DPAFNet: A Multistage Dense-Parallel Attention Fusion Network for Pansharpening
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Since the low-resolution spectral range of LRMS and the spatial details of PAN images are significantly different, it is difficult to adaptively fuse the spatial details of PAN to all bands of LRMS based on the spectral features. Therefore, it is still a great challenge for the network characterization capability to fully extract spectral and spatial information and fuse them;
- (2)
- In the encoder, existing networks do not jointly pay attention to spatial structure and spectral information, and single attention can easily cause a mismatch between spatial and spectral information;
- (3)
- Most networks simply perform single-level decoding in the image reconstruction phase and pay little attention to the loss of information in the extraction phase of features. Such sharpening results in spatial distortion and information distortion easily.
- An end-to-end pansharpening framework. We perform primary and deep feature extraction for PAN and LRMS images. In the deep feature extraction stage, we use parallel attention residual dense block (PARDB) for multi-level extraction, which can extract spatial details and spectral correlations over a wide spectral range. Additionally, PARDB solves the first challenge, which is to promote the representation capability of the network by multi-level feature extraction;
- A parallel attention residual dense block. We propose a parallel attention residual dense block (PARDB) in the encoder, which consists of a Dense Block and a Parallel attention fusion block (PAFB). The PAFB can effectively focus on spectral information and spatial information, and reduce redundancy. Note that the PAFB effectively distinguishes important and redundant information in the feature extraction phase and the fusion phase, solving the second challenge;
- A multi-stage reconstruction network. In the image reconstruction stage, we propose multi-stage reconstruction of residuals (MSRR) for multi-level decoding, meanwhile to supplement the information of image reconstruction. We join the encoded information with the decoded information to act as an information supplement. This effectively solves the third challenge.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Deep-Learning Based Methods
2.2.1. Network Backbone for Pansharpening
2.2.2. Attention Mechanism for Pansharpening
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Statement
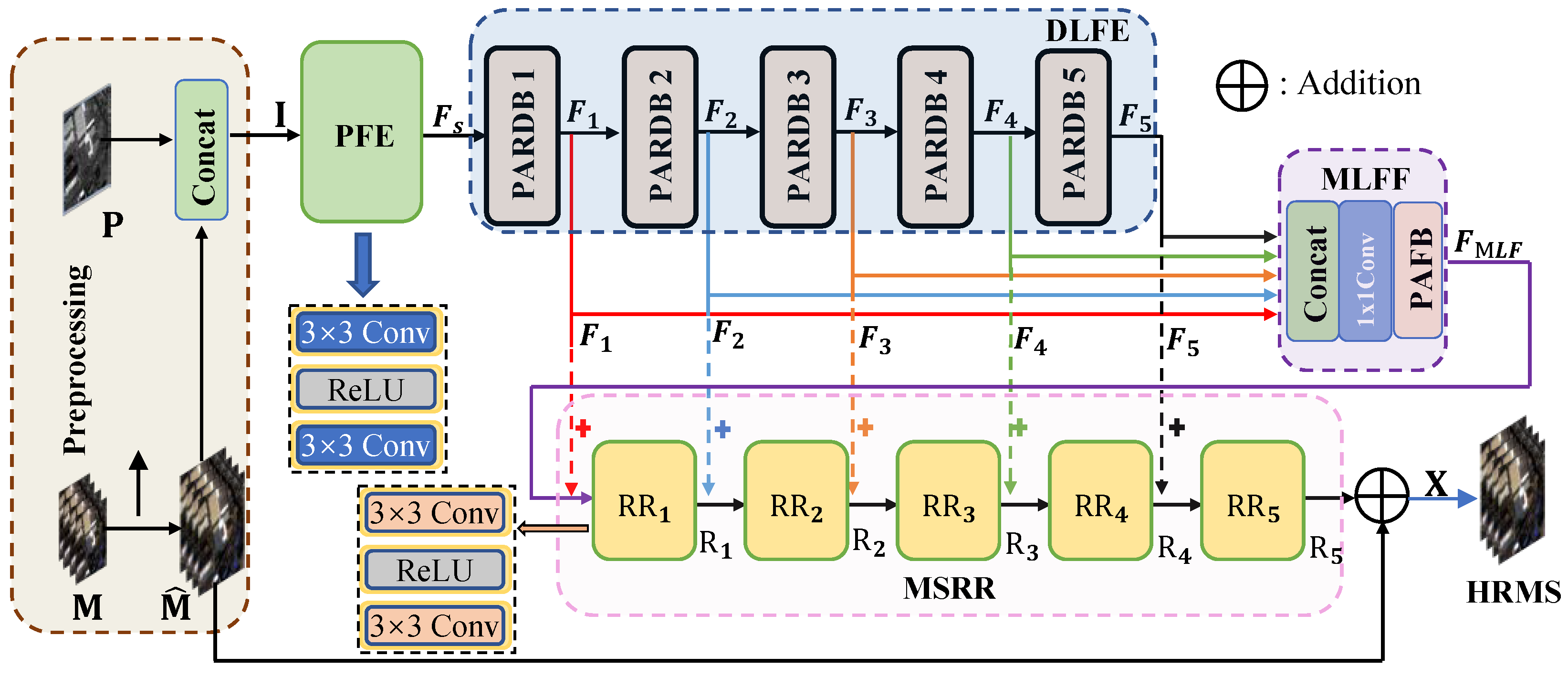
3.2. Network Framework
3.3. DLFE
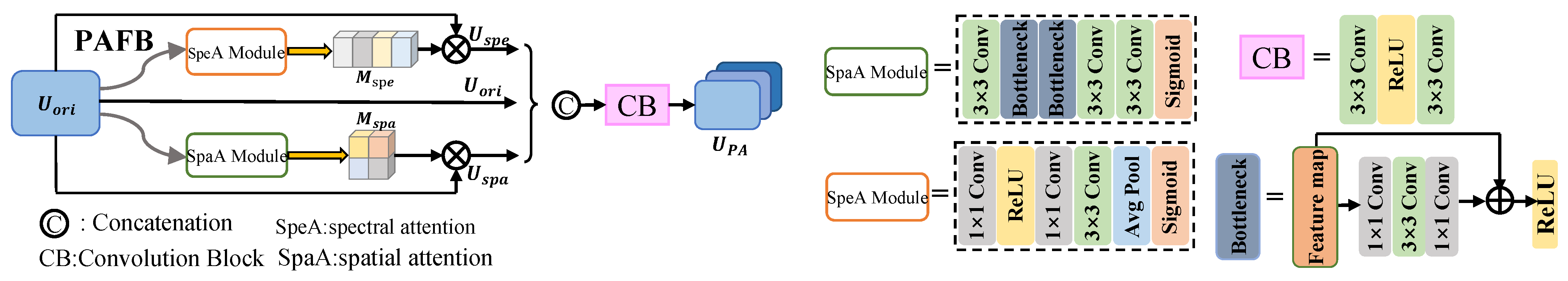
3.3.1. Spectral Attention Module
3.3.2. Spatial Attention Module
3.3.3. PAFB
3.3.4. PARDB
3.4. MLFF Module
3.5. MSRR Module
3.6. Loss Function
3.6.1. Reconstruction Loss
3.6.2. Spatial Loss
3.6.3. Spectral Loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Setup
4.2. Compared Methods
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
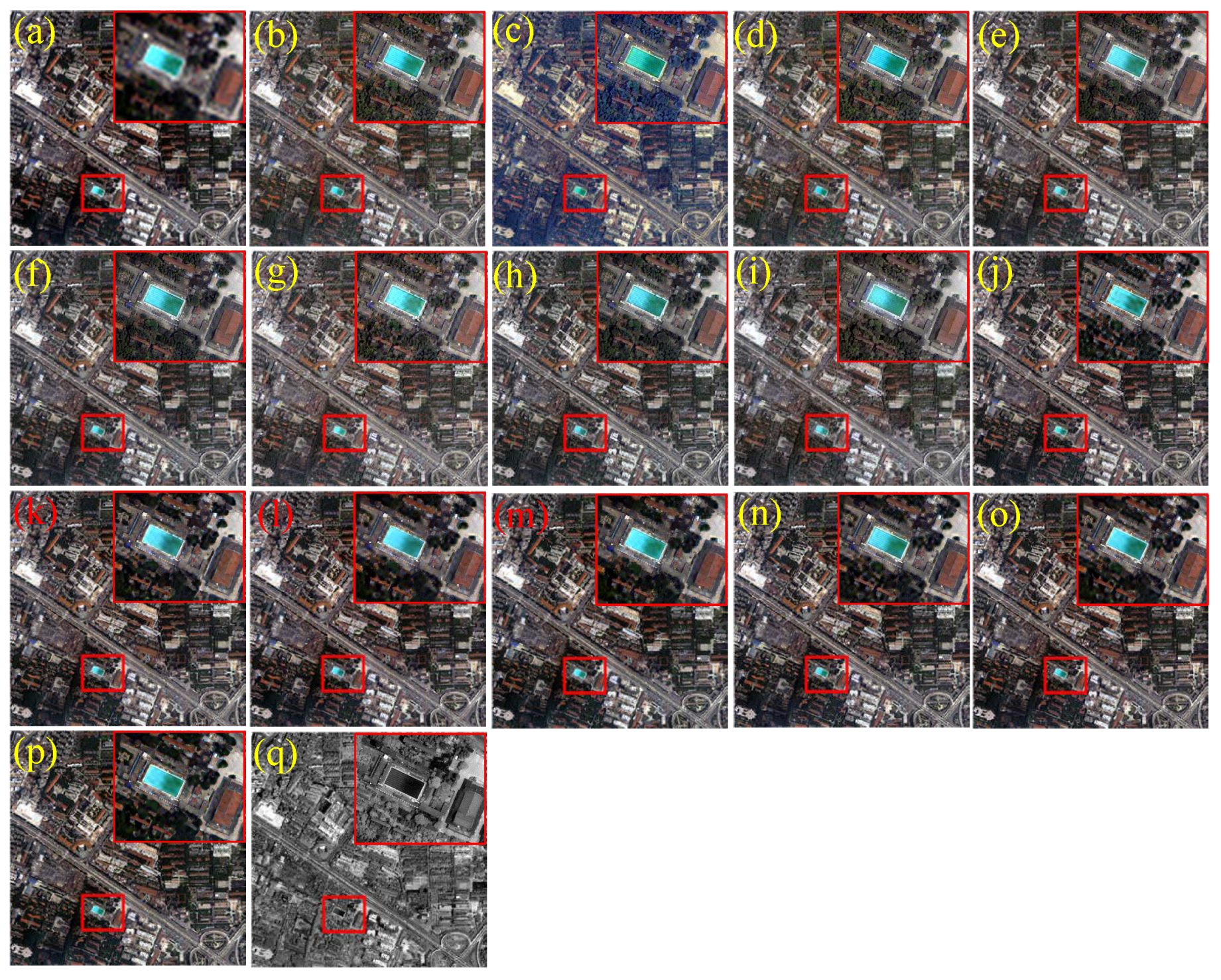
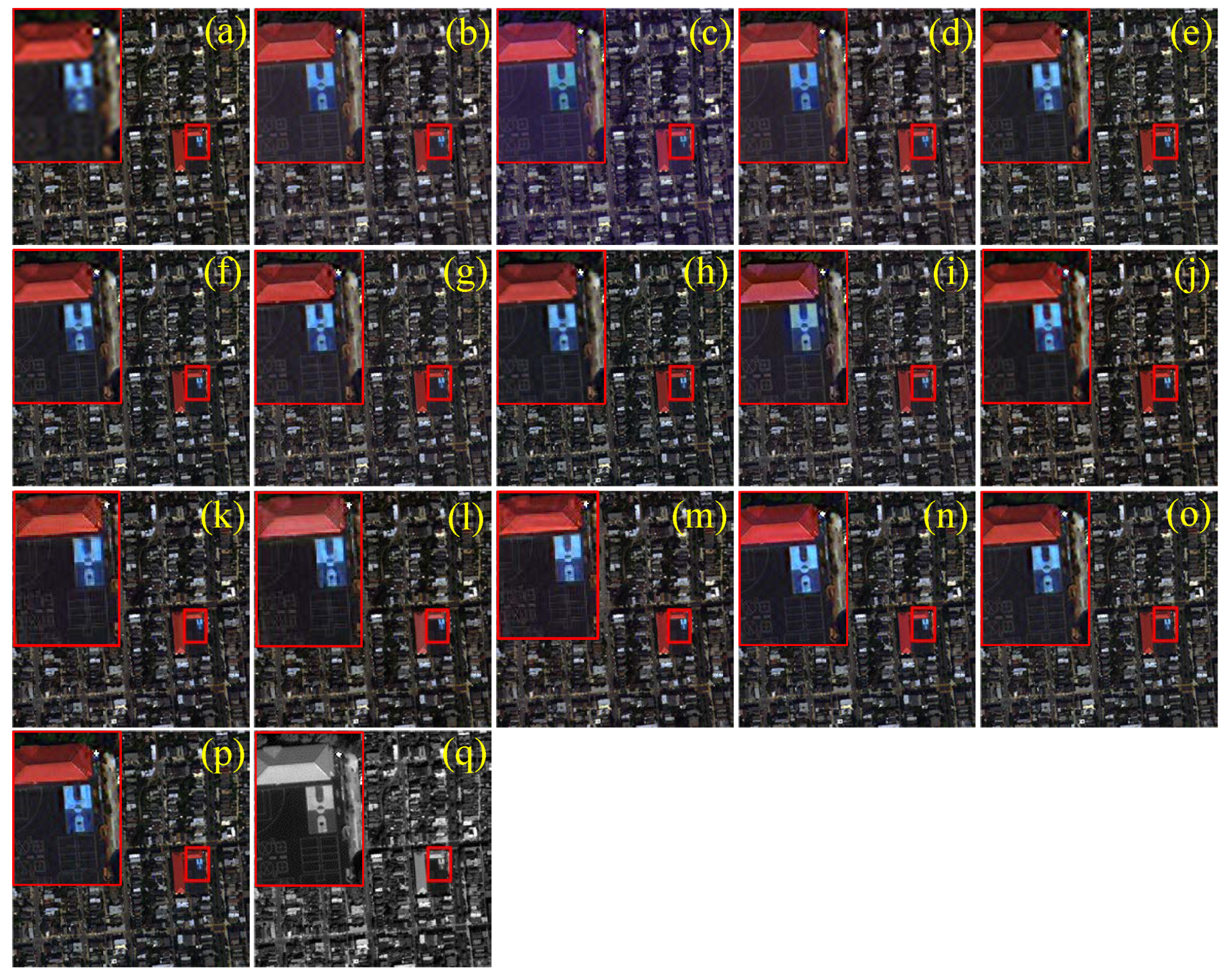
4.4. Visual and Quantitative Assessments
4.5. Parameter Analysis
4.6. Ablation Study
4.6.1. Ablation to Network
4.6.2. Ablation to Loss Function
4.7. Discussion of Spatial Loss
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Gong, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Lu, J.; Yu, D.; Lin, Y. Multi-Feature Information Complementary Detector: A High-Precision Object Detection Model for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Abd-Elrahman, A.; Whitaker, V.; Dalid, C. Prediction of Strawberry Dry Biomass from UAV Multispectral Imagery Using Multiple Machine Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Tateishi, R. Remote sensing and GIS for mapping and monitoring land cover and land-use changes in the Northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Appl. Geogr. 2007, 27, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Thermal infrared remote sensing for urban climate and environmental studies: Methods, applications, and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Understanding image fusion. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens 2004, 70, 657–661. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; So, H.K.H.; Lam, E.Y. Fringe pattern improvement and super-resolution using deep learning in digital holography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 6179–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Zeng, T.; Lam, E.Y. Spatial and angular reconstruction of light field based on deep generative networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 4659–4663. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Nie, R.; Cao, J. SSL-WAEIE: Self-Supervised Learning with Weighted Auto-Encoding and Information Exchange for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.X.; Pan, X.M.; Wang, C.; Shen, H.Z.; Deng, L.J. Spatial and Spectral-Channel Attention Network for Denoising on Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. Convolutional sparse and low-rank coding-based rain streak removal. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 24–31 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1259–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Scarpa, G. Pansharpening by convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.R.; Deng, L.J.; Zhang, T.J.; Jin, X.X. BAM: Bilateral Activation Mechanism for Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 4315–4323. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Liao, W.; Philips, W. MC-JAFN: Multilevel Contexts-Based Joint Attentive Fusion Network for Pansharpening. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhou, S.; Feng, Y.; Xie, J. Pansharpening via unsupervised convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 4295–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.H.; Seo, D.; Jeong, J.; Kim, M. UPSNet: Unsupervised pan-sharpening network with registration learning between panchromatic and multi-spectral images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 201199–201217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotola, M.; Vitale, S.; Mazza, A.; Poggi, G.; Scarpa, G. Pansharpening by convolutional neural networks in the full resolution framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Fei, R.; Xu, S. PercepPan: Towards unsupervised pan-sharpening based on perceptual loss. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. PGMAN: An unsupervised generative multiadversarial network for pansharpening. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6316–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.; Sides, S.C.; Anderson, J.A. Comparison of three different methods to merge multiresolution and multispectral data- Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1991, 57, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, T.M.; Su, S.C.; Shyu, H.C.; Huang, P.S. A new look at IHS-like image fusion methods. Inf. Fusion 2001, 2, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laben, C.A.; Brower, B.V. Process for Enhancing the Spatial Resolution of Multispectral Imagery Using Pan-Sharpening. U.S. Patent 6,011,875, 4 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Smoothing filter-based intensity modulation: A spectral preserve image fusion technique for improving spatial details. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3461–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, L.; Ranchin, T. Liu ‘Smoothing filter-based intensity modulation: A spectral preserve image fusion technique for improving spatial details’. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Restaino, R.; Dalla Mura, M.; Licciardi, G.; Chanussot, J. Contrast and error-based fusion schemes for multispectral image pansharpening. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 11, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Chanussot, J.; Condat, L.; Montanvert, A. Indusion: Fusion of multispectral and panchromatic images using the induction scaling technique. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2008, 5, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiazzi, B.; Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A. Context-driven fusion of high spatial and spectral resolution images based on oversampled multiresolution analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2300–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Grohnfeldt, C.; Bamler, R. Exploiting joint sparsity for pansharpening: The J-SparseFI algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 2664–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xiao, L.; Li, T. A variational pan-sharpening method based on spatial fractional-order geometry and spectral–spatial low-rank priors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 1788–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Simões, M.; Dalla Mura, M.; Restaino, R.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Licciardi, G.A.; Chanussot, J. Pansharpening based on semiblind deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1997–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson, F.; Sveinsson, J.R.; Ulfarsson, M.O.; Benediktsson, J.A. Model-based fusion of multi-and hyperspectral images using PCA and wavelets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, L.; Ranchin, T.; Mangolini, M. Fusion of satellite images of different spatial resolutions: Assessing the quality of resulting images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 691–699. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, M.; Ou, Y. Pan-sharpening using an efficient bidirectional pyramid network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5549–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, W. Multibranch feature extraction and feature multiplexing network for pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.; Lam, E.Y. Multistage dual-attention guided fusion network for hyperspectral pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Qian, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Wan, Y.; Gao, L.; Qian, J.; Liu, J. Attention_FPNet: Two-branch remote sensing image pansharpening network based on attention feature fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11879–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv Preprint 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Wang, N.; Shao, F.; Li, S. Vision Transformer for Pansharpening. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J.; Dalla Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Licciardi, G.A.; Restaino, R.; Wald, L. A critical comparison among pansharpening algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncan, L.; De Almeida, L.B.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Briottet, X.; Chanussot, J.; Dobigeon, N.; Fabre, S.; Liao, W.; Licciardi, G.A.; Simoes, M.; et al. Hyperspectral pansharpening: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Deng, C.; Zhao, B.; Chanussot, J. Feature-Level Loss for Multispectral Pan-Sharpening with Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 8062–8065. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhas, R.H.; Goetz, A.F.; Boardman, J.W. Discrimination among semi-arid landscape endmembers using the spectral angle mapper (SAM) algorithm. In Proceedings of the JPL, Summaries of the Third Annual JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 1–5 June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Alparone, L.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. A global quality measurement of pan-sharpened multispectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F. Hypercomplex quality assessment of multi/hyperspectral images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Civco, D.L.; Silander, J. A wavelet transform method to merge Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 743–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C. A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Wald, L.; Chanussot, J.; Thomas, C.; Gamba, P.; Bruce, L.M. Comparison of pansharpening algorithms: Outcome of the 2006 GRS-S data-fusion contest. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparone, L.; Aiazzi, B.; Baronti, S.; Garzelli, A.; Nencini, F.; Selva, M. Multispectral and panchromatic data fusion assessment without reference. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2008, 74, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X. SDPNet: A deep network for pan-sharpening with enhanced information representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4120–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sensor | Band | MS | PAN | Radiometric | Scaling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IKONOS | 4 | 4 m | 1 m | 11 bits | 4 |
| WV-2 | 8 | 2 m | 0.5 m | 11 bits | 4 |
| Q4 | Q | SAM | ERGAS | SCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| EXP | 0.6103 | 0.6121 | 3.4047 | 3.3219 | 0.6670 |
| PCA | 0.7604 | 0.7419 | 3.6551 | 2.6815 | 0.8711 |
| IHS | 0.7286 | 0.7425 | 3.4511 | 2.5583 | 0.8828 |
| GS | 0.7688 | 0.7765 | 3.2024 | 2.4349 | 0.9055 |
| PRACS | 0.8109 | 0.8088 | 2.9041 | 2.1432 | 0.9057 |
| HPF | 0.8237 | 0.8238 | 2.9118 | 2.0690 | 0.9110 |
| SFIM | 0.8274 | 0.8275 | 2.8673 | 2.0303 | 0.9152 |
| Indusion | 0.7676 | 0.7748 | 3.1378 | 2.5851 | 0.8718 |
| FE-HPM | 0.8471 | 0.8464 | 2.7843 | 1.8539 | 0.9248 |
| PWMBF | 0.7934 | 0.7884 | 3.1957 | 2.1778 | 0.9108 |
| PNN | 0.8741 | 0.8781 | 2.2769 | 1.5588 | 0.9453 |
| DRPNN | 0.9179 | 0.9210 | 1.5225 | 2.1977 | 0.9518 |
| PercepPan | 0.8994 | 0.9036 | 1.6896 | 2.4813 | 0.9416 |
| PGMAN | 0.9046 | 0.9073 | 1.6433 | 2.3442 | 0.9450 |
| BAM | 0.9040 | 0.9058 | 2.3844 | 1.6073 | 0.9439 |
| MC-JAFN | 0.9215 | 0.9230 | 2.1657 | 1.4942 | 0.9527 |
| Ours | 0.9320 | 0.9331 | 1.9569 | 1.3916 | 0.9595 |
| Q8 | Q | SAM | ERGAS | SCC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| EXP | 0.6074 | 0.6113 | 7.9286 | 8.7566 | 0.5099 |
| PCA | 0.8228 | 0.8226 | 7.4781 | 6.1551 | 0.9127 |
| IHS | 0.8251 | 0.8195 | 8.0139 | 6.2805 | 0.8944 |
| GS | 0.8223 | 0.8224 | 7.4535 | 6.1614 | 0.9136 |
| HPF | 0.8631 | 0.8617 | 7.0718 | 5.5755 | 0.9069 |
| SFIM | 0.8651 | 0.8637 | 7.1246 | 5.5025 | 0.9097 |
| Indusion | 0.8214 | 0.8214 | 7.3738 | 6.4526 | 0.8600 |
| FE-HPM | 0.8929 | 0.8906 | 6.9836 | 5.0537 | 0.9098 |
| PWMBF | 0.8963 | 0.8894 | 7.3735 | 5.0706 | 0.9176 |
| PNN | 0.9251 | 0.9256 | 5.8696 | 4.2395 | 0.9372 |
| DRPNN | 0.9566 | 0.9583 | 3.3716 | 5.2837 | 0.9610 |
| PercepPan | 0.9575 | 0.9586 | 3.3543 | 5.1202 | 0.9606 |
| PGMAN | 0.9603 | 0.9614 | 3.2299 | 4.9735 | 0.9638 |
| BAM | 0.9599 | 0.9605 | 5.0647 | 3.2334 | 0.9630 |
| MC-JAFN | 0.9629 | 0.9636 | 4.8988 | 3.1057 | 0.9664 |
| Ours | 0.9662 | 0.9670 | 4.6440 | 2.9638 | 0.9699 |
| Dataset | IKONOS | WorldView-2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | QNR | QNR | ||||
| Reference | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| EXP | 0.0000 | 0.0973 | 0.9027 | 0.0000 | 0.0630 | 0.9370 |
| PCA | 0.0785 | 0.1775 | 0.7666 | 0.0196 | 0.1057 | 0.8768 |
| IHS | 0.1294 | 0.2311 | 0.6808 | 0.0231 | 0.1005 | 0.8787 |
| GS | 0.0802 | 0.1879 | 0.7537 | 0.0193 | 0.1040 | 0.8787 |
| HPF | 0.1224 | 0.1832 | 0.7245 | 0.0475 | 0.0882 | 0.8686 |
| SFIM | 0.1212 | 0.1798 | 0.7285 | 0.0444 | 0.0856 | 0.8738 |
| Indusion | 0.1069 | 0.1504 | 0.7663 | 0.0335 | 0.0795 | 0.8897 |
| FE-HPM | 0.1386 | 0.1935 | 0.7035 | 0.0607 | 0.1079 | 0.8381 |
| PWMBF | 0.1628 | 0.2236 | 0.6575 | 0.0958 | 0.1461 | 0.7724 |
| PNN | 0.0737 | 0.1064 | 0.8395 | 0.0564 | 0.0728 | 0.8749 |
| DRPNN | 0.0499 | 0.0984 | 0.8608 | 0.0394 | 0.0882 | 0.8758 |
| PercepPan | 0.0366 | 0.0961 | 0.8742 | 0.0324 | 0.0955 | 0.8752 |
| PGMAN | 0.0388 | 0.1049 | 0.8648 | 0.0228 | 0.0934 | 0.8860 |
| BAM | 0.0348 | 0.0820 | 0.8865 | 0.0251 | 0.0939 | 0.8833 |
| MC-JAFN | 0.0294 | 0.0741 | 0.8987 | 0.0390 | 0.0748 | 0.8891 |
| Ours | 0.0299 | 0.0713 | 0.9009 | 0.0253 | 0.0759 | 0.9007 |
| Parameter | Metrics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q4 | Q | SAM | ERGAS | SCC | ||
| 0.01 | 0.9312 | 0.9322 | 1.9747 | 1.4045 | 0.9589 | |
| 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.9320 | 0.9333 | 1.9576 | 1.3917 | 0.9595 |
| 0.05 | 0.9326 | 0.9336 | 1.9619 | 1.3993 | 0.9595 | |
| 0.01 | 0.9307 | 0.9317 | 1.9779 | 1.4034 | 0.9587 | |
| 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.9320 | 0.9331 | 1.9569 | 1.3916 | 0.9595 |
| 0.05 | 0.9319 | 0.9329 | 1.9613 | 1.3996 | 0.9593 | |
| 0.01 | 0.9320 | 0.9330 | 1.9562 | 1.3934 | 0.9594 | |
| 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.9313 | 0.9324 | 1.9685 | 1.4016 | 0.9592 |
| 0.05 | 0.9319 | 0.9330 | 1.9544 | 1.3957 | 0.9593 | |
| Ablation | Metrics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skip | SpectralA | SpatialA | Q4 | Q | SAM | ERGAS | SCC |
| ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 0.9263 | 0.9269 | 2.0581 | 1.4541 | 0.9553 |
| ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.9280 | 0.9289 | 2.0361 | 1.4402 | 0.9563 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 0.9283 | 0.9290 | 2.0231 | 1.4339 | 0.9569 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 0.9307 | 0.9317 | 1.9709 | 1.4100 | 0.9586 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 0.9309 | 0.9323 | 2.0277 | 1.4383 | 0.9568 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.9320 | 0.9331 | 1.9569 | 1.3916 | 0.9595 |
| Q4 | Q | SAM | ERGAS | SCC | |||
| ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 0.9313 | 0.9323 | 1.9838 | 1.4069 | 0.9589 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 0.9319 | 0.9331 | 1.9580 | 1.3942 | 0.9594 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 0.9315 | 0.9330 | 1.9572 | 1.3927 | 0.9594 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.9320 | 0.9331 | 1.9569 | 1.3916 | 0.9595 |
| Spatial Loss | Q4 | Q | SAM | ERGAS | SCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9320 | 0.9331 | 1.9569 | 1.3916 | 0.9595 | |
| 0.9342 | 0.9357 | 1.9791 | 1.4089 | 0.9588 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Nie, R.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Li, H. DPAFNet: A Multistage Dense-Parallel Attention Fusion Network for Pansharpening. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215539
Yang X, Nie R, Zhang G, Chen L, Li H. DPAFNet: A Multistage Dense-Parallel Attention Fusion Network for Pansharpening. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215539
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaofei, Rencan Nie, Gucheng Zhang, Luping Chen, and He Li. 2022. "DPAFNet: A Multistage Dense-Parallel Attention Fusion Network for Pansharpening" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215539
APA StyleYang, X., Nie, R., Zhang, G., Chen, L., & Li, H. (2022). DPAFNet: A Multistage Dense-Parallel Attention Fusion Network for Pansharpening. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215539







