Synergistic Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles from Space-Based and Ground-Based Infrared Sounders Using an Optimal Estimation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Model
2.1. Data
2.1.1. AERI
2.1.2. GIIRS
2.1.3. Radiosonde and ERA5 Data
2.2. Forward Model
3. Method
3.1. Data Preprocessing
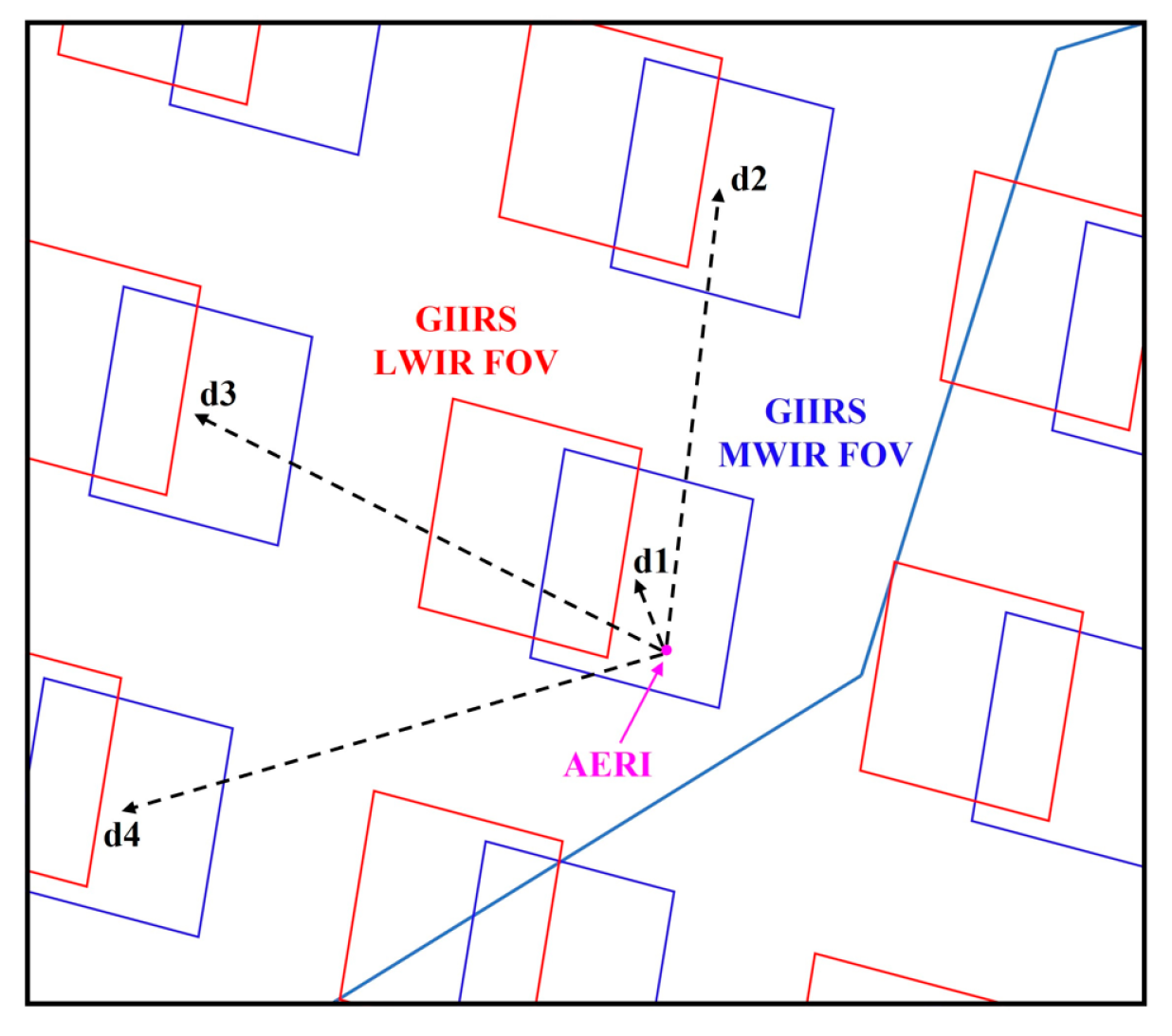
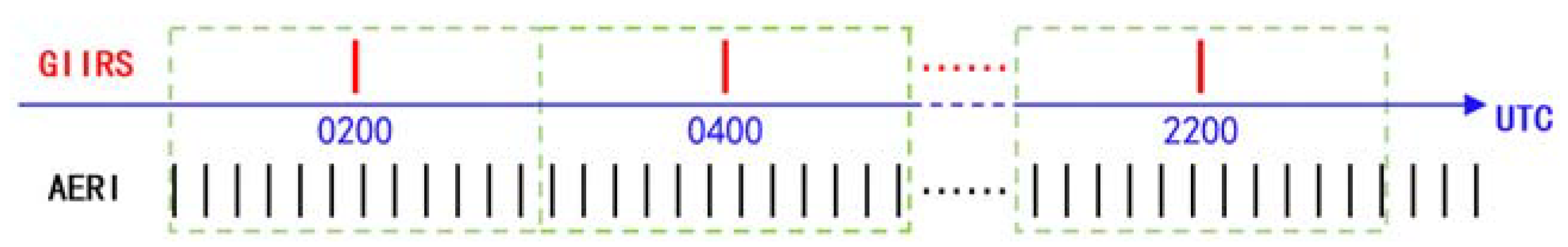
3.1.1. Spatial–Temporal Matching
3.1.2. Cloud Screening
3.1.3. Sounding and ERA5 Data Processing
3.2. Synergistic Retrieval
3.2.1. Mathematical Background
3.2.2. Observation Scale Matching
3.3. Retrieval Process Framework
4. Results and Comparison
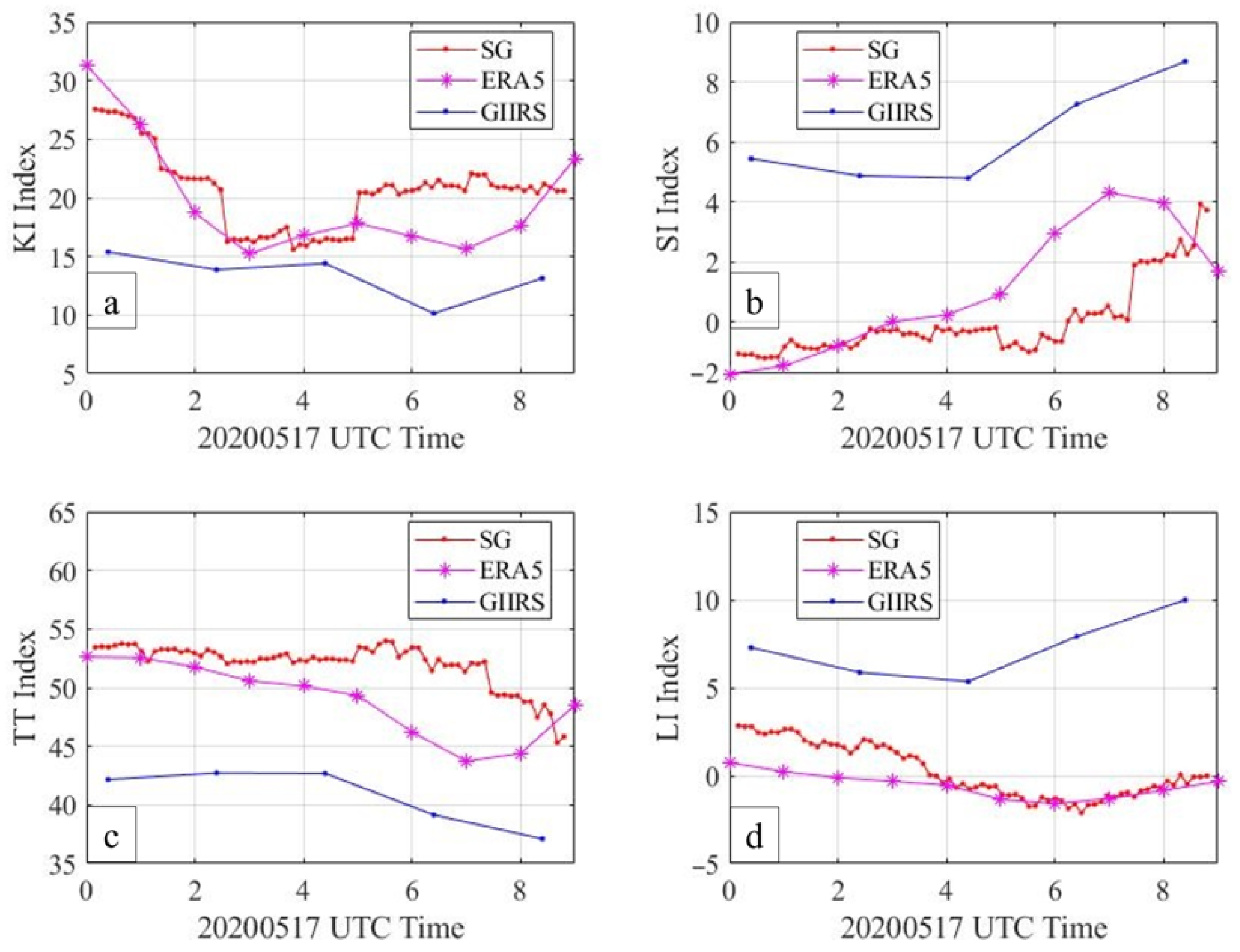
4.1. Case Study
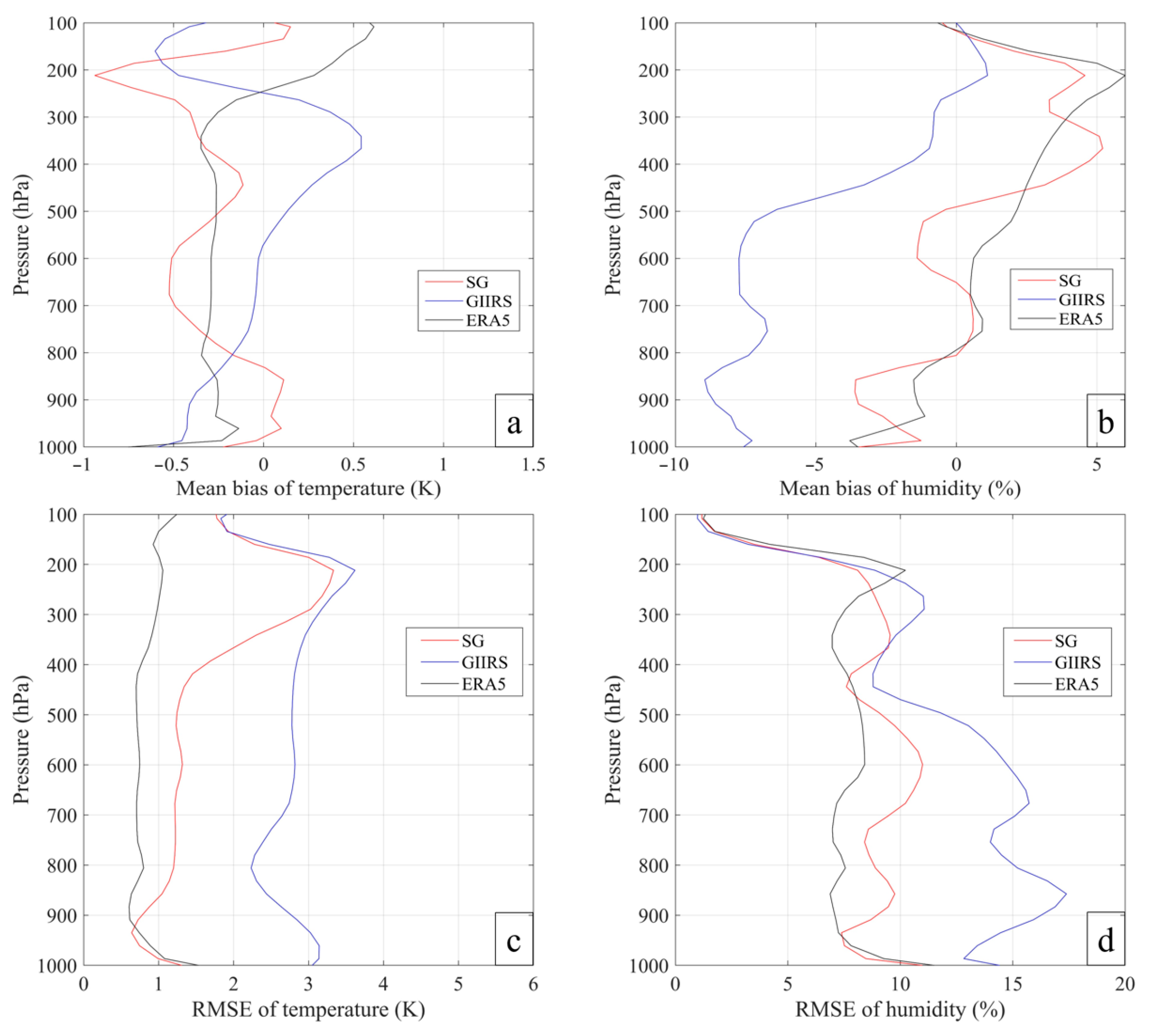
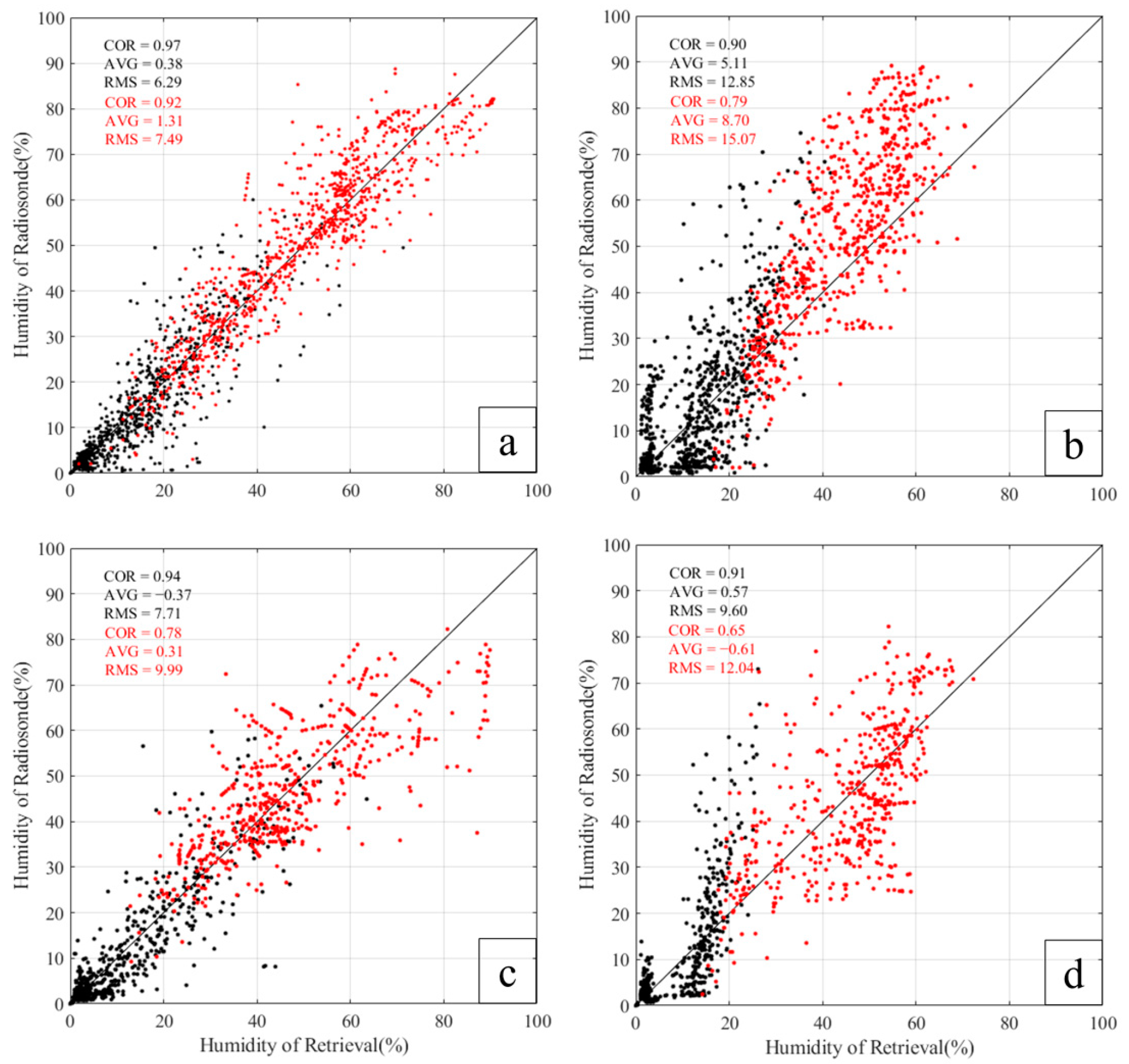
4.2. Statistical Results of Retrieval
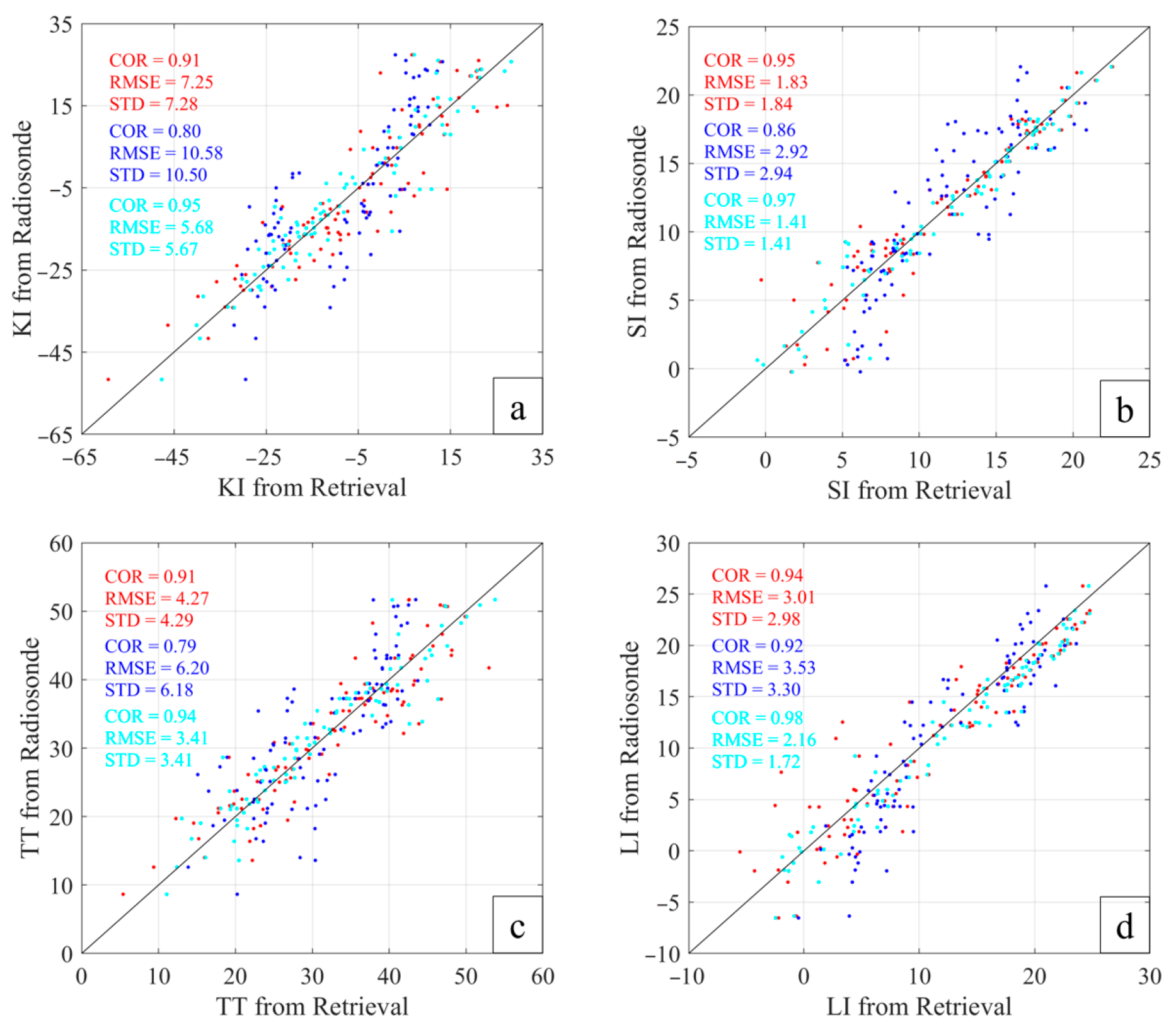
4.3. Calculation and Analysis of Forecast Index
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Influence of cloud radiation. The current retrieval model is applied to clear-sky regions without considering the cloud radiation transmission process. The cloud radiation component in the observation will reduce the accuracy of the retrieval results. However, it is difficult to find clear-sky condition FOVs in preconvection environment.
- (2)
- Observation matching. The ground-based AERI is not necessarily located at the center of the GIIRS FOV. In the coarse matching of observation data, the inverse-distance-weighted data cannot fully represent the actual observation directly above the AERI.
- (3)
- Forward model simulation. Although the calculation accuracy of the radiation transfer model used is very high, some simulation errors can still not be eliminated entirely compared with the actual atmospheric radiation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Interpretation of Forecast Indices
Appendix A.1. K Index
Appendix A.2. Showalter Index
Appendix A.3. Total Totals
Appendix A.4. Lifited Index
References
- Cimini, D.; Nelson, M.; Güldner, J.; Ware, R. Forecast indices from a ground-based microwave radiometer for operational meteorology. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2015, 8, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldner, J.; Spankuch, D. Remote Sensing of the Thermodynamic State of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer by Ground-Based Microwave Radiometry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2001, 18, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Otkin, J.; Schmit, T.J.; Liu, C. Warning Information in a Preconvection Environment from the Geostationary Advanced Infrared Sounding System–A Simulation Study Using the IHOP Case. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2011, 50, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Dadich, J.; Tyagi, B.; Vissa, N.K. Trends of thermodynamic indices thresholds over two tropical stations of north-east India during pre-monsoon thunderstorms. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phy. 2020, 211, 105472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaili, R.B.; Smith, N.; Barnet, C.D.; Berndt, E.B.; White, K.; Dostalek, J.F.; Kahn, B.H.; Sjoberg, W.; Goldberg, M. Adapting satellite soundings for operational forecasting within the hazardous weather testbed. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Wu, F. Biases in Stratospheric and Tropospheric Temperature Trends Derived from Historical Radiosonde Data. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.A.; Velazquez, M.; Manso, M.; Mas, I. Application of LPW and SAI SAFNWC/MSG satellite products in pre-convective environments. Atmos. Res. 2007, 83, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solheim, F.; Godwin, J.R.; Westwater, E.R.; Han, Y.; Keihm, S.J.; Marsh, K.; Ware, R. Radiometrie profiling of temperature, water vapor and cloud liquid water using various inversion methods. Radio Sci. 1998, 33, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartzke, J.; Knuteson, R.; Przybyl, G.; Ackerman, S.; Revercomb, H. Comparison of Satellite-, Model-, and Radiosonde-Derived Convective Available Potential Energy in the Southern Great Plains Region. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2017, 56, 1499–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.I.F. The Radiative Heat Transfer of Planet Earth. In Scientific Uses of Earth Satellites; Van Allen, J.A., Ed.; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1958; Volume 133. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, L.D. Inference of Atmospheric Structure from Remote Radiation Measurements. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1959, 49, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L.; Woolf, H.M. The Use of Eigenvectors of Statistical Covariance Matrices for Interpreting Satellite Sounding Radiometer Observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 1976, 33, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmgren-Hansen, D.; Laparra, V.; Aasbjerg Nielsen, A.; Camps-Valls, G. Statistical retrieval of atmospheric profiles with deep convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, M.T. Inverse Problems in Radiative Transfer: Determination of Atmospheric Parameters. J. Atmos. Sci. 1970, 27, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.I.; Kummerow, C.D. A 1DVAR retrieval applied to GMI: Algorithm description, validation, and sensitivities. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 7415–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L. Iterative solution of the radiative transfer equation for the temperature and absorbing gas profile of an atmosphere. Appl. Opt. 1970, 9, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wolf, W.W.; Menzel, W.P.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Achtor, T.H. Global Soundings of the Atmosphere from ATOVS Measurements: The Algorithm and Validation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1248–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, W.P.; Schmit, T.J.; Zhang, P.; Li, J. Satellite-Based Atmospheric Infrared Sounder Development and Applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, H.H.; Chahine, M.T.; Gautier, C.; Goldberg, M.D.; Kalnay, E.; McMillin, L.M.; Revercomb, H.; Rosenkranz, P.W.; Smith, W.L.; Staelin, D.H.; et al. AIRS/AMSU/HSB on the Aqua mission: Design, science objectives, data products, and processing systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F. Atmospheric Profile Retrieval with AIRS Data and Validation at the ARM CART Site. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 22, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.K.; Smith, W.L.; Larar, A.M.; Liu, X.; Taylor, J.P.; Schlüssel, P.; Strow, L.L.; Mango, S.A. All weather IASI single field-of-view retrievals: Case study–validation with JAIVEx data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2241–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, D.; Petropoulos, G.P.; Zhang, P.; Lu, F.; Lu, Q. Temperature and humidity profiles retrieval in a plain area from fengyun-3D/HIRAS sensor using a 1D-VAR assimilation scheme. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Han, W.; Gao, Z.; Li, J. Impact of High Temporal Resolution FY-4A Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS) Radiance Measurements on Typhoon Forecasts: Maria (2018) Case with GRAPES Global 4D-Var Assimilation System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Guan, L.; Shi, X. One-Dimensional Variational Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles from the FY4A GIIRS. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuteson, R.O.; Revercomb, H.E.; Best, F.A.; Ciganovich, N.C.; Dedecker, R.G.; Dirkx, T.P.; Ellington, S.C.; Feltz, W.F.; Garcia, R.K.; Howell, H.B.; et al. Atmospheric Emitted Radiance Interferometer. Part II: Instrument Performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuteson, R.O.; Revercomb, H.E.; Best, F.A.; Ciganovich, N.C.; Dedecker, R.G.; Dirkx, T.P.; Ellington, S.C.; Feltz, W.F.; Garcia, R.K.; Howell, H.B.; et al. Atmospheric Emitted Radiance Interferometer. Part I: Instrument Design. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 1763–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clive, D.R. Inverse Methods for Atmospheric Sounding: Theory and Practice; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.D.; Löhnert, U. Information Content and Uncertainties in Thermodynamic Profiles and Liquid Cloud Properties Retrieved from the Ground-Based Atmospheric Emitted Radiance Interferometer (AERI). J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2014, 53, 752–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Ma, S.; Xing, F.; Li, S.; Dai, Y. An improvement of the retrieval of temperature and relative humidity profiles from a combination of active and passive remote sensing. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2019, 131, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.D.; Blumberg, W.G. Improvements to the AERIoe Thermodynamic Profile Retrieval Algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.P.; Smith, W.L.; Huang, H.L. Retrieval of atmospheric-temperature and water-vapor profiles by use of combined satellite and ground-based infrared spectral-radiance measurements. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 4057–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebell, K.; Orlandi, E.; Löhnert, U.; Crewell, S.; Hünerbein, A. Combining ground-based with satellite-based measurements in the atmospheric state retrieval: Assessment of the information content. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6940–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, T.; Ulrich, L. Synergy of Satellite- and Ground-Based Observations for Continuous Monitoring of Atmospheric Stability, Liquid Water Path, and Integrated Water Vapor: Theoretical Evaluations Using Reanalysis and Neural Networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 1153–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Loveless, D.M.; Wagner, T.J.; Knuteson, R.O.; Turner, D.D.; Ackerman, S.A. Information Content of a Synergy of Ground-Based and Space-Based Infrared Sounders. Part I: Clear-Sky Environments. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2022, 39, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, S.M.; Sica, R.J.; Martucci, G.; Haefele, A. A 1D Var Retrieval of Relative Humidity Using the ERA5 Dataset for the Assimilation of Raman Lidar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meri, V.; Marja, B.; Jouni, R.; Victoria, A.S.; Heikki, J. Radiosonde comparison of ERA5 and ERA-Interim reanalysis datasets over tropical oceans. Tellus Ser. A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2021, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Khaikin, V.B.; Mironov, A.P.; Kovadlo, P.G. Statistical Analysis of the Water Vapor Content in North Caucasus and Crimea. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2022, 35, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, D.; Damao, Z.; Silber, I.; Scott, R.C.; Kalogeras, P.; Battaglia, A.; Bromwich, D.H.; Cadeddu, M.; Eloranta, E.; Fridlind, A.; et al. The Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) West Antarctic Radiation Experiment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E1069-91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.D.; Feltz, W.F.; Ferrare, R.A. Continuous Water Vapor Profiles from Operational Ground-Based Active and Passive Remote Sensors. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the New Generation of Chinese Geostationary Weather Satellites, Fengyun-4. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, L.B.; Zou, Y.P.; Han, C.P.; Chen, B.Y. Post-launch calibration and validation of the Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS) on FY-4A. Hongwai Yu Haomibo Xuebao/J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2019, 38, 648–654. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Simmons, A.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Payne, V.H.; Smith, W.L.; Kireev, S.; Cady-Pereira, K.E. Performance of the line-by-line radiative transfer model (LBLRTM) for temperature and species retrievals: IASI case studies from JAIVEx. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7397–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.Y.; Tsuchiya, T.; Matsui, T.N.; Shimoda, H.; Ishida, H. Cloud detection performance of spaceborne visible-to-infrared multispectral imagers. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 2601–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masiello, G.; Serio, C.; Antonelli, P. Inversion for atmospheric thermodynamical parameters of IASI data in the principal components space. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2012, 138, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Sohn, B.; Chun, H.; Li, J.; Weisz, E. Improved AIRS Temperature and Moisture Soundings with Local A Priori Information for the 1DVAR Method. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haklander, A.J.; Van Delden, A. Thunderstorm predictors and their forecast skill for the Netherlands. Atmos. Res. 2003, 67, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.C. Notes on Analysis and Severe-Storm Forecasting Procedures of the Air Force Global Weather Central; AWS: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Galway, J.G. The Lifted Index as a Predictor of Latent Instability. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1956, 37, 528–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
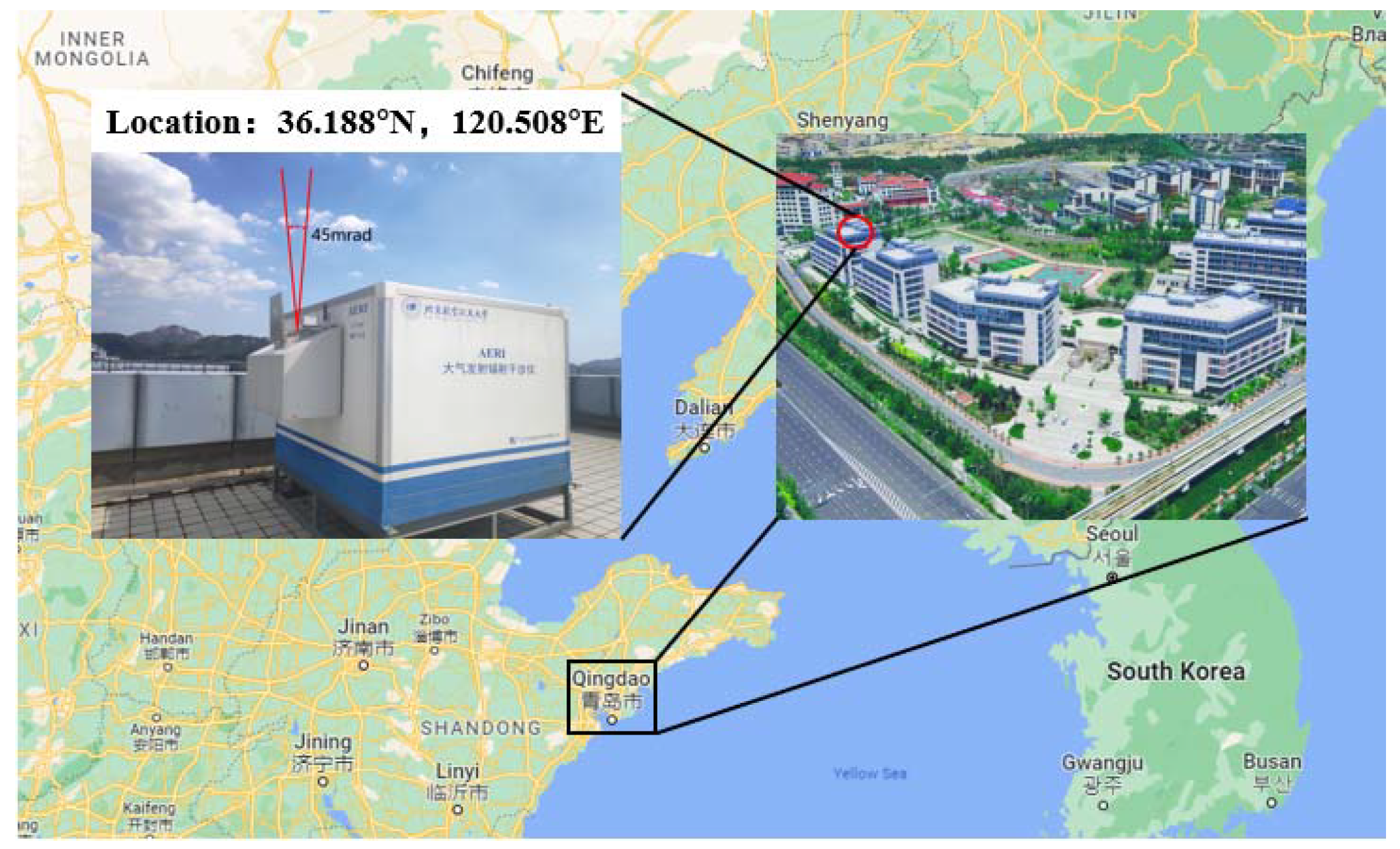






| Parameter | Performance |
|---|---|
| Spectral coverage (wavenumber) | 550–3000 cm−1 (3.3–18.2 μm) |
| Spectral resolution | 0.5 cm−1, unapodized |
| Radiometric calibration | Absolute accuracy: <1% of ambient blackbody radiance Reproducibility: <0.2% of ambient blackbody radiance |
| Wavelength calibration | Channel wavenumber knowledge: better than 0.01 cm−1 |
| Temporal sampling | Repeat cycle: ≈ 10 min |
| Angular field of view | <45 mrad |
| Parameter | Performance |
|---|---|
| Spectral coverage (wavenumber) | Long wave: 700–1130 cm−1 Medium wave: 1650–2250 cm−1 |
| Spectral resolution | 0.625 cm−1 |
| Spectral calibration accuracy | 10 ppm |
| Radiometric calibration accuracy | 1.5 K |
| Spatial resolution | 16 km (Nadir) |
| Time resolution | <1 h (China regions) |
| Area of detection | 5000 × 5000 km2 (China regions) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Ma, X.; Jia, G.; Mi, Z.; Ji, H. Synergistic Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles from Space-Based and Ground-Based Infrared Sounders Using an Optimal Estimation Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205256
Zhao H, Ma X, Jia G, Mi Z, Ji H. Synergistic Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles from Space-Based and Ground-Based Infrared Sounders Using an Optimal Estimation Method. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205256
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Huijie, Xiaohang Ma, Guorui Jia, Zhiyuan Mi, and Huanlin Ji. 2022. "Synergistic Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles from Space-Based and Ground-Based Infrared Sounders Using an Optimal Estimation Method" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205256
APA StyleZhao, H., Ma, X., Jia, G., Mi, Z., & Ji, H. (2022). Synergistic Retrieval of Temperature and Humidity Profiles from Space-Based and Ground-Based Infrared Sounders Using an Optimal Estimation Method. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205256








