Abstract
Earth observation (EO) data can provide large scale, high-resolution, and transferable methodologies to quantify the sprawl and vertical development of cities and are required to inform disaster risk reduction strategies for current and future populations. We synthesize the evolution of Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, which experiences high seismic hazard, and derive new datasets relevant for seismic risk modeling. First, the urban sprawl of Bishkek (1979–2021) was quantified using built-up area land cover classifications. Second, a change detection methodology was applied to a declassified KeyHole Hexagon (KH-9) and Sentinel-2 satellite image to detect areas of redevelopment within Bishkek. Finally, vertical development was quantified using multi-temporal high-resolution stereo and tri-stereo satellite imagery, which were used in a deep learning workflow to extract buildings footprints and assign building heights. Our results revealed urban growth of 139 km2 (92%) and redevelopment of ~26% (59 km2) of the city (1979–2021). The trends of urban growth were not reflected in all the open access global settlement footprint products that were evaluated. Building polygons that were extracted using a deep learning workflow applied to high-resolution tri-stereo (Pleiades) satellite imagery were most accurate (F1 score = 0.70) compared to stereo (WorldView-2) imagery (F1 score = 0.61). Similarly, building heights extracted using a Pleiades-derived digital elevation model were most comparable to independent measurements obtained using ICESat-2 altimetry data and field-measurements (normalized absolute median deviation < 1 m). Across different areas of the city, our analysis suggested rates of building growth in the region of 2000–10,700 buildings per year, which when combined with a trend of urban growth towards active faults highlights the importance of up-to-date building stock exposure data in areas of seismic hazard. Deep learning methodologies applied to high-resolution imagery are a valuable monitoring tool for building stock, especially where country-level or open-source datasets are lacking or incomplete.
1. Introduction
By 2050, an estimated 68% of the world’s population will reside in urban areas [1]. Urbanization concentrates exposure to disaster risk and increases socioeconomic inequalities due to unregulated sprawling development into hazardous areas [2,3,4]. These inequalities are further perpetuated by a lack of data relating to the exposure and vulnerability to disaster events and reported losses following disasters in lower-income countries [5], which also impedes progress towards United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [6]. Earth Observation (EO) satellite capabilities increasingly support progress towards sustainable development using programs of global data collection, such as Landsat, that span over 50 years [7]. EO data are now embedded in the processes of understanding natural hazards and their interactions [8], measuring and monitoring urban growth and intersection with hazards [9], informing disaster risk reduction strategies [10,11], and responding to disaster events [12,13].
Disaster risk reduction strategies require an understanding of the exposure and vulnerability of people and assets to hazards [14]. For example, details of building structure including age, construction method and material, and height, are key information for modeling disaster risk in seismically active regions [4,15,16,17]. The automatic mapping of 2D urban growth using satellite data and image classification techniques is now widespread, e.g., [18,19]; however, retrieving the building-level 3D structure of a city generally requires expensive aerial imagery or light detection and ranging (LiDAR) surveys [20,21] or high-resolution digital elevation models (DEMs) [22]. Recently, approaches that can derive aggregated building height maps over 30–90 m grids have been developed, though they are best suited to buildings less than ~20–30 m tall [23,24]. Other approaches use shadow-based height estimation; however, this does not work well in densely urbanized areas with overlapping shadows [25,26]. Nonetheless, these approaches represent a valuable mechanism to drive the transition towards 4D city mapping, where timely updates could be envisaged.
Open-source mapping datasets such as OpenStreetMap are a valuable source of mapped building footprints for use in exposure datasets or post-disaster humanitarian mapping [27]; however, data are of varying completeness globally with a mapping bias towards regions of high Human Development Index [28]. Deep learning methodologies are capable of classifying building rooftop-derived footprints in high-resolution satellite imagery [29,30], and studies have shown that building heights can be retrieved (average errors ~4–>10 m) from photogrammetrically constructed digital elevation models [16,31]. However, application of these methods is still limited both geographically and in the spatial and temporal extent of specific case studies.
Cities such as Bishkek (Kyrgyzstan) and Almaty (Kazakhstan) in the Tien Shan Mountain range, Central Asia, are exposed to high seismic risk [16,32,33,34] (Figure 1a). A future earthquake in Bishkek could lead to thousands of fatalities and require hundreds of millions of dollars in rebuilding costs [33,35]. Bishkek is expanding horizontally towards active faults and vertically through high-rise developments. Therefore, modeling the impact of future earthquakes on cities near active faults requires up-to-date exposure datasets. One necessary component is details of building structures, including age, height, construction material, and resident population [15,35,36].
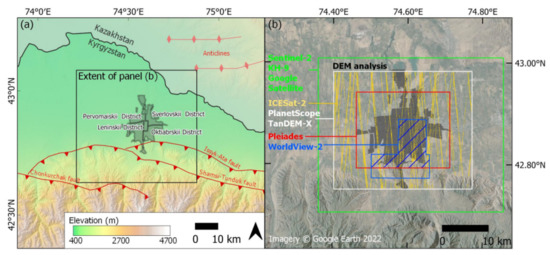
Figure 1.
(a) Location of Bishkek in relation to adjacent active faults overlaid on hillshaded digital elevation model. Faults are from the Kyrgyz Institute of Seismology digitized by the Active Tectonics, Quantitative Structural Geology and Geomorphology Research Group [37]. Anticlines are from Styron [38]. (b) Analysis extents capturing Bishkek’s designated districts (gray shading) based on the spatial availability of each data source shown by colored polygons (colored lines for ICESat-2). The hashed blue polygon shows the intersecting WorldView-2 and Pleiades extents.
In this study, we develop methodologies to quantify urban evolution using satellite data from 1979–2021. Our objectives are to: (1) quantify urban growth and redevelopment 1979–2021 by developing a methodology to classify built-up area in a 1979 declassified KH-9 Hexagon satellite image; (2) use a deep learning methodology and sub-meter resolution satellite imagery to extract and accurately assess building footprints for three time periods (2013, 2019, and 2021); (3) accurately assess stereo and tri-stereo-derived DSMs and use them to assign building heights; and (4) evaluate the methodological capabilities and limitations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Urban Growth
2.1.1. KH-9 Classification
KH-9 satellite imagery was collected by United States reconnaissance programs (1973–1980) at 6–9 m ground resolution and has been used in a range of applications [39,40,41]. A pair of KH-9 satellite images (21 June 1979) (Table S1) were downloaded from USGS EarthExplorer [42]. To our knowledge, no studies have applied image classification techniques to semi-automatically extract built-up areas from KH-9 imagery.
To classify built-up areas in a 21 June 1979 KH-9 image (Figure 2a), the imagery was first used to generate a digital surface model (DSM) in Agisoft Metashape v1.7.2 [43] with predefined camera parameters obtained by Dehecq [41] and 11 ground control points obtained from Google Earth on static features. The DSM was used to orthorectify and georeference the imagery, which was output at a resolution of 4 m. The image was classified into built-up and non-built-up areas using an object-based image analysis (OBIA) segmentation workflow. First, we segmented the orthorectified image using Orfeo ToolBox’s large-scale mean shift segmentation algorithm [44]. A spatial radius of 5 pixels, a spectral range radius of 20, and a minimum segment size of 50 pixels [44] were used, following manual inspection to capture built-up areas and minimize segmented polygons in homogenous agricultural fields. Second, WhiteBox Tools v.1.4.0 Patch Shape Tools was used to add spatial variables of polygon ‘compactness ratio’, ‘linearity index’, and ‘shape complexity index’ [45,46]. Third, 200 built-up and 200 non-built-up polygons were digitized as training data (Figure S1), which were used to extract segmented polygons corresponding to built-up (n = 1859), and non-built-up areas (n = 682). Fourth, SAGA’s parallelepiped supervised classification was used to classify the segmented polygons into built-up or non-built-up classes [47]. Finally, the classification was resampled to 10 m to match the Sentinel-2 classification and applied a slope filter of 5 degrees to remove misclassification on steep slopes using the 30 m Copernicus DSM resampled to 100 m. Isolated patches less than 50 pixels (5000 m2) were also reclassified into the dominant surrounding classification.
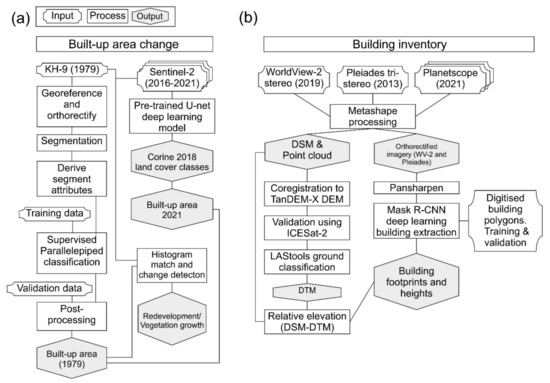
Figure 2.
Study methodology. (a) Built-up area classification and change detection. (b) Extraction of building footprints and heights using high-resolution satellite imagery.
2.1.2. Sentinel-2 Classification
Cloud-free Sentinel-2 imagery from 10 June 2016, 8 June 2017, 23 June 2018, 13 June 2019, 14 June 2020, and 27 June 2021 were classified into Corine 2018 land-cover classes using a pretrained U-net deep learning model with a reported overall accuracy of 82% [48] (Figure 2b). The model used all 13 Sentinel-2 bands at 10 m resolution (resampled where required) [48]. The ‘Urban fabric’ and ‘Industrial commercial and transport units’ classes were merged to form a ‘built-up’ area class.
2.1.3. Other Land-Cover Datasets
Three global classifications of built-up area were evaluated alongside our KH9 and Sentinel-2 classifications (Figure S1). (1) The global human settlement (GHS) classification (30 m resolution, R2018A) classified built-up areas over four epochs (1975, 1975–1990, 1990–2000, and 2000–2014) using Landsat data [49,50]. (2) The world settlement footprint (WSF) (10 m resolution) was available for 2015 and 2019. The 2015 dataset was derived using Sentinel-1 and Landsat data [18], whereas the 2019 dataset was derived using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data [51]. (3) The WSF evolution (WSF-Evo) dataset was derived using Landsat data at 30 m resolution and provides an annual built-up area classification (1985–2015) [51].
2.1.4. Urban Redevelopment
Redevelopment of existing built-up areas in Bishkek was evaluated using the 1979 KH-9 and 2021 Sentinel-2 data for areas falling within the initial 1979 built-up area classification (Figure 2b). Therefore, capturing buildings present in the 1979 built-up classification that were demolished, and new ones which were built, was visible as an increase in the spectral reflectance of the area. Whitebox Tools v.1.4.0 Histogram Match tool was used to match Sentinel-2 band 3 (green) to the single-band KH-9 data and normalized the outputs in the range 0–1. The KH-9 image was downsampled to match the 10 m resolution of Sentinel-2. The normalized KH-9 data were subtracted from the normalized Sentinel-2 data and extracted the mean digital number (DN) change in 20 polygons, which were digitized in areas where the land cover remained consistent 1979–2021 based on visual inspection (Figure S2a). We used this analysis to conservatively mask changes between values of −0.1–0.1 as ‘unchanged’. The remaining negative values (−1–−0.1) represent a DN decrease, which was associated with vegetation growth. These were reclassified into a ‘vegetated’ class. Conversely, positive values (0.1–1) represent a DN increase. These were associated with built-up area redevelopment and were reclassified into a ‘built-up’ class. A low DN could be associated with low-reflectivity buildings with tiled roofs, e.g., [52], rather than vegetation. Therefore, the validity of these assumptions was tested by extracting the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) values for the two classes using 2021 Sentinel-2 imagery:
2.1.5. Land-Cover Accuracy Assessment
KH-9 and Sentinel-2 built-up area classifications were assessed for accuracy using a random distribution of points within built-up (n = 250) and non-built-up (n = 250) classes for each classification (Figure S2). Error matrixes using the validation points were used to report classification confidence intervals [53,54]. We applied an additional constraint to the KH-9 classification to mask the classification to built-up areas classified in 2021. Our urban redevelopment analysis (Section 2.1.4) was assessed for accuracy at 10 m spatial resolution using 250 random points in each class: ‘unchanged’, ‘vegetated’, and ‘built-up’. Google Satellite Basemap (extracted in 2021 with images dated 2021 (Table S1)) was used as a reference dataset alongside the KH-9 and Sentinel-2 satellite imagery.
2.2. Digital Elevation Model Generation and Analysis
High-resolution satellite imagery from Pleiades and WorldView-2 satellites were used to produce DSMs and orthorectified satellite images for building footprint and height extraction (Figure 2b). We used a stereo WorldView-2 acquisition from 10 October 2019 (0.5 m panchromatic, 2 m multi-spectral) and a tri-stereo Pleiades acquisition from 2 November 2013 (0.7 m panchromatic, 2.5 m multi-spectral) (Figure 1b) delivered with rational polynomial coefficients (RPCs) (Table S1). Agisoft Metashape v1.8.0 [55] was used to process the imagery to derive DSMs and orthorectified imagery, e.g., [56]. (1) The panchromatic imagery was aligned in one chunk to produce a sparse point cloud; (2) outliers were removed from the sparse cloud using Metashape’s gradual selection tools to reduce the root mean square reprojection error to ≤0.5 pix; (3) the panchromatic imagery was used to derive a dense point cloud using ‘high’ quality settings and no depth filtering, which was used to interpolate a 1.5 m resolution DSM; (4) this DSM was used to orthorectify both the most nadir panchromatic and multi-spectral satellite images. The Pleiades and WorldView-2 multi-spectral imagery was pansharpened to 0.5 m resolution using the Gram–Schmidt algorithm and the respective sensor model and band weights (Pleiades or WorldView-2) in ArcGIS Pro 2.8 [57].
Two additional DSMs were derived using 3.7 m resolution PlanetScope (PS) imagery [58] to determine whether these DSMs were able to resolve buildings in Bishkek. We used the red, green, and blue bands from 43 level 1B images from the PSB.SD instruments onboard the SuperDove satellite constellation acquired March to April 2021 (Table S1) and followed the same processing workflow described in Metashape, with an additional filter applied to the dense point cloud to minimize noise. The PlanetScope imagery has a near-nadir viewing geometry; therefore, many overlapping images are required to generate a DSM [59]. We removed dense cloud points that were present in less than three depth maps to create DSM ‘v1′, and points present in less than six depth maps to create a DSM ‘v2′, both output at 9 m resolution.
All DSMs were coregistered to the 12 m resolution TanDEM-X DSM [60] following the x, y, z shift correction of Nuth and Kääb [61]. Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite (ICESat-2) altimetry data were used to validate the vertical accuracy of the DSMs (Figure 1b). We downloaded all ATL03 ICESat-2 data [62,63] over Bishkek up to 8 April 2021 using OpenAltimetry [64]. Data spanned 14 November 2018 to 9 November 2020 and included tracks 0272, 0310, 0714, 0752, 1156, 1194. Only ‘high’ confidence photons were used, which were gridded at 5 m resolution and removed cells with fewer than two photons, a range greater than 1 m, and a vertical difference from the TanDEM-X of >80 m to avoid removing points on tall buildings. Accuracy statistics were reported over slopes <10°, e.g., [65], which captures our city area of interest (AOI), and outliers ≥20 m were removed (≥50 m for PlanetScope). Error metrics included root mean square error (RMSE) and normalized absolute median deviation (NMAD), of which the latter is considered more resilient to outliers [66].
2.3. Extracted Building Characteristics and Accuracy Assessment
2.3.1. Building Polygons
Building footprints were extracted from the orthorectified pansharpened WorldView-2 and Pleiades satellite imagery using a Deep Learning workflow applied in ArcGIS Pro 2.8. We also applied the workflow to a ~0.5 m resolution Google Satellite basemap. Here, we masked building detections from the Google Satellite Basemap classifications to the Sentinel-2 2021 built-up area classification. For each dataset, the deep learning workflow involved manually digitizing building polygons within randomly selected 200 m square cells covering built-up areas. All buildings intersecting each cell were digitized, with a total of ~2000 building polygons used for each dataset. Additionally, we digitized a further 1000 validation buildings for each dataset following the same random cell selection method. Training data were exported with a tile size of 400 × 400 pixels and a stride of 200 pixels. A Region-based Convolutional Neural Network Mask R-CNN deep learning model was trained to detect buildings in the high-resolution satellite imagery. Mask R-CNN is an instance segmentation model that provides a segmentation mask and output polygon for each instance of a building detection. Mask R-CNN was chosen owing to its efficient building extraction capabilities applied to high-resolution satellite imagery [30,67,68]. We trained the Mask R-CNN to 20 epochs using an unfrozen ResNet-50 backbone model and 20% of the data used for validation. Buildings were detected from the satellite imagery using the trained Mask R-CNN models with 100-pixel padding. We first ran the deep learning model using the initial 2000 buildings for each dataset and subsequently digitized a further 500 buildings through manual inspection of buildings that were not detected by the first run. Then, 2500 buildings were used to train the final deep learning model for each dataset. Buildings less than 5 m2 were removed. We report commonly used accuracy assessment metrics for binary classification including precision, recall, and the F1 score for buildings with an intersection over union (IoU) of ≥0.5:
For comparison with open access data, we used OpenStreetMap [69] and GlobalMLBuildingFootprints datasets (https://github.com/microsoft/GlobalMLBuildingFootprints (accessed on 19 May 2022)) of building polygons intersecting our AOI. OpenStreetMap data is of unknown date, whereas the GlobalMLBuildingFootprints specified that it was derived from a basemap mosaic containing imagery from 2014–2021 (we estimated the date was 2016 for our study area).
2.3.2. Building Heights
Building heights were assigned to the building polygons using relative heights obtained through differencing digital surface models (DSMs) output from Metashape and digital terrain models (DTMs) (i.e., with surface features such as vegetation and buildings removed) generated using LAStools (v.200509) [70]. To generate DTMs, we used the ‘lasground_new’ tool to with a 50 m step size (‘-metro’), the ‘ultra_fine’ flag and 0.5 m ‘bulge’ to remove buildings and vegetation. Relative heights were obtained by subtracting DTMs from DSMs. We assigned heights to building polygons using a mean of all intersecting pixels where the following criteria were met: (1) the building height was ≥2 m; (2) ≥80% of the building polygon featured valid height pixels; and (3) the polygons did not intersect with the occurrence of water obtained from Pekel et al. [71]. These criteria were designed to remove misclassifications. Furthermore, we applied internal buffers of −1 m, −2 m, and −3 m to the building polygons and used the same criteria to assign building heights. Internal buffers removed edge effects around building polygons caused by irregularities in the extracted footprint or vegetation overlapping with the building roof that could bias the extracted building height. The number of building stories was estimated using a sample of 300 buildings where we counted vertical window occurrence in Google Street View imagery (dated 2015). A linear relationship was derived between the building height and number of stories, which incorporated variation due to variable roof heights (Figure S3).
2.3.3. Building Height Validation
We used 11 field-measured building heights and ICESat-2 altimetry data as an independent check of our DSM-DTM-derived building heights. They were obtained using a laser range finder (TruPulse 360R) in June 2019 for buildings 16–57 m tall (Table S2).
Buildings common to both the Pleiades (2013) and WorldView-2 (2019) datasets, which were separated by six years, were extracted using a polygon IoU threshold of 0.8 to ensure robust comparisons. Where our gridded ICESat-2 pixels (Section 2.3) intersected with these buildings, the elevation value was assigned to produce three independent height measurements for cross-comparison.
3. Results
3.1. Urban Growth
We observed a near doubling in built-up area of 139 km2 (92%) (1979–2021), from 153 ± 11 km2 in 1979 to 293 ± 22 km2 in 2021 (Figure 3). This occurred alongside a doubling of the population over the same period to 1.06 million in 2021 (Figure 2d). Much of Bishkek’s expansion was to the south of the city into previously agricultural areas (Figure 2). This is also the case for the most recent expansion 2016–2021, which occurred largely on the southeast and southwest edge of the city (Figure 3b). The WSF Evolution dataset most closely matched our analysis using Sentinel-2 data; however, the built-up area in 1991 (140 km2) was smaller than our 1979 classification (153 ± 11 km2). The WFS Evolution classification in 1985 was also an outlier to the trend (Figure 3d).
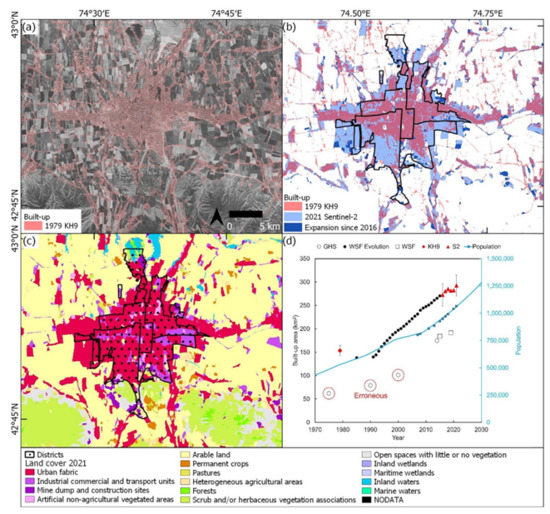
Figure 3.
Built-up area change in Bishkek. (a) 1979 KH-9 built-up area classification. (b) Difference in built-up area 1979–2016–2021 with Bishkek’s districts overlaid. (c) Landcover classification of the 2021 Sentinel-2 image. (d) Change in built-up area through time for the same AOI (a–c). 95% confidence intervals are shown for the KH-9 and Sentinel-2 ‘S2′ classifications (2016 and 2021). Population estimates (blue line) are from Macrotrends [72] and United Nations Statistics Division [73] (blue squares).
The GHS built-up area tracked lower than all other classifications, and the northeast of the city was missing until the 2000–2014 timestamp (Figure 3d and Figure S1a). The KH-9, WSF-Evo, and Sentinel-2 classifications appeared consistent in the areas classified as built-up and the areas excluded (e.g., greenspace areas in Figure S4). Our accuracy assessment applied to the KH-9 and Sentinel-2 classifications (2016 and 2021) showed overall accuracies of 83% (KH-9), 93% (Sentinel-2 2016), and 94% (Sentinel-2 2021) (Tables S3–S5).
3.2. Urban Redevelopment
Areas of built-up redevelopment were clustered in the southwest and east of the city (Figure 4a). Some of these areas correspond to the ‘Industrial commercial and transport units’ class (Figure 2c), where developments produced an increase in DN value (Figure 4b). Conversely, areas of the city in the southeast showed a DN decrease, which corresponded to increased vegetation around building structures that remained unchanged 1979–2021 (Figure 4a,c). The classified areas for built-up redevelopment, vegetated, and unchanged were 59 km2, 58 km2, and 108 km2, respectively (Table S6). Our accuracy assessment suggested an overall accuracy of 76.4% for this land-cover change assessment, suggesting that DN change within built-up areas was a reasonable proxy for areas of redevelopment or vegetation growth (Table S6).
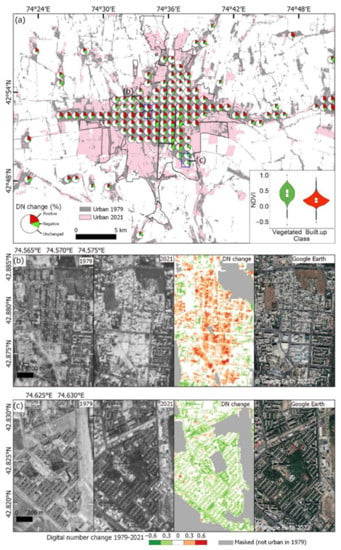
Figure 4.
Redevelopment within Bishkek (1979–2021). (a) Digital number change 1979–2021 from the difference of KH-9 and Sentinel-2 imagery (Section 2.1.4). Pie charts show the proportional DN change aggregated to a 1 km2 grid for areas ≥50% built-up. Inset shows a violin and boxplot of Sentinel-2 NDVI values for negative DN change (vegetated) and positive DN change (built-up redevelopment) classes. (b) Example of redevelopment of an area in central Bishkek where the building layout noticeably changes. (c) Example increased vegetation (trees) around buildings in south Bishkek. Extents of (b,c) are shown on panel (a).
3.3. Building Classification
Within the respective data extents (Figure 1b), we extracted 205,056 buildings from the 2013 Pleiades imagery, 67,091 from the 2019 WorldView-2 imagery, and 429,001 from the 2021 Google Satellite Basemap imagery. OpenStreetMap buildings within the same AOI as the Google Satellite Basemap detections totaled 160,141. We extracted all building detections falling within the intersecting WorldView-2, Pleiades, and Google Satellite Basemap imagery extents (83 km2) (Figure 1b) to enable a comparison across all datasets through time. Buildings totaled 49,502 for the Pleiades imagery (2013), 61,102 for the WorldView-2 imagery (2019), 65,349 for the Google Satellite Basemap imagery (2021), 63,597 for GlobalMLBuildingFootprints (dated ~2016 for Bishkek, see Section 2.3.1), and 33,283 for OpenStreetMap (unknown date). The number of buildings within the intersecting AOI therefore increased by 11,600, as observed by the Pleiades (2013) and WorldView-2 (2019) datasets, and 15,847, as observed using the Pleiades and Google Satellite Basemap (2021). Within the larger Pleiades AOI (Figure 1b), there was a 42% (85,658) increase in buildings 2013–2021 observed from the 2013 Pleiades data (205,056 buildings) and 2021 Google Satellite Basemap (290,714 buildings). Buildings from the GlobalMLBuildingFootprints dataset within the Pleiades AOI totaled 275,462, which was therefore in the range of the Pleiades and Google Satellite Basemap-derived estimates.
Leninsk District had the most buildings overall and by square kilometer (1351 buildings/km2) (Figure 5, Table 1). Oktiabrskii District had the largest buildings on average (208 ± 461 m2), which corresponded with the presence of industrial/commercial areas (Figure 3c) and the larger observed building size in these areas (mean of 176 m2) (Figure 5d).
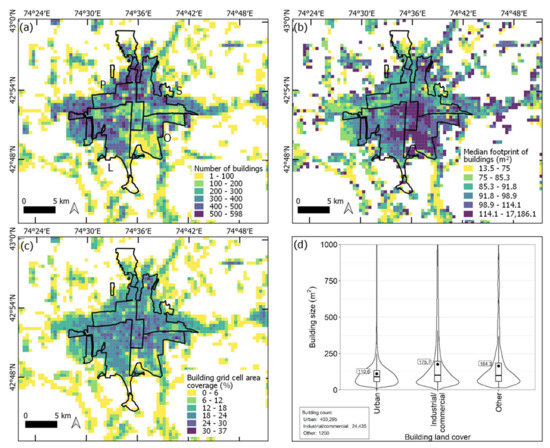
Figure 5.
(a–d) Spatial characteristics of buildings extracted from the Google Satellite Basemap imagery (2021) aggregated to 500 m grid cells. Labels in (a) show Pervomaiskii District (P), Sverlovskii District (S), Leninskii District (L), and Oktiabrskii District (O). Median sizes of buildings (b) were classified as equal count (quantile) in each class. Land-cover classes in (d) were extracted from Figure 3c.

Table 1.
Summary of buildings by district extracted from the 2021 Google Satellite Basemap imagery.
The Pleiades classification featured the highest precision, recall, and F1 score (0.72, 0.68, and 0.70, respectively) (Table 2), followed by Google Satellite Basemap (0.70, 0.64, 0.67) and WorldView-2 (0.64, 0.59, 0.61). Examples of detections and validation data are shown in Figure 6.

Table 2.
Validation of the building detection deep leaning classification (see Section 2.3.1).
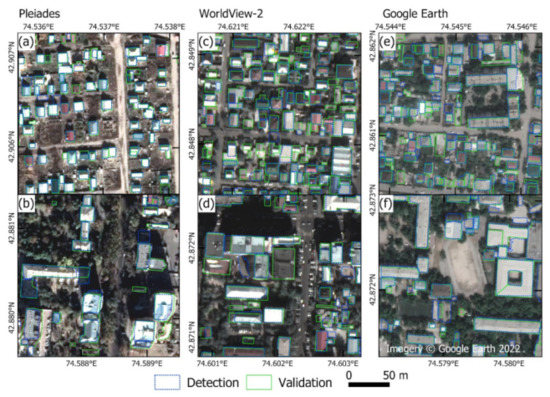
Figure 6.
(a–f) Examples of building detections (blue) and validation (green) within 200 m analysis windows for Pleiades, WorldView-2, and Google Satellite Basemap imagery (Section 2.3.1). The top row (a,c,e) shows examples of low-rise residential areas, and the bottom row (b,d,f) shows examples of medium/high-rise buildings).
3.4. Building Characteristics
High-resolution DSMs were used to assign heights to building polygons following the workflow outlined in Section 2.3.2. The Pleiades and WorldView-2 DSMs had comparable errors (NMAD = 0.62 and 0.51, respectively) (Figure 7). Within the same intersecting AOI extents (Figure 1b), data gaps were greatest in the WorldView-2 DSM, which featured 91% coverage, compared to 99% for the Pleiades DSM.
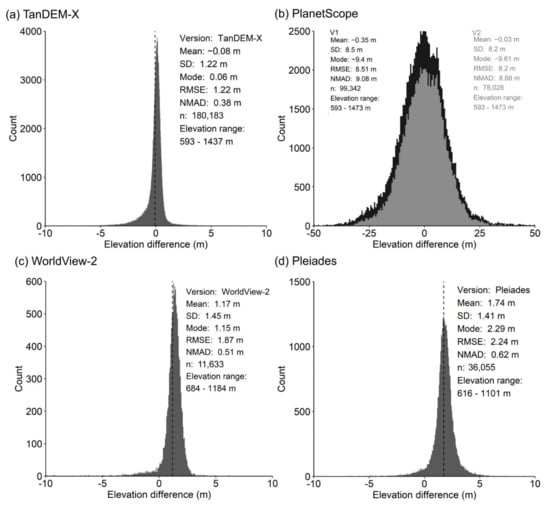
Figure 7.
(a–d) Elevation accuracy statistics for DSMs compared to ICESat-2 data over their respective AOIs (Figure 1b).
Mean and one standard deviation of elevation values were assigned to individual building polygons using internal polygon buffers of ranging from zero to three meters (Figure 8). The standard deviation of building height was observed to decrease with increasing buffer size. For example, standard deviation decreased from 0.9 m to 0.6 m in the Pleiades dataset for building polygons with no buffer and a buffer of −2 m, respectively (Figure 8b). The most stringent internal buffer (−3 m) did not lead to further improvement and notably reduced the number of buildings with valid heights assigned (following Section 2.3.2). We therefore used building heights extracted with a buffer of −2 m (Figure 8).
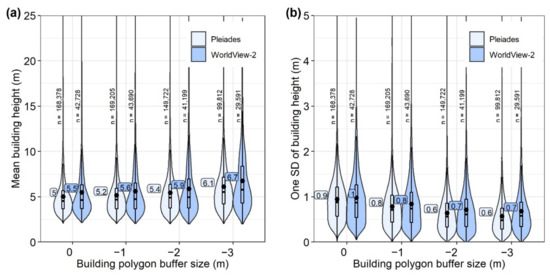
Figure 8.
(a) Mean building heights for the dataset of Pleiades and WorldView-2 detections. (b) One standard deviation of building height for Pleiades and WorldView-2 detections. Boxplot annotation (a,b) shows mean values. Building counts (n) are shown for each dataset buffer.
Independent Pleiades and WorldView-2 derived building heights (MAE = 0.79 m) and absolute elevations (DSM elevation values) (MAE = 0.50 m) (Figure 9a,b) showed close agreement. Similarly, comparing DSM-derived elevation values to ICESat-2 altimetry data revealed that the DSM elevation values were systematically lower than the ICESat-2 data by ~2 m (median values of −1.9 m and −1.6 m for Pleiades and WorldView-2, respectively) (Figure 9c). NMAD values from the DSM and ICESat-2 comparison were 0.67 m for Pleiades and 0.68 m for WorldView-2, whereas MAE values were closer to 2 m (Figure 9c). The building height MAE 1.74 m (Pleiades) and 1.78 m (WorldView-2) for buildings observed in the field were comparable to those obtained in the ICESat-2 comparison (1.86 m—Pleiades and 1.72 m—WorldView-2) (Figure 9c). The NMAD was lowest for the Pleiades-derived building heights for both the ICESat-2 (0.67 m) and field comparisons (0.43 m) (Figure 9c,d). We show the distribution of Pleiades-derived building heights, which covered most of Bishkek’s districts in Figure 10. The tallest buildings are clustered in the center of Bishkek and the southeast.
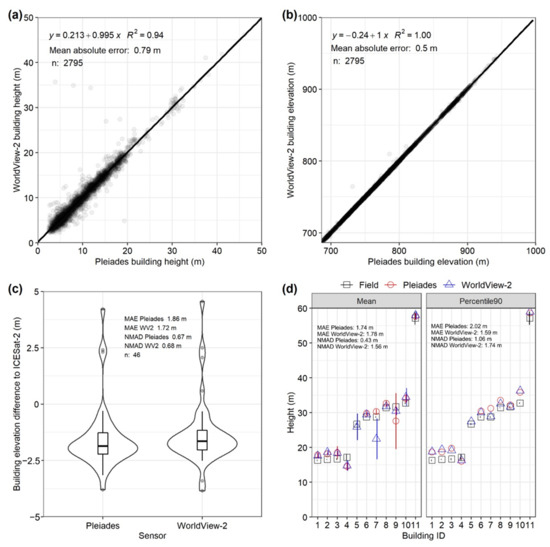
Figure 9.
Comparison of Pleiades and WorldView-2 derived building heights (a) and absolute elevations (b) for buildings common to both datasets n = 2795. (c) Building height difference compared to ICESat-2 data. (d) Comparison of DSM-derived building heights and field measurements. Two methods of extracting the building height are shown using the mean (left) or 90th Percentile (right) of elevation values within the building polygon.
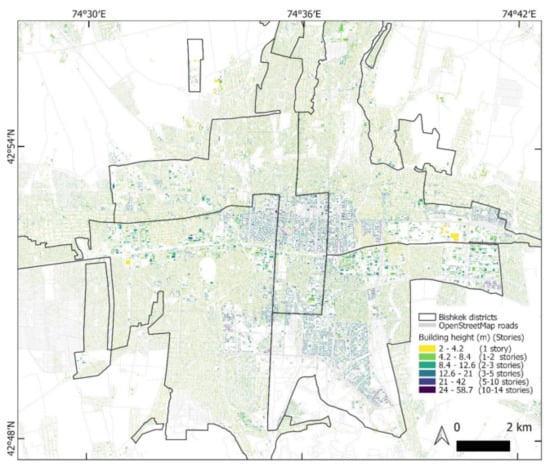
Figure 10.
Building detections from the Pleiades data with respective heights.
4. Discussion
Our analysis focused on deriving information relevant to updating city exposure datasets, particularly where both horizontal and vertical urban growth creates dynamic disaster risk. Historically, earth observation based urban growth assessments produce observations of 2D urban sprawl from image classifications applied to optical satellite imagery archives, such as those from the Landsat series [7]. Notably, these datasets do not show urban areas that undergo redevelopment through time, where low-rise buildings are replaced with taller vertical structures to accommodate urbanizing populations and economic activity (e.g., Figure 4). Therefore, these datasets cannot be used to assign building ages without first considering areas of redevelopment.
4.1. Urban Change Mapping
Our analysis revealed a ~139 km2 expansion of Bishkek (1979–2021) alongside a doubling of the city’s population. Much of this expansion was to the south of the city, where urban areas are in closer proximity to the Issyk-Ata fault (Figure 3b). This trend was also observed by earlier land-cover change assessments of Wieland et al. [15] and Omurakunova et al. [52]. This region of southern Bishkek potentially features the greatest earthquake hazard, and Erdik et al. [33] suggested casualties could reach 34,000. Bindi et al. [74] suggested lower casualties (16,600). Damages from an earthquake close to Bishkek would clearly be high, having also increased over the last decade with urban growth (Figure 3d) [35]. We found that the WSF-Evo dataset [51] most closely matched our analysis of urban growth, though the match was best in recent years.
Modern satellite sensors featuring near infrared and red bands can effectively monitor vegetation presence and change. Similarly, with multi-temporal high-resolution DSMs as used in our study, difference maps clearly highlight new buildings (e.g., Figure 11). However, our use of single-band KH-9 data offers a valuable historical perspective on urban redevelopment and vegetation growth at a resolution unavailable from multi-spectral sensors in the 1970s (e.g., ~80 m Landsat Multispectral Scanner).
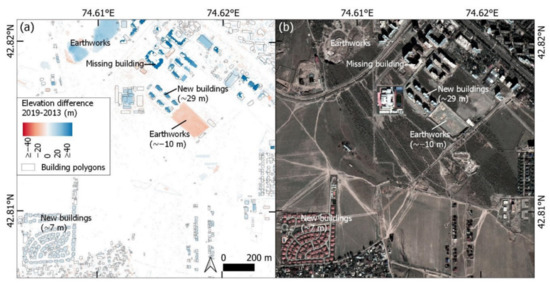
Figure 11.
(a) Elevation difference between Pleiades and WorldView-2 DSMs with building polygons overlaid. (b) Corresponding WorldView-2 ortho image. Indicative elevation change values are shown in brackets for selected features.
We observed redevelopment of built-up areas concentrated in the east and southwest of the city (Figure 4). Some of these redevelopments fell within the ‘Industrial commercial and transport units’ class (Figure 3c) and were linked to commercial developments (e.g., Figure 4b). Greenspace distribution in cities is becoming increasingly valued for a range of societal and environmental benefits [75,76,77]. Against a backdrop of urban sprawl and redevelopment, our analysis identified urban greening, which could otherwise be masked within a general trend of urbanization and greenspace depletion, e.g., [52]. This analysis also offers a simple method of updating exposure datasets where ages are assigned to built-up areas, e.g., [15], since ~26% of Bishkek’s built-up area classified in 1979 was observed to have redeveloped.
4.2. Building Detection and Bishkek’s Expansion
Our deep learning building detection workflow was of comparable accuracy to other studies. Tiede et al. [67] observed an F1 score of 0.78, compared to 0.70 in our study (Pleiades dataset—Table 2). However, their study was concerned with the total number of buildings detected for population estimation, rather than the correct spatial intersection of detections and validation data. Zhao et al. [30] observed an overall score (mean for detections over four cities) of 0.71 as part of the DeepGlobe Building Extraction Challenge. Similarly, Li et al. [29] achieved an F1 score of 0.70 using WorldView-3 multispectral imagery. Despite comparable DSM accuracy between Pleiades and WorldView-2 (Figure 9), the lower building detection performance for WorldView-2 data (Table 2) is potentially linked to larger data gaps (e.g., Figure 12) and greater image orthorectification errors due to the stereo viewing geometry compared to tri-stereo for Pleiades (Table S7). Tri-stereo satellite image acquisitions improves data coverage and reduces DSM uncertainty [65], which is important in cities where medium- and high-rise buildings would otherwise obscure the ground as viewed from the satellite. Due to their larger pixel size, the 12 m TanDEM-X and 9 m PlanetScope DSM were not able to resolve individual buildings (Figure 12c), and the PlanetScope DSM also featured the highest vertical error (~8.5 m RMSE) (Figure 7b). The TanDEM-X has been used to derive average building heights aggregated to a 90 m grid, e.g., [24]; whereas the vertical error in PlanetScope DSMs produced using RPCs (without ground control points) likely precludes such applications despite advantages of higher resolution and high revisit frequency.
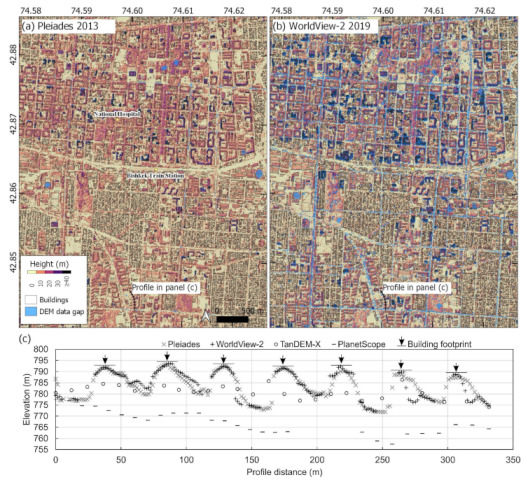
Figure 12.
Example hillshaded DSMs for Pleiades (a) and WorldView-2 (b) over central Bishkek. (c) Example DSM elevation profile through seven buildings shown on panels (a,b). Profile runs south to north. The building footprints are shown by an arrow and horizontal line. The horizontal line is shown at the peak elevation values for each building and does not reflect the true building height, which was not known.
Within the Pleiades AOI, we observed a 42% (85,658) increase in buildings 2013–2021 to a total of 290,714 buildings in 2021 (~10,700/year). Bishkek’s population increased ~20% (~180,000) over the same time period (Figure 3d). Wieland et al. [15] derived an empirical estimate of 112,293 buildings in 2009, though over a smaller area of Bishkek. Additionally, Erdik et al. [33] reported a total of 77,150 buildings in Bishkek (with an undefined spatial extent) in 2005, of which the majority (75,000) were stated to be private apartment houses. Comparing the 2005 data to our 2021 Google Satellite Basemap estimate would equate to a construction of 13,300 buildings per year. Notably, within the smaller WorldView-2 AOI (Figure 1b), the increase in buildings was smaller at 11,600 (2013–2019) and 15,847 (2013–2021), or ~2000 buildings per year. Though our accuracy assessment revealed similar scores between classifications (Table 2), deep learning building extraction using high-resolution satellite imagery still presents issues, particularly regarding the underestimation of closely built or adjoining buildings [67], which may deliberately be marked as a single building at the training stage [78]. The prevalence of partially complete (i.e., with a roof but unoccupiable) or unoccupied buildings is also not considered.
Automated workflows are required to utilize a vastly increasing dataset of high-resolution imagery and to produce dynamic city inventories. For Bishkek, seismic risk models require up-to-date exposure data, since the expansion trajectory does not appear to be slowing. The median distance of built-up areas from active faults has reduced from 9.7 to 8.8 km, and there is an additional 83 km2 of built-up area (1979–2021) within 10 km of active faults (Figure 13).
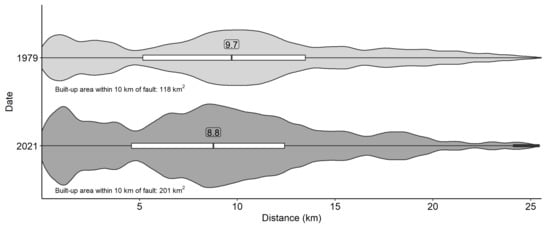
Figure 13.
Violin plot of built-up area proximity to active faults (Figure 1) in 1979 and 2021.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we assessed the growth of Bishkek through time, including deriving a workflow to classify built-up area and areas of redevelopment in a 1979 KH-9 Hexagon satellite image. We used high-resolution stereo and tri-stereo satellite imagery to derive building polygons and their heights, which were validated using ICESat-2 altimetry data. Bishkek expanded by ~139 km2 (92%) (1979–2021), particularly towards active faults located at the south of the city and ~26% (59 km2) of Bishkek’s built-up area classified in 1979 was observed to have redeveloped by 2021. We found that building polygons extracted using a deep learning workflow applied to high-resolution tri-stereo (Pleiades) satellite imagery were most accurate (F1 score = 0.70) compared to stereo (WorldView-2) imagery (F1 score = 0.61), and that building heights extracted using a Pleiades-derived digital elevation model were most comparable to independent measurements (normalized absolute median deviation < 1 m). Across different areas of the city, our analysis suggested rates of building growth in the region of 2000–10,700 buildings per year. The horizonal and vertical expansion of Bishkek demonstrates the importance of up-to-date exposure data, which are required to produce seismic risk models. Our analysis highlighted the capabilities and limitations of using earth-observation data to update estimates of building stock, where country-level or open access datasets are lacking or incomplete.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs14225790/s1, Figure S1: Bishkek’s urban growth quantified by global datasets including the Global Human Settlement (a), World Settlement Footprint (b), and World Settlement Evolution (c); Figure S2. (a) Reference polygons used as training data for the KH-9 built-up classification. Accuracy assessment points are also shown for the KH-9 built-up classification, and the KH-9 classification masked to the built-up area classified using 2021 Sentinel-2 imagery. (b) Stable areas used to quantify DN values for masking out areas of insignificant change when investigating areas of the city that underwent redevelopment or vegetation growth. Accuracy assessment points are also shown for the DN change analysis. Accuracy assessment points for the deep learning classification applied to Sentinel-2 imagery from 2016 (c) and 2021 (d); Figure S3. Relationship between the number of building stories and building height for a sample of 300 buildings in Bishkek. Building stories were derived by counting vertical window occurrence in Google Street View (imagery from 2015). Building heights were assigned using 2013 Pleiades data (Figure 10); Figure S4. Examples of built-up area classification for the KH-9 analysis (a,b), World Settlement Footprint (c,d), and Sentinel-2 2021 (e–f). Panels in the left column (a,c,e) and right column (b,d,f) show the same area for each classification; Table S1. Optical satellite image IDs used in this study; Table S2. Comparison between field-measured building heights and those derived from the DSM-DTM difference for Pleiades and WorldView-2 data; Table S3. KH9 1979 accuracy assessment (masked to Sentinel-2 2021 built-up extent) using 500 validation points. The validation points were used to report area-adjusted classification confidence intervals and producers, users, and overall accuracy percentages; see [53,54]. Briefly, these error-adjusted metrics use the validation points to weight the classified areas accounting for omission or commission within each class. Confidence intervals are the same where the number of classes equals two, since errors are dependent. Overall accuracy is the correctly mapped proportion of the area. Producer’s accuracy is the proportion of the area in a class according to the reference (ground truth) information that is also mapped as that class. User accuracy is the proportion of the area mapped as a class that belonged to that class according to the reference information; Table S4. Sentinel-2 2016 accuracy assessment; Table S5. Sentinel-2 2021 accuracy assessment; Table S6. KH9 1979 land-cover change accuracy assessment; Table S7. Acquisition information for tri-stereo (Pleiades) and stereo (WorldView-2) imagery.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.W., J.R.E. and R.M.J.A.; Formal analysis, C.S.W.; Funding acquisition, J.R.E.; Methodology, C.S.W. and J.R.E.; Project administration, J.R.E. and K.E.A.; Validation, C.S.W.; Visualization, C.S.W.; Writing—original draft, C.S.W. and J.R.E.; Writing—review and editing, C.S.W., J.R.E., R.M.J.A. and K.E.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been supported a NERC Innovation award (grant number NE/S013911/1), the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF) Urban Disaster Risk Hub (NE/S009000/1) (Tomorrow’s Cities), and COMET. COMET is the NERC Centre for the Observation and Modeling of Earthquakes, Volcanoes and Tectonics, a partnership between UK Universities and the British Geological Survey. John Elliott is supported by a Royal Society University Research fellowship (UF150282).
Data Availability Statement
Datasets supporting this study will be made available in the Zenodo repository: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6619130 (accessed on 29 September 2022).
Acknowledgments
Pleiades images made available by CNES in the framework of the CEOS Working Group for Disasters. © CNES (2013), and Airbus DS, all rights reserved. Commercial uses forbidden. Worldview-2 imagery Copyright 2020 DigitalGlobe Incorporated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- UN DESA. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.L. Climate Change, Disaster Risk, and the Urban Poor; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, O.; Aalst, M.; Birkmann, J.; Fordham, M.; McGregor, G.; Perez, R.; Pulwarty, R.; Schipper, L.; Sinh, B. Determinants of Risk: Exposure and Vulnerability, in Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 65–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittore, M.; Wieland, M.; Fleming, K. Perspectives on global dynamic exposure modelling for geo-risk assessment. Nat. Hazards 2016, 86, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallemacq, P.; Unisdr, C. Economic Losses, Poverty and Disasters 1998–2017; United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2020. 2020. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2020/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2020.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Roy, D.P.; Crawford, C.J.; Masek, J.G.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; et al. Current status of Landsat program, science, and applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, D.; Watson, C.S.; Rounce, D.R.; Shugar, D.H.; Kargel, J.S.; Haritashya, U.K.; Amatya, P.; Shean, D.; Anderson, E.R.; Jo, M. The State of Remote Sensing Capabilities of Cascading Hazards Over High Mountain Asia. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patino, J.E.; Duque, J.C. A review of regional science applications of satellite remote sensing in urban settings. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2013, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarian, S.; Kerle, N.; Filatova, T. Remote sensing-based proxies for urban disaster risk management and resilience: A review. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, K. Satellite remote sensing for disaster management support: A holistic and staged approach based on case studies in Sentinel Asia. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 33, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessis, J.L.; Béquignon, J.; Mahmood, A. The International Charter “Space and Major Disasters” initiative. Acta Astronaut. 2004, 54, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.J.-P.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Kettner, A.J.; Kashif, R.; Niebuhr, E. Assisting Flood Disaster Response with Earth Observation Data and Products: A Critical Assessment. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNISDR. Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030. 2015. Available online: https://www.undrr.org/publication/sendai-framework-disaster-risk-reduction-2015-2030 (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Wieland, M.; Pittore, M.; Parolai, S.; Zschau, J. Exposure Estimation from Multi-Resolution Optical Satellite Imagery for Seismic Risk Assessment. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2012, 1, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amey, R.M.J.; Elliott, J.R.; Hussain, E.; Walker, R.; Pagani, M.; Silva, V.; Abdrakhmatov, K.E.; Watson, C.S. Significant Seismic Risk Potential from Buried Faults Beneath Almaty City, Kazakhstan, revealed from high-resolution satellite DEMs. Earth Space Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, B.; Ghafory-Ashtiany, M.; Amini-Hosseini, K.; Nourjou, R.; Mousavi, M. Building Seismic Loss Model for Tehran. Earthq. Spectra 2010, 26, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconcini, M.; Metz-Marconcini, A.; Üreyen, S.; Palacios-Lopez, D.; Hanke, W.; Bachofer, F.; Zeidler, J.; Esch, T.; Gorelick, N.; Kakarla, A.; et al. Outlining where humans live, the World Settlement Footprint 2015. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbane, C.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T.; Politis, P.; Florczyk, A.J.; Syrris, V.; Melchiorri, M.; Sabo, F.; Soille, P. Automated global delineation of human settlements from 40 years of Landsat satellite data archives. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 140–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltezos, E.; Doulamis, A.; Doulamis, N.; Ioannidis, C. Building Extraction from LiDAR Data Applying Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestnall, G.; Jaafar, J.; Duncan, A. Extracting urban features from LiDAR digital surface models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2000, 24, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, U.; Förstner, W. Towards automatic building extraction from high-resolution digital elevation models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1995, 50, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Clinton, N.; Gong, P. Estimating building height in China from ALOS AW3D30. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 185, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Brzoska, E.; Dech, S.; Leutner, B.; Palacios-Lopez, D.; Metz-Marconcini, A.; Marconcini, M.; Roth, A.; Zeidler, J. World Settlement Footprint 3D-A first three-dimensional survey of the global building stock. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Feng, D.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y. Multi-Scene Building Height Estimation Method Based on Shadow in High Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Thiel, K.H. Delimiting the building heights in a city from the shadow in a panchromatic SPOT-image—Part 1. Test of forty-two buildings. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; Jones, N.; Mannix, J. Assessing OpenStreetMap Completeness for Management of Natural Disaster by Means of Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Three Small Island States (Haiti, Dominica and St. Lucia). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herfort, B.; Lautenbach, S.; Porto de Albuquerque, J.; Anderson, J.; Zipf, A. The evolution of humanitarian mapping within the OpenStreetMap community. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; He, C.; Fang, J.; Zheng, J.; Fu, H.; Yu, L. Semantic Segmentation-Based Building Footprint Extraction Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Images and Multi-Source GIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, J.; Jung, J.; Sohn, G. Building Extraction from Satellite Images Using Mask R-CNN with Building Boundary Regularization. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 242–2424. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Wen, D.; Chen, H.; Gong, J. Assessing the quality of building height extraction from ZiYuan-3 multi-view imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.R. Earth Observation for the Assessment of Earthquake Hazard, Risk and Disaster Management. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 1323–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdik, M.; Rashidov, T.; Safak, E.; Turdukulov, A. Assessment of seismic risk in Tashkent, Uzbekistan and Bishkek, Kyrgyz Republic. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2005, 25, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Earthquake Model. Country Profile for Kyrgyzstan Version 1.2. 2022. Available online: https://downloads.openquake.org/countryprofiles/KGZ.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Amey, R.M.J.; Elliott, J.; Watson, C.S.; Walker, R.; Pagani, M.; Silva, V.; Hussain, E.; Abdrakhmatov, K.; Baikulov, S.; Kyzyz, G.T. Improving Urban Seismic Risk Estimates for Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, Incorporating Recent Geological Knowledge of Hazards. EarthArXiv. Prepr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Cavalca, D.; Jaiswal, K.; Huyck, C.; Crowley, H. The GED4GEM project: Development of a global exposure database for the global earthquake model initiative. In Proceedings of the 15th WCEE, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–28 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Active Tectonics Research Group. Active Tectonics of the Northern Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan. Available online: http://activetectonics.asu.edu/N_tien_shan/N_tien_shan_data.html (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Styron, R. GEMScienceTools/gem-global-active-faults: First release of 2019 (Version 2019.0). ZENODO 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerlich, F.; Bolch, T.; Mukherjee, K.; Pieczonka, T. Glacier Mass Loss during the 1960s and 1970s in the Ak-Shirak Range (Kyrgyzstan) from Multiple Stereoscopic Corona and Hexagon Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surazakov, A.; Aizen, V. Positional accuracy evaluation of declassified Hexagon KH-9 mapping camera imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehecq, A.; Gardner, A.S.; Alexandrov, O.; McMichael, S.; Hugonnet, R.; Shean, D.; Marty, M. Automated Processing of Declassified KH-9 Hexagon Satellite Images for Global Elevation Change Analysis Since the 1970s. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 8, 566802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Earth Explorer. 2022. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Agisoft Metashape v1.7.2. Available online: https://www.agisoft.com/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Orfeo Toolbox. User Guide. 2021. Available online: https://www.orfeo-toolbox.org/CookBook/C++/UserGuide.html (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Lindsay, J.B. Whitebox GAT: A case study in geomorphometric analysis. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 95, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J. The Whitebox Geospatial Analysis Tools project and open-access GIS; 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271205138_The_Whitebox_Geospatial_Analysis_Tools_project_and_open-access_GIS (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Böhner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esri. Land Cover Classification (Sentinel-2). 2021. Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=afd124844ba84da69c2c533d4af10a58 (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Florczyk, A.J.; Corbane, C.; Ehrlich, D.; Freire, S.; Kemper, T.; Maffenini, L.; Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P.; Schiavina, M. GHSL data package 2019. Luxemb. EUR 2019, 29788, 290498. [Google Scholar]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Florczyk, A.; Freire, S.; Halkia, M.; Julea, A.; Kemper, T.; Soille, P.; Syrris, V. Operating procedure for the Production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat Data of the Epochs 1975, 1990, 2000, and 2014; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Marconcini, M.; Metz-Marconcini, A.; Esch, T.; Gorelick, N. Understanding Current Trends in Global Urbanisation-The World Settlement Footprint Suite. GI_Forum 2021, 9, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omurakunova, G.; Bao, A.; Xu, W.; Duulatov, E.; Jiang, L.; Cai, P.; Abdullaev, F.; Nzabarinda, V.; Durdiev, K.; Baiseitova, M. Expansion of Impervious Surfaces and Their Driving Forces in Highly Urbanized Cities in Kyrgyzstan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E. Making better use of accuracy data in land change studies: Estimating accuracy and area and quantifying uncertainty using stratified estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agisoft Metashape v1.8.0. Available online: https://www.agisoft.com/ (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Lastilla, L.; Belloni, V.; Ravanelli, R.; Crespi, M. DSM Generation from Single and Cross-Sensor Multi-View Satellite Images Using the New Agisoft Metashape: The Case Studies of Trento and Matera (Italy). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ArcGIS Pro 2.8.0. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Planet Labs. Planet Imagery Product Specifications. 2021. Available online: https://assets.planet.com/docs/Planet_Combined_Imagery_Product_Specs_letter_screen.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Ghuffar, S. DEM Generation from Multi Satellite PlanetScope Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, P.; Martone, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Wecklich, C.; Borla Tridon, D.; Bräutigam, B.; Bachmann, M.; Schulze, D.; Fritz, T.; Huber, M.; et al. Generation and performance assessment of the global TanDEM-X digital elevation model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 132, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuth, C.; Kääb, A. Co-registration and bias corrections of satellite elevation data sets for quantifying glacier thickness change. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, T.A.; Martino, A.J.; Markus, T.; Bae, S.; Bock, M.R.; Brenner, A.C.; Brunt, K.M.; Cavanaugh, J.; Fernandes, S.T.; Hancock, D.W.; et al. The Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite—2 mission: A global geolocated photon product derived from the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, T.A.; Brenner, A.; Hancock, D.; Robbins, J.; Saba, J.; Harbeck, K.; Gibbons, A.; Lee, J.; Luthcke, S.B.; Rebold, T. ATLAS/ICESat-2 L2A Global Geolocated Photon Data, Version 3; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalsa, S.J.S.; Borsa, A.; Nandigam, V.; Phan, M.; Lin, K.; Crosby, C.; Fricker, H.; Baru, C.; Lopez, L. OpenAltimetry—Rapid analysis and visualization of Spaceborne altimeter data. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 15, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Parsons, B.; Elliott, J.R.; Barisin, I.; Walker, R.T. Assessing the ability of Pleiades stereo imagery to determine height changes in earthquakes: A case study for the El Mayor-Cucapah epicentral area. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 8793–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhle, J.; Höhle, M. Accuracy assessment of digital elevation models by means of robust statistical methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, D.; Schwendemann, G.; Alobaidi, A.; Wendt, L.; Lang, S. Mask R-CNN-based building extraction from VHR satellite data in operational humanitarian action: An example related to Covid-19 response in Khartoum, Sudan. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, D.; Stark, T.; Wurm, M.; Dech, S.; Taubenböck, H. Large-scale building extraction in very high-resolution aerial imagery using Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- OpenStreetMap Contributors. OpenStreetMap. 2015. Available online: https://www.openstreetmap.org (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Isenburg, M. LAStools—Efficient LiDAR Processing Software, (200509, Academic). 2019. Available online: http://rapidlasso.com/LAStools (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrotrends. Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan Metro Area Population 1950–2022. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net/cities/21770/bishkek/population (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- United Nations Statistics Division. City Population by Sex, City and City Type. 2022. Available online: https://data.un.org/ (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Bindi, D.; Mayfield, M.; Parolai, S.; Tyagunov, S.; Begaliev, U.T.; Abdrakhmatov, K.; Moldobekov, B.; Zschau, J. Towards an improved seismic risk scenario for Bishkek, Kyrgyz Republic. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 31, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.; Banay, R.F.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F. A Review of the Health Benefits of Greenness. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, M.F.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Evans, K.L.; Goddard, M.A.; Lerman, S.B.; MacIvor, J.S.; Nilon, C.H.; Vargo, T. Biodiversity in the city: Key challenges for urban green space management. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.S.; Elliott, J.R.; Ebmeier, S.K.; Vásquez, M.A.; Zapata, C.; Bonilla-Bedoya, S.; Cubillo, P.; Orbe, D.F.; Córdova, M.; Menoscal, J.; et al. Enhancing disaster risk resilience using greenspace in urbanising Quito, Ecuador. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.; Koperski, K.; Lindenbaum, D.; Pang, G.; Huang, J.; Basu, S.; Hughes, F.; Tuia, D.; Raskar, R. Deepglobe 2018: A challenge to parse the earth through satellite images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 172–181. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).