A Continuous PDR and GNSS Fusing Algorithm for Smartphone Positioning
Abstract
1. Introduction
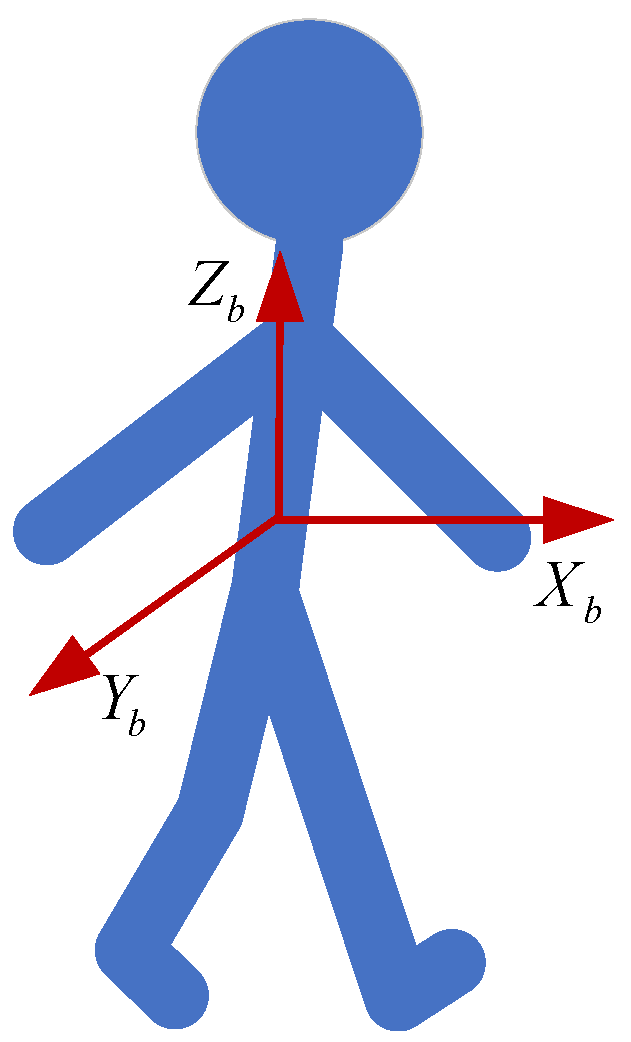
2. PDR Model and Its Characteristics
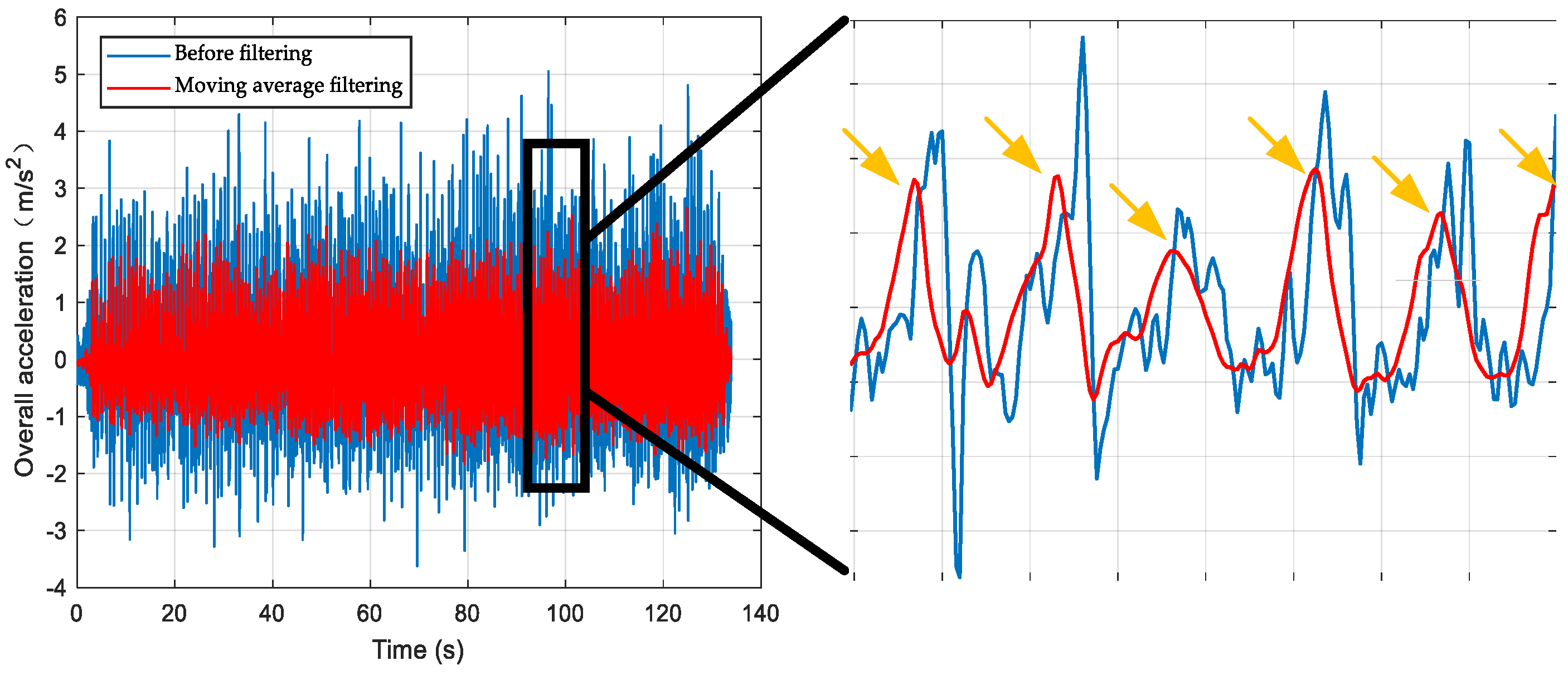
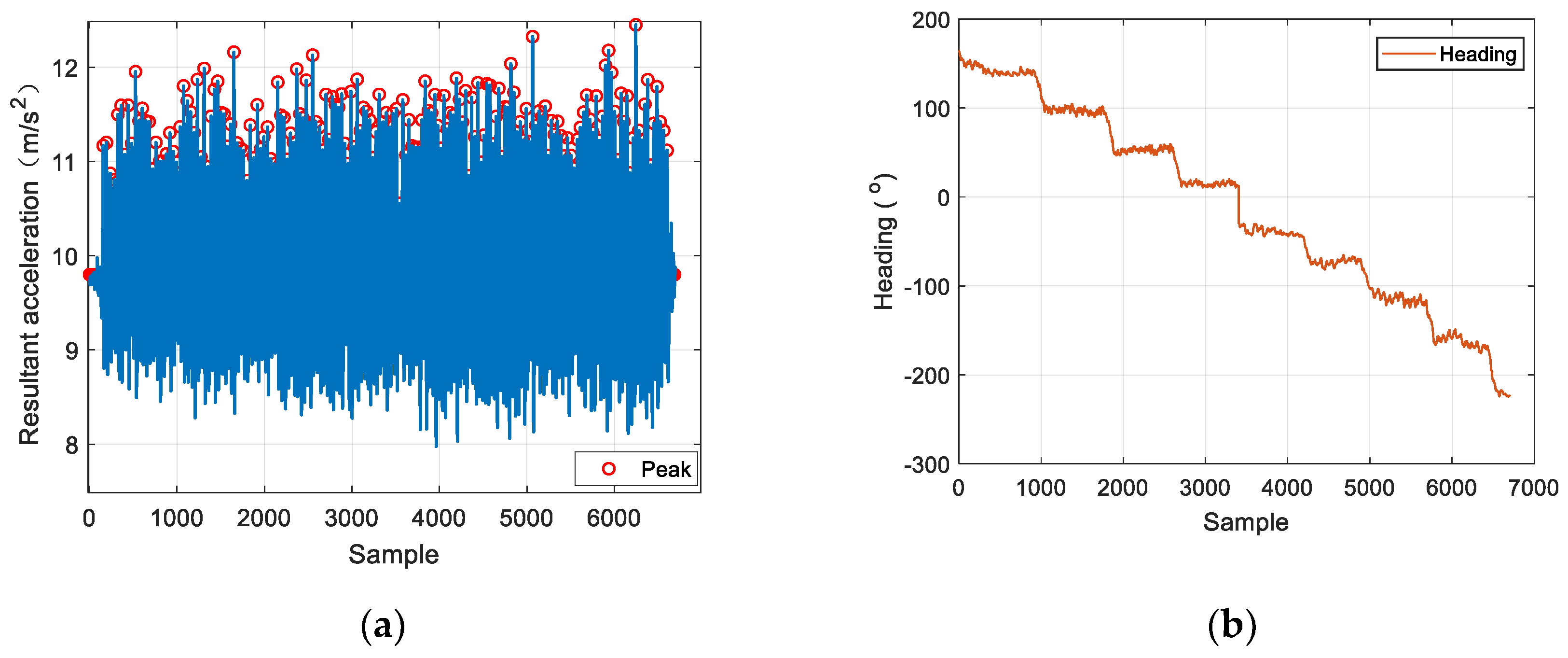
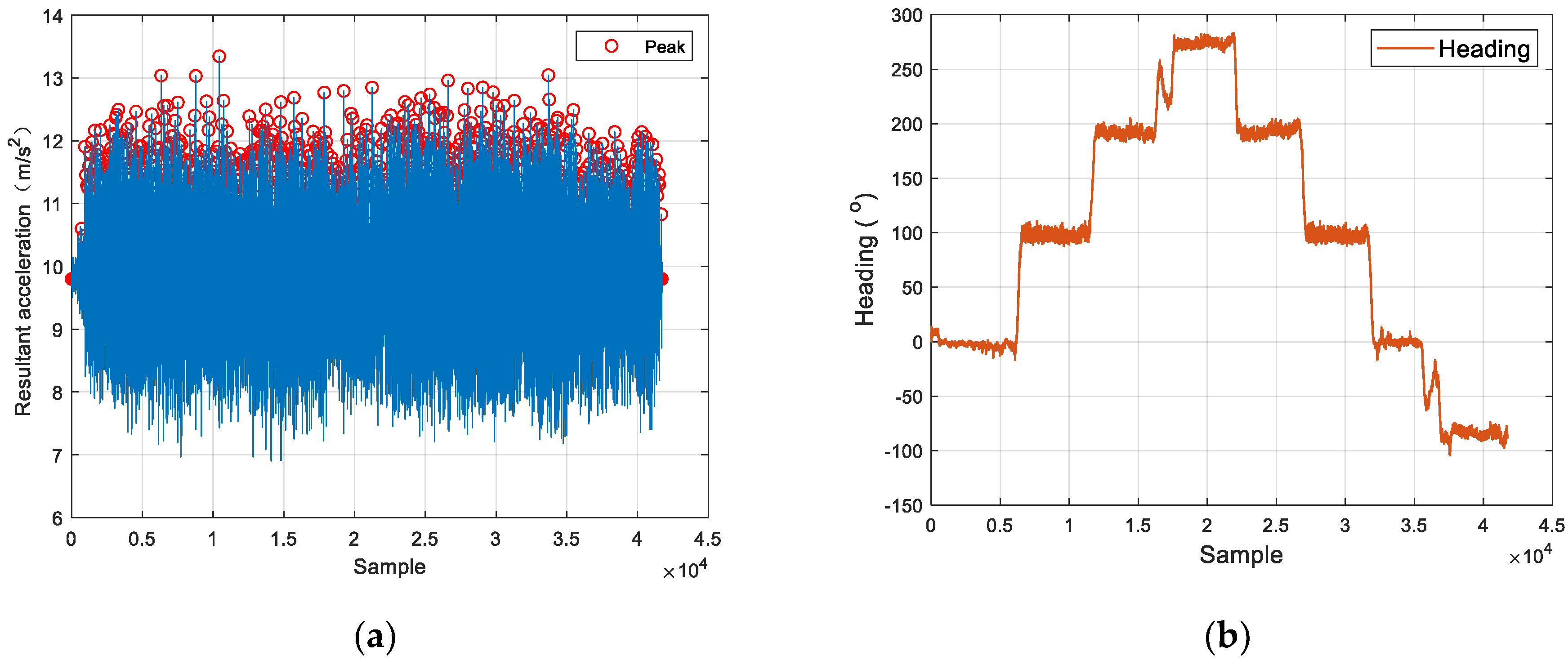
2.1. Peak Detection
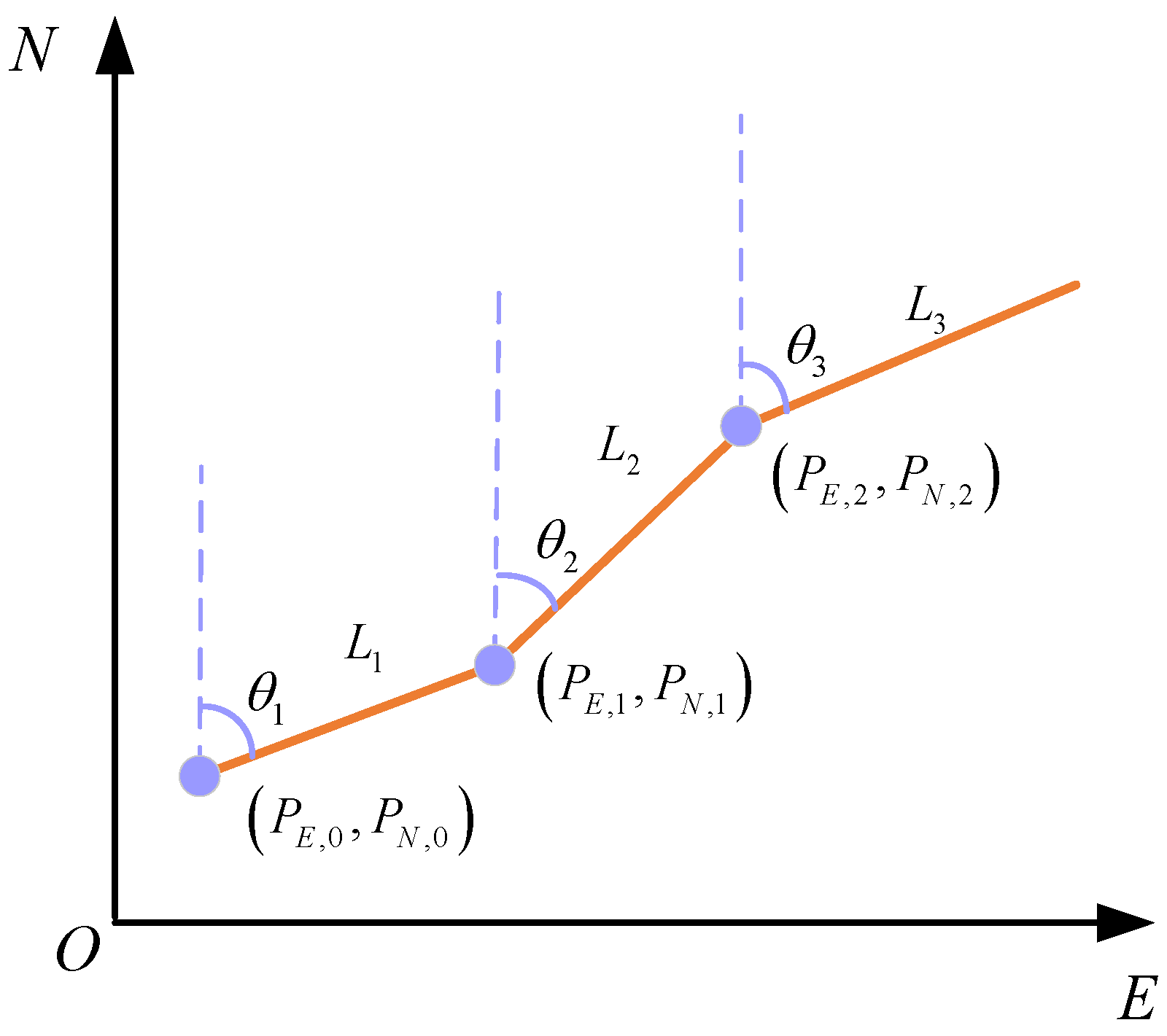
2.2. Problem Formulation
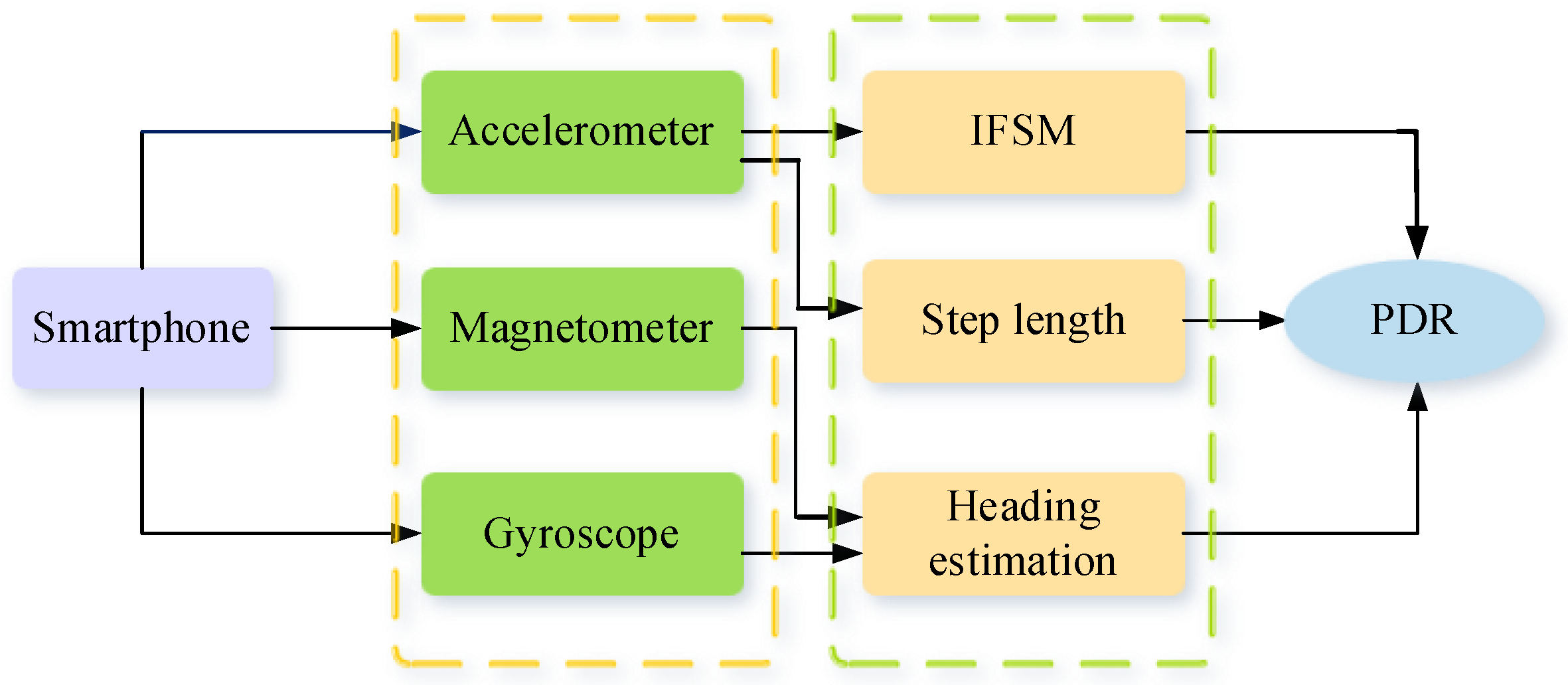
3. The Proposed OBPDR Method
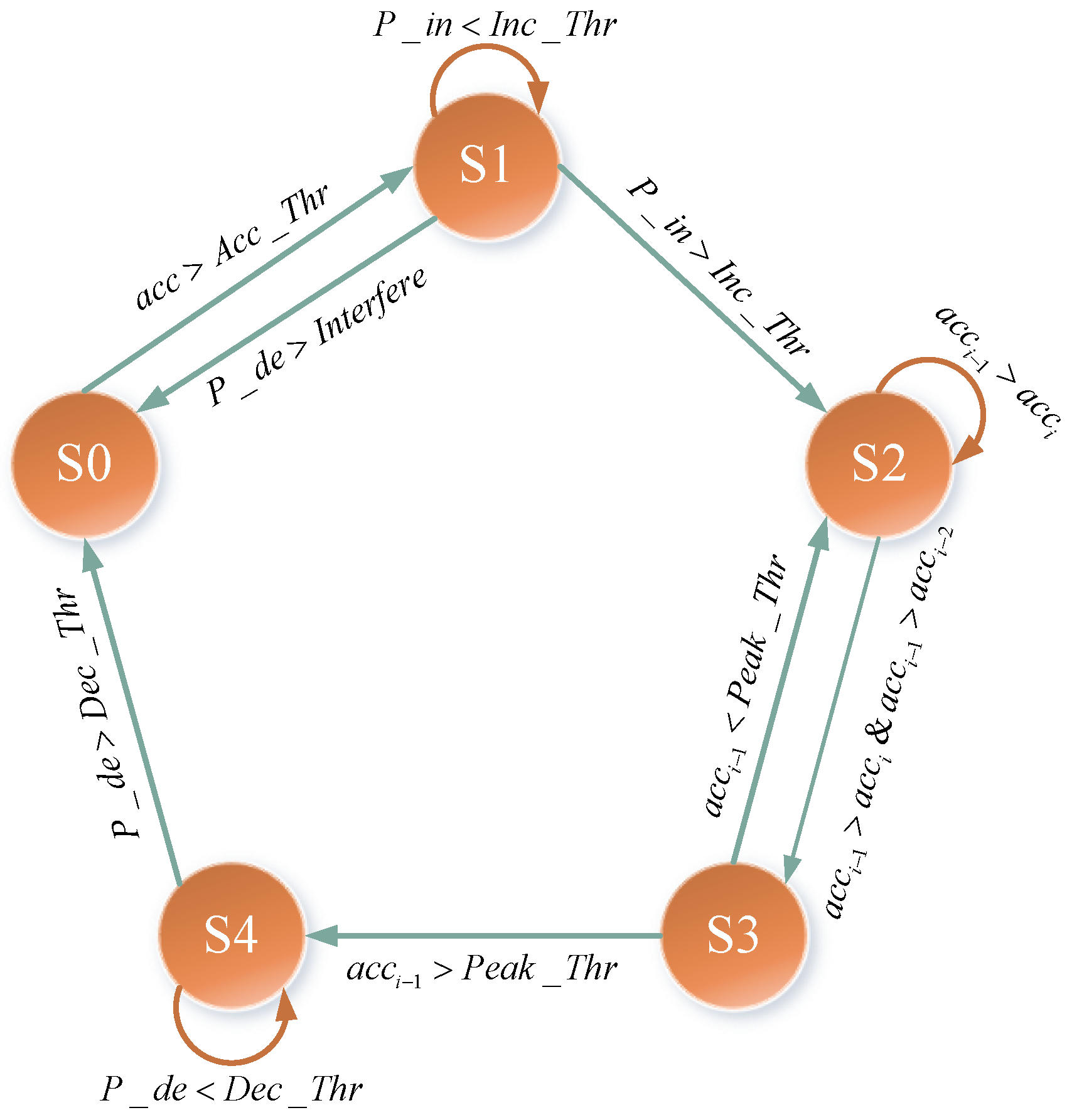
3.1. IFSM Gait Detection Algorithm
- (1)
- At the beginning, it is in a stable state, . If the current acceleration is larger than , it enters the state , and and are set to zero at the same time;
- (2)
- The noise shielding mechanism is introduced in the rising state . If there is substantial noise in the data obtained by the accelerometer, the acceleration waveform will fluctuate violently, i.e., and will increase at the same time. Since is smaller than , it will first meet , and the system will return to the stable state for re-detection;
- (3)
- After entering the rising state, if exceeds , the system will enter the state ;
- (4)
- If is less than the current peak after entering the next state, the system will enter the state , otherwise it will return to state ;
- (5)
- In state , if continues to increase until it is greater than , the system returns to state , and the number of steps increases by 1.
3.2. The Dynamic Model of PDR
3.3. Fusion of a PDR Algorithm with a GNSS System
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
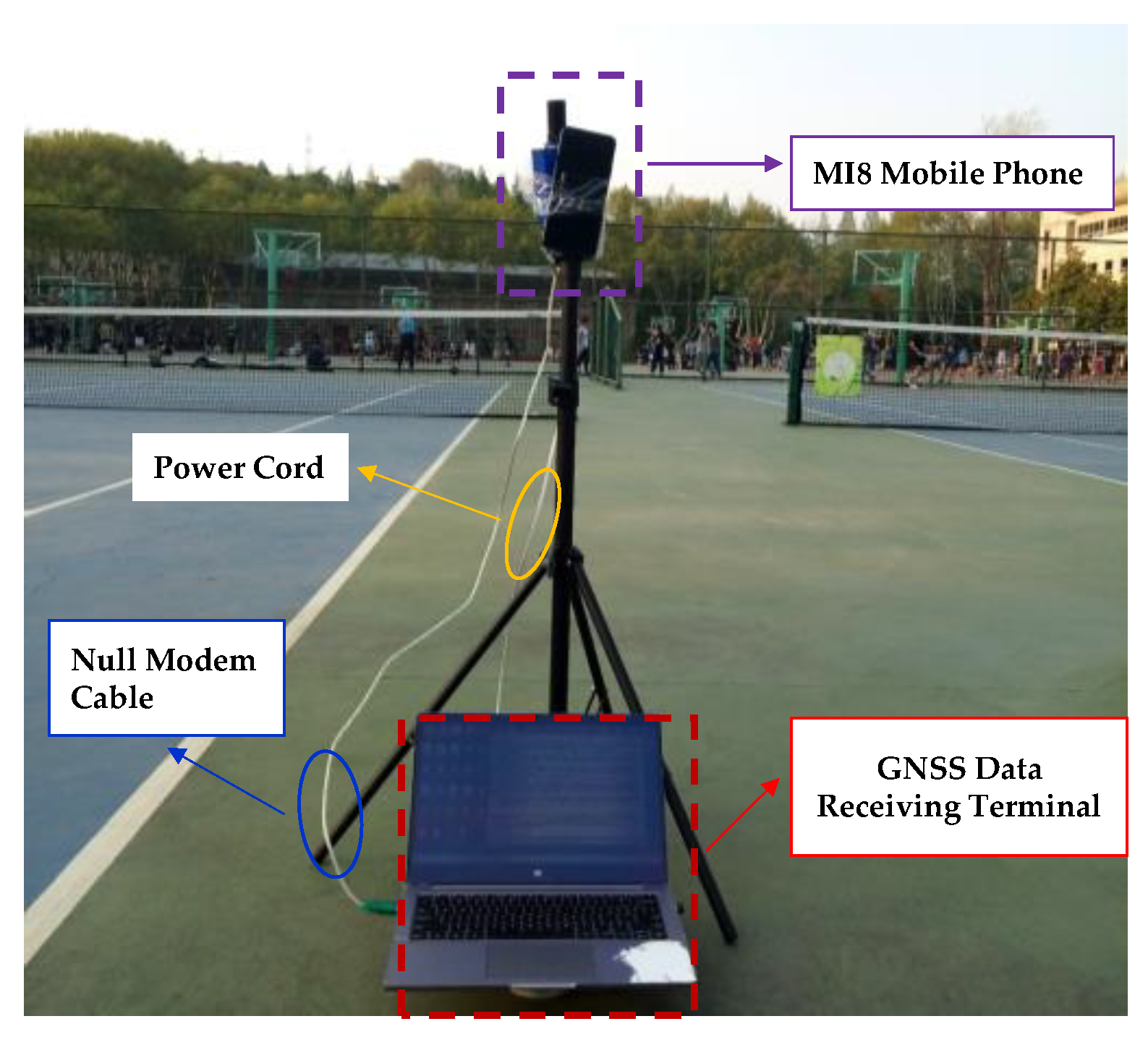
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Performance Analysis of GNSS Positioning
4.3. Performance Analysis of the IFSM Algorithm
4.4. Performance Analysis of the OBPDR Method
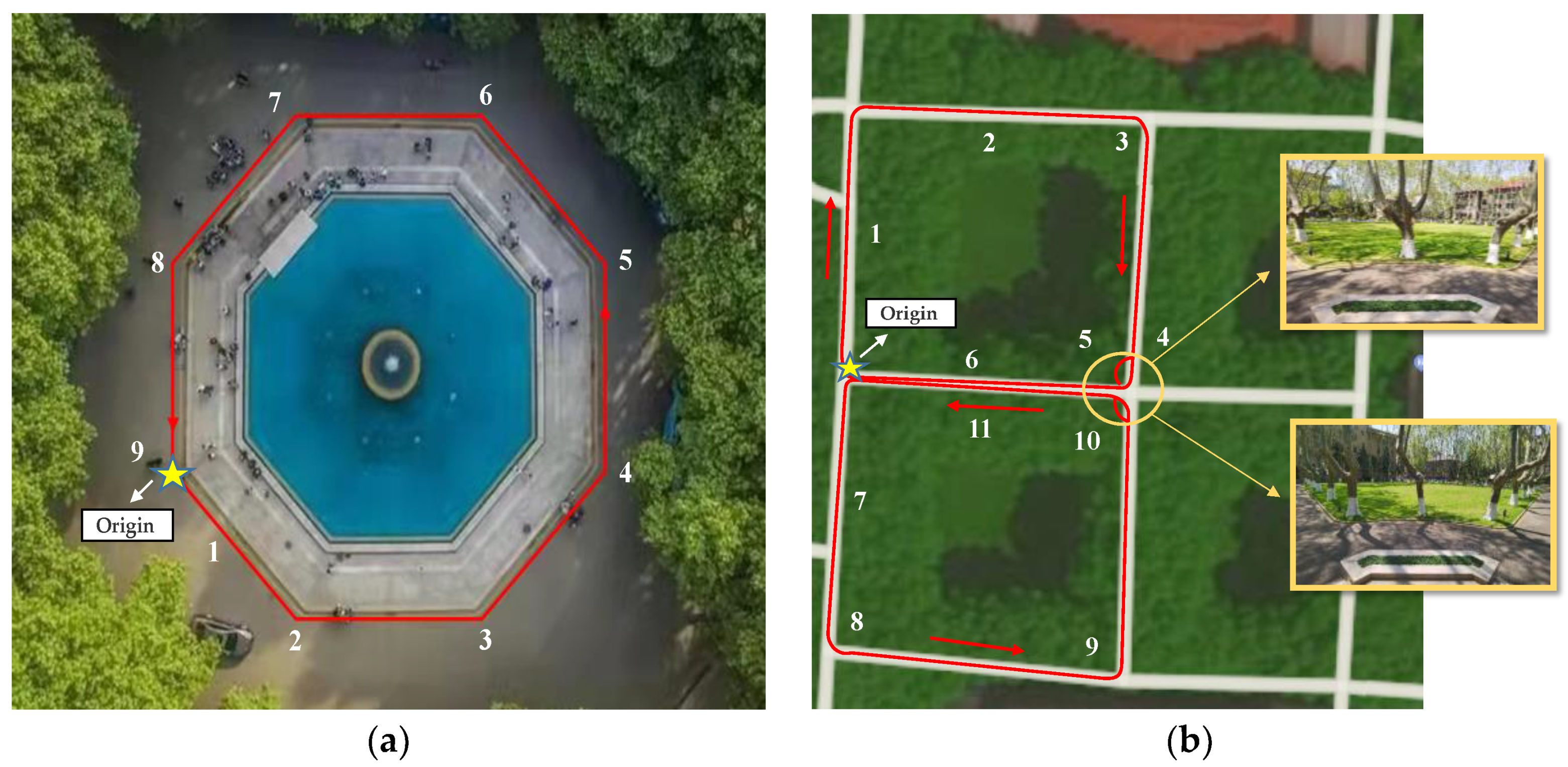
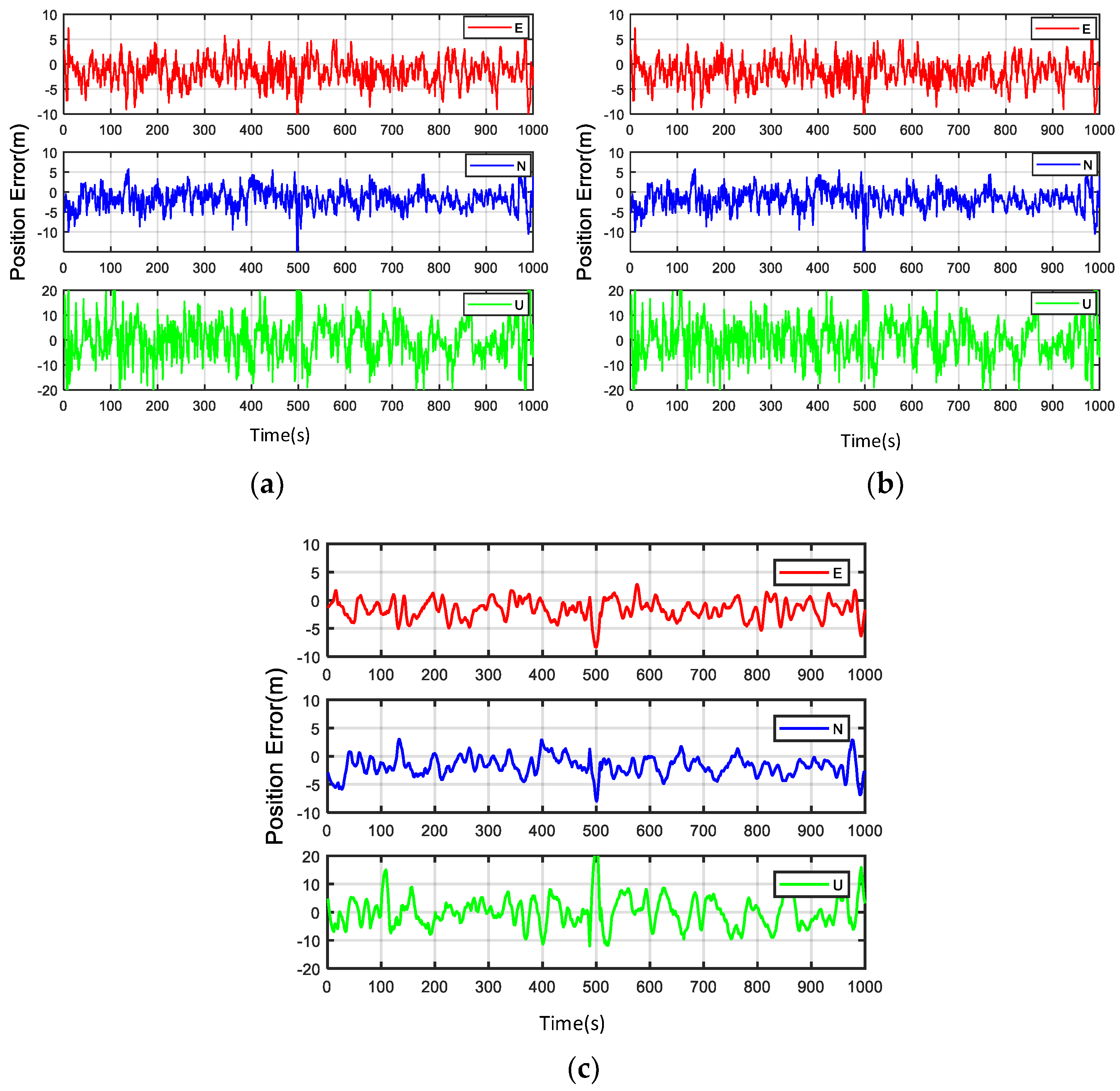
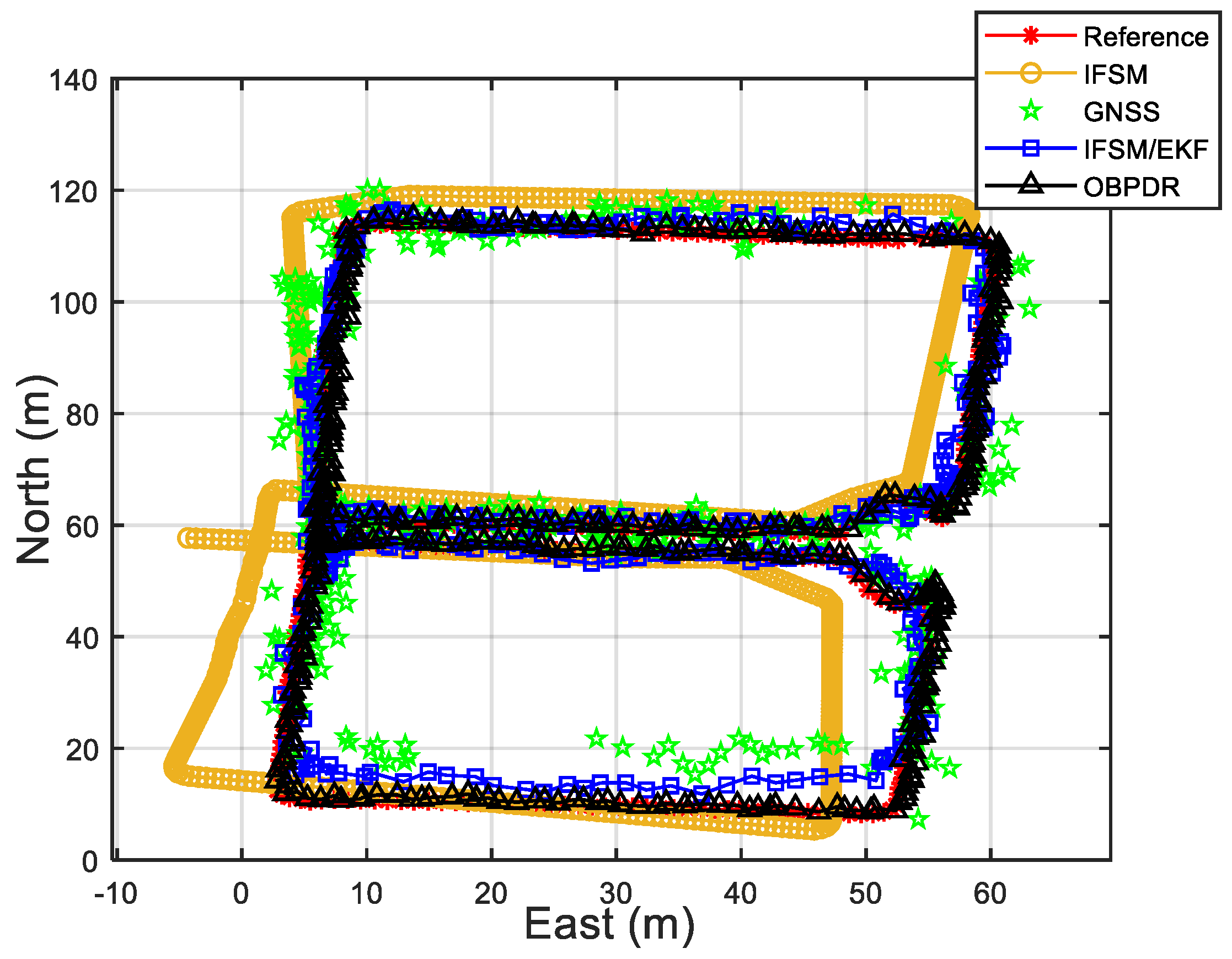
4.4.1. Analysis of the Results of the Fountain Experiment
4.4.2. Analysis of the Results of the Shade Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuptametee, C.; Aunsri, N. A review of resampling techniques in particle filtering framework. Measurement 2022, 193, 110836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ma, C.; Poslad, S.; Selviah, D.R. An Adaptive Human Activity-Aided Hand-Held Smartphone-Based Pedestrian Dead Reckoning Positioning System. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Vijayakumar, P.; Shen, J.; Gupta, B.B. A location-based privacy-preserving oblivious sharing scheme for indoor navigation. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 137, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. Smartphone sensor based indoor positioning: Current status, opportunities, and future challenges. Electronics 2020, 9, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Chen, R.; Ye, F.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, Z. A Pose Awareness Solution for Estimating Pedestrian Walking Speed. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Na, Z.; Liu, X.; Deng, Z. WiFi/PDR-integrated indoor localization using unconstrained smartphones. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 3728127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q. Hybrid urban canyon pedestrian navigation scheme combined PDR, GNSS and beacon based on smartphone. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. A Bluetooth/PDR integration algorithm for an indoor positioning system. Sensors 2015, 15, 24862–24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Tao, X.; Liu, W.; Shi, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X. Walker: Continuous and precise navigation by fusing GNSS and MEMS in smartphone chipsets for pedestrians. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Niu, X.; Chen, X. Robust pedestrian dead reckoning based on MEMS-IMU for smartphones. Sensors 2018, 18, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, H.; Yu, B.; Gan, X.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, R. Combination of smartphone MEMS sensors and environmental prior information for pedestrian indoor positioning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, X.; Huang, B.; Qi, G. A novel walking detection and step counting algorithm using unconstrained smartphones. Sensors 2018, 18, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Heo, S.J.; Park, C.G. Accelerometer-based smartphone step detection using machine learning technique. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Pattaya, Thailand, 8–10 March 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Yang, M.; Jin, S. A multi-mode PDR perception and positioning system assisted by map matching and particle filtering. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zou, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Soh, Y.C.; Xie, L. Fusion of WiFi, smartphone sensors and landmarks using the Kalman filter for indoor localization. Sensors 2015, 15, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Qi, H.; Hu, X. Indoor positioning tightly coupled Wi-Fi FTM ranging and PDR based on the extended Kalman filter for smartphones. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 49671–49684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.-S.; Lin, H.-W. A step counting algorithm for smartphone users: Design and implementation. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 15, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Costa, A.; Nicolau, M.J. Autocorrelation analysis of accelerometer signal to detect and count steps of smartphone users. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Pisa, Italy, 30 September–3 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, P.; Yang, H. Integrated WiFi/PDR/Smartphone using an unscented kalman filter algorithm for 3D indoor localization. Sensors 2015, 15, 24595–24614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Duan, N.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, F.; Qiu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, G. Indoor PDR positioning assisted by acoustic source localization, and pedestrian movement behavior recognition, using a dual-microphone smartphone. Wirel. Commun. Mobile Comput. 2021, 2021, 9981802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.; Barger, J.A.; Kaveh, M. A parametric model for the distribution of the angle of arrival and the associated correlation function and power spectrum at the mobile station. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2002, 51, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzantot, M.; Youssef, M. UPTIME: Ubiquitous pedestrian tracking using mobile phones. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Paris, France, 1–4 April 2012; pp. 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Liang, J.Z.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.J. Acceleration Difference Finite State Machine Step Algorithm. Comput. Sci. Explor. 2016, 10, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, H. Autonomous 3D indoor localization based on crowdsourced Wi-Fi fingerprinting and MEMS sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 5248–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, P.; Buzio, M.; Di Capua, V.; Grassini, S.; Parvis, M.; Pentella, M. Drift-Free Integration in Inductive Magnetic Field Measurements Achieved by Kalman Filtering. Sensors 2021, 22, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattha, M.; Naqvi, I.H. Pilot: A precise IMU based localization technique for smart phone users. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 84th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Montréal, QC, Canada, 18–21 September 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Jiang, J.; Wu, J.; Yan, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. A Robust GNSS/PDR Integration Scheme with GRU-Based Zero-Velocity Detection for Mass-Pedestrians. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Rohm, W.; Klingbeil, L.; Tchórzewski, J. Experimental 2D extended Kalman filter sensor fusion for low-cost GNSS/IMU/Odometers precise positioning system. Measurement 2022, 193, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Z.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Z.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Ren, K. Learning-based Practical Smartphone Eavesdropping with Built-in Accelerometer. In Proceedings of the NDSS 2020, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–26 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hobara, H.; Saito, S.; Hashizume, S.; Sakata, H.; Kobayashi, Y. Individual Step Characteristics During Sprinting in Unilateral Transtibial Amputees. J. Appl. Biomech. 2018, 34, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, V.; Ånonsen, K.B.; Bekkeng, J.K. Relative heading estimation for pedestrians based on the gravity vector. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 8218–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honglong, C.; Liang, X.; Chengyu, J.; Kraft, M.; Weizheng, Y. Combining Numerous Uncorrelated MEMS Gyroscopes for Accuracy Improvement Based on an Optimal Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2012, 61, 3084–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Threshold Name | Symbol | |
|---|---|---|
| Two adjacent acceleration change thresholds | 0.04 | |
| Gait onset acceleration threshold | 9.8 | |
| Rising state maximum | 6 | |
| Falling state maximum | 6 | |
| Lower bound threshold of wave crest | 10.5 | |
| Interference shielding threshold | 3 |
| Scheme | E(m) | N(m) | U(m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo range single point positioning | 1.08 | 1.13 | 1.25 |
| Pseudo range differential positioning | 2.21 | 1.38 | 1.15 |
| Phase smoothed pseudo-range difference | 1.67 | 4.51 | 1.92 |
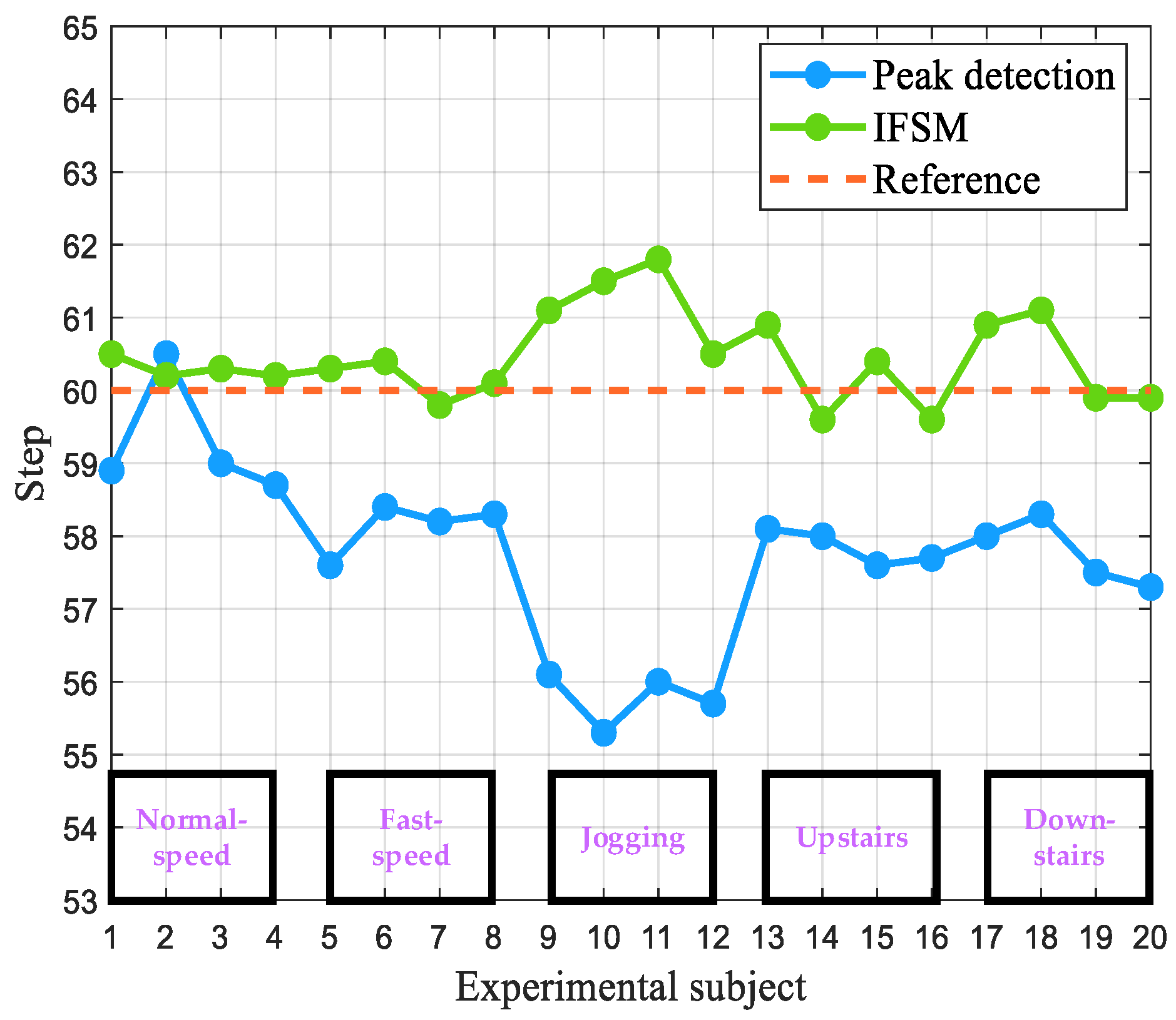
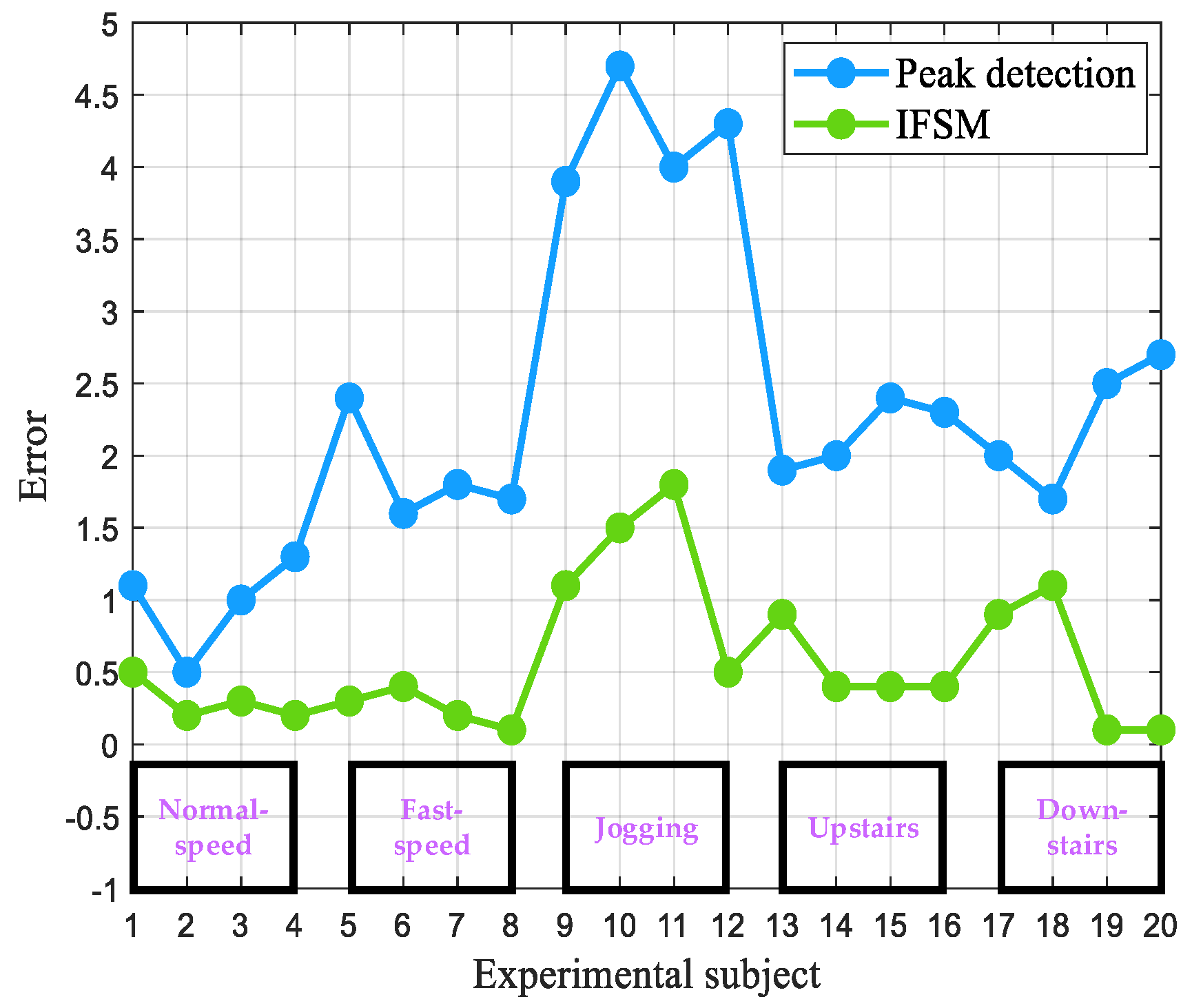
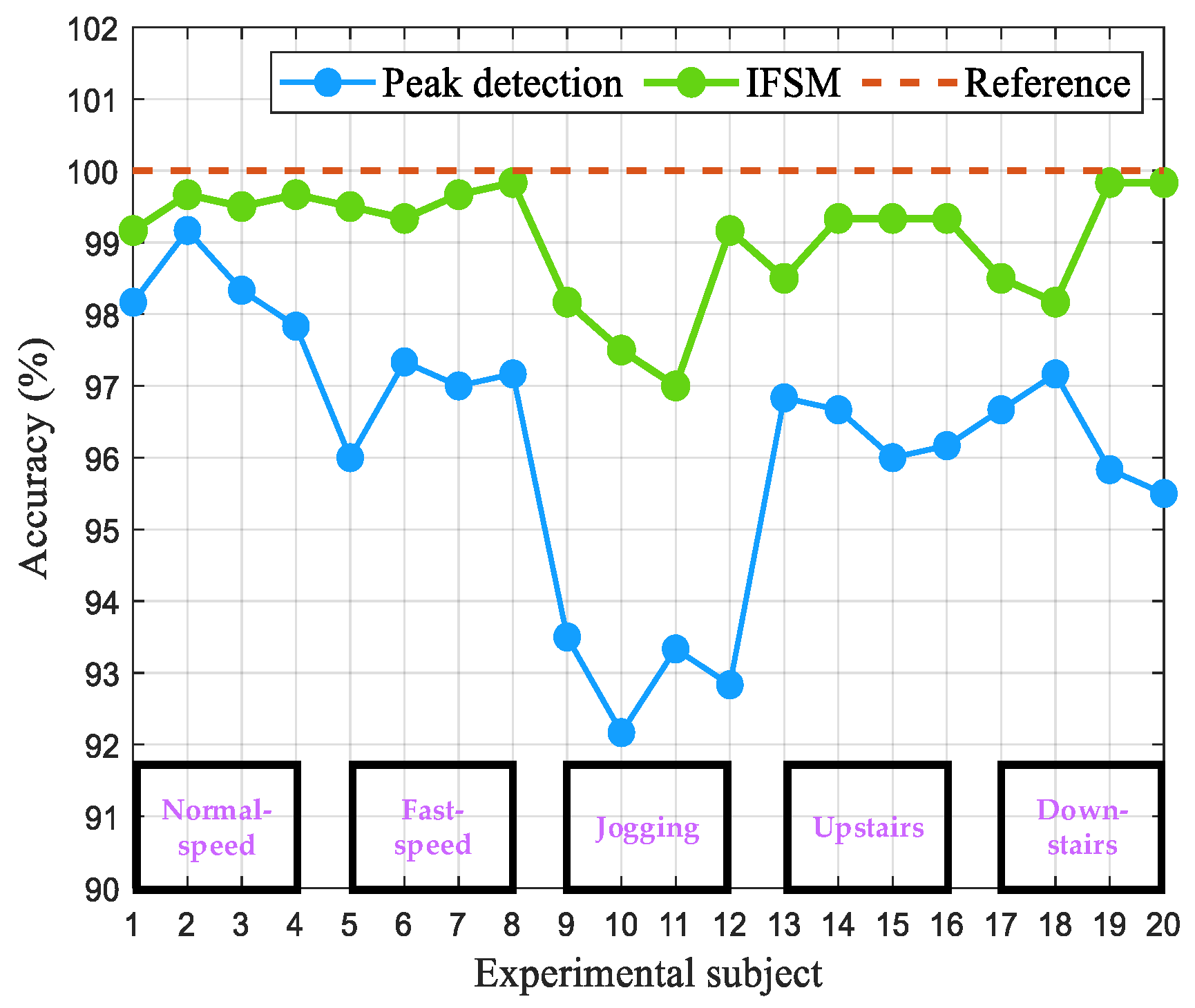
| Motion State | Experimental Subjects | Peak Detection Method | Improved FSM Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result (Step) | Accuracy | Result (Step) | Accuracy | ||
| Normal-speed walking | A | 58.9 | 98.1% | 60.5 | 99.2% |
| B | 59.2 | 98.6% | 60.5 | 99.2% | |
| C | 59.0 | 98.3% | 60.3 | 99.5% | |
| D | 58.7 | 97.8% | 60.2 | 99.6% | |
| Fast-speed walking | A | 57.6 | 96.0% | 60.3 | 99.5% |
| B | 58.4 | 97.3% | 60.4 | 99.3% | |
| C | 58.2 | 97.0% | 59.8 | 99.6% | |
| D | 58.3 | 97.1% | 60.1 | 99.8% | |
| Jogging | A | 56.1 | 93.5% | 61.1 | 98.1% |
| B | 55.3 | 92.1% | 61.5 | 97.5% | |
| C | 56.0 | 93.3% | 61.8 | 97.1% | |
| D | 55.7 | 92.8% | 60.5 | 99.3% | |
| Upstairs | A | 58.1 | 96.8% | 60.9 | 98.3% |
| B | 58.0 | 96.6% | 59.6 | 99.3% | |
| C | 57.6 | 96.0% | 60.4 | 99.3% | |
| D | 57.7 | 96.1% | 59.6 | 99.3% | |
| Downstairs | A | 58.0 | 96.6% | 60.9 | 98.5% |
| B | 58.3 | 97.1% | 61.1 | 98.1% | |
| C | 57.5 | 95.8% | 59.9 | 99.8% | |
| D | 57.3 | 95.5% | 59.9 | 98.8% | |
| Reference Point | IFSM (m) | GNSS (m) | IFSM/EKF(m) | OBPDR (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.08 | 1.13 | 1.25 | 1.24 |
| 2 | 2.21 | 1.38 | 1.15 | 1.12 |
| 3 | 1.67 | 4.51 | 1.92 | 1.81 |
| 4 | 2.01 | 3.42 | 2.20 | 2.15 |
| 5 | 1.68 | 3.55 | 1.60 | 1.57 |
| 6 | 2.59 | 5.63 | 2.15 | 2.12 |
| 7 | 5.40 | 2.46 | 3.03 | 2.99 |
| 8 | 11.03 | 1.25 | 1.65 | 1.64 |
| 9 | 11.16 | 1.17 | 1.18 | 1.17 |
| Reference Point | IFSM (m) | GNSS (m) | IFSM/EKF(m) | OBPDR (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.04 | 2.18 | 1.69 | 1.65 |
| 2 | 5.80 | 3.70 | 3.32 | 3.12 |
| 3 | 6.39 | 4.89 | 3.23 | 3.09 |
| 4 | 7.35 | 4.16 | 4.13 | 3.99 |
| 5 | 2.12 | 5.68 | 2.81 | 2.72 |
| 6 | 4.27 | 2.66 | 2.21 | 1.99 |
| 7 | 5.28 | 2.07 | 1.65 | 1.57 |
| 8 | 7.98 | 6.06 | 5.30 | 5.23 |
| 9 | 4.82 | 10.01 | 7.41 | 7.28 |
| 10 | 9.03 | 3.22 | 2.95 | 2.89 |
| 11 | 1.23 | 5.70 | 2.09 | 2.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Mi, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. A Continuous PDR and GNSS Fusing Algorithm for Smartphone Positioning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205171
Zhang R, Mi J, Li J, Wang Q. A Continuous PDR and GNSS Fusing Algorithm for Smartphone Positioning. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205171
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Jing Mi, Jing Li, and Qing Wang. 2022. "A Continuous PDR and GNSS Fusing Algorithm for Smartphone Positioning" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205171
APA StyleZhang, R., Mi, J., Li, J., & Wang, Q. (2022). A Continuous PDR and GNSS Fusing Algorithm for Smartphone Positioning. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5171. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205171








