering in co-polarization, , and cross-polarization, ). As for SWE, snow density and wetness can be estimated by using polarimetric—HH, VV, VH, HV—SAR data (e.g., [9,10]) but ancillary in situ data are needed to link remote sensing measurements and snow properties in a backscattering inversion model accurately. SWE has also been estimated through SAR interferometry, relating the interferometric phase changes to SWE temporal changes; interferometric data have to be calibrated using ancillary in situ measurements (e.g., [11]). Besides, SD and SWE have been retrieved from dual polarization SAR data, relying on co-polar phase difference and particle anisotropy (e.g., [5] for X-band SAR).
The pattern of SD during accumulation and snowmelt seasons exhibits considerable spatial and temporal variability. Field surveys show that snow accumulation in mountain areas is extremely irregular even at small scales, due to topography, strong snow redistribution by wind and spatial heterogeneity of the land cover. Images recorded during very snowy years show a greater spatial dispersion (i.e., small- to large-scale variations in contrast) with respect to less snowy years; seasonal changes of C–band radar backscattering is also dependent on land cover and viewing conditions. As for land cover, different areas show varying median values for the same cover classes, thus common backscattering thresholds can not be delineated (e.g., [12]). As for viewing conditions, backscattering from wet snow depends on the local incidence angle (LIA) more than backscattering from dry snow. Backscattering coefficients of wet snow, dry snow, and snow-free surfaces in co- and cross–polarization have often been used in the threshold polarization ratio algorithm by [13]; however, threshold values have to be customized location by location and even changed over time to detect SCE and SD (e.g., [14,15]). Proper threshold values for each local incidence angle have also been used to identify snow-covered areas from interferometric coherence (e.g., [4]). Unfortunately, most studies using SAR backscattering are restricted to one or two observation years and very few studies, or none at all, provide multi-year SCE or SD time series (e.g., [1] and references therein).
Without demanding completeness, we mention that the most accurate estimation of SD are obtained from airborne lidar measurements (e.g., [16]), but they are only applicable at the local scale, and that SWE can be mapped using passive microwave sensors (for a review, see, e.g., [17]), but spatial resolution is coarse. As for active microwave sensors, SD and SWE have also been retrieved based on dual-frequency (X, 2.4 to 3.8 cm, and Ku, 1.7 to 2.4 cm) measurements available in the past (e.g., [18,19]).
In this work we use Sentinel-1A radar images from a 451-km study area in Central Pyrenees to obtain a seven-year-long SD time series, not relying on any threshold. We investigate (i) time series of spatial dispersion, (ii) spatial distribution of pixelwise temporal standard deviation, and (iii) fundamental modes of evolution by non-negative matrix factorization. Both spatial dispersion evolution and the first fundamental mode are highly correlated (correlation coefficients larger than 0.9) to SD evolution during the whole analyzed period, including snowy and non-snowy months. The three suggested approaches complement and support one another.
2. Study Area
The 451 km study area is located in the Spanish side of the Central Pyrenees (Figure 1) close to the Laboratorio Subterràneo de Canfranc, where deformation related to snow load and snow melting has been recorded by two underground high-resolution strainmeters ([20,21]). Landscape is characterized by high reliefs, up to about 2800 m above sea level (asl), and shaped by glacial and river—Aragón river and its tributaries—erosion. High reliefs are mainly characterized by bare rock, natural grassland and sparsely vegetated areas; steep slopes are usually covered by forests.
Generally speaking, temperature and precipitation are very heterogeneous in the Pyrenees because of morphology and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean to the West and the Mediterranean Sea to the East. In the western part most precipitations occur between December and March, whereas in the eastern part most precipitations occur in spring and autumn (April–June, September–November) (e.g., [22]). Snow mostly accumulates during winter in the western part (where heavy snowfalls most likely occur) and during late autumn, winter, and spring in the eastern part [23]. From late autumn onward, precipitations occur as snow at altitudes higher than 1500–1600 m over the entire mountain range [24], but snowfall spatial distribution cannot be clearly inferred from elevation and position [23]. Snowpack is persistent above around 1600 m during the whole cold period and between 1600 and 1300 m during the coldest months, usually December–February [25].
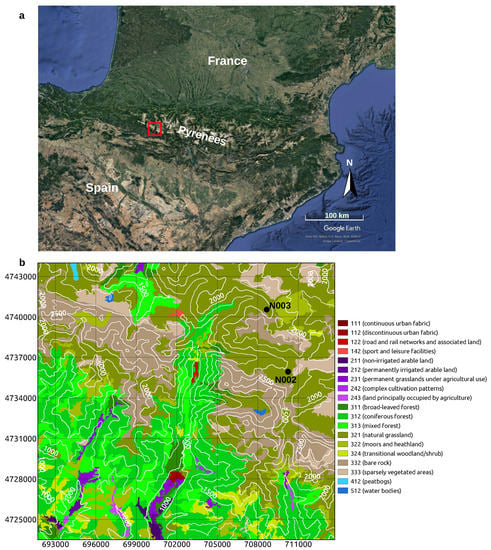

Figure 1.
Map of the 451 km study area. (a) Pyrenees location between France and Spain (maps data: Google, @2021 Landsat/Copernicus); the red rectangle shows the study area. (b) Study area; colors indicate land cover [26], white curves give topography [27], labeled black dots indicate stations N002 and N003 (map generated using QGIS v.3.10). UTM WGS84 30N coordinates.
3. Materials and Methods
Figure 2 shows pre-processing and processing steps employed in this study. We use Ground–Range Detected (GRD) Sentinel-1A interferometric wide swath imagery [8], provided by the European Space Agency (ESA) and downloaded from the Alaska Satellite Facility [28]. Level–1 GRD products consist of focused SAR data that has been detected, multi-looked and georeferenced to geographic coordinates using the Earth ellipsoid WGS84, but are still in SAR geometry. Thus, geocoding and radiometric terrain corrections are required, and are particularly important because of the high topographic variation in the study area.
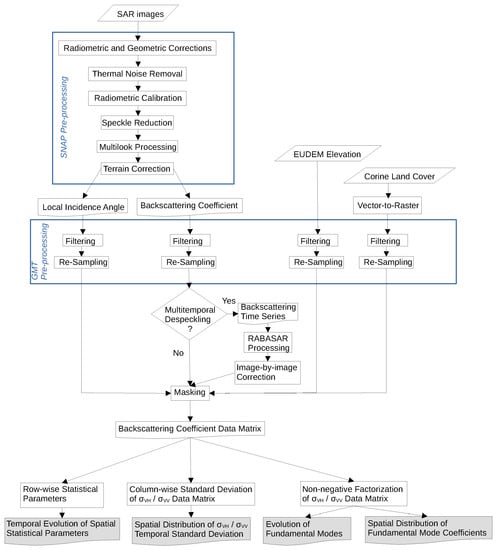
Figure 2.
Schematic flowchart illustrating pre-processing and processing steps employed in this study.
We analyze 201 ascending–orbit images, acquired at about 6 pm UTC, and 197 descending–orbit images, acquired at about 6 am UTC. Since the study area longitude is about −0.5, UTC is very close to true solar time (TST). Images cover seven hydrological years (October 2014–August 2021) which are characterized by different amounts of snowfall, as shown by snow depth measurements (Figure 3i,j) at two stations—N002, around 2080 m asl, and N003, around 1970 m asl—located inside the study area (Figure 1b).
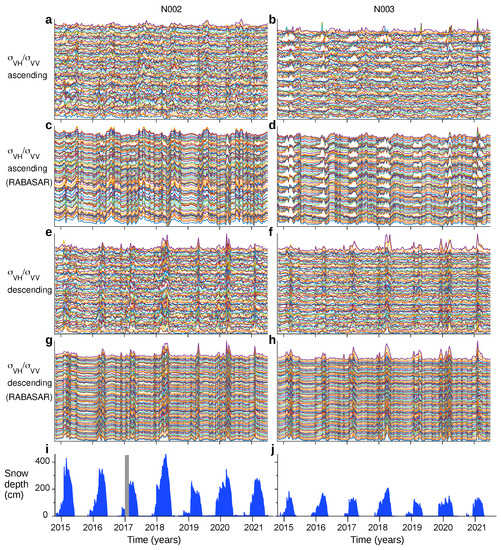
Figure 3.
Time series of at two square grids of 9 × 9 pixels each, centered on stations N002 and N003, respectively. Panels (c,d,g,h) have been obtained after applying RABASAR to SAR images, in order to lower speckle noise and make plots more readable. All plots have been arbitrarily shifted along the y–axis for clearness. (a,c) Pixels nearby N002, ascending orbit. (b,d) Pixels nearby N003, ascending orbit. (e,g) Pixels nearby N002, descending orbit. (f,h) Pixels nearby N003, descending orbit. (i) Snow depth at N002, daily data; the gray rectangle indicates lacks of measurements. (j) Snow depth at N003, daily data.
We pre–process Sentinel-1A GRD images by using the Sentinel Application Platform (SNAP) v.8 [29] and following a standard procedure—application of radiometric and geometric corrections, thermal noise removal, radiometric calibration, speckle reduction (Refined Lee filter), multilook processing (three range looks), and terrain correction (e.g., [30]). At last, we obtain and georeferenced maps with a spatial resolution of about 30 m. Using Generic Mapping Tools (GMT6) v. 6 [31], each map is filtered (nearneighbor tool) and re-sampled in order to generate a rectangular grid—UTM WGS84 30N coordinates; x from 691,700 to 713,700 m, y from 4,723,500 to 4,744,000 m—of pixels, 50 m × 50 m in size.
Pixels affected by shadowing are masked out. We also mask out pixels not labeled as 321 (natural grassland), 322 (moors and heathland), 324 (transitional woodland/shrub), 332 (bare rock) and 333 (sparsely vegetated areas) in CORINE Land Cover inventory 2018 (CLC, [26]) (Figure 1b) because of the complex SAR-woods interactions (e.g., [32]). The actual studied area diminishes to 266 km and hereinafter by “all pixels” we always mean CLC pixels 321, 322, 324, 332, and 333. Altitude, slope, and exposure are computed using European Union Digital Elevation Model (EU-DEM) v. 1.1 [27].
To enhance readability of some figures, multitemporal despeckling is performed using the Ratio-Based Multitemporal SAR Images Denoising (RABASAR) method; RABASAR is based on the use of the ratio image, namely the ratio between an image and the temporal mean of the stack, which is easier to denoise than a single image thanks to its improved stationarity [33].
We start from the analysis of backscattering time series at pixels surrounding N002 and N003. Subsequent analyses relate to (i) the time series of selected statistical parameters—mean, median, standard deviation (stdev), mean absolute deviation (mad)—of the spatial distribution of , , and inside the whole region or parts of it, (ii) the spatial distribution of the standard deviation of the time series at each pixel, and (iii) the search for dominant coherent variations (i.e., fundamental modes) in the time series of .
We arrange data in an intrinsically non-negative data matrix U which has as many rows as the number of images () and as many columns as the number of pixels (). Each column gives the time series of a selected backscattering coefficient—, , or —at a specific pixel; each row gives the backscattering coefficient pixel by pixel at the same time.
Row-wise mean and median—value which is greater than and less than at most half of the population, in other words the 50th percentile of the population—give characteristic evolution of backscattering, whereas stdev—i.e., , where is mean—and mad—i.e., —give spatial dispersion. Generally speaking, assessing the dispersion of a data set implies knowing its variability near the center and in the tails; standard deviation and mean absolute deviation measure both variabilities, but mad is less affected by extreme observations than stdev is. Column-wise standard deviation gives temporal standard deviation pixel-by-pixel.
As for the search for dominant coherent variations in the time series of , we approximate its data matrix through the product of two non-negative matrices W and H by Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) [34]. Column vectors of W can be regarded as basis vectors in the data space (i.e., the fundamental modes of the time series), and rows of H can be regarded as coefficients that scale the basis vectors (i.e., to what extent a pixel follows each fundamental mode of the time series). The number of W columns and H rows is the factorization rank r. For each , multiplying the column vector , , by the row vector , , gives a matrix product representing evolution at each pixel because of the fundamental mode k of the time series. Total variance (sum of column-wise variances) of the matrix product is a measure of the relative importance of the k–th fundamental mode with respect to the other fundamental modes.
In the NMF original formulation, matrices W and H minimize the objective function (difference between the data matrix and its reconstruction by the decomposed matrices, U–WH), by L2-norm (squared) error. This approach is prone to outliers; minimizing the L2,1-norm error decreases the effects of outliers on the objective function [35]. L2,1-norm means that the L2-norm is applied to columns, thus obtaining a vector of column-wise squared errors; then, the L1-norm is applied to the squared-error vector, thus obtain the final cost of the objective function. We have tested both L2-norm and L2,1-norm error minimization, getting the same factorization of data matrix U. Thus, here we show only what obtained by using the nmf function in MATLAB® R2020a, where matrix factorization is optimized by L2-norm minimization of the objective function.
In principle, results may differ when analyzing ascending– or descending–orbit images, because of the different LIA and acquisition hours. To check for advantage and/or disadvantage of a combined analysis, we also define a combined data matrix including from both ascending– and descending–orbit images. The number of pixels in ascending–orbit images is slightly different from that in descending–orbit images, because of shadowing. In principle, ascending– and descending–orbit images should be coeval to be combined. Descending–orbit images are acquired 36 h before ascending–orbit ones; they are sufficiently coeval to our purposes and we assign the average acquisition time to each couple. The number of analyzed image couples is 191, since a few images are unavailable. We consider the average of the two rows (time series) related to each pixel for computing temporal evolution of spatial statistical parameters. To search for and evidence common fundamental modes, we apply non-negative factorization to the combined data matrix, thus obtaining two coefficients related to the same fundamental mode for each pixel which is in both ascending- and descending-orbit images.
4. Results
4.1. Backscattering Nearby Stations N002 and N003
We start from considering two square grids of 9 × 9 pixels each, centered on stations N002 and N003, respectively; thus, side of each square is 450-m long.
Time series of —arbitrarily shifted along the y–axis for clearness—are plotted in Figure 3 for both ascending–orbit and descending–orbit images. Units are not shown because unimportant; y-axis scale is the same for all curves in each plot but differs from plot to plot. For the sake of comparison, panels in Figure 3 show time series which have been obtained both applying and without applying RABASAR multitemporal despeckling to images. Signal amplitude varies noticeably from pixel to pixel, even after applying RABASAR. For completeness, Supplementary Material Figures S1 and S2 show the same plots as Figure 3, but as regards and , respectively.
Figure 4 and Supplementary Material Figures S3 and S4 are intended to emphasize the shape of the time series more than their amplitude. The three figures show evolution of , where may be (Figure 4), (Supplementary Material Figure S3), or (Supplementary Material Figure S4); and indicate maximum and minimum values of for each pixel. Again, for the sake of comparison, panels show time series which have been obtained both applying and without applying RABASAR multitemporal despeckling to images.
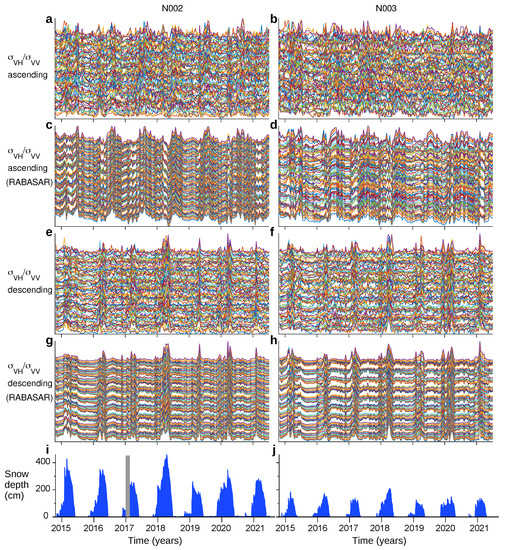
Figure 4.
Normalized time series of at two square grids of 9 × 9 pixels each, centered on stations N002 and N003, respectively. Normalization evidences common paths among backscattering time series. Panels (c,d,g,h) have been obtained after applying RABASAR to SAR images, in order to lower speckle noise and make plots more readable. All plots have been arbitrarily shifted along the y–axis for clearness. (a,c) Pixels nearby N002, ascending orbit. (b,d) Pixels nearby N003, ascending orbit. (e,g) Pixels nearby N002, descending orbit. (f,h) Pixels nearby N003, descending orbit. (i) Snow depth at N002, daily data; the gray rectangle indicates lacks of measurements. (j) Snow depth at N003, daily data.
The shape of the time series is approximately the same for all the pixels nearby the same station, but depends on plotted quantity and acquisition orbit. Ratio seems to follow two distinct patterns according to the two acquisition orbits. As for data collected in ascending orbit, is usually larger during summer than during winter for all the pixels nearby N002 and more pixel-dependent (i.e., larger during summer than during winter or, less frequently, vice versa) nearby N003. Winter maxima of for pixels nearby N003 are more pronounced than summer maxima for pixels nearby N002. As for data collected in descending orbit, exhibits “short-lasting” late winter maxima for all the pixels, whereas it is small and flat during the rest of the year. Thus, ratio is usually larger in summer than in winter for ascending-orbit images, whereas the opposite occurs for descending-orbit images.
Although common patterns are clearly visible, nevertheless it is hard to correlate or anticorrelate backscattering time series to the SD evolution at N002 and N003 (Figure 3i,j and Figure 4 and Supplementary Material Figures S1–S4) strictly. Reasoning in terms of backscattering thresholds seems, at least in this case, ineffective also in small areas.
4.2. Evolution of Spatial Distribution of Backscattering in the Study Area
As backscattering time series differ from orbit to orbit and from pixel to pixel (Figure 3 and Figure 4), we investigate the possibility of inferring SD evolution in the study area by using temporal evolution (i.e., changes from image to image) of backscattering spatial distribution.
Figure 5 compares evolution of the four analyzed statistical descriptors—mean, median, stdev, mad—with SD evolution at N002, N003, and the additional station N004, which is located about 19 km East of N003, out of the area shown in Figure 1b.
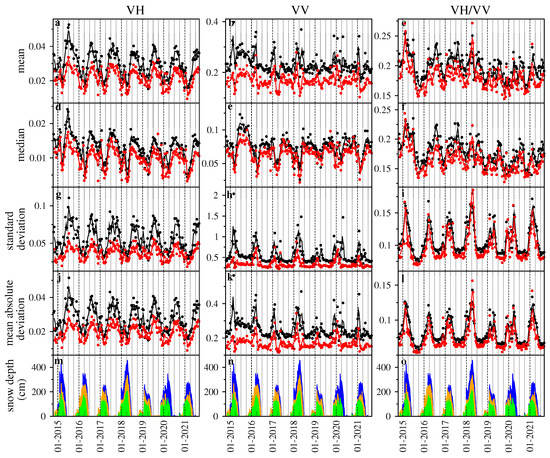
Figure 5.
Comparison between temporal evolutions of selected statistical descriptors of the backscattering spatial distribution and snow depth. (a) Mean, . (b) Mean, . (c) Mean, . (d) Median, . (e) Median, . (f) Median, . (g) Standard deviation, . (h) Standard deviation, . (i) Standard deviation, . (j) Mean absolute deviation, . (k) Mean absolute deviation, . (l) Mean absolute deviation, . (a–l) Black dots, ascending orbit; red dots, descending orbit. Black and red lines give moving average over three consecutive black and red dots, respectively. (m–o) Snow depth (daily data) at stations N002 (blue), N003 (green), and N004 (orange).
Time evolution of all the four statistical descriptors show large yearly oscillations, very similar to one another, which neither correlate nor anticorrelate with snow depth well. As an example, evolution during non-snowy periods (late spring to mid-autumn) is not flat. As for , results are conflicting; during winter, mean exhibits pronounced maxima during snow accumulation while median exhibits pronounced minima during snow melting; stdev and mad are relatively large during snow accumulation, but do not correlate with SD well. As for , evolution of mean and median show large yearly oscillations, very similar to each other, which neither correlate nor anticorrelate with SD well; instead, evolution of stdev and mad are very similar to each other and strongly resemble SD evolution, for both ascending and descending orbit data. Concordance between time evolution of stdev and mad indicate robustness of dispersion estimates, making dispersion an eligible investigation tool for inferring SD evolution.
To deepen our understanding of the tool capability, we plot evolution of spatial dispersion by altitude. Evolution of stdev is shown in Figure 6; for comparison, mad evolution is shown in Supplementary Material Figure S5. As expected, time evolution of stdev and mad are very similar to each other regardless from altitude, although amplitudes may differ. Both stdev and mad evolve like SD at stations N002, N003, and N004 (Figure 6c) when considering altitudes higher than about 1500 m, i.e., where snowpack is persistent during the whole cold period [25]. On the contrary, stdev and mad yearly variations are small below about 1500 m. Thus, pixels at altitudes below 1500 m have a very small effect on plots in Figure 5i,l and, for brevity, we do not show a refined version of Figure 5 after removing pixels at altitudes below 1500 m.
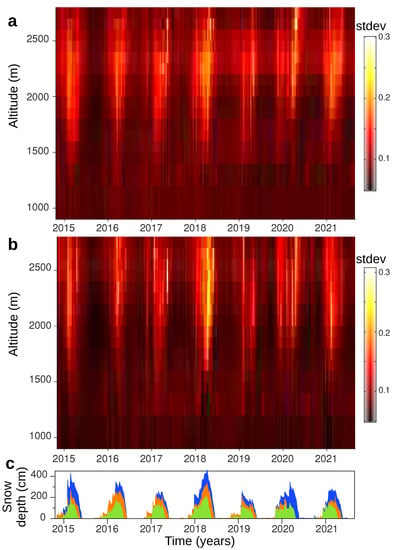
Figure 6.
Temporal evolution of the spatial standard deviation of by altitude bands. Altitude ranges 900–2800 m, at 100 m large intervals. (a) Ascending orbit. (b) Descending orbit. For comparison, (c) gives snow depth (daily data) at stations N002 (blue), N003 (green), and N004 (orange).
To quantify resemblance between evolution of spatial dispersion and SD, we plot scatter diagrams and compute Pearson’s (linear) and Spearman’s (rank) correlation coefficients between stdev—computed on pixels above 1500 m—and SD—computed by averaging N002 and N003 values— as well as between mad and SD (Figure 7). Each year, SD data are zero padded 15 July–15 October because the study area is free from snow, as confirmed by satellite—Landsat 7, Landsat 8, Sentinel-2 (easily visualizable, e.g., at https://apps.sentinel-hub.com/eo-browser/, accessed on 8 December 2021)—images; consequently, reported non-zero SD values are spurious. To decrease noise, stdev and mad evolution are smoothed applying a moving average over three consecutive images, whereas snow data are averaged over five consecutive days. Correlation coefficients are around or larger than 0.9 for both ascending and descending orbits.
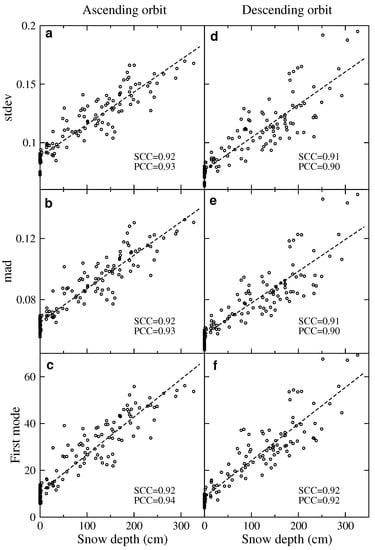
Figure 7.
Correlation diagrams for evolution of and snow depth, computed as mean of N002 and N003 values. Pixel altitude is higher than 1500 m. (a) Spatial standard deviation, ascending orbit. (b) Spatial mean absolute deviation, ascending orbit. (c) First mode from non-negative matrix factorization, ascending orbit. (d) Spatial standard deviation, descending orbit. (e) Spatial mean absolute deviation, descending orbit. (f) First mode from non-negative matrix factorization, descending orbit. In each panel, SCC and PCC give Spearman’s (rank) and Pearson’s (linear) correlation coefficients, respectively.
When we analyze the combined data matrix which includes ascending– and descending–orbit images, results are very similar to those presented so far; thus, for conciseness we do not show them.
4.3. Spatial Dispersion of the Standard Deviation of Backscattering Evolution at Each Pixel
To extend previous investigation, we pass from the evolution of selected statistical indicators of the spatial distribution in each image to the spatial distribution of the standard deviation of evolution at each pixel. In other words, we pass from the temporal evolution of a spatial distribution to the spatial distribution of a temporal evolution. Standard deviation of evolution at each pixel is a measure of the amplitude of yearly oscillations, as far as they are larger than noise.
Figure 8 shows spatial distribution of the standard deviation of evolution at each pixel by altitude. To make them clearer, bivariate (2D) histograms in Figure 8 give relative frequency of scaled temporal standard deviation (STSD). By STSD we mean the standard deviation of evolution at each pixel for each year (e.g., 1 October 2014–30 September 2015), divided by the overall summertime mean of (i.e., the arithmetic mean during all the seven periods 1 July–31 August belonging to the seven investigated years) in the altitude band where the pixel is. Sub-panels refer to the different years. Histograms show very narrow distributions below about 1500 m and larger distributions above about 1500 m, where snowpack is persistent during the whole cold period [25]. Distribution width changes from year to year, following SD evolution, at least approximately. These findings are consistent with those in Section 4.2, but temporal resolution is obviously much poorer.
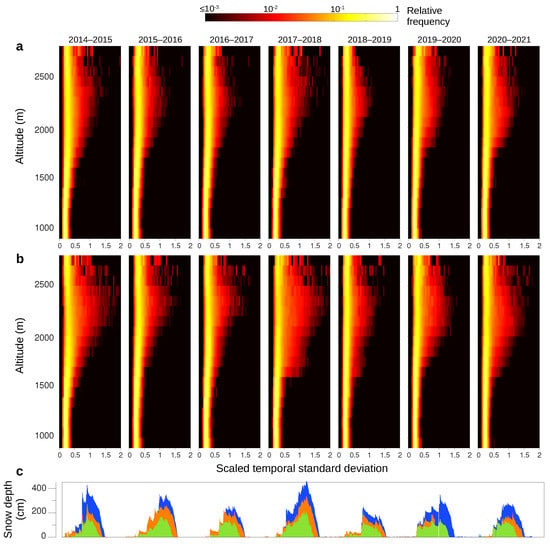
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of the standard deviation of evolution at each pixel, by altitude. Bivariate (2D) histograms give relative frequency of scaled temporal standard deviation by altitude. Scaled temporal standard deviation: standard deviation of evolution at each pixel computed each year in the period 1 October–30 September and divided by the mean over in each altitude band during the seven periods 1 July–31 August related to the seven investigated years. Sub-panels refer to different years. Altitude ranges 900–2800 m, at 100 m large intervals. (a) Ascending orbit. (b) Descending orbit. For comparison, (c) gives snow depth (daily data) at stations N002 (blue), N003 (green), and N004 (orange).
4.4. Non-Negative Factorization of Data Matrix
From Section 4.1 we know that evolution seems to follow two distinct patterns nearby N002 and N003, thus now we search for the two fundamental modes that best account for observed evolution in the whole study area.
Figure 9a,b show the two fundamental modes of evolution at all altitudes, as obtained by NMF (Section 3). For both ascending and descending orbits, the first mode (Figure 9a) evolves like SD (Figure 9g), e.g., successfully identifying the snowiest years. The second mode (Figure 9b) is characterized by yearly oscillations with summer maxima and winter minima; its rising period (April–July) seems correlated with snow melting, while its falling period extends from July to early December. Thus, the two modes actually resemble the two temporal patterns observed for data acquired in ascending and descending orbits at N002 and N003 (Section 4.1 and Figure 4).
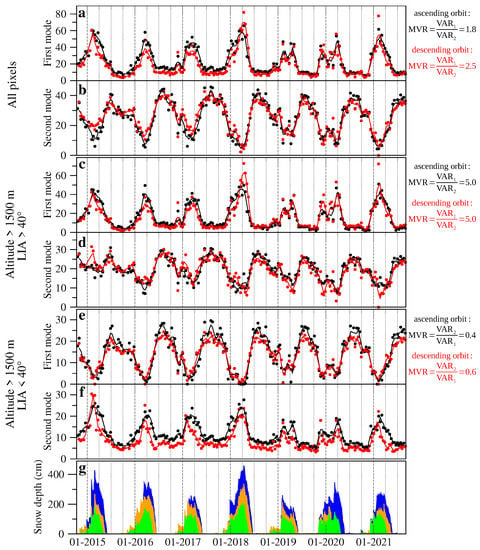
Figure 9.
Fundamental modes of the time series. (a) Pixels at all altitudes, first mode. (b) Pixels at all altitudes, second mode. (c) Pixels at altitudes higher than 1500 m, LIA larger than 40, first mode. (d) Pixels at altitudes higher than 1500 m, LIA larger than 40, second mode. (e) Pixels at altitudes higher than 1500 m, LIA smaller than 40, first mode. (f) Pixels at altitudes higher than 1500 m, LIA smaller than 40, second mode. (a–f) Black dots, ascending orbit; red dots, descending orbit. Black and red lines give moving average over three consecutive black and red dots, respectively. For each case—all altitudes; altitudes > 1500 m and LIA > 40; altitudes > 1500 m and LIA < 40—MVR is ratio of total variance of evolution because of the fundamental mode correlated to SD evolution to total variance because of the fundamental mode uncorrelated to SD evolution. For comparison, (g) gives snow depth (daily data) at stations N002 (blue), N003 (green), and N004 (orange).
Using notation in Section 3, matrix product represents evolution at each pixel because of the first fundamental mode. Its total variance is a measure of data variability accounted for by the first fundamental mode. We find that is about 1.8 and 2.5 times larger than total variance of the matrix product , related to the second fundamental mode, for ascending and descending orbits, respectively, (Figure 9). Thus, total variance of evolution because of the fundamental mode which is highly correlated to SD is about twice the total variance because of the fundamental mode uncorrelated to SD.
If we consider only pixels located above 1500 m, we obtain fundamental modes so similar to those plotted in Figure 9a,b that we think it useless to show them. In this case, is about 1.9 and 2.7 for ascending and descending orbits, respectively. Pearson’s (linear) and Spearman’s (rank) correlation coefficients between the first fundamental mode—computed on pixels above 1500 m—and SD—computed by averaging N002 and N003 values—are larger than 0.91 (Figure 7c,f). Before computing correlations, the first mode is smoothed applying a moving average over three consecutive images, whereas snow data are averaged over five consecutive days.
Each pixel usually has non-zero coefficients for both fundamental modes, and its evolution is approximated by a linear combination of the two modes. Multiplication of the standard deviation of the k–th fundamental mode by the related coefficient gives a measure of the amplitude of the k–th fundamental mode at each pixel. We indicate the resulting product with . Thus, evolution resembles the first fundamental mode more than the second one where ratio is positive; the opposite occurs where ; obviously because and are both positive.
Figure 10 shows distribution in the study area, for both (a) ascending and (b) descending orbits. At altitudes higher than around 1500 m, pixels where for the ascending orbits usually have for the descending orbits and vice versa, even if many other pixels have for both orbits. At lower altitudes, is usually small and negative, thus the yearly oscillating behavior slightly dominates. The different behavior of pixels located below or above 1500 m is confirmed by the scatter plots in Figure 11a,b, and it is consistent with the persistent snow line altitude during cold months. Thus, we only consider pixels located above 1500 m to further investigate possible correlations. Scatter plots in Figure 11c,d suggest strong correlation between and North-to-East exposure. However, eastern exposure gives for ascending orbits and for descending orbits; the opposite occurs for western exposure, thus correlation between exposure and is a consequence of the satellite line-of-sight azimuth. On the contrary, correlation between and LIA is very similar for ascending and descending orbits (Figure 11e,f), suggesting that LIA actually drives .
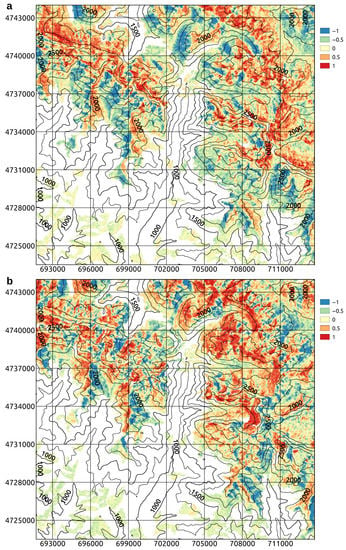
Figure 10.
Maps showing ratio in the study area. Parameter is the standard deviation of the k–th fundamental mode times its coefficient. (a) Ascending orbits. (b) Descending orbits. Black curves give topography. Maps generated using QGIS v.3.10, UTM WGS84 30N coordinates.
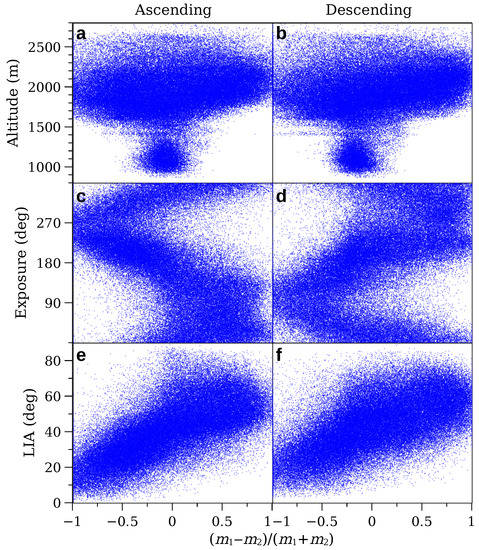
Figure 11.
Scatter plots related to ratio . Parameter is the standard deviation of the k–th fundamental mode times its coefficient. (a) Altitude vs. , ascending orbits. (b) Altitude vs. , descending orbits. (c) Exposure (Eastward from True North) vs. , altitude m, ascending orbits. (d) Exposure (Eastward from True North) vs. , altitude m, descending orbits. (e) Local incidence angle vs. , altitude m, ascending orbits. (f) Local incidence angle vs. , altitude m, descending orbits.
To further investigate the LIA role, we apply NMF to pixels located above 1500 m, separating those whose LIA is larger than 40 from those whose LIA is smaller than 40. We choose this LIA threshold somewhat arbitrarily, but it is a round number which is consistent with Figure 11e,f, as well as close to the mean incidence angle (37.5) for Sentinel-1A interferometric wide swath imagery [8]. For LIA larger than 40 the two fundamental modes are shown in Figure 9c and Figure 9d, respectively. The first mode is almost identical to the one obtained by considering all pixels (Figure 9a,b), but now is about 5 for both ascending and descending orbits. Thus, data variability accounted for by the first fundamental mode—the one highly correlated to SD—is much larger than in the case all pixels are considered.
Figure 9e,f show the two fundamental modes when we apply NMF to pixels located above 1500 m and whose LIA is smaller than 40. Now the second mode resembles SD (Figure 9g), while the first mode is similar to the second mode obtained for LIA . Thus, yearly oscillations (uncorrelated to SD) dominate.
When we apply NMF to the combined data matrix which includes ascending– and descending– orbit images (Section 3), we obtain fundamental modes which are so similar to those plotted in Figure 9a–d that we think it useless to show them. MVR is 2.0. For each pixel we also compute using coefficients related to ascending– and descending–orbit images and select the larger one. That is to say, each pixel is assigned the orbit with the larger . As a result, the first fundamental mode predominates almost everywhere at altitudes higher than about 1500 m (Figure 12a,c). First mode predominance decreases on south–facing slopes, as expected (Figure 12b).
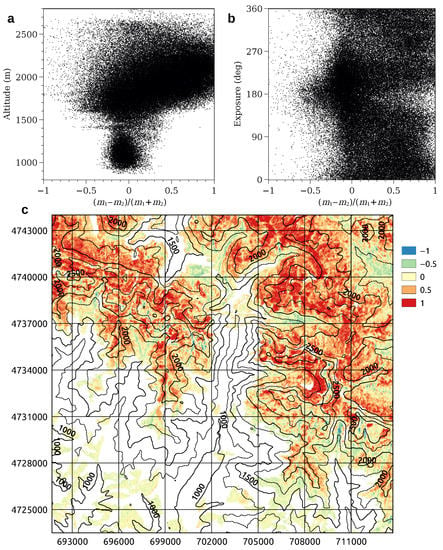
Figure 12.
Larger value of ratio between the two related to ascending– and descending–orbit images for each pixel. Parameter is the standard deviation of the k–th fundamental mode times its coefficient. Non-negative factorization was applied to a combined data matrix including ascending– and descending–orbit images. (a) Scatter plot of altitude vs. . (b) Scatter plot of exposure (Eastward from True North) vs. . (c) Map showing ratio in the study area.
5. Discussion
Our analyses show that typical evolution of , , and —as expressed by the time series of the mean and/or median values for each image—neither correlate nor anticorrelate well with snow depth evolution. Lack of good correlation is mainly evident in summer, when the study area is completely free from snow but a secondary maximum of is present. These findings are consistent with Figure 3 in [2], where two-year-long time series at four sites are shown.
We demonstrate that snow depth evolution may be inferred following three complementary approaches; the three approaches can also distinguish between snowy and non-snowy months. Our results are also probably indicative for an area which is much larger than the study area, as suggested by the consistency of snow depth measurements at stations N002, N003 and N004.
As for the first approach, time series of spatial dispersion—as expressed by the time series of standard deviation and/or mean absolute deviation for each image—is so similar to snow depth evolution during the whole time period that Pearson’s (linear) and Spearman’s (rank) correlation coefficients are around or larger than 0.9 for both ascending and descending orbits. Spatial dispersion of always remains small in areas below about 1500 m in altitude, i.e., where snowpack is not persistent even during cold months. Above about 1500 m, spatial dispersion allows also to retrieve snow depth temporal evolution by altitude.
As for the second approach, we consider the spatial distribution of the standard deviation of evolution at each pixel by altitude, for each year. Distribution width changes from year to year, following SD evolution, at least approximately.
As for the third approach, we obtain the two evolutionary fundamental modes for by non-negative factorization of the data matrix. The first mode is so similar to snow depth evolution that Pearson’s (linear) and Spearman’s (rank) correlation coefficients are larger than 0.91 for both ascending and descending orbits. Total variance of related to the first mode is about twice and triple that related to the second mode, for ascending and descending orbits, respectively. Thus, a large variability is captured by the first mode, making it a powerful tool for estimating snow depth. The second mode is characterized by yearly oscillations with minima during winter and maxima during summer. Because of this second mode, at many pixels evolution does not correlate with SD, mainly in summer.
Although images are acquired at about 6 p.m. TST in ascending orbit and 6 a.m. TST in descending orbit—thus in very different conditions with respect to snow melt-refreeze processes—there is small difference in the results obtained when analyzing images acquired in ascending or descending orbits. Instead, pixels essentially follows the first fundamental mode when LIA is larger than about 40, regardless from the acquisition orbit.
When we select pixels with LIA , total variance of evolution because of the fundamental mode which is highly correlated to SD is about five times larger than total variance related to the fundamental mode uncorrelated to SD, for both ascending and descending orbits.
When time series of ascending– and descending–orbit images are combined in a single data matrix regardless from LIA, the fundamental mode correlated to SD evolution predominates almost everywhere at altitudes where snow pack persists during winter (Figure 12a,c), because most pixels with LIA for the ascending orbit have LIA for the descending orbit, and most pixels with LIA for the descending orbit have LIA for the ascending orbit.
It is already known that backscattering depends on LIA for both wet and, to a lower extent, dry snow; dependence characteristics differ for different polarizations (e.g., [13]). Based on geometrical considerations, LIA impact is often reduced by incidence angle normalization (e.g., [15]). Additionally, InSAR-based and PolSAR-based techniques are affected by LIA (e.g., [4,36]). Dependency on LIA can be evaluated as high, medium, and low in approaches based on backscattering, InSAR, and PolSAR, respectively; low LIA dependency is usually considered a merit (e.g., [1]).
In this work, the role of LIA is different from that in previous studies. We show that discriminating pixels according to LIA brings out a fundamental evolutionary mode of which is highly correlated to SD and allows good detection of SD evolution. Thus, our approach is a paradigm change: LIA is no more a factor whose influence has to be removed, but it determines the ability to monitor SD evolution.
6. Conclusions
We analyze Sentinel-1A SAR backscattering to obtain seven-year-long time series of snow depth in a mountain region, not relying on any threshold. We follow three approaches which complement and support one another; they consist in producing and investigating (i) time series of spatial dispersion, (ii) spatial distribution of pixelwise temporal standard deviation, and (iii) fundamental modes of evolution by non-negative matrix factorization.
Both spatial dispersion evolution and the first fundamental evolutionary mode are highly correlated (correlation coefficients larger than 0.9) to snow depth evolution during the whole seven-year-long period, including snowy and non-snowy months.
Being based on spatial dispersion and non-negative data matrix factorization, our approach is intrinsically unable to reach high spatial resolutions. Moreover, obtaining quantitative snow depth estimates probably requires region-by-region conversion factors (ad hoc calibration). However, the capability of our approach to reproduce snow depth evolution during several consecutive years, including snowy and non-snowy months, makes it a potentially very effective tool, which can be used in many other mountain areas, e.g., for water resources management and monitoring of climate change effects. Even if proper calibration may be hard, e.g., because of lack of in situ snow depth data, our approach can still provide quantitative information on relative snow abundance from year to year.
In the next future, we aim to investigate the ultimate spatial resolution of the approach, test it in other mountain areas where in situ now depth data are available, and lastly apply it in mountain regions where in situ snow depth data are scarse or absent.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs1010000/s1, Figure S1: time series of nearby stations N002 and N003, Figure S2: time series of nearby stations N002 and N003, Figure S3: normalized time series of nearby stations N002 and N003, Figure S4: normalized time series of nearby stations N002 and N003, Figure S5: mean-absolute-deviation evolution by altitude.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and L.C.; formal analysis, A.A. and L.C.; investigation, R.C.; software, A.A. and L.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A., L.C. and R.C.; writing—review and editing, A.A. and L.C.; supervision, A.A.; funding acquisition, A.A.; visualization, A.A. and L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by University of Salerno grant number 300391FRB19AMORU.
Data Availability Statement
Figures have been produced using open-source software Veusz (https://veusz.github.io/, accessed on 8 December 2021), GMT (https://www.generic-mapping-tools.org/, accessed on 8 December 2021), Grace (https://plasma-gate.weizmann.ac.il/Grace/, accessed on 8 December 2021), and LibreOffice Draw (https://www.libreoffice.org/, accessed on 8 December 2021). Sentinel-1 images can be download from Alaska Satellite Facility at https://asf.alaska.edu/data-sets/sar-data-sets/sentinel-1/, accessed on 8 December 2021. Stations N002, N003, and N004 are managed by Sistema Automático de Información Hidrológica de la Cuenca Hidrográfica del Ebro/Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro (SAIH Ebro/CH Ebro, http://www.chebro.es, accessed on 8 December 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Sistema Automático de Información Hidrológica de la Cuenca Hidrográfica del Ebro/Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro for providing data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| SCE | snow cover extent |
| SD | Snow depth |
| SWE | Snow water equivalent |
| LIA | Local incidence angle |
| NMF | Non-negative matrix factorization |
| stdev | Standard deviation |
| mad | Mean absolute deviation |
| STSD | Scaled temporal standard deviation |
| VAR | Matrix total variance |
| MVR | Mode variance ratio |
| TST | True solar time |
References
- Tsai, Y.-L.S.; Dietz, A.; Oppelt, N.; Kuenzer, C. Remote Sensing of Snow Cover Using Spaceborne SAR: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lievens, H.; Demuzere, M.; Marshall, H.P.; Reichle, R.H.; Brucker, L.; Brangers, I.; de Rosnay, P.; Dumont, M.; Girotto, M.; Immerzeel, W.W.; et al. Snow depth variability in the Northern Hemisphere mountains observed from space. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarnicola, C.; Ratti, R.; Maddalena, V.; Schellenberger, T.; Ventura, B.; Zebisch, M. Seasonal Snow Cover Mapping in Alpine Areas Through Time Series of COSMO-SkyMed Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Feng, X.; Xiao, P.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Guo, J. Dry and Wet Snow Cover Mapping in Mountain Areas Using SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2575–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Gulab, S.; Rüdiger, C. Retrieval of Snow Depth and Snow Water Equivalent Using Dual Polarization SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awasthi, S.; Varade, D. Recent advances in the remote sensing of alpine snow: A review. GIsci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 852–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-1 Acquisition Modes, Stripmap (SM). Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar/acquisition-modes/stripmap (accessed on 8 December 2021).
- Sentinel-1 Acquisition Modes, Interferometric Wide Swath. Available online: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-1-sar/acquisition-modes/interferometric-wide-swath (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Surendar, M.; Bhattacharya, A.; Singh, G.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Venkataraman, G. Development of A snow wetness inversion algorithm using polarimetric scattering power decomposition model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2015, 42, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Verma, A.; Kumar, S.; Ganju, A.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kulkarni, A.V. Snowpack density retrieval using fully polarimetric TerraSAR-X data in the Himalayas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6320–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, V.; Nico, G.; Mateus, P.; Catalão, J.; Kontu, A.; Gritsevich, M. On the estimation of temporal changes of snow water equivalent by spaceborne SAR interferometry: A new application for the Sentinel-1 mission. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2019, 67, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widhalm, B.; Bartsch, A.; Goler, R. Simplified Normalization of C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Data for Terrestrial Applications in High Latitude Environments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagler, T.; Rott, H.; Ripper, E.; Bippus, G.; Hetzenecker, M. Advancements for Snowmelt Monitoring by Means of Sentinel-1 SAR. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manickam, S.; Barros, A. Parsing Synthetic Aperture Radar Measurements of Snow in Complex Terrain: Scaling Behaviour and Sensitivity to Snow Wetness and Landcover. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lievens, H.; Brangers, I.; Marshall, H.-P.; Jonas, T.; Olefs, M.; De Lannoy, G. Sentinel-1 snow depth retrieval at sub-kilometer resolution over the European Alps. Cryosphere 2022, 16, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deems, J.S.; Painter, T.H.; Finnegan, D.C. Lidar measurement of snow depth: A review. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saberi, N.; Kelly, R.; Flemming, M.; Li, Q. Review of snow water equivalent retrieval methods using spaceborne passive microwave radiometry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 996–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CoReH2O–Report for Mission Selection—An Earth Explorer to Observe Snow and Ice. ESA SP-1324-2. Available online: http://esamultimedia.esa.int/docs/EarthObservation/SP1324-2_CoReH2Or.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Rott, H.; Yueh, S.H.; Cline, D.W.; Duguay, C.; Essery, R.; Haas, C.; Hélière, F.; Kern, M.; Macelloni, G.; Malnes, E.; et al. Cold Regions Hydrology High-Resolution Observatory for Snow and Cold Land Processes. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amoruso, A.; Crescentini, L.; Costa, R. Different couplings between precipitation and deformation at the same site: A case study at Central Pyrenees (Spain). Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR031081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, A.; Crescentini, L.; Bayo, A.; Fernández Royo, S.; Luongo, A. Two high-sensitivity laser strainmeters installed in the Canfranc underground laboratory (Spain): Instrument features from 100 to 0.001 mHz. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Goyette, S.; Beniston, M. Impact of climate change on snowpack in the Pyrenees: Horizontal spatial variability and vertical gradients. J. Hydrol. 2009, 374, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro-Serrano, F.; López-Moreno, J.I. Spatio-temporal analysis of snowfall events in the Spanish Pyrenees and their relationship to atmospheric circulation. Cuad. De Investig. Geográfica (Geographical Res. Lett.) 2017, 43, 233–254. [Google Scholar]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; García-Ruiz, J.M. Influence of snow accumulation and snowmelt on streamflow in the central Spanish Pyrenees. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2004, 49, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moreno, J.I.; Goyette, S.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beniston, M. Effects of climate change on the intensity and frequency of heavy snowfall events in the Pyrenees. Clim. Chang. 2011, 105, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CORINE Land Cover CLC2018. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- European Union Digital Elevation Model (EU-DEM) v. 1.1. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/imagery-insitu/eu-dem/eu-dem-v1.1 (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Alaska Satellite Facility. Available online: https://asf.alaska.edu/data-sets/sar-data-sets/sentinel-1/ (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Santinel Application Platform. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/toolboxes/snap/ (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- SAR Basics Tutorial. Available online: https://step.esa.int/main/docs/tutorials/S1TBXSARBasicsTutorial.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The Generic Mapping Tools version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, T. Assessment of Snow Status Changes Using L-HH Temporal-Coherence Components at Mt. Dagu, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11602–11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Deledalle, C.-A.; Denis, L.; Maître, H.; Nicolas, J.-M.; Tupin, F. Ratio-Based Multitemporal SAR Images Denoising: RABASAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3552–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. Learning the parts of objects by non-negative matrix factorization. Nature 1999, 401, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Ding, C.; Huang, H. Robust nonnegative matrix factorization using l21-norm. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference Information and Knowledge Management, Glasgow, Scotland, UK, 24–28 October 2011; pp. 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Usami, N.; Muhuri, A.; Bhattacharya, A.; Hirose, A. PolSAR Wet Snow Mapping with Incidence Angle Information. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).