A Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network for Detection and Instance Segmentation of Marine Ships in SAR Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The Architecture of the Proposed MS-FPN Model
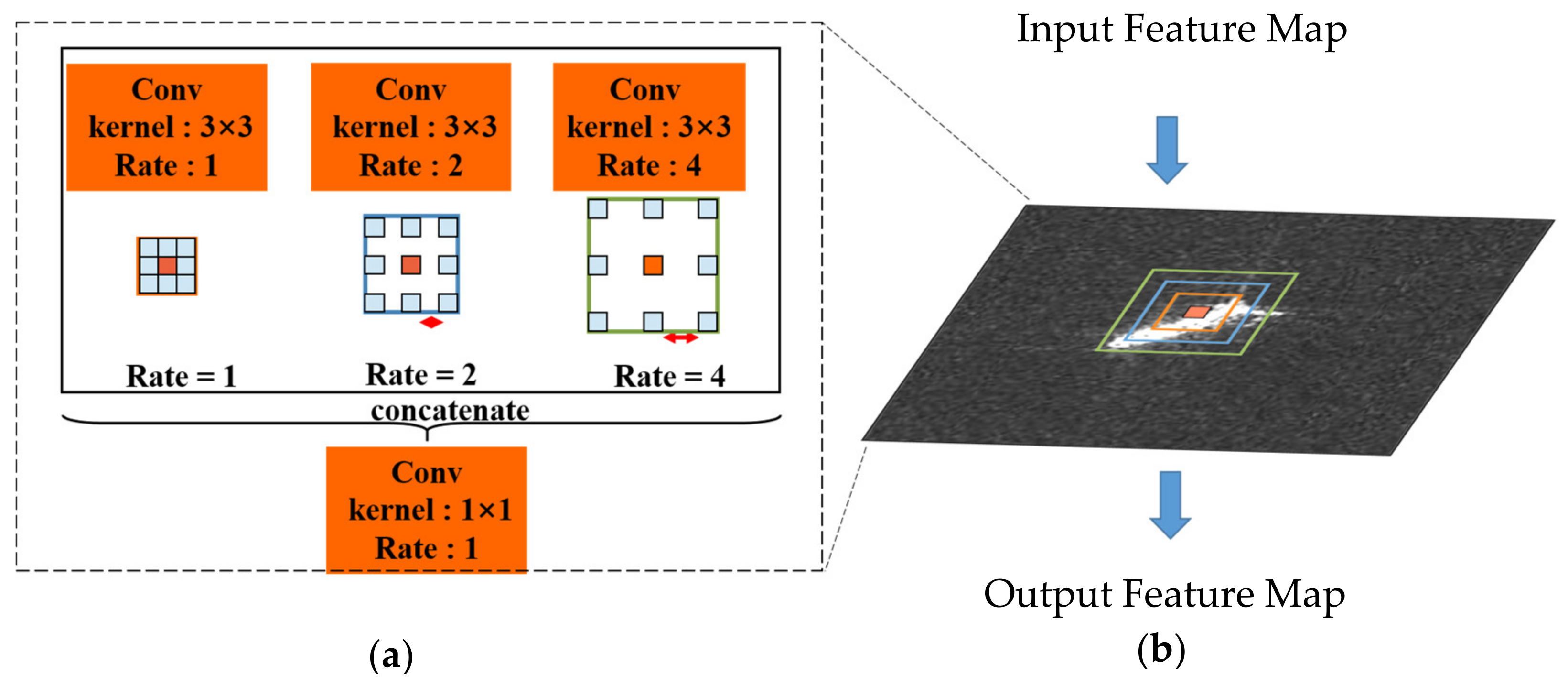
2.2. The Atrous Convolution Pyramid Module
2.3. The Multi-Scale Attention Mechanism
3. Experiments
3.1. DataSet and Settings
3.2. Evaluation Criteria
3.3. Evaluation of MS-FPN
3.3.1. The Detection and Segmentation Performance of MS-FPN
3.3.2. The Effect of Combining MSAM and ACP
3.3.3. The Comparison of ACP with ASPP
3.3.4. Performance Comparison of MSAM
3.3.5. The Effect of the Size of Receptive Field on Model Performance
3.3.6. The Effect of Pooling Functions on Model Performance
3.3.7. Comparison with Other Advanced Models Using a Different Backbone and an Image Input Size
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brusch, S.; Lehner, S.; Fritz, T.; Soccorsi, M.; Soloviev, A.; van Schie, B. Ship Surveillance with TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Liu, L.; Zhao, L.; Shi, G.; Kuang, G. An Adaptive and Fast CFAR Algorithm Based on Automatic Censoring for Target Detection in High-Resolution SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldhuset, K. An automatic ship and ship wake detection system for spaceborne SAR images in coastal regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, M.; Lopez-Martinez, C.; Mallorqui, J.J. A novel algorithm for ship detection in SAR imagery based on the wavelet transform. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Xie, C.; Yuan, X. An Improved Iterative Censoring Scheme for CFAR Ship Detection with SAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4585–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ke, X. Quad-FPN: A Novel Quad Feature Pyramid Network for SAR Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Shi, G. CFAR Ship Detection in Nonhomogeneous Sea Clutter Using Polarimetric SAR Data Based on the Notch Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4811–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Huang, Y.; Pei, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, Q.; Yang, J. Ship Detection from Ocean SAR Image Based on Local Contrast Variance Weighted Information Entropy. Sensors 2018, 18, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. A CenterNet plus plus model for ship detection in SAR images. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 112, 7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. A polarization fusion network with geometric feature emb e dding for SAR ship classification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Hong, W.; Fu, K.; Sun, X. A Densely Connected End-to-End Neural Network for Multiscale and Multiscene SAI Ship Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 20881–20892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zeng, X.; Qu, Q.; Wang, M.; Su, H.; Shi, J. HRSID: A High-Resolution SAR Images Dataset for Ship Detection and Instance Segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 120234–120254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, Q.; Bian, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. A Novel Ship Detection Method Based on Gradient and Integral Feature for Single-Polarization Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Gao, S.; He, J.; Li, G. Adaptive Ship Detection in Hybrid-Polarimetric SAR Images Based on the Power-Entropy Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5394–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Guo, C. Ship Detection in SAR Images Based on Lognormal rho-Metric. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhou, S.; Zou, H.; Gao, G. A CFAR Detection Algorithm for Generalized Gamma Distributed Background in High-Resolution SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegmann, C.P.; Kleynhans, W.; Salmon, B.P. Manifold Adaptation for Constant False Alarm Rate Ship Detection in South African Oceans. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bi, F.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L. An Intensity-Space Domain CFAR Method for Ship Detection in HR SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, B.; Li, B.; Guo, W.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, W. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to Sentinel-1 ship interpretation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.J.N. Hebbian-based neural networks for bottom-up visual attention and its applications to ship detection in SAR images. Neurocomputing 2011, 74, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Kolouri, S.; Eaton, E.; Kim, K. Deep Transfer Learning for Few-Shot SAR Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, L. MEA-Net: A Lightweight SAR Ship Detection Model for Imbalanced Datasets. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Z. A Lightweight Network Based on One-Level Feature for Ship Detection in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Wei, S.; Liu, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X. HQ-ISNet: High-Quality Instance Segmentation for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-H.; Xu, T.-X.; Liu, J.-J.; Liu, Z.-N.; Jiang, P.-T.; Mu, T.-J.; Zhang, S.-H.; Martin, R.R.; Cheng, M.-M.; Hu, S.-M. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Electr Network, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1910.03151. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Liu, N. Dense Attention Pyramid Networks for Multi-Scale Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8983–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Ji, K.; Leng, X.; Kuang, G. Squeeze and Excitation Rank Faster R-CNN for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, B.; Kuang, G. Attention Receptive Pyramid Network for Ship Detection in SAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2738–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Pan, Z.; Lei, B.; Hu, Y. LR-TSDet: Towards Tiny Ship Detection in Low-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Duan, M.; Ding, H.; Hu, B.; Wong, E.K. Attention Mask R-CNN for Ship Detection and Segmentation from Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 9325–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, F. Intelligent Ship Detection in Remote Sensing Images Based on Multi-Layer Convolutional Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z. SDGH-Net: Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images Based on Gaussian Heatmap Regression. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Miao, L.; An, Z.; Xiao, X. Domain Adaptive Ship Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hussain, F.; Zhou, H. Anchor-Free SAR Ship Instance Segmentation with Centroid-Distance Based Loss. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11352–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Zitnick, C.L.; Bala, K.; Girshick, R. Inside-Outside Net: Detecting Objects in Context with Skip Pooling and Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2874–2883. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Sun, K.; Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, Y. Blendmask: Top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8573–8581. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Shen, C.; Kong, T.; Li, L. SOLO: A Simple Framework for Instance Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T. GCBANet: A Global Context Boundary-Aware Network for SAR Ship Instance Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. HTC plus for SAR Ship Instance Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Shi, J. Contextual Squeeze-and-Excitation Mask R-CNN for SAR Ship Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), New York, NY, USA, 21–25 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P. Rethinking Imagenet Pre-Training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4918–4927. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Xu, R.; Liu, Z.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D. CARAFE: Content-Aware ReAssembly of FEatures. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3007–3016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, T.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. High-resolution representations for labeling pixels and regions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.04514. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: High Quality Object Detection and Instance Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liang, Y.; Ma, X.; Huai, Y.; Xing, M. DSDet: A Lightweight Densely Connected Sparsely Activated Detector for Ship Target Detection in High-Resolution SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollar, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5987–5995. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, L.; Gong, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, X. Mask Scoring R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6402–6411. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT Real-time Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9156–9165. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, L.; Karimi, A.; Prati, A. A Novel Region of Interest Extraction Layer for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Electr Network, Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 2203–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Pan, C.; Huo, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Filtered Convolution for Synthetic Aperture Radar Images Ship Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. A Full-Level Context Squeeze-and-Excitation ROI Extractor for SAR Ship Instance Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Pang, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Hybrid Task Cascade for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 4969–4978. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, H.J. HOTR: End-to-End Human-Object Interaction Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Electr Network, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Zhou, P.; Guo, L. Multi-class geospatial object detection and geographic image classification based on collection of part detectors. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 98, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.-S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A Large-scale Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Tuggener, L.; Satyawan, Y.P.; Pacha, A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Stadelmann, T. The DeepScoresV2 Dataset and Benchmark for Music Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Electr Network, Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 9188–9195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, Y.; Wan, J.; Xia, H.; Li, S.Z.; Guo, G. WiderPerson: A Diverse Dataset for Dense Pedestrian Detection in the Wild. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-S.; Astrid, M.; Yoon, H.-J.; Lee, S.-I. Small Object Detection using Context and Attention. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (IEEE ICAIIC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Anwer, R.M.; Cholakkal, H.; Khan, F.S.; Pang, Y.; Shao, L. Enriched Feature Guided Refinement Network for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9536–9545. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Cheng, M.-M. P2T: Pyramid Pooling Transformer for Scene Understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 2765, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Mask R-CNN | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | |
| FPN [24] | 58.5 | 81.1 | 67.1 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 79.3 | 61.2 | 50.4 |
| FPN-CARAFE [48] | 58.6 (+0.1) | 80.7 | 67.1 | 59.7 | 51.0 (+0.1) | 78.8 | 62.1 | 50.6 |
| HRFPN [49] | 59.1 (+0.6) | 81.0 | 67.9 | 60.2 | 51.3 (+0.4) | 79.7 | 62.0 | 51.0 |
| PAFPN [50] | 59.3 (+0.8) | 81.4 | 68.2 | 60.3 | 51.4 (+0.5) | 79.4 | 62.0 | 51.0 |
| MS-FPN (ours) | 60.2 ± 0.1 (+1.7) | 82.3 ± 0.2 | 69.4 ± 0.4 | 61.3 ± 0.4 | 52.4 ± 0.1 (+1.5) | 80.3 ± 0.2 | 63.4 ± 0.5 | 52.0 ± 0.2 |
| ACP | MSAM | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | ||
| × | × | 58.5 | 81.1 | 67.1 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 79.3 | 61.2 | 50.4 |
| √ | × | 59.7 | 81.6 | 68.6 | 60.6 | 51.9 | 79.8 | 62.4 | 51.4 |
| × | √ | 59.9 | 82.7 | 69.0 | 61.1 | 51.9 | 80.9 | 62.3 | 51.5 |
| √ | √ | 60.1 | 82.4 | 69.3 | 61.2 | 52.3 | 80.4 | 62.7 | 51.8 |
| Mask R-CNN | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | |
| Baseline | 58.5 | 81.1 | 67.1 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 79.3 | 61.2 | 50.4 |
| ASPP [46] | 59.2 | 81.5 | 67.5 | 60.0 | 51.7 | 79.7 | 62.5 | 51.2 |
| ACP | 59.7 | 81.6 | 68.6 | 60.6 | 51.9 | 79.8 | 62.4 | 51.4 |
| Mask R-CNN | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | |
| Baseline | 58.5 | 81.1 | 67.1 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 79.3 | 61.2 | 50.4 |
| ECA-Net [28] | 59.1 | 81.3 | 67.5 | 60.1 | 51.4 | 79.4 | 62.3 | 51.0 |
| SENet [38] | 59.2 | 81.5 | 67.6 | 60.2 | 51.7 | 80.2 | 62.1 | 51.1 |
| CBAM [51] | 59.2 | 81.5 | 67.5 | 59.9. | 51.3 | 79.0 | 62.3 | 50.6 |
| CA [27] | 59.3 | 81.5 | 67.5 | 60.2 | 51.6 | 79.5 | 62.2 | 51.3 |
| MSAM (ours) | 59.9 | 82.7 | 69.0 | 61.1 | 51.9 | 80.9 | 62.3 | 51.5 |
| Mask R-CNN | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | |
| Baseline | 58.5 | 81.1 | 67.1 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 79.3 | 61.2 | 50.4 |
| S = 2 | 59.5 | 82.0 | 68.2 | 60.5 | 51.7 | 80.1 | 62.2 | 51.4 |
| S = 4 | 59.9 | 82.7 | 69.0 | 61.1 | 51.9 | 80.9 | 62.3 | 51.5 |
| S = 8 | 59.3 | 81.8 | 68.1 | 60.4 | 51.7 | 79.9 | 62.2 | 51.5 |
| Mask R-CNN | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | |
| Baseline | 58.5 | 81.1 | 67.1 | 59.6 | 50.9 | 79.3 | 61.2 | 50.4 |
| Max | 59.0 | 81.7 | 67.4 | 60.1 | 51.6 | 80.1 | 62.2 | 51.3 |
| Avg | 59.9 | 82.4 | 68.5 | 61.0 | 51.8 | 80.5 | 62.0 | 51.4 |
| Max and Avg | 59.9 | 82.7 | 69.0 | 61.1 | 51.9 | 80.9 | 62.3 | 51.5 |
| Method | Backbone | Detection | Segmentation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | AP | AP50 | AP75 | APS | ||
| Mask R-CNN [53] | ResNet-101 | 65.1 | 87.7 | 75.5 | 66.1 | 54.8 | 85.7 | 65.2 | 54.3 |
| Mask Scoring R-CNN [56] | ResNet-101 | 65.2 | 87.6 | 75.4 | 66.5 | 54.9 | 85.1 | 65.9 | 54.5 |
| Cascade Mask R-CNN [52] | ResNet-101 | 65.1 | 85.4 | 74.4 | 66.0 | 52.8 | 83.4 | 62.9 | 52.2 |
| PANet [50] | ResNet-101 | 65.4 | 88.0 | 75.7 | 66.5 | 55.1 | 86.0 | 66.2 | 54.7 |
| YOLACT [57] | ResNet-101 | 47.9 | 74.4 | 53.3 | 51.7 | 39.6 | 71.1 | 41.9 | 39.5 |
| GroIE [58] | ResNet-101 | 65.4 | 87.8 | 75.5 | 66.5 | 55.4 | 85.8 | 66.9 | 54.9 |
| Filtered Convolution [59] | ResNet-101 | 68.6 | 89.2 | 77.6 | 67.4 | - | - | - | - |
| FL-CSE-ROIE [60] | ResNet-101 | 69.0 | 90.2 | 79.5 | 69.9 | 57.9 | 88.6 | 69.5 | 57.3 |
| GCBANet [43] | ResNet-101 | 69.4 | 89.8 | 79.2 | 70.4 | 57.3 | 88.6 | 68.9 | 57.0 |
| HTC [61] | ResNet-101 | 66.6 | 86.0 | 77.1 | 67.6 | 55.2 | 84.9 | 66.5 | 54.7 |
| HTC+ [44] | MRFEN | 71.5 | 92.3 | 82.5 | 72.6 | 59.1 | 90.3 | 71.0 | 58.7 |
| Mask R-CNN MS-FPN (ours) | ResNet-101 | 66.3 | 88.4 | 76.0 | 67.4 | 56.3 | 86.3 | 67.6 | 55.5 |
| Cascade Mask R-CNN-MS-FPN (ours) | ResNet-101 | 69.2 | 88.8 | 79.9 | 70.0 | 57.4 | 87.7 | 69.7 | 56.5 |
| HTC-MS-FPN (ours) | ResNet-101 | 69.2 | 89.2 | 79.4 | 69.9 | 57.6 | 87.4 | 69.3 | 56.7 |
| HTC-MS-FPN (ours) | ResNext-101-64xd | 70.1 | 89.4 | 80.9 | 70.7 | 58.5 | 88.2 | 71.6 | 57.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Meng, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, S. A Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network for Detection and Instance Segmentation of Marine Ships in SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246312
Sun Z, Meng C, Cheng J, Zhang Z, Chang S. A Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network for Detection and Instance Segmentation of Marine Ships in SAR Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246312
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zequn, Chunning Meng, Jierong Cheng, Zhiqing Zhang, and Shengjiang Chang. 2022. "A Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network for Detection and Instance Segmentation of Marine Ships in SAR Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246312
APA StyleSun, Z., Meng, C., Cheng, J., Zhang, Z., & Chang, S. (2022). A Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Network for Detection and Instance Segmentation of Marine Ships in SAR Images. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6312. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246312






