Dynamic Modelling of Water and Wind Erosion in Australia over the Past Two Decades
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Estimates of Water Erosion Using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)
2.2.1. Rainfall Erosivity (R) Factor
2.2.2. Cover-Management (C) Factor
2.2.3. Slope-Steepness (LS) Factor
2.2.4. Soil Erodibility (K) Factor
2.3. Estimates of Wind Erosion by the Revised Wind Erosion Equation (RWEQ)
2.4. DustWatch PM10 Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Assessment and Comparison of Three Satellite Precipitation Products in Rainfall Erosivity
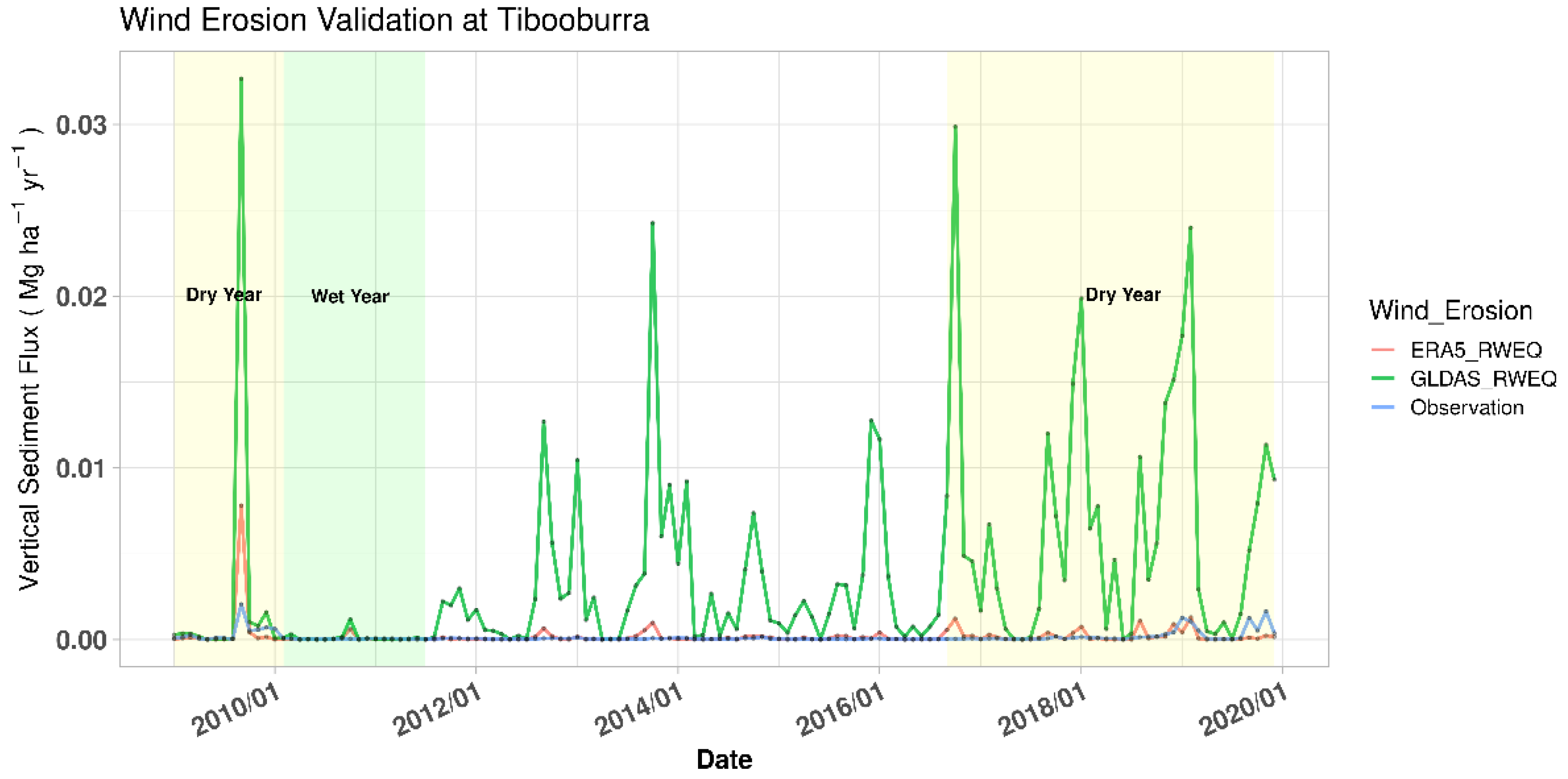
3.2. Validation of Wind Erosion Rates with In Situ Observations
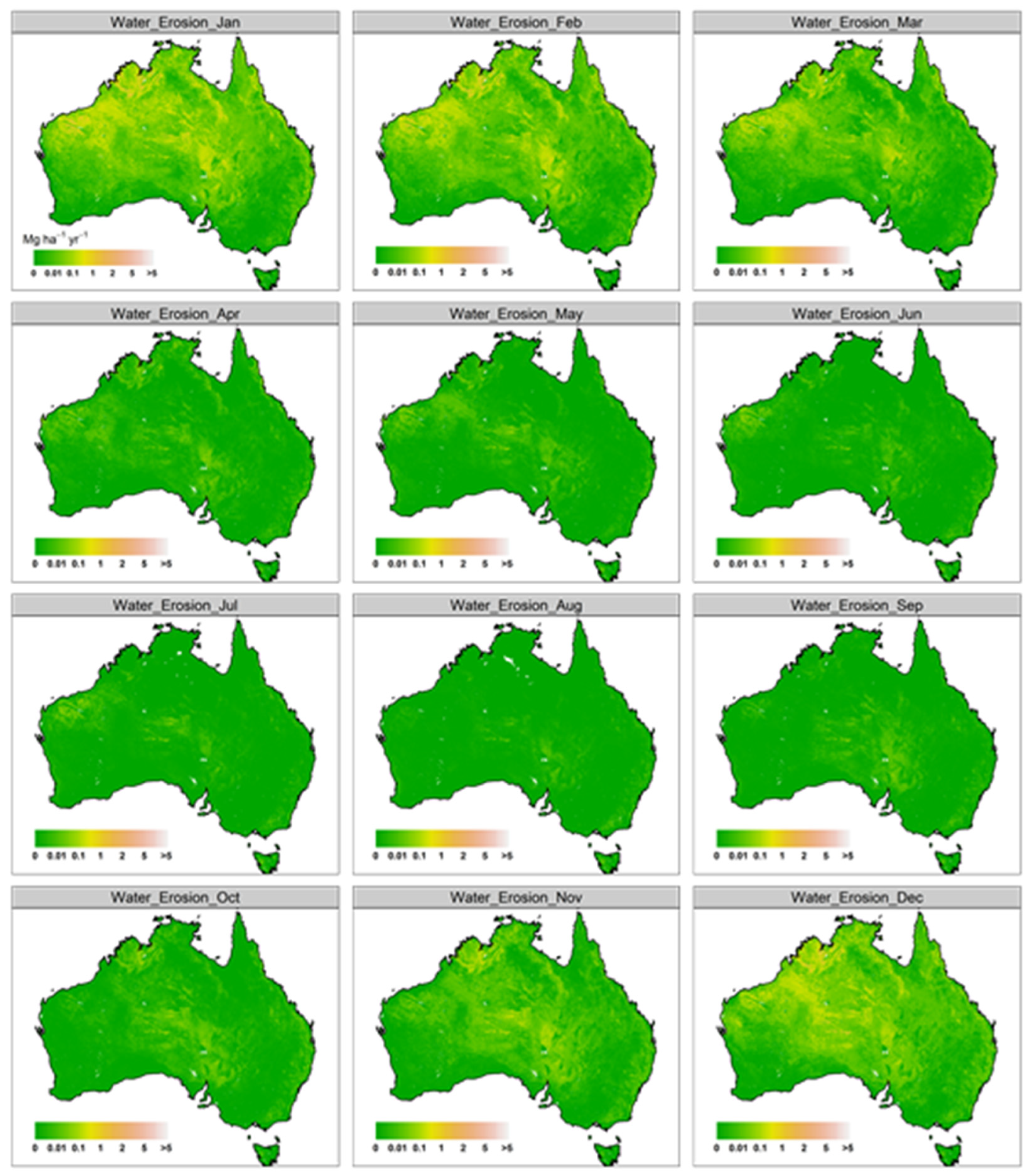
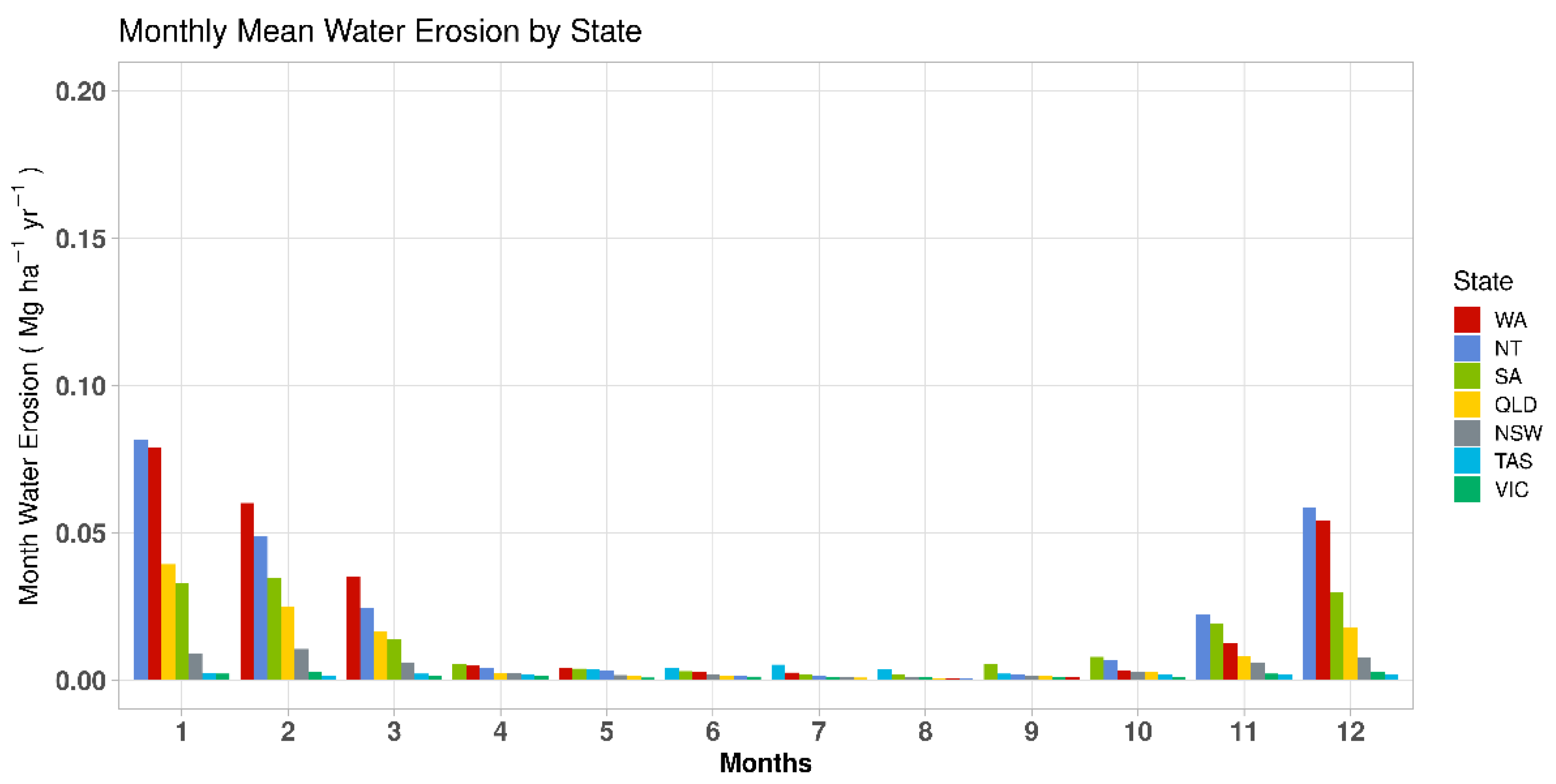
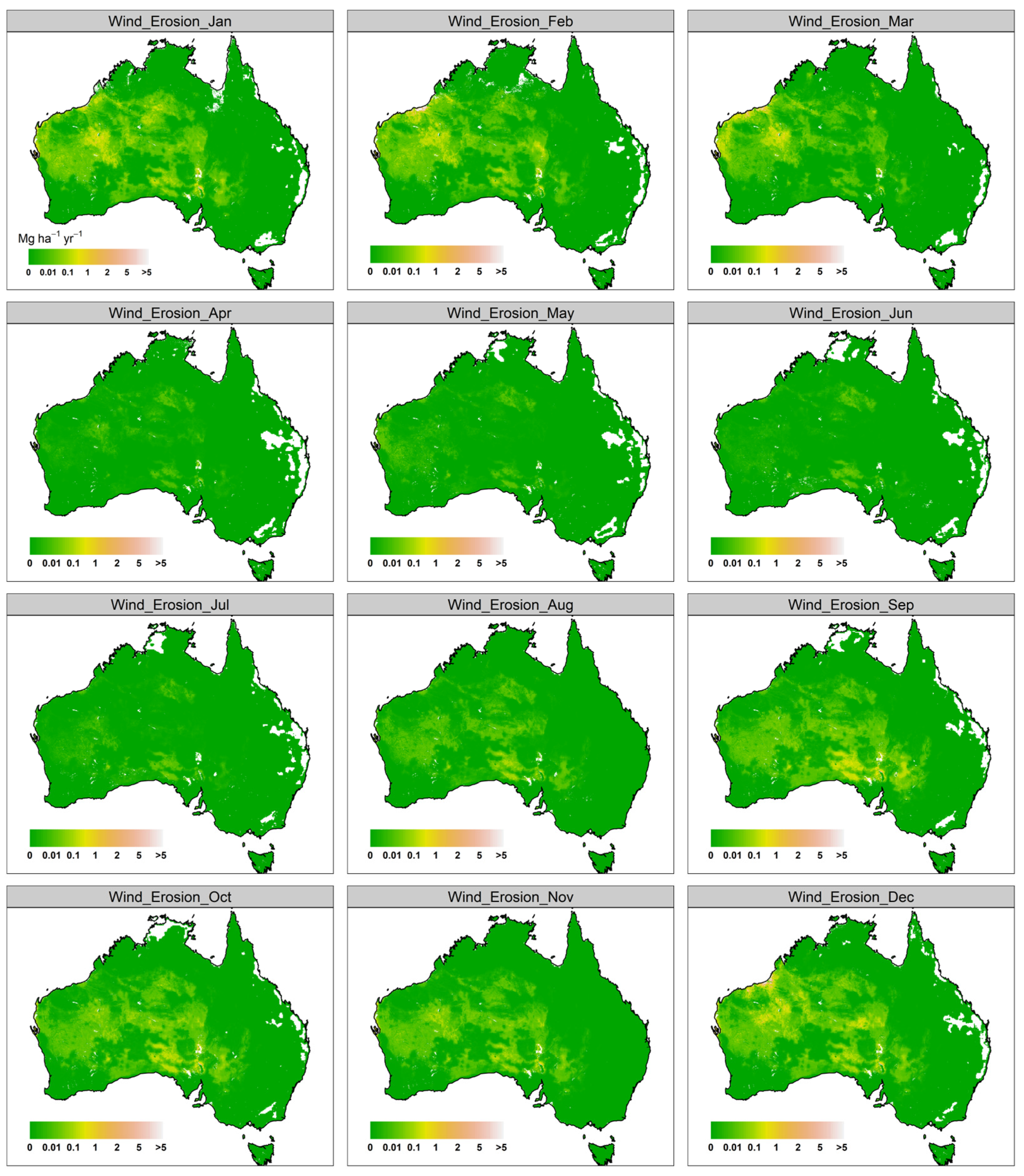
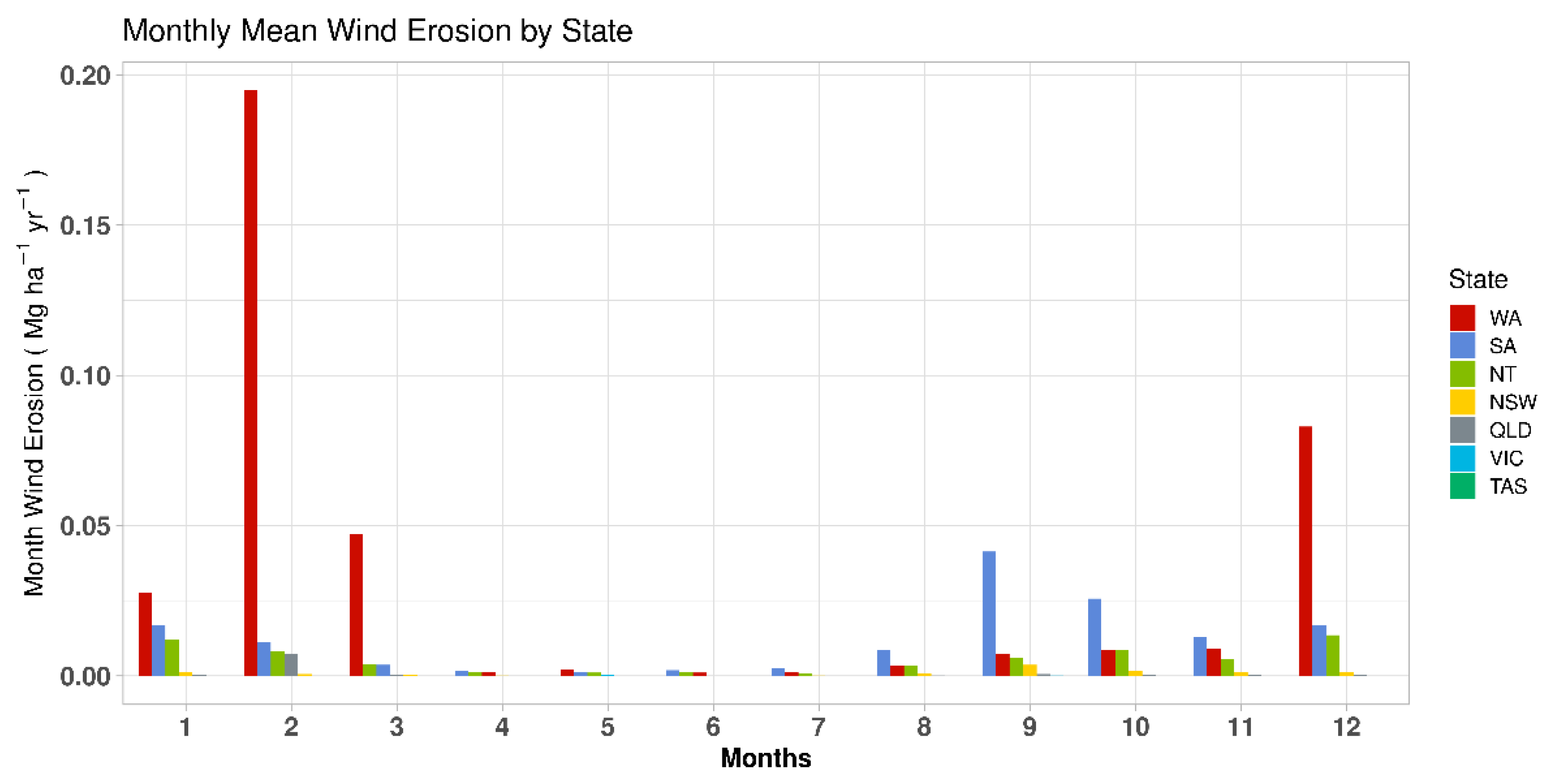
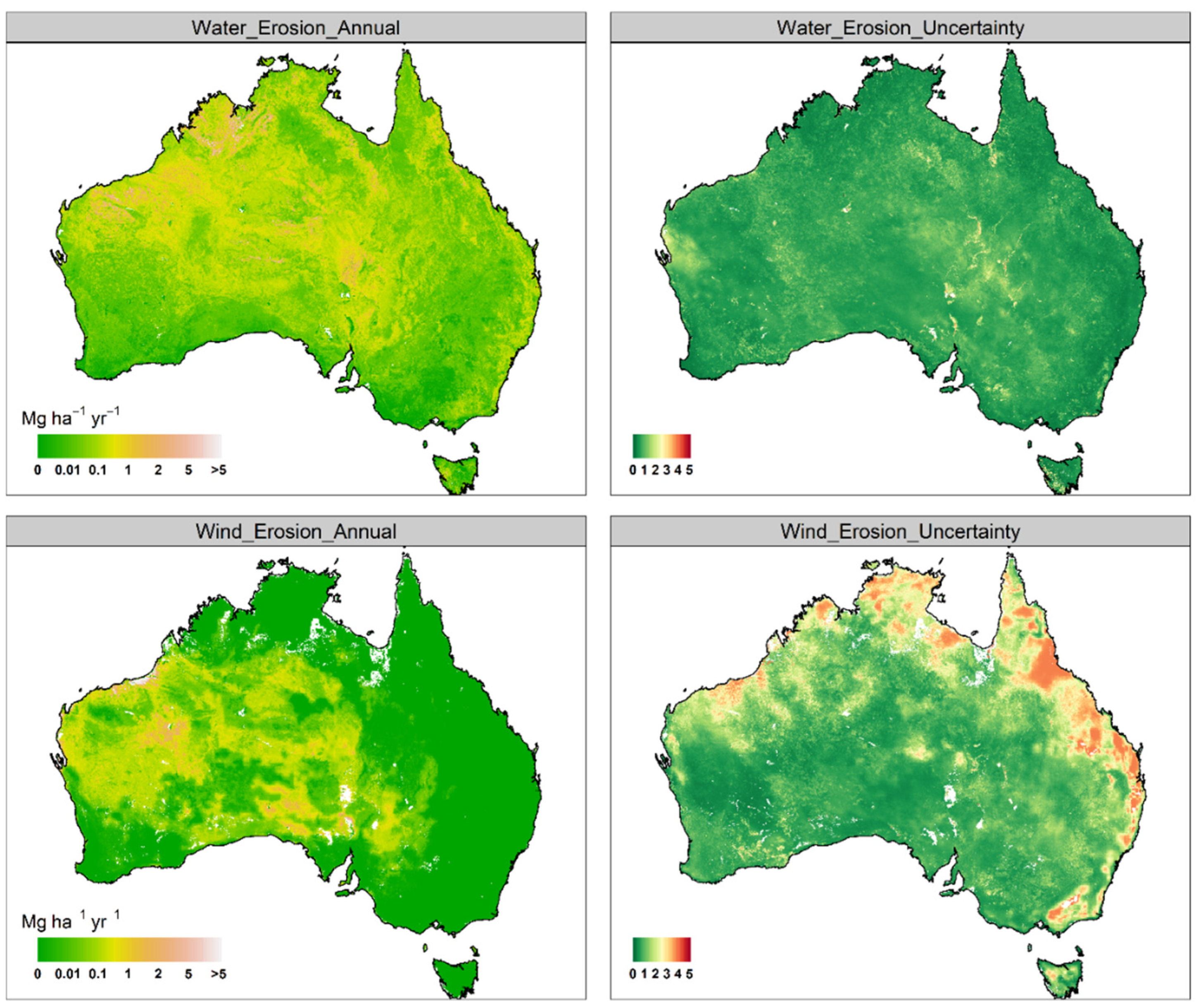
3.3. Monthly and Annually Wind–Water Erosion Maps
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)–Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Telles, T.S.; Dechen, S.C.F.; de Souza, L.G.A.; Guimarães, M.D.F. Valuation and assessment of soil erosion costs. Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faeth, P. Building the Case for Sustainable Agriculture: Policy Lessons from India, Chile, and Chile, and the Philippines. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 1994, 36, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P.; Leys, J.F.; Waters, C.M.; Orgill, S.; Eyres, M.J. Minimising soil organic carbon erosion by wind is critical for land degradation neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N. Variability and Trends in Dust Storm Frequency on Decadal Timescales: Climatic Drivers and Human Impacts. Geosciences 2019, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, E.; Hancock, G.; Chappell, A.; Gregory, L. Evaluation of Tolerable Erosion Rates and Time to Critical Topsoil Loss in Australia; CSIRO Land and Water: Canberra, Australia, 2010; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, A.; Hancock, G.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Loughran, R. Spatial uncertainty of the137Cs reference inventory for Australian soil. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, F04014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Oliveira, L.; Ollivier, Q.R.; Faulkner, S.; Roff, A. Rapid Assessment of Hillslope Erosion Risk after the 2019–2020 Wildfires and Storm Events in Sydney Drinking Water Catchment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, J.F.; Heidenreich, S.K.; Strong, C.L.; McTainsh, G.H.; Quigley, S. PM10 concentrations and mass transport during “Red Dawn”–Sydney 23 September 2009. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Panagos, P.; Gitas, I.Z. A classification of water erosion models according to their geospatial characteristics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.; Reudenbach, C.; Hengl, T.; Katurji, M.; Nauss, T. Improving performance of spatio-temporal machine learning models using forward feature selection and target-oriented validation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 101, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflen, J.M.; Elliot, W.; Flanagan, D.; Meyer, C.; Nearing, M. WEPP-predicting water erosion using a process-based model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1997, 52, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Rose, C. Application of a physically based soil erosion model, GUEST, in the absence of data on runoff rates I. Theory and methodology. Soil Res. 1999, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Tahmasebipour, N.; Haghizadeh, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Feizizadeh, B. Evaluation of different machine learning models for predicting and mapping the susceptibility of gully erosion. Geomorphology 2017, 298, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryrear, D.; Bilbro, J.; Saleh, A.; Schomberg, H.; Stout, J.; Zobeck, T. RWEQ: Improved wind erosion technology. The wind erosion prediction system and its use in conservation planning. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P. Using albedo to reform wind erosion modelling, mapping and monitoring. Aeolian Res. 2016, 23, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarko, J.; Wagner, L.; Fox, F. The wind erosion prediction system and its use in conservation planning. Wind. Eros. Predict. Syst. Its Use Conserv. Plan. 2019, 8, 71–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, J.F.; Mahowald, N.M.; Fratini, G.; Gillies, J.A.; Ishizuka, M.; Leys, J.F.; Mikami, M.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.U.; van Pelt, R.S.; et al. An improved dust emission model–Part 1: Model description and comparison against measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13023–13041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P.; Guerschman, J.P.; Thomas, D.T.; Mata, G.; Handcock, R.N.; Leys, J.F.; Butler, H.J. Improving ground cover monitoring for wind erosion assessment using MODIS BRDF parameters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, F.; Visser, S.; Karssenberg, D.; Bruggeman, A.; Erpul, G. Calibration of RWEQ in a patchy landscape; a first step towards a regional scale wind erosion model. Aeolian Res. 2012, 3, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. A New Assessment of Soil Loss Due to Wind Erosion in European Agricultural Soils Using a Quantitative Spatially Distributed Modelling Approach. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, H.; Sharratt, B.; Feng, G.; Lei, J. Evaluation of two empirical wind erosion models in arid and semi-arid regions of China and the USA. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 91, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Rossel, R.V.; Shi, Z.; Behrens, T.; Chappell, A.; Bui, E. Assimilating satellite imagery and visible–near infrared spectroscopy to model and map soil loss by water erosion in Australia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 77, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, N.; Hairsine, P.; Gregory, L.; Austin, J.; Baldock, J.; Webb, M.; Mewett, J.; Cresswell, H.; Welti, N.; Thomas, M. Priorities for Improving Soil Condition across Australia's Agricultural Landscapes; CSIRO Agriculture and Food: Canberra, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. State and trends of hillslope erosion across New South Wales, Australia. CATENA 2020, 186, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiqul Islam, M.; Yu, B.; Cartwright, N. Assessment and comparison of five satellite precipitation products in Australia. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D. Model-based assessment soil loss by wind and water erosion in China's Loess Plateau: Dynamic change, conservation effectiveness, and strategies for sustainable restoration. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 172, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.-J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Quarterly J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Hill, M.J. Calibration and validation of the Australian fractional cover product for MODIS collection 6. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Chen, C.; Grundy, M.J.; Searle, R.; Clifford, D.; Campbell, P.H. The Australian three-dimensional soil grid: Australia’s contribution to the GlobalSoilMap project. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 845–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, B. Modelling and mapping rainfall erosivity in New South Wales, Australia. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Foster, G. Storm erosivity using idealized intensity distributions. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 379–0386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Yu, B.; Tulau, M.; McInnes-Clarke, S.; Nolan, R.H.; Du, Z.; Yu, Q. Estimation of event-based rainfall erosivity from radar after wildfire. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Deriving RUSLE cover factor from time-series fractional vegetation cover for hillslope erosion modelling in New South Wales. Soil Res. 2014, 52, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Digital mapping of RUSLE slope length and steepness factor across New South Wales, Australia. Soil Res. 2015, 53, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, N.; Jacquier, D.; Ashton, L.; Cresswell, H. Estimation of Soil Properties Using the Atlas of Australian Soils, in CSIRO Land Water Technical Report; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2000; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Leys, J.; Strong, C.; Heidenreich, S.; Koen, T. Where She Blows! A Ten Year Dust Climatology of Western New South Wales Australia. Geosciences 2018, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Q. Effects of DEM resolutions on LS and hillslope erosion estimation in a burnt landscape. Soil Res. 2019, 57, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Prosser, I.P.; Moran, C.J.; Gallant, J.C.; Priestley, G.; Stevenson, J.G. Predicting sheetwash and rill erosion over the Australian continent. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 1037–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. CATENA 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.-q.; Xue, X.; Wang, T. Mapping the risk of water erosion in the watershed of the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Teng, J.; Ji, F.; Anwar, M.R.; Feng, P.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Waters, C. Characterizing spatiotemporal rainfall changes in 1960–2019 for continental Australia. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 41, 2420–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Sun, R.; Jing, Y.; Xiong, M.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Global assessment of wind erosion based on a spatially distributed RWEQ model. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2021, 46, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, N.P.; McGowan, H.A.; Phinn, S.R.; Leys, J.F.; McTainsh, G.H. A model to predict land susceptibility to wind erosion in western Queensland, Australia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Description | Spatial Resolution | Time Period | Data Portal | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SILO | Scientific Information for LandOwner’s climate database | 5 km | 1920–2020, daily | GEE | RUSLE |
| DEM | Australian SRTM Hydrologically Enforced Digital Elevation Model | 30 m | 2010 | GEE | RUSLE/RWEQ |
| FVC | Fractional Vegetation Cover | 500 m | 2000–2020, daily | CSIRO | RUSLE/RWEQ |
| GPM | Global Precipitation Measurement | 10 km | 3 h | GEE | RUSLE |
| TRMM | The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission | 25 km | 3 h | GEE | RUSLE |
| SLGA | Soil and Landscape Grid of Australia | 90 m | - | GEE | RUSLE/RWEQ |
| GLDAS | Global Land Data Assimilation System | 25 km | 3 h | GEE | RWEQ |
| ERA5 | ECMWF Reanalysis 5 (ERA5) atmospheric reanalysis | 25 km | 3 h | GEE | RWEQ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Zhu, Q.; Leys, J.; Gray, J.M.; Yu, Q.; Yang, X. Dynamic Modelling of Water and Wind Erosion in Australia over the Past Two Decades. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215437
Zhang M, Viscarra Rossel RA, Zhu Q, Leys J, Gray JM, Yu Q, Yang X. Dynamic Modelling of Water and Wind Erosion in Australia over the Past Two Decades. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215437
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Mingxi, Raphael A. Viscarra Rossel, Qinggaozi Zhu, John Leys, Jonathan M. Gray, Qiang Yu, and Xihua Yang. 2022. "Dynamic Modelling of Water and Wind Erosion in Australia over the Past Two Decades" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215437
APA StyleZhang, M., Viscarra Rossel, R. A., Zhu, Q., Leys, J., Gray, J. M., Yu, Q., & Yang, X. (2022). Dynamic Modelling of Water and Wind Erosion in Australia over the Past Two Decades. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5437. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215437







