Analysis of BDS-3 Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset Estimated in Global and Asia-Pacific and the Corresponding PPP Performances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Un-Differenced Approach
2.2. Epoch-Differenced Method
2.3. Mixed Differenced Model
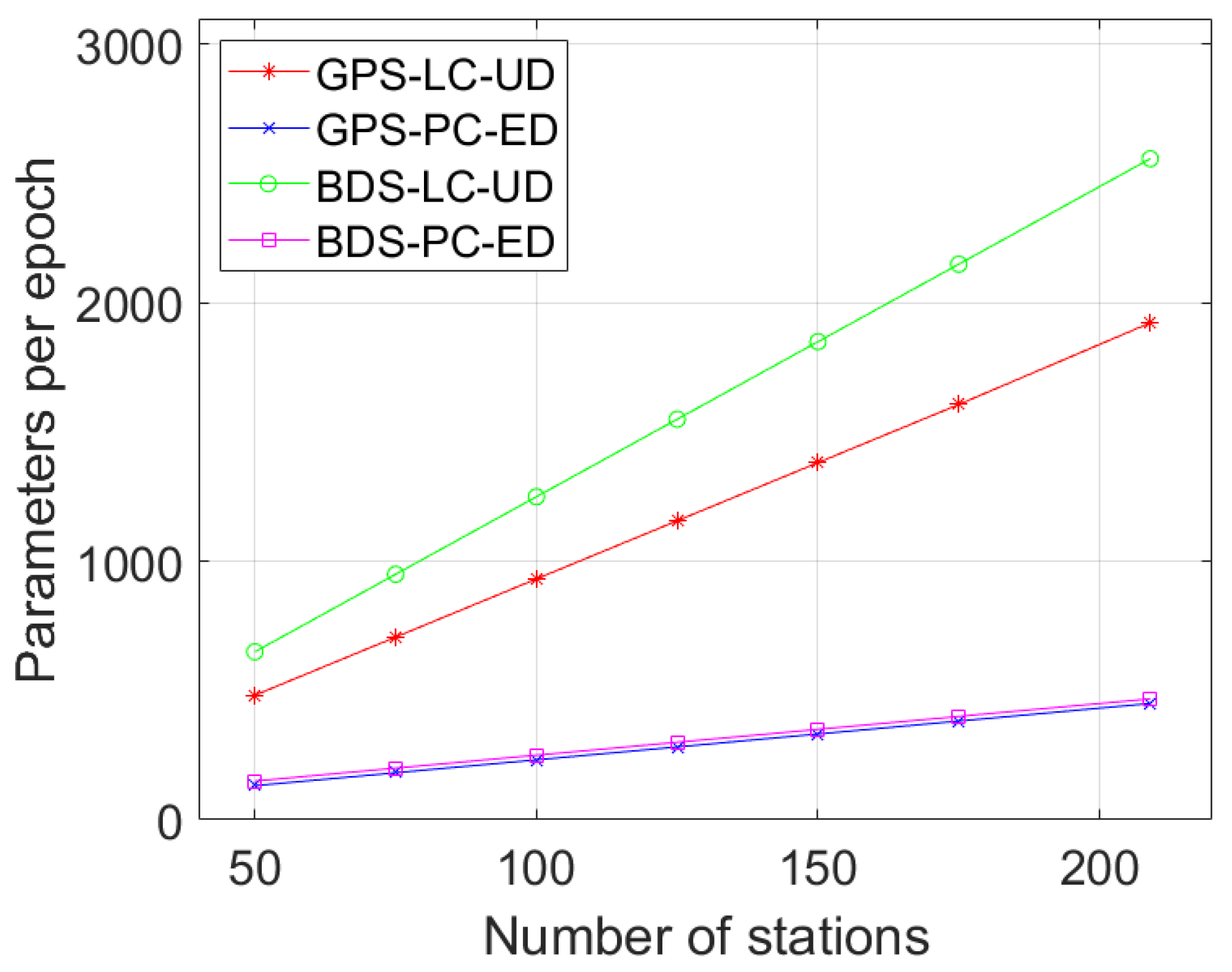
2.4. Efficiency of Different Models
3. BDS-3 Satellite Clock Offset
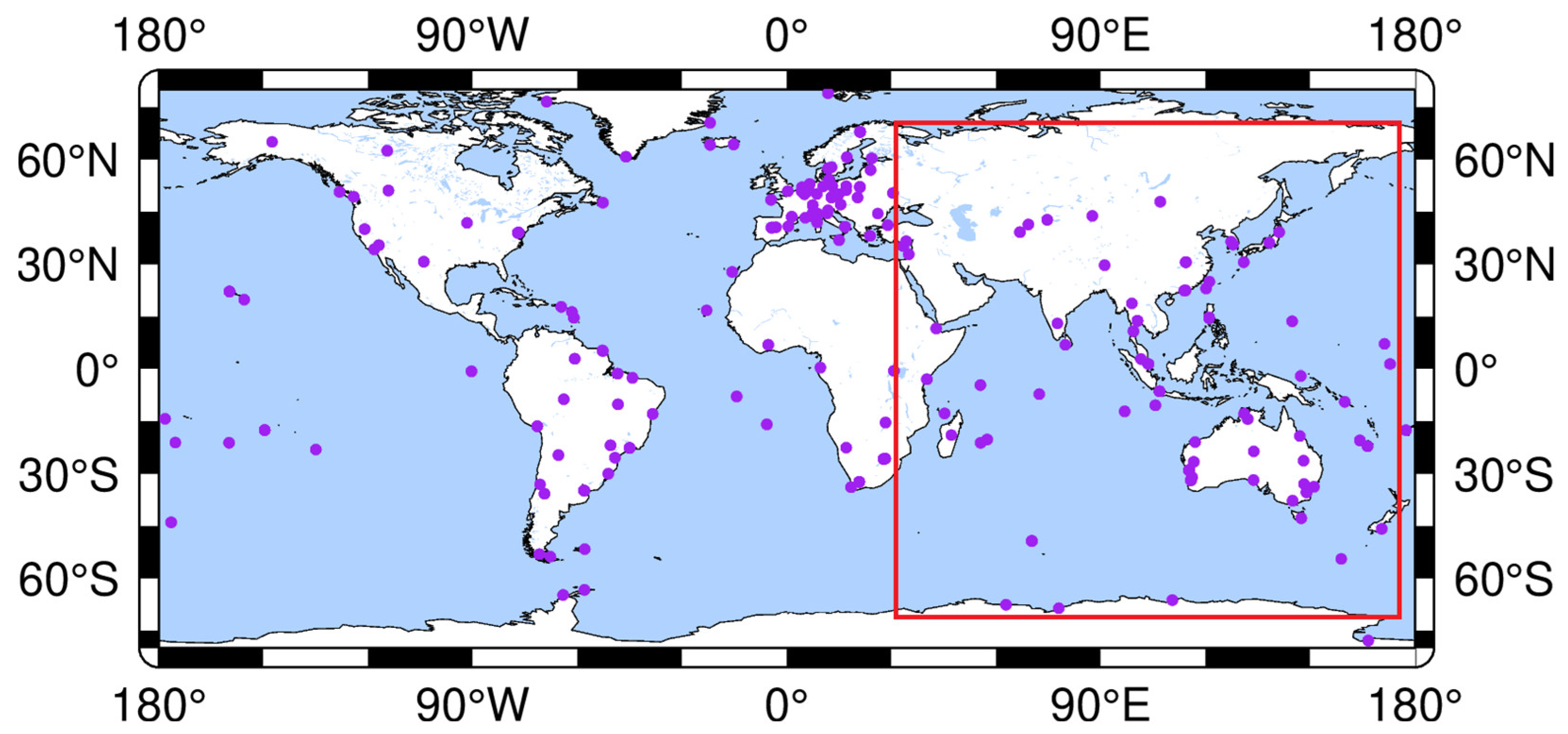
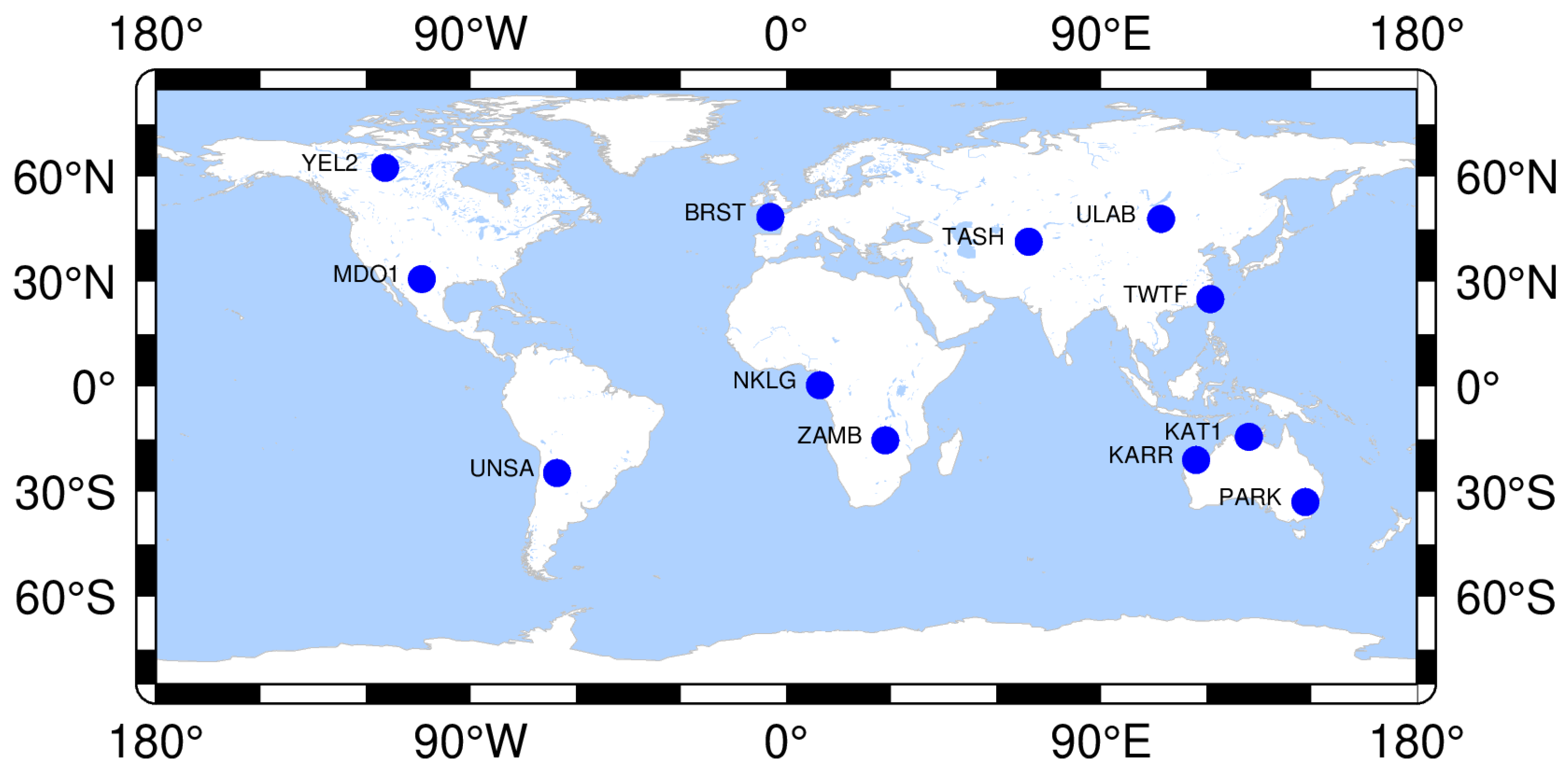
3.1. Data and Strategy
3.2. Estimated BDS-3 Clocks
3.3. Characteristics of BDS-3 Atomic Clock
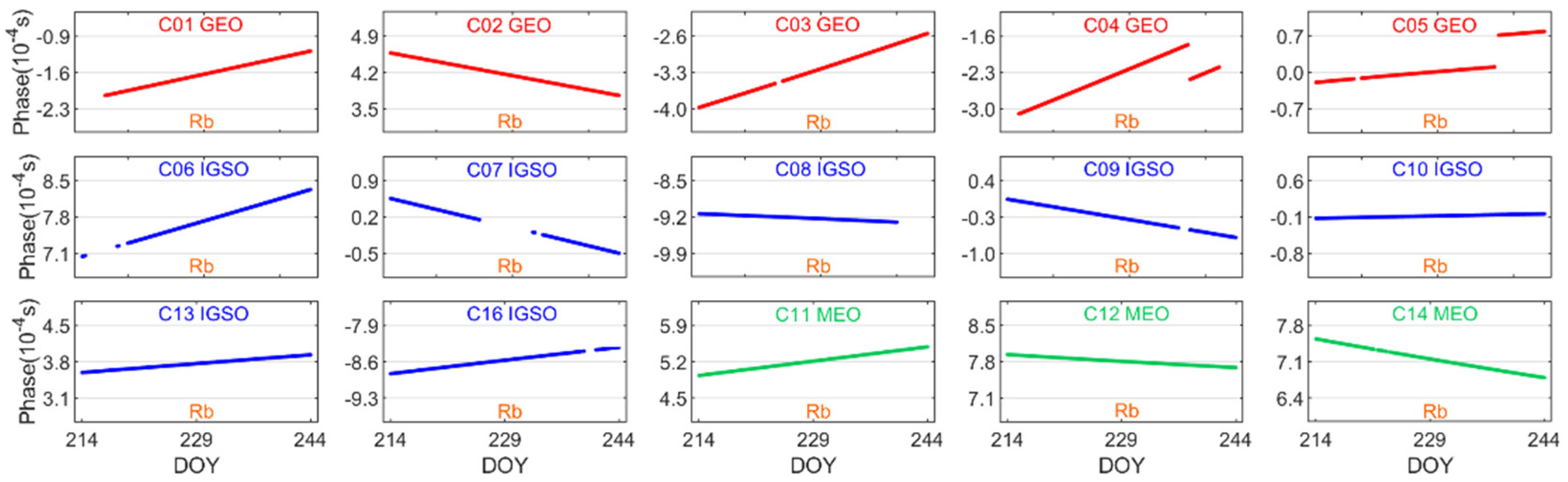
3.3.1. Phase Series
3.3.2. Frequency Series
3.3.3. Frequency Drift Series
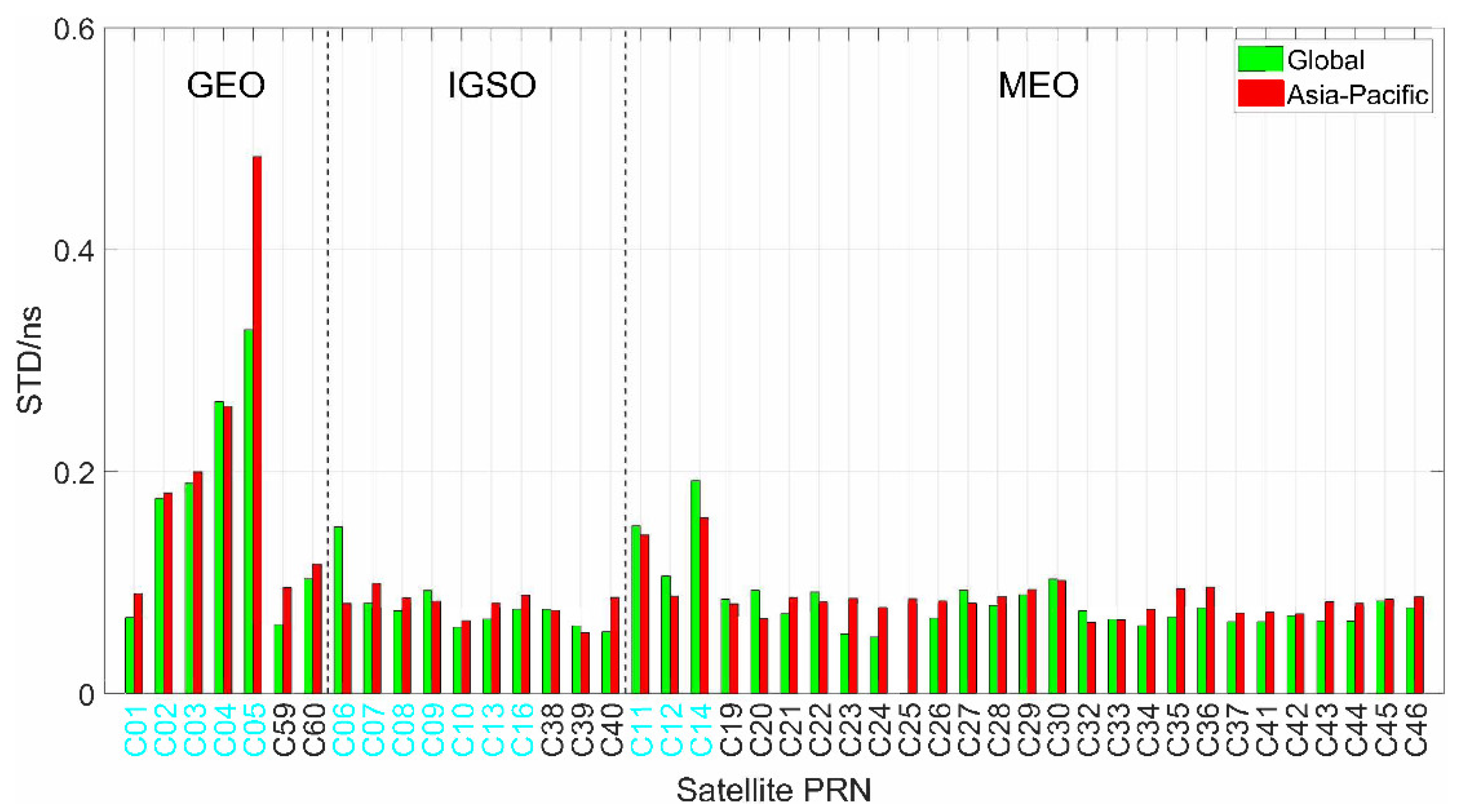
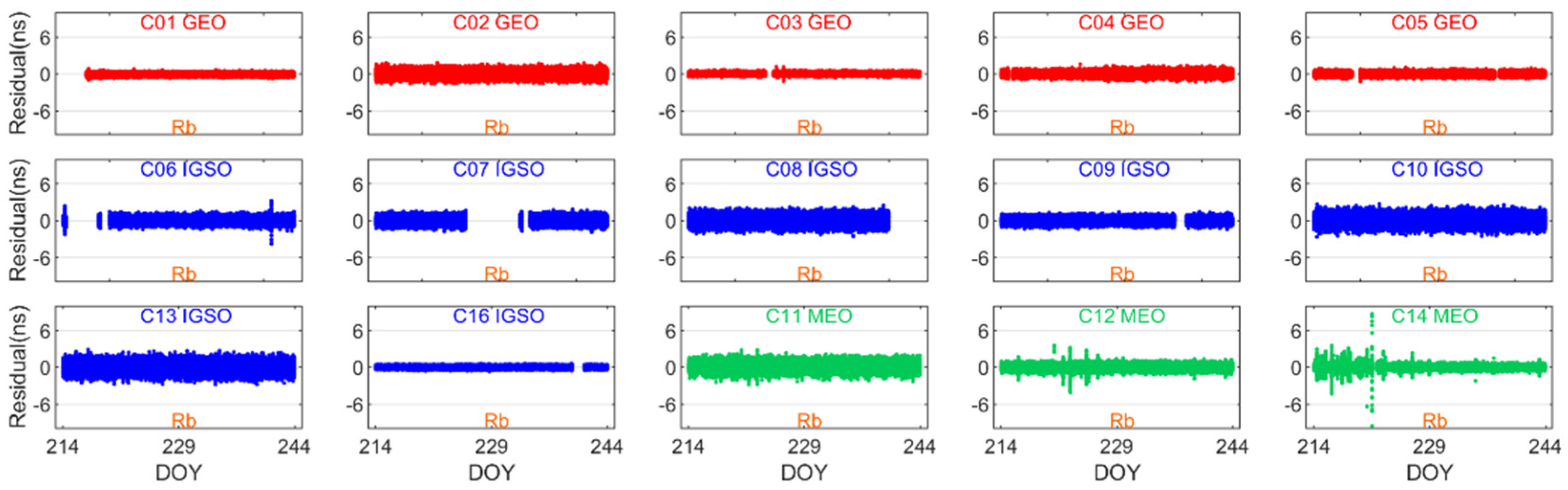
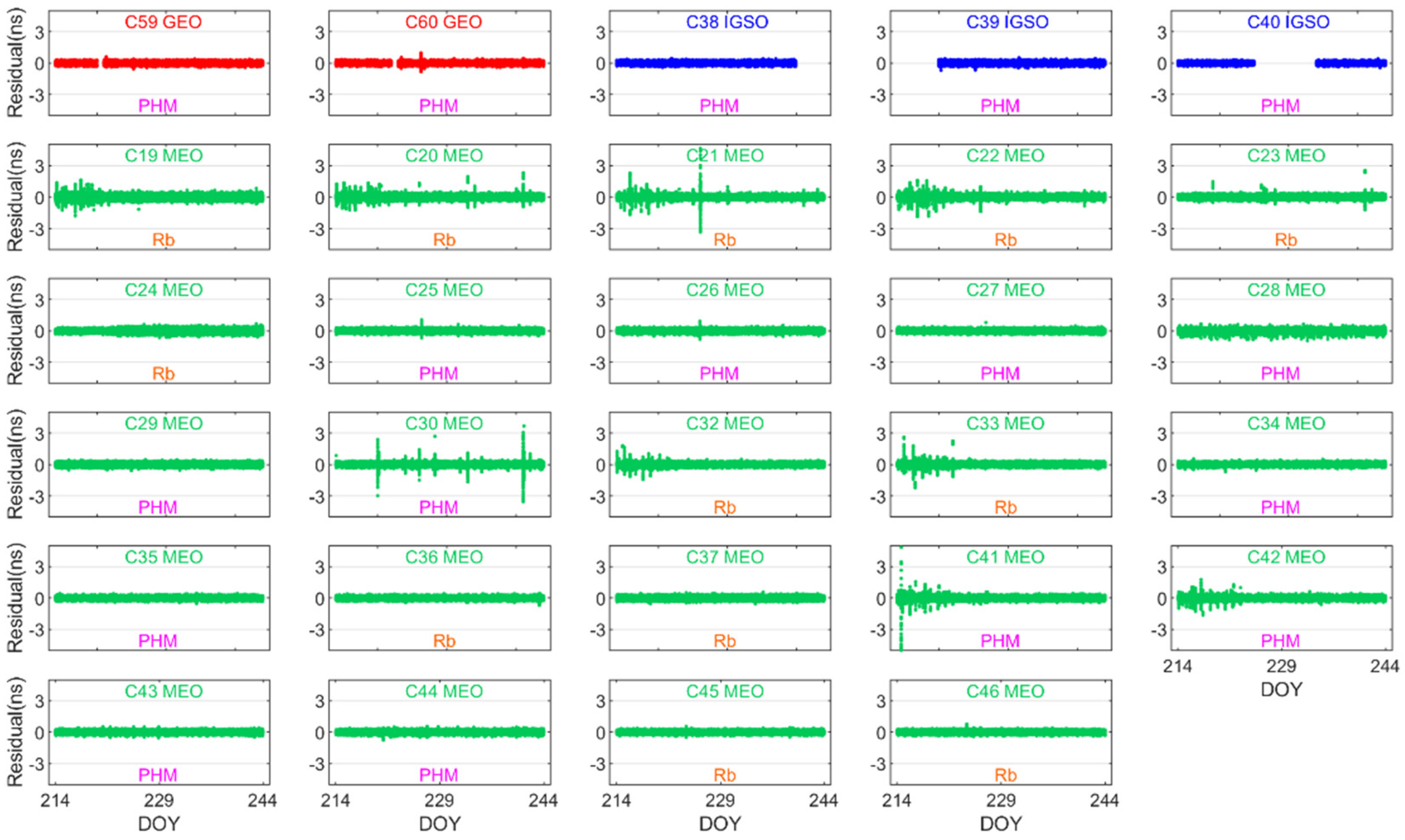
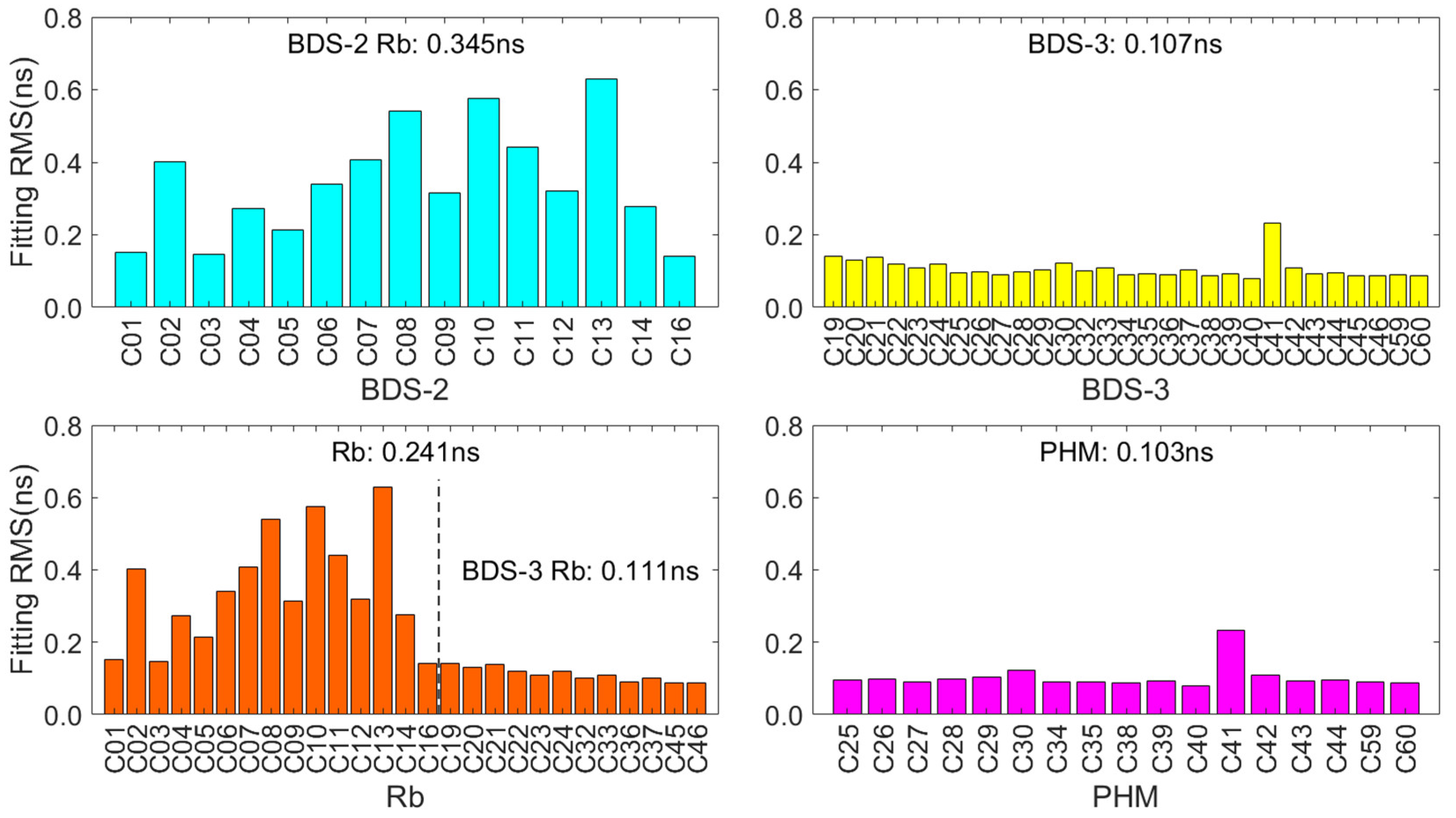
3.3.4. Residual and Fitting Precision
4. Kinematic PPP Validation
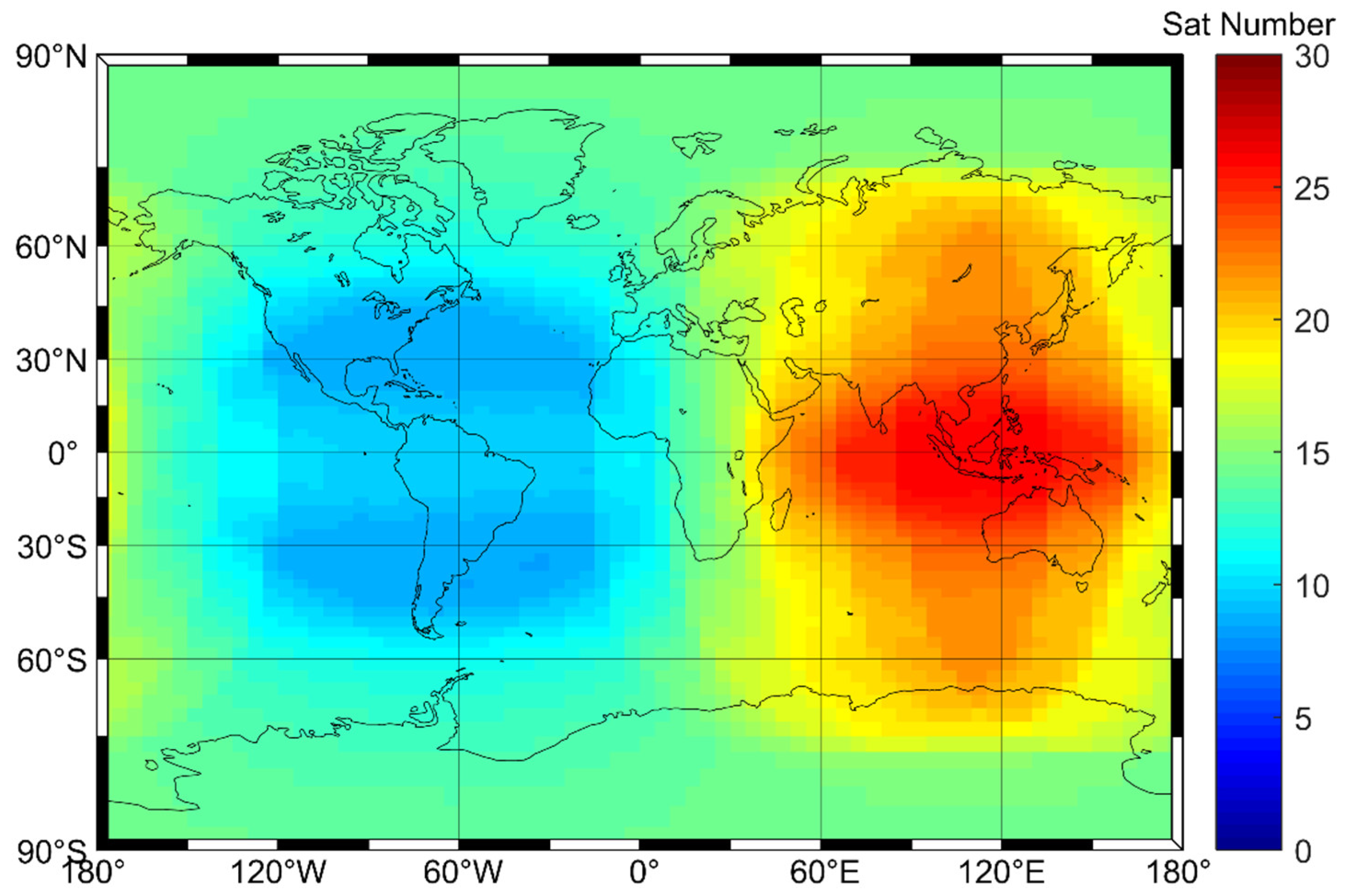
4.1. Positioning Data
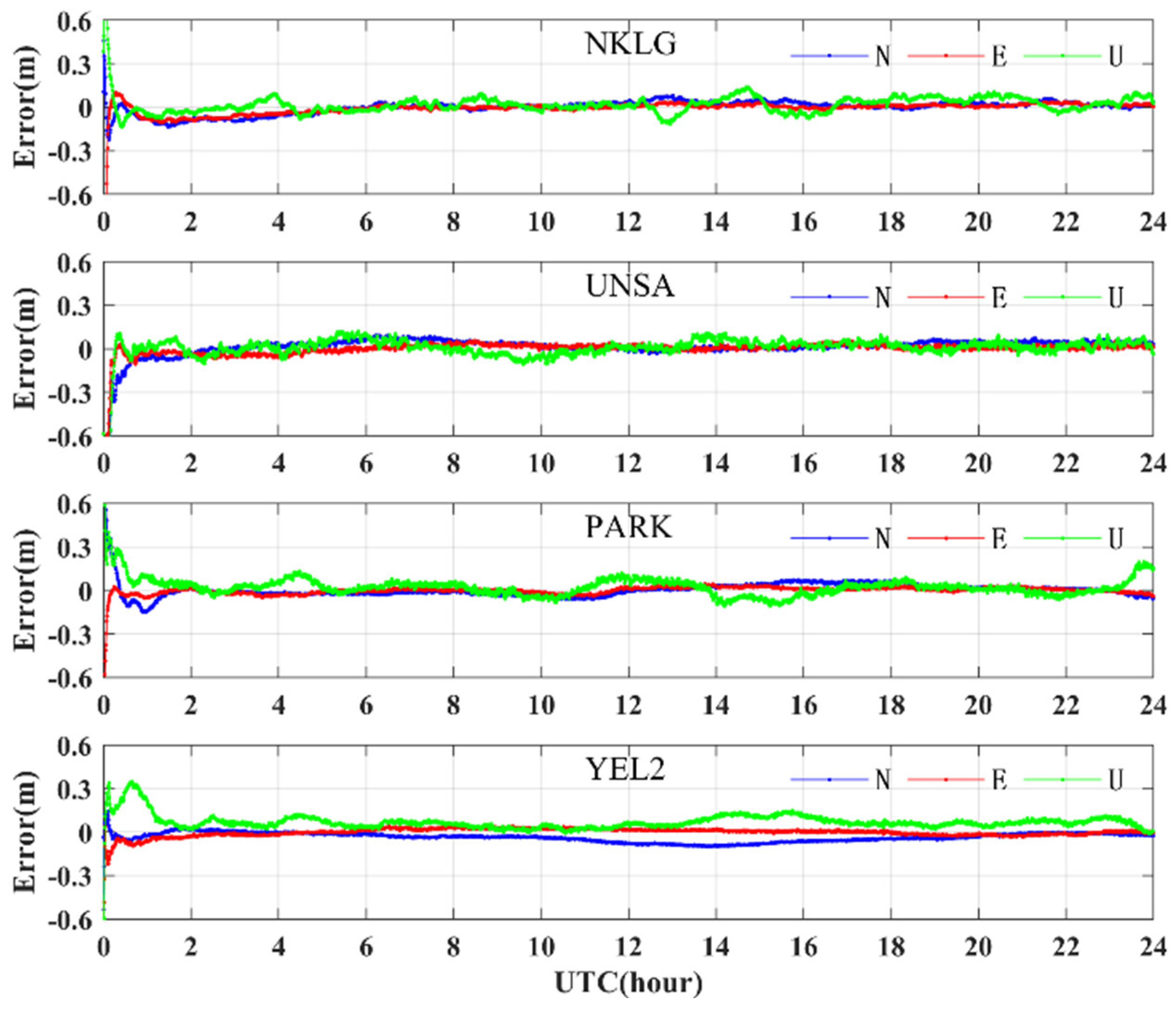
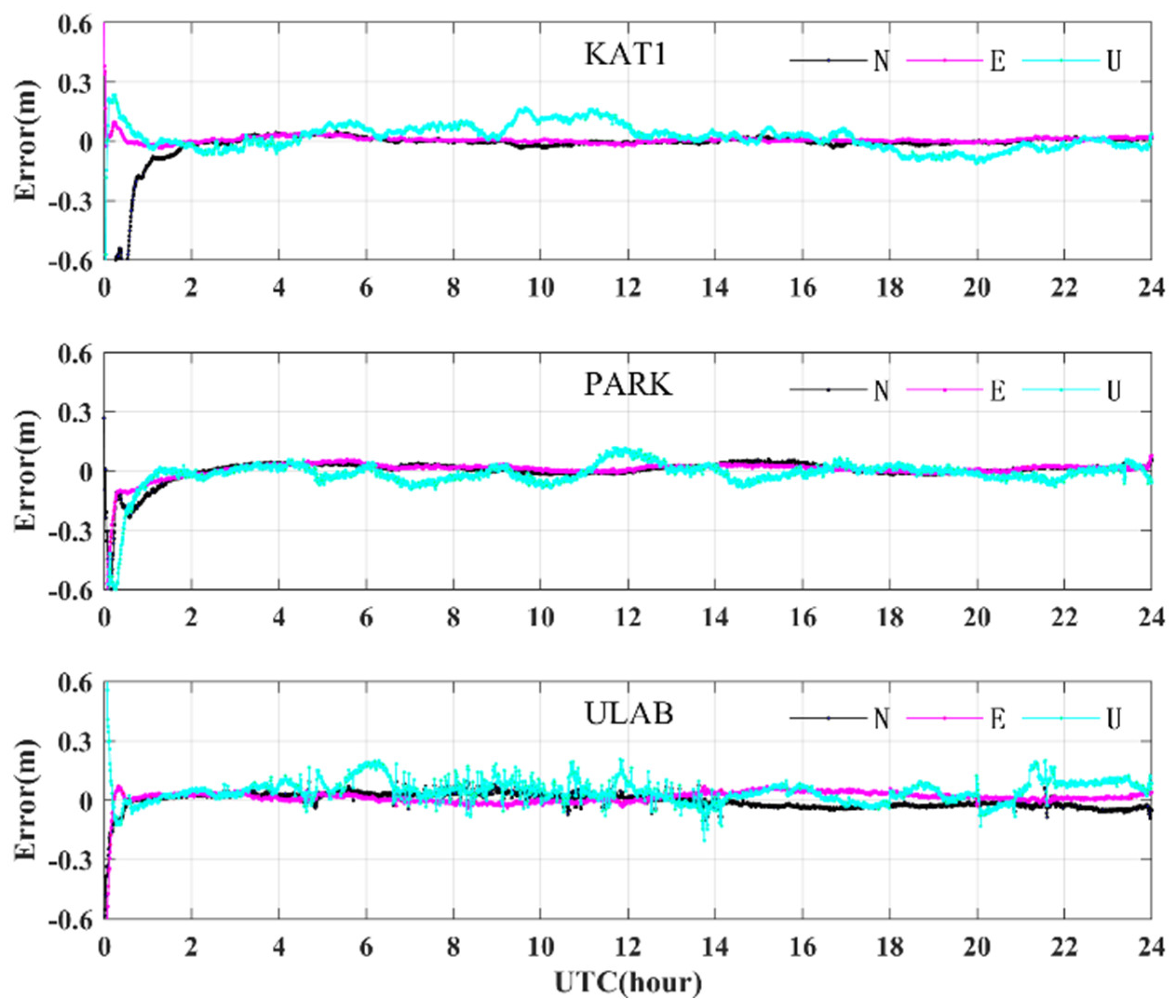
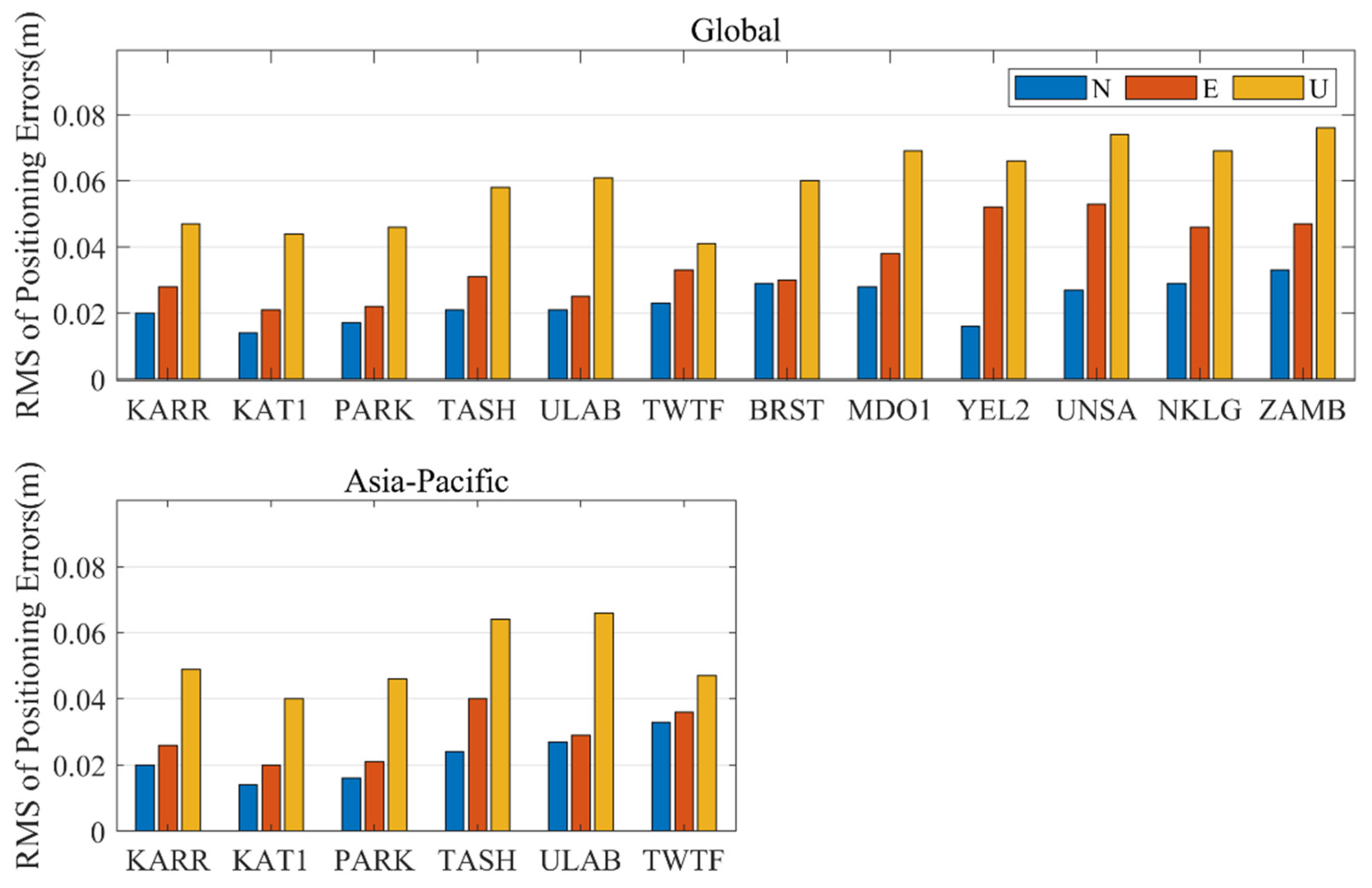
4.2. Kinematic Positioning Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, Y.; Melgar, D. Physical applications of GPS geodesy: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Sturze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)—Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Guo, S.; Mao, Y.; Yang, Y. Introduction to BeiDou-3 navigation satellite system. Navigation 2019, 66, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Ground-based Augmentation Service Interface Control Document (Version 1.0). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/P020200803362071652972.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B.; Ren, X. Featured services and performance of BDS-3. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Tang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G. Time synchronization of new-generation BDS satellites using inter-satellite link measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.; Verhagen, S.; Psychas, D.; Liu, X. Assessing the performance of multi-GNSS PPP-RTK in the local area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Chen, L.; Lu, X.; Ruan, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, R. Interactive multiple-model vertical vibration detection of structures based on high-frequency GNSS observations. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Psychas, D.; Xing, X.; Zhao, Q.; Verhagen, S.; Liu, X. Influence of the inhomogeneous troposphere on GNSS positioning and integer ambiguity resolution. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 1914–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Kalman-filter-based GPS clock estimation for near realtime positioning. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Guo, F. Satellite clock estimation at 1 Hz for realtime kinematic PPP applications. GPS Solut. 2011, 15, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Qin, Z. Real-time estimation of satellite clock offset using adaptively robust Kalman filter with classified adaptive factors. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Ding, W.; Ai, Q. A modified mix-differenced approach for estimating multi-GNSS real-time satellite clock offsets. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaduszliwer, B.; Camparo, J. Past, present and future of atomic clocks for GNSS. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G. Real-time estimation of BDS/GPS high-rate satellite clock offsets using sequential least squares. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, K.; Wang, J.; Han, H. Real-time BDS-3 clock estimation with a multi-frequency uncombined model including new B1C/B2a signals. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Jiang, R.; Lv, Y.; Xie, X. Analysis of BDS-3 onboard clocks based on GFZ precise clock products. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Mao, F.; Gong, X.; Lou, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y. Evaluation of BDS-2 and BDS-3 satellite atomic clock products and their effects on positioning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Chen, J.; Douša, J.; Gendt, G.; Wickert, J. A computationally efficient approach for estimating high-rate satellite clock corrections in realtime. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzum, B.; Petit, G. The IERS Conventions (2010): Reference systems and new models. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2012, 10, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Hajj, G.; Bertiger, W.; Lichten, S. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr. Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, R.; Dach, R.; Collilieux, X.; Jäggi, A.; Schmitz, M.; Dilssner, F. Absolute IGS antenna phase center model igs08. atx: Status and potential improvements. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilssner, F.; Springer, T.; Schönemann, E.; Enderle, W. Estimation of satellite antenna phase center corrections for BeiDou. In Proceedings of the IGS Workshop 2014, Pasadena, CA, USA, 23–27 June 2014; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bierman, G. Factorization Methods for Discrete Sequential Estimation; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the theory of atmospheric refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO-TARC. Fundamental PNT Service. Available online: http://www.csno-tarc.cn/en/system/constellation (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Zhang, W.; Lou, Y.; Gu, S.; Shi, C.; Haase, J.; Liu, J. Joint estimation of GPS/BDS real-time clocks and initial results. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Zha, J.; Zhao, C. An efficient undifferenced method for estimating multi-GNSS high-rate clock corrections with data streams in real time. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1435–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Ya, S.; Zhu, S. Comparison and assessment of long-term performance of BDS-2/BDS-3 satellite atomic clocks. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

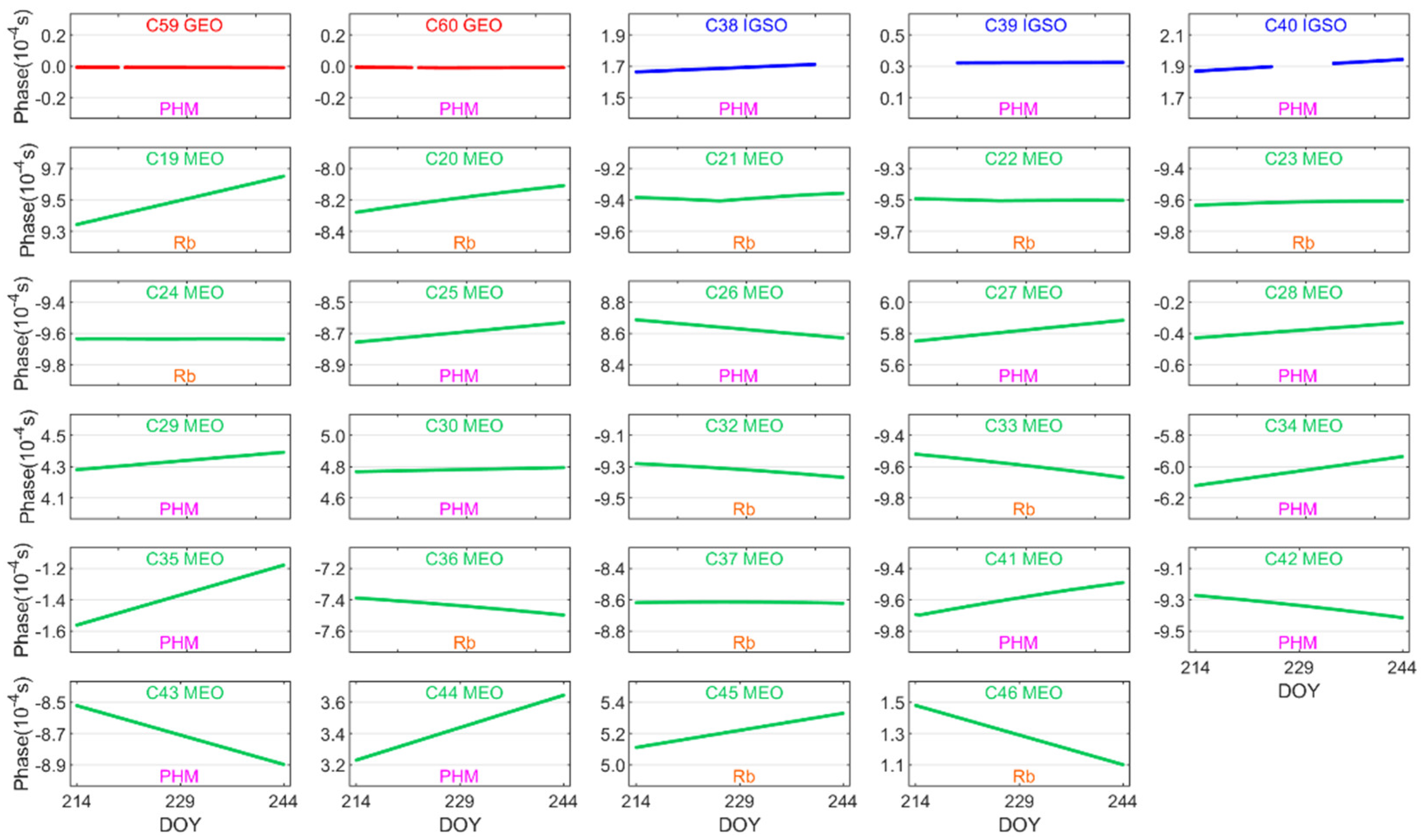
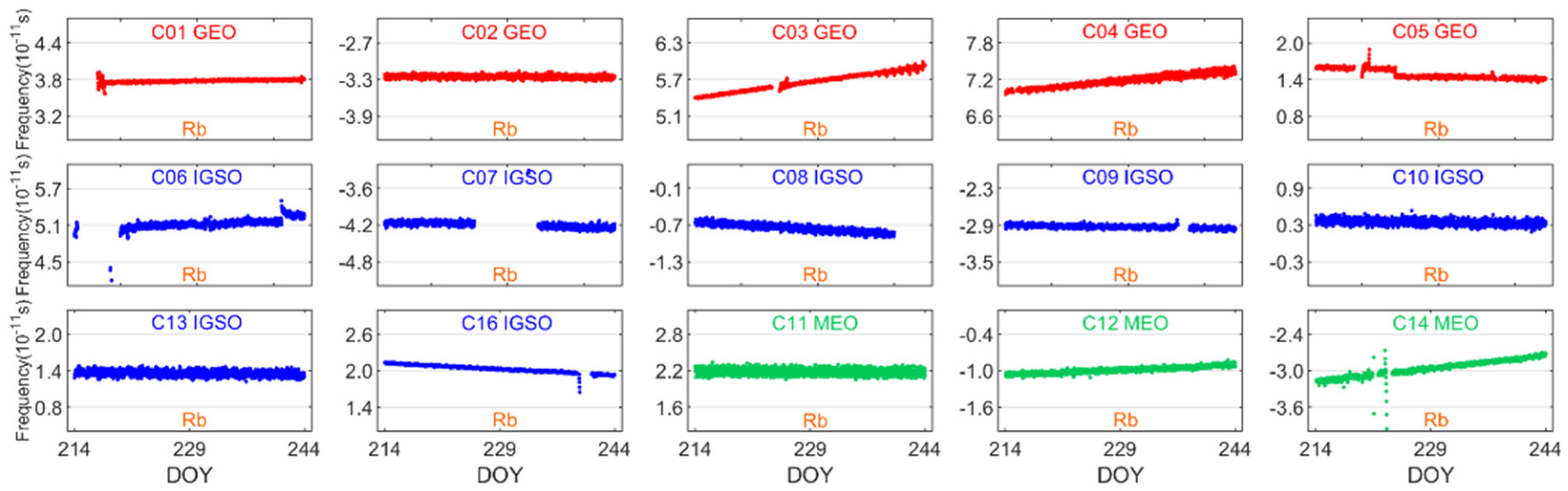

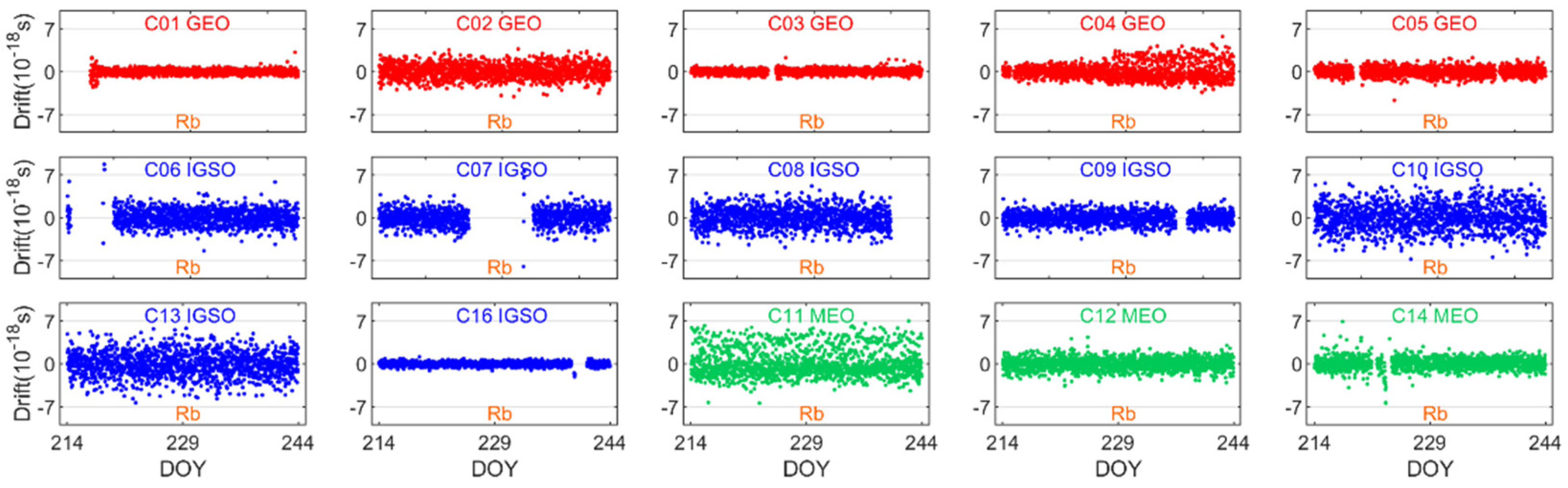
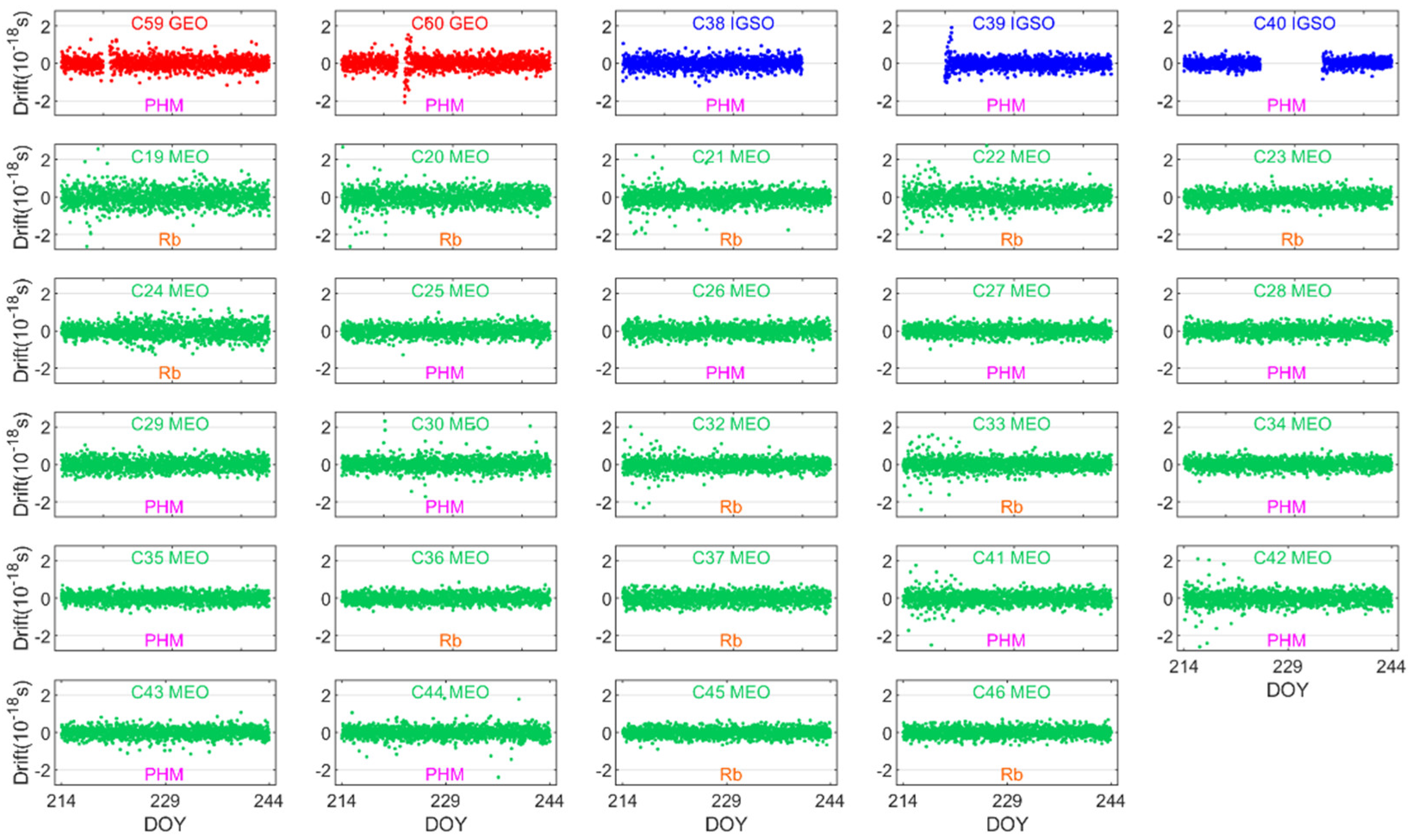
| Parameter | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Observations | UD range and ED phase |
| Cut-off elevation | 7° |
| Observation weights | Elevation-dependent weight |
| Intervals | 1 s |
| Earth solid tides | IERS conventions 2010 [21] |
| Ocean tides | IERS conventions 2010 [21] |
| Phase wind-up | Corrected [22] |
| Satellite PCV | uncorrected |
| GEO satellite PCO | IGS14.atx [23] |
| IGSO/MEO satellite PCO | ESA Mode [24] |
| Receiver PCV/PCO | IGS14.atx |
| Relativistic effects | Correct |
| Reference clock | Receiver with stable atomic clock (e.g., PARK) |
| Adjustment model | Square root information filtering [25] |
| Ephemeris | Ultra-rapid ephemeris of GFZ |
| Tropospheric delay | Saastamoinen model [26] + GMF mapping function random-walk process [27] |
| Satellite/Receiver clock | Estimated as white noise |
| Station coordinates | Fixed |
| Satellite Generations | Orbit Type | PRN | Clock Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDS-2 | GEO | C01 C02 C03 C04 C05 | Rb |
| IGSO | C06 C07 C08 C09 C10 C13 C16 | ||
| MEO | C11 C12 C14 | ||
| BDS-3 | GEO | C59 C60 | PHM |
| IGSO | C38 C39 C40 | ||
| MEO | C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C32 C33 C36 C37 C45 C46 | Rb | |
| C25 C26 C27 C28 C29 C30 C34 C35 C41 C42 C43 C44 | PHM |
| Orbit Type | Global (BDS-2/BDS-3) | Asia-Pacific (BDS-2/BDS-3) |
|---|---|---|
| GEO | 0.171 (0.207/0.083) | 0.204 (0.243/0.106) |
| IGSO | 0.072 (0.076/0.064) | 0.077 (0.079/0.072) |
| MEO | 0.082 (0.126/0.075) | 0.085 (0.103/0.082) |
| Mean | 0.093 (0.130/0.074) | 0.102 (0.138/0.082) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Hou, Y.; Ren, Y. Analysis of BDS-3 Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset Estimated in Global and Asia-Pacific and the Corresponding PPP Performances. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6206. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246206
Wang H, Li P, Wang J, Ma H, Hou Y, Ren Y. Analysis of BDS-3 Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset Estimated in Global and Asia-Pacific and the Corresponding PPP Performances. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6206. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246206
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hu, Pengyuan Li, Jiexian Wang, Hongyang Ma, Yangfei Hou, and Yingying Ren. 2022. "Analysis of BDS-3 Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset Estimated in Global and Asia-Pacific and the Corresponding PPP Performances" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6206. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246206
APA StyleWang, H., Li, P., Wang, J., Ma, H., Hou, Y., & Ren, Y. (2022). Analysis of BDS-3 Real-Time Satellite Clock Offset Estimated in Global and Asia-Pacific and the Corresponding PPP Performances. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6206. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246206








