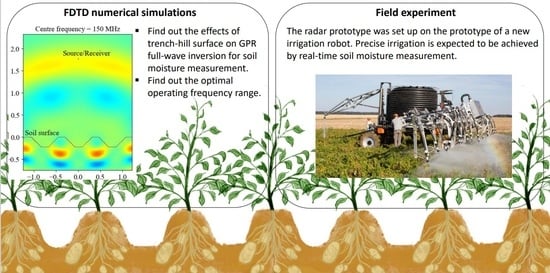
Ground-Penetrating Radar Full-Wave Inversion for Soil Moisture Mapping in Trench-Hill Potato Fields for Precise Irrigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Full-Wave Inversion to Retrieve Soil Moisture
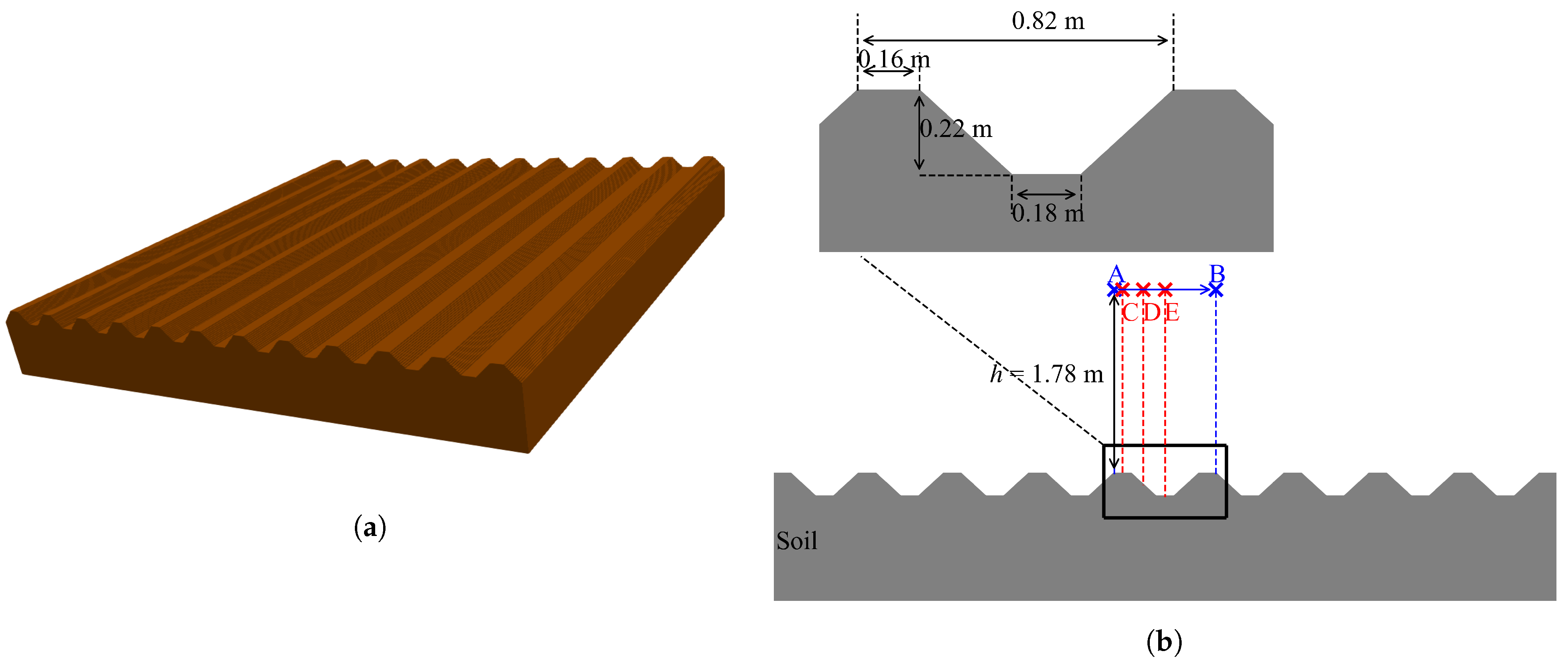
2.2. FDTD Numerical Simulation and Calibration
3. Numerical Experiments
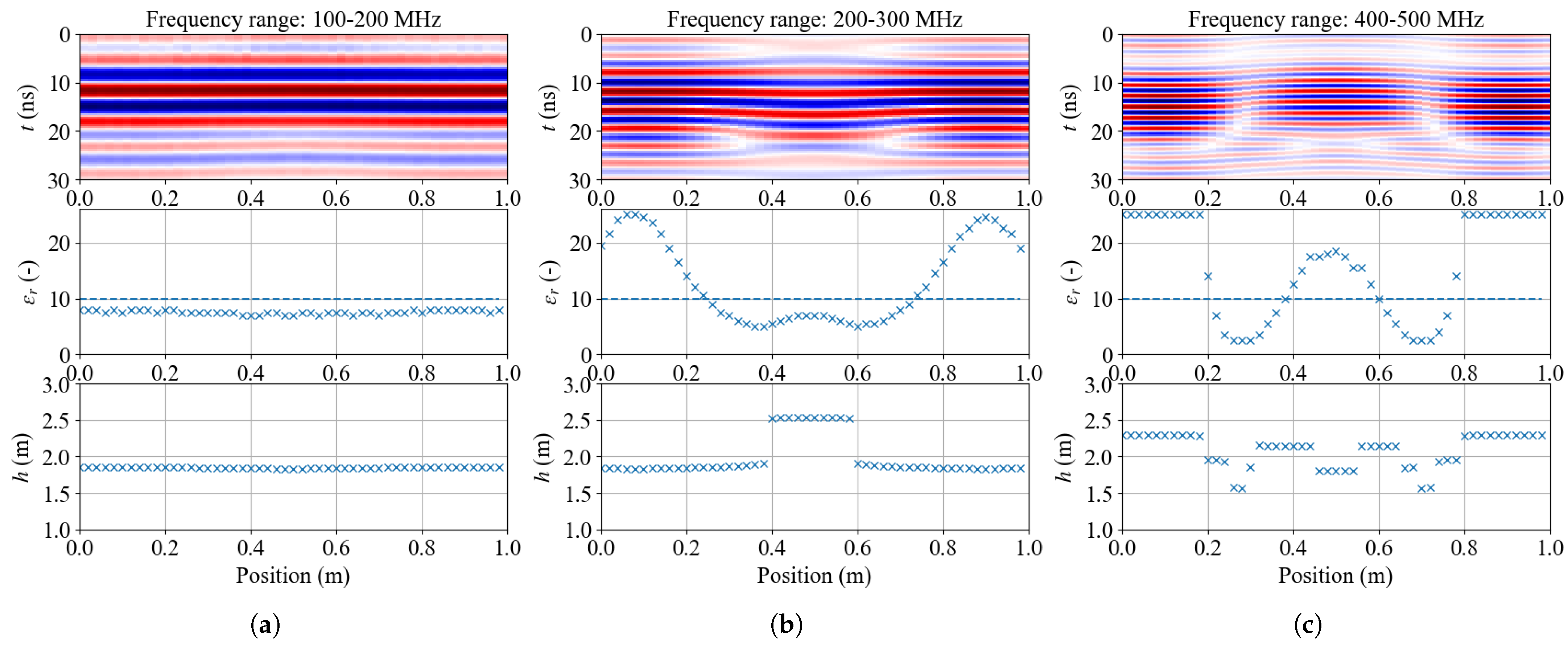
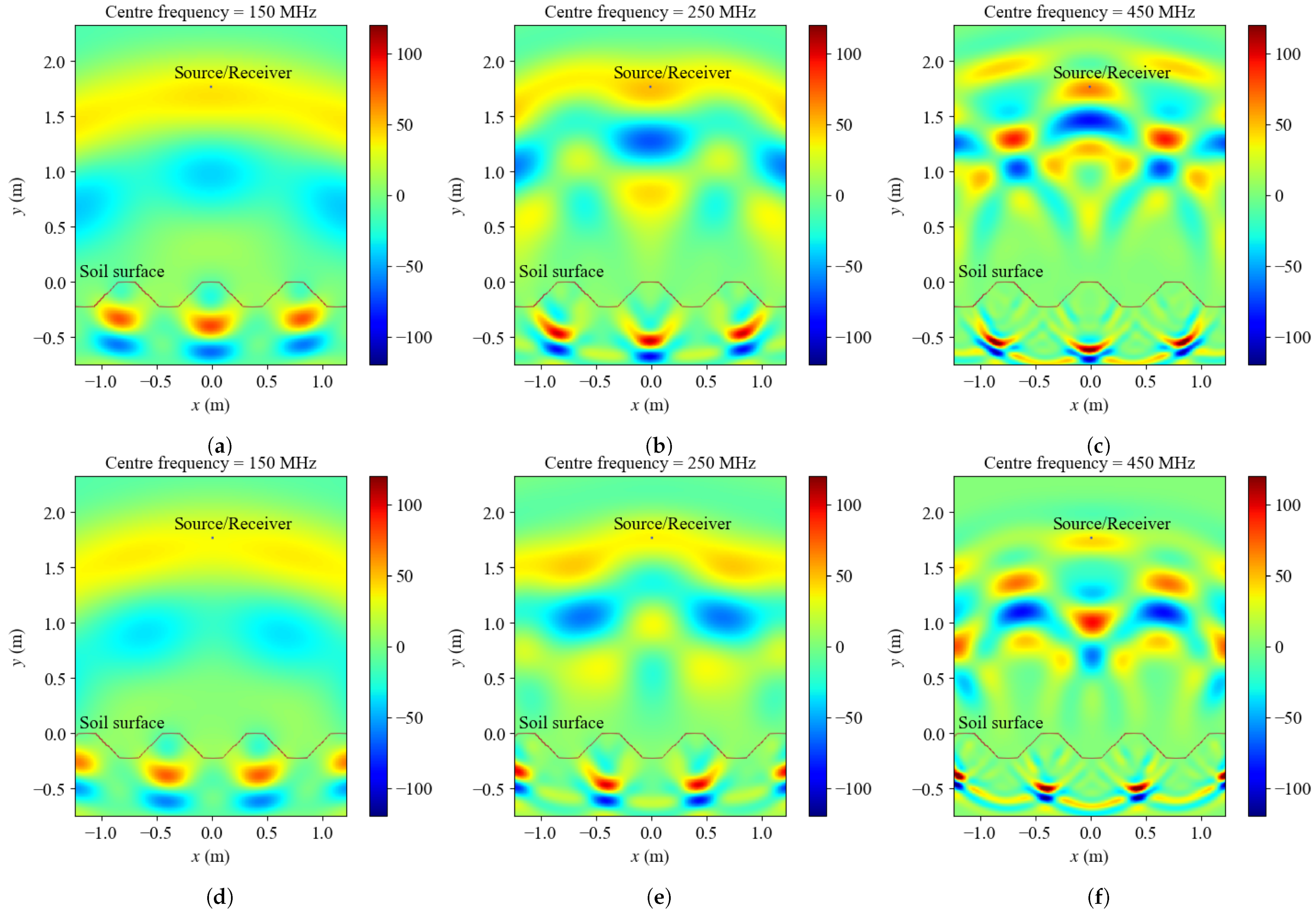
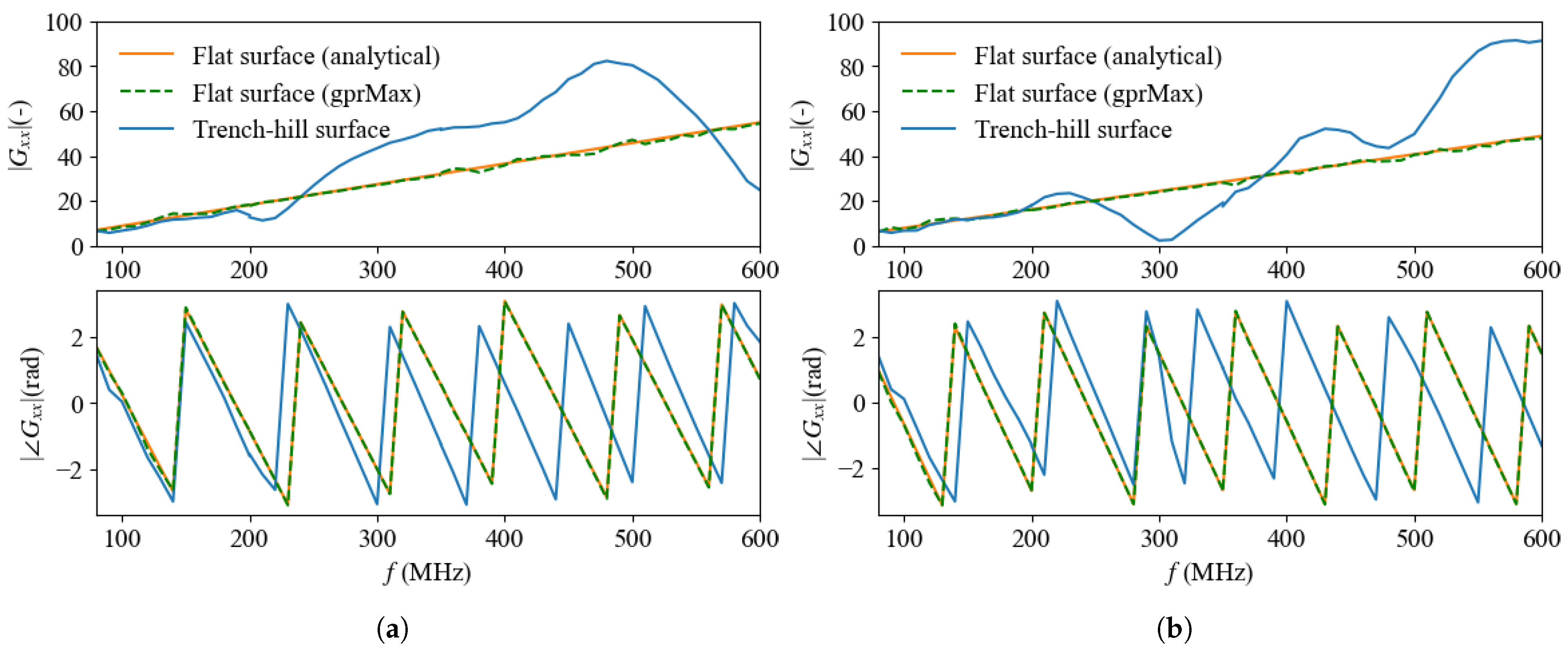
3.1. Configuration 1: 3 Sources with Different Centre Frequencies
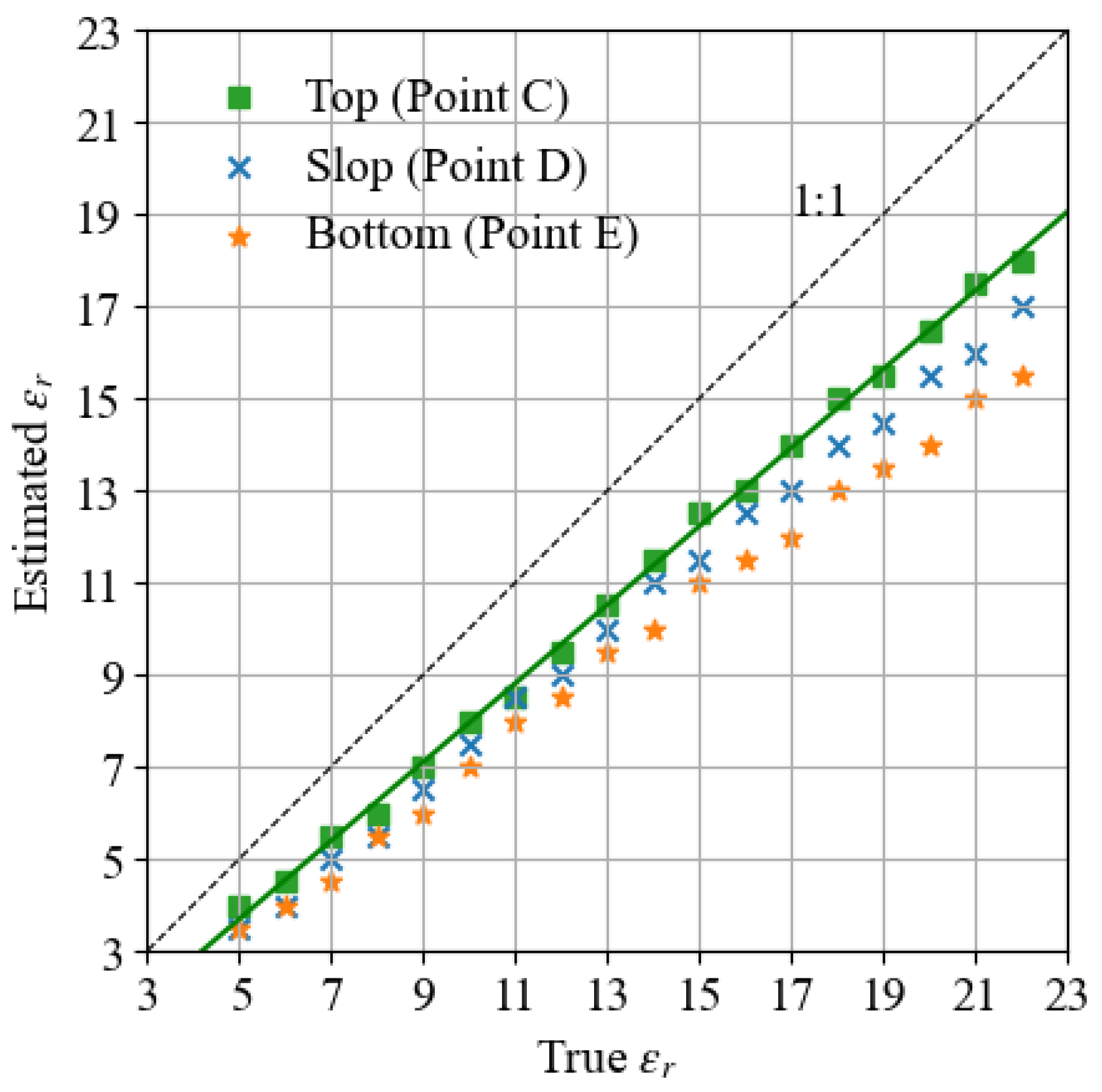
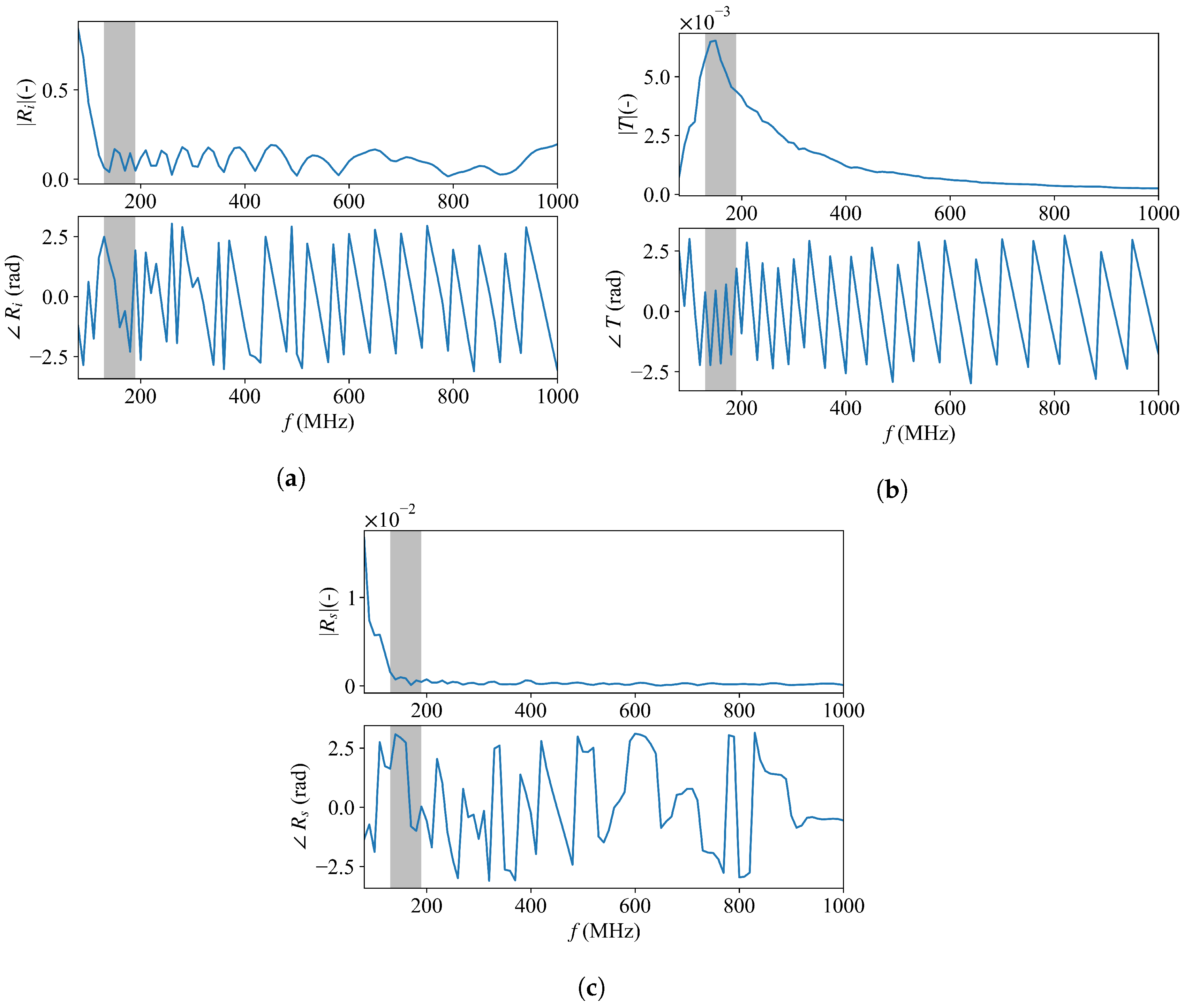
3.2. Configuration 2: 150 MHz Source over the Soil Surface with Different Positions and Soil Properties
4. Field Experiments
4.1. Ground-Penetrating Radar
4.2. Time–Domain Reflectometry
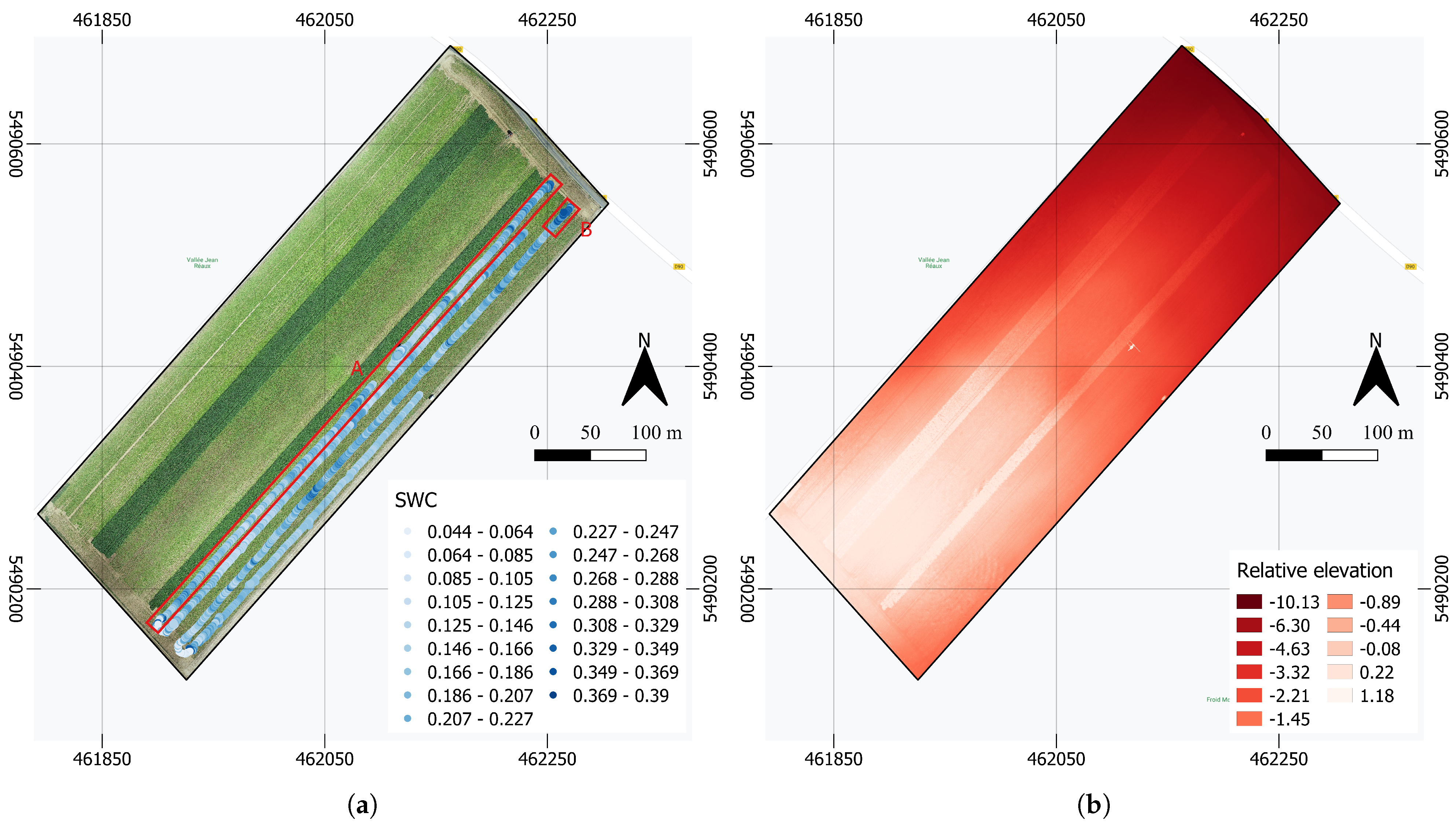
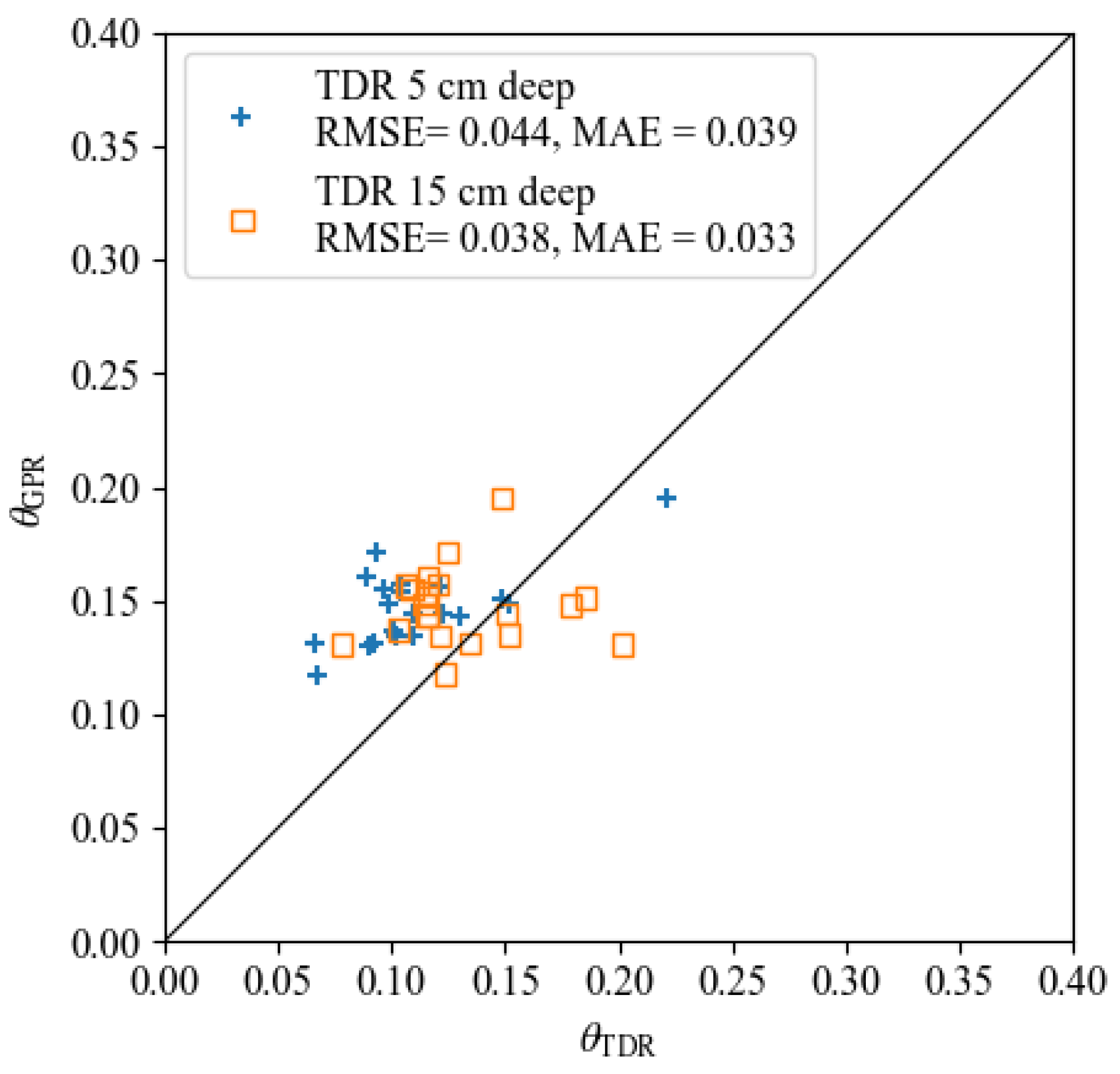
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escobar, V.; Vander Zaag, P. Field performance of potato (Solanum spp.) cuttings in the warm tropics: Influence of planting system, hilling, density and pruning. Am. Potato J. 1988, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.; Kelling, K.; Lowery, B.; Arriaga, F.; Speth, P. Hill Shape Influences on Potato Yield, Quality, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Am. J. Potato Res. 2013, 90, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelling, K.A.; Arriaga, F.J.; Lowery, B.; Jordan, M.O.; Speth, P.E. Use of hill shape with various nitrogen timing splits to improve fertilizer use efficiency. Am. J. Potato Res. 2015, 92, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G. A review of the soil-moisture relationship in potatoes. Am. Potato J. 1969, 46, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Mauromicale, G. Tuber yield and irrigation water productivity in early potatoes as affected by irrigation regime. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeian, E.; Sadeghi, M.; Jones, S.B.; Montzka, C.; Vereecken, H.; Tuller, M. Ground, proximal, and satellite remote sensing of soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 530–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanzy, A.; Tarussov, A.; Bonn, F.; Judge, A. Soil Water Content Determination Using a Digital Ground-Penetrating Radar. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.A.; Sperl, C.; Bouten, W.; Verstraten, J.M. Soil water content measurements at different scales: Accuracy of time domain reflectometry and ground-penetrating radar. J. Hydrol. 2001, 245, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.A.; Snepvangers, J.J.J.C.; Bouten, W.; Heuvelink, G.B.M. Mapping spatial variation in surface soil water content: Comparison of ground-penetrating radar and time domain reflectometry. J. Hydrol. 2002, 269, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.A.; Hubbard, S.S.; Redman, J.D.; Annan, A.P. Measuring Soil Water Content with Ground Penetrating Radar: A Review. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzsche, A.; Jonard, F.; Looms, M.; van der Kruk, J.; Huisman, J. Measuring Soil Water Content with Ground Penetrating Radar: A Decade of Progress. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 180052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajícová, K.; Chuman, T. Application of ground penetrating radar methods in soil studies: A review. Geoderma 2019, 343, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, Q.; Cao, X.; Chen, X. Measurement of soil water content using ground-penetrating radar: A review of current methods. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Winship, P.; Middleton, R.; Pokar, M.; West, J. High-resolution characterization of vadose zone dynamics using cross-borehole radar. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2639–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buursink, M.; Clement, W.; Knoll, M. Use of Vertical-Radar Profiling to Estimate Porosity at Two New England Sites and Comparison with Neutron Log Porosity. In Proceedings of the 15th EEGS Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–14 February 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galagedara, L.; Parkin, G.W.; Redman, J.D.; von Bertoldi, A.; Endres, A. Field studies of the GPR ground wave method for estimating soil water content during irrigation and drainage. J. Hydrol. 2005, 301, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinelli, E.; Vannaroni, G.; Pasquo, B.; Mattei, E.; Di Matteo, A.; De Santis, A.; Annan, P. Correlation between near-surface electromagnetic soil parameters and early-time GPR signals: An experimental study. Geophysics 2007, 72, A25–A28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteo, A.D.; Pettinelli, E.; Slob, E. Early-Time GPR Signal Attributes to Estimate Soil Dielectric Permittivity: A Theoretical Study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinelli, E.; Di Matteo, A.; Beaubien, S.E.; Mattei, E.; Lauro, S.E.; Galli, A.; Vannaroni, G. A controlled experiment to investigate the correlation between early-time signal attributes of ground-coupled radar and soil dielectric properties. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 101, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeo, J.; Van Dam, R.; Slater, L. Early-Time GPR: A Method to Monitor Spatial Variations in Soil Water Content during Irrigation in Clay Soils. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comite, D.; Galli, A.; Lauro, S.E.; Mattei, E.; Pettinelli, E. Analysis of GPR Early-Time Signal Features for the Evaluation of Soil Permittivity Through Numerical and Experimental Surveys. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, J.R.; Maurer, H.; Green, A.G.; Holliger, K. Full-Waveform Inversion of Crosshole Radar Data Based on 2D Finite-Difference Time-Domain Solutions of Maxwell’s Equations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2807–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meles, G.A.; Kruk, J.V.d.; Greenhalgh, S.A.; Ernst, J.R.; Maurer, H.; Green, A.G. A New Vector Waveform Inversion Algorithm for Simultaneous Updating of Conductivity and Permittivity Parameters From Combination Crosshole/Borehole-to-Surface GPR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3391–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.; Van Der Kruk, J.; Bikowski, J.; Vereecken, H. Quantitative conductivity and permittivity estimation using full-waveform inversion of on-ground GPR data. Geophysics 2012, 77, H79–H91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Slob, E.C.; Van Bosch, I.D.; Stockbroeckx, B.; Vanclooster, M. Modeling of ground-penetrating radar for accurate characterization of subsurface electric properties. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2004, 42, 2555–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; André, F. Full-wave modeling of near-field radar data for planar layered media reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2295–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Weihermüller, L.; Huisman, J.A.; Vereecken, H.; Vanclooster, M.; Slob, E.C. Analysis of air-launched ground-penetrating radar techniques to measure the soil surface water content. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Slob, E.; Chavarro, D.; Lubczynski, M.; Vereecken, H. Measuring soil surface water content in irrigated areas of southern Tunisia using full-waveform inversion of proximal GPR data. Surf. Geophys. 2008, 6, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, F.; Weihermuller, L.; Jadoon, K.Z.; Schwank, M.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Mapping Field-Scale Soil Moisture With L-Band Radiometer and Ground-Penetrating Radar Over Bare Soil. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.P.; Bogaert, P.; Wiaux, F.; Vanclooster, M.; Lambot, S. High-resolution space–time quantification of soil moisture along a hillslope using joint analysis of ground penetrating radar and frequency domain reflectometry data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, J.; Bogaert, P.; Vanclooster, M.; Lambot, S. Validation of ground penetrating radar full-waveform inversion for field scale soil moisture mapping. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zajc, M.; Jacquemin, E.; Clément, M.; De Coster, A.; Lambot, S. A new drone-borne GPR for soil moisture mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, S.; Yamamoto, G. Light Scattering by a Spheroidal Particle. Appl. Opt. 1975, 14, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taflove, A.; Brodwin, M. Numerical Solution of Steady-State Electromagnetic Scattering Problems Using the Time-Dependent Maxwell’s Equations. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1975, 23, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, T. General Aspects of Solving Helmholtz’s Equation Underlying Eigenvalue and Scattering Problems in Electromagnetic Wave Theory. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 1999, 13, 867–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urusovskii, I.; Wood, J. Diffraction of a plane wave by a rough surface. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1992, 38, 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Charnotskii, M.I. Wave scattering by periodic surface at low grazing angles: Single grazing mode. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2000, 26, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Craeye, C.; Sobieski, P.; Bliven, L. Scattering by artificial wind and rain roughened water surfaces at oblique incidences. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2241–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craeye, C.; Sobieski, P.W.; Bliven, L.F.; Guissard, A. Ring-waves generated by water drops impacting on water surfaces at rest. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1999, 24, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lemaire, D.; Bliven, L.; Craeye, C.; Sobieski, P. Drop size effects on rain-generated ring-waves with a view to remote sensing applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.; Li, Z.; Chen, K. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, W. Quantitative roughness characterization of geological surfaces and implications for radar signature analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2397–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.; Toan, T.L.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Manninen, T.; Borgeaud, M. On the characterization of agricultural soil roughness for radar remote sensing studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambot, S.; Antoine, M.; Vanclooster, M.; Slob, E.C. Effect of soil roughness on the inversion of off-ground monostatic GPR signal for noninvasive quantification of soil properties. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, A.; Diamanti, N. Numerical modeling of Ground Penetrating Radar response from rough subsurface interfaces. Surf. Geophys. 2008, 6, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, F.; WeihermüLler, L.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Accounting for soil surface roughness in the inversion of ultrawideband off-ground GPR signal for soil moisture retrieval. Geophysics 2012, 77, H1–H7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonard, F.; André, F.; Pinel, N.; Warren, C.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Modeling of multilayered media Green’s functions with rough interfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7671–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, A. Modelling ground penetrating radar by GprMax. Constr. Build. Mater. 2005, 19, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, C.; Giannopoulos, A.; Giannakis, I. gprMax: Open source software to simulate electromagnetic wave propagation for Ground Penetrating Radar. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2016, 209, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, W.C. Waves and Fields in Inhomogeneous Media; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Slob, E.; Fokkema, J. Coupling effects of two electric dipoles on an interface. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, K. Numerical solution of initial boundary value problems involving maxwell’s equations in isotropic media. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1966, 14, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, K.A. Timing of herbicide application and potato hilling. Am. Potato J. 1992, 69, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.; Rees, H. Effects of potato hilling on water runoff and soil erosion under simulated rainfall. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 74, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, S.; Jacques, D.; Lambot, S. A Layered Vegetation Model for GPR Full-Wave Inversion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Jonard, F.; Jonard, M.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Accounting for Surface Roughness Scattering in the Characterization of Forest Litter with Ground-Penetrating Radar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Lambot, S. Analysis of Low-Frequency Drone-Borne GPR for Root-Zone Soil Electrical Conductivity Characterization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Lambot, S. Effect of Radar Incident Angle on Full-Wave Inversion for the Retrieval of Medium Surface Permittivity for Drone-Borne Applications. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, K.; Desesquelles, H.; Cockenpot, R.; Guyard, L.; Cuisiniez, V.; Lambot, S. Ground-Penetrating Radar Full-Wave Inversion for Soil Moisture Mapping in Trench-Hill Potato Fields for Precise Irrigation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236046
Wu K, Desesquelles H, Cockenpot R, Guyard L, Cuisiniez V, Lambot S. Ground-Penetrating Radar Full-Wave Inversion for Soil Moisture Mapping in Trench-Hill Potato Fields for Precise Irrigation. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236046
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Kaijun, Henri Desesquelles, Rodolphe Cockenpot, Léon Guyard, Victor Cuisiniez, and Sébastien Lambot. 2022. "Ground-Penetrating Radar Full-Wave Inversion for Soil Moisture Mapping in Trench-Hill Potato Fields for Precise Irrigation" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236046
APA StyleWu, K., Desesquelles, H., Cockenpot, R., Guyard, L., Cuisiniez, V., & Lambot, S. (2022). Ground-Penetrating Radar Full-Wave Inversion for Soil Moisture Mapping in Trench-Hill Potato Fields for Precise Irrigation. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6046. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236046