Abstract
The semi-enclosed bays impacted by heavy anthropogenic activities have weak water exchange and purification capacities. Most of the sea bays have suffered severe eutrophication, water quality deterioration, ecosystem degradation and other problems. Although many countries and local governments have carried out corresponding environmental protection actions, the evaluation of their effectiveness still requires monitoring technology and data support for long-term water environment change. In this study, we take Yueqing Bay, the fourth largest bay in China, as a case to study the satellite-based water quality monitoring and variation analysis. We established a nutrient retrieval model for Yueqing Bay to produce a long-term series of nutrient concentration products in Yueqing Bay from 2013 to 2020, based on Landsat remote sensing images and long-term observation data, combined with support vector machine learning and water temperature and satellite spectra as input parameters, and then we analyzed its spatiotemporal variations and driving factors. In general, nutrient concentrations in the western part of the bay were higher than those in the eastern part. Levels of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) were lower in summer than in spring and winter, and reactive phosphate (PO4-P) levels were lower in summer and higher in autumn. In terms of natural factors, physical effects (e.g., seasonal variations in flow field) and biological effects (e.g., seasonal differences in the intensity of plankton photosynthesis) were the main causes of seasonal differences in nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay. Nutrient concentration generally increased from 2013 to 2015 but decreased slightly after 2015. Over the past decade, the economy and industry of Yueqing Bay basin have developed rapidly. Wastewater resulting from anthropogenic production and consumption was transported via streams into Yueqing Bay, leading to the continuous increase in nutrient concentrations (the variation rates: ), which directly or indirectly caused high nutrient concentrations in some areas of the bay (e.g., Southwest Shoal at the mouth of Yueqing Bay). After 2015, the various ecological remediation policies adopted by cities around Yueqing Bay have mitigated, to some extent, the increasing nutrient concentration trends (the variation rates: ), but not significantly (P > 0.1). The environmental restoration of Yueqing Bay also requires continuous and long-term ecological protection and restoration work to be effective. This research can provide a reference for ecological environment monitoring and remote sensing data application for similar semi-enclosed bays, and support the sustainable development of the bay.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the coastal economy and continuous urbanization, over 60% of the world’s population live within 200 km of a coastline [1], and more than 40% of China’s population are centered in coastal areas [2]. As such, the impact of anthropogenic activity on the regional environment has also increased, natural resources are exploited on an ever-larger scale, and natural coastal areas and marine ecosystems are under pressure from intensive economic development and coastal zone projects [3,4,5]. At present, ~41% of sea areas worldwide, especially estuaries and bays, have been seriously disturbed by anthropogenic activities [3]. As a result of ever-increasing urbanization, continuous mariculture scale-up, and rapid development of the ocean economy, land-derived pollutants (e.g., nitrogen and phosphorus) are continuously entering into waters, resulting in water quality deterioration and eutrophication in local areas. In particular, as typical ecologically sensitive areas heavily disturbed by land–sea interactions and anthropogenic activities, semi-enclosed and enclosed bays exhibit weaker water exchange and purification capacities, and thus are highly vulnerable environments [6,7,8]. As reported by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China, 9.4% of nearshore seawaters in China are worse than grade IV in quality, with particularly high levels of dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and reactive phosphate (PO4-P) [9]. Therefore, to monitor variations in water quality of nearshore seas and bays, it is essential to conduct dynamic monitoring of nitrogen and phosphorus elements in water and investigate their driving factors, and then implement corresponding measures and policies to control and improve water quality status.
The accumulation of observation data provides an important basis for regional water quality monitoring. Based on measured DIN, PO4-P, and chlorophyll data from Chesapeake Bay, Harding et al. reported that DIN concentration doubled from 1945 to 1980, leading to an increase in chlorophyll concentration and serious ecosystem damage, but DIN concentration and eutrophication decreased somewhat from 1981 to 2012 due to the control of freshwater influx and DIN concentration [10]. Based on annual and monthly field measurement data of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), chlorophyll, and nutrients, Atsushi et al. investigated long-term trends in water quality status in Tokyo Bay, and showed that total input of land-derived pollutants has decreased to some extent due to gradual improvement in coastal wastewater treatment measures in recent years [11,12]. Based on field measurement data at monitoring stations, hydrological characteristics, and status of land-derived sewage, Cao et al. investigated nearshore marine pollution in Hangzhou Bay and found that serious nutrient pollution was primarily affected by topography, hydrological environment, and industrial development in the bay area [13]. The addition of land-derived nutrients, eutrophication, and other issues have led to water quality deterioration in bays heavily affected by anthropogenic activities, prompting governments to take corresponding measures, including strict control of the total amount of pollutants discharged into the sea, strengthening the pollutants treatment, and restricting the human activities in the bay [14,15], as well as protecting the natural shoreline, restoring the ecological environment of mudflats and wetlands, promoting the ecological functions of the bay, etc. [15,16,17]. To evaluate remediation performance and assess and modify existing management measures, continuous monitoring data are still needed, while the large-scale and long-term simultaneous observation of water quality data in major bays is generally insufficient. Satellite remote sensing technology has the advantages of long time series, large-scale simultaneous observation, and historical backtracking, which can overcome the shortcomings of in situ surveys and enable the observation of spatiotemporal variations in water quality.
Water quality parameters with optical activity, such as chlorophyll, colored dissolved organic matter, total suspended matters and turbidity, can be retrieved by the satellite monitoring spectrum [18,19,20,21,22,23,24] and are widely used for the satellite-based monitoring of water quality [25,26,27,28]. However, nutrients are not directly linked to the spectral signal and the variation mechanism is extremely complex, making nutrient retrieval a difficult task [29]. Although some studies had attempted to retrieve nutrients by optically active variables [30,31,32], these algorithms were extremely regionally applicable and depended heavily on field measurement data, making them difficult to apply to other regions. Nevertheless, remote sensing is still an effective tool for water quality monitoring, with satellites such as the Landsat series and MODIS having been applied quite successfully to this aspect [33,34,35,36]. Therefore, the establishment of nutrient retrieval models based on field measured data can help to clarify the spatiotemporal change patterns of water quality in a region and explore the influencing factors, thereby providing theoretical and scientific support for water and ecological environment governance decisions.
Yueqing Bay is a typical semi-enclosed tidal bay and the fourth largest in area in China. Its tidal range, tidal influx, water exchange capacity, and other hydrological properties are representative of semi-enclosed tidal bays, to some extent. Moreover, Yueqing Bay has complex water exchange processes, including exchange between incoming offshore waters and internal bay water and between bay mouth waters and diluted waters from the Ou River. From the outlet to the bay head, internal waters vary considerably in water exchange capacity, as it takes less than 5 days for 90% of the waters near the outlet to be replaced by offshore waters, compared to 40 days for 90% of the waters in the whole bay to be replaced [37,38]. In addition, more than 30 streams crisscross along Yueqing Bay, and the bay mouth is located on the north side of the Ou River estuary, one of the eight major river systems in Zhejiang, China. Hence, given these natural geographic conditions, Yueqing Bay is greatly affected by land area change. In recent decades, cities along Yueqing Bay have witnessed rapid economic development, dense population growth, and surging demand for urban land for industries and agriculture. Human demand for ocean space development has increased significantly, and since the 1950s, reclaimed tidal flats along Yueqing Bay have increased to 165.1 km2, accounting for 38% of total tidal flat area and 18% of total sea area in the bay [39]. Along with accelerated urbanization, intensified anthropogenic activities, and increased domestic sewage and industrial and agricultural wastewater discharge, total input of land-derived pollutants into the bay has increased, further affecting water quality. Under highly intensive anthropogenic activities, the environment along Yueqing Bay has experienced rapid and dramatic deterioration. Since 2006, local governments have undertaken various measures for marine environment pollution remediation and controlled the use of phosphorus and land-derived pollutants. Based on nutrient data observed in May and August from 2000 to 2014, Guo et al. studied interannual variations in nutrient salt concentrations in the fishing waters of Yueqing Bay and found that concentrations increased continuously from 2002 to 2006 due to high river runoff and industrial and agricultural wastewater and domestic sewage, but that the rising trend slowed slightly after 2006 due to the implementation of national policies and measures to control pollutant discharge [40]. Given the intense anthropogenic activities, in-depth study of variations in environmental status and the main driving factors of Yueqing Bay could offer effective reference for environmental remediation of this and other semi-enclosed bays worldwide and may be of importance to the rapidly developing global bay economy.
Based on water quality data of Yueqing Bay collected from 2014 to 2020 (provided by Wenzhou Environmental Monitoring Center) and Landsat-8 remote sensing data, we built a nutrient concentration retrieval model for Yueqing Bay using support vector machine (SVM) learning with water temperature, red-light waveband, near-infrared waveband, and short infrared waveband as input parameters, and then, spatiotemporal variations in nutrient concentration in the bay retrieved from remote sensing data (2013–2020) were studied along with influencing factors, such as hydrodynamic and environmental information, river basin-related management policies, and anthropogenic activities. This study can provide an effective reference for the remote sensing dynamic monitoring of water quality and provide technical support for the management of environmental protection and remediation of similar bays.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
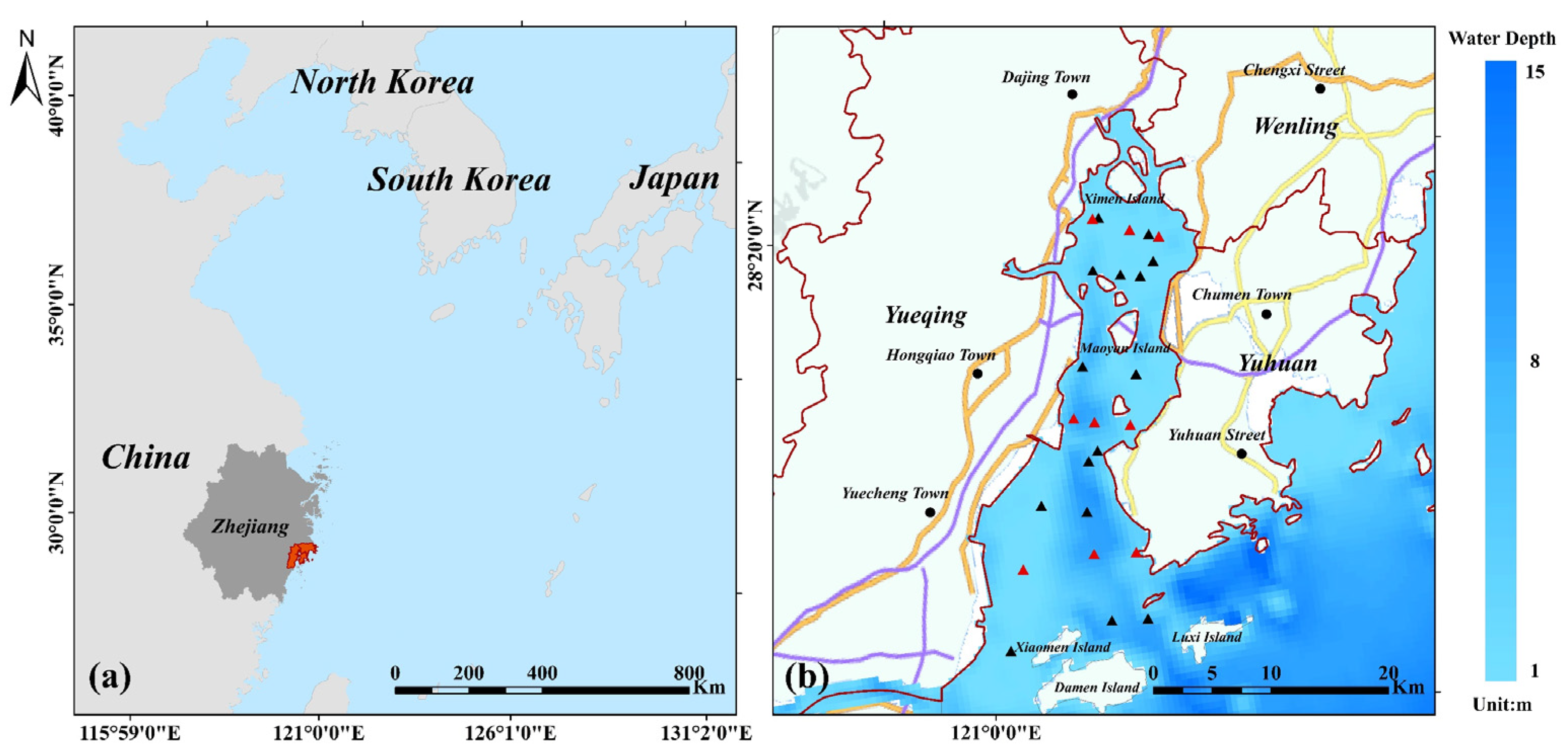
Located along the southern coast of Zhejiang, China (as shown in Figure 1a), on the north side of the Ou River estuary (27°59′09″–28°24′26″N, 120°57′55″–121°17′09″E), Yueqing Bay is the fourth largest bay in China and the largest semi-enclosed bay in Zhejiang, China, with a total sea area of 463.6 km2 and total shoreline length of 42 km. The bay is 10 km wide, on average, with a 21 km wide outlet and 4.5 km wide narrowest section. Average water depth is 10 m and mean tidal inflow/outflow is ~20 × 108 m3. Tidal waves propagate from the East China Sea to Yueqing Bay, and except for Haishan and Jiangxia, which experience irregular semidiurnal tides, the other areas of the bay are under regular semidiurnal tides [41]. More than 30 streams of varying size drain into the bay, including the Qing River, Bai Creek, Ling Creek, and Jiangxia Creek [42], and mean annual runoff of the river basin is 10.3 × 108 m3 [41]. The western part of Yueqing Bay belongs to Yueqing, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China, while the northern and eastern parts belong to Wenling, Yuhuan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China, respectively (as shown in Figure 1b). The Yueqing Bay river basin is densely populated, and the three largest cities along the bay have a total population of about 3 million [43]. Surging activities, such as aquatic breeding and sea reclamation, have significantly increased economic revenue and development [43].
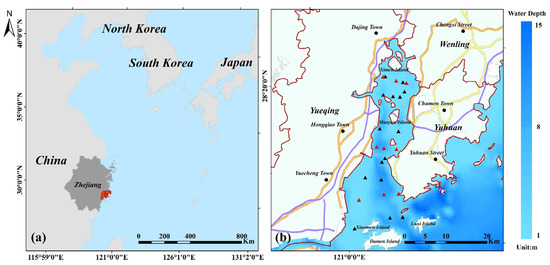
Figure 1.
Location of study area (a) and cities along Yueqing Bay: Yueqing, Wenling, and Yuhuan (b). (Red triangles in (b) are nine fixed survey stations for each survey and black triangles are non-fixed survey stations; geographical map is sourced from China National Geographic Information Public Service Platform (https://www.tianditu.gov.cn/, accessed on 21 October 2021)).
Situated in the subtropical monsoon climate zone, Yueqing Bay is subject to various environmental factors, such as topography and marine climate, resulting in a land-bay microclimate with good heat, moisture, and temperature, resulting in a mean annual air temperature of 17–17.5 °C and mean annual rainfall of 1191.7–1506.8 mm [44]. Yueqing Bay contains 54,527.9 acres of tidal flats, and over 20 species of commercial fish, 58 species of shellfish, and 60 species of crustaceans, and is thus a natural farm of shellfish breeding. Furthermore, with a mean tidal range of more than 4 m (maximum of 8.53 m) [41], Yueqing Bay has considerable tidal energy, which is useful for tidal power plants, e.g., the Jiangxia pilot tidal power plant has an installed capacity of up to 550,000 kW [39,42].
Our study area included Yueqing Bay and its three main coastal cities, namely, Yueqing, Wenling, and Yuhuan. We investigated the spatiotemporal variational patterns in nutrient concentration in the waters from 2013 to 2020 as well as the main driving factors.
2.2. Data Source
2.2.1. Satellite Remote Sensing Data
Land satellite Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) high-spatial-resolution (30 m) multi-spectral remote sensing data (released by United States Geological Survey (USGS)) were used for analysis. Since its launch in 2013, data from the OLI has been widely applied in long-term water quality monitoring for inland rivers, lakes, nearshore seas, and bays. The Landsat-8 OLI remote sensing data were downloaded from the USGS website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/, accessed on 30 August 2021), and remote sensing images of the study area (strip no.: 118040) during 2013–2020 with sky cover less than 30% were selected. In total, 63 Landsat Level-1 remote sensing scenes met the above criteria (Table 1), including more than 10 remote sensing images per season and more than five remote sensing images per year covering most months, seasons, and years. To obtain the remote sensing reflectance product, we performed radiometric calibration and atmospheric correction of the data using ENVI v5.3 (Exelis Visual Information Solutions (Boulder, CO, USA)), with atmospheric correction conducted using the FLAASH algorithm in ENVI v5.3 [45].

Table 1.
Valid Landsat-8 remote sensing images from January 2013 to December 2020 (green cells and numbers represent presence of data and quantity of valid data, respectively, while white cells represent absence of data).
2.2.2. Field Measurement Data
For this study, environmental water quality survey data of Yueqing Bay were provided by Wenzhou Environmental Monitoring Center. During 2014–2020, monthly voyage observations were performed, and in situ sampling and observation and data acquisition were conducted at nine fixed stations and several non-fixed stations. Monitoring parameters included DIN (nitrite–nitrogen, nitrate–nitrogen, and ammonia–nitrogen), PO4-P, water temperature, chlorophyll, dissolved oxygen, salinity, and pH. Both sampling and testing were performed in accordance with the Code of Practice for Marine Monitoring Technology [46]. During 2014–2020, the in situ sampling period and statistical sampling size were relatively stable and more than 45 pairs of observed DIN and PO4-P data per month were retained, representing primary characteristics of nutrients in Yueqing Bay.
2.3. Analytical Methods and Related Supplementary Data
2.3.1. Matching Satellite and Field Measurement Data
In this study, satellite data were matched with field measurement data. Spatially, 1 × 1 pixels (30 m × 30 m) closest to a survey station in latitude and longitude were matched; temporally, satellite data differing from field measurement data in observation time by less than ±3 days were matched, which was an optimal choice to obtain enough representative data in the shortest possible time interval. We could not obtain enough matchup data for the satellite algorithm development if we set up a shorter time interval, due to the long revisiting period of 16 days for Landsat and the limited number of field measurements. To extract reflectance and other information, the “ExtractMultiValuesToPoints” feature of ArcGIS v10.7 (Environmental Systems Research Institute, Inc. (Redlands, CA, USA)) was used to generate a vector file based on latitude and longitude information of a data observation station, with corresponding remote sensing reflectance information then extracted.
Using the above matching approach for data during 2014–2020, 80 matched DIN data pairs and 73 matched PO4-P data pairs were generated. We randomly sampled 65% of the data as a training dataset for algorithm construction, while the remaining 35% of data served as a validation dataset for algorithm accuracy assessment. In general, the matched data encompassed and reflected spatiotemporal variability of the field measurement data, and thus could be used to construct and assess the nutrient retrieval algorithm for waters of Yueqing Bay over a long time series.
2.3.2. SVM Algorithm and Statistical Parameters of Model Assessment
Machine learning-based regression algorithms, e.g., random forest, artificial neural network, and SVM algorithms, have been widely applied in water quality research [47,48,49]. In this study, based on matched data pairs, we used the SVM algorithm to construct a nutrient retrieval algorithm for waters of Yueqing Bay. This was mainly due to the smaller data size, as the random forest and artificial neural network algorithms are prone to overfitting. In contrast, the SVM algorithm attempts to map training data points to high-dimensional eigenspace based on kernel function, resulting in many decision-making boundaries (hyperplanes) in eigenspace that can separate different classes of data points. In addition, the SVM algorithm does not involve probability measures or the law of large numbers; moreover, the purpose of SVM optimization is to minimize structuring risk rather than empirical risk, thereby reducing the risk of overfitting [50]. Regarding prediction, the training process generated an SVM model with multiple input parameters for automatic optimization. Based on the trained SVM model, we predicted dependent variables (e.g., DIN and PO4-P) by inputting new training parameters (e.g., remote sensing reflectance).
During analysis, SVM algorithm construction, parameter tuning, simulation, assessment, and prediction were performed using Matlab R2020b (MathWorks (Natick, MA, USA)).
The fitting effect during algorithm construction was expressed by coefficients of determination (R2) and significance level (P) resulting from statistical analysis. In addition, to assess the accuracy of the model-predicted results quantitatively, the following statistical parameters were used: (1) bias, i.e., general bias information of the predicted result; (2) Mean Absolute Error (MAE), i.e., mean value of absolute error between predicted and true values; and (3) Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), i.e., square root of the ratio of squared bias between observed and true values to number of observations. Results were statistically analyzed using Microsoft Excel 2016 (Microsoft (Redmond, Washington, DC, USA)):
where and are the predicted and observed results, respectively, and N is the number of data pairs, .
2.3.3. Hydrodynamic Model for Yueqing Bay
The Finite Volume Coastal Ocean Model (FVCOM) was used to simulate three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamics of Yueqing Bay. FVCOM is a 3D model for nearshores, estuaries, and oceans based on the finite volume method [51,52]. Unstructured triangular meshes were used in the horizontal direction and the σ coordinate system was used in the vertical direction to better resolve the complex shorelines and topography of Yueqing Bay. This model was previously validated and applied by our research team in the Changjiang River estuary [53].
The model consisted of 14,197 points in the horizontal direction and 26,959 triangular meshes, the mesh resolution of the bay was 1000 m, and the mesh resolutions of the open bounds were 4–20 km. In the model, the S-57 electronic navigational chart was used for water depth data of Yueqing Bay and the waters near Wenzhou Port. For the open bounds, the model superposed the predicted tidal levels of eight main tidal constituents, namely, M2 (12.42 h), N2 (12.66 h), S2 (12.00 h), K2 (11.97 h), K1 (23.93 h), O1 (25.82 h), P1 (24.07 h), and Q1 (26.87 h), and background flow field data from HYCOM, among which the predicted tidal levels had a temporal resolution of 1 h and the background flow field data had a temporal resolution of 1 month. On the river bounds, climatological mean discharges of the Yangtze, Qiantang, Tiao, Yong, Jiao, Ou, Feiyun, and Ao rivers, and three major mountain creek-based riverlets, flowing into Yueqing Bay were superposed. Discharge data for the Yangtze and Qiantang rivers were sourced from Bulletin of River Sediments in China for 2002–2020, while discharge data for other rivers were estimated from the TRMM 3B43 climatological mean precipitation product for 1998–2019 using the river discharge estimation formula of Liu et al. (2020) [54]. For the sea-air upper bounds, wind data were sourced from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), with a spatial resolution of 0.125° × 0.125° and a temporal resolution of 6 h.
2.3.4. Characterization of Intensity of Anthropogenic Activities in Cities along Yueqing Bay
Based on the administrative boundaries of Yueqing, Wenling, and Yuhuan along Yueqing Bay, point-of-interest (POI) data of the various cities in 2020 were acquired using the “POI retrieval” feature in Baidu Maps (http://lbsyun.baidu.com/index.php?title=webapi accessed on 30 August 2021), which are a type of vector point data containing latitude and longitude coordinates, facility name, and facility type [55]. Each vector point in space represents one facility space in real life and corresponds to commercial and human socioeconomical activities, such as traveling and dining, and governmental services. The POI data are applicable for analysis of anthropogenic activities, economic development status, and distribution from a spatial perspective [56,57].
Since many categories of facilities are closely associated with each other in functional properties, POI data are often manifested in aggregated form in geographic space, i.e., hot spots [58]. Usually, “density” is used to characterize aggregation intensity of POI data in a local area quantitatively, while kernel density estimation is a common and effective density estimation method [59] for nonparametric analysis of geospatial distribution, reflecting the effect of a geographic phenomenon attenuating with increasing spatial distance. Given an arbitrary point in space, kernel density is the sum of weights of all sample points within a circle with a given radius whose center is at the point. Such a weight is inversely proportional to the distance between the sample point and point [60,61]. Here, kernel density was calculated using the following formula:
where f(x) represents the kernel density function of point x; h is the bandwidth, i.e., radius of the circle; n is the number of sample points within the circle; K is the spatial weight function; and () is the distance between the sample point and point x.
Given the above understanding, intensities of anthropogenic activities in cities along the Yueqing Bay were spatially analyzed based on POI data by means of kernel density estimation.
3. Results
3.1. Algorithm Construction and Validation
Nutrients are non-optically active substances, and their concentrations have no significant spectral features [62]. However, nutrients are to some extent related to the physical properties of water, such as water temperature, and optically active substances in water, such as suspended solids and chlorophyll-a [63,64,65], which are associated with spectra [66,67,68,69,70]. In this study, waveband information was used as a variable input to retrieve nutrient concentrations in the waters of Yueqing Bay.
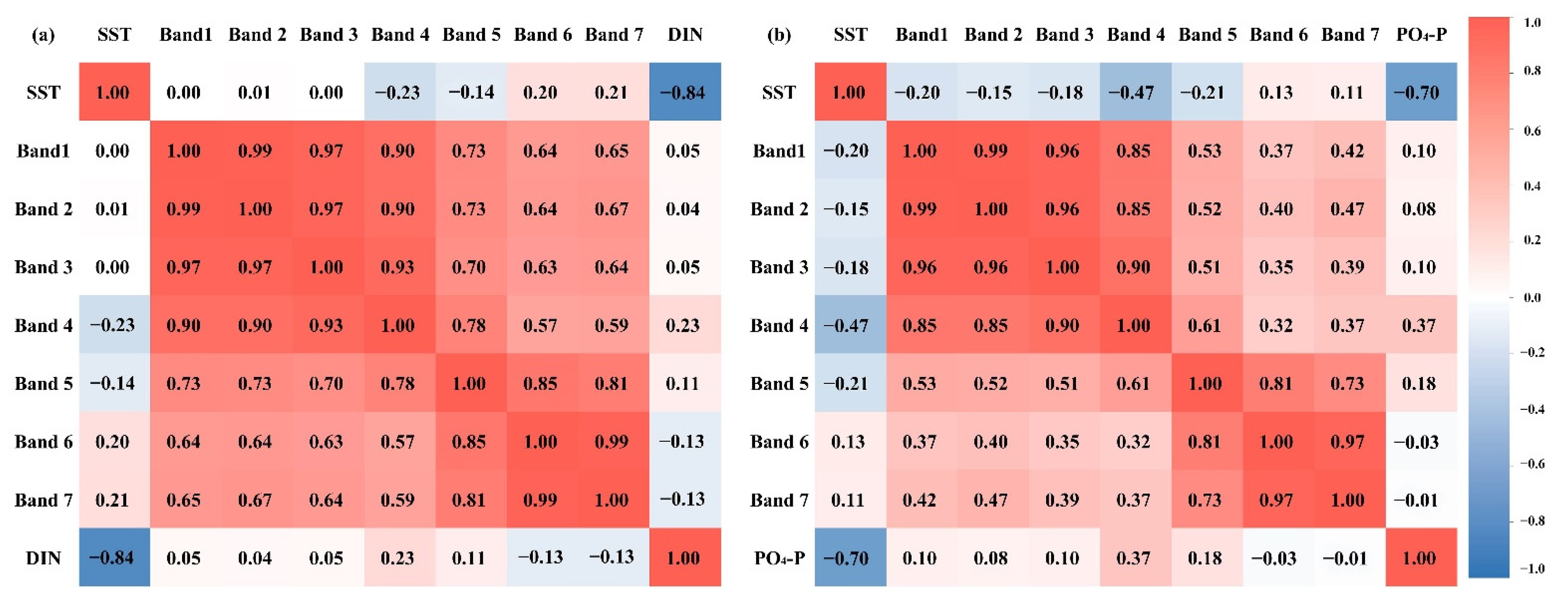
Correlation analysis was carried out for temperature and waveband information. As shown in Figure 2, DIN was highly correlated with sea surface temperature (SST) (R = −0.84), as well as the red-light (Band 4), near-infrared (Band 5) (R > 0.1), and short infrared wavebands (Bands 6 and 7) (R < −0.1); PO4-P was highly correlated with SST (R = −0.70), as well as the red-light (Band 4) and near-infrared wavebands (Band 5) (R > 0.15). Therefore, SST and the red-light, near-infrared, and two short infrared wavebands were selected as input parameters of the DIN retrieval model, and SST, red-light waveband, and near-infrared waveband were selected as input parameters of the PO4-P retrieval model.
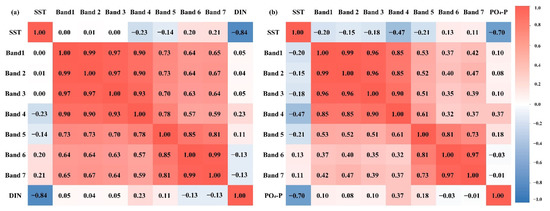
Figure 2.
Correlation analysis of input variables versus output variables: (a) correlation between DIN and each factor; (b) correlation between PO4-P and each factor.
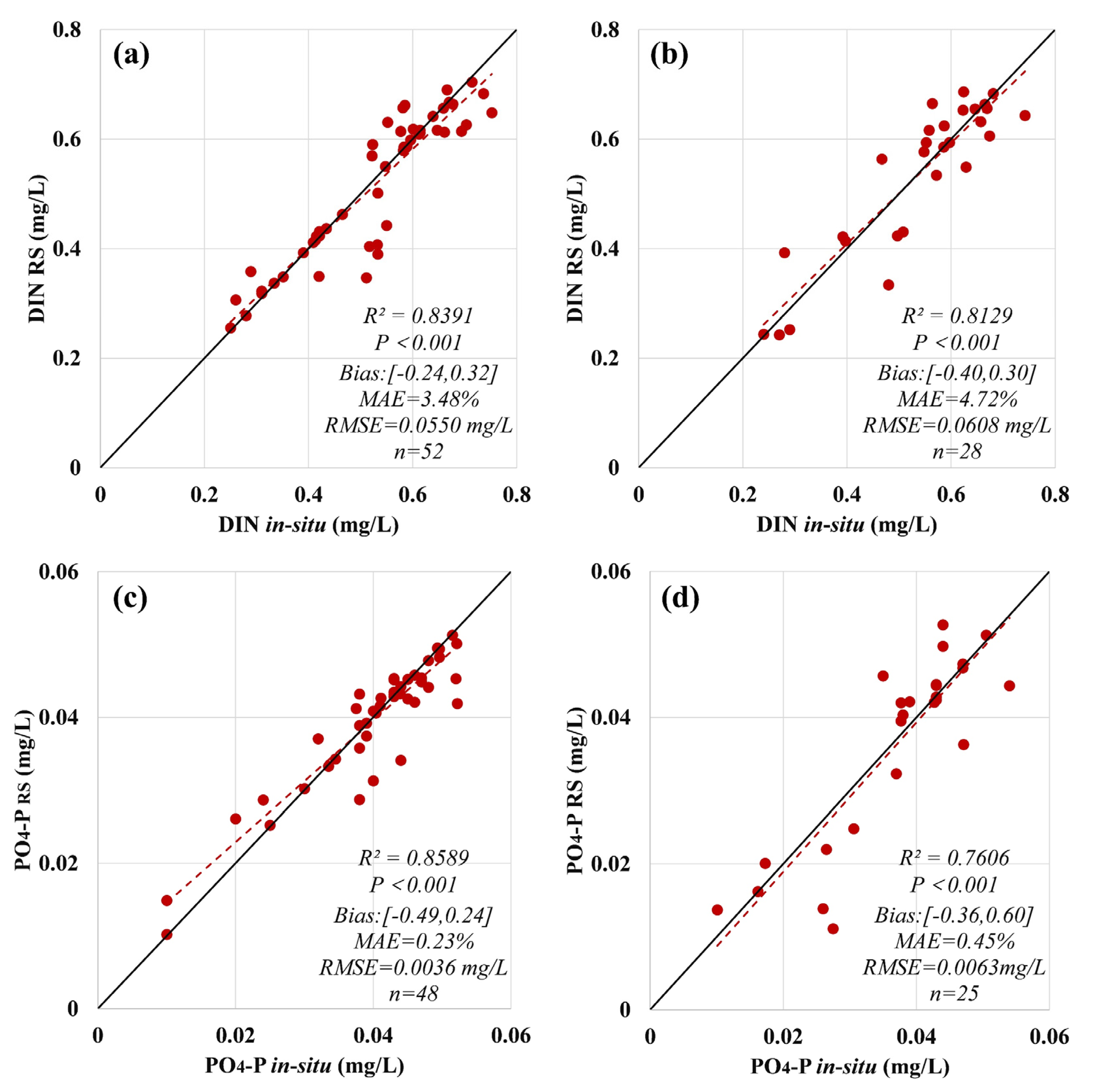
Based on the data arrays acquired by matching, a nutrient retrieval model for Yueqing Bay was obtained by SVM. As shown in Figure 3a,b, for the training set of the DIN retrieval model, R2 = 0.8391, P < 0.001, bias was (−0.24,0.32), MAE = 3.48%, and RMSE = 0.0550 mg/L, and for the validation set of the DIN retrieval model, R2 = 0.8129, P < 0.001, bias was (−0.40,0.30), MAE = 4.72%, and RMSE = 0.0608 mg/L; for the training set of the PO4-P retrieval model, R2 = 0.8589, P < 0.001, bias was (−0.49,0.24), MAE = 0.23%, and RMSE = 0.0036 mg/L, and for the validation set of the PO4-P retrieval model, R2 = 0.7606, P < 0.001, bias was (−0.36, 0.60), MAE = 0.45%, and RMSE = 0.0063 mg/L.
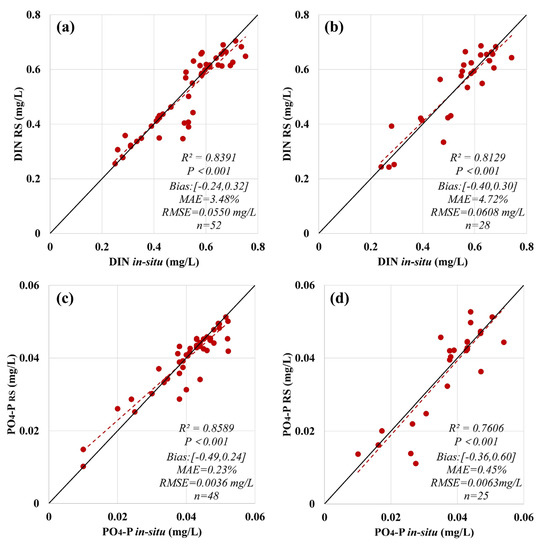
Figure 3.
Model validation: (a) DIN training set; (b) DIN validation set; (c) PO4-P training set; (d) PO4-P validation set.
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in Nutrient Concentrations in Yueqing Bay
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution of Nutrient Concentrations in Yueqing Bay
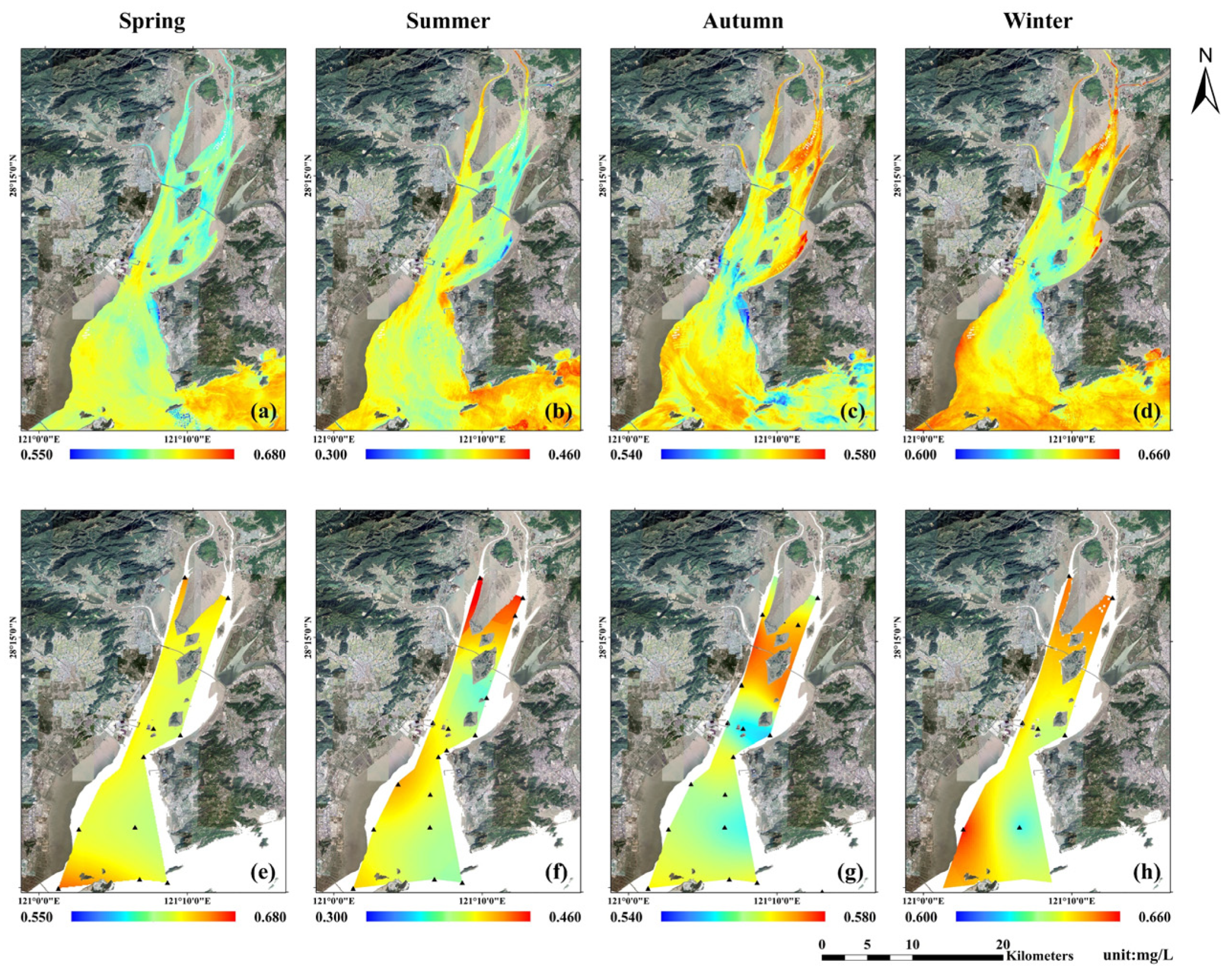
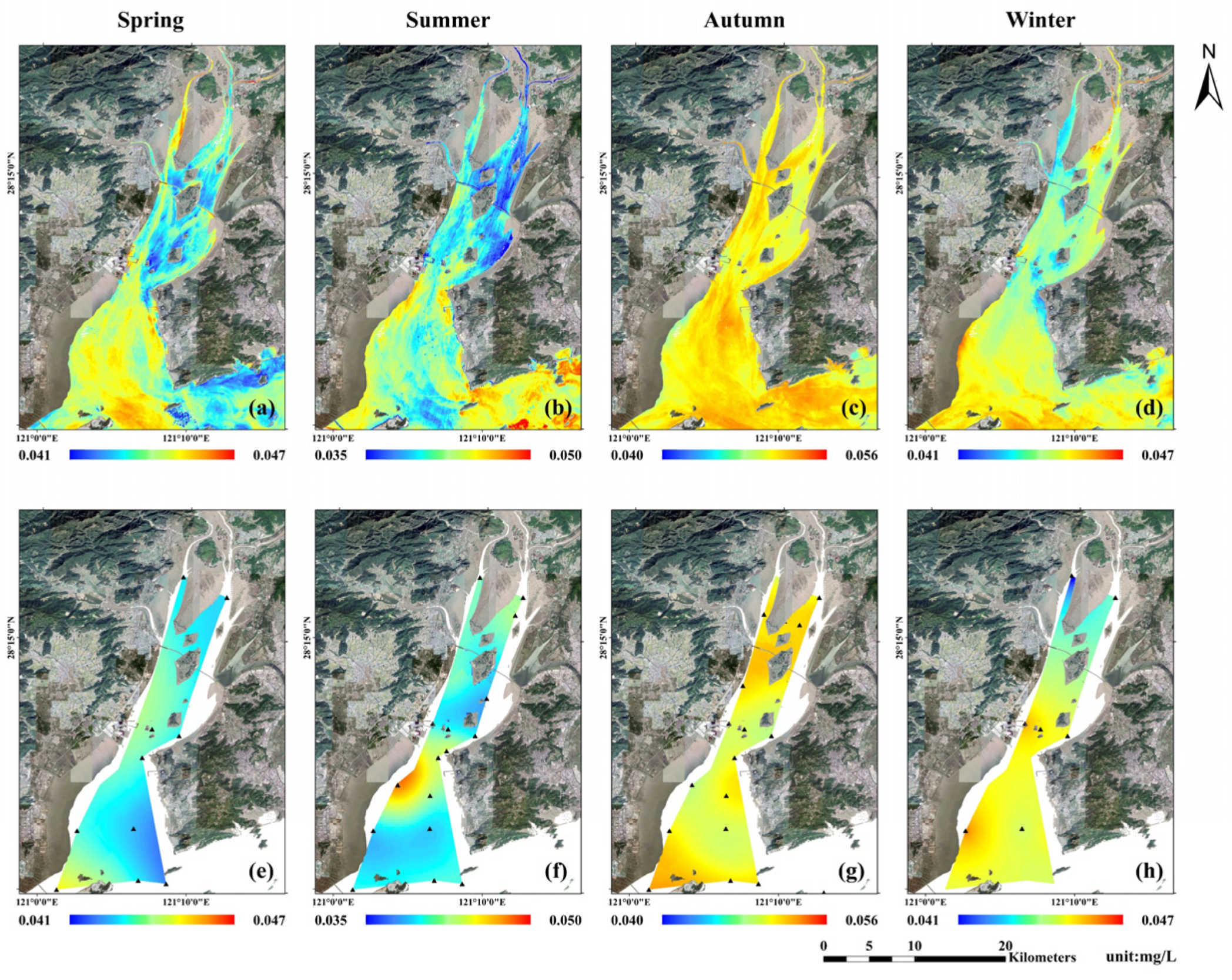
From the perspective of the spatial distribution of nutrient concentration based on remote sensing retrieval, in spring, there were two high DIN regions in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay and Southwest Shoal at the bay mouth, while DIN concentrations were more uniform in most other areas. In summer, high DIN values remained in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay and Southwest Shoal, while at the bay head, DIN concentrations on the west side of Ximen Island were slightly higher than those on the east side. In autumn, high DIN concentrations were mainly observed in the stream on the east side of Ximen Island at the bay head, Southwest Shoal at the bay mouth, and the sea area on the north side of Damen Island, while low concentrations were mainly observed in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay and coastal area to the southwest side of Yuhuan Island. In winter, high DIN concentrations were observed in the stream on the east side of Ximen Island at the bay head, Southwest Shoal at the bay mouth, and sea areas on the north side of Damen and Xiaomen islands, while low concentrations were observed in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay through the sea area in the middle of the bay mouth (Figure 4a–d).
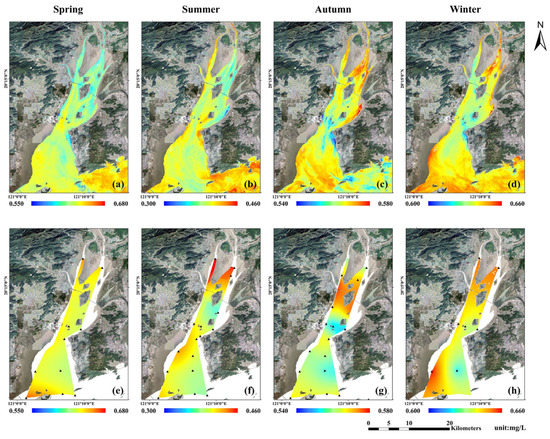
Figure 4.
Seasonal spatial distribution of DIN concentrations in Yueqing Bay: (a–d): seasonal average of retrieval results based on remote sensing data from 2013 to 2020; (e–h): Kriging interpolation results based on the seasonal average of field measurement data from 2014 to 2020. (Black triangles in (e–h) are survey stations).
In spring, there was a high PO4-P concentration zone in the Southwest Shoal through the sea area in the middle of the Yueqing Bay mouth, while low concentrations were observed in the sea areas near Maoyan Island and the southwest side of Yuhuan Island. In summer, high PO4-P concentrations were observed in the Southwest Shoal, while low concentrations were observed at the bay head and sea area between Yuhuan Island and Damen Island. In autumn, a high PO4-P concentration zone was observed in the middle part of the bay through the sea area on the north side of Damen Island, while low concentrations were mainly observed in the coastal area of the Southwest Shoal. In winter, high PO4-P concentrations were observed in the Southwest Shoal and sea area on the north sides of Damen and Xiaomen islands, while low concentrations were observed in the stream on the west side of Ximen Island at the bay head and in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay (Figure 5a–d).
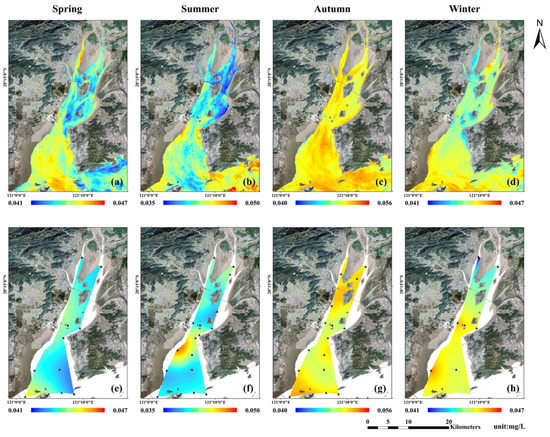
Figure 5.
Seasonal spatial distribution of PO4-P concentrations in Yueqing Bay: (a–d): seasonal average of retrieval results based on remote sensing data from 2013 to 2020; (e–h): Kriging interpolation results based on the seasonal average of field measurement data from 2014 to 2020. (Black triangles in (e–h) are survey stations).
Based on field measurement data from 2014 to 2020, the spatial distribution of nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay was obtained by Kriging interpolation (Figure 4e–h and Figure 5e–h), and a comparison was made with the remote sensing retrieval results (Figure 4 4a–d and Figure 5a–d). In general, the spatial distribution of the satellite-derived nutrient concentration was consistent with that of the field measured data; high-value zones were situated in the streams on both sides of Ximen Island at the bay head, narrowest area of the middle part of the bay, and Southwest Shoal at the bay mouth, while low-value zones were situated in the sea area on the west side of Yuhuan Island. Due to the limited sampling data and coverage, there were no data in the nearshore and the distribution of interpolation results might be unreasonable in the nearshore. As shown in Figure 5f, there was an obvious mutation in the concentration of PO4-P from the middle of the bay to the bay mouth, which might be the artificial error by interpolation. The spatial distribution of satellite-derived nutrients was more complete in spatial coverage.
The distribution of nutrient concentrations reported by Zeng et al. [71] in Yueqing Bay from 2006 to 2007 was basically consistent with our satellite retrieval results, that is, the high nutrient concentrations were mainly concentrated in the Southwest Shoal and the narrowest part of the middle part of the bay, and the low concentrations were mainly concentrated in the west side of Yuhuan Island. Through model simulation, Li et al. [72] found that the nutrient concentrations in the western part of the bay were higher than those in the eastern part. However, Li et al. [72] reported that high nutrient concentrations were observed in the bay head and low nutrient concentrations were observed in the bay mouth, and there were no obvious high nutrient concentrations in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay, which was slightly different from the results of this study. The main reason would be the different input parameters of the nutrient concentration retrieval model. The water quality model constructed by Li et al. [72] mainly considered the influence of water flow and diffusion, while we used the temperature and spectral information as the main parameters to retrieve the nutrient concentrations. At the same time, on both sides, the narrowest part in the middle part of the bay might be affected by two power plants, the Huaneng Yuhuan Power Plant (put into operation in 2007) and the Zheneng Yueqing Power Plant (put into operation in 2008). Although the influence range of warm water drainage of the power plant was limited, it may still have a certain impact on the satellite-derived nutrient concentrations in the narrowest part of the middle part of the bay. Therefore, more data are needed for refined verification and analysis.
3.2.2. Seasonal Variations in Nutrient Concentrations in Yueqing Bay
Based on analysis of the remote sensing retrieval results (Table 2), seasonal DIN concentrations varied within 0.211–0.687 mg/L, with levels lowest in summer (averaging 0.3940 mg/L), highest in spring and winter (averaging 0.6189 mg/L and 0.6396 mg/L, respectively), and reaching 0.5648 mg/L in autumn. The PO4-P concentrations varied seasonally within 0.016–0.056 mg/L, with levels lowest in summer (averaging 0.0414 mg/L), highest in autumn (averaging 0.0508 mg/L), and reaching 0.0439 mg/L and 0.0444 mg/L in spring and winter, respectively.

Table 2.
Minimum, maximum, and mean nutrient concentrations retrieved by remote sensing in each season in Yueqing Bay.
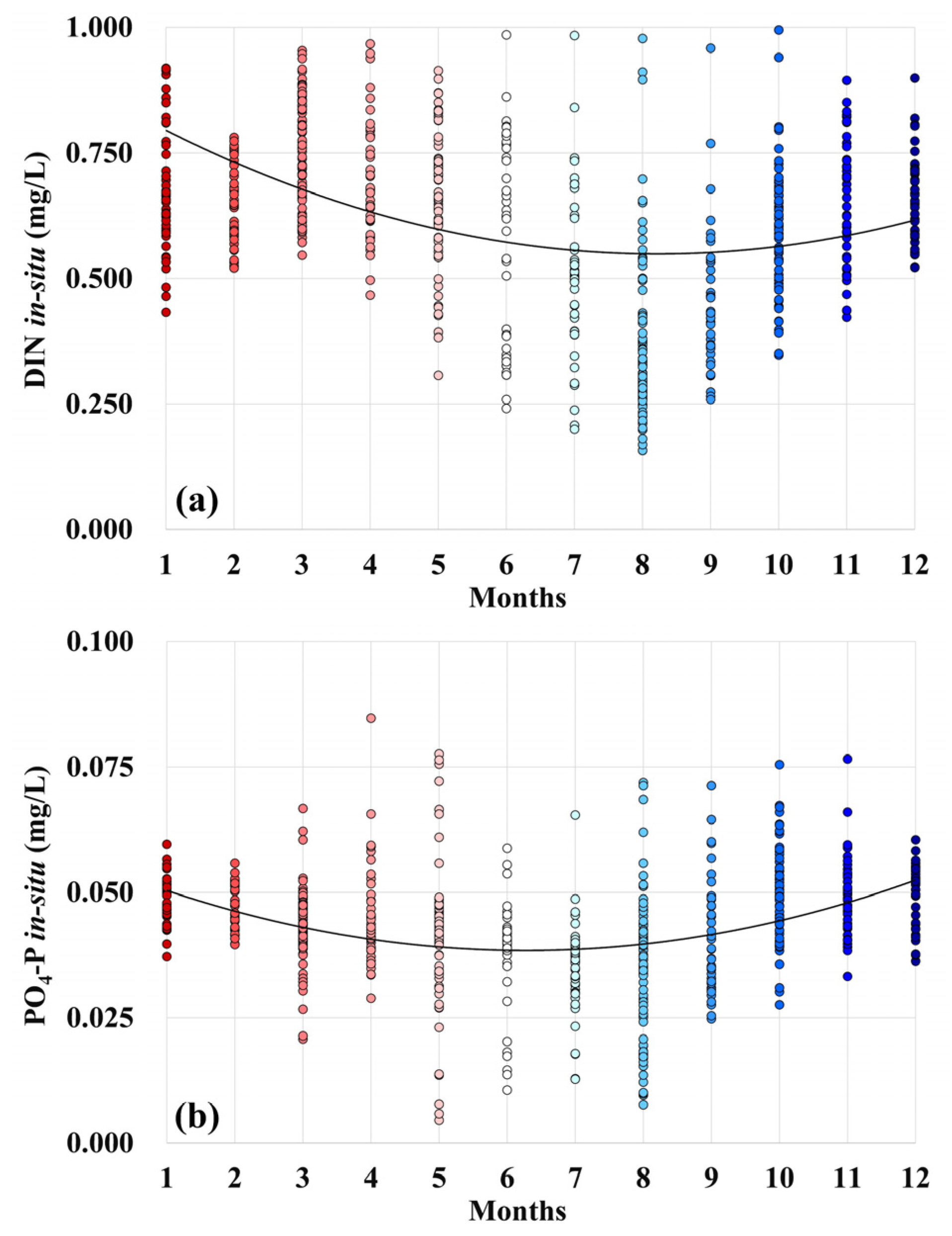
Based on the field measurement data (Figure 6) in Yueqing Bay, DIN concentrations were lower in summer (mean: 0.482 mg/L) and higher in spring and winter (means: 0.73 mg/L and 0.66 mg/L, respectively); PO4-P concentrations were lower in summer (mean: 0.043 mg/L) and higher in autumn and winter (means: 0.047 mg/L and 0.048 mg/L, respectively). Nutrient concentrations varied greatly, with the DIN concentration ranging from 0.2 to 1.0 mg/L and PO4-P concentration ranging from 0.01 to 0.08 mg/L.
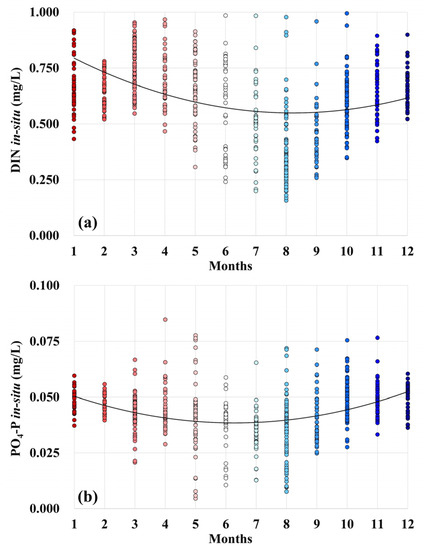
Figure 6.
Observed nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay during 2014–2020: (a) monthly variations in DIN concentration; (b) monthly variations in PO4-P concentration; each point represents field measurement data at one station.
3.2.3. Long Time-Series Variations in Nutrient Concentrations in Yueqing Bay
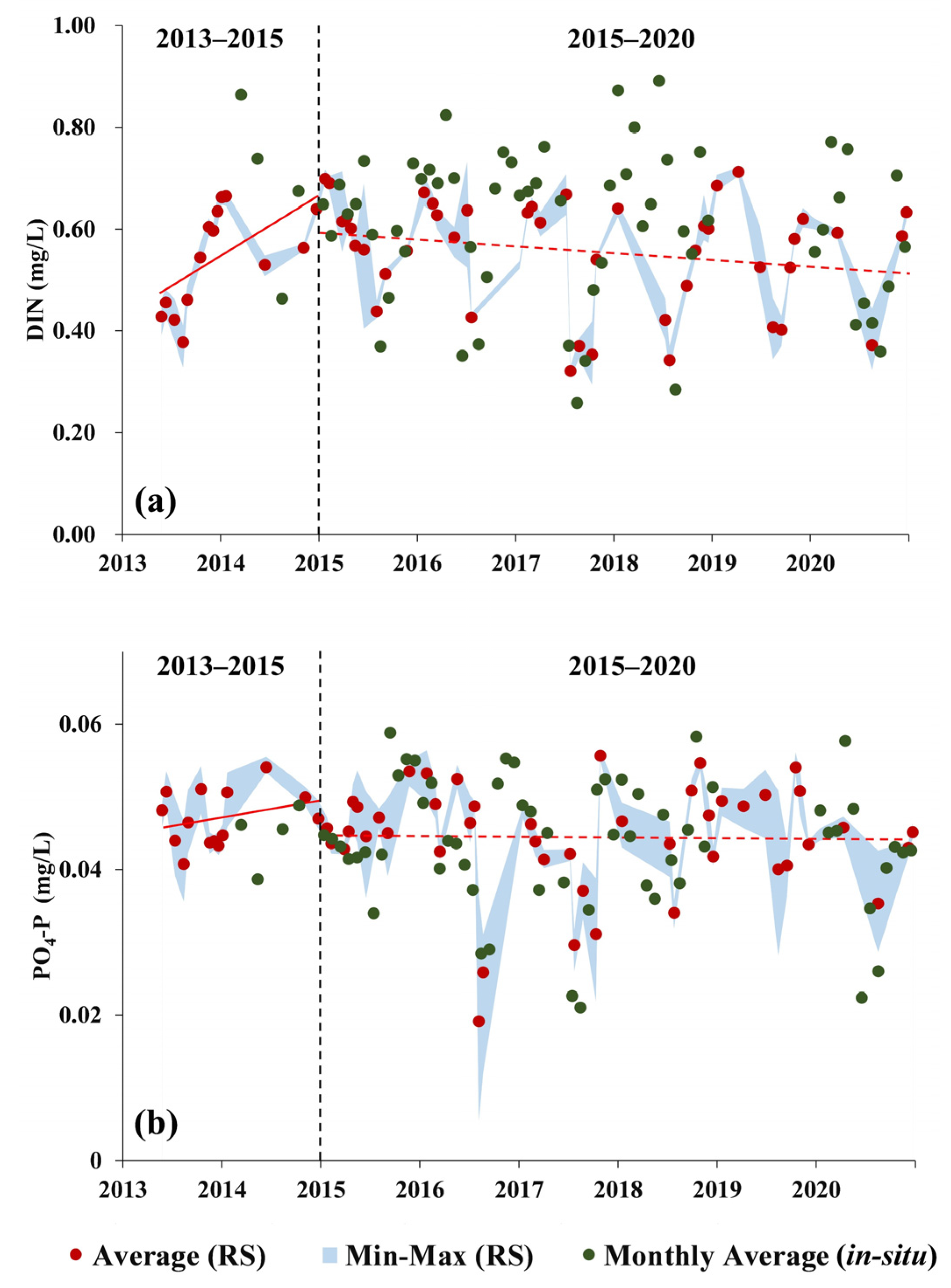
As shown in Figure 7a, the DIN concentration in Yueqing Bay exhibited a notable rising trend (P = 0.0262, t = 2.5341) during 2013–2015 and a non-significant decreasing trend during 2015–2020 (P = 0.1233, t = −1.5729). As shown in Figure 7b, the PO4-P concentration in Yueqing Bay exhibited a non-significant increasing trend (P = 0.3196, t = 1.0383) during 2013–2015 and a non-significant decreasing trend (P = 0.8906, t = −0.1383) during 2015–2020.
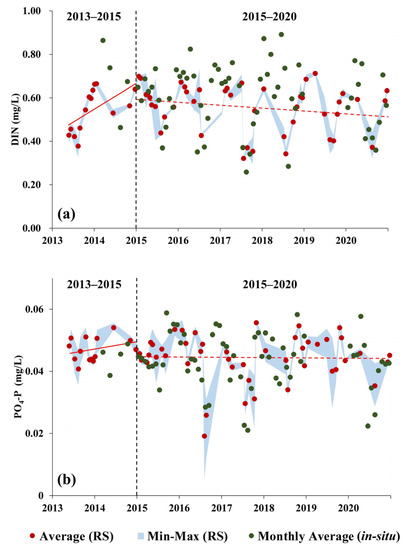
Figure 7.
Interannual time-series variations in region-averaged nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay from 2013 to 2020: (a) interannual time-series variations in DIN concentrations; (b) interannual time-series variations in PO4-P concentrations. (Red scatter points represent mean region-averaged nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay; green scatter points represent monthly means of observed nutrient concentrations; upper bound of blue zone represents maximum nutrient concentration within corresponding time interval, while lower bound represents minimum nutrient concentration within corresponding time interval; vertical black dashed lines correspond to 2015; red solid lines represent trend lines during 2013–2015; red dashed lines represent trend lines during 2015–2020).
Comparing field measurement data with the remote sensing retrieval results (Figure 7), the long time-series variation trends in remote sensing retrieval generally agreed with the observed results, but due to the acquisition time of satellite remote sensing images and other objective factors, the field measurement data of high DIN concentration could not be matched during the data matching process, resulting in the DIN retrieval results being slightly lower than the field measurement data in some periods. At the same time, abnormally low nutrient concentrations were found in Yueqing Bay in the summer of 2017.
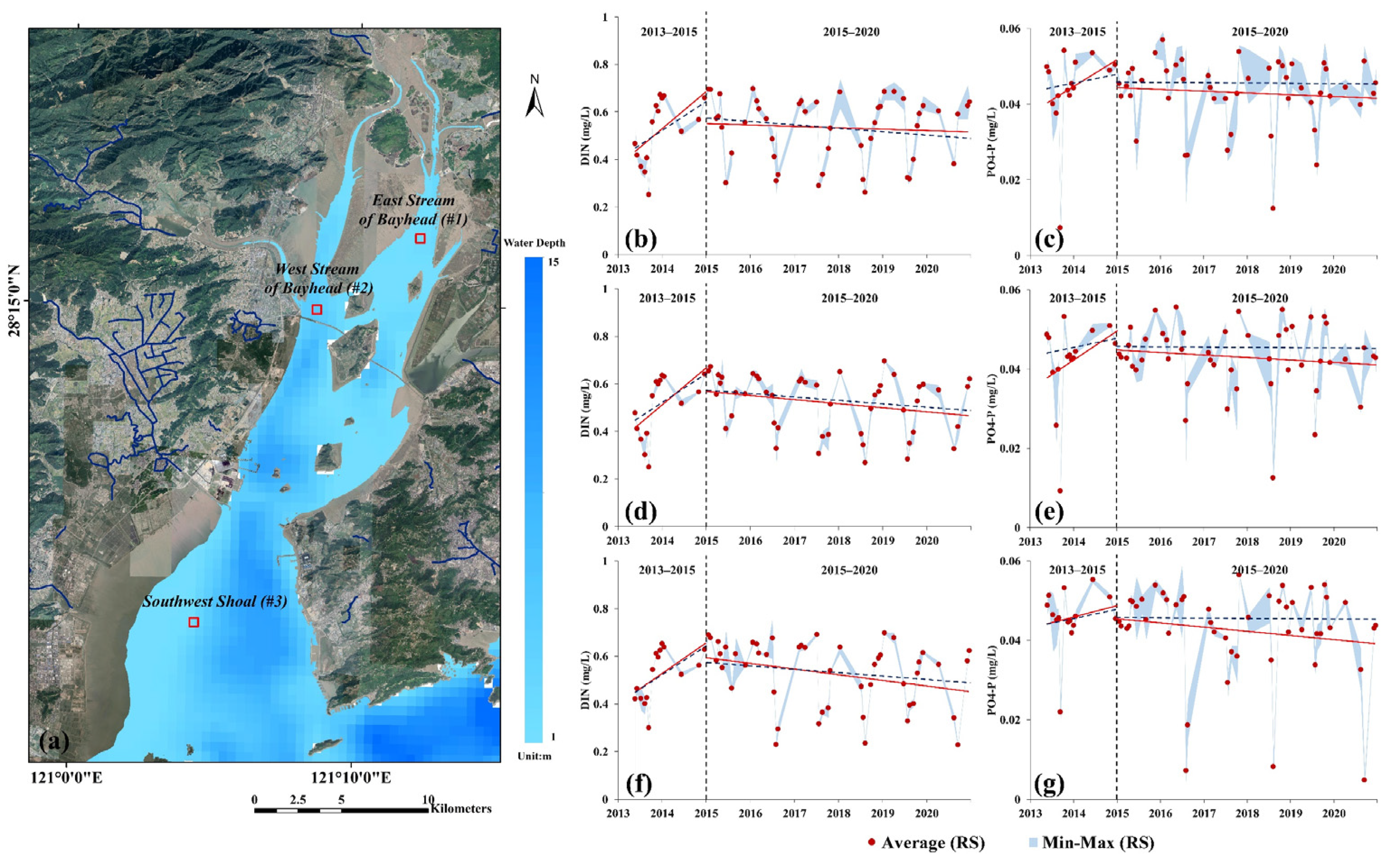
To further elucidate the water quality trends in local regions of Yueqing Bay under strong anthropogenic impact, three 500 m × 500 m regions located at coastal stream estuaries were selected (Figure 8a), i.e., East Stream of the bay head on the east side of Ximen Island (#1), West Stream of the bay head on west side of Ximen Island and at Qing River estuary (#2), and Southwest Shoal at the bay mouth (#3), where mean, maximum, and minimum nutrient concentrations were extracted. As shown in Figure 8b–g, during 2013–2015, the increasing nutrient concentrations in these three regions were all higher than the mean nutrient concentration rate in Yueqing Bay (see slopes in Table 3). Among these results, the PO4-P concentrations in the East Stream (#1) and West Stream of the bay head (#2) increased at the fastest rate (Figure 8c,e), aPO4-P(#1) = 1.98 × 10−5, aPO4-P(#2) = 2.03 × 10−5). After 2015, nutrient levels in the waters of the three regions decreased to variable extents. Notably, the nutrient concentrations in the East Stream (#1) decreased at a slower rate than Yueqing Bay overall (Figure 8b,e), especially DIN (aDIN(#1) = −1.30 × 10−5), while the decreasing nutrient concentrations in the West Stream (#2) and Southwest Shoal (#3) were higher than the mean decreasing rate in Yueqing Bay (Figure 8d–g), especially PO4-P in Southwest Shoal (#3) (aPO4-P(#3) = −2.90 × 10−6). Table 3 shows the statistical parameters of the time-series regression of nutrient concentrations in the waters of various regions and Yueqing Bay.
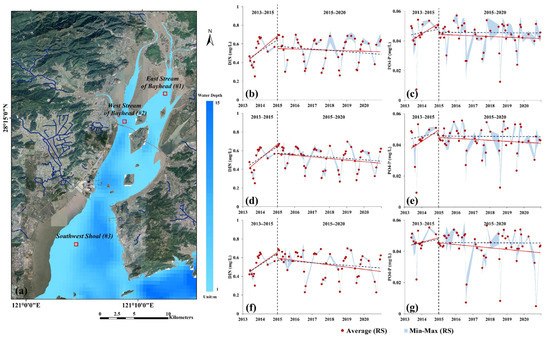
Figure 8.
Long time-series variation in nutrient concentrations retrieved by remote sensing in local regions of Yueqing Bay: (a) spatial distribution map of data extraction regions; (b) variations in DIN concentration in East Stream of the bay head; (c) variations in PO4-P concentration in East Stream of the bay head; (d) variations in DIN concentration in West Stream of the bay head; (e) variations in PO4-P concentration in West Stream of the bay head; (f) variations in DIN concentration in Soutwest Shoal; (g) Variations in PO4-P concentration in Southwest Shoal. (Red scatter points represent mean nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay; upper bound in blue zone represents maximum nutrient concentration within corresponding time interval, while lower bound represents minimum nutrient concentration within corresponding time interval; vertical black dashed lines correspond to 2015; red solid lines represent trend lines of nutrient concentration in various local regions; blue dashed lines represent trend lines of nutrient concentration in the whole of Yueqing Bay).

Table 3.
Statistical regression analysis of nutrient concentration in local regions of Yueqing Bay.
4. Discussion
4.1. Influences of Rivers, Hydrodynamics, and Biological Effects
Yueqing Bay is the largest semi-enclosed bay in Zhejiang and is influenced by the offshore Fujian-Zhejiang Coastal Current and Taiwan Warm Current [73,74]. Although there is no large river along the bay providing land-derived input, Yueqing Bay is on the north side of the Ou River estuary and more than 30 streams are distributed in the bay area [42]. Based on HYCOM background flow field, runoff, wind farm, and tidal data, the climatological flow field of nearshore sea areas in the middle and southern parts of Zhejiang and Yueqing Bay in summer and winter was acquired by FVCOM numerical simulation.
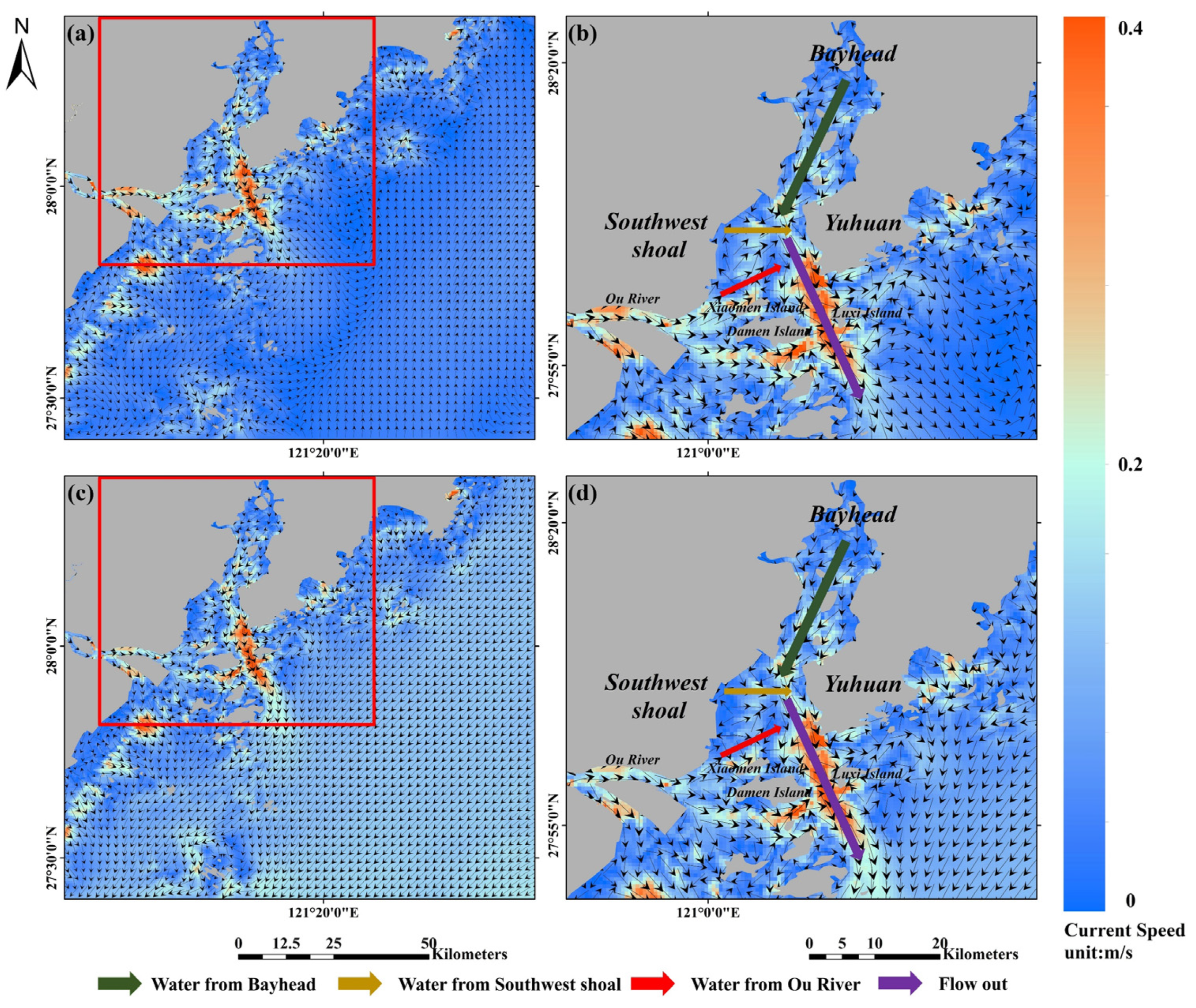
Based on variations in flow fields in the nearshore sea areas in summer (Figure 9a) and winter (Figure 9c), the high-temperature low-nutrient Taiwan Warm Current flowing from south to north was the dominant water mass in summer [74], while in winter, the Taiwan Warm Current weakened significantly and retreated towards the south, and the low-temperature, nutrient-rich Fujian-Zhejiang Coastal Current flowing from north to south gradually became the dominant water mass, with a flow field intensity much higher than that of the Taiwan Warm Current [73].
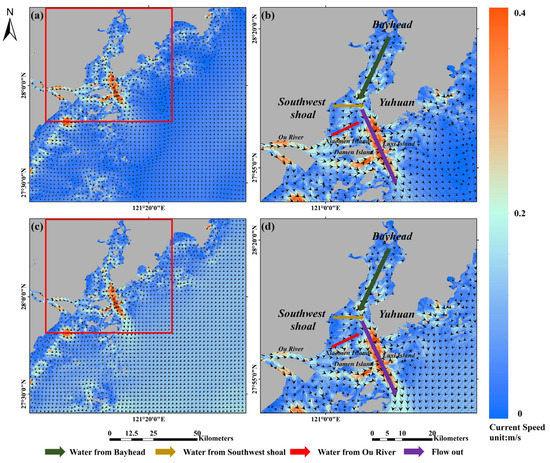
Figure 9.
Distribution of flow fields in sea areas along the coasts in the middle and southern parts of Zhejiang and Yueqing Bay in summer and winter: (a) distribution of flow fields in sea areas of Zhejiang in summer; (b) distribution of flow fields in Yueqing Bay in summer; (c) distribution of flow fields in sea areas of Zhejiang in winter; (d) distribution of flow fields in Yueqing Bay in winter. (Black arrow represents flow field direction, length of black arrow represents flow field intensity; green, yellow, red, and purple arrows represent directions of water from bay head, Southwest Shoal, Ou River, and final outflowing stream, respectively).
Waters in Yueqing Bay are affected by streams inside the bay and water from the Ou River (Figure 9). These waters are mainly manifested by bay head water flowing past the bay center and turning to the west side of Yuhuan Island, then flowing out; by waters in the Southwest Shoal flowing to the east and converging with water from the bay head; and by a small amount of water from the Ou River flowing past the north side of Damen Island and Xiaomen Island, draining likewise into the water stream from the bay head, and finally flowing out of the channel between Luxi Island and Damen Island. As seen in Figure 4a–d and Figure 5a–d, the spatial distribution and transport direction of nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay remained generally consistent with the above results, indicating that river transport has a great impact on the spatial distribution of nutrients in the bay. In addition, Yueqing Bay is affected by multiple influencing factors, including inflowing streams, the Ou River, tides, and flow fields, and thus the bay mouth zone is hydrodynamically active, with frequent resuspension activity [75]. Sediment resuspension results in the redistribution of nutrients at the sediment–water interface, which can have an obvious impact on migration, transformation, and storage of nitrogen and phosphorus [76,77]. Thus, the complex water environment of Yueqing Bay is subjected to many factors.
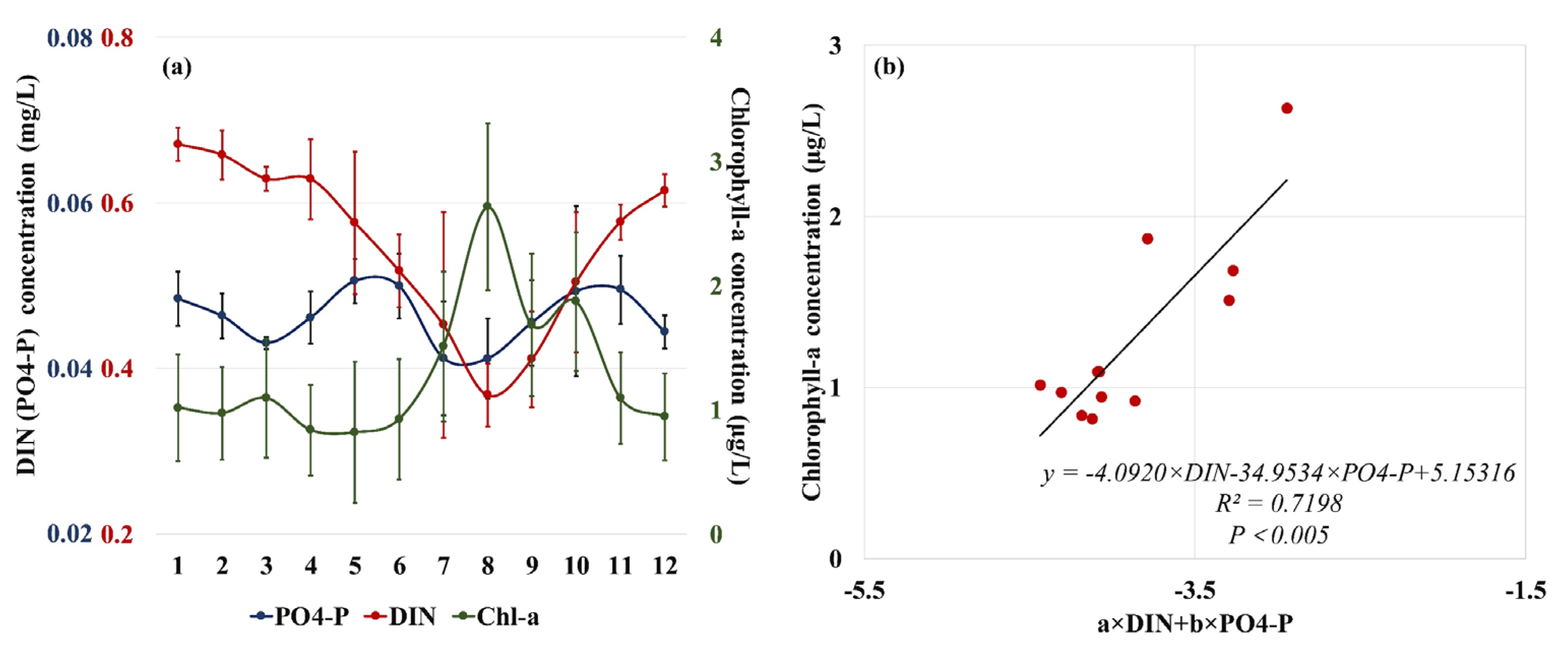
In addition, observed chlorophyll concentration was used to characterize biomass and photosynthesis intensity and their relationship to nutrient concentration. The results show that, in summer (June to August), chlorophyll concentration increased significantly, resulting in high primary productivity, while in autumn and winter, chlorophyll concentration started to decline significantly (Figure 10a), resulting in lower primary productivity; correspondingly, in summer, nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay decreased markedly until autumn and winter when the nutrient concentration began to increase again. Based on multi-linear curve fitting, we fit the climatological mean values of DIN, PO4-P, and chlorophyll concentration during 2014–2020. As shown in Figure 10b, a significant inverse correlation existed between chlorophyll concentration and DIN and between chlorophyll concentration and PO4-P (R2 = 0.7192, P < 0.005), i.e., DIN and PO4-P concentrations decreased with increasing chlorophyll. Thus, seasonal variation in photosynthesis intensity has a certain impact on nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay. In spring and summer, plankton photosynthesis was intense, and high levels of DIN and PO4-P were consumed, while in autumn and winter, plankton photosynthesis was weakened, thereby contributing to the accumulation of DIN and PO4-P.
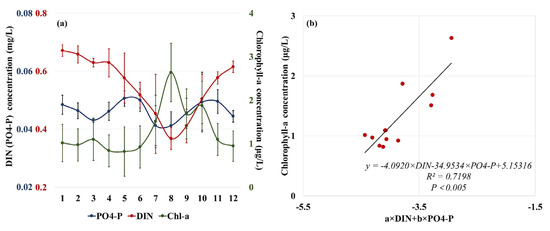
Figure 10.
Inter-monthly variations (a) and correlation analysis (b) of nutrient and chlorophyll concentrations in Yueqing Bay during 2013–2020. (In (b), abscissa represents sum of DIN concentration multiplied by a constant and PO4-P concentration multiplied by another constant after multi-linear curve fitting, which was used to characterize nutrient level in water. Ordinate represents chlorophyll concentration in water. Formula represents a relational formula for fitting nutrient and chlorophyll concentrations. As DIN and PO4-P concentrations are multiplied by negative constants, nutrient concentrations are inversely correlated to chlorophyll concentration).
According to the available data analysis, from the perspective of natural factors, physical effects, such as the Fujian-Zhejiang Coastal Current and Taiwan Warm Current, combined with biological effects, such as seasonal variation in the intensity of plankton photosynthesis in the bay have an important impact on the seasonal variation of nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay, but more parameters are needed for detailed comprehensive analysis.
4.2. Influences of Intensity of Anthropogenic Activities in River Basin
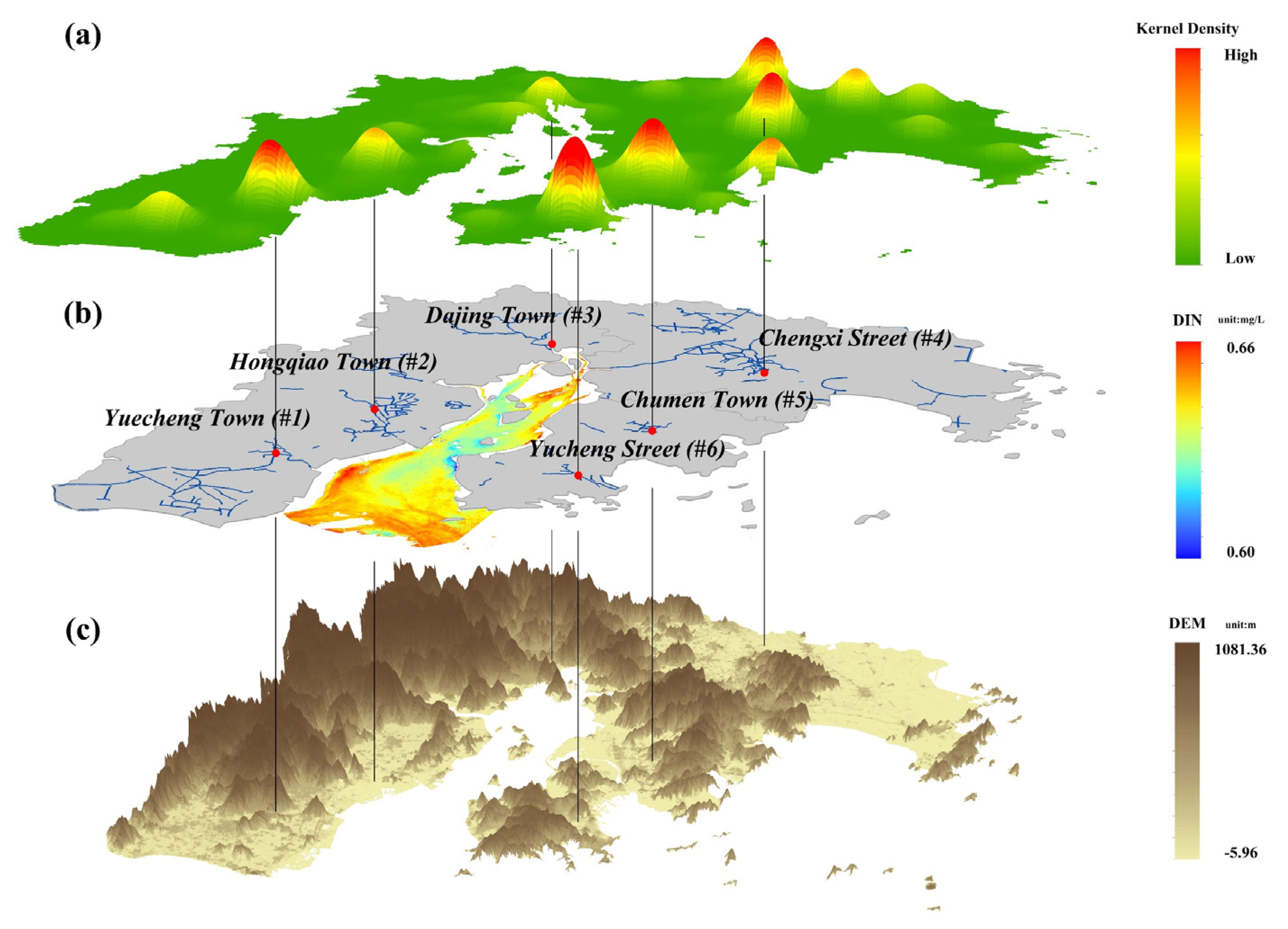
Changes in the intensity of anthropogenic activities inside the river basin can have an immediate impact on nutrient level in land-derived water. To investigate the impact of anthropogenic activities and stream transport on the spatial distribution of nutrient concentration in the bay, the intensity of anthropogenic activities along Yueqing Bay and spatial distribution status were analyzed by kernel density using POI data. As shown in Figure 11a, six regions along Yueqing Bay had strong anthropogenic activities, namely, Yuecheng Town (#1), Hongqiao Town (#2), and Dajing Town (#3) in Yueqing City, Chengxi Subdistrict (#4) in Wenling, and Chumen Town (#5) and Yucheng Subdistrict (#6) in Yuhuan. Based on water system distribution, elevation, and other geographic information of the bay (Figure 11b,c), streams flowing past Yuecheng Town (#1), Hongqiao Town (#2), and Dajing Town (#3) eventually drain into Yueqing Bay. Dajing Town (#3) is nearest to Yueqing Bay, but anthropogenic intensity in this region was weaker than that in the other regions (low kernel density); streams passing the Chengxi Subdistrict (#4) eventually flow into Yueqing Bay, but they are farther away. Streams flowing past Chumen Town (#5) are situated in Xuanmen Bay, but water flow is blocked by dams inside Xuanmen Bay and thus water is not continuously transported to Yueqing Bay; streams flowing past Yucheng Subdistrict (#6) eventually drain into the sea area on the east side of Yuhuan Island without having an immediate impact on the waters in Yueqing Bay. Based on the spatial distribution of nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay (Figure 11b), high-concentration zones were situated in shoals southwest of the bay mouth (corresponding to Yuecheng Town (#1) and Hongqiao Town (#2)), streams on both sides of Ximen Island at the bay head (corresponding to Dajing Town (#3) and Chengxi Subdistrict (#4)), and coastal sea areas beyond the Xuanmen Bay dams (corresponding to Chumen Town (#5)), whereas low-concentration zones were situated in the sea area on the west side of Yuhuan Island (corresponding to the Yucheng Subdistrict (#6)). These results indicate that the intensity of coastal anthropogenic activity and transport of inflowing streams are the main driving factors contributing to the high or low concentrations of nutrients in waters in local regions inside the bay.
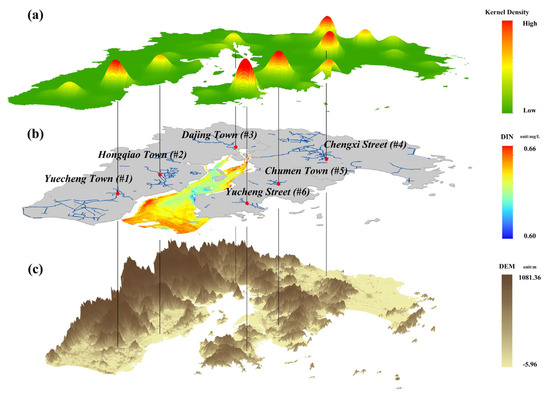
Figure 11.
Spatial distribution of intensity of anthropogenic activities along Yueqing Bay and nutrient concentration inside Yueqing Bay: (a) spatial distribution of intensity of anthropogenic activities; (b) distribution of inflowing streams and nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay; (c) digital elevation model (DEM), where nutrient concentration data in (b) are sourced from Figure 4d.
4.3. Influences of Urban Management in River Basin and Changes in Bay Governance Policy
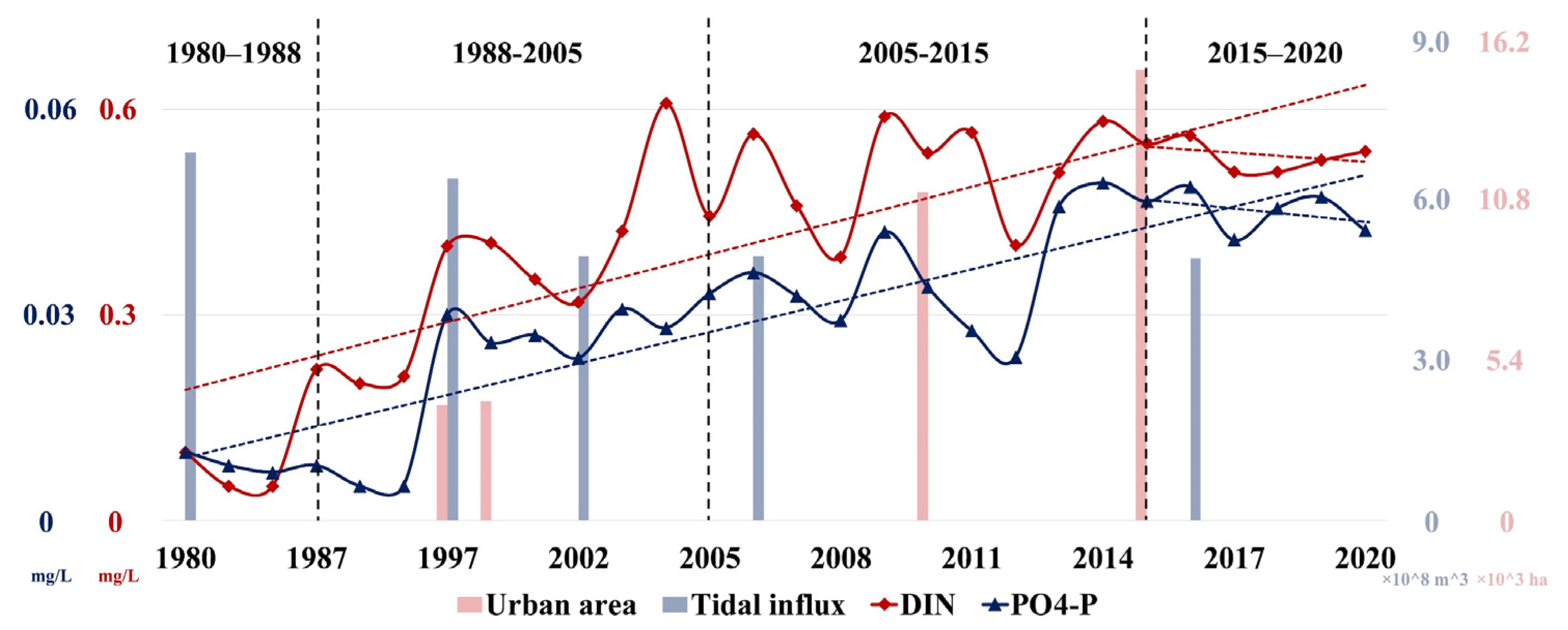
Since its development in 1980, Yueqing Bay has also experienced many problems similar to the world-famous bay areas (e.g., Tokyo Bay), such as increased pollutant discharge and ecosystem damage [11,12]. As shown in Figure 12, compared to 1980, nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay have increased about 5–7-fold. From 1988 to 2005, cities along Yueqing Bay have undertaken significant land reclamation in the bay to address urban land shortages, totaling 61.81 km2. As a continuation of the coastal reclamation plan of Xuanmen Bay in Yuhuan, Xuanmen phase II further strengthened the reclamation of land from the sea on the basis of the construction of Xuanmen dam in Xuanmen phase I, and the reclamation area reached 37.34 km2. The implementation of Xuanmen phase I reclamation project directly blocked the exchange of water in Xuanmen Port and waters inside and outside the bay, while the large-scale reclamation of land from the sea in Xuanmen phase II further resulted in a remarkable decline in tidal influx in the bay. During 1988–2005, tidal influx from the bay center to the bay head decreased by 10%–20% and the water exchange rate declined significantly. Nutrients in the bay failed to be transported to the open sea and thus accumulated inside the bay, resulting in a marked nutrient concentration increase during this period [72]. After 2005, sea reclamation, urban areas, and anthropogenic activities increased, with an accompanying increase in the total discharge of land-derived pollutants and their transportation along inflowing streams to Yueqing Bay, resulting in further enhancement of nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay [40,43]. By 2018, the Yueqing Bay River basin contained a population of about 3 million and small enterprises had expanded, with industrial wastewater discharge in the bay increasing accordingly (up to 3 million tons each year). In addition, the aquatic farming industry in the bay has continued to develop. Since 2011, annual gross output of aquatic products in the three cities along Yueqing Bay has exceeded 80 million tons [43,78]; urban domestic sewage, coastal sewage outfalls, and pollutants from aquatic farming have drained continuously into Yueqing Bay.
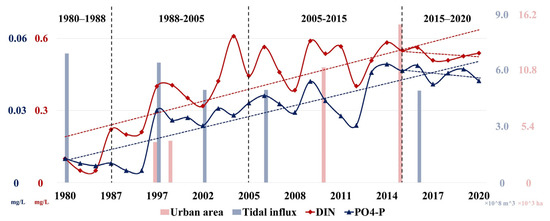
Figure 12.
Variations in coastal urban development, tidal influx, and nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay during 1980–2020. (Tidal influx and urban area data as well as nutrient concentration data of Yueqing Bay during 1980–2013 were sourced from the literature [40,43,72], nutrient concentration data of Yueqing Bay during 2013–2020 were sourced from remote-sensing-retrieved data in this study, vertical black dashed lines correspond to 1998, 2005, and 2015, respectively, and red and blue dashed lines are trend lines of DIN and PO4-P, respectively).
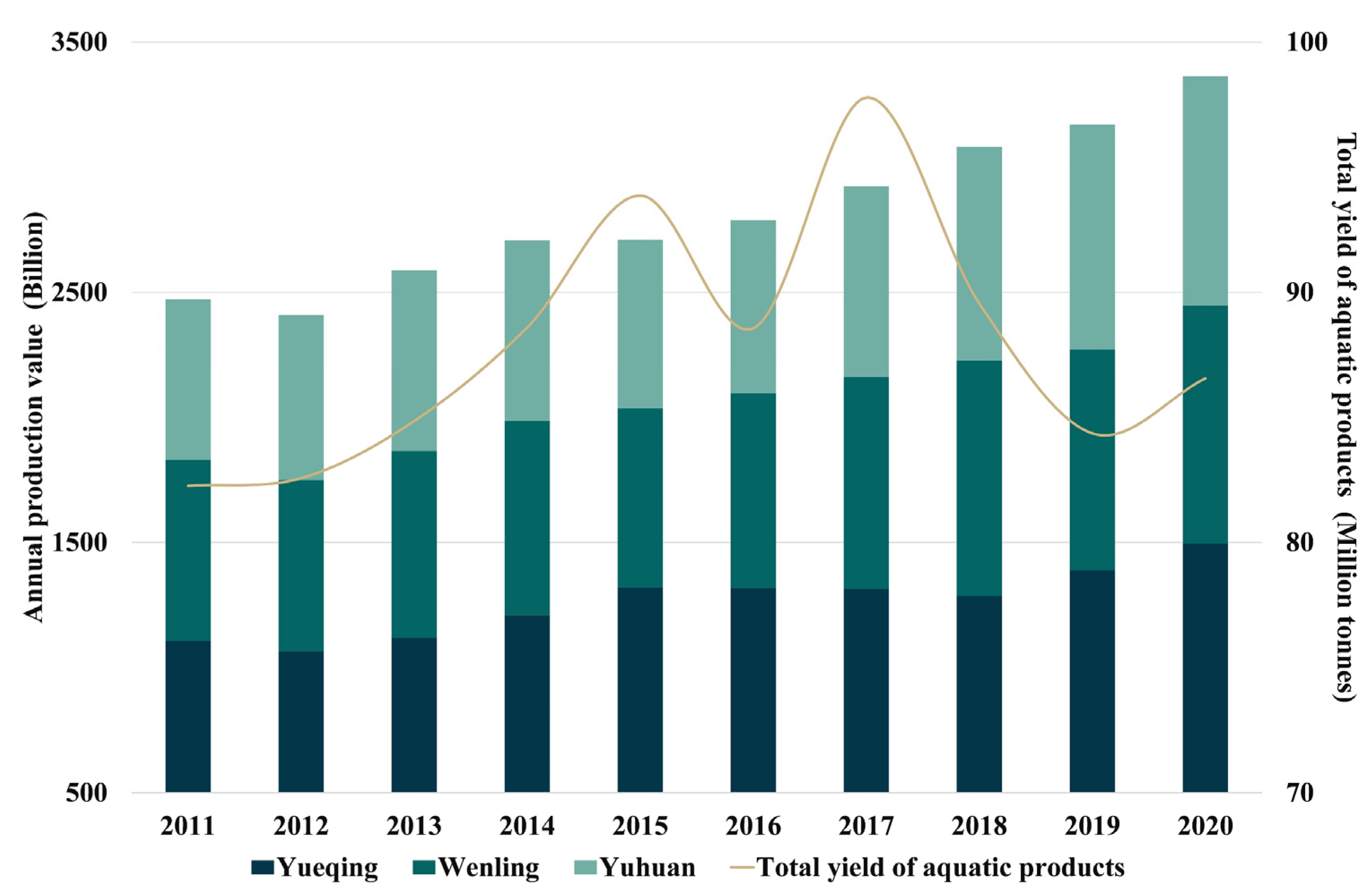
As seen in Figure 13, gross output values of the primary sectors and industrial in cities along Yueqing Bay have shown a growing tendency. During 2011–2020, gross output values of both sectors increased by about RMB 90 billion, while gross output of aquatic products generally increased by ~16 million tons over the seven years, decreased somewhat after 2017, and decreased to 86.5 million tons by 2020. Most inflowing streams along Yueqing Bay run past rural towns. Many are classified as grade IV–V surface water due to increasing input from industrial wastewater, agricultural irrigation run-off, domestic sewage, and aquatic farming pollutants. Gao et al. [79] reported that most inflowing streams in Yueqing Bay have a total nitrogen and phosphorus content of 1.5–6.0 mg/L and 0.06–0.2 mg/L, respectively. At present, the output value of various industries continues to grow, the total population in the basin continues to increase, and rural towns continue to develop. Although the influence of the current pollution control plan, which highlighted the control of total nitrogen and total phosphorus emissions from rivers entering the sea and direct discharge sea pollution sources, achieved results and controlled the nutrient concentration in surface water to a certain extent, land-based pollution is still one of the main sources of pollutants in Yueqing Bay at this stage.
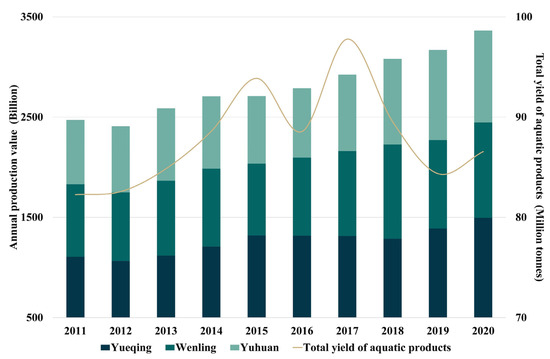
Figure 13.
Variations in gross output values of the primary sectors and industrial and gross aquatic product output in cities along Yueqing Bay during 2011–2020. (Data were sourced from statistical yearbook for cities along the Yueqing Bay for the years of 2011–2020 [80,81,82]).
Time-series variations in nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay during 2013–2020 (Figure 5) showed abnormally low nutrient concentrations in the summer of 2017, which was mainly due to prolonged drought, with monthly mean rainfall lower than perennial monthly mean rainfall; indeed, only 2 days in August showed precipitation >5 mm and monthly total rainfall was only 51.2 mm in Yueqing City [82]. The drought led to a significant decline in water levels and river discharge and a lower total content of nutrient transported by streams into Yueqing Bay, resulting in abnormally low nutrient concentrations in the bay. This climatic event showed that industrial wastewater, agricultural irrigation water, domestic sewage, and aquatic farming pollutants in cities along Yueqing Bay are the main sources of nutrient pollution, and inflowing streams are the main mode of pollutant transport.
In May 2014, the “Five Water Treatment Actions” program (i.e., wastewater treatment, flood control, stagnant water drainage, water supply assurance, and water conservation) was implemented in Zhejiang for the purpose of water control, and mandatory water quality indicators have been used to control pollutant discharge and increase sustainable development [83]. In the context of this program, various ecological governance and remediation policies were proposed to address issues such as pollutant discharge control and environmental protection in cities along Yueqing Bay and to improve water quality in the bay by human intervention. In 2016, the Yueqing municipal government proposed policies to rationalize marine resource exploitation and utilization, control entry of polluting enterprises, and develop the ecological sector to control land-derived pollutants and pollutant discharge entering Yueqing Bay [84]. In 2021, the Yuhuan municipal government also proposed actions to govern and monitor pollutants discharged into the sea to improve water quality status in the bay by ecosystem remediation and pollutant control [85]. In addition to relevant pollution control and ecological remediation policies, after 2017, the development of the agricultural, forestry, husbandry, fishing, and aquatic product sectors along Yueqing Bay increased at somewhat slower rates, which had a positive impact on total input of land-derived pollutants and pollution control.
As seen in Figure 7, after 2015, the DIN and PO4-P concentrations in Yueqing Bay decreased slightly but non-significantly (P > 0.1), also with no further growth noted, indicating that the ecological governance and remediation policies proposed by the cities along Yueqing Bay have had a positive impact on water quality status in Yueqing Bay.
As seen in Figure 8, for stream estuaries corresponding to regions along Yueqing Bay with intense anthropogenic activity (i.e., Yuecheng Town (#1), Hongqiao Town (#2), Dajing Town (#3), and Chengxi Subdistrict (#4) in Figure 12), nutrient concentrations changed distinctly before and after 2015. During 2013–2015, nutrient concentrations in all three regions increased at higher rates than the mean increasing rate in Yueqing Bay. In the East Stream (#1 in Figure 8) and West Stream of the bay head (#2 in Figure 8), the PO4-P concentration increased at the fastest rate (Figure 8c,e and Table 3). After 2015, nutrient levels in the three regions declined to variable extents. In the East Stream (#1), nutrient concentrations in the water decreased at a slower rate, in particular, DIN decreased at a slightly lower rate than that in Yueqing Bay, while in the West Stream (#2 in Figure 8) and Southwest Shoal (#3 in Figure 8), nutrient concentrations decreased at a higher rate than that in Yueqing Bay, especially in the Southwest Shoal (#3 in Figure 8), where PO4-P decreased markedly. On the west side of the bay, remediation polies to control PO4-P were initiated relatively earlier by Yueqing city [40], resulting in significantly lower PO4-P concentrations on the west side of Yueqing Bay. After 2015, a series of ecological governance and remediation policies were issued and implemented by local city governments along Yueqing Bay. These measures slowed the rise in nutrient concentrations in the bay and mitigated the water quality deterioration trend, especially in Yueqing City, where PO4-P concentrations in inflowing streams were effectively controlled, resulting in a reduction in concentrations in the sea area on the west side of the bay. However, despite the mitigation effects, nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay remain high. For example, DIN concentrations only reach grade III seawater criteria (0.30 mg/L < DIN ≤ 0.40 mg/L) in summer, with levels higher than the upper limit specified for grade IV seawater (0.40 mg/L < DIN ≤ 0.50 mg/L) in the other seasons; furthermore, PO4-P concentrations exceed grade IV seawater criteria (0.30 mg/L < PO4-P ≤ 0.045 mg/L) all year [86].
The restoration of bay ecosystems is a long process; thus, continuous long-term ecological remediation efforts are essential for ecosystem restoration and regeneration. As an important semi-enclosed bay in the Kanto Area of Japan, Tokyo Bay is surrounded by several large cities, including Tokyo, Yokohama, and Kawasaki. During its development, coastal engineering, rapid urbanization, and other anthropogenic activities resulted in significant sea reclamation, pollutant discharge, ecosystem damage, and water quality deterioration in the bay [11,12]. In response, the Japanese government launched the “Tokyo Bay Restoration Plan” in 2001 to address these ecological problems, including the specific policies on wastewater discharge control, river dredging, wetland ecosystem restoration, and monitoring system establishment, etc. After years of governance and remediation, total pollutants (e.g., nitrogen and phosphorus) in Tokyo Bay have decreased, and water quality, while still poor, has not deteriorated further [87]. That is, although ecological regeneration policies have shown some success, the environment inside Tokyo Bay remains poor due to its early and high intensity development and deterioration. In comparison, Yueqing Bay developed much later, and ecological remediation has been implemented gradually over the past few years. Thus, from the perspective of the developmental and remediation history of Tokyo Bay, long-term ecological remediation efforts are still needed to improve the environment in Yueqing Bay and to eliminate or reduce the negative impacts of coast engineering and other anthropogenic activities.
5. Conclusions
This paper focused on water quality monitoring and variation analysis of a semi-enclosed bay (Yueqing Bay) in China, which is under strong anthropogenic impact. By constructing a regional remote sensing retrieval algorithm, the long time series remote sensing monitoring of water quality changes in Yueqing Bay is realized. On this basis, the impact of relevant management policies and anthropogenic activities in the basin on water quality variations in the bay can be understood, which can provide an effective reference basis for ecological environmental protection and restoration work in Yueqing Bay and other similar bays.
Based on long time-series Landsat-8 satellite remote sensing data, field measurement data, and supplementary statistical data, we constructed a model to retrieve nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay using SVM, and further investigated the spatiotemporal variations and main influencing mechanisms of nutrient concentrations in the bay during 2013–2020.
The nutrient retrieval results show that DIN concentration varied seasonally within 0.211–0.687 mg/L, with the lowest level in summer (averaging 0.3940 mg/L); PO4-P concentration varied seasonally within 0.016–0.056 mg/L, with the lowest level in summer (averaging 0.0414 mg/L) and highest level in autumn (averaging 0.0508 mg/L). From a spatial distribution perspective, nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay were generally higher in the west and lower in the east, with high-concentration zones observed in the narrowest area of the middle part of the bay, Southwest Shoal at the bay mouth, and sea area on the north side of Damen and Xiaomen islands, and low-concentration zones observed in coastal waters on the west side of Yuhuan Island. During 2013–2015, the DIN and PO4-P concentrations in Yueqing Bay showed an increasing tendency (DIN, P = 0.0262, t = 2.5341; PO4-P, P = 0.3196, t = 1.0383), whereas, during 2015–2020, the DIN and PO4-P concentrations showed a decreasing though non-significant tendency (P > 0.1).
The observed and remote-sensing-retrieved data were highly consistent in terms of seasonal variations, long time-series variations, and the spatial distribution of nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay. The field measurement data were mainly sourced from in situ surveys by marine research vessels, with high labor and material costs, limited observation stations, small spatial coverage, and low observation frequency. Based on its spatiotemporal continuity, field measurement data are less effective for investigations into the complex issues in Yueqing Bay, such as large-scale pollution prevention, dynamic monitoring of environmental pollution, long time series recording, multiple driving factors, and environmental remediation and restoration. In contrast, remote sensing technology not only shortens the data acquisition period but also improves the timeliness and spatial coverage of marine data. Hence, in comparison to field measurement data, the satellite remote sensing imagery of bays can be used to acquire environmental data with larger coverage and more continuous time series to investigate variation trends and driving factors.
Based on numerical simulation, kernel density estimation, and related literature data, seasonal variations in nutrient concentration in Yueqing Bay were mainly controlled by physical effects, including the Taiwan Warm Current and Fujian-Zhejiang Coastal Current, and biological effects, such as seasonal variations in the intensity of plankton photosynthesis in the bay. Furthermore, spatial distribution characteristics of nutrient concentration were mainly affected by synergy between the intensity of anthropogenic activities and transport by rivers along Yueqing Bay. Compared to 1980, nutrient concentrations in Yueqing Bay have increased 5–7-fold, mainly due to significantly enhanced anthropogenic activities from 1998 to 2015; in particular, during 1988–2005, large-area reclamation projects (e.g., Xuanmen phase II project) have resulted in a remarkable decline in tidal influx in the bay and a significant decrease in the water exchange rate, with nutrients thus accumulating inside the bay, rather than being transported to the open sea, resulting in a significant increase in nutrient concentration during this period. After 2005, the urban area along Yueqing Bay increased significantly, resulting in an increase in anthropogenic activities, discharge of land-derived pollutants, and transportation of pollutants along inflowing streams into Yueqing Bay, and thus caused the second rapid increase in nutrient concentrations in the bay waters [40,43]. Since 2011, the overall GDP of the three cities along Yueqing Bay has increased continuously, e.g., from 2011 to 2020, the GDP of the primary and secondary sectors increased by ~RMB 90 billion and annual aquatic production exceeded 80 million tons [43,76]. Due to this rapid development, industrial wastewater, agricultural irrigation run-off, domestic sewage, and aquatic farming pollutants increased, resulting in the gradual rise in nutrient concentrations in inflowing streams and the bay, especially the estuaries. After 2015, the main cities along Yueqing Bay implemented various restoration policies, and after 2017, the rising trend in gross aquatic product output slowed, leading to a decline (though non-significant) in the nutrient concentrations in waters inside the bay and improvement in water quality deterioration, with an overall positive impact on ecological remediation in Yueqing Bay.
Compared with Tokyo Bay, Yueqing Bay developed much later, and ecological remediation has been implemented gradually over the past few years. Thus, from the perspective of the developmental and remediation history of Tokyo Bay, long-term ecological remediation efforts are still needed to improve the environment in Yueqing Bay and to eliminate or reduce the negative impacts of coast engineering and other anthropogenic activities.
This paper demonstrates the satellite remote sensing techniques to monitor water quality variation in a bay under strong anthropogenic impact. An updated satellite algorithm is still needed in future work with more data collection and a deep mechanism understanding of the nutrient variation. The ±3 day time interval we used in this study to guarantee enough matched data for regional algorithm development may induce errors. Moreover, satellite remote sensing only relates to the surface layer, and the detection of profile information should also be considered, although the water column was mixing in the coast and bay much more than in the open ocean under the highly dynamic hydrological condition. In general, satellite remote sensing data with a high spatial resolution have a strong ability to monitor the water quality of bays and gulfs, but they still need to be updated and combined with more field observations to provide better data support for environmental management and in-depth mechanism understanding.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.Z. and Y.B.; methodology, B.Z. and X.H.; software, Z.W.; validation, B.Z.; investigation, Z.Z., S.Z. and Q.D.; data curation, Z.Z., S.Z. and Q.D.; writing—original draft preparation, B.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.B. and X.H.; visualization, B.Z. and Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant #2017YFA0603003), and Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (GML2019ZD0602), Scientific Research Fund of the Second Institute of Oceanography, MNR (Grant #YJJC2105), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants #41825014), and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017R52001, LR18D060001)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository that does not issue DOIs. Landsat series data were downloaded from https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 30 August 2021). The Point of Interest data were obtained from the Baidu Maps and can be found here: http://lbsyun.baidu.com/index.php?title=webapi (accessed on 30 August 2021). HYCOM series data were download from https://www.hycom.org/ (accessed on 30 August 2021). TRMM_3B43 Rainfall Estimate data were download from https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 30 August 2021). ECMWF-ERA5 hourly wind field data were download from https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 30 August 2021).
Acknowledgments
We thank SOED/SIO/MNR satellite ground station, satellite data processing & sharing center, and marine satellite data online analysis platform (SatCO2) for their help with data collection and processing. We thank Wenzhou Environmental Monitoring Center for their help with field measurement data collection and processing. We thank United States Geological Survey (USGS) (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 30 August 2021)) for providing the Landsat series satellite data and Baidu map (http://lbsyun.baidu.com/index.php?title=webapi (accessed on 30 August 2021)) for providing the Point of Interest data. We thank the National Ocean Partnership Program (NOPP) (https://nopp.org/ (accessed on 30 August 2021)) for providing the HYCOM series data. We thank the Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC) (https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 30 August 2021)) for providing the TRMM_3B43 Rainfall Estimate data. We thank the European Union’s Copernicus Earth Observation Programme (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 30 August 2021)) for providing the ECMWF-ERA5 hourly wind field data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Creel, L. Ripple Effects: Population and Coastal Regions; Population Reference Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Han, H. Research on countermeasures of coastal zone management. Mar. Dev. Manag. 2007, 6, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Worm, B.; Hilborn, R.; Baum, J.K.; Branch, T.A.; Collie, J.S.; Costello, C.; Fogarty, M.J.; Fulton, E.A.; Hutchings, J.A.; Jennings, S.; et al. Rebuilding global fisheries. Science 2009, 325, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. Assessing ecological risks caused by human activities in rapid urbanization coastal areas: Towards an integrated approach to determining key areas of terrestrial-oceanic ecosystems preservation and restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, K.; Okada, T. Tokyo Bay: Its environmental status—Past, present, and future. In The Environment in Asia Pacific Harbours; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbe, J.; Wolff, J.-O.; Staneva, J.; Gräwe, U. Assessing water renewal time scales for marine environments from three-dimensional modelling: A case study for Hervey Bay, Australia. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2008, 23, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, A.D.; Prince, S.D. Effects of urban and non-urban land covers on nitrogen and phosphorus runoffs to Chesapeake Bay. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Bulletin on China’s Ecological Environment in 2020. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/ (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Harding, L.W.; Gallegos, C.L.; Perry, E.S.; Miller, W.D.; Adolf, J.E.; Mallonee, M.E.; Paerl, H.W. Long-term trends of nutrients and phytoplankton in Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coasts 2016, 39, 664–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, A.; Hashihama, F.; Kanda, J.; Horimoto-Miyazaki, N.; Ishimaru, T. Long-term variability of nutrient and dissolved organic matter concentrations in Tokyo Bay between 1989 and 2015. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, S209–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, A.; Kanda, J. Coastal urbanization alters carbon cycling in Tokyo Bay. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.F.; Dai, K.; Tao, Q.R.; Fan, C.Y.; He, L.L. Marine pollution status of nearshore areas of Hangzhou Bay and its governance countermeasures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, H.; Janicki, A.; Sherwood, E.T.; Pribble, R.; Johansson, J.O.R. Ecosystem responses to long-term nutrient management in an urban estuary: Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Estuar. Coastal Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, A1–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bi, Y.P.; Gong, Y.J.; Xi, X.H.; Lei, L.Y. Integrated restoration of ecological environments in typical bays:in a case of Jinzhou Bay and Hulushan Bay in Liaoning Province. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2014, 29, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, B.; Palmer, M.; Bernhardt, E.; Smith, S.; Carr, J.; Hart, D. Restoring watersheds project by project: Trends in Chesapeake Bay tributary restoration. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, W. Elements of South Florida’s Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan. Ecotoxicology 2004, 13, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Moses, W.; Rundquist, D.C.; Barrow, T.; Fisher, T.R.; Gurlin, D.; Holz, J. A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: Validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.; Giardino, C.; Zilioli, E. Determination of chlorophyll concentration changes in lake garda using an image-based radiative transfer code for Landsat TM images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.A.; Giardino, C.; Zilioli, E. Validation of satellite data for quality assurance in lake monitoring applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.B.; Siegel, D.A. Chromophoric DOM in the open ocean. In Biogeochemistry of Marine Dissolved Organic Matter; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 547–578. [Google Scholar]
- Somvanshi, S.; Kunwar, P.; Singh, N.B.; Shukla, S.P.; Pathak, V. Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach for water quality analysis of gomti river, Uttar Pradesh. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Schiebe, F.R.; Mchenry, J.R. Remote sensing of suspended sediments in surface waters. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1976, 42, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Hasmadi, I.; Norsaliza, U. Analysis of SPOT-5 data for mapping turbidity level of river klang, peninsular malaysia. Appl. Remote Sens. J. 2010, 1, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Choi, M. Assessment of water quality based on Landsat 8 operational land imager associated with human activities in Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alparslan, E.; Coskun, H.G.; Alganci, U. Water quality determination of Küçükçekmece Lake, Turkey by using multispectral satellite data. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahraiyni, T.H.; Schaale, M.; Fell, F.; Fischer, J.; Preusker, R.; Vatandoust, M.; Shouraki, B.S.; Tajrishy, M.; Khodaparast, H.; Tavakoli, A. Application of the active learning method for the estimation of geophysical variables in the caspian sea from satellite ocean colour observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 4677–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Han, M.I.N. Mapping chlorophyll—A concentration in Laizhou Bay using Landsat 8 oli data. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busse, L.B.; Simpson, J.C.; Cooper, S.D. Relationships among nutrients, algae, and land use in urbanized southern California streams. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 2621–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, R.; Yli-Halla, M.; Turtola, E. Suspended soil as a source of potentially bioavailable phosphorus in surface runoff waters from clay soils. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Hyun, C.-U. High resolution ocean color products estimation in Fjord of Svalbard, arctic sea using Landsat-8 oli. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2014, 30, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allan, M.G.; Hamilton, D.P.; Hicks, B.J.; Brabyn, L. Landsat remote sensing of chlorophyll a concentrations in central north island lakes of new zealand. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 2037–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, J. Water quality monitoring in a slightly-polluted inland water body through remote sensing—Case study of the Guanting Reservoir in Beijing, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2008, 2, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Duan, H.; Barnes, B.B.; Ma, R. An EOF-based algorithm to estimate chlorophyll a concentrations in Taihu Lake from MODIS land-band measurements: Implications for near real-time applications and forecasting models. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10694–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J. Hydraulic Properties of Environment in the Yueqing Bay. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.; Liao, G.H.; Yang, C.H.; Xu, X.H. Study on the features of water exchange in Yueqingwan Bay. J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 29, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Bays Compiling Committee. Chinese Harbours and Embayments; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.M.; Zhu, J.P.; Gu, J.; Bao, J.J.; He, Y.N.; Liu, Q. Interannual variations of nutrient contents in fishing waters of the Yueqing Bay in May and August during 2000–2014. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.B.; Wen-Ren, Y.Z.; Ying, C. Impact of Tidal Flat Reclamation on Water Exchange in the Yueqing Bay. In Proceedings of the 14th National Conference on Hydrodynamics and the 28th National Symposium on Hydrodynamics: Changchun, Jilin, China, 8–10 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.J. Environment and Resource Characteristics and Integrated Coastal Zone Management of the Yueqing Bay in Zhejiang Province. Resour. Sci. 2001, 22, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.J. Response of Landscape Pattern of the Yueqing Bay Coastal Zone to Human Disturbance; Zhejiang Normal University: Jinhua, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H. Zhejiang Islands; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, T.; Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.L.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Chetwynd, J.H.; Gardner, J.A.; Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Berk, A.; et al. FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based atmospheric correction algorithm, its application and validation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 1414–1418. [Google Scholar]
- State Oceanic Administration (Now the Ministry of Natural Resources of The People’s Republic of China). Code of Practice for Marine Monitoring Technology; State Oceanic Administration: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kupssinskü, L.S.; Guimaraes, T.T.; De Souza, E.M.; Zanotta, D.C.; Veronez, M.R.; Gonzaga, L., Jr.; Mauad, F.F. A method for chlorophyll-a and suspended solids prediction through remote sensing and machine learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, D.; Salvador, P.; Sanz, J.; Casanova, J.L. A new approach to monitor water quality in the Menor sea (Spain) using satellite data and machine learning methods. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, N.; Acharya, T.D.; Lee, D.H. A comprehensive review on application of machine learning algorithms for water quality parameter estimation using remote sensing data. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 3879–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. A Practical Guide to Support Vector Classification. 2003. Available online: https://www.ee.columbia.edu/~sfchang/course/svia/papers/svm-practical-guide.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Beardsley, R.C. An unstructured grid, finite-volume, three-dimensional, primitive equations ocean model: Application to coastal ocean and estuaries. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.C.; Cowles, G. Finite volume coastal ocean. Oceanography 2006, 19, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Tao, B.; Li, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Gong, F. Estimating particulate organic carbon flux in a highly dynamic estuary using satellite data and numerical modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Huang, T.-H.; Pan, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L. Changes in riverine organic carbon input to the ocean from mainland China over the past 60 years. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.N.; Gao, X.L. A novel method for identifying the boundary of urban built-up areas with POI data. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Jiao, L.M.; Dong, T.; Gu, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.L. Quantitative Identification and Visualization of Urban Functional Area Based on POI Data. J. Geomat. 2016, 41, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, G. Urban Spatial Structure of Port City in South China Sea Based on Spatial Coupling between Nighttime Light Data and POI. J. Geo.-Inf. Sci. 2018, 20, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Ai, T.H.; Liu, P.C.; He, Y.K. Network Kernel Density Estimation for the Analysis of Facility POI Hotspots. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Ai, T.H. The Visualization and Analysis of POI Features under Network Space Supported by Kernel Density Estimation. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, H. Spatial Data Analysis Methods; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 66–69. ISBN 978-7-03-018966-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.H.; Ai, T.H.; Yang, M.; Liu, J.P. Detecting “Hot Spots” of Facility POIs Based on Kernel Density Estimation and Spatial Autocorrelation Technique. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2016, 41, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaneveld, J.; Ronald, V. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 60–63. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/26231610 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Brodie, J.; Schroeder, T.; Rohde, K.; Faithful, J.; Masters, B.; Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Maughan, M. Dispersal of suspended sediments and nutrients in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon during river-discharge events: Conclusions from satellite remote sensing and concurrent flood-plume sampling. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2010, 61, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, M.; Lyu, H.; Zhu, A.; Huang, T. Using remote sensing to track variation in phosphorus and its interaction with chlorophyll-a and suspended sediment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4171–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Fan, D.; Liu, D.; Song, L.; Ji, D.; Hui, E. Nutrient estimation by HJ-1 satellite imagery of Xiangxi bay, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Chen, J.; Pan, D.; Tao, B.; Zhu, Q. A regional remote sensing algorithm for total suspended matter in the East China Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurlin, D.; Gitelson, A.A.; Moses, W.J. Remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters—Return to a simple two-band NIR-red model? Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3479–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.A.; Gitelson, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.; Ioannou, I.; Ahmed, S.A. Algorithms for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in coastal and inland waters using red and near infrared bands. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24109–24125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knaeps, E.; Ruddick, K.G.; Doxaran, D.; Dogliotti, A.I.; Nechad, B.; Raymaekers, D.; Sterckx, S. A SWIR based algorithm to retrieve total suspended matter in extremely turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.N.; Pan, J.M.; Liang, C.J.; Chen, Q.Z. Comprehensive Investigation Report on the Ecological Environment of Key Harbors in Zhejiang Province; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J. Numerical Simulation of DIN&DIP Distribution in Yueqing Bay and Their Response to Important Coastal Engineerings. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Guo, X.F.; Fang, J.; Li, Q.S. Characteristics of seasonal spatial expansion of Fujian and Zhejiang Coastal Current and their bay effects. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2018, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Li, H.S.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.S.; Zhang, C.S. Preliminary discussion about hydrochemical properties of Taiwan Warm Current in summer and their influences on harmful algal bloom-prevalent zones in East China Sea. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2013, 44, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhu, D.K. Study on Marine Environment and Recent Coastal Evolution of Yueqing Bay, Zhejiang Province, China. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2006, 25, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Hu, W.; Gao, G.; Luo, L.; Zhang, J. Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.P. Effects of Sediment Resuspension in the Yangtze River Estuary and Neighboring Sea Areas on Nutrients in Waters; Ocean University of China: Qingdao, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Qiu, J.B.; Chen, S.B.; Xie, Q.L.; Li, S.L.; Huang, X.L. The study on the vulnerability of the ecosystem in Yueqing Bay. J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 27, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Q.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, J.N.; Yao, L.K.; Gao, D.W. Characteristics of the Aquatic Environment and Causative Analysis of Eutrophication in Yueqing Bay. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2005, 24, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenling Municipal People’s Government. Statistical Bulletin. Available online: http://www.wl.gov.cn/col/col1402302/index.html (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Yuhuan Municipal People’s Government. Statistical Bulletin. Available online: http://www.yuhuan.gov.cn/col/col1229302012/index.html (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Yueqing Municipal People’s Government. Statistical Bulletin. Available online: http://www.yueqing.gov.cn/col/col1229248995/index.html (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Liu, H.Z.; Shan, B.Q.; Zhang, W.Q.; Shen, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.D. Exploration of Successful Water Pollution Control Strategy in a Province with Serious Water Pollution—Achievement of Water Co-governance in Zhejiang Province and Suggestions of Future Promotion. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2015, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Yu, X.X.; Huang-Ye, Q.H. Yueqing City to forge modern spatial planning pattern of national land by “integrating multiple plans”. Zhejiang Land Resour. 2020, 201, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.D. Yuhuan to construct practice innovation bases on islands while cherishing the idea “Lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets”. Zhejiang Econ. 2021, 688, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3097-1997; Quality Criteria for Seawater. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Xiong, H.X.; Dai, M.X.; Peng, S.T.; Hu, J.B. Enlightenments of Tokyo bay revitalization action plan (2003~2012) in Janpan to Bohai bay in China. J. Waterw. Harb. 2020, 41, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).