Abstract
Coal mine surface subsidence detection determines the damage degree of coal mining, which is of great importance for the mitigation of hazards and property loss. Therefore, it is very important to detect deformation during coal mining. Currently, there are many methods used to detect deformations in coal mining areas. However, with most of them, the accuracy is difficult to guarantee in mountainous areas, especially for shallow seam mining, which has the characteristics of active, rapid, and high-intensity surface subsidence. In response to these problems, we made a digital subsidence model (DSuM) for deformation detection in coal mining areas based on airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR). First, the entire point cloud of the study area was obtained by coarse to fine registration. Second, noise points were removed by multi-scale morphological filtering, and the progressive triangulation filtering classification (PTFC) algorithm was used to obtain the ground point cloud. Third, the DEM was generated from the clean ground point cloud, and an accurate DSuM was obtained through multiple periods of DEM difference calculations. Then, data mining was conducted based on the DSuM to obtain parameters such as the maximum surface subsidence value, a subsidence contour map, the subsidence area, and the subsidence boundary angle. Finally, the accuracy of the DSuM was analyzed through a comparison with ground checkpoints (GCPs). The results show that the proposed method can achieve centimeter-level accuracy, which makes the data a good reference for mining safety considerations and subsequent restoration of the ecological environment.
1. Introduction
Deformation detection has been defined as the identification of geometric state differences based on multiple periods of data capturing. The detection of the surface subsidence of coal mining areas is a part of deformation detection and has become a hot topic to mitigate hazards and property loss.
Generally, the surface subsidence caused by coal mining is the main source of danger for the destruction of buildings and structures, inevitably causing surface collapse and environmental damage [1,2,3]. Therefore, scholars have adopted various methods to observe the surface subsidence of coal mining areas. The traditional geodetic method detects surface subsidence with fixed points on the ground [4,5]. Although high-precision data can be obtained, it is still point-to-point acquisition, which is inefficient and expensive. Moreover, this method only measures local subsidence, and full coverage of a mining area cannot be obtained. Recently, Shi et al. [6,7,8,9] tried to detect surface deformation with the method of interferometry synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), which can obtain accurate vertical displacement measurements. However, the speed of the surface subsidence of a shallow coal seam is relatively fast, and a long period of SAR satellite observation easily causes incoherence of SAR images [8,9]. UAV oblique photogrammetry can obtain the three-dimensional (3D) coordinate information of ground features [10,11,12,13,14]. Many scholars have tried to use oblique photogrammetry to detect the surface subsidence of mining areas [15,16,17,18]. However, the 3D point cloud generated by UAV oblique images includes a large number of vegetation points [19], which leads to limited accuracy without control points. Martínez-Carricondo et al. [20] improved the accuracy of UAV oblique photogrammetry with high-density control points. However, there are landslides, ground fissures, and other hazards in mining areas, which cannot allow high-density control points. Terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) has been used to detect the deformation of landslide, dam, and mining areas, and accurate detection results have been achieved [21,22,23,24]. However, TLS adopts station-type scanning, with which there are problems, such as ground obstructions, narrow fields of view, heavy workloads, and special terrain not being scannable. Airborne LiDAR can capture large-scale, dense 3D point clouds [25]. It can be divided into manned and unmanned airborne LiDAR. Yu and AO [26,27,28] tried to apply manned airborne LiDAR to the surface deformation monitoring of a large mining area, which can achieve comprehensive observations without being restricted by terrain. Moreover, ground point clouds in the presence of vegetation can be obtained through vegetation gaps. However, manned airborne LiDAR data collection requires a lot of manpower and material resources, making it unsuitable for small-scale observations. Making airborne LiDAR unmanned greatly reduces the costs (equipment cost and data acquisition cost) and improves the efficiency, which we term UAV-based LiDAR in this paper. It has been widely used in topographic surveys [29], power line diagnoses [30], dam deformation monitoring [31], vegetation height measurements [32,33], and so on. However, few scholars have applied UAV-based LiDAR to detecting the subsidence of the working face of a mining area. Therefore, we took a working face as our study area, which has the characteristics of active, rapid, and high-intensity surface subsidence, to explore the utility of UAV-based LiDAR in the deformation detection of the working face of a coal mining area.
The purpose of this study was to determine the potential of UAV-based LiDAR in the deformation detection of the working face of a coal mining area. Two field measurement campaigns using UAV-based LiDAR were performed to collect data during 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021. The main contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) we proposed and made a DSuM with multiple periods of DEM difference calculation for deformation detection based on UAV-based LiDAR. (2) Data mining was conducted based on DSuM to obtain parameters such as the maximum surface subsidence value, a subsidence contour map, the subsidence range, the subsidence area, and the subsidence boundary angle. (3) The accuracy of DSuM was analyzed through comprehensive comparisons with GCPs. The results showed that the proposed method can achieve centimeter-level accuracy.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Following this introduction, Section 2 describes the study area, reference data, and data processing method. Then, Section 3 describes the experimental results. Section 4 shows the discussion of the experimental results. Finally, the conclusions and future research directions are presented in Section 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Physical Geography and Environment
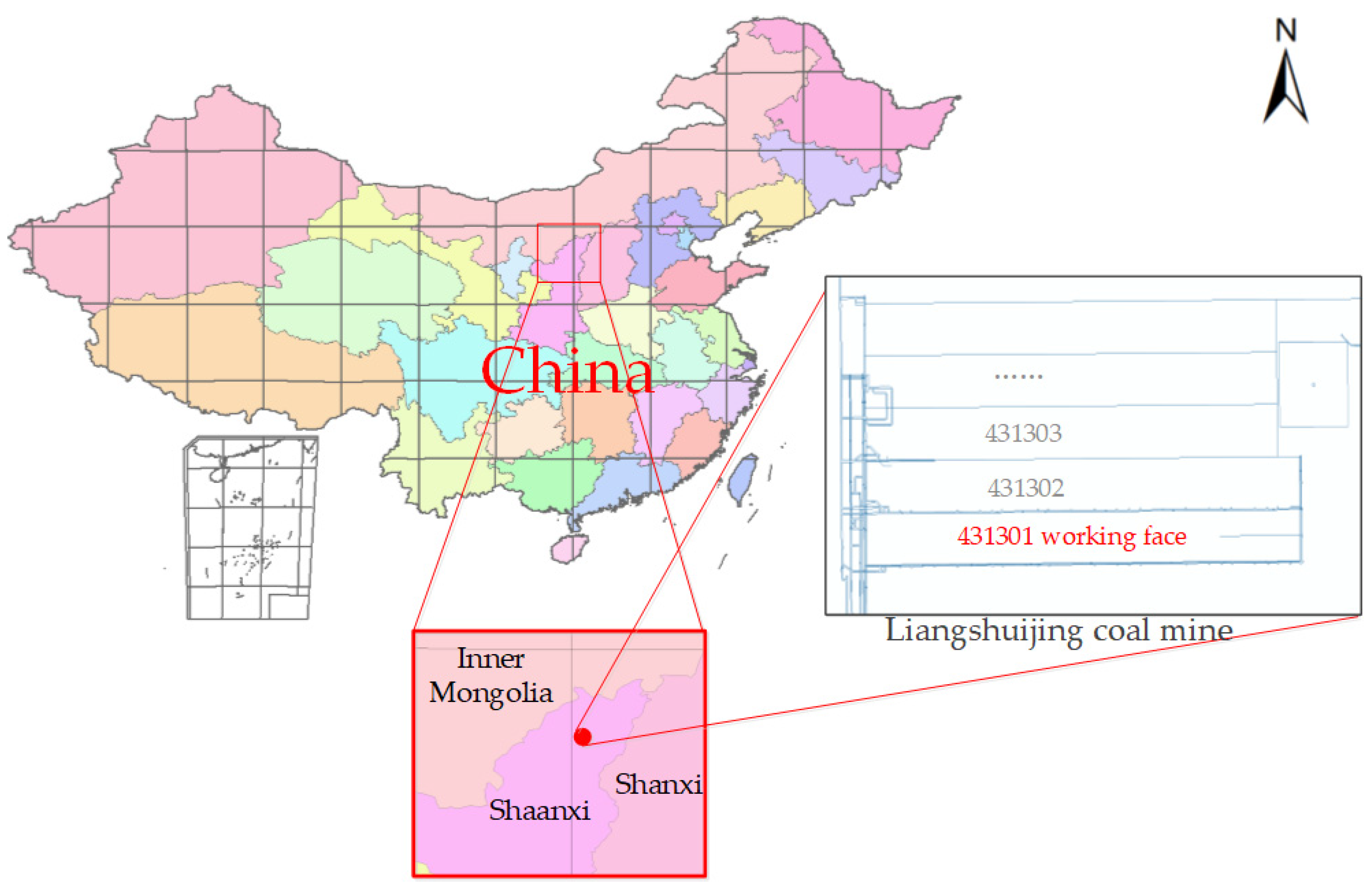
Liangshuijing Coal Mine belongs to Yushen Coal Field, located in northwest Shaanxi, China, as shown in Figure 1. Its geographical location is 38°47′29″–38°53′24″ north, 110°14′22″–110°21′24″ east, and the coal mine covers an area of 68.91 km2. Its altitude is from 1100 to 1326 m above sea level. The terrain is generally high in the west and low in the east.
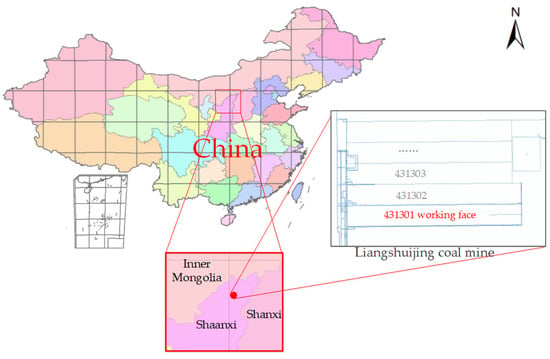
Figure 1.
The location of the study area and the working face.
Yushen Coal Field is located in the transition zone of the Muus Desert and the Loess Plateau. The eastern part consists of a loess ridge and a valley; the western part consists of wavy dunes. The study area has a mid-temperate, continental, semi-arid climate. There are regular droughts. There is little rain (mean annual precipitation of 435.7 mm; the annual average evaporation is 1774.1 mm, which is 4–5 times the precipitation), sparse vegetation, and serious soil erosion. The ecological environment is very fragile [34]. Thus, it is of great significance to monitor the deformation of the coal mining areas. In this study, a local part of a working face was selected as the study area. UAV-based LiDAR was used to obtain the surface deformation data, and checkpoints were obtained by leveling.
2.1.2. Mining and Geological Conditions
We took the 431,301 working face of Liangshuijing Coal Mine as the study area. The working face, which mined 3–4 coal seams, is stable and has flat seams. The coal seam thickness is 1.17–1.43 m, the average thickness is 1.3 m, and the average depth of coal seam is 138 m. The working face adopts the longwall, fully mechanized, and full-seam mining method, the roof of which is managed with the all fall method. The ground is covered by loose sandy soil with a strong flow characteristic. The entire study area is 858 m long from east to west and 466 m long from north to south, giving an area of 399,431 m2. The location of the study area and the working face is shown in Figure 1.
2.2. Reference Data
Our data include airborne laser scanning data and geodetic data. The geodetic data were obtained by laying observation piles on the ground. Then, static and dynamic GNSS [35], total station observation, and precision leveling were used to obtain geodetic data. In the study, the checkpoints include plane (RTK observation) and elevation (leveling observation) data.
2.2.1. LiDAR Data
UAV-based LiDAR was used to collect initial data, and the DSuM was generated by the data for detecting the deformation. The endurance time of UAV in each flight was 35 min, and the effective working time was about 20 min. The laser scanner was a RIEGL miniVUX-1UAV with scanning range of 250 m. The same aerial survey parameters were used to ensure each data acquisition would have the same system error. The parameters included flying height, flying speed, laser scanning speed, pulse emission frequency, and weather conditions. The flying height was 50 m, and the flying speed was 8 m/s. The laser scanning speed was 100 lines/s, and the pulse emission frequency was 100 kHz. Each laser beam had five echoes, and data collection was performed under the same conditions on different dates. Two groups of point clouds were obtained by UAV-based LiDAR.
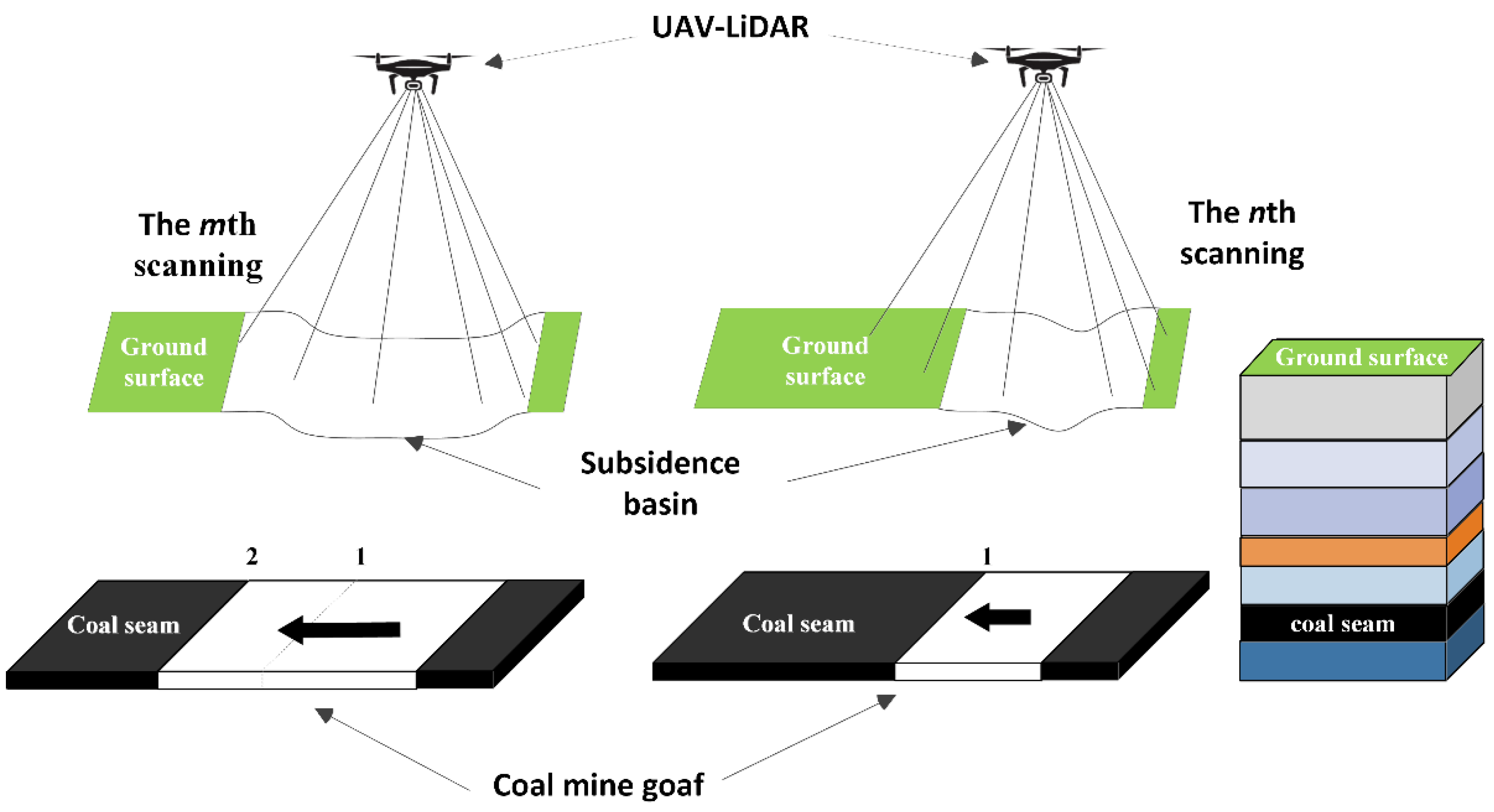
The diagram of the UAV-based LiDAR data collection and the mining process of the underground working face is shown in Figure 2. The nth LiDAR data collection was carried out to obtain the initial shape of the surface. After a period of time, the coal seams were mined, which caused surface deformation. The m-th LiDAR data collection was carried out to obtain the current surface morphology. With the calculation of two phases of LiDAR data, the surface shape change caused by underground working face mining was obtained, which is called the subsidence basin.
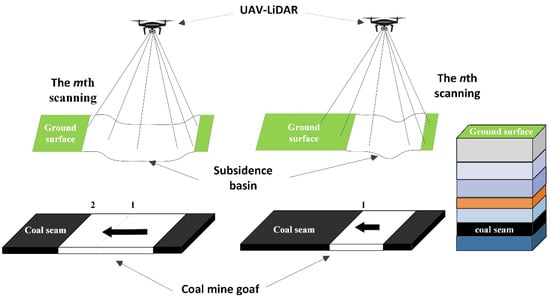
Figure 2.
The diagram of ground deformation monitoring by UAV-based LiDAR.
Figure 2 shows the process of mining subsidence. The layered structure on the right of Figure 2 represents the geological structure, which includes the ground surface, sandy soil layer, rock layer, coal seam, and other strata. The main part of Figure 2 shows the relationship between coal seam mining and surface deformation. The surface deformation was different at different mining locations. The black arrow indicates the mining direction of the coal seam. Numbers 1 and 2 indicate the locations of the shearer on different dates. The continuous mining produced a goaf in the coal seam, caused surface deformation, and formed a subsidence basin on the surface.
The data collection dates were 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021, and the corresponding coal seam mining locations are shown in Figure 3. The original point cloud statistics are shown in Table 1.
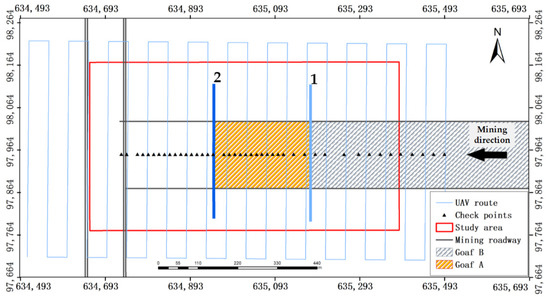
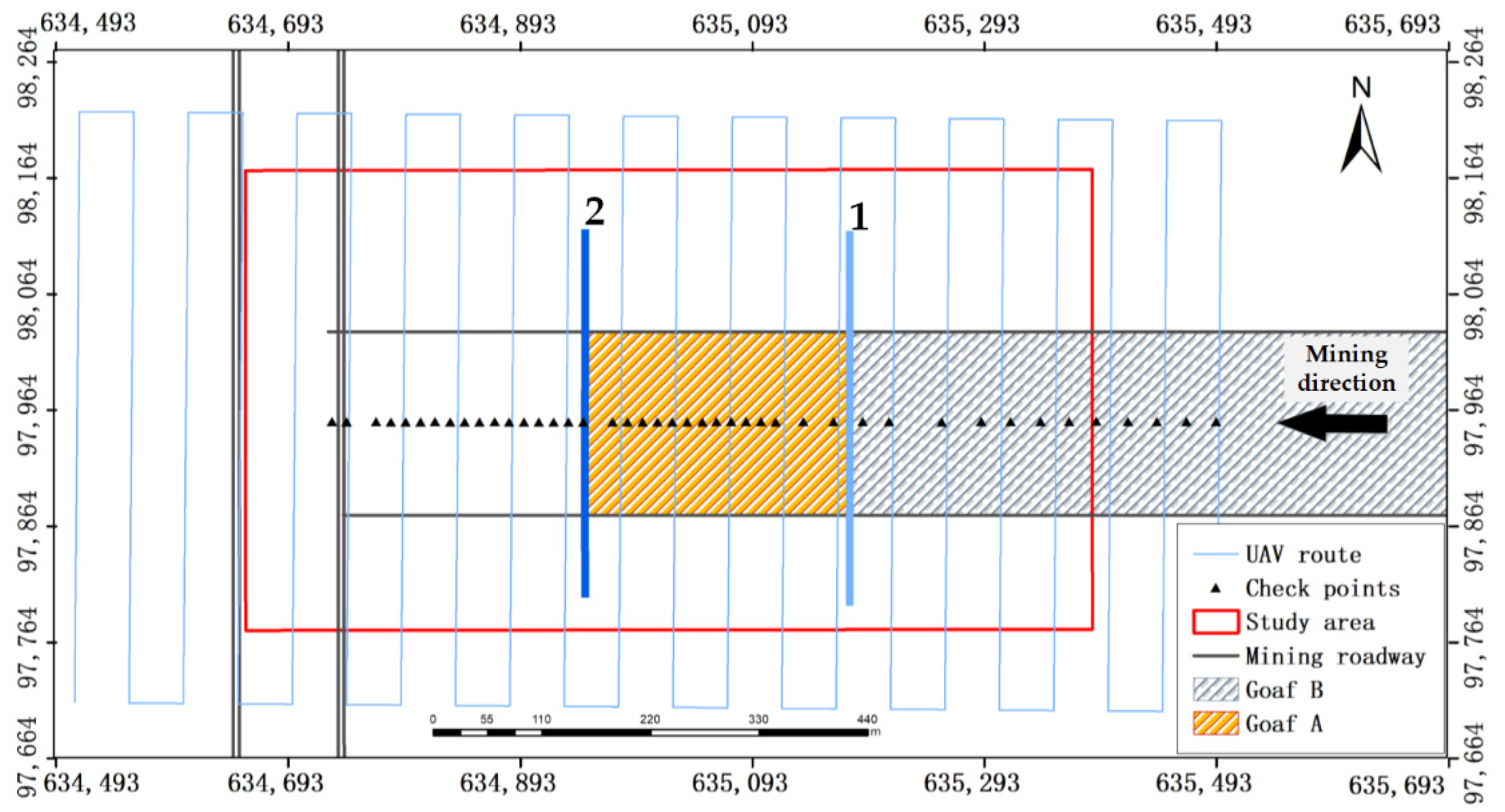
Figure 3.
The map of the ground and underground facilities.

Table 1.
Statistics of the point cloud in the study area.
Figure 3 shows the 2D relations between the ground facilities and underground facilities, but they had different elevations. The ground facilities included the UAV route, checkpoints, and study area. The UAV route indicated by the light blue line shows the data acquisition range. The black triangles indicate the locations of the ground checkpoints. The underground facilities included a mining roadway and goaf. Mining roadways are indicated by black lines, which were used for transportation and ventilation. Goaf B represents the existing goaf at the time of the first observation. Goaf A represents the area mined during the period between the first and second observations. The light blue line (number 1) and dark blue line (number 2) in Figure 3 represent the positions of the shearer on 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021, and they have the same meaning as the numbers in Figure 2.
2.2.2. Ground Checkpoints
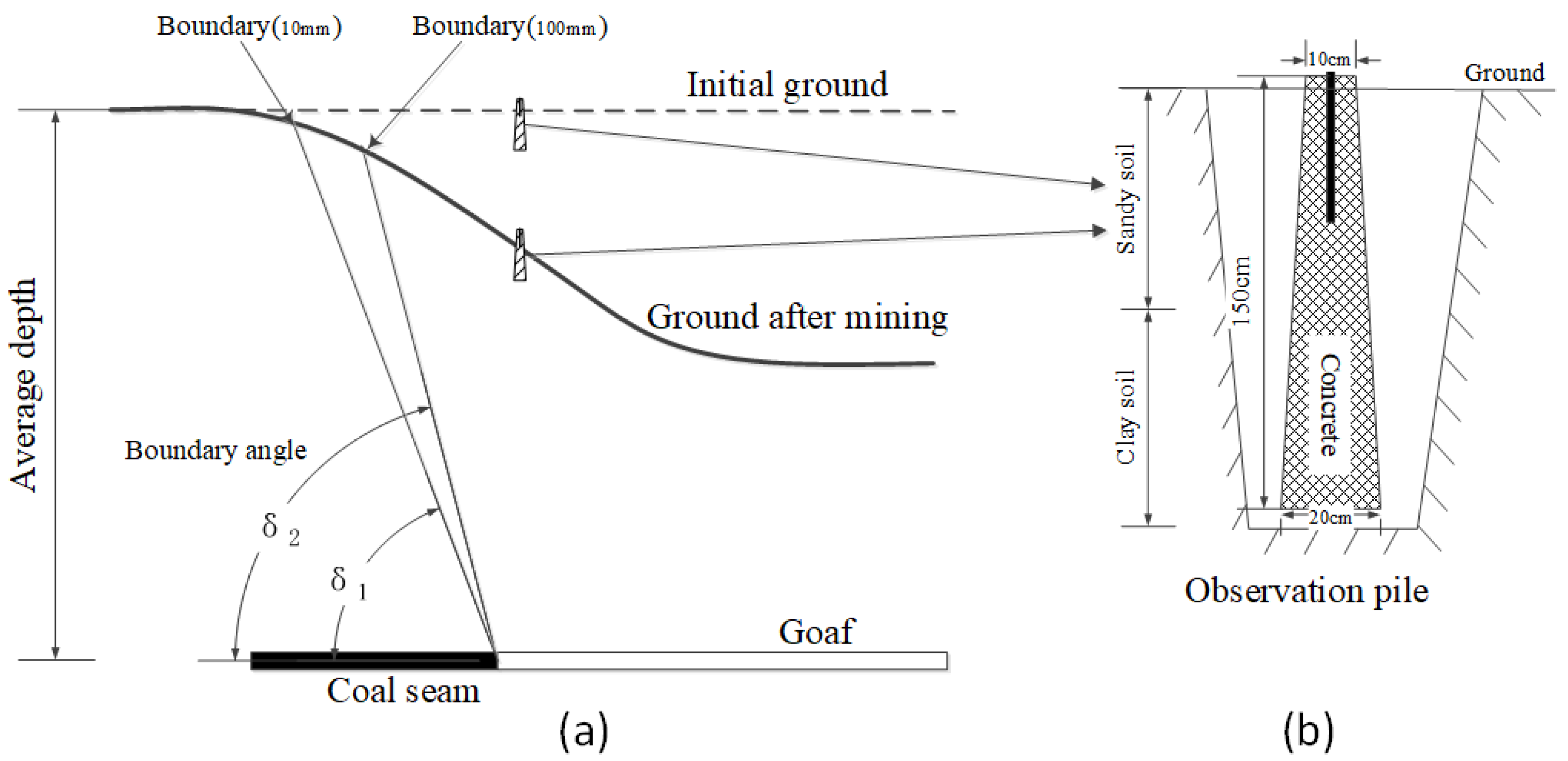
The fixed observation piles were used as the objects to obtain the partial subsidence value of the ground surface, because there were few fixed markers in the study area. The observation piles were made by precasting concrete, whose structure is shown in Figure 4b, and the locations of the observation piles are shown as black triangles in Figure 3; they are also called ground checkpoints. The processing of GCPs included the design of ground checkpoints’ locations, observation pile burying, geodetic surveying, measurement calculations, and subsidence polyline drawing, as shown on the right-hand side of Figure 5. In order to verify the measurement accuracy of the point cloud, DEM, and DSuM, the observation piles were measured on 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021, the same dates as the UAV-based LiDAR scanning. The results of GCPs were also used to calculate the max subsidence value and boundary angle.
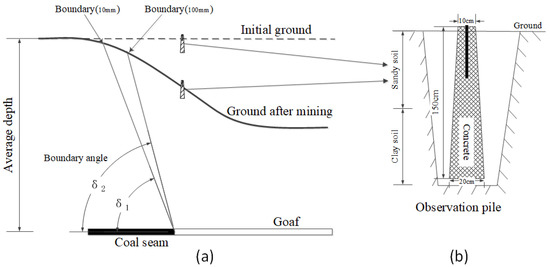
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic diagram of boundary angle calculation, where δ1 and δ2 represent the boundary angle with threshold values of 10 and 100 mm; (b) sectional view of the ground observation pile.
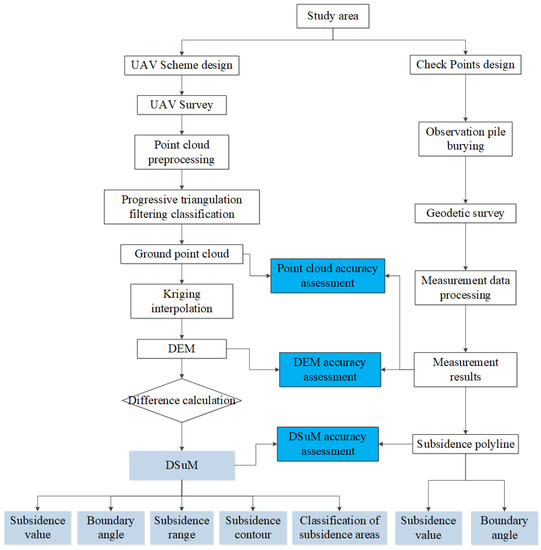
Figure 5.
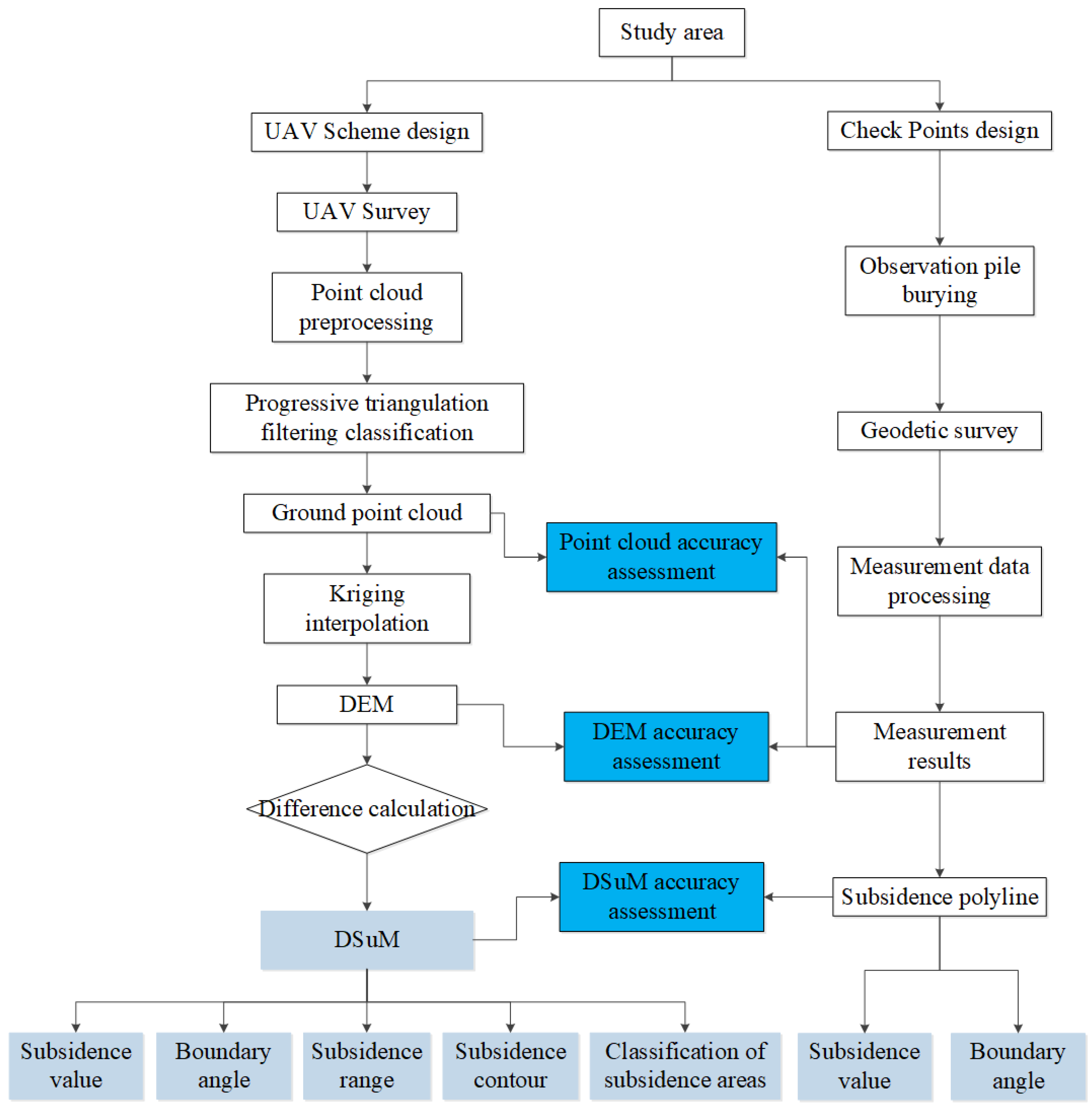
Flow diagram of the proposed method.
2.3. Data Processing
When the shearer mined different positions on the working face, the two periods of UAV-based LiDAR surveying were carried out to obtain the surface morphology of the working face in different periods, as shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The GCPs were mainly used to verify the accuracy of the point cloud, DEM, and DSuM, which were all generated directly or indirectly based on LiDAR. Similarly to previous related studies [7,17,35,36,37], we used geodetic data as a reference to analyze the accuracy of the point cloud, DEM, and DSuM. The multi-scale morphological algorithm [38] and progressive triangulation filter algorithm [39,40] were chosen for filtering the point cloud, and the Kriging interpolation algorithm [41] was chosen for generating DEM. This paper also analyzes the influence of resolution on DEM accuracy and proposes a new model termed DSuM based on the optimal resolution of DEM to detect the deformation of coal mining areas. The main purposes of coal mining subsidence monitoring are subsidence value acquisition and boundary angle calculation. This section introduces the calculation methods for the subsidence value and boundary angle, and the process of generating DSuM from the UAV-based LiDAR data.
2.3.1. Subsidence Value and Boundary Angle
Subsidence data analysis includes data preprocessing, data calculation, subsidence polyline drawing, and boundary angle calculation. The data preprocessing is used to remove error data caused by human factors; data calculation is to obtain the difference between the two periods’ data. Then, subsidence polyline diagram is drawn, and boundary angles are obtained. The subsidence of the observation points is calculated by Formula (1):
where represents the subsidence value of point n; and represent the elevation of point n during the first and the m-th observations.
The boundary angle is used to determine the range and boundary of the subsidence caused by coal mining. Due to the observation error and the seasonal variations of the soil, an observation point with a subsidence value close to zero could not be accurately determined, so points with subsidence values of 10 and 100 mm were taken as the boundaries of the subsidence basin, as shown in Figure 4. Boundary angles calculated by different boundary thresholds are different. The boundary angle is calculated as follows:
where represents the horizontal distance between the boundary of the underground goaf and the strike or incline boundary of the subsidence basin, represents the average depth of the coal seam, and represents the boundary angle.
2.3.2. UAV-Based LiDAR Data Processing
The data processing of UAV-based LiDAR mainly included data checking, point cloud processing, and interpolation calculation. Data checking was to remove erroneous data; point cloud processing included registration, denoising, and filtering; the purpose of interpolation calculation was to generate the DEM. After data checking, the produced raw data were converted to point clouds. The point cloud was roughly registered by pose data generated by GNSS/INS integration, and then fine registration was carried out based on the iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm. Subsequently, we removed the noise points with the morphological method [42]. Then, the PTFC algorithm was used to obtain the ground point cloud, and the DEM was generated from the ground point cloud. Finally, an accurate DSuM was obtained through multiple periods of DEM difference calculation.
We compared the GCPs and the point cloud data at the same location to verify the point cloud accuracy, which is a direct accuracy verification method. Subsequently, we evaluated the accuracy of the DEM by comparing it with GCPs. The Kriging interpolation algorithm was used to generate the DEM, and the most suitable grid size was determined by trial and error.
There are two methods to evaluate the accuracy of a DEM. The elevation error statistical analysis method compares the DEM with the reference DEM or checkpoints; the logical analysis method is a qualitative method for overall accuracy evaluation, including a visual interpretation method, contour analysis, visual analysis, and other methods [41]. We adopted the method of comparing DEM to checkpoints. The differences in elevation between the checkpoints and the DEM with different resolutions were calculated, and the results were displayed by box plots. Meanwhile, the mean error (ME), the mean absolute error (MAE), and the root mean square error (RMSE), were calculated [19]:
where represents the value of the DEM and represents the value of a checkpoint.
Since directly calculating the difference between two point clouds is difficult, we used the difference between any two DEMs created by the point cloud to represent the ground surface subsidence deformation during the period. The difference between the two DEMs is called the DSuM. Finally, the accuracy of the DSuM was analyzed by GCPs. The analysis of a point cloud, DEM, and DSuM is shown in Figure 5.
2.4. Pipeline of DSuM
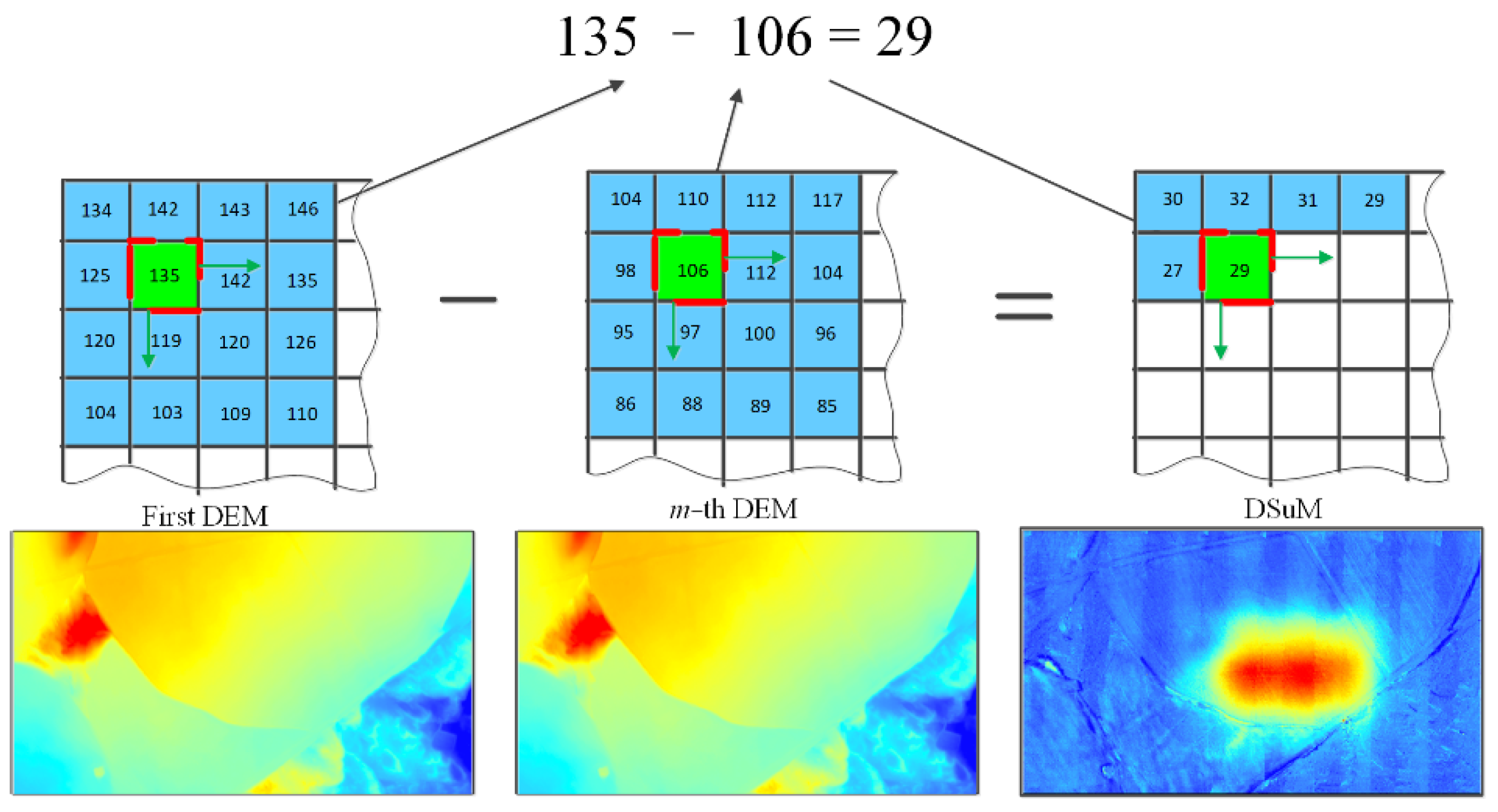
The difference between DEMs obtained on any two different dates can be calculated to obtain the ground surface elevation change during this period, in our case, the ground surface subsidence value caused by underground coal mining. In this paper, the difference between the DEMs was calculated, and represented by DSuM, which is a digital model that represents the value of ground subsidence in an ordered array of values. Each pixel value of the DSuM represents the subsidence value of the pixel location caused by coal mining. The schematic diagram of DSuM generation is shown in Figure 6, which is a digital expression of whole ground surface subsidence value. A DSuM can be calculated from any two DEMs obtained on different dates, and can represent the subsidence value of any position in the ground surface during the mining processing. Finally, data mining was conducted based on the DSuM to obtain outputs such as the maximum surface subsidence value, a subsidence contour map, the subsidence range, the subsidence area, and the subsidence boundary angle, as shown in Figure 5.
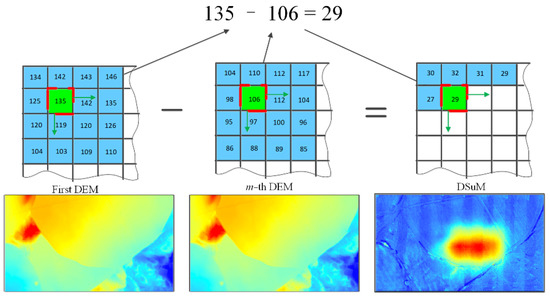
Figure 6.
The schematic diagram of DSuM calculation.
After point cloud data collection, the DEMs were generated from clean ground point clouds, and the DSuM was obtained through multiple periods of DEM difference calculation. Then, coal mining subsidence was analyzed based on the DSuM. We adopted point, line, and area analysis from different perspectives. The point analysis used the method of simulating traditional monitoring to extract subsidence values from points, which involves drawing the strike and incline subsidence polyline and obtaining the max subsidence value. The line analysis easily extracted high-density points from the DSuM, which was used to extract points in the strike and incline direction in this paper. It is robust for discrete monitoring points, and it can plot the subsidence curve graph and calculate the strike and incline boundary angle. The area analysis can analyze the whole subsidence area. It was used to calculate subsidence area, maximum subsidence value, and the ratio of subsidence area.
Finally, data mining was carried out based on the DSuM to obtain the maximum subsidence value, subsidence area, subsidence distribution of surface, boundary angle, and other parameters for later analysis.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. GCPs Analysis
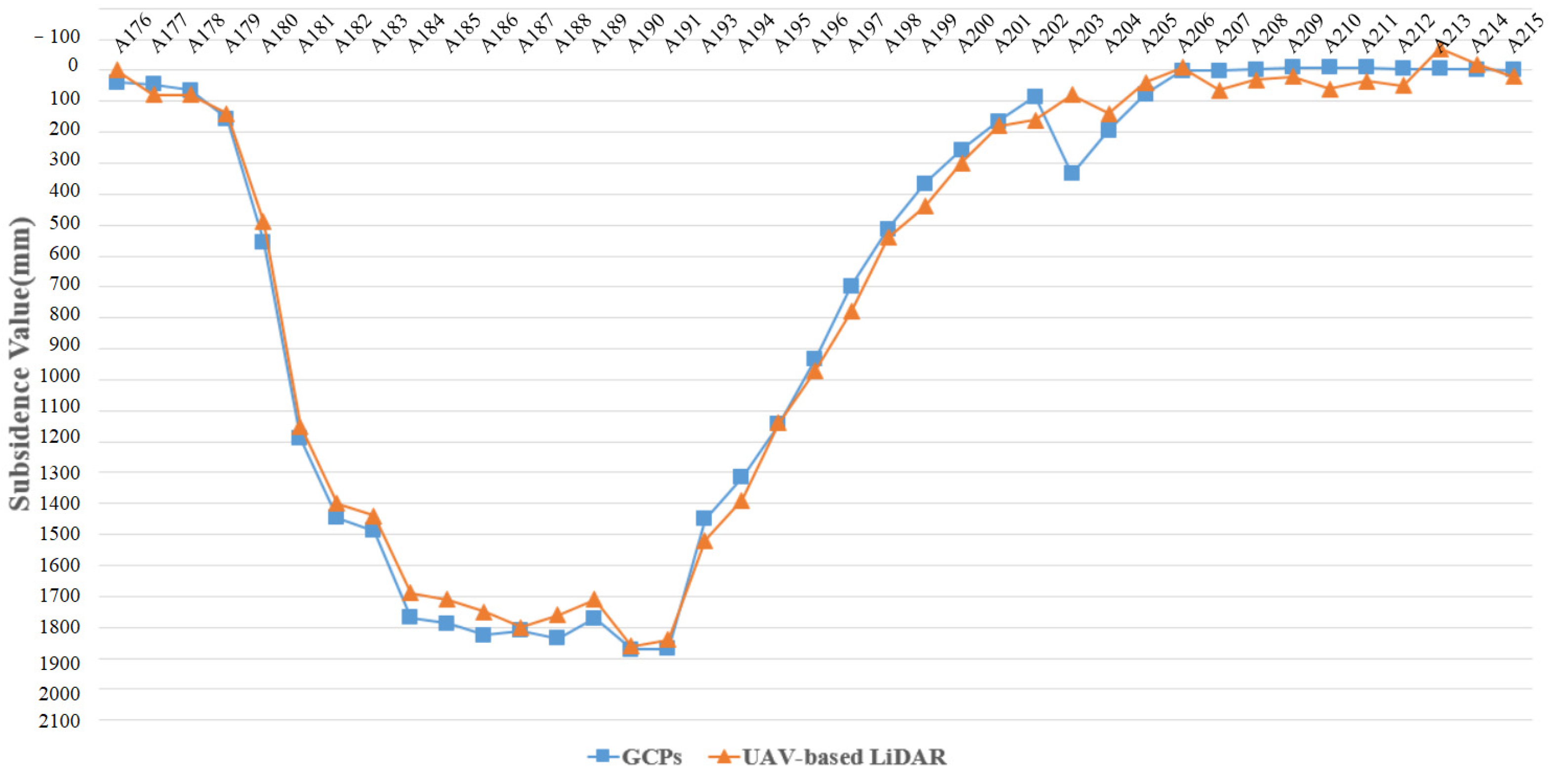
The GCPs results were obtained by Formula (1) based on the geodetic data. The results indicate that the maximum ground subsidence value of the working face was 1826 mm, and the minimum subsidence value was 0 mm, during 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021, respectively. Taking ground observation point A176 as the origin, the subsidence values of all GCPs are shown as blue squares in Figure 7.
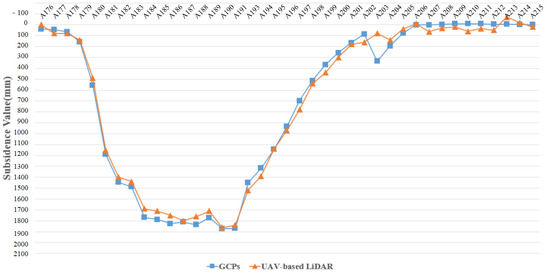
Figure 7.
The comparison of subsidence values between the GCPs and DSuM.
The GCPs covered the entire subsidence area, including the non-subsidence area and the maximum subsidence area, and can reflect the surface subsidence in a period of time. The blue polyline in Figure 7 shows that the subsidence boundary with the threshold of 10 mm located between A205 and A206, and the horizontal distances of A205 and A206 from the boundary of goaf were 121 and 136 m, respectively. The average mining depth of the coal seam was 138 m. According to Formula (2), the mining subsidence boundary angle with subsidence threshold of 10 mm was between 45° and 48.7°. The average was 46.9°. Similarly, the boundary angle with a subsidence threshold of 100 mm was 61.2°.
3.2. Accuracy Assessment
The ground point cloud could be obtained after filtering the original point cloud. Since a ground point cloud is composed of a series of discrete points, we took the average elevation values of points near the GCP to calculate the differences between ground point cloud and GCPs, and the distances from the selected points to the GCPs had to be less than a set threshold. The results indicate that the RMSE of elevation was 60.6 mm on 7 November 2020, and 59.9 mm on 19 May 2021, and the results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The statistics of the absolute values of point cloud error.
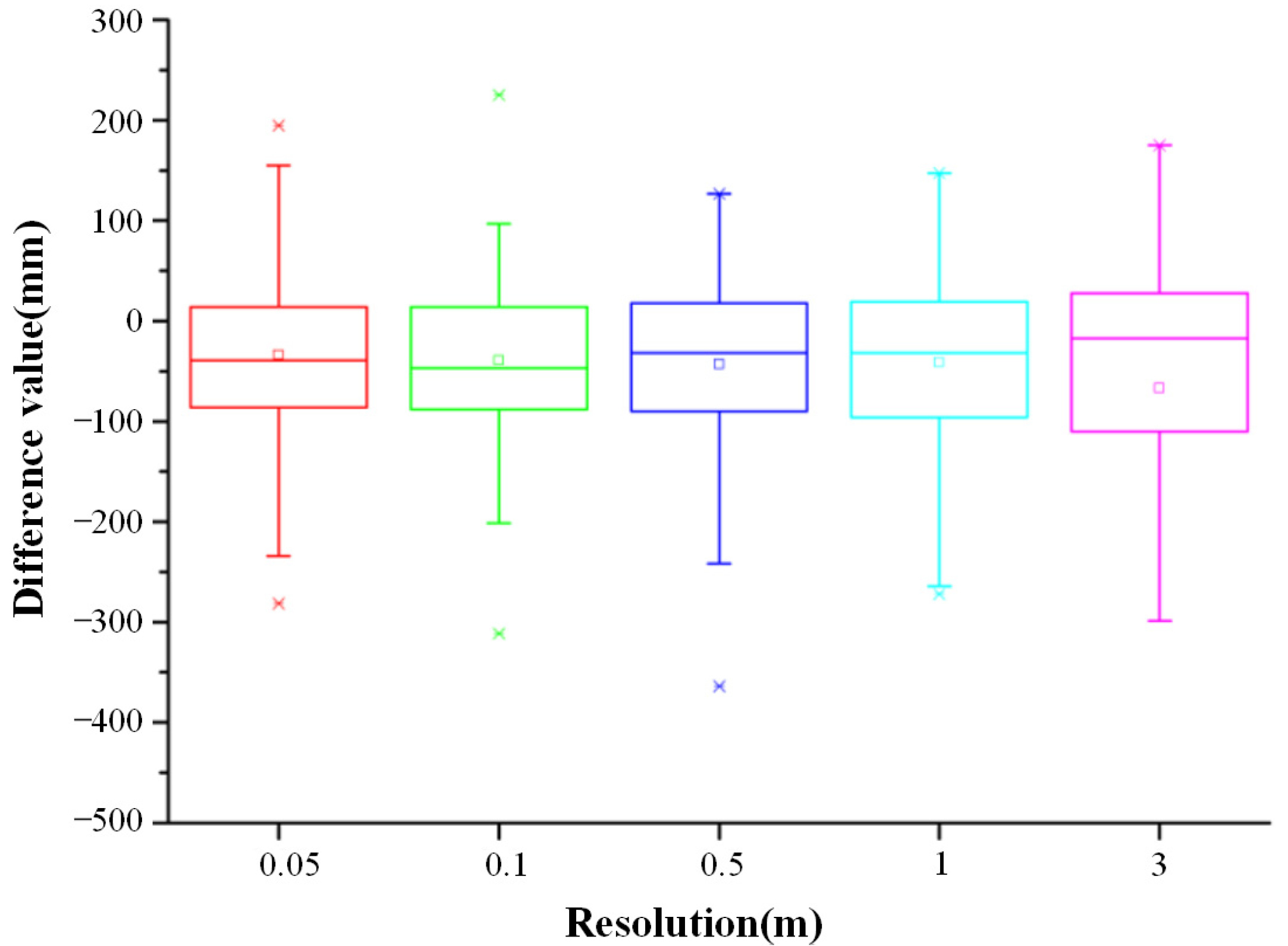
Next, we calculated the accuracy of the DEM and analyzed the influence of resolution on DEM accuracy. The differences between DEM and GCPs are shown in Figure 8. As resolution increases, the average error remains basically unchanged, but the error distribution becomes more discrete. The error distribution of the resolution of 0.1 m was most concentrated, and all errors were less than 100 mm.
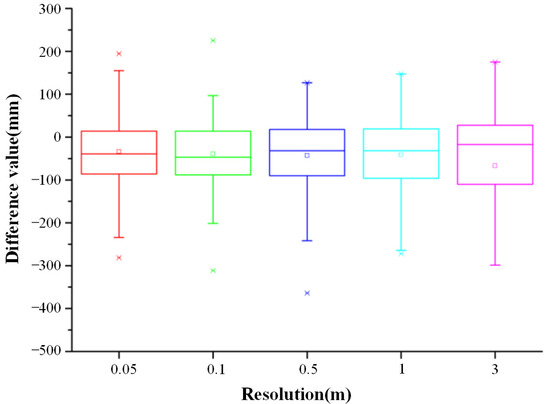
Figure 8.
The difference distribution statistics of DEM and the checkpoints.
The difference results of DEM from data at different resolutions and GCPs are shown in Table 3. The results include ME, MAE, and RMSE, and indicate that with different resolutions, the maximum ME is 323 mm and the minimum is –34 mm; the maximum MAE is 537 mm and the minimum is 74 mm; and the maximum RMSE is 97 mm.

Table 3.
The statistics of DEM error.
The ME did not change, and the optimal state was in the range of 0.05–1 m, but it increased when the grid size was larger than 1 m. The change in MAE was similar to that of the ME. Similarly, the RMSE reached an equilibrium state within 0.05–1 m. When the resolution was greater than 1 m, the RMSE gradually increased as the grid size increased, and it increased sharply when the resolution became greater than 1 m.
According to Figure 8, the data with 0.1 m grid size are the most concentrated. Therefore, we selected 0.1 m as the parameter for conducting the study to ensure research accuracy.
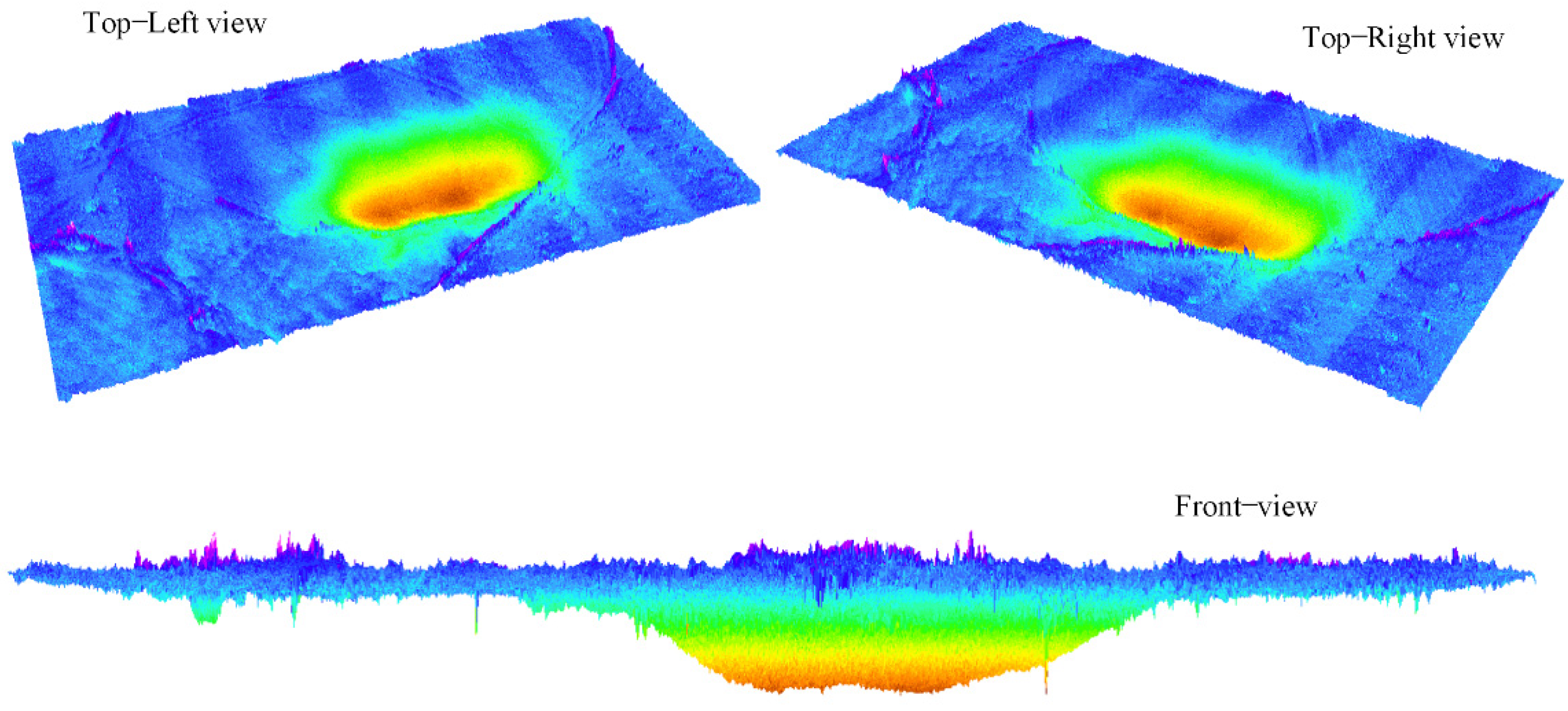
Finally, the accuracy of the DSuM was analyzed. The DSuM of the study area was obtained by the subtraction of DEM in 7 November 2020 from DEM in 19 May 2021, as shown in Figure 9. Different colors represent different subsidence values in the DSuM. Additionally, the main area of subsidence caused by coal mining is mainly distributed in the goaf and its surroundings.
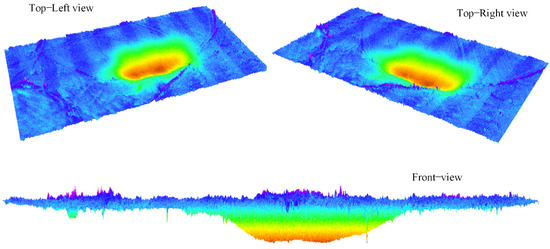
Figure 9.
The different 3D views of the DSuM.
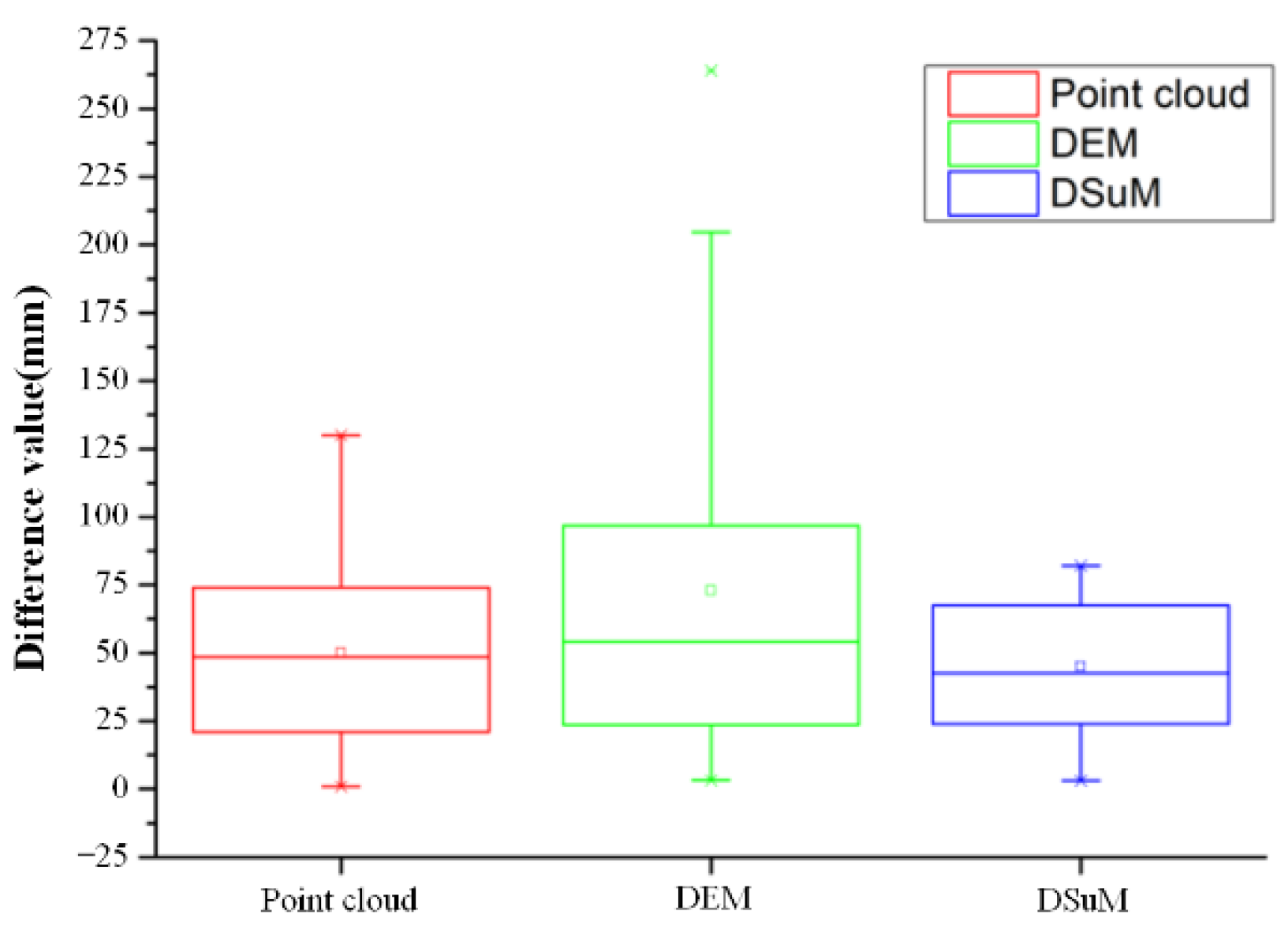
The DSuM contains plane coordinate (X, Y) and subsidence value. The subsidence value of any position can be acquired. The subsidence monitoring accuracy of UAV-based LiDAR can be acquired by comparing the subsidence value of the DSuM with those of the GCPs. The results are shown in Figure 10.
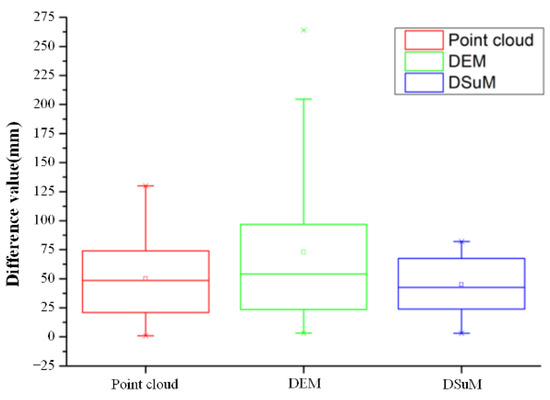
Figure 10.
The absolute values of differences.
Figure 7 shows the maximum subsidence value and minimum subsidence value. The subsidence polyline trends obtained by DSuM and GCPs were basically consistent. The maximum subsidence value calculated by DSuM was 1860 mm, and the maximum subsidence value of GCPs was 1872 mm. The inflection points of the subsidence polyline were consistent. After removing the abnormal subsidence value of ground checkpoint (A 203), the maximum and minimum of the subsidence difference’s absolute values were 82 and 3 mm, the average difference was 45 mm, and 75% of the difference was within 50 mm. All of the differences were less than 100 mm, and their distribution was relatively uniform. The absolute values of differences among the point cloud, DEM, and DSM are shown in Figure 10.
3.3. Analysis of DSuM
In order to comprehensively verify the accuracy of the DSuM, we conducted point, line, and area analysis based on the DSuM.
3.3.1. Point Analysis
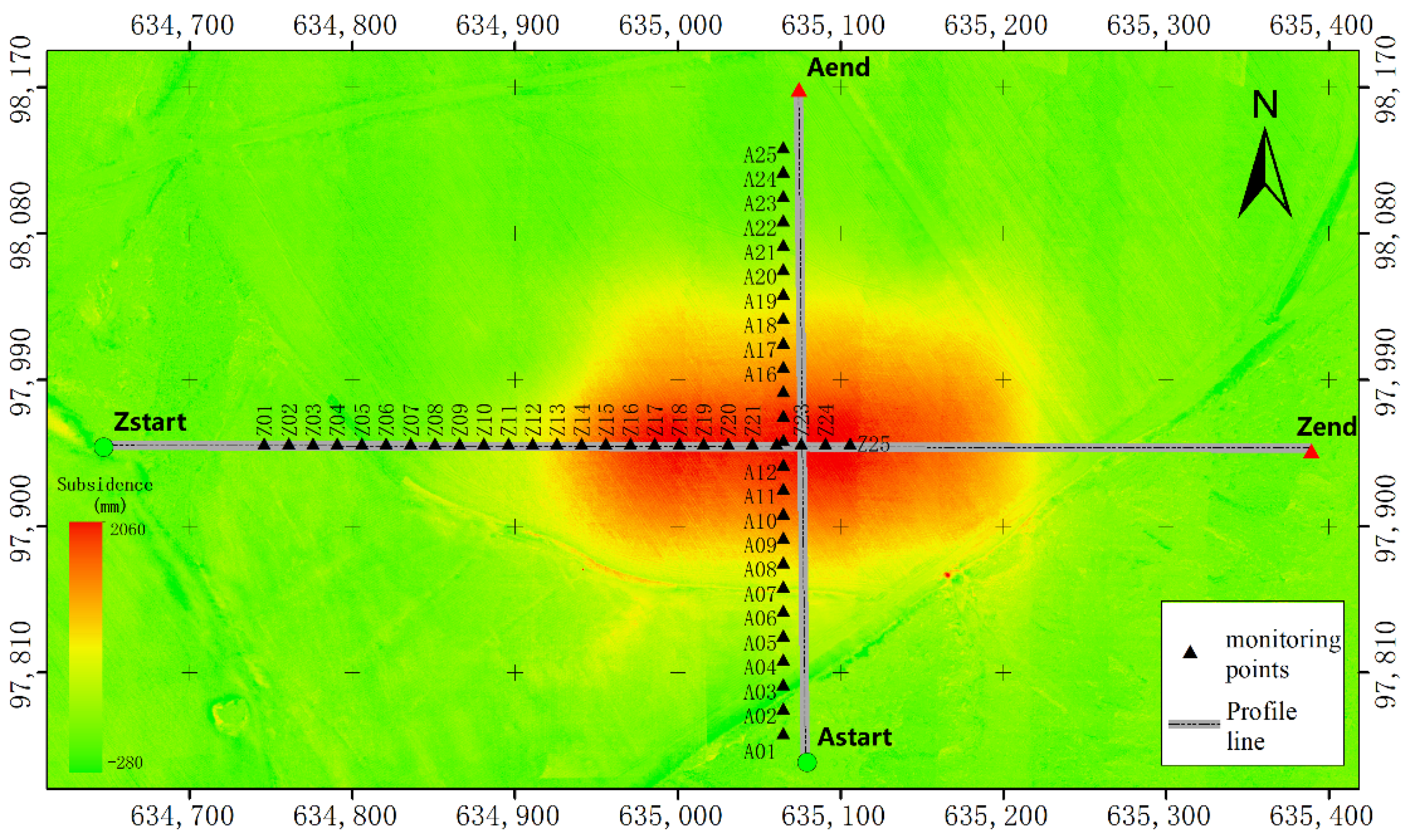
The traditional method of coal mining subsidence monitoring is geodetic surveying by a fixed observation pile, which is a point survey method. For the point analysis of DSuM, we used the method of simulating traditional monitoring to extract subsidence values point by point. The locations of monitoring points were set according to requirements of relevant specifications. The interval between adjacent points was 15 m, the total number was 50, and the whole surface subsidence change area was covered, as shown in Figure 11, by black triangles.
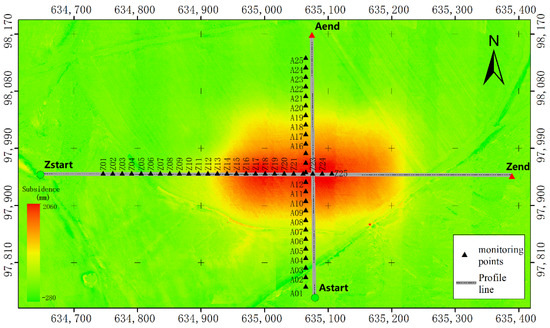
Figure 11.
The locations of monitoring points, and the strike and incline observation lines, where Z represents the strike observation line and A represents incline observation line.
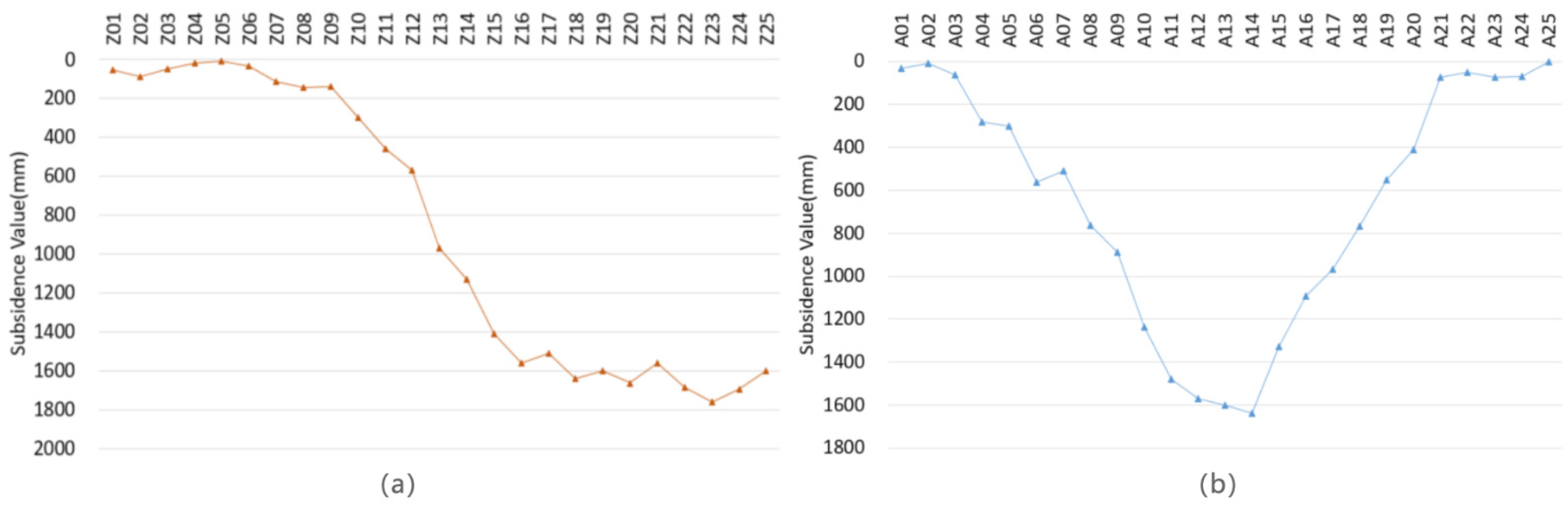
The subsidence value of each monitoring point was extracted by DSuM and is shown in the form of a polyline graph in Figure 12.
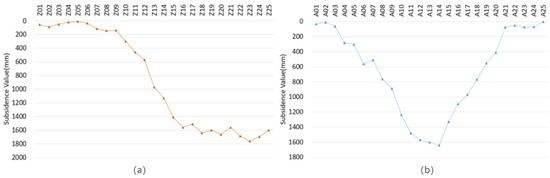
Figure 12.
The subsidence values of monitoring points. (a) The strike observation polyline; (b) the incline observation polyline.
The results indicate that the average maximum value of the subsidence basin is approximately 1650 mm, and the maximum single point subsidence is 1761 mm. The shape of the strike and incline polyline graph is the same as that of the standard mining subsidence polyline graph, whose shape is like a basin or a half-basin. The results can reflect the elevation deformation of the surface caused by coal mining, and meet the requirements of mining subsidence monitoring.
3.3.2. Line Analysis
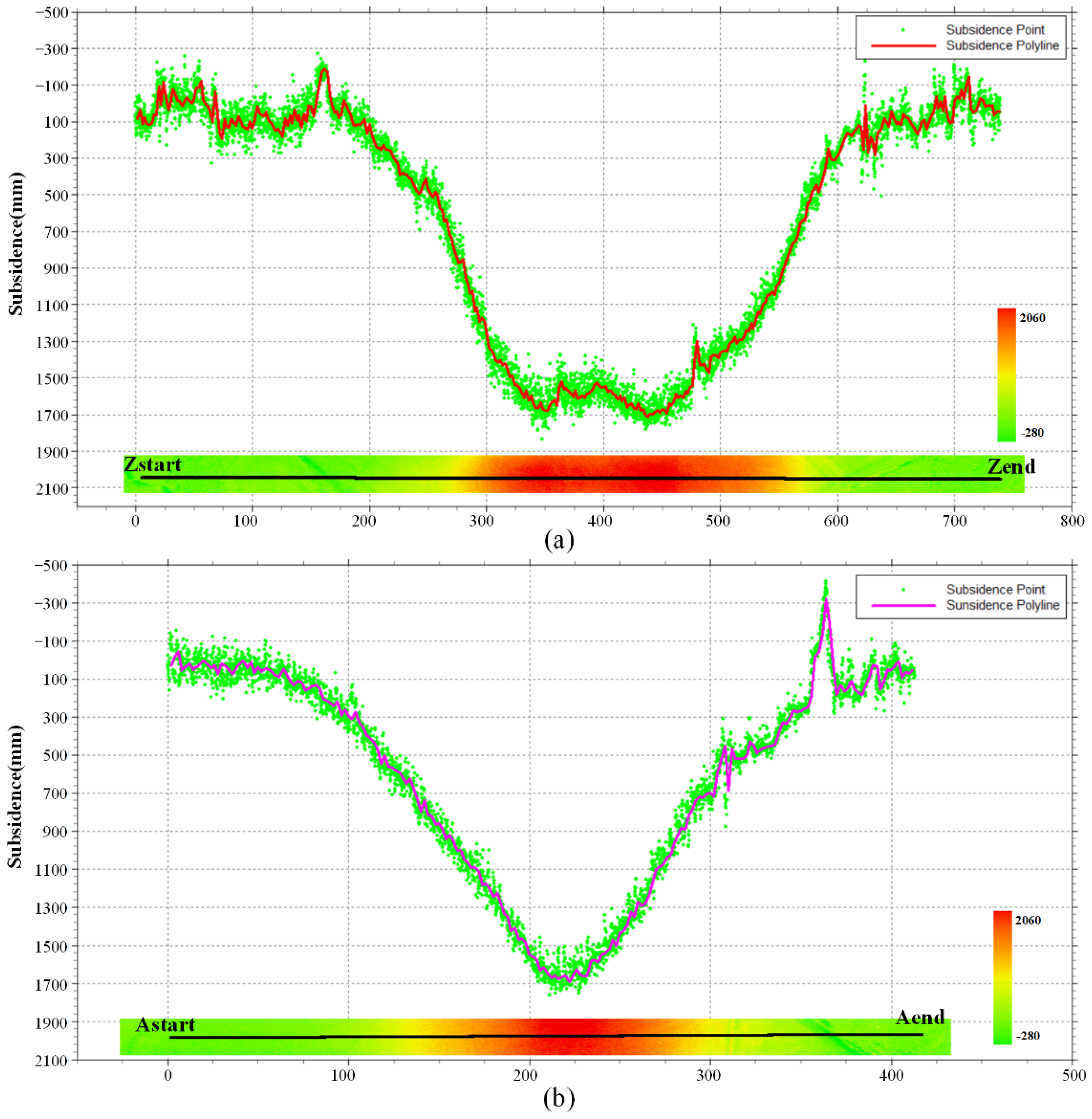
Line analysis is robust for discrete monitoring points. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain high-density points on the observation line. We extracted high-density points from DSuM in the strike and incline directions and plotted the subsidence curve graph in Figure 13. The locations of strike and cline lines are shown in Figure 11 in gray. The strike observation line started from the point named Zstart and ended at the point named Zend, with a total length of 740 m. The incline observation line started with the point named Astrat and ended with the point named Aend, with a total length of 413 m.
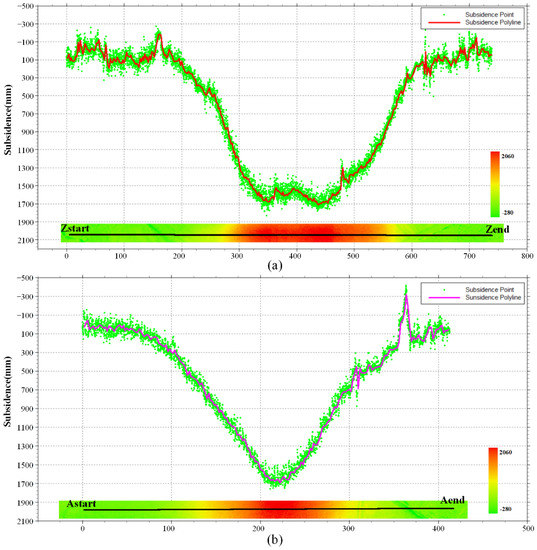
Figure 13.
The subsidence of observation curves. (a) The strike observation curve; (b) the incline observation curve.
We extracted monitoring points from DSuM in an interval of 0.1 m, and drew the points on graphs, as shown in Figure 13a,b—the green points. Finally, we extracted and drew the strike and incline curves, as shown in Figure 13 as the red curves.
The strike curve is shaped like a basin, conforming to the characteristics of mining subsidence, and it shows that a super-full mining state in the strike direction was reached. The incline observation line is in a valley state and is symmetrically distributed due to the small width of the working face. According to the strike and incline curves, we found that the maximum subsidence value is about 1700 mm. Since the average accuracy of UAV-based LiDAR data cannot reach 10 mm, 100 mm was used as the subsidence boundary threshold to extract and calculate the boundary angle by Formula (2). In the strike direction, the horizontal distance between the subsidence boundary and the goaf boundary is 68 m; in the incline direction, the horizontal distance is 60 m, and the average coal mining depth is 138 m. Therefore, when the boundary subsidence threshold is 100 mm, the strike and cline boundary angle are 63.8° and 66.5°.
3.3.3. Area Analysis
In order to accurately express the subsidence values of different areas and the subsidence area with different subsidence values, it was necessary to perform area statistical analysis based on the DSuM. Therefore, we classified and counted the DSuM at the interval of 100 mm. The results are shown in Figure 14.
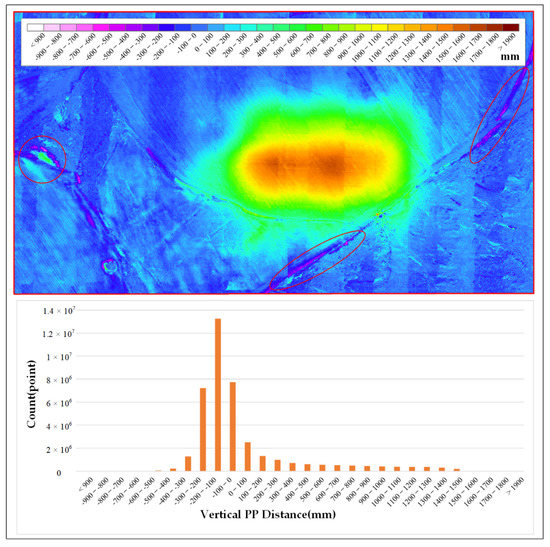
Figure 14.
The subsidence classification and statistics map.
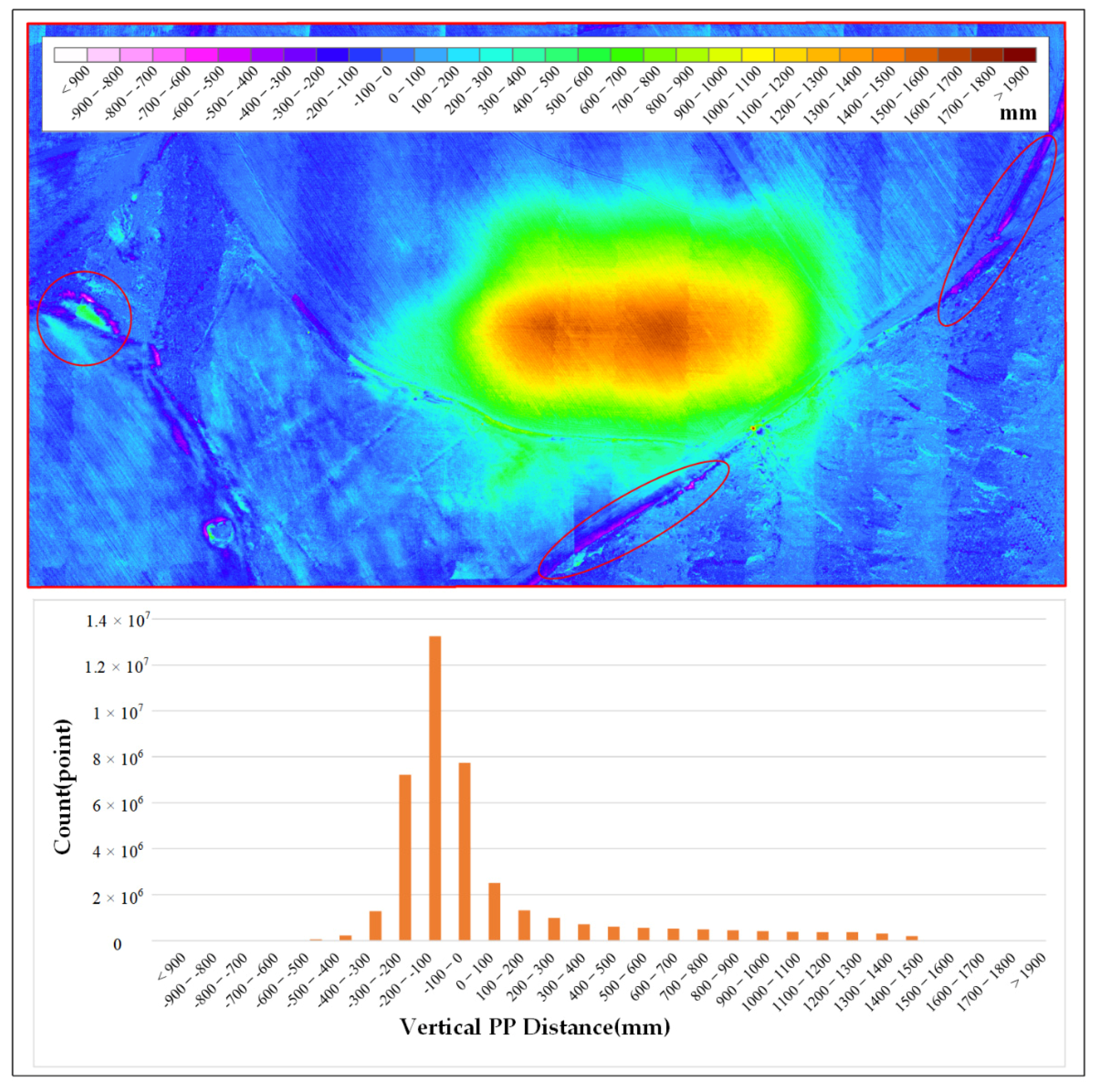
The upper half of Figure 14 is the subsidence classification map of the study area. It shows the locations of different subsidence values, and the different colors represent different subsidence values. The lower part of Figure 14 is a histogram which represents the number of pixels for each subsidence value. According to the classification map, there are some areas with negative subsidence values, especially the red circled area, which are caused by man—excavation, road construction, etc.
Figure 14 shows that the subsidence area is distributed in an oval shape. The main subsidence area is located at the center of the study area. Due to the influence of natural rainfall, there is a large area with subsidence values less than 100 m. In particular, there are very few areas where the subsidence value is less than −100 mm, as shown in the red circle in Figure 14. In addition, according to the histogram in Figure 14, we found that the larger the subsidence value, the smaller the number of the corresponding grids. Next, we counted the number of grids with different subsidence values, and calculated the areas of different subsidence values. The results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Statistics of the areas with different subsidence values.
Table 4 indicates that areas with a subsidence value of less than 100 mm occupied more than 55% of the study area, in which most of the subsidence values are caused by external factors. In order to determine the subsidence area caused by coal mining, we took 100 mm as the minimum subsidence threshold caused by coal mining. The area of subsidence value larger than 100 mm is about 180,075 m2. The goaf area is 49,789 m2. The ratio is 3.6:1. According to Table 4, the area with a subsidence value of 100–300 mm is 102,585 m2, which means the majority of subsidence was caused by coal mining. The maximum subsidence value is about 1700 mm. We found that the larger the subsidence value, the smaller the corresponding area, and the area ratios of different subsidence values are shown in Table 4.
The isoline map is a classical graphical representation, such as a contour map, which can be used to represent elevation of terrain. In this study, we took the isoline map to express the subsidence value, named the subsidence isoline map, which can clearly show the surface subsidence values in different locations. The subsidence isoline map shows different forms when setting different interval values, as shown in Figure 15.
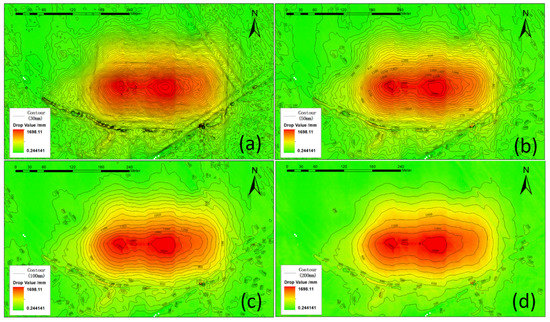
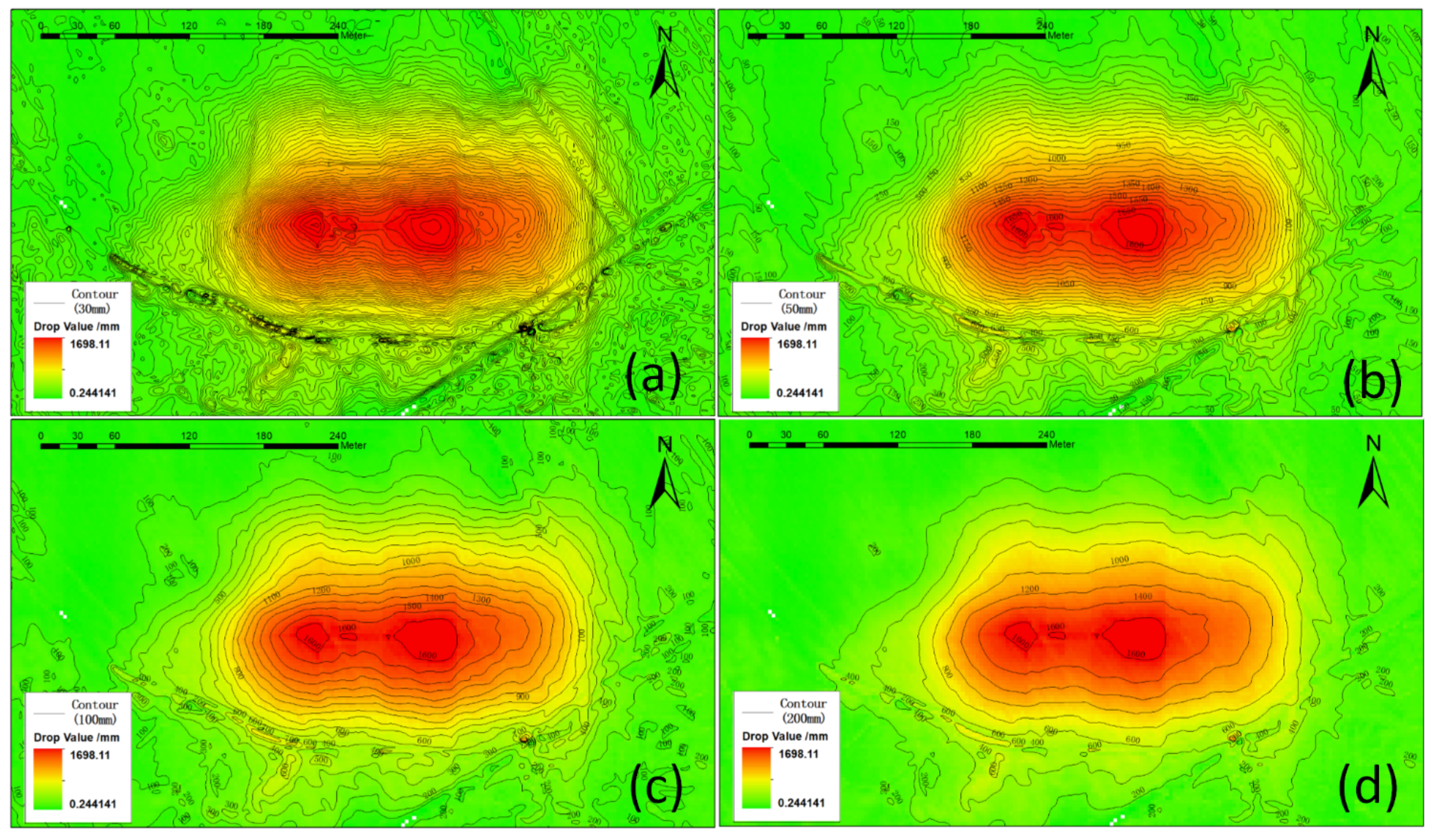
Figure 15.
The subsidence isoline map with different interval values: ((a): 30 mm, (b): 50 mm, (c): 100 mm, and (d): 200 mm).
It can be seen in Figure 15 that the detailed characteristics of the subsidence isoline map with different interval values are different. The smaller isoline interval values correspond to more detailed subsidence characteristics, but also cause the noise to be more pronounced. Through a comprehensive comparison, we found that the isoline map with a subsidence interval value of 100 mm can retain the details of subsidence characteristics of coal mining and reduce the impact of noise.
After analysis of the subsidence isoline map with an interval value of 100 mm, we took the subsidence value of 100 mm as the minimum subsidence threshold and extracted the subsidence boundary. The result is shown in Figure 16.
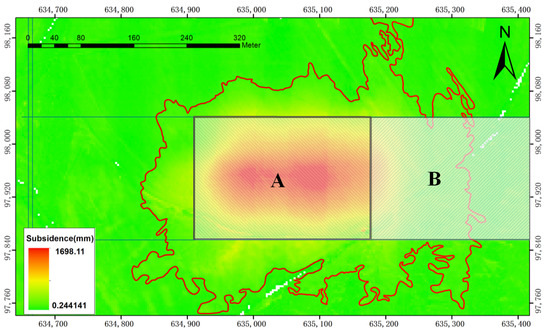
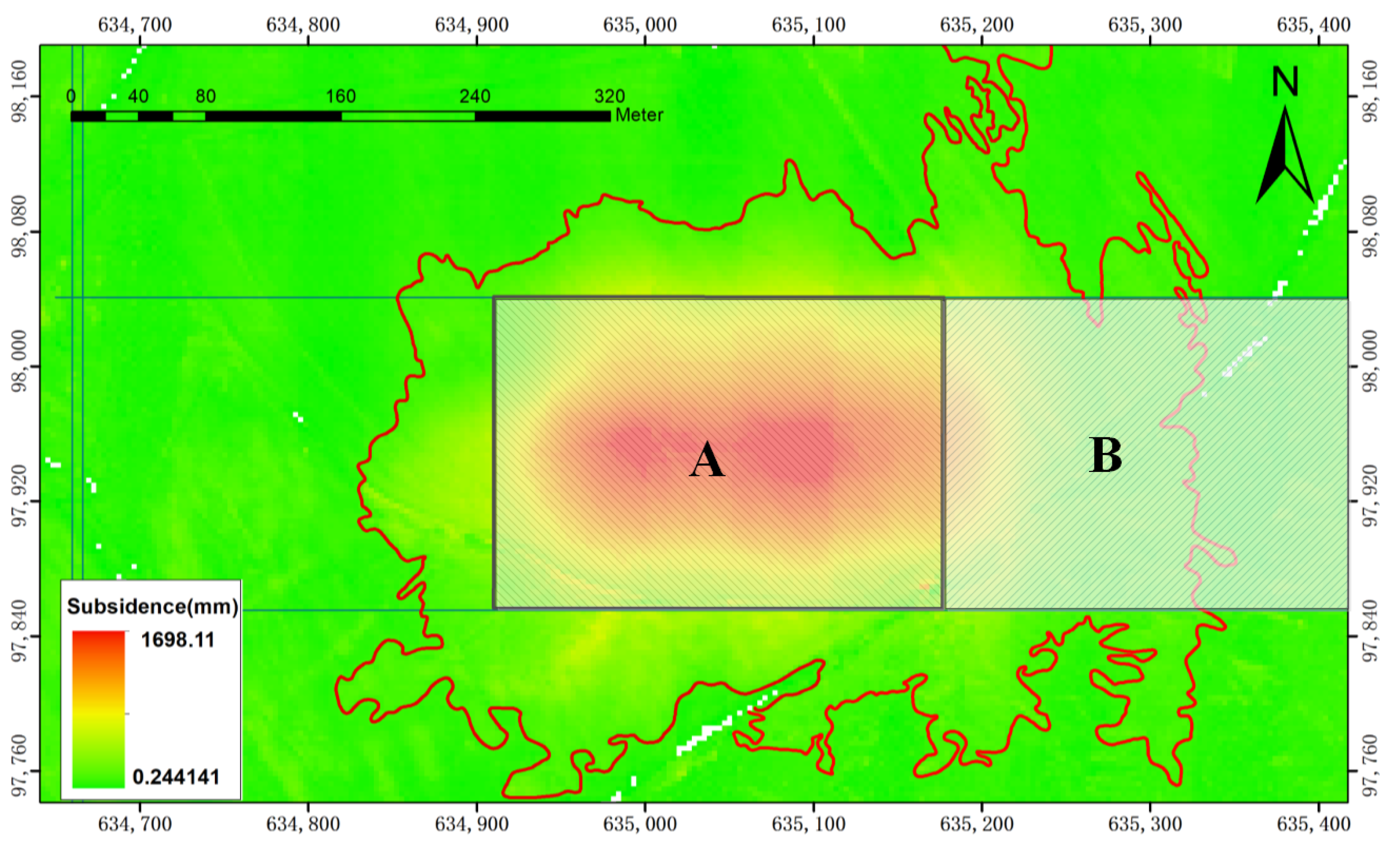
Figure 16.
The subsidence area caused by coal mining. (A) Goaf generated between 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021; (B) goaf generated before 2020.11.
Figure 16 indicates that the area of subsidence is larger than the goaf area, and the subsidence area is offset to the right relative to the goaf. The subsidence area was 140,271 m2 during 7 November 2020 and 19 May 2021, which is smaller than the 180,075 m2 calculated in Table 4, and the ratio of subsidence area to goaf was 2.8:1.
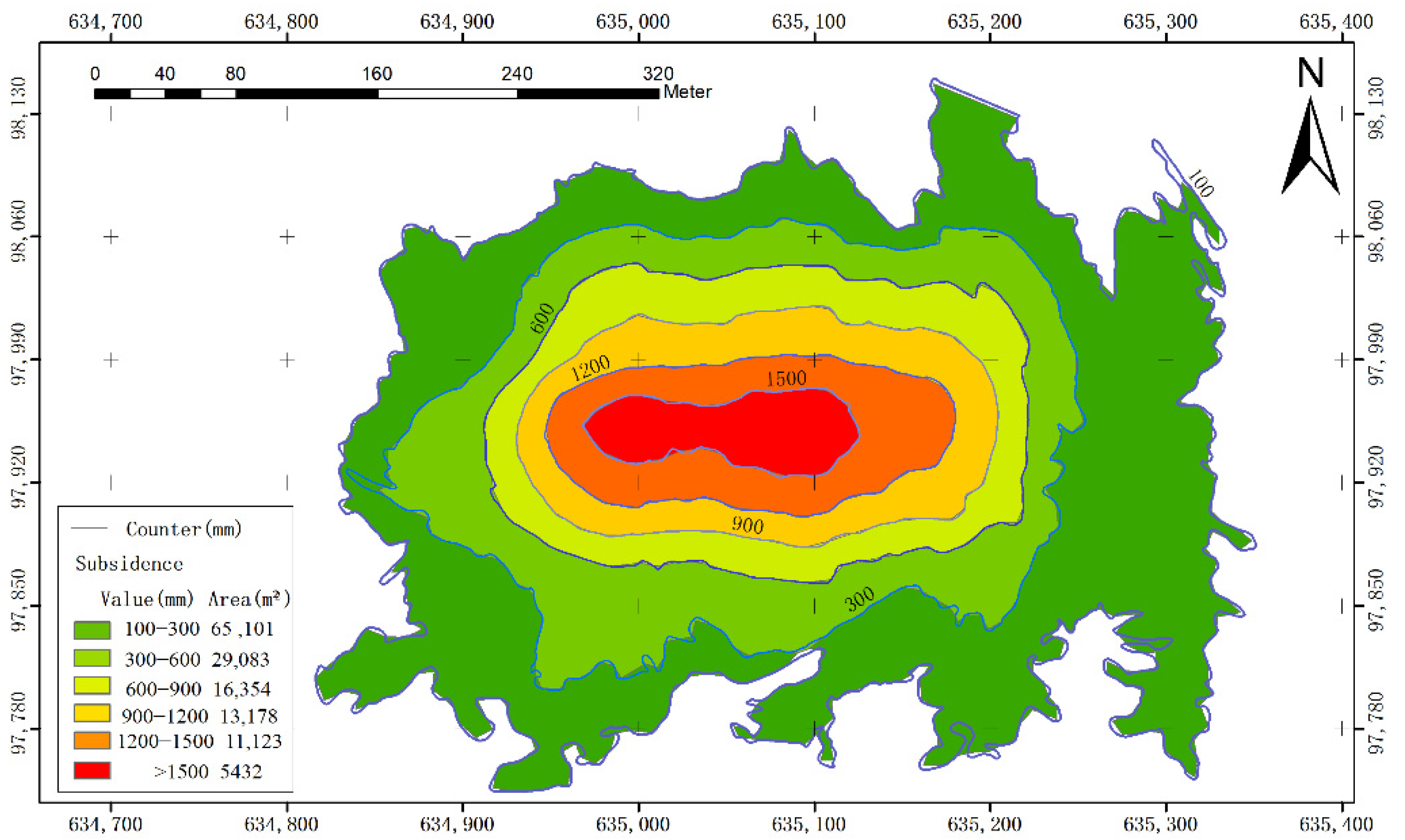
A subsidence value larger than 100 mm is considered to be caused by coal mining. We divided the subsidence values into six grades, and the corresponding area of each grade was calculated, and then expressed in a specific color, as shown in Figure 17.
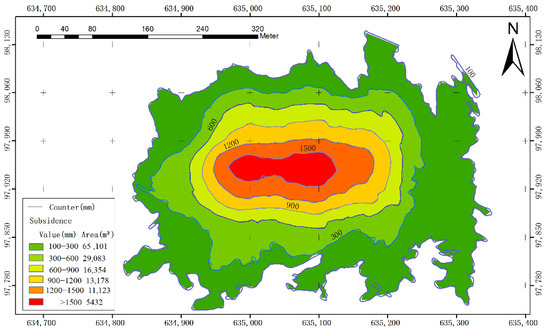
Figure 17.
The different subsidence grades.
As shown in Figure 17, the areas with different subsidence grades gradually expanded outward with the goaf from the center. The subsidence can be divided into six grades: 100–300 mm, 300–600 mm, 600–900 mm, 900–1200 mm, 1200–1500 mm, and more than 1500 mm. The corresponding subsidence areas are 65,101, 29,083, 16,354, 13,178, 11,123, and 5432 m2. The ratio among the subsidence grades is 46:21:12:9:8:4.
4. Discussion
The accuracy of the DSuM was determined by point cloud and DEM. Therefore, we analyzed the accuracy of the point cloud and DEM, and the results are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. We also analyzed the influence of interpolation grid size (resolution of DEM) on the accuracy of the DEM. The results indicate that the grid size of 0.1 m is suitable for the study area (Table 3, Figure 8). Compared to the results of Yu H. et al. [26], the average error of DEM generated by UAV-based LiDAR increased from 0.32 to 0.039 m. Although UAV oblique photogrammetry can achieve centimeter-level accuracy by arranging high-density ground control points [43], it is not applicable in coal mining subsidence monitoring due to the difficulty of setting ground control points in the coal mining area. The proposed method can achieve centimeter accuracy without ground control points. This paper analyzed and compared the accuracy of point cloud, DEM, and DSuM. The results indicate that the accuracy of the DSuM is better than the accuracy of point clouds and DEMs, as shown in Table 2 and Table 3 and Figure 7 and Figure 10. The reason is that the DSuM generated by two periods of UAV-based LiDAR data adopts the same flight parameters, and the data processing process is exactly the same. Therefore, it can eliminate some systematic errors and improve the accuracy.
We calculated the strike and incline boundary angles with the threshold of 100 mm, which are 63.8° and 66.5°, respectively. The boundary angle value is similar to the strike boundary angle of 61.2° calculated by GCPs. The result indicates that line analysis could be applied to the calculation of boundary angle with the subsidence threshold of 100 mm, but it is difficult to detect a boundary of 10 mm. In the area analysis, there was a series of subsidence values less than zero. The reasons for this may be external factors, such as rain wash and crop farming. Therefore, to further determine the subsidence area caused by coal mining, we set the subsidence value of 100 mm as the maximum threshold value caused by non-coal mining to eliminate the influences of other factors. We calculated and drew the subsidence isoline map with four different interval values. The result indicates that the subsidence isoline map with an interval of 100 mm is suitable for subsidence monitoring; see Figure 15. It can perfectly express the characteristics of coal mining subsidence. We calculated the area of subsidence area according to the entire study area and the isoline map (Figure 14 and Figure 16 and Table 4). The results show that the area calculated by the isoline map is smaller than the area calculated according to the entire study area, the reason for which is that the area calculated by the entire study area includes some subsidence not caused by coal mining. The final subsidence area caused by coal mining should be the result calculated by the isoline map with interval value of 100 mm.
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Subsidence detection is important work for coal mining safety. There are various methods used to detect the deformation of mining areas. However, the accuracy is difficult to guarantee in mountainous areas. In this study, UAV-based LiDAR was used to monitor the ground surface subsidence of the working face of a coal mining area, and a new model termed DSuM is proposed to detect the subsidence deformation of a coal mining area. The accuracy of the DSuM was verified by GCPs, and the data mining was performed based on the DSuM to obtain the parameters required for coal mining subsidence monitoring. Subsequently, point, line, and area analyses of the DSuM were conducted. The results indicate that UAV-based LiDAR can be used to monitor continuous changes of the working face in a coal mining area, which provides basic information for subsidence prediction and damage recovery in mining areas.
Some issues are still worth investigating. The accuracy of UAV-based LiDAR can reach the centimeter level, which is not suitable for areas with small subsidence values, especially when the subsidence values are less than 100 mm. On the other hand, the ground surface deformation also includes horizontal movement, but the DSuM cannot express horizontal deformation. Therefore, future work will be focused on further improving the accuracy of the DSuM and creating a model that can represent horizontal deformation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, and methodology, J.Z. and W.Y.; data curation and investigation, B.M. and L.B.; formal analysis and writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing and validation supervision, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under project 41977059.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Shaanxi 185 Coalfield Geology Co., Ltd. for providing the checkpoint data and the staff at Liangshuijing Coal Mine for allowing us to conduct our studies at the experimental site.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bell, F.G.; Stacey, T.R.; Genske, D.D. Mining subsidence and its effect on the environment: Some differing examples. Environ. Geol. 2000, 40, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Baumgartl, T.; Matthew, P.; Glenn, V. The impact of underground longwall mining on prime agricultural land: A review and research agenda. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Fu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lv, X. Effects of land use transitions due to underground coal mining on ecosystem services in high groundwater table areas: A case study in the Yanzhou coalfield. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Barbato, J.; Dai, H.; Peng, S.S.; Agioutantis, Z.; Adhikary, D.; Qu, Q.; Wilkins, A.H.; Poulsen, B.A.; Guo, H.; et al. Surface subsidence damage, mitigation and control. In Surface Subsidence Engineering: Theory and Practice; Peng, S., Ed.; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 2020; pp. 105–131. [Google Scholar]
- Stoch, T. Horizontal Displacement in Mining Area Protection; AGH University of Science and Technology Press: Kraków, Poland, 2019; ISBN 978-83-66364-19-6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, J.; Ma, D. Monitoring and prediction of mining subsidence combined with SBAS-InSAR and support vector regression. Remote Sens. Inf. 2021, 36, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, X.S. Progress of large gradient deformation monitoring technology in mining area combined with InSAR. Surv. Mapp. Bull. 2018, 7, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS techniques to determine mining-related deformations using Sentinel-1 data: The case study of Rydutowy mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przyłucka, M.; Herrera, G.; Graniczny, M.; Colombo, D.; Béjar-Pizarro, M. Combination of conventional and advanced DInSAR to monitor very fast mining subsidence with TerraSAR-X data: Bytom city (Poland). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5300–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, G.; Tanteri, L.; Tofani, V.; Vannocci, P.; Casagli, N. Multitemporal UAV surveys for landslide mapping and characterization. Landslides 2018, 15, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindner, G.; Schraml, K.; Mansberger, R.; Hübl, J. UAV monitoring and documentation of a large landslide. Appl. Geomat. 2015, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Li, X.; Ng, H.M. UAV for mining applications: A case study at an open-cut mine and a longwall mine in New South Wales, Australia. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, S.; Luan, K.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Jin, Y.; et al. Integration of UAV-based photogrammetry and terrestrial laser scanning for the three-dimensional mapping and monitoring of open-pit mine areas. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6635–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, X.; Liu, X.; Ge, L.; Hu, H.; Wu, Y. Time-series unmanned aerial vehicle photogrammetry monitoring method without ground control points to measure mining subsidence. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 024505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignjatovi Stupar, D.; Roer, J.; Vuli, M. Investigation of unmanned aerial vehicles-based photogrammetry for large mine subsidence monitoring. Minerals 2020, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P. Research on Mining Subsidence Monitoring Method of UAV Tilt Photogrammetry. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wikaa, P.; Gruszczyński, W.; Stoch, T.; Puniach, E.; Wójcik, A. UAV Applications for determination of land deformations caused by underground mining. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Qi, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, B.; Guo, L. Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry technology for dynamic mining subsidence monitoring and parameter inversion: A case study in China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 16372–16386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauhala, A.; Tuomela, A.; Davids, C.; Rossi, P.M. UAV remote sensing surveillance of a mine tailings impoundment in sub-arctic conditions. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Carricondo, P.; Mesas-Carrascosa, F.J.; García-Ferrer, A.; Agüera-Vega, F.; Pérez-Porras, F.J. Assessment of UAV-photogrammetric mapping accuracy based on variation of ground control points. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, K.; Christophe, D.; Pascal, A.; Pierre, P.; Marion, J.; Eric, V. Application of a terrestrial laser scanner (TLS) to the study of the Séchilienne landslide (Isère, France). Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2785–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Li, J.; Feng, H.; Zhao, J. Application of 3D laser scanning technology in dam subsidence monitoring in mining area. Mine Surv. 2014, 6, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W. Monitoring mining subsidence by three-dimensional laser scanning technology. Metal Mines 2017, 1, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, D.; Wu, K.; Zhou, B. Study on subsidence monitoring technology using terrestrial 3D laser scanning without a target in a mining area: An example of Wangjiata coal mine, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 3575–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brede, B.; Lau, A.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Kooistra, L. Comparing RIEGL RiCOPTER UAV LiDAR derived canopy height and DBH with terrestrial LiDAR. Sensors 2017, 17, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Gang, C.; Ge, X. Detection and volume estimation of mining subsidence based on multi-temporal LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Geoinformatics (IEEE 2011), Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Ge, X.; Cheng, G. Digital terrain model extraction from airborne LiDAR data in complex mining area. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics (IEEE 2010), Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, J.; Wu, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Subsidence monitoring using lidar and morton code indexing. J. Surv. Eng. 2016, 142, 06015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, P.; Dornbusch, U.; Thomas, I.; Dan, A.; Bovington, J.; Horn, D. Coincident beach surveys using UAS, vehicle mounted and airborne laser scanner: Point cloud inter-comparison and effects of surface type heterogeneity on elevation accuracies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siranec, M.; Hger, M.; Otcenasova, A. Advanced power line diagnostics using point cloud data—Possible applications and limits. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakuła, K.; Pilarska, M.; Salach, A.; Kurczyński, Z. Detection of levee damage based on UAS data—Optical imagery and LiDAR point clouds. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Hang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Study on extraction method of vegetation restoration height in mining area based on lidar. Coal Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Streutker, D.R.; Glenn, N.F. LiDAR measurement of sagebrush steppe vegetation heights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S. Quantitative Evaluation of Ecological Environment Damage Caused by Coal Mining in Yushenfu Mining Area. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Chan, Y.C.; Hu, J.C. Digital elevation model differencing and error estimation from multiple sources: A case study from the Meiyuan Shan landslide in Taiwan. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, X. A point cloud filtering approach to generating DTMs for steep mountainous areas and adjacent residential areas. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salach, A.; Bakua, K.; Pilarska, M.; Ostrowski, W.; Górski, K.; Kurczyński, Z. Accuracy assessment of point clouds from LiDAR and dense image matching acquired using the UAV platform for DTM creation. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Huang, R.; Dong, Z.; Li, J. Two-step adaptive extraction method for ground points and breaklines from lidar point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, P. DEM generation from laser scanner data using adaptive TIN models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, X.H. Research on Airborne LiDAR Point Cloud Filtering Algorithm and DEM Interpolation Method. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Ji, L.; Jiao, Q.; Zhang, J. Comparative study on interpolation methods based on ground lidar point cloud data. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 4, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, E.R. An Introduction to Morphological Image Processing; SPIE Optical Engineering Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Maciuk, K.; Lewińska, P. High-rate monitoring of satellite clocks using two methods of averaging time. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).