Novel Asymmetric Pyramid Aggregation Network for Infrared Dim and Small Target Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An end-to-end gated multiple pyramid structure is proposed for detecting small infrared targets. Specially, the pyramid structure is first built to encode multi-scale enhanced features of small infrared targets. And then the inverted pyramid structure is built to decode asymmetric local information of small infrared targets in multi-scale and multi-level features.
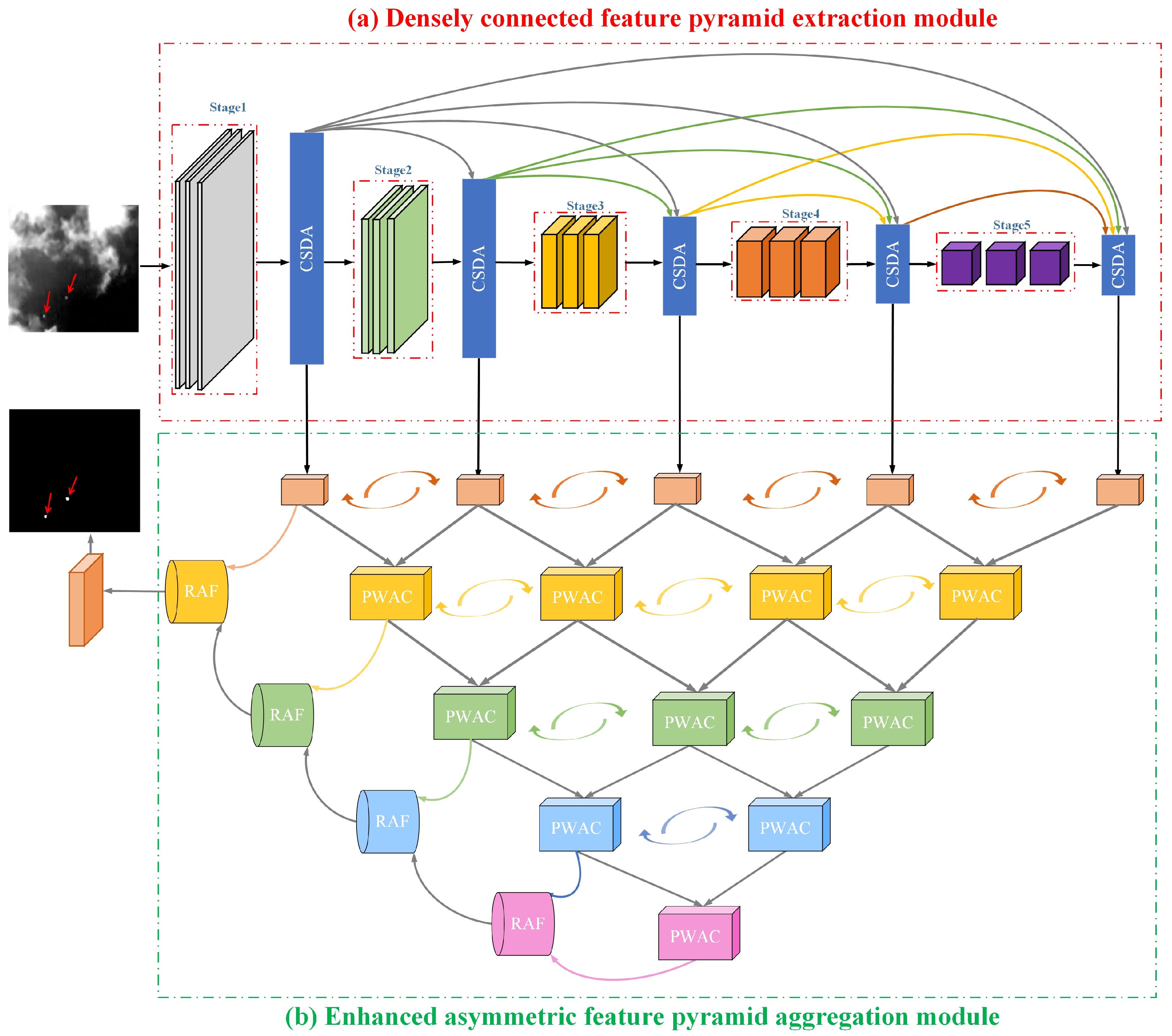
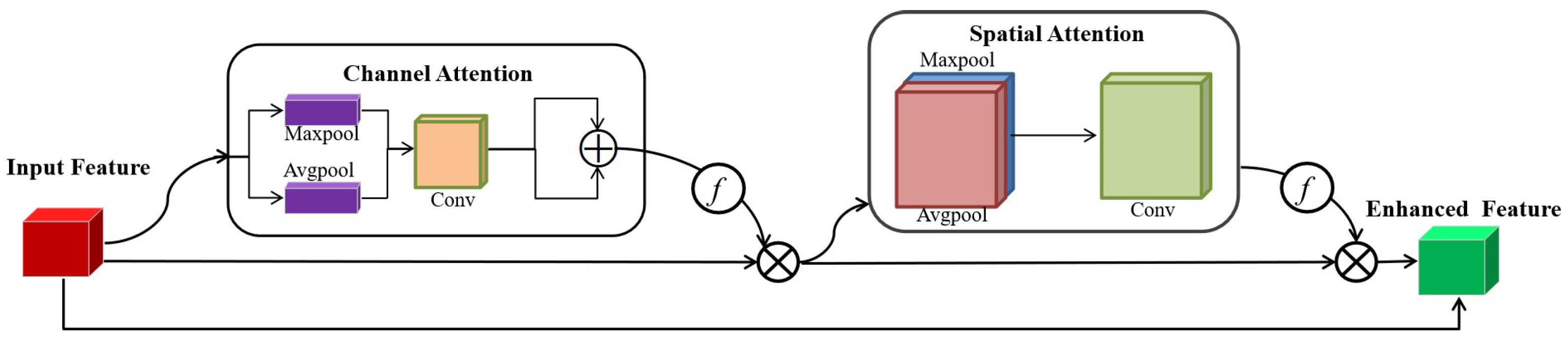
- A densely connected feature pyramid extraction module is proposed to continuously enhance and retain the details of small infrared target in different scale features. Specially, based on the different forms of information flow transmission on the backbone network, two different variants of feature pyramid extraction are designed, which can transfer detailed features enhanced by dual attention of small target from lower-level large-scale space to higher-level small-scale space.
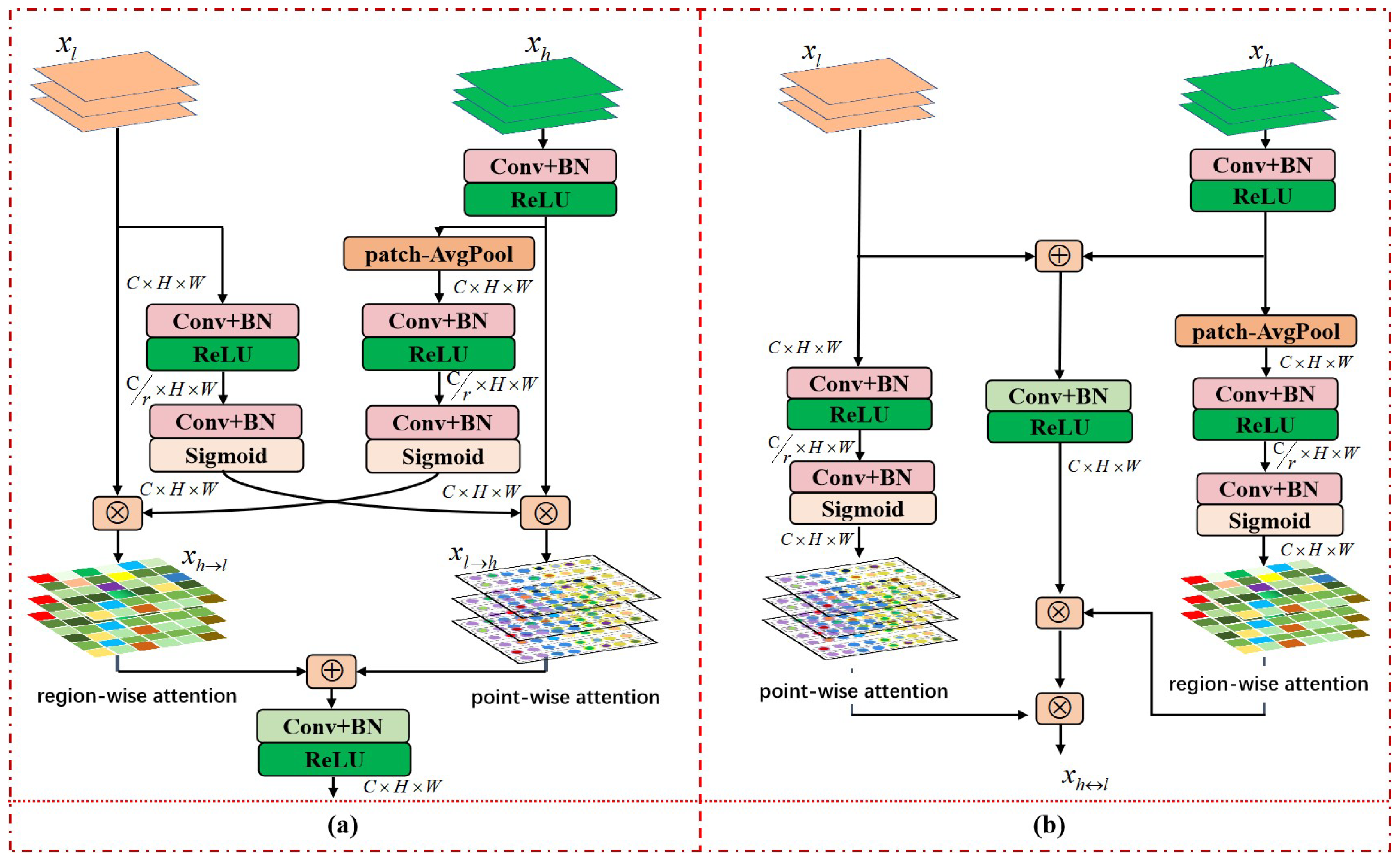
- An enhanced asymmetric feature pyramid aggregation module is proposed to dynamically highlight the fine details of small targets and suppress complex backgrounds. The module can modulate and aggregate cross-layer local information in pairwise asymmetric manner and recursive asymmetric manner, respectively. In particular, two different aggregation paths, each with two different interaction strategies: parallel gated fusion and hierarchical gated fusion.
2. Related Work
2.1. Small Infrared Target Detection
2.2. Pyramid Structure
2.3. Attention Mechanism
2.4. Cross-Layer Feature Aggregation
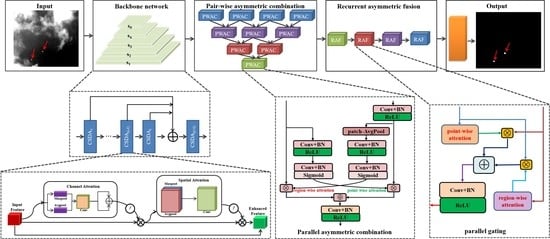
3. Method
3.1. Densely Connected Feature Pyramid Extraction Module
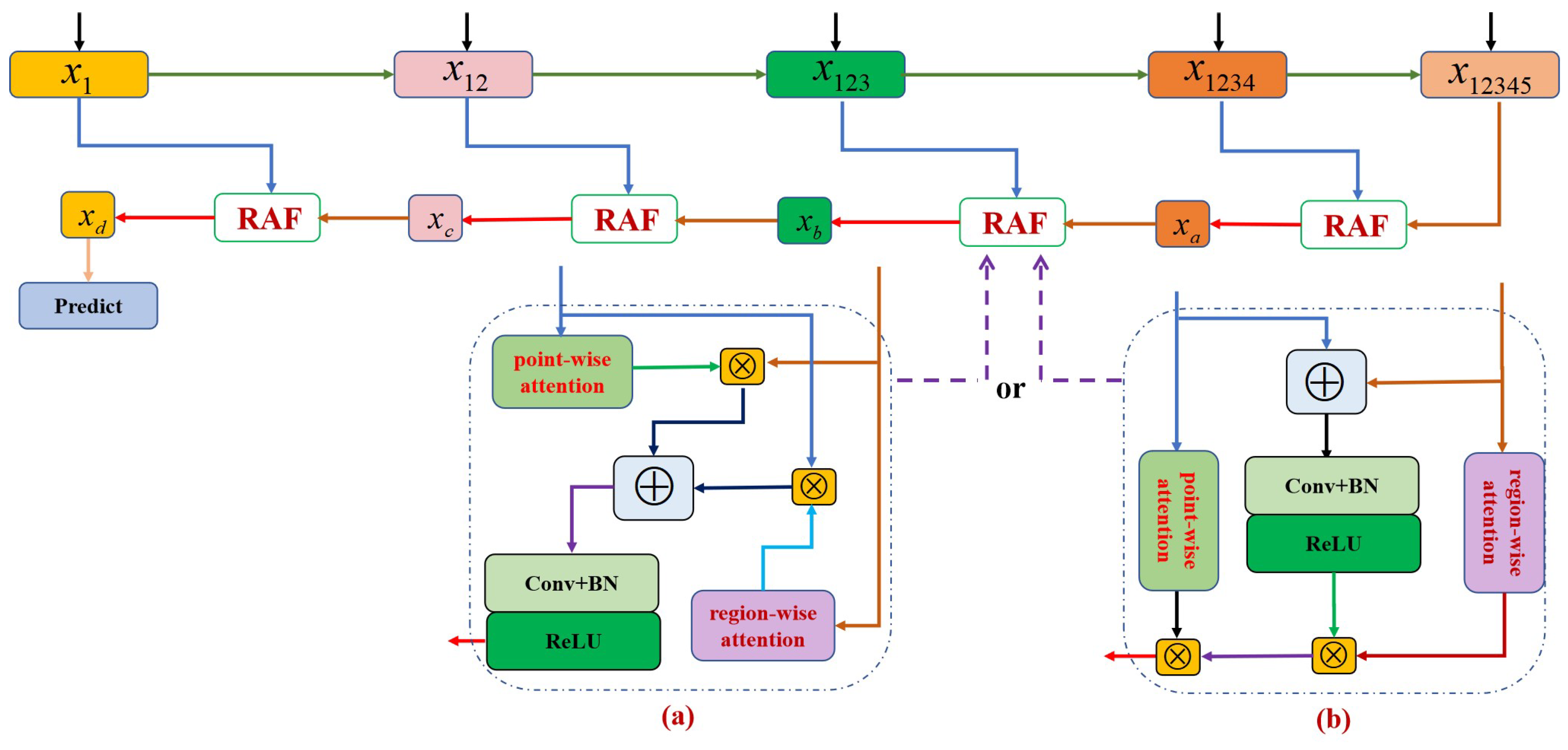
3.2. Enhanced Asymmetric Feature Pyramid Aggregation Module
3.2.1. Pair-Wise Asymmetric Combination
3.2.2. Recurrent Asymmetric Fusion
3.3. End-to-End Learning
4. Result
4.1. Dataset Description
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Comparison to State-of-the-Art Methods
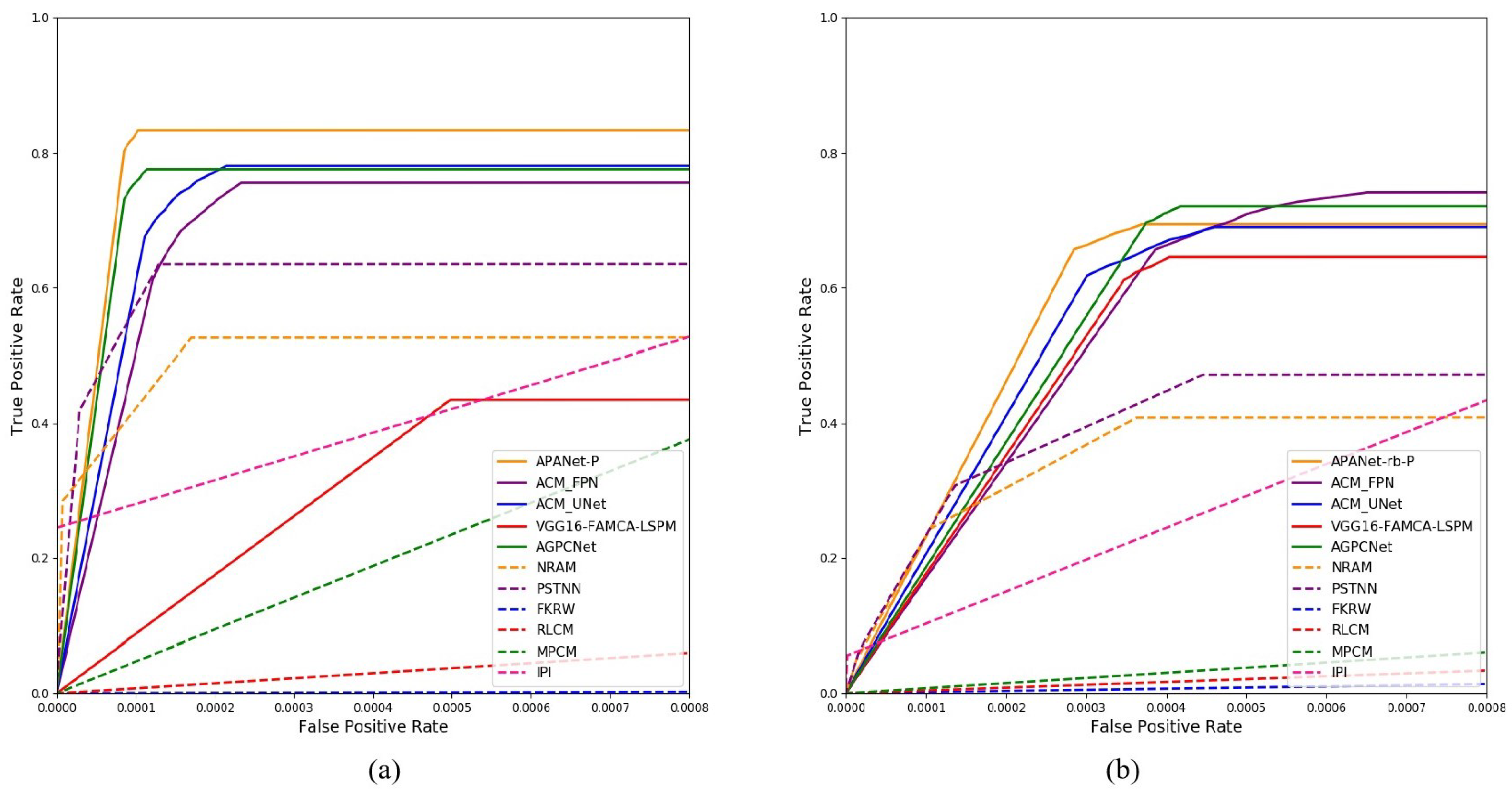
4.4.1. Quantitative Evaluation
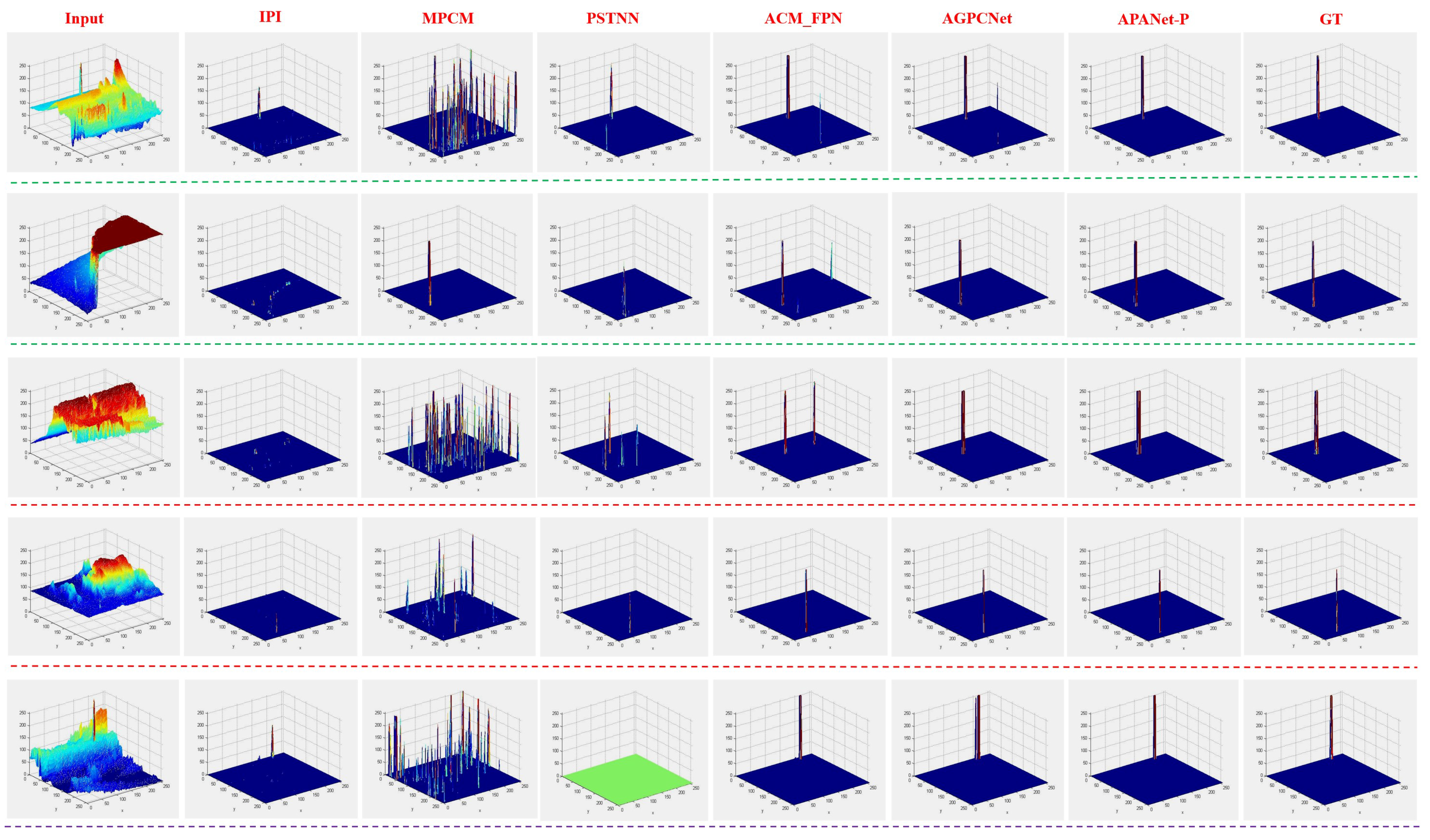
4.4.2. Qualitative Evaluation
5. Discussion
- APANet-P_without_DCCS: Remove the setting of dense connection based on CSDA of pyramid extraction module in APANet-P, that is, only the multi-scale features generated by the 5-stage convolutional layers are used for feature pyramid aggregation.
- APANet-P_without_RAF: Remove the setting of RAF of the asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P, that is, only using the feature generated in the PWAC for small target detection.
- APANet-P_sum: Replace the setting of RAF of asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P with the direct feature fusion, that is, the features summed by , , , and are used for small target detection.
- APP-Net: Replace the settings of top-down region-wise attention and bottom-up point-wise attention of the asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P with top-bottom point-wise attention and bottom-up point-wise attention.
- ALP-Net: Replace the settings of top-down region-wise attention and bottom-up point-wise attention of the asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P with top-down region-wise attention and bottom-up region-wise attention.
- APANet-P-6: Modify the parameter size of the local region in the top-down region-wise attention of the asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P to 6.
- APANet-P-10: Modify the parameter size of the local region in the top-down region-wise attention of the asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P to 10.
- APANet-P-12: Modify the parameter size of the local region in the top-down region-wise attention of the asymmetric pyramid aggregation module in APANet-P to 12.
- APANet-P: Our proposed novel asymmetric pyramid aggregation network, which consists of DCMSF, PAC, and RAF based on parallel gating.
5.1. Effectiveness of Densely Connected Feature Extraction
5.2. Effectiveness of Pair-Wise Asymmetric Combination
5.3. Effectiveness of Recurrent Asymmetric Fusion
5.4. Influence of the Size of the Local Region in Region-Wise Attention
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prasad, D.; Rajan, D.; Rachmawati, L.; Rajabally, E.; Quek, C. Video processing from electro-optical sensors for object detection and tracking in a maritime environment: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 1993–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.; Verma, S.; Kumar, Y. Review on recent development in infrared small target detection algorithms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. The design of top-hat morphological filter and application to infrared target detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2006, 48, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xia, T.; Yan, Y. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Fan, F.; Liang, K.; Fang, Y. A robust infrared small target detection algorithm based on human visual system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, D.; Chen, H. Infrared small target detection based on local intensity and gradient properties. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 89, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, B.; Dang, C.; Deng, J. Low-Contrast Infrared Target Detection Based on Multiscale Dual Morphological Reconstruction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hauptmann, A. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Ren, M. Infrared small target detection based on patch image model with local and global analysis. Int. J. Image Graph. 2018, 18, 1850002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Adaptive pyramid context network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 7519–7528. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Dai, S.; Huang, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, H. Infrared small target segmentation with multiscale feature representation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 116, 103755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Su, L.; Huang, Q. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3907–3916. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Towards bridging semantic gap to improve semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4230–4239. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Barnard, K. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 950–959. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Pu, T.; Peng, Z. AGPCNet: Attention-Guided Pyramid Context Networks for Infrared Small Target Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03580. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, S.; Er, M.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Chan, P. Max-mean and max-median filters for detection of small targets. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1999, Denver, CO, USA, 20–22 July 1999; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1999; Volume 3809, pp. 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Qin, T. Infrared maritime dim small target detection based on spatiotemporal cues and directional morphological filtering. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 115, 103657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; You, X.; Li, H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 58, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Infrared small target detection utilizing the multiscale relative local contrast measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, L.; Hui, M.; Wang, S. Image small target detection based on deep learning with SNR controlled sample generation. Curr. Trends Comput. Sciene Mech. Autom. 2017, 1, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Wang, H. Infrared dim and small target detection based on denoising autoencoder network. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 25, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, P.; Liu, L.; Wu, N. TBC-Net: A real-time detector for infrared small target detection using semantic constraint. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2001.05852. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. Denseaspp for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3684–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kweon, I. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective kernel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Lei, Y.; Lu, H. Deep gated attention networks for large-scale street-level scene segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 88, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, Y. Deep contrast learning for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 478–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Ruan, X. Amulet: Aggregating multi-level convolutional features for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (RNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) network. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Wang, Y. Optimizing intersection-over-union in deep neural networks for image segmentation. In International Symposium on Visual Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 234–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. Miss detection vs. false alarm: Adversarial learning for small object segmentation in infrared images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8509–8518. [Google Scholar]
- Duchi, J.; Hazan, E.; Singer, Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2121–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Bruzzone, L.; Gao, C.; Li, B. Infrared small target detection based on facet kernel and random walker. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7104–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, S.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l2,1 norm. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]




| Stage | Output | Backbone |
|---|---|---|
| Stage1 | ||
| Stage2 | ; | |
| Stage3 | ; | |
| Stage4 | ; | |
| Stage5 | ; |
| Methods | Hyper-Parameter Settings |
|---|---|
| IPI [9] | Patch size: , sliding step: 10, , |
| MPCM [28] | Window size: , , , K = 5 |
| RLCM [29] | = 5, = [2, 5, 9], = [4, 9, 16] |
| FKRW [48] | Window size: , K = 4, p = 6, = 200, |
| PSTNN [11] | Patch size: , sliding step: 40, , |
| NRAM [49] | Patch size: , sliding step: 10, , , |
| Methods | Precision | Recall | mIoU | F-measure | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPCM [28] | 0.1313 | 0.7181 | 0.1249 | 0.2220 | 0.8580 |
| RLCM [29] | 0.0406 | 0.7975 | 0.0402 | 0.0773 | 0.8933 |
| FKRW [48] | 0.0017 | 0.4688 | 0.0017 | 0.0034 | 0.6525 |
| IPI [9] | 0.2221 | 0.8959 | 0.2165 | 0.3560 | 0.9472 |
| NRAM [49] | 0.6452 | 0.5258 | 0.4079 | 0.5794 | 0.7628 |
| PSTNN [11] | 0.7431 | 0.6348 | 0.5205 | 0.6847 | 0.8173 |
| ACM_FPN [24] | 0.7098 | 0.6948 | 0.5411 | 0.7023 | 0.8761 |
| ACM_UNet [24] | 0.7359 | 0.7410 | 0.5854 | 0.7385 | 0.8880 |
| VGG16-FAMCA-LSPM [21] | 0.3392 | 0.4347 | 0.2354 | 0.3811 | 0.7171 |
| AGPCNet [25] | 0.8186 | 0.7546 | 0.6465 | 0.7853 | 0.8868 |
| Ours | |||||
| APANet-P | 0.8364 | 0.8192 | 0.7060 | 0.8277 | 0.9147 |
| APANet-H | 0.8089 | 0.8192 | 0.6864 | 0.8140 | 0.9133 |
| APANet-rb-P | 0.8143 | 0.8231 | 0.6930 | 0.8187 | 0.9185 |
| APANet-rb-H | 0.8141 | 0.7863 | 0.6666 | 0.7999 | 0.9071 |
| Methods | Precision | Recall | mIoU | F-measure | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPCM [28] | 0.0392 | 0.6439 | 0.0383 | 0.0738 | 0.8168 |
| RLCM [29] | 0.0318 | 0.6970 | 0.0313 | 0.0608 | 0.8403 |
| FKRW [48] | 0.0135 | 0.3851 | 0.0132 | 0.0260 | 0.6815 |
| IPI [9] | 0.2880 | 0.6290 | 0.2462 | 0.3951 | 0.8139 |
| NRAM [49] | 0.4669 | 0.4082 | 0.2784 | 0.4356 | 0.7039 |
| PSTNN [11] | 0.4520 | 0.4719 | 0.3002 | 0.4617 | 0.7358 |
| ACM_FPN [24] | 0.5247 | 0.7092 | 0.4318 | 0.6032 | 0.8748 |
| ACM_UNet [24] | 0.5780 | 0.6551 | 0.4431 | 0.6141 | 0.8440 |
| VGG16-FAMCA-LSPM [21] | 0.5673 | 0.6281 | 0.4246 | 0.5961 | 0.7757 |
| AGPCNet [25] | 0.5820 | 0.7098 | 0.4701 | 0.6396 | 0.8554 |
| Ours | |||||
| APANet-P | 0.5771 | 0.6800 | 0.4538 | 0.6243 | 0.8221 |
| APANet-H | 0.5507 | 0.7104 | 0.4498 | 0.6205 | 0.8579 |
| APANet-rb-P | 0.6162 | 0.6772 | 0.4763 | 0.6453 | 0.8469 |
| APANet-rb-H | 0.5862 | 0.7088 | 0.4724 | 0.6417 | 0.8589 |
| Methods | mIoU | F-measure |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness of densely connected feature extraction | ||
| APANet-P_without_DCCS | 0.6444 | 0.7837 |
| Effectiveness of pair-wise asymmetric combination | ||
| APP-Net | 0.6464 | 0.7852 |
| ALP-Net | 0.6829 | 0.8116 |
| Effectiveness of recurrent asymmetric fusion | ||
| APANet-P_without_RAF | 0.6959 | 0.8207 |
| APANet-P_sum | 0.6865 | 0.8141 |
| Influence of the size of the local region in region-wise attention | ||
| APANet-P-6 | 0.6790 | 0.8088 |
| APANet-P-10 | 0.6749 | 0.8059 |
| APANet-P-12 | 0.6799 | 0.8095 |
| Ours | ||
| APANet-P | 0.7060 | 0.8277 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, G.; Dong, L.; Liang, J.; Xu, W. Novel Asymmetric Pyramid Aggregation Network for Infrared Dim and Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225643
Lv G, Dong L, Liang J, Xu W. Novel Asymmetric Pyramid Aggregation Network for Infrared Dim and Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225643
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Guangrui, Lili Dong, Junke Liang, and Wenhai Xu. 2022. "Novel Asymmetric Pyramid Aggregation Network for Infrared Dim and Small Target Detection" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225643
APA StyleLv, G., Dong, L., Liang, J., & Xu, W. (2022). Novel Asymmetric Pyramid Aggregation Network for Infrared Dim and Small Target Detection. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5643. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225643