A Method to Estimate Clear-Sky Albedo of Paddy Rice Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
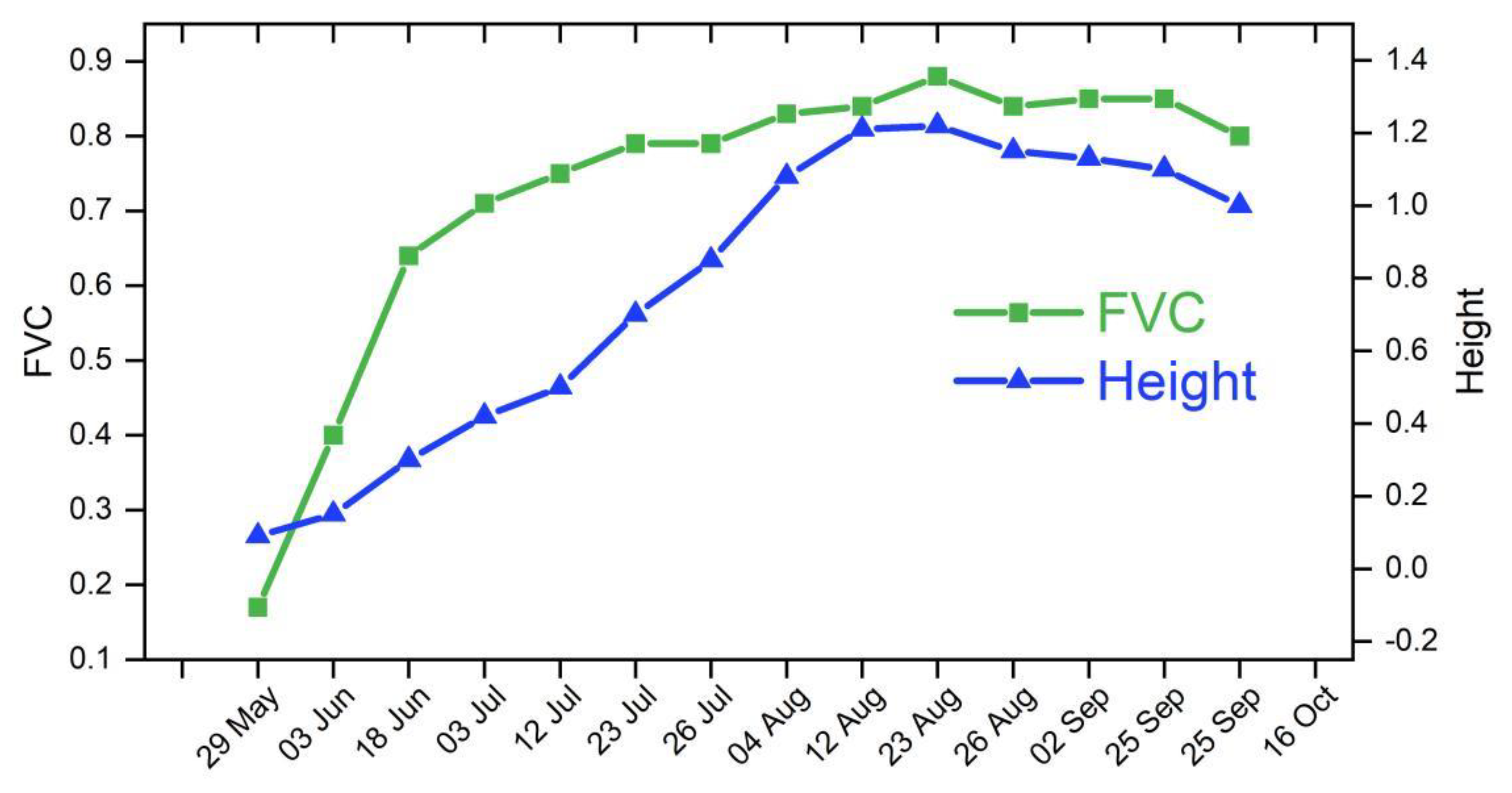
2.1. Study Area and Paddy Rice Growing Features
2.2. Data Preparation
2.2.1. Directional Reflectance
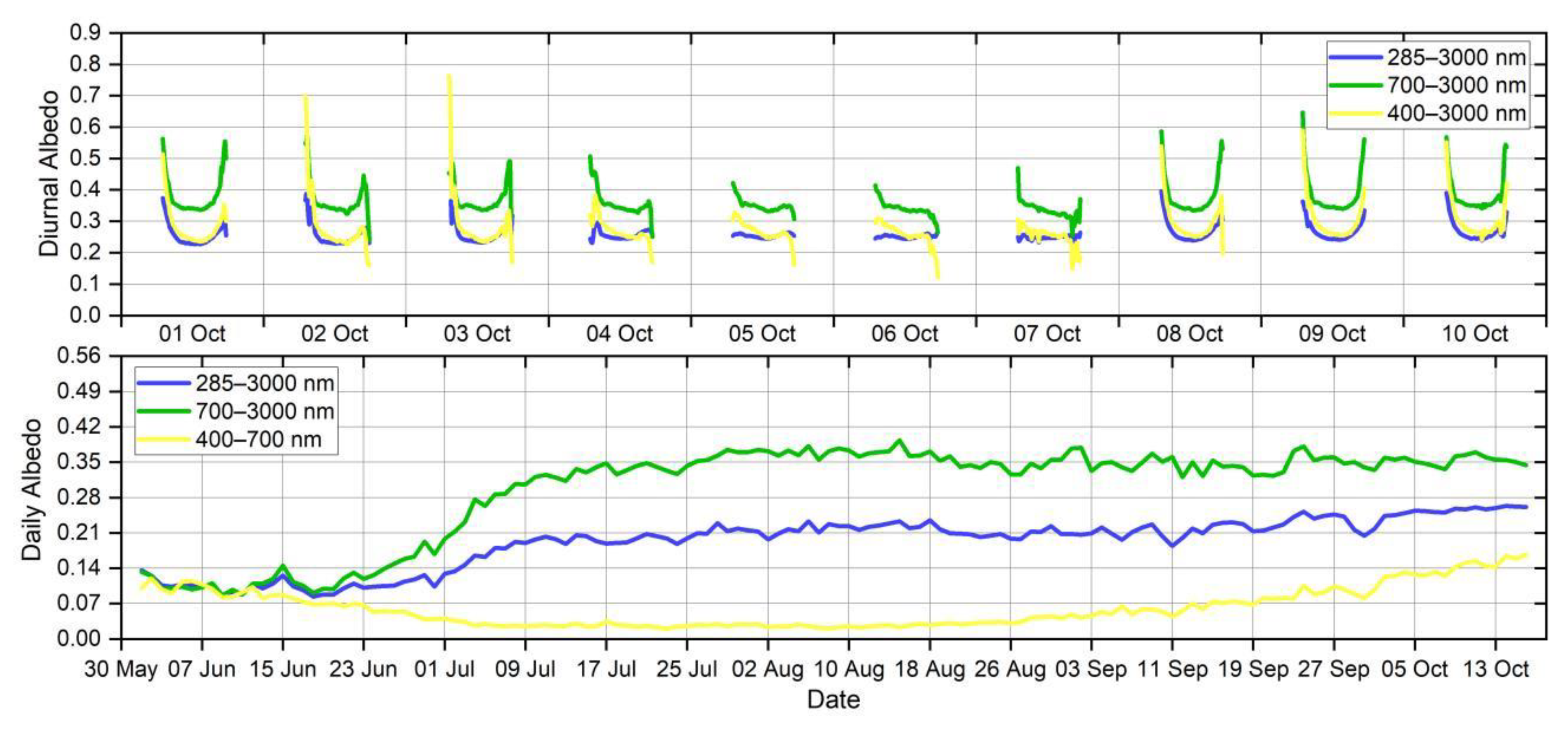
2.2.2. Albedo Observations
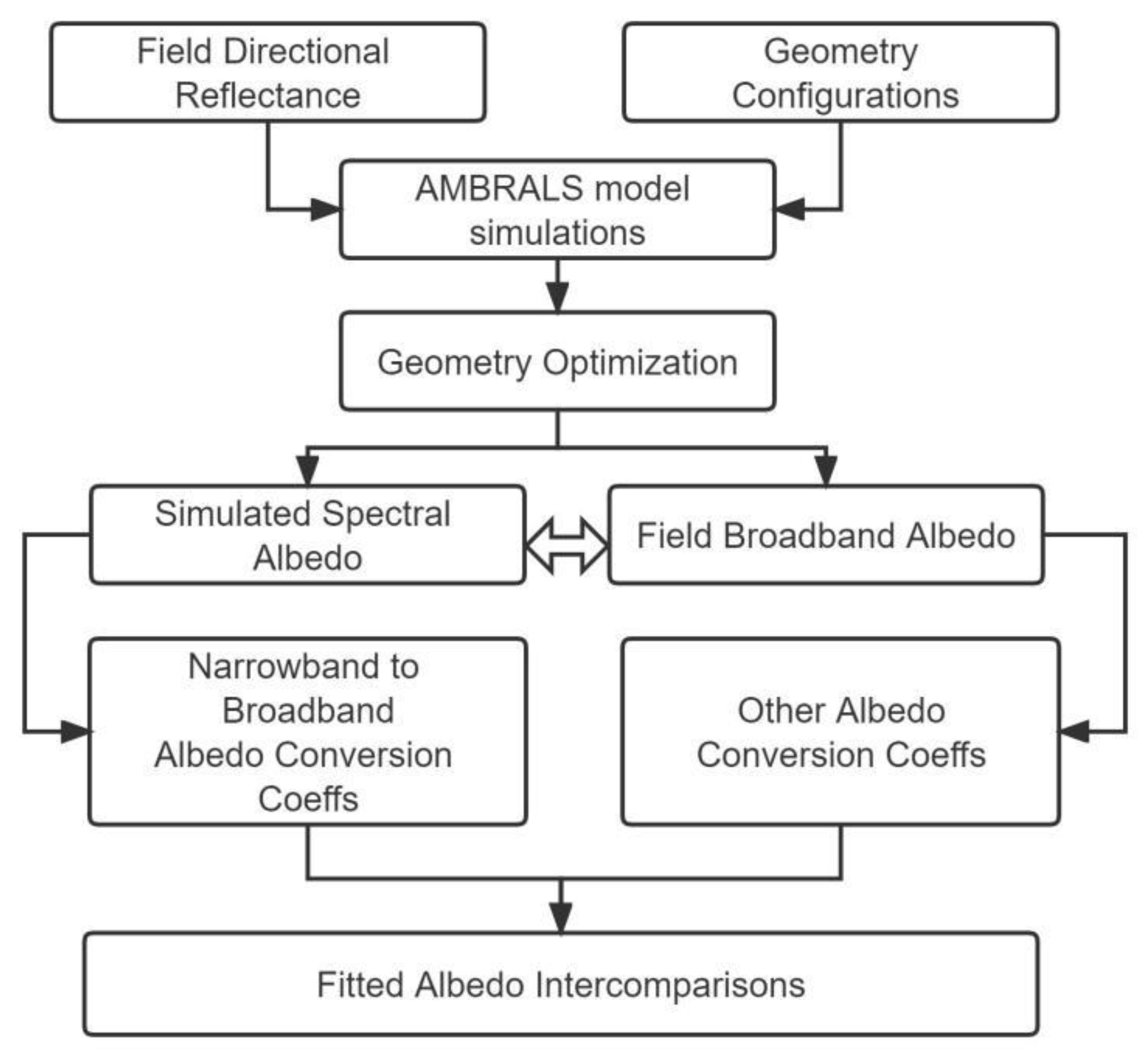
2.3. Proposed Method
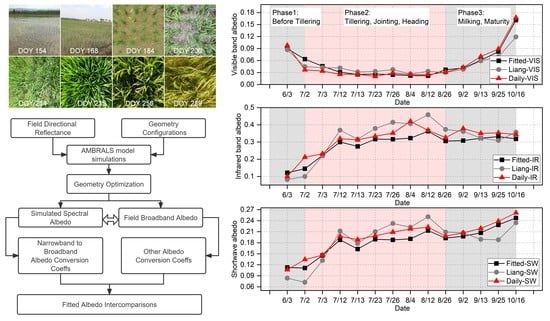
3. Results
3.1. Generation of Spectral Albedo from Directional Reflectance
3.2. Conversion Formulas from Narrowband to Broadband
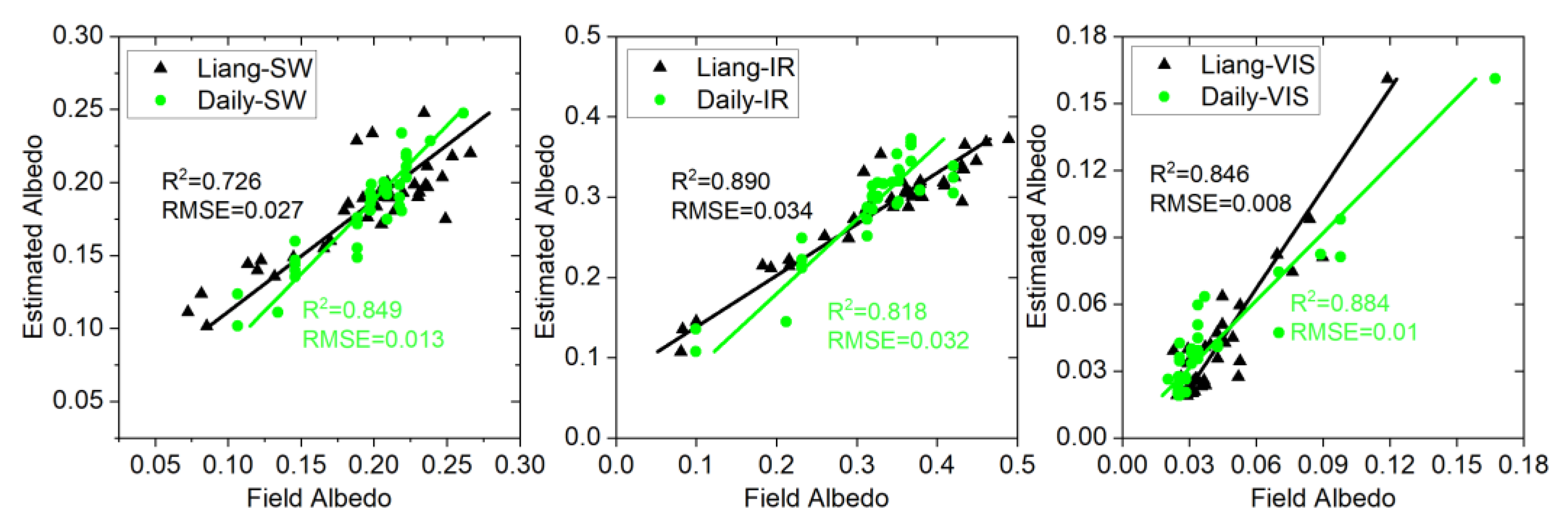
3.3. Intercomparison of Broadband Albedo
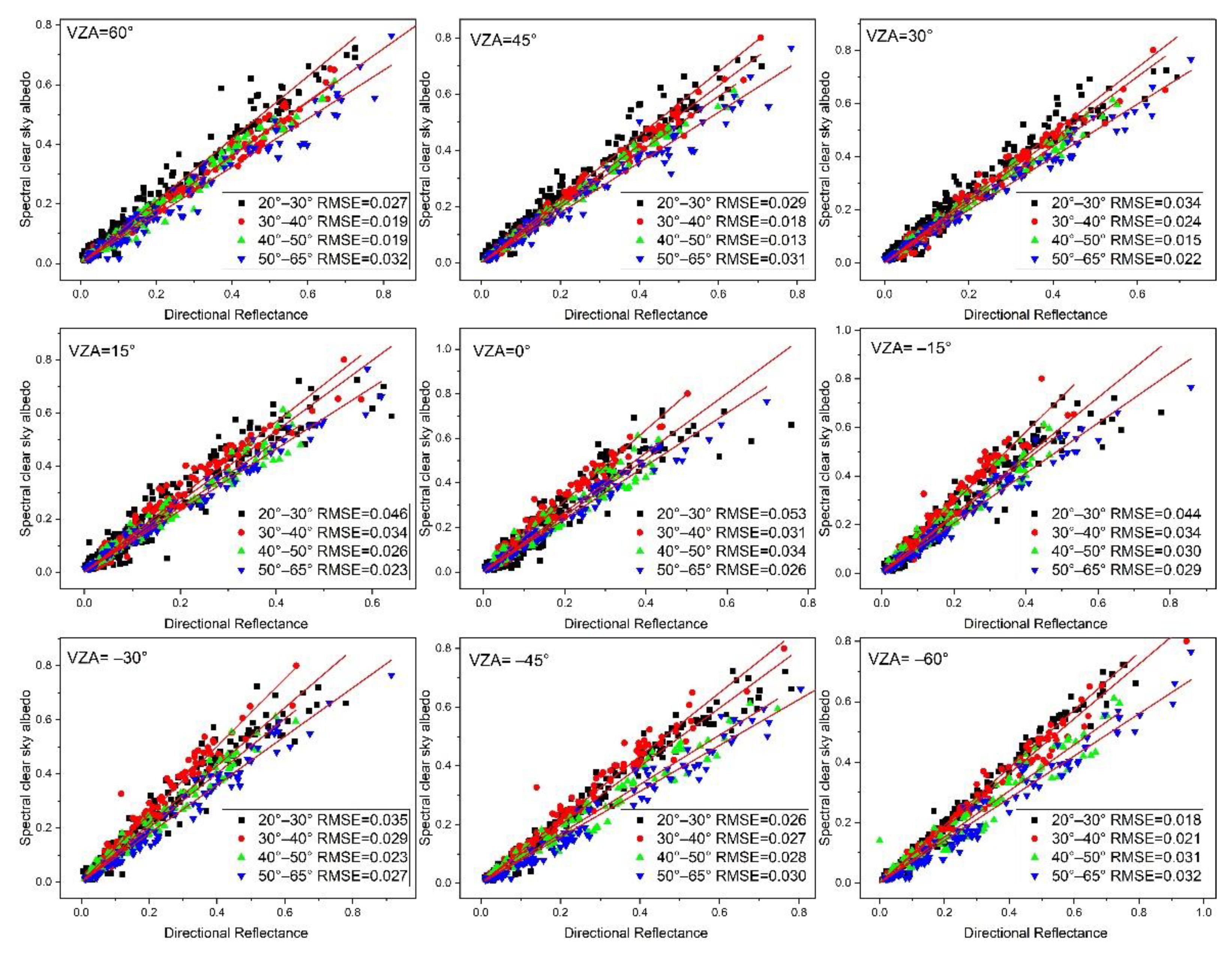
4. Discussion
4.1. SZA Dependence on Broadband Albedo Conversion
4.2. Spectral Dependence on Broadband Albedo Conversion
4.3. Applicability of the Proposed Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hall, A. The role of surface albedo feedback in climate. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 1550–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avis, C.A.; Weaver, A.J.; Meissner, K.J. Reduction in areal extent of high-latitude wetlands in response to permafrost thaw. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Jacob, D.J.; Shen, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Scarpelli, T.R.; Nesser, H.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Bloom, A.A.; et al. Global distribution of methane emissions: A comparative inverse analysis of observations from the TROPOMI and GOSAT satellite instruments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 14159–14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Bradley, E.S.; Cheung, R.; Leifer, I.; Dennison, P.E.; Margolis, J.S. Mapping methane emissions from a marine geological seep source using imaging spectrometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Niu, C.; Xu, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H. Canopy modeling of aquatic vegetation: A radiative transfer approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 186–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Russell, B.; Randolph, K.; Dierssen, H. A physics-based method for the remote sensing of seagrasses. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.P.; Du, K.; Voss, K.J.; Zibordi, G.; Lubac, B. An inherent-optical-property-centered approach to correct the angular effects in water-leaving radiance. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 3155–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beget, M.E.; Bettachini, V.A.; di Bella, C.M.; Baret, F. SAILHFlood: A radiative transfer model for flooded vegetation. Ecol. Model. 2013, 257, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Fang, H.; Liu, W.; Ye, Y. Impact of water background on canopy reflectance anisotropy of a paddy rice field from multi-angle measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liang, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J. Estimation of surface albedo and directional reflectance from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. Geometric-optical bidirectional reflectance modeling of the discrete crown vegetation canopy: Effect of crown shape and mutual shadowing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 1992, 30, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.L.; Leroy, M.; Deschamps, P.Y. A bidirectional reflectance model of the Earth’s surface for the correction of remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 20455–20468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Muller, J. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.H.; Strahler, A. Validation of kernel-driven semiempirical models for the surface bidirectional reflectance distribution function of land surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privette, J.L.; Eck, T.F.; Deering, D.W. Estimating spectral albedo and nadir reflectance through inversion of simple BRDF models with AVHRR/MODIS-like data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 29529–29542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, W.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. An algorithm for the retrieval of albedo from space using semiempirical BRDF models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2000, 38, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sütterlin, M.; Schaaf, C.B.; Stöckli, R.; Sun, Q.; Hüsler, F.; Neuhaus, C.; Wunderle, S. Albedo and reflectance anisotropy retrieval from AVHRR operated onboard NOAA and MetOp satellites: Algorithm performance and accuracy assessment for Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knap, W.H.; Oerlemans, J. The surface albedo of the Greenland ice sheet: Satellite-derived and in situ measurements in the Sondre Stromfjord area during the 1991 melt season. J Glaciol. 1996, 42, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shuey, C.J.; Russ, A.L.; Fang, H.; Chen, M.; Walthall, C.L.; Daughtry, C.S.; Hunt, R., Jr. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo: II. Validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunlin, L. A direct algorithm for estimating land surface broadband albedos from MODIS imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yu, Y.; Defelice, T.P. VIIRS narrowband to broadband land surface albedo conversion: Formula and validation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1019–1025. Available online: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01431160512331340156 (accessed on 17 January 2020). [CrossRef]
- Govaerts, Y.M.; Pinty, B.; Taberner, M.; Lattanzio, A. Spectral Conversion of Surface Albedo Derived From Meteosat First Generation Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, J.I.; Manninen, T.; Suomalainen, J.; Hakala, T.; Puttonen, E.; Riihelä, A. Land Surface Albedos Computed from BRF Measurements with a Study of Conversion Formulae. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1918–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja, J.; Recondo, C.; Peón, J.; Fernández, S.; de la Cruz, F.; González-Piqueras, J. A New Method for the Estimation of Broadband Apparent Albedo Using Hyperspectral Airborne Hemispherical Directional Reflectance Factor Values. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoni, S.; Sekertekin, A. Albedo retrieval from Sentinel-2 by new narrow-to-broadband conversion coefficients. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuell, W.; Reijmer, C.H.; Oerlemans, J. Narrowband-to-broadband albedo conversion for glacier ice and snow based on aircraft and near-surface measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greuell, W.; Oerlemans, J. Narrowband-to-broadband albedo conversion for glacier ice and snow: Equations based on modeling and ranges of validity of the equations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 89, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Stroeve, J.; Box, J.E. Mapping daily snow/ice shortwave broadband albedo from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS): The improved direct retrieval algorithm and validation with Greenland in situ measurement. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dalum, C.T.; van de Berg, W.J.; Libois, Q.; Picard, G.; van den Broeke, M.R. A module to convert spectral to narrowband snow albedo for use in climate models: SNOWBAL v1.2. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2019, 12, 5157–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, C.; Moore, J.; Wang, G.; Niu, G.Y. Physics-Based Narrowband Optical Parameters for Snow Albedo Simulation in Climate Models. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2020MS002431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Tamura, M.; Takahashi, H. Atmospheric and spectral corrections for estimating surface albedo from satellite data using 6S code. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, D.M.; Wu, Q.; Pathak, C.S. Variability of Albedo and Utility of the MODIS Albedo Product in Forested Wetlands. Wetlands 2011, 31, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.; Weiss, M.; Baret, F.; Courault, D.; Hagolle, O.; Gallego-Elvira, B.; Olioso, A. The MODIS (collection V006) BRDF/albedo product MCD43D: Temporal course evaluated over agricultural landscape. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Song, K. Validation of global evapotranspiration product (MOD16) using flux tower data from Panjin coastal wetland, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlan, L.; Mangiarotti, S.; Mougin, E.; Mazzega, P.; Hiernaux, P.; Ledantec, V. Assimilation of SPOT/VEGETATION NDVI data into a sahelian vegetation dynamics model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1381–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, A.; Desai, A.R.; Huang, J.; Griffis, T.J.; Reed, D.E.; Chen, J. Evaluation of prediction and forecasting models for evapotranspiration of agricultural lands in the Midwest U.S. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B. The Land Surface Climatology of the NCAR Land Surface Model Coupled to the NCAR Community Climate Model. J. Clim. 1998, 15, 3123–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, B.; Jacobs, J.M.; Judge, J. Intercomparison study of the land surface process model and the common land model for a prairie wetland in Florida. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Mercado, L.M.; Sitch, S.; Jones, C.D.; Gedney, N.; Best, M.J.; Pryor, M.; Rooney, G.G.; Essery, R.L.H.; Blyth, E.; et al. The Joint UK Land Environment Simulator (JULES), model description—Part 2: Carbon fluxes and vegetation dynamics. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2011, 4, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumedah, G.; Walker, J.P. Intercomparison of the JULES and CABLE land surface models through assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture in southeast Australia. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 74, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, W.; Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. On the derivation of kernels for kernel-driven models of bidirectional reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 21077–21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ding, A.; Kokhanovsky, A.; Schaaf, C.; Bréon, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S. Development of a snow kernel to better model the anisotropic reflectance of pure snow in a kernel-driven BRDF model framework. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, W.; Wei, S.; Jiang, C. Seasonal variation of leaf area index (LAI) over paddy rice fields in NE China: Intercomparison of destructive sampling, LAI-2200, digital hemispherical photography (DHP), and AccuPAR methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 198–199, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Li, W.; Ye, Y.; Sun, T.; Liu, W. Validation of global moderate resolution leaf area index (LAI) products over croplands in northeastern China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, W. Expected retrieval accuracies of bidirectional reflectance and albedo from EOS-MODIS and MISR angular sampling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 8763–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liang, S.; Wang, D.; Cao, Y.; Gao, F.; Yu, Y.; Feng, M. Evaluating land surface albedo estimation from Landsat MSS, TM, ETM +, and OLI data based on the unified direct estimation approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Barnsley, M.J. Influence of the sky radiance distribution on various formulations of the earth surface albedo. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Physical Measurements and Signatures in Remote Sensing, ISPRS 1994, Val d’Isere, France, 17–21 January 1994; pp. 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Lucht, W.; Hyman, A.H.; Strahler, A.H.; Barnsley, M.J.; Hobson, P.; Muller, J. A Comparison of Satellite-Derived Spectral Albedos to Ground-Based Broadband Albedo Measurements Modeled to Satellite Spatial Scale for a Semidesert Landscape. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Mitomi, Y.; Takamura, T. An empirical anisotropy correction model for estimating land surface albedo for radiation budget studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Tian, J.; Tian, Q.; Xu, K.; Xu, N. Development of soil moisture indices from differences in water absorption between shortwave-infrared bands. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegleb, B.P.; Minnis, P.; Ramanathan, V.; Harrison, E. Comparison of regional clear-sky albedos inferred from satellite observations and model computations. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1986, 25, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Olioso, A. Derivation of diurnal courses of albedo and reflected solar irradiance from airborne POLDER data acquired near solar noon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

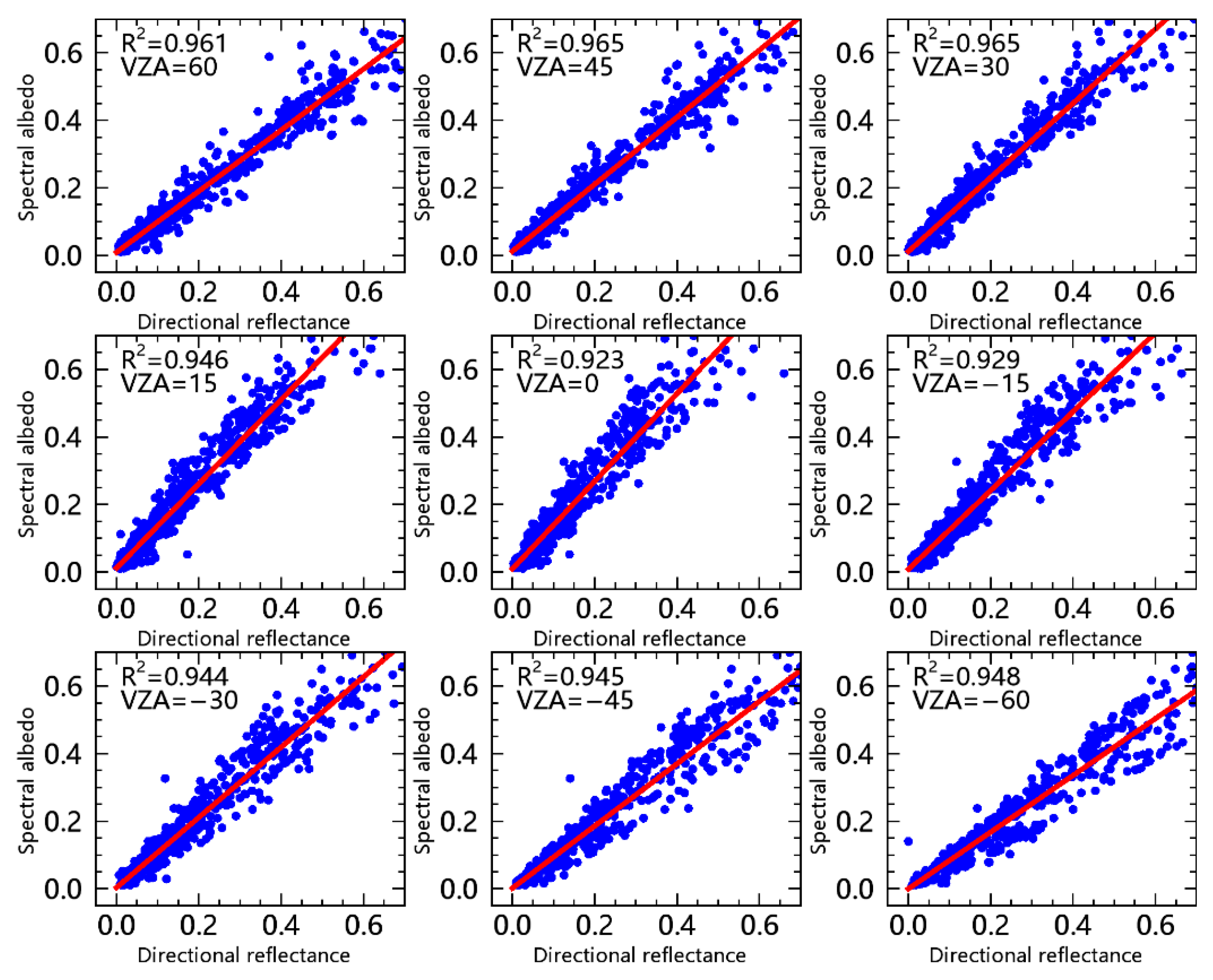

| Data Info | Coefficient | Statistics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VZA | k1 | k2 | R2 | RMSE |
| 60° | 1.063 | −0.003 | 0.961 | 0.036 |
| 45° | 0.972 | −0.006 | 0.965 | 0.031 |
| 30° | 0.879 | −0.004 | 0.964 | 0.029 |
| 15° | 0.758 | −0.001 | 0.945 | 0.031 |
| 0° | 0.711 | 0.003 | 0.923 | 0.035 |
| −15° | 0.795 | 0.004 | 0.928 | 0.038 |
| −30° | 0.908 | 0.006 | 0.944 | 0.038 |
| −45° | 1.025 | 0.009 | 0.944 | 0.043 |
| −60° | 1.128 | 0.011 | 0.947 | 0.045 |
| Mean values | - | - | 0.947 | 0.037 |
| Spectral Albedo | Shortwave | Infrared * | Visible * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Coeff | SE | Coeff | SE | Coeff | SE |
| −1.524 | 0.023 | - | - | −1.357 | 0.402 | |
| 0.197 | 0.693 | - | - | 1.1718 | 0.137 | |
| 0.128 | 0.282 | - | - | −0.0528 | 0.019 | |
| 1.1263 | 0.048 | 0.556 | 0.257 | - | - | |
| 0.0713 | 0.266 | 0.407 | 0.079 | - | - | |
| 0.0894 | 0.064 | 0.205 | 0.138 | - | - | |
| −0.023 | 0.091 | −0.055 | 0.121 | - | - | |
| Intercept | 0.063 | 0.069 | 0.075 | 0.028 | 0.0525 | 0.012 |
| VZA and SZA | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 20°–30° | 30°–40° | 40°–50° | 50°–65° |
| 60° | 0.987 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.984 |
| 45° | 0.985 | 0.994 | 0.996 | 0.986 |
| 30° | 0.980 | 0.991 | 0.995 | 0.993 |
| 15° | 0.963 | 0.982 | 0.987 | 0.992 |
| 0° | 0.951 | 0.985 | 0.978 | 0.990 |
| −15° | 0.967 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.987 |
| −30° | 0.979 | 0.987 | 0.989 | 0.989 |
| −45° | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.984 | 0.987 |
| −60° | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.981 | 0.985 |
| 470 nm | 550 nm | 660 nm | 850 nm | 1243 nm | 1640 nm | 2151 nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60° | 1.117 | 0.981 | 1.064 | 0.938 | 0.913 | 0.912 | 0.971 |
| 45° | 1.195 | 1.125 | 1.102 | 1.025 | 1.020 | 1.049 | 1.056 |
| 30° | 1.050 | 1.177 | 1.073 | 1.117 | 1.135 | 1.224 | 1.162 |
| 15° | 1.096 | 1.303 | 1.090 | 1.288 | 1.295 | 1.422 | 1.172 |
| 0° | 1.099 | 1.235 | 1.081 | 1.335 | 1.358 | 1.450 | 1.159 |
| −15° | 0.989 | 1.089 | 1.005 | 1.198 | 1.208 | 1.285 | 1.076 |
| −30° | 0.853 | 0.931 | 0.877 | 1.051 | 1.065 | 1.073 | 0.994 |
| −45° | 0.814 | 0.792 | 0.722 | 0.933 | 0.938 | 0.923 | 0.892 |
| −60° | 0.720 | 0.709 | 0.654 | 0.853 | 0.849 | 0.816 | 0.799 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Fang, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, R. A Method to Estimate Clear-Sky Albedo of Paddy Rice Fields. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205185
Sun T, Fang H, Chen L, Sun R. A Method to Estimate Clear-Sky Albedo of Paddy Rice Fields. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205185
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tao, Hongliang Fang, Liding Chen, and Ranhao Sun. 2022. "A Method to Estimate Clear-Sky Albedo of Paddy Rice Fields" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205185
APA StyleSun, T., Fang, H., Chen, L., & Sun, R. (2022). A Method to Estimate Clear-Sky Albedo of Paddy Rice Fields. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5185. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205185