Abstract
Remote sensing object detection plays a major role in satellite imaging and is required in various scenarios such as transportation, forestry, and the ocean. Deep learning techniques provide efficient performance in remote sensing object detection. The existing techniques have the limitations of data imbalance, overfitting, and lower efficiency in detecting small objects. This research proposes the spiral search grasshopper (SSG) optimization technique to increase the exploitation in feature selection. Augmentation is applied in input images to generate more images, and this helps to train the model and reduces data imbalance problems. The VGG-19 and ResNet50 model is applied for feature extraction, and this helps to extract deep features to represent objects. The SSG feature selection technique increases the exploitation and select unique features for object detection that helps to overcome the data imbalance and overfitting problem. The SSG feature selection model helps to balance the exploration and exploitation that escape from the local optima trap. The SSG model has 82.45% mAP, the SSD model has 52.6% mAP, and the MPFP-Net model has 80.43% mAP.
1. Introduction
Remote sensing object detection has a wide range of applications in civilian and military fields, and is used in various scenarios such as transportation, forestry, and the ocean. Remote sensing images are obtained from satellite sensors, and these have a different angle view compared to natural imagery. They consists of various complex landscapes and are less susceptible to spatial details, lighting differences, background clutter and the atmosphere. Additionally, remote sensing images are also larger in terms of area coverage and data size. Object detection is an attractive research field for academia and industry regaridng remote sensing images of higher spatial resolution and images consisting of rich information [1,2]. Deep learning techniques of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) were applied for remote sensing due to their efficiency in handling images. CNN models have lower efficiency in extracting the information of remote sensing images and detection results of post-processing that result in high false alarm rates and missed detection rates for dense targets and complex images [3]. Automatic classification of aerial images was widely carried out using multi-class object detection and this is important for a wide range of applications such as precision agriculture, urban planning, and intelligent monitoring [4]. Locating specific objects and classifying the categories in aerial images present some challenging problems such as wide multi-scale distribution, larger background, complicated scenery, variations, and huge orientation [5].
Recently, deep learning methods have shown significantly high performance in various fields including image classification, segmentation, and feature extraction, etc. [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Deep learning rapid progress involves the development of several advanced CNN models such as ResNet, GoogLeNet, VGGNet, and AlexNet in computer vision fields. The deep learning CNN automatically extracts high-dimensional features. The CNN models are applied in aircraft feature extraction and increase the efficiency of the model [14]. The remote sensing object detection scale properties and orientation have been widely used in deep learning-based object detection methods [15]. Remote sensing images of high resolution with different resolutions and swathes are often combined and applied for more accurate and faster object classification [16,17]. There have been significant efforts applied to developing methods for remote sensing object detection. Many methods provide lower efficiency in detecting a small object in remote sensing images. Many types of research on object detection using scene classification share the limitation of the object categories of small objects being higher than those of large-sized objects. Many methods lack diversity, and this affects the small object detection performance in remote sensing images [18]. The objectives and contribution of this research are given as follows:
- The SSG method uses the spiral search technique to increase the exploitation in feature selection for object detection. The SSG method selects unique features that help to overcome data imbalance and overfitting problems.
- The VGG-19 and ResNet50 model is applied for feature extraction for a better representation of the object in the images. The SSG method selects the relevant features that help to classify small objects in the dataset.
- The SSG method is evaluated in two datasets and compared with various feature selection and deep learning techniques. The SSG method demonstrates higher performance than existing methods in remote sensing object classification.
The organization of the paper is as follows: the literature survey is given in Section 2, and the explanation of SSG, VGG19, and ResNet50 is given in Section 3. The implementation details are given in Section 4 and the results of SSG are given in Section 5. The conclusion of this research paper is given in Section 6.
2. Literature Survey
Object detection in remote sensing images is required in many applications such as urban planning and traffic monitoring. Deep learning techniques were applied for object detection and achieved significant performance in detection. Some of the recent techniques in object detection were reviewed in this section.
Sun et al. [19] applied a unified part-based CNN model named as PBNet for object detection in satellite images. PBNet considered objects as a parts group, and part information was applied in the contextual information to improve object detection. Correct part information helps to predict composite objects and solve problems of various shapes and sizes. A part localization module is learned for classification and the generation of accurate part information. The PBNet model has considerable performance in object detection in satellite images. The PBNet model fails to identify the small objects in the images and imbalanced dataset problems affect the performance.
Ming et al. [20] applied a discriminative features role in an object detection model named CFCNet to improve the classification accuracy. The CFCNet model consists of three aspects: optimizing label assignment, refining preset anchors, and building powerful feature representation. The classification and regression features are decoupled and the polarization attention module (PAM) technique was applied for constructing robust critical features. The CFCNet model has a data imbalance problem and lower efficiency in detecting a small object. Xu et al. [21] applied the Swin transformer based on CNNs and transformer to design a local perception of Swin transformer (LPSW) for object detection in satellite images. The Cascade framework was applied to help to improve the segmentation accuracy and combine it with a new network for classification. The LPSW technique can classify small objects and the overfitting problem affects the classification performance.
Huang et al. [22] applied a lightweight oriented object detector (LO-Det) for object detection in satellite images to improve the accuracy. Stacked separable convolutions (SConvs) were applied to replace the conventional CNN model and this involves precision losses. A channel separation aggregation (CSA) structure was applied to reduce the dynamic receptive field (DRF) and SConvs complexity to improve the accuracy of the model. The LO-Det model performance was affected by data imbalance problems and lower efficiency in detecting small objects. Huang et al. [23] applied a cross-scale feature fusion pyramid network (CF2PN) for object detection in satellite images. A cross-scale fusion module (CSFM) was applied to extract semantic information from features to perform fusion on multi-scale. The U-shaped module was applied for target detection using a feature pyramid and extracting features on multi-level fusion. A focal loss was applied to reduce the negative samples generated in the feature fusion process. The overfitting and data imbalance problem affects the performance of the classification in object detection.
Cheng et al. [24] applied an anchor-free oriented proposal generator (AOPG) for object detection in satellite images. The coarse location module was applied to produce coarse-oriented boxes for the detection. A fast R-CNN model was applied for the detection process and improved the performance in classification. The AOPG model has lower efficiency in data imbalance problems and the detection of small objects in the datasets. Shamsolmoali et al. [25] applied a pyramid network of rotation equivariant features named REFIPN for object detection in satellite images. The single shot detector was adopted in the model for a lightweight image pyramid module to extract feature representation and an optimization technique was used to generate the region of interest. The convolution filters were applied to extract features in a wide range of orientations and scales. Features were used to determine the angle and weight of orientation and generate vector fields for spatial locations. The developed model shows considerably good performance in small-scale detection. The data imbalance problem affects the performance of the classification in satellite images.
Ming et al. [26] applied representation invariance loss (RIL) to optimize the regression for object detection in satellite images. The RIL model represents an oriented object for multiple local minima equivalents and transforms regression with adaptive matching. The optimal regression strategy is adopted by the Hungarian matching algorithm. A normalized rotation loss is applied to the weak correlation between unbalanced loss and different variables in representation. The developed model performance was affected by an imbalanced dataset and lower efficiency in small object detection. Shamsolmoali et al. [27] applied a multiple patch feature pyramid network (MPFP-Net) for object detection in satellite images. The MPFPNet model patches are divided into class-affiliated subsets that are based on related patches and primary loss functions. A smooth loss functions sequence was measured for a subset to improve the object detection in satellite images. The MPFPNet model performance was affected by the overfitting problem and data imbalance problem.
Lu et al. [28] applied end-to-end networks with feature fusion and attention SSD for object detection. The semantic information was enhanced from shallow features using the structure of multi-layer feature fusion. The feature information was screened using the dual path attention model in SSD. Channel attention and spatial attention were used in the model to reduce background noise and focus on key features. The network ability of feature representation was improved using the module of multi-scale receptive field. The loss function was applied to balance positive and negative samples on the imbalanced dataset. The end-to-end model had an overfitting problem that degrades the performance of classification. Ming et al. [29] applied a sparse label assignment (SLA) for remote sensing object detection to select high-quality sparse anchors. The balanced training was applied for better performance and to alleviate the inconsistency between regression and classification. A feature pyramid network was applied to detect small and densely arranged objects. The model performance was affected by an imbalance of data and an overfitting problem.
According to the literature, several deep learning algorithms were used for object detection and produced notable performance in detection. The development of techniques for detecting objects using remote sensing has received significant efforts. Many techniques are less effective in finding small objects in distant sensing photos. There are restrictions on object categories of little items that are higher than large-sized objects in many sorts of research on object identification using scene categorization. The efficiency of small item detection in remote sensing images is negatively impacted by the lack of diversity in many methods. Additionally, an overfitting issue and a data imbalance had an impact on the model’s performance. To solve those concerns, the SSG approach is used to increase the feature exploitation, which supports in the detection of small objects and minimizes overfitting issues.
3. Proposed Method
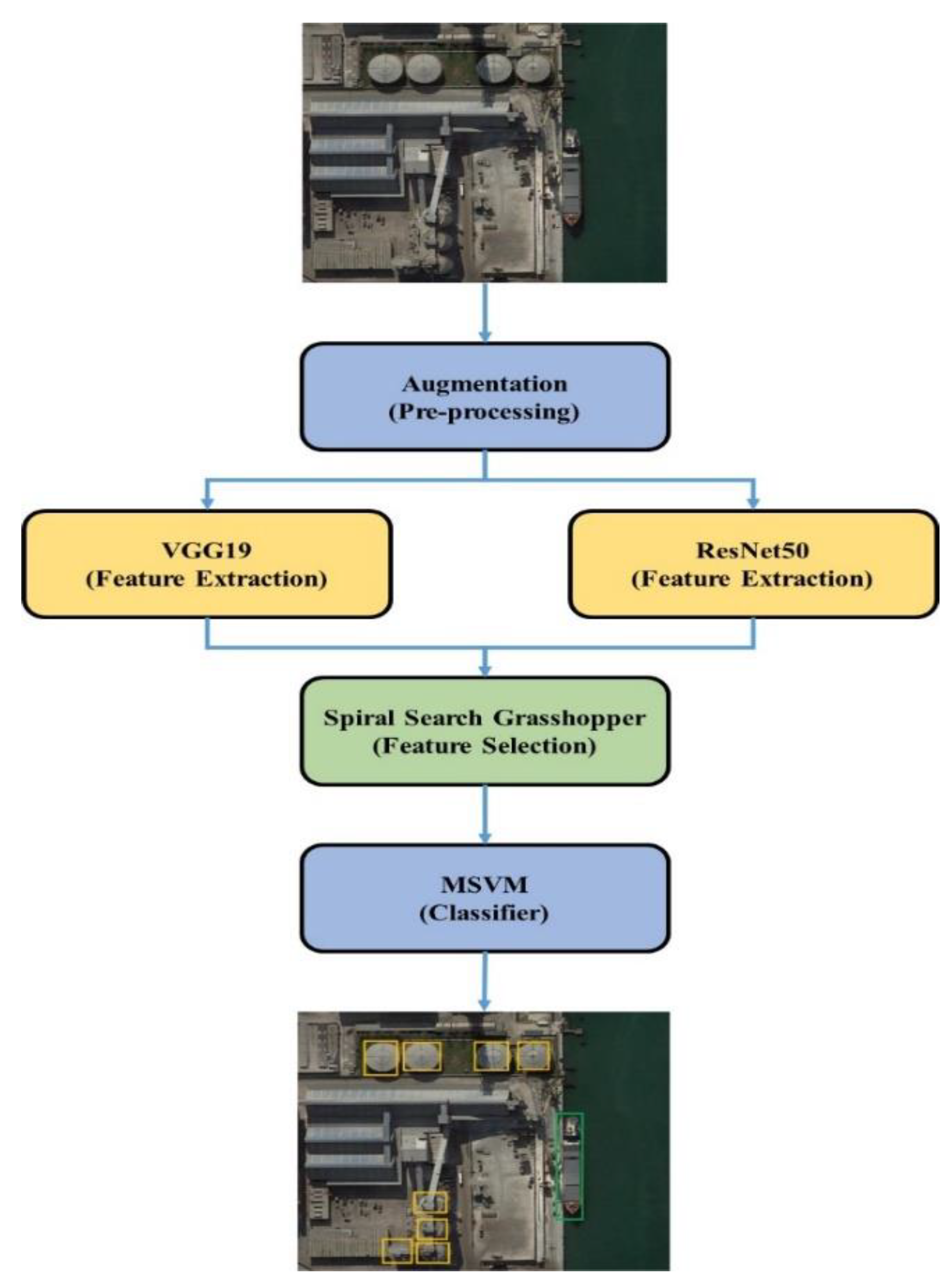
The images from the datasets are augmented to increase the number of images and to help increase the learning rate in training. Two CNN models, VGG19 and ResNet50 architectures, are used for extracting features. The SSG technique is applied to increase the exploitation in the feature selection which helps to detect small objects and reduce overfitting problems. The overview of the SSG method in remote sensing object detection is shown in Figure 1.
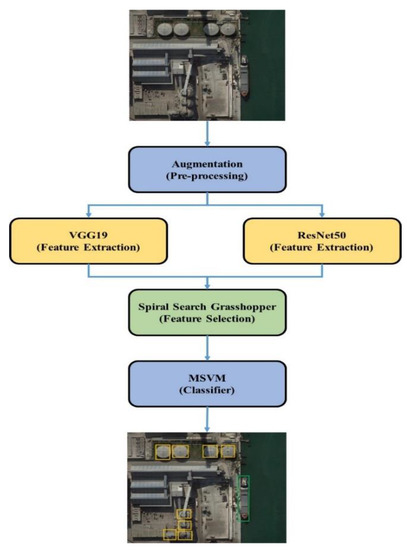
Figure 1.
The SSG model in remote sensing object detection.
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
Testing and training samples are resized to 224 pixels of interpolation. Data augmentation is applied in the training phase using random flipping (left-right and up-down), and images are randomly rotated for various sets of angles (e.g., 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°).
3.2. CNN Models in Feature Extraction
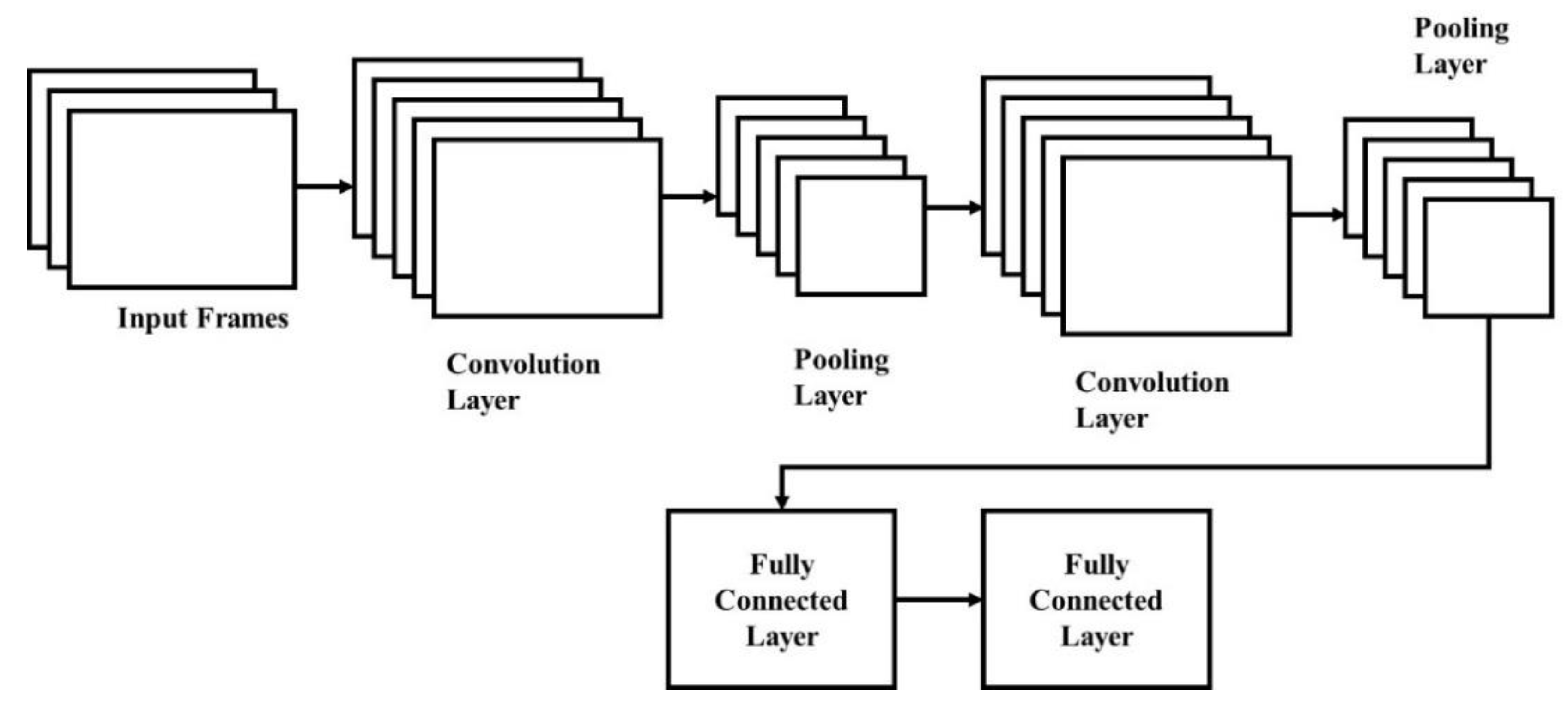
The way that humans understand images is a fascinating process, and this is a simple task for us. There are a lot of hidden complexities in the ways that a machine understands an image. CNN model is a deep learning algorithm that is inspired by the visual cortex of the brain [30] and this aims to imitate animals’ visual machinery. CNNs represents a quantum leap in the image processing field that involves detection, localization, segmentation, and classification, etc. The CNN efficiency in image classification is high and this is the main reason for the model’s high usage. The CNN model involves applying the convolutional layer of learnable weights and biases similar to animal neurons. The CNN model’s core building blocks are fully-connected layers, activation functions, and convolutional layers, as shown in Figure 2. The brief introduction to the CNN model is explained in this study and a detailed discussion of CNN can be found elsewhere [31,32].
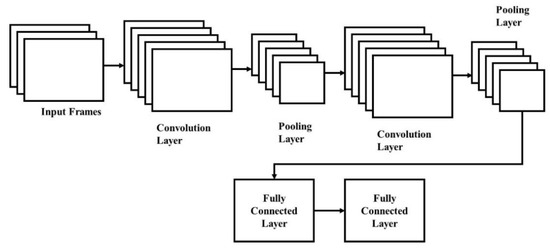
Figure 2.
CNN model architecture.
Convolutional layer: animal brain neuronal cells of the visual cortex are involved in extracting the features of the images. Various features are extracted by each neuronal cell, which helps to understand an image. Neuronal cells are modeled as convolutional layers and this can extract features such as gradient orientation, texture, colors, and edges. Convolutional filters or kernels are learnable filters in convolutional layers and the size is , where the image depth is . The kernels are convolved during the forward pass across the height and width of the input volume and the dot product is measured for filter entries and input. Filters are learned by CNN to activate across texture, colors, and edge, etc. The convolution layer output is applied as an activation function layer.
Activation function: activation functions of non-linear transformation of data are used since real-world data are mostly non-linear. This ensures input space representation that is mapped to different output space as per requirements.
This requires to be a real-value number, and it must be converted into a range of 0 and 1. Large negative and positive inputs in particular are placed near 0 and unity, respectively. This is expressed in Equation (1).
A real-value number is considered in non-linear function and converts to 0 if is negative. The ReLU activation function is a commonly used non-linear function that requires less computation time and is faster than the sigmoid and tanh functions, as shown in Equation (2).
Pooling: convolving the features of a non-linear down sampling is carried out by the pooling layer. This reduces the computational power of data processing using dimensional reduction. Data are aggregated over feature type or space to reduce the spatial size, while the rotational variance of images overcomes translation and control overfitting. Inputs are partitioned using a pooling operation into a rectangle patch set. A single value is calculated based on the type of pooling process to replace each patch. The most commonly used pooling types are maximum pooling and average pooling.
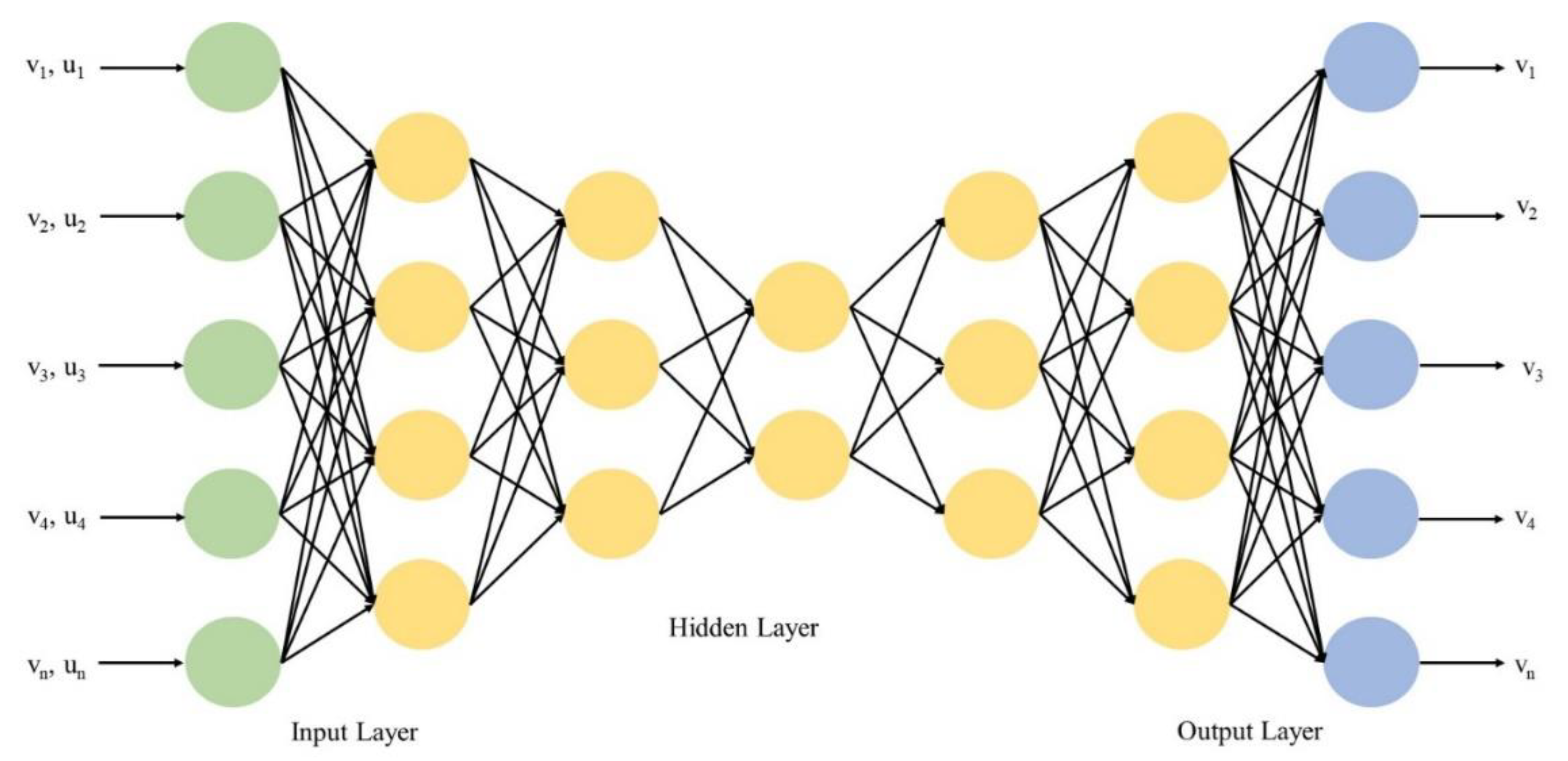
Fully connected layer: fully connected layer is similar to an artificial neural network, where inputs are connected to each node in the next layer and weight values are associated with each node. The sum of inputs multiplied by corresponding weights is the output of the model. The sigmoid activation function is connected to a fully connected layer to perform the classification job. The fully connected layer in CNN is shown in Figure 3.
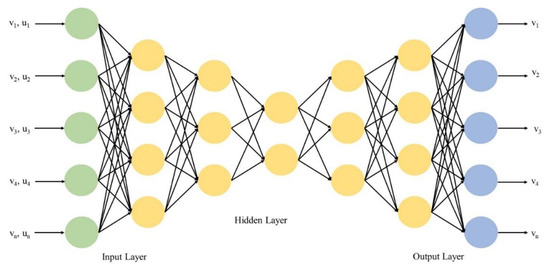
Figure 3.
Fully connected layer in CNN model.
3.2.1. VGG19
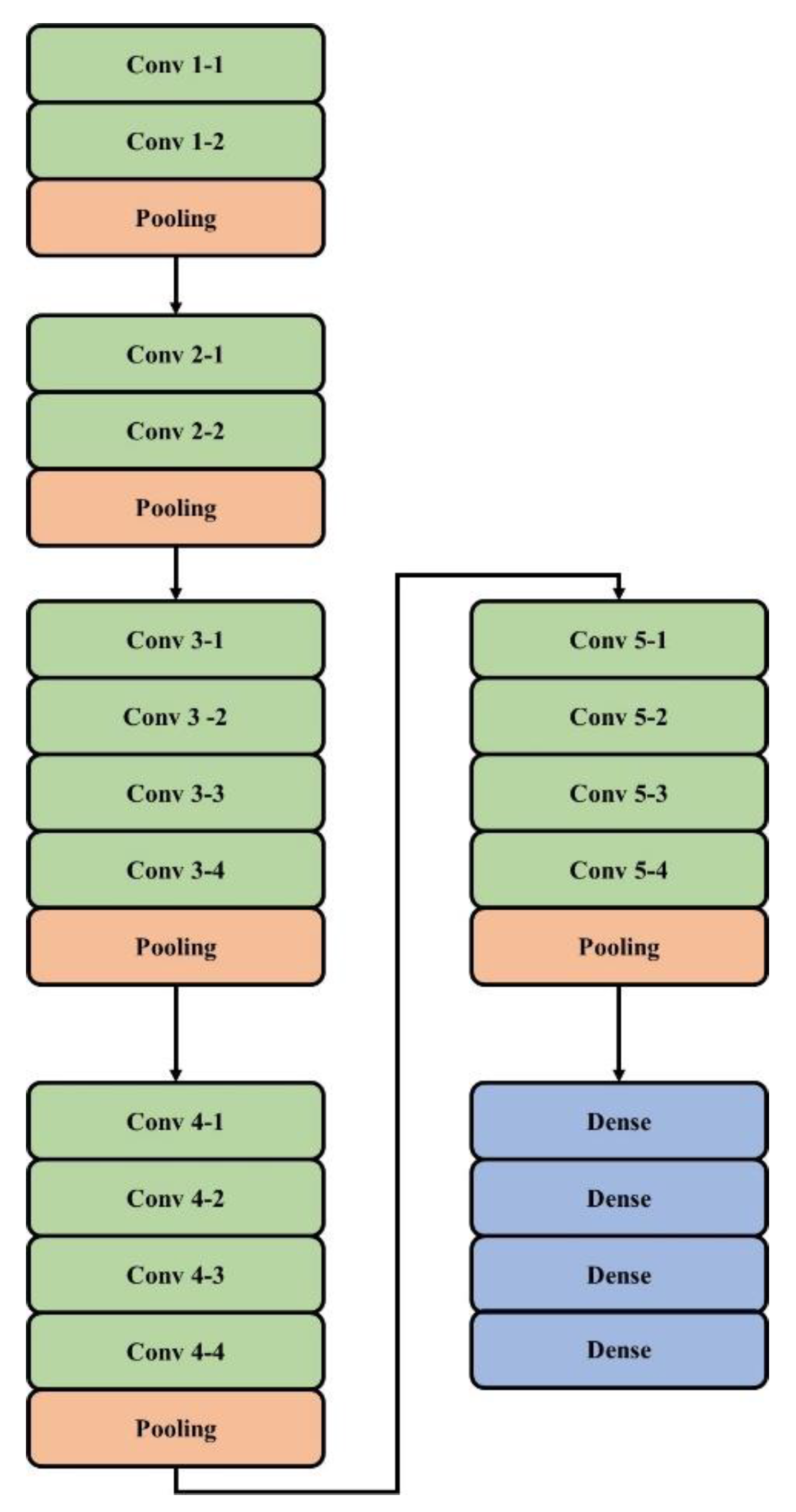
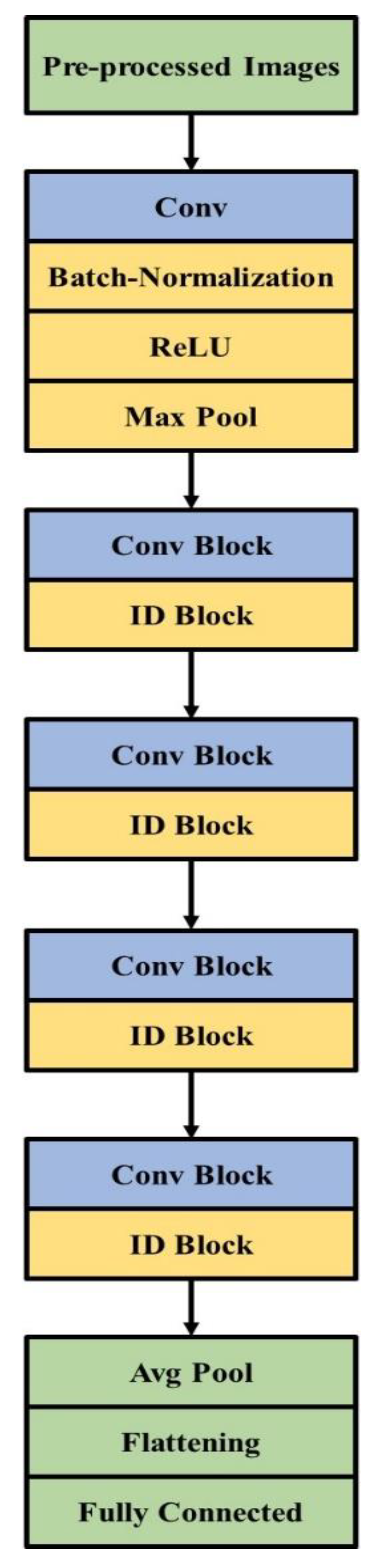
The Oxford Robotics Institute developed a type of CNN model which is named Visual Geometry Group Network (VGG) [33,34,35]. VGGNet provides good performance in the data cluster of ImageNet data. Five building blocks are present in VGG19. Two convolutional layers and one pooling layer are present in the first and second building blocks, followed by four convolutional layers and one pooling layer, which are present in the third and fourth blocks. Four convolutional layers are present in the final block and small filters are used. The VGG19 architecture in feature extraction is shown in Figure 4.
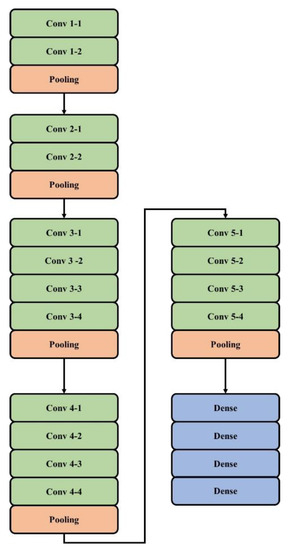
Figure 4.
VGG19 architecture for feature extraction.
3.2.2. ResNet
Residual networks consist of 50 layers in their architecture, named ResNet50 [36,37,38]. An additional identity is present in ResNet50 compared to VGG-16, and the ResNet model predicts the delta that is required in the final prediction from one layer to the next. The alternate path is provided by ResNet50 which allows the gradient to flow, and this helps to solve the vanishing gradient problem. Identity mapping is used by the ResNet model that helps to bypass the CNN weight layer if the current layer is not required. This model solves the overfitting problem in the training set and 50 layers are present in feature extraction in ResNet50. The ResNet model in feature extraction is shown in Figure 5.
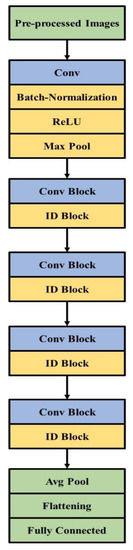
Figure 5.
ResNet50 model for feature extraction.
VGG19 is one of the popular algorithms used in image classification. However, if it is also used for feature extraction, it provides the following advantages.
Initially, the features of VGG19 are flat and capable of achieving optimal values. Additionally, it is a pre-trained model which is trained on a large dataset and fine-tuned to fit the image with ease. Similarly, ResNet50 is much deeper than VGG19 and its architecture size is substantially smaller due to the usage of fully connected layers which reduces the architecture size. In ResNet50, networks with a large number of layers are trained easily without increasing the training error percentage.
However, the subspace value is wider in VGG19 when compared to ResNet50 which creates more error in the architecture. While considering the ResNet50, the subspace value is optimal, but there may be a chance of overlapping in the feature subspace. While those features in the training and testing stage were deliberate, the subspace error value of some classes is affected. Further, ResNet50 usually requires an increased time period for training, therefore, it is practically unfeasible in real-world applications.
In order to obtain more informative features, optimal values from both the VGG19 and ResNet50 models are collected. Then, the output from VGG19 and ResNet50 are combined and applied in feature extraction for a better representation of the object.
3.3. Spiral Search Grasshopper Optimization
Saremi et al. [39] developed a grasshopper optimization technique based on grasshopper swarm behaviors. A design solution for a grasshopper position in a flock or population. The grasshopper position updates are influenced by wind advection, gravity, and social interaction [40,41]. The grasshopper position update is carried out by this process and expressed in Equation (3):
where a social force function is represented as as in Equation (4).
is a distance between solutions i and j.
The grasshopper position is defined as at iteration. The grasshopper attraction strength is denoted as variable and is the attractive length. Grasshopper positions or solutions with lower and upper limits are and , respectively. The target position vector of a -dimension is defined as and a shrinking factor denotes comfort zone decreases, as in Equation (5).
The minimum and maximum values are denoted as and . The a variable provides a particular run of maximum iterations.
The GOA search process starts with the grasshopper’s population or flock and this position is analogous to design vectors. The grasshopper positions are updated using Equations (3)–(5) to identify the best grasshopper. This reproduction function of the swarm is carried out until the termination condition of optimization is achieved for the best grasshopper at the final iteration which is considered an optimum solution.
The GOA second state is involved in randomly generating a position in space. This blind operation slows the algorithm convergence speed. In order to address this issue, the spiral search approach is utilized. In order to boost the grasshopper’s capabilities and to identify global solutions in the optimization process, more options are given to the grasshopper using the spiral search technique. The search space’s spiral structure trajectory is utilized to calculate the separation between the grasshopper’s ideal position and its starting point. Equation (6) provides the updated mathematical expression.
where the distance of grasshopper and current best position is denoted as , logarithmic spiral shape is denoted as and a random number is in the range of [−1, 1].
In this method, the basic GOA updates its search agent based on the current position and biological habits of the grasshopper. By contrasting the spiral solution with the original solution, we are able to maintain the best solution for grasshopper space. The original GOA’s search efficiency and optimization capability are enhanced by the spiral motion method by choosing a better search and exploitation scheme. At this point, introducing the spiral movement strategy will successfully boost population variety and prevent a descent towards the local optimum. Additionally, it contributes to balanced exploration and exploitation. While considering the hyper-parameters, the proposed model is tested with 3 constant learning rates: 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001. From that analysis, 0.1 is too large, 0.001 is too small, and therefore, 0.01 tends to be better for the tested networks used in this research.
3.4. Multi-Class Support Vector Machine
Classification is the final stage in image processing, and this is based on the selected features. Various machine learning techniques are present, such as Bayesian classifier, K-nearest neighbor (KNN), neural networks, SVM, and decision tree [42,43]. This study uses multi-class SVM due to its efficiency in handling high-dimensional data. The SSG selected features are applied to the multi-class SVM model for training and testing the model. The SVM model is capable of handling pattern classification, reducing overfitting, and is robust to noise. The SVM uses appropriate kernel functions to provide good discriminative classification. Kernels are students independent of the learning algorithm, due to the separation of kernel functions and learning algorithm. Different kernel functions are used to design and experiment without the need for a learning algorithm. The Gaussian RBF or polynomial kernels are used in various applications based on data types.
4. Simulation Setup
The SSG model implementation details of parameter settings, metrics, system requirements and datasets are discussed in this Section.
Dataset: DOTA [44] is a remote sensing object detection and publicly available dataset. This dataset has 188,282 annotated instances and 2806 aerial images. The 15 categories of images are present, the original image size is .
The DIOR [45] is a remote sensing object detection dataset, which consists of 190,288 object examples and 23,463 images. The image resolution ranges from 0.5 m to 30 m and the image size is .
Parameter settings: For VGG-19 and ResNet50 [46], the learning rate is set as 0.01, the dropout is set as 0.1, and some epochs are 8. For the SSG technique [47], the population size is set as 50 and the total iteration is set as 50.
Metrics: The mean average precision (mAP) is a common metric to measure the performance of remote sensing object detection and its formula is given in Equations (7)–(9).
System Requirement: The SSG technique is implemented on an Intel i9 processor, 22 GB graphics card, windows 10 OS, and 128 GB RAM. The five-fold cross validation is applied to test the performance of the model.
5. Results
The SSG technique is applied to two datasets and evaluated the performance to compare with existing techniques. The grey wolf optimization (GWO), firefly (FF), whale optimization algorithm (WOA), and grasshopper optimization (GO) techniques were compared with SSG in feature selection.
5.1. DOTA Dataset
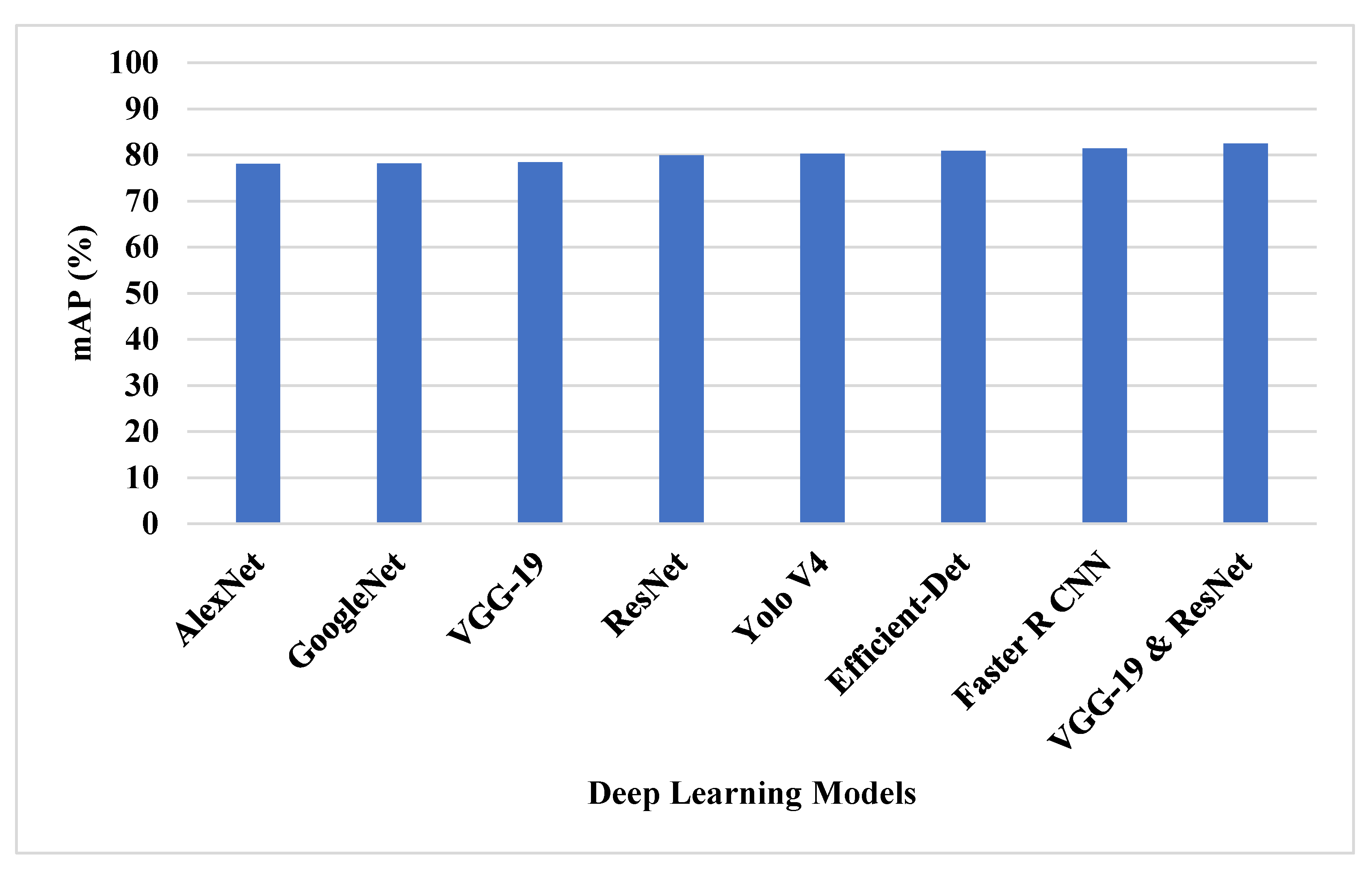
The SSG feature selection technique with VGG-19 and ResNet50 feature extraction was tested on the DOTA dataset. Various deep learning architecture is tested with SSG feature selection and various features selection technique is applied with VGG-19 and ResNet50 for object detection classification. The deep learning techniques of ResNet, VGG-19, GoogleNet, AlexNet, Yolo V4, Efficient-Det and Faster R CNN were compared with VGG-19 and ResNet50 feature extraction techniques, as shown in Table 1 and Figure 6.

Table 1.
Deep learning model feature extraction performance on DOTA dataset.
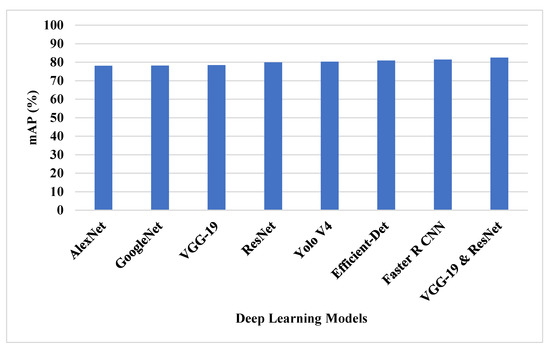
Figure 6.
The mAP of deep learning techniques on DOTA dataset.
The VGG-19 and ResNet50 model provides a better feature representation of the model that helps to detect the small objects and the SSG technique solves the overfitting problem using spiral search to increase the exploitation. The existing feature selection techniques have lower efficiency in providing feature representation. The VGG-19 and ResNet50 model has 82.45% mAP, ResNet50 model has 79.97 mAP, and VGG-19 has 78.41% mAP.
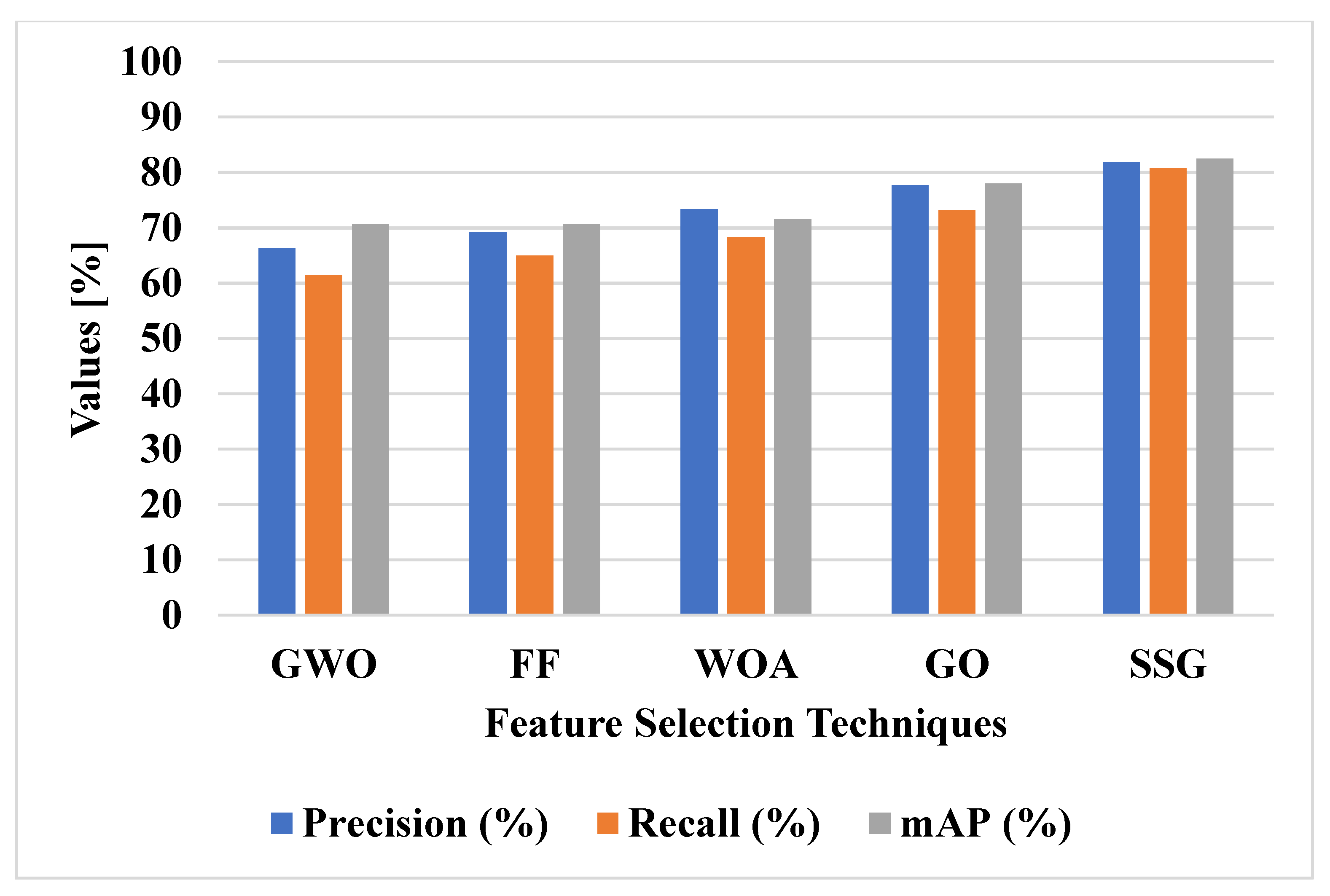
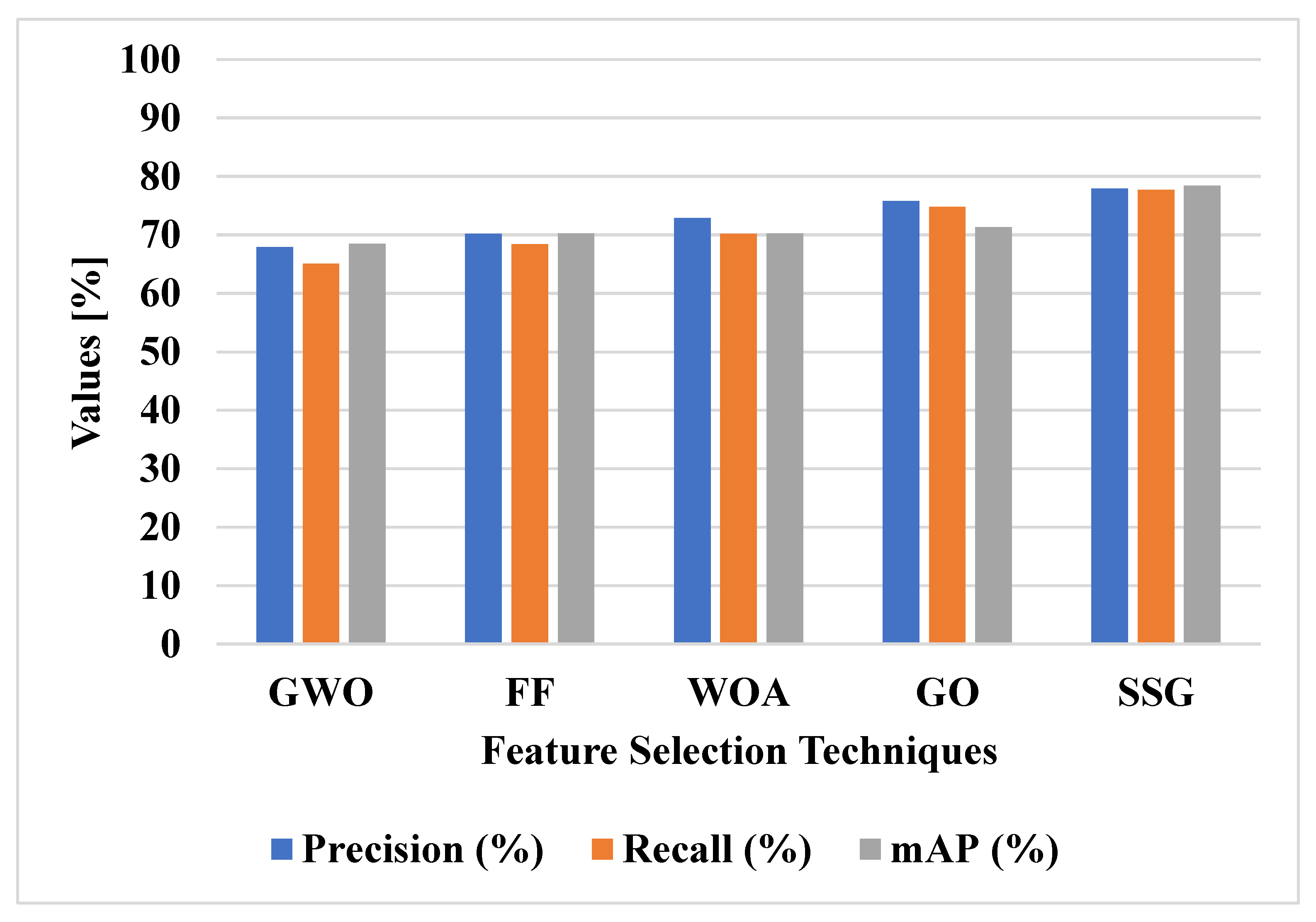
Figure 7 shows the graphical analysis of various feature selection techniques on the DOTA dataset in terms of mAP, precision and recall. Various feature selection techniques were applied with VGG-19 and ResNet50 model feature extraction for object detection, as shown in Figure 7 and Table 2. The SSG method has the advantage of using the spiral search technique to increase the exploitation of the feature selection process. The increase in the exploitation of feature selection helps to classify small objects in the remote sensing images. The SSG technique tradeoff the balance between exploration and exploitation to select the relevant features. The GWO, FF, and WOA techniques have lower convergence in feature selection and the GO technique has trap into local optima. The SSG model has 82.45% mAP, GO method has 77.95% mAP, and WOA method has 71.57 mAP. Furthermore, the proposed SSG technique achieves better precision (81.88%) and recall (80.87%) when compared with other feature selection techniques.
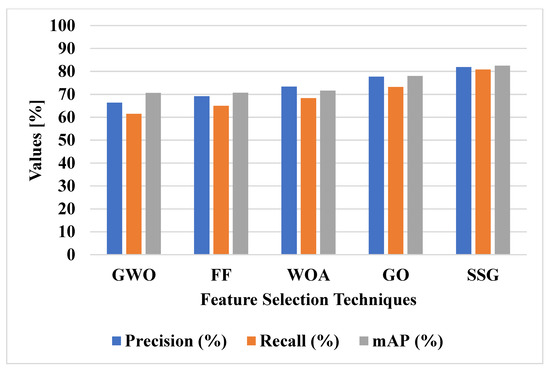
Figure 7.
Performance of feature selection techniques on DOTA dataset.

Table 2.
Feature selection techniques performance on DOTA dataset.
5.2. DIOR Dataset
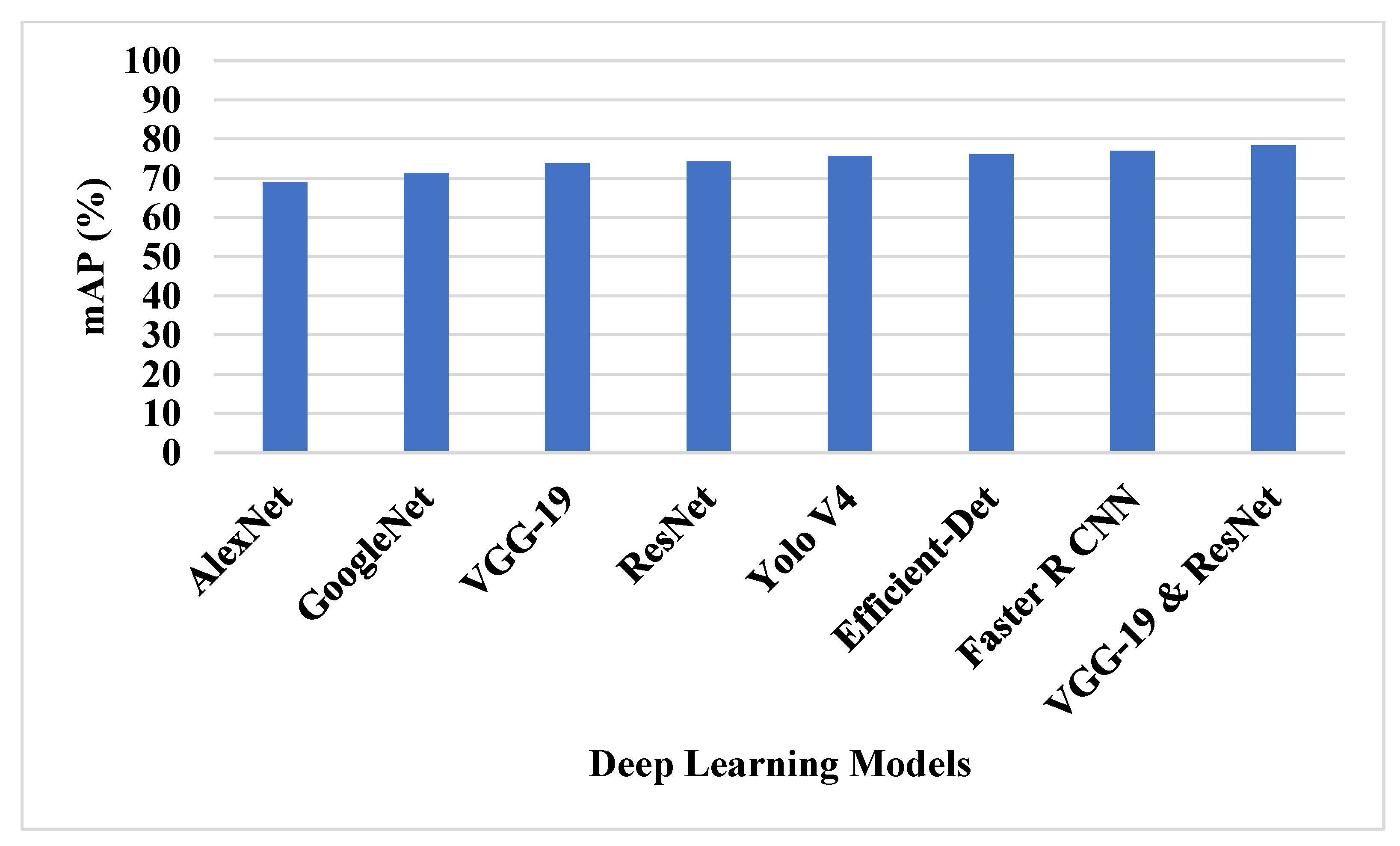
Various deep learning techniques and feature selection techniques were applied on DIOR dataset to test the performance. The VGG-19 and ResNet50 feature extraction model is compared with various deep learning architectures in feature extraction, as shown in Table 3 and Figure 8.

Table 3.
Deep learning model feature extraction performance on DIOR dataset.
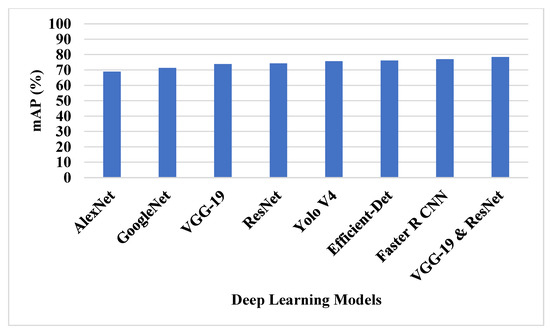
Figure 8.
The mAP of deep learning techniques on DIOR dataset.
The SSG technique in VGG-19 and ResNet50 helps to overcome the overfitting problem. The VGG-19 and ResNet50 technique extracts the relevant features to detect the small objects in the dataset. The existing deep learning techniques have lower efficiency in detecting small objects. Figure 9 shows the graphical analysis of various feature selection techniques on DIOR dataset in terms of mAP, precision and recall.
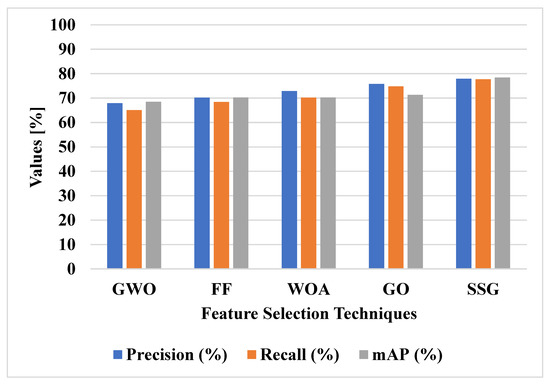
Figure 9.
Performances of feature selection techniques on the DIOR dataset.
The SSG feature selection technique is compared with other feature selection techniques, as shown in Table 4 and Figure 9. The SSG model applies the spiral search technique to increase the exploitation of the feature selection. This helps to select the relevant features for classifying small objects in the images. The GWO, FF, and WOA techniques have lower convergence, and the GO technique has lower exploitation in feature selection. The SSG model has 78.42% mAP, the GO technique has 71.33% mAP, and the WOA technique has 70.3% mAP. Furthermore, the proposed SSG technique achieves better precision (77.98%) and recall (77.74%) when compared with other feature selection techniques.

Table 4.
Feature selection techniques performance on DIOR dataset.
5.3. Comparative Analysis
Various deep learning models were applied for remote sensing object detection and some of recent techniques were compared.
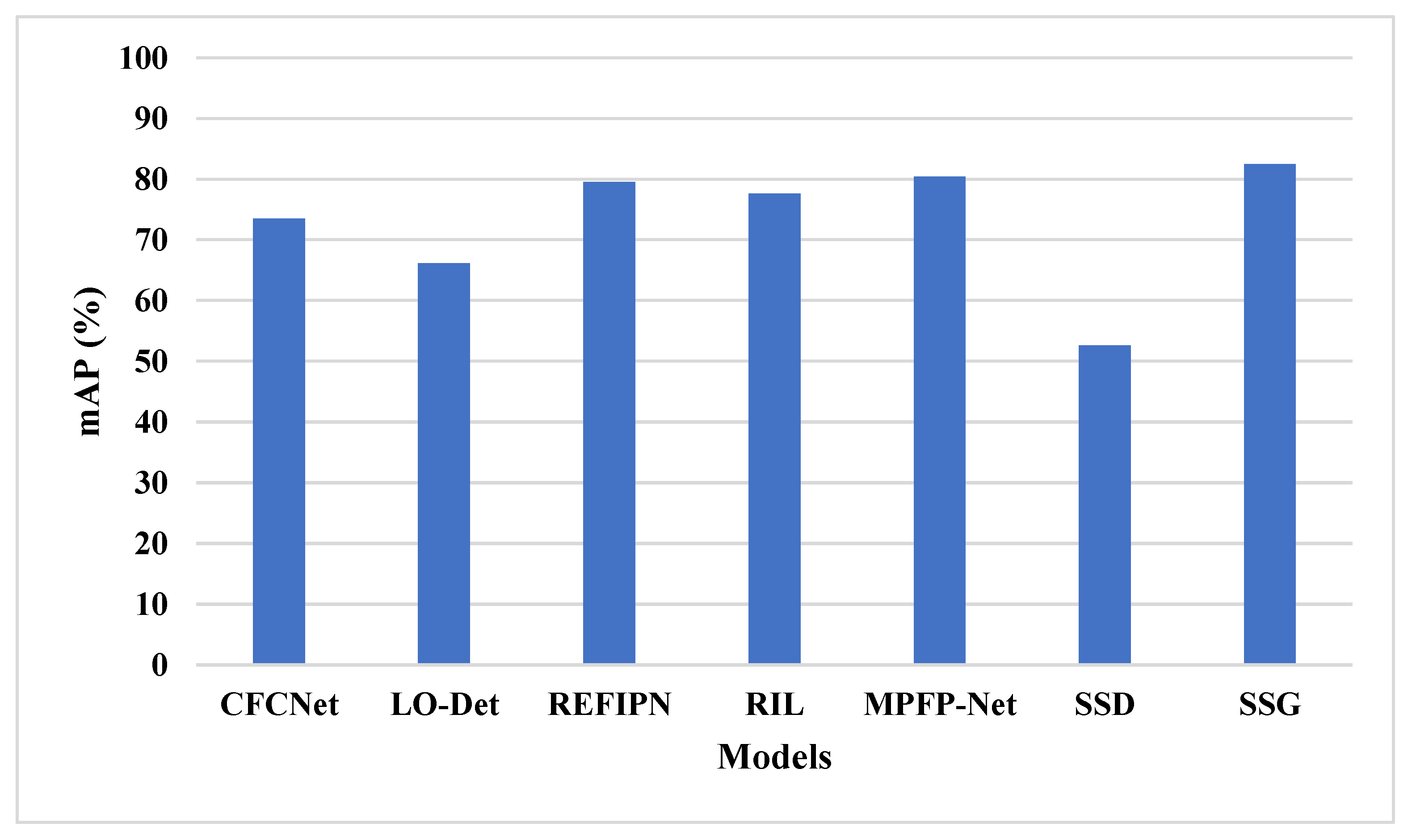
The SSG feature selection technique is compared with existing techniques in remote sensing object detection, as shown in Table 5 and Figure 10. The existing techniques have the limitations of the data imbalance problem, overfitting and lower efficiency in detecting small object. The SSG technique applies spiral search to increase the exploitation in feature selection that helps to select more relevant features. The increase in exploitation helps to overcome data imbalance and overfitting. The VGG-19 and ResNet50 feature extraction and SSG feature selection helps to detect small objects effectively. The SSG model has 82.45% mAP, the SSD [28] has 52.6% mAP, and the MPFP-Net [27] model has 80.43% mAP.

Table 5.
Existing model comparison on DOTA dataset.
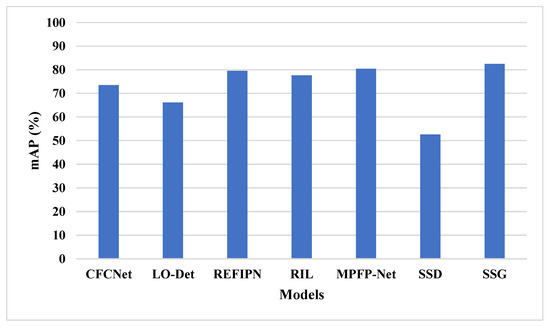
Figure 10.
Existing methods comparison on DOTA dataset.
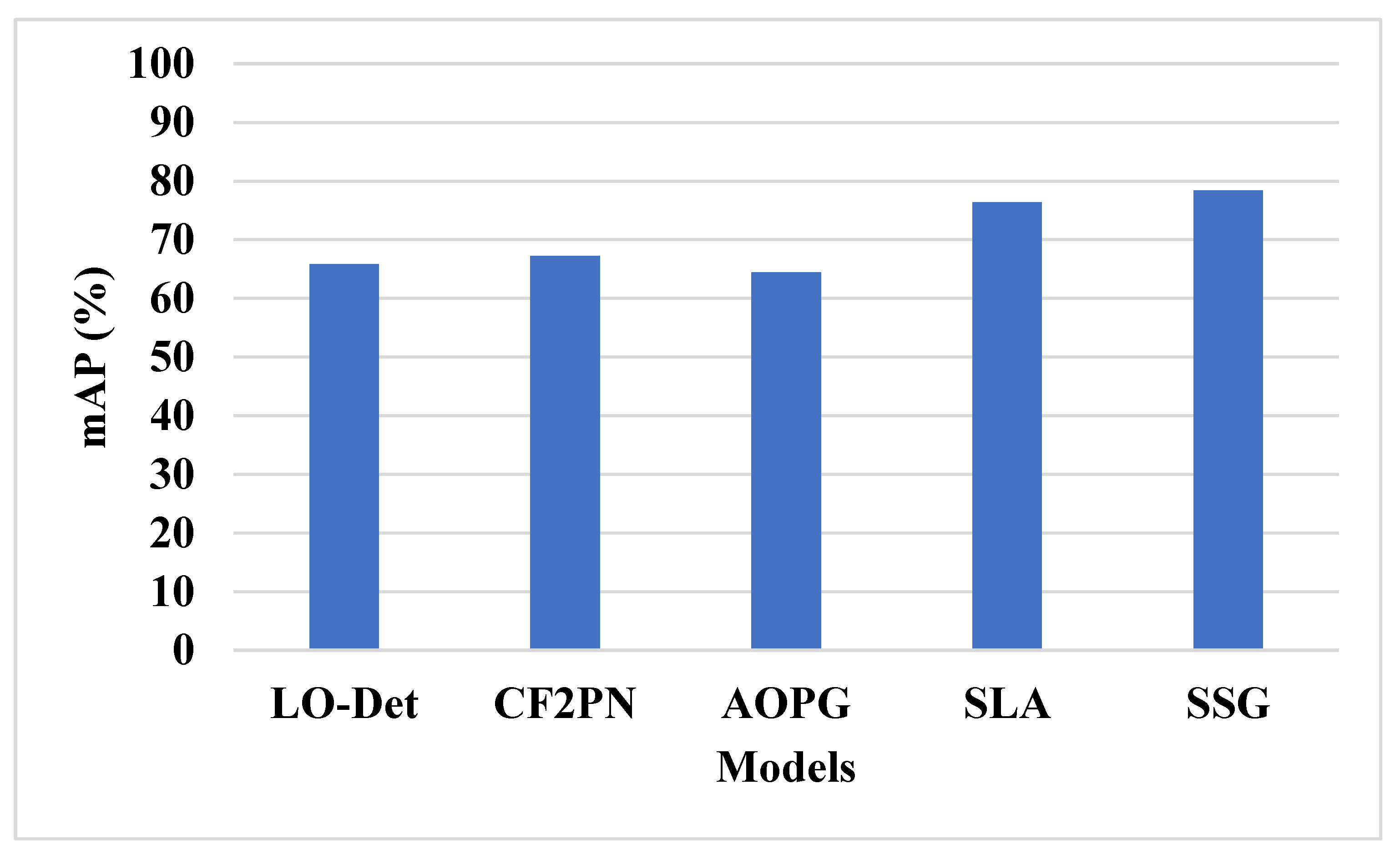
The SSG technique is tested on the DIOR dataset and compared with existing techniques, as shown in Table 6 and Figure 11. The SSG technique has applied the spiral search technique to increase the exploitation of the feature selection. The spiral search model helps to give priority to exploitation that in turn helps to escape the local optima trap. This selects more relevant features for small object detection and helps to solve imbalance and overfitting problems. The existing techniques have an overfitting problem due to the generation of more features and imbalance of data. The SSG model has 78.42% mAP, SLA [29] model has 76.36% mAP, and AOPG [24] model has 64.41% mAP.

Table 6.
Existing model comparison on DIOR dataset.
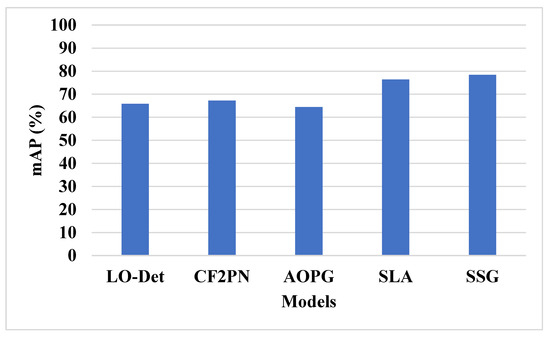
Figure 11.
Existing methods comparison on DIOR dataset.
5.4. Discussion
The SSG model is used in this study to select the features more effectively and enhance the object detection. The SSG keeps the balance between exploration and exploitation, which aids in the selection of the relevant features, and helps to increase the exploitation of the feature selection. For better object representation in the images, the VGG-19 and ResNet50 model extracts the features. The SSG technique improves object classification performance by choosing the relevant features from extracted features. The SSG model has 78.42% and 82.45% mAP on the DIOR and DOTA datasets, respectively, according to the result analysis. This proposed SSG model is better than the existing LO-Det [22], CF2PN [23], AOPG [24], and SLA [29] models in both DOTA and DIOR datasets.
The first 10 categories in the DOTA dataset are common. The remaining 10 categories are difficult to detect for each architecture when split into large ones (harbor, bridge, large vehicle, helicopter, roundabout) and small ones (tennis court, basketball court, ground track field, soccer ball field), because there is obvious difference between these two sub-categories in aerial images. While in the DIOR dataset, some images, i.e., harbour, ship, stadium, train station, expressway toll station contain noise and targets in motion would be blurred. Therefore, it has a high degree of inter-class similarity and intra-class diversity. These characteristics greatly increase the difficulty of detection.
6. Conclusions
Remote sensing object detection is an important application in satellite images and is required in many applications such as transportation, forest region monitoring, and urban planning, etc. CNN-based models were widely applied in remote sensing object detection due to their efficiency in feature extraction and classification. Deep learning techniques in remote sensing object detection have the limitations of data imbalance, overfitting problem and lower efficiency in small object detection. The deep learning model extracts more features from input images, and this creates an overfitting problem. The feature selection technique is required to select relevant features and overcome overfitting problems in object detection. This research applies the SSG model for effective feature selection and to improve the performance of object detection. The spiral search technique in SSG helps to increase the exploitation of the feature selection. The SSG maintains the balance between exploration and exploitation that helps to select the relevant features. The existing feature selection techniques have the limitation of the trap into local optima and have lower convergence. The VGG-19 and ResNet50 model extract the features for the better representation of object in the images. The SSG technique selects the relevant features from extracted features to improve object classification performance. In the DIOR dataset, the SSG model has 78.42% mAP, SLA model has 76.36% mAP, and AOPG model has 64.41% mAP. The future work of this model involves the application of new deep learning architecture such as Dense Net, ResNet 101, Squeezenet for feature extraction and selection to analyze the classification performance.
Author Contributions
The paper investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, and visualization were completed by G.U.K. and G.B. The paper conceptualization, software, were conducted by K.R.C. and K.A.S. The validation and formal analysis, methodology, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition of the version to be published were conducted by A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tian, L.; Cao, Y.; He, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, C.; Li, D. Image enhancement driven by object characteristics and dense feature reuse network for ship target detection in remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappriya, S.N.; Priyadarsini, M.J.P.; Stateczny, A.; Puttamadappa, C.; Parameshachari, B.D. Cascade object detection and remote sensing object detection method based on trainable activation function. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Ming, D.; Zeng, B.; Yu, J.; Qing, Y.; Du, T.; Zhang, X. Aircraft detection in high spatial resolution remote sensing images combining multi-angle features driven and majority voting CNN. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Chang, F.; Li, S.; Nie, Z. Adaptive multi-level feature fusion and attention-based network for arbitrary-oriented object detection in remote sensing imagery. Neurocomputing 2021, 451, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, F.; Han, S.; Liu, H. Ship object detection of remote sensing image based on visual attention. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, M.; Roy, D.; Mohan, C.K. Discriminative feature extraction from X-ray images using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 917–921. [Google Scholar]
- Ijjina, E.P.; Mohan, C.K. Human action recognition based on recognition of linear patterns in action bank features using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 13th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Detroit, MI, USA, 3–6 December 2014; pp. 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, R.; Jha, N.K.; Das, B.; Mittal, S.; Mohan, C.K. Ulsam: Ultra-lightweight subspace attention module for compact convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1627–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, K.; Chandrakala, S.; Mohan, C.K. Residual spatiotemporal autoencoder for unsupervised video anomaly detection. Signal Image Video Process. 2021, 15, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Murty, K.S.R.; Mohan, C.K. Unsupervised universal attribute modeling for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 21, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, N.; Roy, D.; Mohan, C.K. Spontaneous expression recognition using universal attribute model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 5575–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Ishizaka, T.; Mohan, C.K.; Fukuda, A. Vehicle trajectory prediction at intersections using interaction based generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 2318–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D. Snatch theft detection in unconstrained surveillance videos using action attribute modelling. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 108, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xu, K.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Qin, K. Multiple Instance Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Fine-Grained Aircraft Recognition. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Ji, S. A new spatial-oriented object detection framework for remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 4407416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Feng, P.; He, R. ShipRSImageNet: A large-scale fine-grained dataset for ship detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8458–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiang, H.; Jiang, M.; Tang, E.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Sparse anchoring guided high-resolution capsule network for geospatial object detection from remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bashir, S.M.A.; Khan, M.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, R.; Song, Y.; Guo, Z.; Niu, Y. Remote sensing image super-resolution and object detection: Benchmark and state of the art. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 197, 116793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Fu, K. PBNet: Part-based convolutional neural network for complex composite object detection in remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Q.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, Y. CFC-Net: A critical feature capturing network for arbitrary-oriented object detection in remote-sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5605814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Feng, Z.; Cao, C.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Shang, Y.; Ye, S. An improved swin transformer-based model for remote sensing object detection and instance segmentation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wei, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Arbitrary-oriented object detection in remote sensing images based on polar coordinates. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 223373–223384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Ju, M.; Qu, J. CF2PN: A cross-scale feature fusion pyramid network based remote sensing target detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Xie, X.; Lang, C.; Yao, Y.; Han, J. Anchor-free oriented proposal generator for object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5625411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareapoor, M.; Chanussot, J.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J. Rotation Equivariant Feature Image Pyramid Network for Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5608614. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Q.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Dong, Y. Optimization for arbitrary-oriented object detection via representation invariance loss. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 8021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsolmoali, P.; Chanussot, J.; Zareapoor, M.; Zhou, H.; Yang, J. Multipatch feature pyramid network for weakly supervised object detection in optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5610113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ji, J.; Xing, Z.; Miao, Q. Attention and feature fusion SSD for remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5501309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Q.; Miao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, X. Sparse label assignment for oriented object detection in aerial images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Han, R.; Song, M.; Liu, C.; Chang, C.I. A simplified 2D-3D CNN architecture for hyperspectral image classification based on spatial–spectral fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2485–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, P.; Zhao, L. Remote sensing image scene classification using CNN-CapsNet. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Gui, G. Classification of high-spatial-resolution remote sensing scenes method using transfer learning and deep convolutional neural network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires de Lima, R.; Marfurt, K. Convolutional neural network for remote-sensing scene classification: Transfer learning analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, F. Efficient deep feature selection for remote sensing image recognition with fused deep learning architectures. J. Supercomput. 2020, 76, 8413–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, H. Distribution consistency loss for large-scale remote sensing image retrieval. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, K.; Min, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y. Triplet-Metric-Guided Multi-Scale Attention for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification with a Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, A.; Ali, N.; Ahmed, J.; Zafar, B.; Rasheed, A.; Sajid, M.; Ahmed, A.; Dar, S.H. Satellite and scene image classification based on transfer learning and fine tuning of ResNet50. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5843816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.Z.; Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I. Grasshopper optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, B.S.; Pholdee, N.; Bureerat, S.; Yildiz, A.R.; Sait, S.M. Enhanced grasshopper optimization algorithm using elite opposition-based learning for solving real-world engineering problems. Eng. Comput. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraihi, Y.; Gabis, A.B.; Mirjalili, S.; Ramdane-Cherif, A. Grasshopper optimization algorithm: Theory, variants, and applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 50001–50024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.N.T.; Apopei, B.; Alameh, K. Effective plant discrimination based on the combination of local binary pattern operators and multiclass support vector machine methods. Inf. Process. Agric. 2019, 6, 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hu, K.; Wu, J.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y. Multisensory data-driven health degradation monitoring of machining tools by generalized multiclass support vector machine. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47102–47113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wan, G.; Cheng, G.; Meng, L.; Han, J. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Derbel, B.; Won, K.-J.; Hong, B.-W. Learning-Rate Annealing Methods for Deep Neural Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gui, W.; Heidari, A.A.; Liang, G.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Turabieh, H.; Mafarja, M. Spiral motion mode embedded grasshopper optimization algorithm: Design and analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71104–71132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).