Abstract
The accurate calculation of sustainable development indicators is essential for the accurate assessment of the Sustainable Development Goals. This study develops a methodology that combines nighttime light indices, population distribution data, and statistics in order to examine changes and key drivers of SDG7 in the Aral Sea Basin from 2000–2020. In this study, the best-performing combination of four light indices and five simulation methods (two linear regression methods and three machine learning methods) was selected to simulate the spatial distribution of GDP in the Aral Sea Basin. The results showed that: (1) The prediction using the XGBoost model with TNL had better performance than other models. (2) From 2000 to 2020, the GDP of the Aral Sea Basin shows an uneven development pattern while growing rapidly (+101.73 billion, +585.5%), with the GDP of the lower Aral Sea and the Amu Darya River gradually concentrating in the middle Aral Sea and Syr Darya River basins, respectively. At the same time, the GDP of the Aral Sea Basin shows a strong negative correlation with the area of water bodies. (3) Although there is a small increase in the score (+6.57) and ranking (+9) of SDG7 for the Aral Sea Basin from 2000 to 2020, it is difficult to achieve SDG7 in 2030. Deepening inter-basin energy cooperation, enhancing investment in renewable energy, and increasing energy intensity is key to achieving SDG7.
1. Introduction
The United Nations’ 193 member states established 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015 to help countries around the world achieve an end to poverty and peace and prosperity for all by 2030 [1,2]. Among them, SDG7 states that everyone should have access to modern, dependable, cheap energy [3]. Due to the important role of energy in keeping the country stable, maintaining a functioning society, meeting people’s daily needs, and promoting economic development, there is also a non-negligible linkage with other sustainable development goals [4]. Therefore, quantifying the progress of SDG7 is important for the development of relevant policies and the achievement of sustainable development goals [5].
Every year, data on the global energy economy are compiled and analyzed by organizations such as the World Bank and the International Energy Agency. In addition, the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations records relevant data on SDG indicators for each country in the SDG Indicator Bank. However, these data are counted on a national basis, and it is not possible to obtain the distribution of electricity and economy across borders, much less to calculate the development of SDG7 at the basin scale, so they need to be reasonably estimated with the help of data such as remote sensing and population.
In addition to direct feature detection, remote sensing is now widely used to estimate a range of economic activities such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP) [6], electricity consumption [7], and carbon emissions [8]. Numerous studies have shown that Nighttime Lights (NL) have a significant positive relationship with GDP [6,9,10,11]. Dong et al. found that the growth of NL in mainland China provinces was closely related to the growth of GDP from 2013–2019, with an average R2 between the two variables reaching above 0.7 [12]. Meanwhile, Bennett et al. show that using NL data enables a more fine-grained spatialization of GDP than official data, and also estimates the change in GDP for unreported areas at high temporal frequencies [13,14,15]. It is because of all the advantages of NL data that Doll et al. (2006) produced a raster map of GDP for selected European countries and the United States [16]. In addition, some studies have also found a significant positive correlation between population and GDP [17,18].
Currently widely used NL data from the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Operational Linescan System (DMSP-OLS) stable NL data and the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (NPP-VIIRS) NL data [15,19,20]. Global night lighting products were converted from DMSP data to VIIRS data in 2012 as DMSP/OLS ceased operations in 2013 [15]. However, the image resolution and performance of the two sensors are different, Chen et al. used a deep learning approach to establish an extended time series of NPP-VIIRS-like NL data (2000–2018) by performing a new cross-sensor calibration on the composition of DMSP-OLS data (2000–2012) and NPP-VIIRS monthly data (2013–2018) [20]. However, the relationship between NL data and GDP is not easily described quantitatively, and most existing statistical models do not reflect the non-linear relationship between them.
Machine learning (ML) methods can improve statistical model performance by examining non-linear correlations between predictors and dependent variables, and it has also solved many SDG problems in the last few years [21,22,23]. Asadikia et al. used a boosted regression tree model to identify synergistic relationships among sustainable development goals to assist decision-makers in putting into practice efficient resource-allocation strategies [24]. Molina et al. use ML methods to study the relationship between air quality and sustainable development in cities [25]. Canhoto et al. apply ML methods to SDG16 to model unusual financial behavior [26]. Ferreira et al. assess the contribution of ML algorithms and how well they can help attain the SDGs and strongly recommend the use of new machine learning techniques for deeper and more effective analysis of existing data to support countries in achieving the SDGs [27]. Although there is a consensus to apply ML methods to SDGs, there are few studies that apply multiple ML methods to calculate specific SDGs.
It is noteworthy that most of the SDG studies have been conducted on a national basis, while few studies have been conducted on a watershed scale due to the lack of relevant data. Although NL data are widely used in GDP simulations, few studies evaluate SDG with the help of NL data and machine learning methods. This study uses multiple ML methods, NL, and population datasets to predict basin-wide GDP while incorporating national statistics to assess the development of SDG 7 in the basin. This study has three objectives: (1) compare the performance of various ML algorithms in GDP forecasting based on NL and population datasets. (2) Select the optimal algorithm and NL index to spatialize the GDP of the Aral Sea Basin (ASB). (3) Combining NL, GDP, and population data to map country-based sustainable development data to the basin scale to obtain results for the SDG 7 of ASB for 2000–2020. Under this assumption, this study simulated the spatial distribution of GDP in the ASB from 2000 to 2020 through various machine learning algorithms and different datasets and combined with other statistical data to calculate the basin-wide development trend of SDG7 from 2000 to 2020. This research can offer information and suggestions for comprehending the evolutionary process of the economy within the ASB, the distribution of resources, and the coordinated development of the region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The ASB (Figure 1) is located in the area where Central Asia and Southwest Asia meet, which covers more than 1.7 million km2 [28,29]. Its topography is high in the southeast and low in the northwest, and the major rivers in the basin all originate from the snow and ice melt water in the highland mountains in the southeast [30]. The climate of the ASB is semiarid to arid with cold winters and hot summers [31]. It is due to the arid climate that the two main rivers in the basin (Syr Darya River and Amu Darya River) are inland, and eventually feed into the Aral Sea. Due to the scarcity of water resources, most of the population, cities, and cultivated land in the study area are distributed along the rivers. The middle and upper reaches are rich in cultivated and forested land due to the abundance of water resources, and the population and cities are more concentrated.
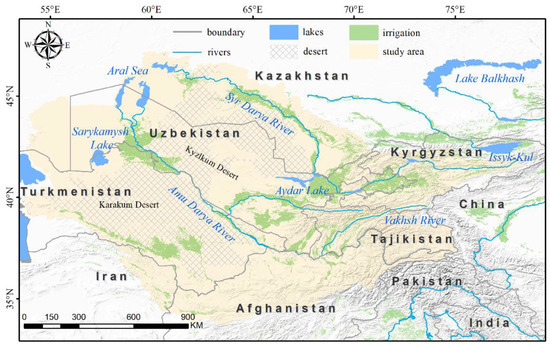
Figure 1.
A map showing the location of the ASB. National boundary data were acquired from the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping, and Geoinformation with No. GS (2016) 1665.
2.2. Data Source and Pre-Processing
In this study, four types of data were used: gridded population datasets, NL data, and National statistics (Table 1). The population datasets were obtained from WorldPop at high resolution (1 km × 1 km) for all countries. The data utilize a semi-automatic symmetric modeling approach that integrates census and auxiliary data into a random forest, and the results of this method are compared with those of other methods in three countries (Vietnam, Cambodia, and Kenya), all showing high precision (minimum root mean square error and mean absolute error) [32,33]. NL data for 2000–2020 come from the global NPP-VIIRS class NL datasets calibrated across sensors at higher resolution (500 m × 500 m), which shows good uniformity at the pixel and city levels (R2 = 0.87 and 0.95, respectively) [20,34]. The GDP data were provided by WorldBank. Statistic data for SDG 7 are derived from the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations. The missing years of some countries in the GDP and statistics are obtained by fitting the existing data. The NL data (500 m) were resampled to 1 km by ArcGIS10.2 to match population datasets. All datasets were extracted by a mask of seven countries’ boundaries and The ASB border in ArcGIS10.2.

Table 1.
The detail descriptions of the data and resources.
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Prediction Models
In order to create prediction models, three ML methods-Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine Regression (SVR), and EXtreme Gradient Boost (XGBoost)) were combined with two linear regression methods-Least Absolute Shrinkage, Selection Operator regression (Lasso), and Ridge Regression (Ridge)) to establish prediction models between NL, population, and GDP, and their performances were also compared.
It is common practice to employ multiple linear regression models in order to analyze the relationship between the dependence of a single dependent variable on the variation of multiple independent variables [35]. If the dependence of the two variables can be portrayed in linear form, a multivariate linear model can be developed for the analysis [36,37]. Lasso is a regularized regression analysis method, which adds a penalty paradigm to the multiple linear regression, and this penalty paradigm has the effect of enhancing model stability and filtering model features [38]. Ridge is a modified least squares estimation method that gives up the unbiased nature of least squares to obtain a more realistic and reliable regression [39]. The GDP of a region is closely related to nighttime lights and population, which meets the essential requirement of multiple linear regression, so Lasso and Ridge regressions are chosen to investigate the linear relationship between lights, population, and GDP in this study. The alpha parameters in the Lasso and Ridge models were obtained by means of grid search and cross-validation.
RF is an integrated learning technique for regression, which is based on the principle of building multiple decision trees during training and outputting the average prediction of each decision tree to achieve regression analysis [40]. Since RF can detect nonlinear relationships without prior knowledge, and has the advantages of being insensitive to noise, requiring fewer parameters, and effectively avoiding over-fitting, it is widely used as an important machine learning method [41,42]. In this study, random search and five-fold cross-validation are used in order to select the hyperparameters.
SVR is a binary classification model, which is an important application branch in support vector machines. In contrast with support vector machines, which maximize the interval between multiple classes of sample points, SVR minimizes the total deviation of all sample points from the hyperplane [43,44]. In the process of applying SVR, the selection of kernel function is the key step, which enables the mapping of the original input data to the higher dimensional space [38]. The linear function is a frequently-used kernel function in different kernelized learning algorithms [45,46]. In order to obtain relatively accurate results, the linear kernel for SVR was chosen in this study. In addition, two hyperparameters of penalty coefficient C and the kernel coefficient gamma were tuned using the grid search.
XGBoost is an algorithm based on the Gradient Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT), which is an additive model based on the idea of boosting integration and greedy learning by using a forward distribution algorithm during training [47]. XGBoost uses the second-order Taylor formula to optimize the loss function and improve the computational accuracy; it uses the regular term to simplify the model and avoid overfitting. Furthermore, it combines the primary and quadratic coefficients to obtain the final objective function, which has the advantages of high efficiency, flexibility and portability [38]. The hyperparameters were tuned using the random search with five-fold cross-validation.
We subject all variables to zero-mean normalization before importing them into the model to eliminate the effect of errors due to their different dimensions. For each simulation, we distributed the entire dataset at random into 70% training data and 30% testing data. Meanwhile, the test data are imported into the trained completed model, and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and the coefficient of determination (R2) are used to assess the model’s performance. In order to validate the robustness of the models, each model was calculated over the 50 training-testing splits.
2.3.2. Nighttime Light Index
The light index is used to characterize the strength of the night light data, which are a secondary interpretation of the original light data. In previous studies, several scholars have constructed different lighting indices to reflect the development of socio-economic levels, and commonly used indicators include Total Light Intensity (TNL), Average Light Intensity (I), Light Area Ratio (S), and Comprehensive Light Index (CNLI) [48,49].
where, DNi and ni are the pixel values of the level i in the region and the corresponding number of pixels, respectively. NL and An are the total numbers of pixels in the region and the area occupied in the [DNmin, DNmax] interval, respectively. A is the total area of the region. The different lighting indices focus on describing different light properties, and it is difficult to directly determine which light index is more appropriate in different study areas. Therefore, all light indexes need to be compared to determine the optimal option.
2.3.3. Spatialized Basin GDP
Since GDP statistics are country-based, they need to be pre-processed before model fitting to avoid scale effect problems. First resample the light raster data to 1 km to match the population raster data, and let each country’s GDP, total population, and TNL be divided by the respective number of rasters. Normalization is then performed with Z-score. Despite this, since the TNL of the whole country is replaced by the TNL of the individual image elements for simulation, a linear correction is applied to the GDP of the seven countries to reduce the error:
where GDPc is the GDP of the post-correction country j spatialization, and GDPj is the GDP of the country j simulated before correction. GDPr and GDPR are the simulated and actual GDP of j countries, respectively. After calculating the GDP raster results of each country, the area where each country intersects with the ASB is extracted, and the Spatialized GDP of the ASB is mosaic.
2.3.4. Calculation of Basin SDG
According to Sachs et al.’s calculation, a region’s SDG score is used to indicate how good it is and its position among all countries in the world [50]. Their maximum and minimum values are first determined by examining the upper and lower limits of the UN statistics. For targets 7.1 (7.1.1 and 7.1.2), which have explicit SDG targets, use 0 and 100 as absolute quantitative thresholds. For targets 7.2, 7.3, and 7. b, use the average of the top and bottom 5 performers as maximum and minimum, respectively. After determining the bounds of each indicator, the values of each indicator are scaled to the interval [0; 100] using the following formula, and all indicators are assigned fixed and equal weights.
where x is raw data value, while max and min denote the bounds for best and worst performance, respectively. Furthermore, x’ is the normalized value after rescaling. All values over the upper bound were scored at 100, while all values below the lower bound were scored at 0.
2.3.5. Evaluation Metrics
In order to quantitatively compare the forecast GDP against actual GDP, three statistical indices including Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), the coefficient of determination (R2) and a comprehensive index called the distance between indices of simulation and observation (DISO) [51,52] were employed in this study. DISO is a composite metric that can measure data error in three dimensions. As DISO becomes closer to zero, the closer the simulated value is to the observed value, and the higher the accuracy. These evaluation metrics are expressed as follows:
where and are the simulations GDP and actual GDP for each year, n is the number of years, and are the mean values of simulations and observations. The closer the R2 is to 1, the better the model fits the data, and the closer the RMSE and DISO are to zero, the higher the model accuracy is indicated.
2.3.6. Experiment Design
In order to accomplish the research objectives proposed in the introduction, the following experiments and procedures were designed (Figure 2). First, the lighting data and population data are resampled to the same resolution using ArcGIS10.2 software, and four lighting indices, total populations and GDP of each country are calculated. Second, we subject all variables to zero-mean normalization before importing them into the model to eliminate the effect of errors due to their different dimensions. Next, we distributed the entire dataset at random into 70% training data and 30% testing data to training GDP simulation model, and each model was calculated over the 50 training-testing splits to validate the robustness of the models. After that, the correction coefficient of each country is determined according to the actual GDP and the forecast GDP of the seven countries, and the GDP raster data of each country are corrected, and the GDP raster results of the ASB are obtained. Finally, using population, GDP and light indicators, country-based statistics were mapped to the ASB and the results of SDG 2000–2020 were calculated.
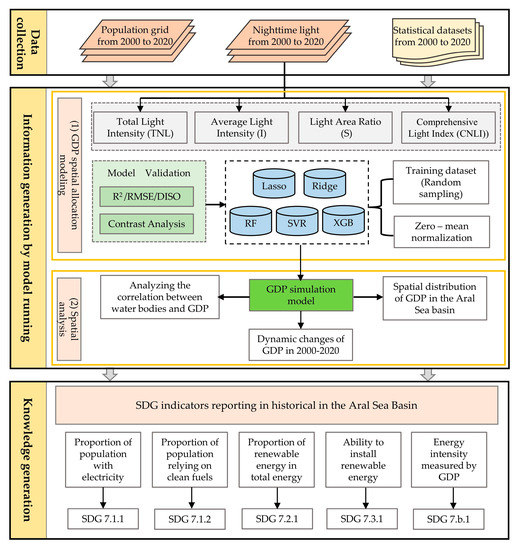
Figure 2.
The framework of the SDG7 in the ASB.
3. Results
3.1. The Performance of Regression and Machine Learning Models in Different NL Index
In order to visually compare the performance of different lighting indexes in different models, four sets of lighting indexes are integrated into different models for comparison. We found that all models achieved good performance in predicting GDP. Overall, the best R2 ranged from 0.78 to 0.86 and the lowest RMSE ranged from 0.36 to 0.46 USD/km2 for XGBoost, which also had the highest accuracy (Figure 3). The lowest R2 ranged from 0.51 to 0.70, and the greatest RMSE ranged from 0.56 to 0.65 USD/km2 for SVR, which also had the lowest accuracy. Lasso and Ridge had similar accuracies in predicting GDP with four NL indexes. The RF model outperformed Lasso, Ridge, and SVR but fell short of XGBoost in terms of performance, which R2 in the range of 0.65 to 0.80 while RMSE is between 0.45 to 0.52 USD/ km2 (Figure 3).
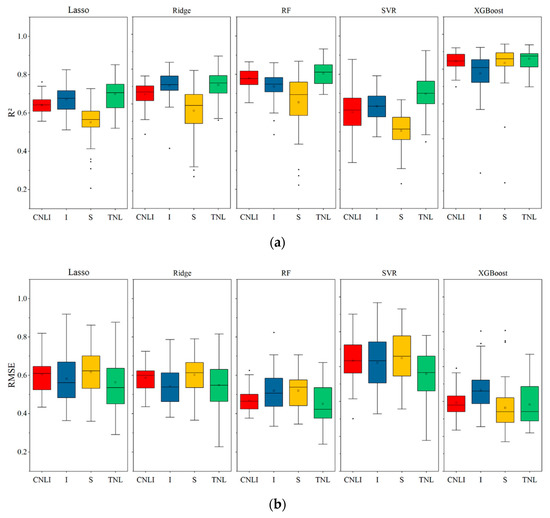
Figure 3.
The performance testing of GDP forecasts using light indices and demographic variables for the period 2000–2020. The performance metrics for R2 (a) and RMSE (b) were calculated for 50 random training-test samples.
The result shows that TNL had high R2 in different models (Lasso −0.70, Ridge −0.71, RF-0.81, SVR-0.70, XGBoost-0.86), the RMSE is 0.56, 0.55, 0.45 0.56 and 0.38, respectively. The light index S performs worst among all models except XGBoost, with the lowest R2 and the highest RMSE. However, S does have R2 (TNL:0.86, S:0.84) similar to TNL and RMSE lower than TNL (TNL:0.38, S:0.36) in the XGBoost model. Considering that the S index has more outliers over R2 and RMSE than TNL, TNL was chosen to calculate GDP.
3.2. Spatial Distribution Pattern of GDP in the ASB
The mutual verification of GDP forecast results with actual GDP is an important method to test the stability and accuracy of the model. We used the correlation between the projected GDP of different countries and their ratios to the real GDP to verify the projections of GDP in the ASB. First, to verify the reliability of the model simulation results, we analyze the correlation between the model’s simulation outcomes and actual GDP (Figure 4). Second, to further verify the accuracy of the simulated GDP, we divided the annual simulated GDP of each country by the actual GDP and compared the result with one. The correlation analysis results show that the adjustment R2 between the projected GDP and the real GDP is: Afghanistan—0.69, Iran—0.46, Kazakhstan—0.97, Kyrgyzstan—0.95, Tajikistan—0.99, Turkmenistan—0.97, Uzbekistan—0.89, and the total of the seven countries—0.79. This suggests that the two influencing factors of light and population and the XGBoost model explain the changes in their GDP by 69%, 46%, 97%, 95%, 99%, 97%, 89%, and 79%, respectively. The validation passed the significance test of 0.001 level, and the RMSE were 1.08, 128.11, 18.34, 0.61, 0.27, 4.55, 10.26, and 124.38, respectively. The results of the simulations and actual values show that the median ratios for all five countries, except for Afghanistan and Iran, have median ratio of nearly 1, which accounts for 84% of the total area of the study area, in addition to the average of all countries having a ratio of 1 (Figure 4). Accordingly, Afghanistan and Iran have large DISO values (Afghanistan: 0.28, and Iran: 0.40) among all seven countries. These verification results show that the selected model has high reliability and accuracy when simulating GDP.
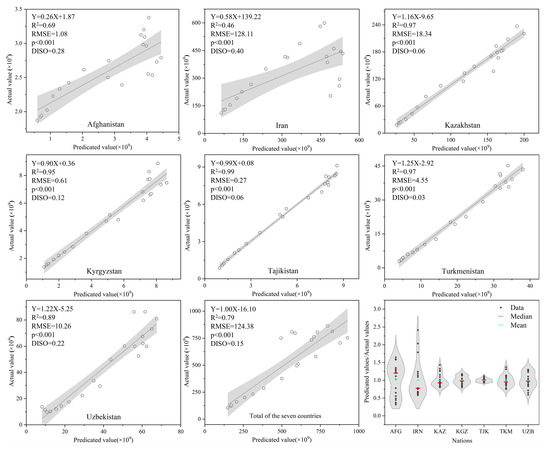
Figure 4.
The actual GDP versus projected GDP for seven countries in the ASB, 2000–2020.
Figure 5 presents the spatial distribution of GDP in the ASB from 2000 to 2020. Overall, the total GDP of the ASB has been increasing continuously from 2000–2015 and has been fluctuating at a high level after reaching a peak of USD 140.53 billion in 2015 (Figure 5). The GDP of the ASB in 2020 increased by USD 101.73 billion or 585.5% from 2000, while the highest GDP per unit area increased from USD 169 thousand in 2000 to USD 929 thousand in 2020.
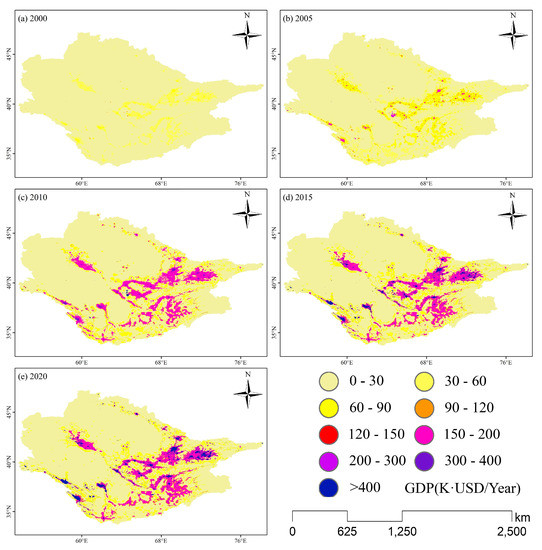
Figure 5.
The spatial distribution of GDP in the ASB from 2000 to 2020 (a–e).
The ASB is divided into five parts: the Syr Darya River Basin, the Amu Darya River Basin, and the upstream, middle, and downstream, and the distribution of GDP in different regions are counted, respectively. According to the statistical results, from 2000 to 2020 the Amu Darya basin (+73.01 billion, +569.31%), the Syr Darya basin (+28.70 billion, +631.49%) and the upper (+22.21 billion, +568.04%), middle (+65.76 billion, + 607.74%) and downstream (+13.72 billion, +520.86%) all showed significant increases in GDP. The GDP of the Amu Darya River basin is significantly higher than that of the Syr Darya River basin, and their proportion in the total GDP of the study area is 73.13% and 26.87%, respectively. However, the proportion of GDP of the Amu Darya River shows a gradually decreasing trend, from 73.81% in 2000 to 72.06% in 2020. The GDP of the ASB shows an uneven distribution pattern, with most of the GDP concentrated in the middle reaches, accounting for 63.10% of the total GDP of the study area, while the upstream and downstream account for 21.99% and 14.85% of the total GDP, respectively.
At the same time, the areas with higher GDP are consistent with the distribution range of cultivated land and water bodies, so we draw on the research results of Chen et al. [53] to calculate the total water area and GDP of the ASB from 2000 to 2020 and further analyze the relationship between them (Figure 6). The results showed a strong negative correlation between GDP and water area, with R2 being 0.8, and Pearson’s being 0.89.
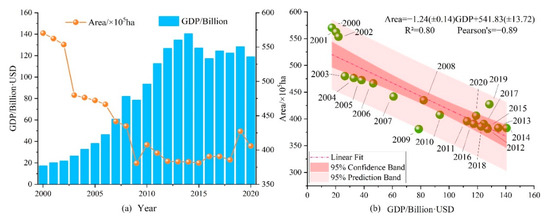
Figure 6.
The changes in the area of water bodies and GDP in the ASB from 2000 to 2020 (a), and the linear relationship between water body area and GDP (b).
3.3. The Process of Changes of SDG7 in the ASB
The ASB SDG7 score has continued to rise from 2000–2020, from 28.48 to 35.06, corresponding to a global ranking from 134 to 125 (Figure 7). In the five indicators of SDG7, the scores from high to low were 7.1.1 > 7.1.2 > 7.3.1 > 7.b.1 > 7.2.1 (Table S2), and the global ranking was: 7.b.1 > 7.1.2 > 7.1.1 > 7.2.1 > 7.3.1 (Table S3). The SDG7 indicator with the fastest growing score is 7.3.1, with an increase of 20.24 points from 2000 to 2020, followed by SDG 7.1.1 with an increase of 15.19 points. SDG 7.2.1 and SDG 7.1.2 also showed varying degrees of growth. The score of SDG 7.b.1, however, shows a decreasing trend, with a decrease of 9.11 points from 2000 to 2020. In terms of global rankings for each indicator, SDG 7.1.1 and SDG 7.3.1 increased slightly, SDG 7.1.2 and SDG 7.b.1 showed a decreasing trend, and SDG 7.2.1’s ranking remained almost unchanged. Nevertheless, the overall ranking of the ASB in the world is still rising. Since the same weights are used for each indicator, it is mainly thanks to the higher scores for indicators 7.1.1 and 7.3.1.
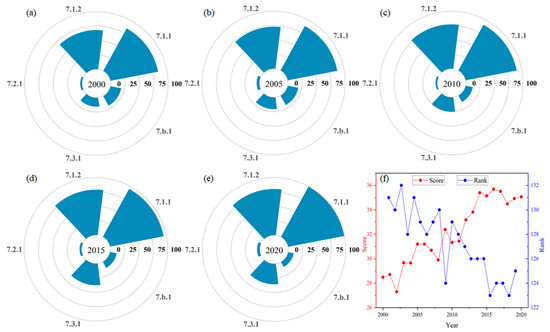
Figure 7.
The scores of SDG7.1.1, SDG7.1.2, SDG7.2.1, SDG7.3.1 and SDG7.b.1 in the ASB, 2000–2020 (a–e), and the scores and ranking of SDG7 in the ASB (f).
Since the ASB is shared by seven countries, the change in the SDG value of each country is transmitted to the SDG value of the ASB. The global ranking order of the seven countries SDG7 is (based on 2020): Tajikistan > Kyrgyzstan > Kazakhstan > Afghanistan > Uzbekistan > Iran > Turkmenistan. At the same time, the SDG7 rankings of seven countries also showed greater differentiation, with Tajikistan ranking in the top 10 in the world and Turkmenistan ranking in the bottom 5%. In terms of rankings, Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan have all seen different degrees of decline in the rankings from 2000–2020, while Afghanistan and Uzbekistan have shown an upward trend, and Turkmenistan’s ranking has hardly changed.
4. Discussion
4.1. Compare the Performance between Different Lighting Indexes and Machine Learning Algorithms
The result shows that the four light indexes and five statistical methods all have different performances. We found that the TNL is a more accurate reflection of the GDP status of the study area than other lighting indices, which is consistent with previous studies. Shi et al. found an R2 of 0.87 for TNL and GDP at the provincial level, which reaches 0.81 at the prefectural level [7]. Zhao et al. found an R2 of 0.89 in South China for TNL and prefecture GDP [54]. The reason may be that TNL calculates GDP directly based on the pixel value of the lighting data, which are more reflective of the real condition of the surface than the lighting index after other secondary calculations. We also find that the two machine learning methods outperform the linear regression method, with XGBoost having the best performance, which is consistent with previous studies [55,56]. The reason may be that the ML methods can describe the non-linear relationship between the independent variables and GDP better than the traditional linear regression methods [57]. In addition, the machine learning method SVR performs the worst, much less than the two linear regression methods, probably due to the small number of independent variables used to characterize GDP in this study, which cannot take advantage of the stronger generalization ability of SVR. More relevant variables can better exploit the simulation performance of machine learning [58]. In addition to the light index and population, factors such as road network density and distance to water sources (especially in arid areas) that affect spatial differences in GDP should be considered, which will be the next research direction.
4.2. Analysis of the Development Trend and Causes of GDP in the ASB
While the total GDP of each region in the ASB is increasing from 2000 to 2020 (Figure 6a), their respective proportions of the total GDP of the ASB show a different trend (Figure A1). The proportion of downstream GDP to the total GDP of the ASB is continuously decreasing, and the midstream region accounts for nearly 2/3 of the total GDP of the ASB, and this proportion has been increasing. Similar trends are observed in the Syr Darya and Amu Darya basins, although the total GDP of both basins is increasing, the share of GDP in the Amu Darya basin is on a decreasing trend, while the Syr Darya is continuously increasing (Figure A1).
Zhang et al. concluded that the ASB GDP increased by USD 137.7 billion in 2015 compared to 2000, based on the analysis of GDP data from various countries [59], and our results show that the ASB GDP increased by USD 109.9 billion in the same time frame. Since it is difficult to count GDP at the basin scale and there is an extreme lack of relevant studies, this study analyzes the development of industries related to GDP. Martius et al. found that agriculture is an important industry affecting GDP within the ASB, which contributed to GDP is around 38% and is gradually increasing, and more than half of all the labor in the basin is employed in agriculture [60,61]. According to Chen et al., the area of cultivated land and construction land in the midstream region showed a rapid increase from 2000 to 2020 [53], which demonstrates that the GDP of the midstream region is continuously increasing. The reasons for the change in GDP in the Syr Darya and Amu Darya basins are similar. Meanwhile, we found a strong negative correlation between the area of water bodies in the ASB and GDP. Wang et al. found that GDP increased with industrial water use in the ASB [62]; Chen et al. suggest that the massive consumption of water bodies in the middle reaches of the ASB is principally to blame for the Aral Sea’s drying up [53]. Combining the results of GDP simulations for midstream and downstream, we believe that GDP growth in arid regions has a strong dependence on water bodies. This is because irrigated agriculture, industrial production, and the service sector are dependent on a stable supply of water. Therefore, in the period 2000–2020, the ASB’s GDP shows a trend of clustering from downstream to midstream and from the Amu Darya River to the Syr Darya River.
4.3. Attribution Analysis of SDG Changes in the ASB and Suggestions for Measures
The ASB SDG7 scores and ranks are jointly influenced by the seven countries in the basin, and the different performances of the seven countries on the same indicators together contribute to the final SDG7 scores. The poor performance of Afghanistan in SDG7.1.1 lowers the score and ranks of the ASB in SDG7.1.1, which is consistent with the study of Rusydiana et al. who found that the energy access level of Afghanistan in 2010 was only 1/3 that of Iran and Turkmenistan, and by 2017 it was only 1/2 that of them, which is still a big gap with other countries [63]. The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) believes that the countries of the ASB have huge amounts of clean energy such as solar (>200,000 MW) and wind (>2000 MW), but the actual application of clean energy is <1 MW [64]. In agreement with the ESCAP study, we discovered that the ASB’s ultimate energy use has a low fraction of renewable energy, and the corresponding indicator 7.2.1 is in the bottom 15% of the global international ranking for 2000–2020. Similarly, Rusydiana found that 100% of Turkmenistan’s electricity comes from fossil fuels [63]. At the same time, Nabiyeva et al. concluded that the high cost and long payback period of new energy in the ASB are the main reasons that hinder the development of new energy in the region [65,66].
Among the four Targets in SDG7, the worst performer is Target7.3, which remains in the bottom 5% of the world, although the ranking for this indicator has risen from 131th in 2000 to 125th in 2020. According to ESCAP, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan are among the top 10 global exporters of coal and natural gas, respectively, and Uzbekistan is also a net exporter of energy [64], perhaps because of the region’s abundant energy resources, which leads to a sloppy approach to energy use and low energy use efficiency. In contrast, Target7.b has a good performance in the global rankings. Hamidov et al. found that the countries of the ASB downstream region are rich in fossil energy sources such as oil and gas, but upstream Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan have scarce fossil energy reserves [67,68]. Their countries’ energy needs are highly dependent on energy supply from hydroelectric power plants, which in 2015 accounted for 95% and 85% of the total electricity generation in both countries, respectively [69], which is the main reason for the better performance of the ASB in this indicator.
Among the indicators of SDG7 in the ASB, 7.2 and 7.3 perform worse than 7.1 and 7. b. According to Cannikin’s law, improving the score and ranking of 7.2 and 7.3 is the key to improving the overall ranking of the ASB. Since the ASB is an inland river basin, it involves the distribution of resources and energy sources. Upstream countries build reservoirs to achieve energy security, which raises concerns about agricultural water security in downstream countries and leads to geopolitical tensions [70]. Although these countries have taken some steps to address the problem, such as the 1998 water-energy exchange agreement between Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan, the lack of an effective regulatory framework for the agreement has made its implementation difficult [70]. The ASB is rich in solar and wind energy resources [64], conducting deep national energy cooperation in the basin, increased investment in renewable energy facilities and energy intensity is key to achieving SDG7 and healthy development in the region.
4.4. Uncertainty and Prospects
In this study, various linear regression and ML methods are used to predict the spatial distribution of GDP using different lighting indices and population data. It is also used as a variable to calculate the development of SDG7 in the ASB. Our study satisfactorily predicts the spatial distribution of GDP and the SDG7 scores and ranks in the ASB. However, there are some uncertainties in this study. First, this study only uses the nighttime lighting index and population as independent variables to predict the distribution of GDP, without considering other variables that affect GDP (e.g., city area, road network distribution, etc.). Second, this study puts the nighttime lighting index of seven countries together with GDP statistics to train the model, which reduces the accuracy of the machine learning model to predict the GDP of the ASB. In future studies, different models will be trained by country to improve the accuracy of GDP projections based on obtaining enough sample data.
Due to the combined effects of the changes in the sources’ spectra and angular ra-diation patterns, the wavelength-dependent atmospheric propagation processes and the differences in the detector spectral sensitivity bands. There may be a discrepancy between the nighttime light values observed from the remote sensing images and the actual light values [71,72,73]. Although chen et al. have aligned both DMSP and VIIRS datasets [20], since the two datasets were acquired at different times and different sensor, there are some errors in the results due to the transmission of errors. Furthermore, this dataset uses statistically correlated control (population census) instead of physically related proxies, which may lead to a GDP raster where low values are pulled up and high values are pulled down.
Since the Aral Sea basin is an inland river basin involving extensive energy-water-food exchange between upstream and downstream, combining SDG7, SDG6 and SDG2 in the Aral Sea basin to analyze the coupling relationship is the next step in our study. In addition, we note that new approaches to quantifying the relationship between SDGs and ecosystem services have recently been used by scholars [74,75], and this is within our scope of consideration.
5. Conclusions
In this study, five fitting models (Lasso, Ridge, SVR, RF and XGBoost) and four nighttime light indices (TNL, I, S and CNLI) were used to integrate nighttime light variables and demographic variables for predicting the spatial distribution of GDP in the ASB. Overall, the machine learning approach outperformed the linear regression approach, with the combination of the XGBoost model and TNL achieving optimal performance. This study found that the ASB achieved rapid GDP growth (+101.73 billion USD, +585.5%) from 2000–2020, but showed an uncoordinated development within the basin. GDP in the ASB showed a tendency to converge from downstream to midstream and from the Amu Darya to the Syr Darya river from 2000–2020. Secondly, this study shows that the GDP of the ASB has a strong negative correlation with the water body area, which indicates that the GDP growth in the region has a strong dependence on the water body. Finally, this study found that although the score (+6.57) and ranking (+9) of SDG7 in the ASB are increasing from 2000 to 2020, they are still far from achieving SDG7. Through detailed analysis of the SDG7 indicators, we believe that deepening energy cooperation among the countries in the basin, increasing investment in renewable energy, and improving energy intensity by optimizing the industrial structure of mainly labor-intensive and light industries are the keys to achieving SDG7.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs14236131/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C. and X.C.; methodology, C.C.; software, C.C. and J.S.; validation, C.C., G.J. and S.W.; formal analysis, J.Q.; investigation, X.X.; resources, J.Q.; data curation, C.C. and J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C.; writing—review and editing, C.C. and Z.H.; visualization, C.C.; supervision, C.C.; project administration, X.C.; funding acquisition, J.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Pan-Third Pole Environment Study for a Green Silk Road (Pan-TPE XDA20060303), Shenzhen International S&T Cooperation Project (GJHZ20190821155805960), CAS Research Center for Ecology and Environment of Central Asia (Grant No. Y934031), National Natural Science Foundation of P.R. China (Grant No. 42230708), Overseas Science and Education Cooperation Center Deployment Project of the Bureau of International Cooperation Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. 131965KYSB20210024) and Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2022A0505050059).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the academic editor and reviewers for their constructive comments which greatly helped us to improve the quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Appendix A
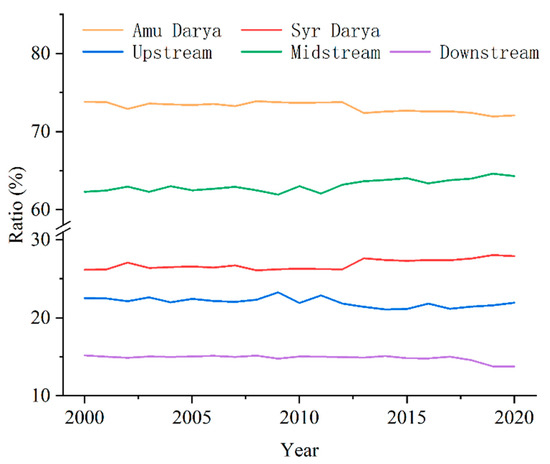
Figure A1.
The proportion of GDP of different basins of the Aral Sea to the total GDP of the ASB.
References
- Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Teksoz, K.; Durand-Delacre, D.; Sachs, J.D. National baselines for the Sustainable Development Goals assessed in the SDG Index and Dashboards. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colglazier, W. Sustainable development agenda: 2030. Science 2015, 349, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iea, I.; Unsd, W. Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Santika, W.G.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Bahri, P.A.; Shafiullah, G.; Rupf, G.V.; Urmee, T. From goals to joules: A quantitative approach of interlinkages between energy and the Sustainable Development Goals. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 50, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chau, S.N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Dietz, T.; Wang, J.; Winkler, J.A.; Fan, F.; Huang, B. Assessing progress towards sustainable development over space and time. Nature 2020, 577, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ziskin, D.; Tuttle, B.T. Creating a global grid of distributed fossil fuel CO2 emissions from nighttime satellite imagery. Energies 2010, 3, 1895–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Boe-Gibson, G. Nighttime lights and county-level economic activity in the United States: 2001 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, R.; McCord, G.C. What can we learn from nighttime lights for small geographies? measurement errors and heterogeneous elasticities. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Tong, Z. Intercalibration Between Night-Time DMSP/OLS Radiance Calibrated Images and NPP/VIIRS Images Using Stable Pixels. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8838–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.M.; Smith, L.C. Advances in using multitemporal night-time lights satellite imagery to detect, estimate, and monitor socioeconomic dynamics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 176–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Duffy, J.P.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Contrasting trends in light pollution across Europe based on satellite observed night time lights. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Zhang, Q.; de Miguel, A.S.; Roman, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.P.; Morley, J.G. Mapping regional economic activity from night-time light satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.S.; Razman, M.R.; Awang, A. The nexus of population, GDP growth, electricity generation, electricity consumption and carbon emissions output in Malaysia. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2020, 10, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, S.; Gutierrez, E. Non-parametric frontier approach to modelling the relationships among population, GDP, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 66, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, M.; Gao, J.; Han, L.; Niu, Z.; Chen, F. Modelling Electricity Consumption in Cambodia Based on Remote Sensing Night-Light Images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, S.; Qian, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, J. An extended time series (2000–2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 889–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porciello, J.; Ivanina, M.; Islam, M.; Einarson, S.; Hirsh, H. Accelerating evidence-informed decision-making for the Sustainable Development Goals using machine learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikhani, A.; Suominen, A. Mapping the sustainable development goals (SDGs) in science, technology and innovation: Application of machine learning in SDG-oriented artefact detection. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 6661–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, J.; Mengersen, K. Statistical Machine Learning Methods and Remote Sensing for Sustainable Development Goals: A Review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadikia, A.; Rajabifard, A.; Kalantari, M. Systematic prioritisation of SDGs: Machine learning approach. World Dev. 2021, 140, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Gomez, N.I.; Diaz-Arevalo, J.L.; Lopez-Jimenez, P.A. Air quality and urban sustainable development: The application of machine learning tools. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canhoto, A.I. Leveraging machine learning in the global fight against money laundering and terrorism financing: An affordances perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 131, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, B.; Iten, M.; Silva, R.G. Monitoring sustainable development by means of earth observation data and machine learning: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliry, S.I.; Avdan, Z.Y.; Do, N.T.; Avdan, U. Assessment of human-induced environmental disaster in the Aral Sea using Landsat satellite images. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriman, L. The future of the Aral Sea lies in transboundary co–operation article reproduced from United Nations Environment Program (Unep) Global Environmental Alert Service (Geas). Environ. Dev. 2014, 10, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Lioubimtseva, E. A multi-scale assessment of human vulnerability to climate change in the Aral Sea Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezlin, N.P.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Li, B.L. Inter-annual variability and interaction of remote-sensed vegetation index and atmospheric precipitation in the Aral Sea region. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 62, 677–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatem, A.J. WorldPop, open data for spatial demography. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, F.R.; Gaughan, A.E.; Linard, C.; Tatem, A.J. Disaggregating census data for population mapping using random forests with remotely-sensed and ancillary data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0107042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xia, B. Dynamics of ecosystem services in response to urbanization across temporal and spatial scales in a mega metropolitan area. Sust. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G.; Pitts, S.C. Multiple Linear Regression. Handbook of Psychology. 2003, pp. 481–507. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471264385.wei0219 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Tranmer, M.; Elliot, M. Multiple linear regression. Cathie Marsh Cent. Census Surv. Res. (CCSR) 2008, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Uyanık, G.K.; Güler, N. A study on multiple linear regression analysis. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 106, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, P. Exploring the superiority of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence data in predicting wheat yield using machine learning and deep learning methods. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, G.C. Ridge regression. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2009, 1, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, Z.; Linder, F. Exploratory data analysis using random forests. In Proceedings of the 73rd Annual MPSA Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–19 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Duan, H.; Cao, Z.; Xue, K.; Qi, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Huang, C.; Song, X. Sentinel-3 OLCI observations of water clarity in large lakes in eastern China: Implications for SDG 6.3. 2 evaluation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smola, A.J.; Scholkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.; Khanna, R. Support Vector Regression. In Efficient Learning Machines, 1st ed.; Spahr, W., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, S.R. Support vector machines for classification and regression. ISIS Tech. Rep. 1998, 14, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Tian, Q.; Niyogi, D. Improving the Forecasting of Winter Wheat Yields in Northern China with Machine Learning-Dynamical Hybrid Subseasonal-to-Seasonal Ensemble Prediction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, NY, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.-J.; Toshiaki, I. The study on urbanization process in China based on DMSP/OLS data: Development of a light index for urbanization level estimation. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 7, 168–175. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.; Chen, J. Application of compound night light index derived from DMSP/OLS data to urbanization analysis in China in the 1990s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, J.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Woelm, F. The sustainable development goals and COVID-19. Sustain. Dev. Rep. 2020, 2020, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, D.; Li, J. DISO: A rethink of Taylor diagram. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, X. Decompositions of Taylor diagram and DISO performance criteria. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5726–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Qian, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Xing, X.; Yimamaidi, D.; Zhakan, Z.; Sun, J.; Wei, S. Spatiotemporal changes, trade-offs, and synergistic relationships in ecosystem services provided by the Aral Sea Basin. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12623. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. GDP spatialization and economic differences in South China based on NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; Mulder, T. Nowcasting New Zealand GDP Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3256578 (accessed on 28 September 2018).
- Yoon, J. Forecasting of real GDP growth using machine learning models: Gradient boosting and random forest approach. Comput. Econ. 2021, 57, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; van Florenstein Mulder, T.; Vehbi, T. Nowcasting GDP using machine-learning algorithms: A real-time assessment. Int. J. Forecast. 2021, 37, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaminos, D.; Salas, M.B.; Fernández-Gámez, M.A. Quantum computing and deep learning methods for GDP growth forecasting. Comput. Econ. 2022, 59, 803–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, H. Changes of vegetation and its forces driving in the Aral Sea Basin of Central Asia. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 269, 01013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmatullaev, S.; Huneau, F.; Kazbekov, J.; Le Coustumer, P.; Jumanov, J.; El Oifi, B.; Motelica-Heino, M.; Hrkal, Z. Groundwater resources use and management in the Amu Darya river basin (Central Asia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martius, C.; Froebrich, J.; Nuppenau, E.-A. Water Resource Management for Improving Environmental Security and Rural Livelihoods in the Irrigated Amu Darya Lowlands. In Facing Global Environmental Change, 1st ed.; Brauch, H.G., Grin, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 749–761. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zan, C.; Ling, Y.; Guo, C. Analysis of the Water Demand-Supply Gap and Scarcity Index in Lower Amu Darya River Basin, Central Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusydiana, A.S.; Laila, N. Energy efficiency in OIC countries: SDG 7 output. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2021, 11, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN ESCAP. Information Brief: Energy Prospective in North and Central Asia. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12870/4144 (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Shadrina, E. Non-hydropower renewable energy in central Asia: Assessment of deployment status and analysis of underlying factors. Energies 2020, 13, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiyeva, K. Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency in Central Asia: Prospects for German Engagement. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/aiymgul_kerimray.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2015).
- Kaliakparova, G.S.; Gridneva, Y.E.; Assanova, S.S. International economic cooperation of Central Asian countries on energy efficiency and use of renewable energy sources. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 2020, 10, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidov, A.; Daedlow, K.; Webber, H.; Hussein, H.; Abdurahmanov, I.; Dolidudko, A.; Seerat, A.Y.; Solieva, U.; Woldeyohanes, T.; Helming, K. Operationalizing water-energy-food nexus research for sustainable development in social-ecological systems: An interdisciplinary learning case in Central Asia. Ecol. Soc. 2022, 27. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358410567 (accessed on 20 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Palicka, O. Central Asia: Conflict Potential in the Amu Darya & Syr Darya River Basins. Available online: https://www.internationalaffairshouse.org/central-asia-conflict-potential-in-the-amu-darya-syr-darya-river-basins/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Abdulloev, A. Water, Energy, and Food Nexus in the Amu-Darya River Basin: Analysis of Water Demand and Supply Management Infrastructure Development at Transboundary Level. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bara, S.; Rigueiro, L.; Lima, R.C. Monitoring transition: Expected night sky brightness trends in different photometric bands. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 239, 106644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, A.S.D.; Bennie, J.; Rosenfeld, E.; Dzurjak, S.; Gaston, K.J. Environmental risks from artificial nighttime lighting widespread and increasing across Europe. Sci Adv. 2022, 8, eabl6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Ghosh, T.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Sparks, T.; Bazilian, M.; Sutton, P.C.; Houngbedji, K.; Goldblatt, R. Fifty years of nightly global low-light imaging satellite observations. Front. Remote Sens. 2022, 79, 919937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Peng, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. Responses of spatial relationships between ecosystem services and the Sustainable Development Goals to urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhan, J.; Wang, C.; Twumasi-Ankrah, M.J. Coupling coordination analysis and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between sustainable development and ecosystem services in Shanxi Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).