Mapping Large-Scale Plateau Forest in Sanjiangyuan Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Few-Shot Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
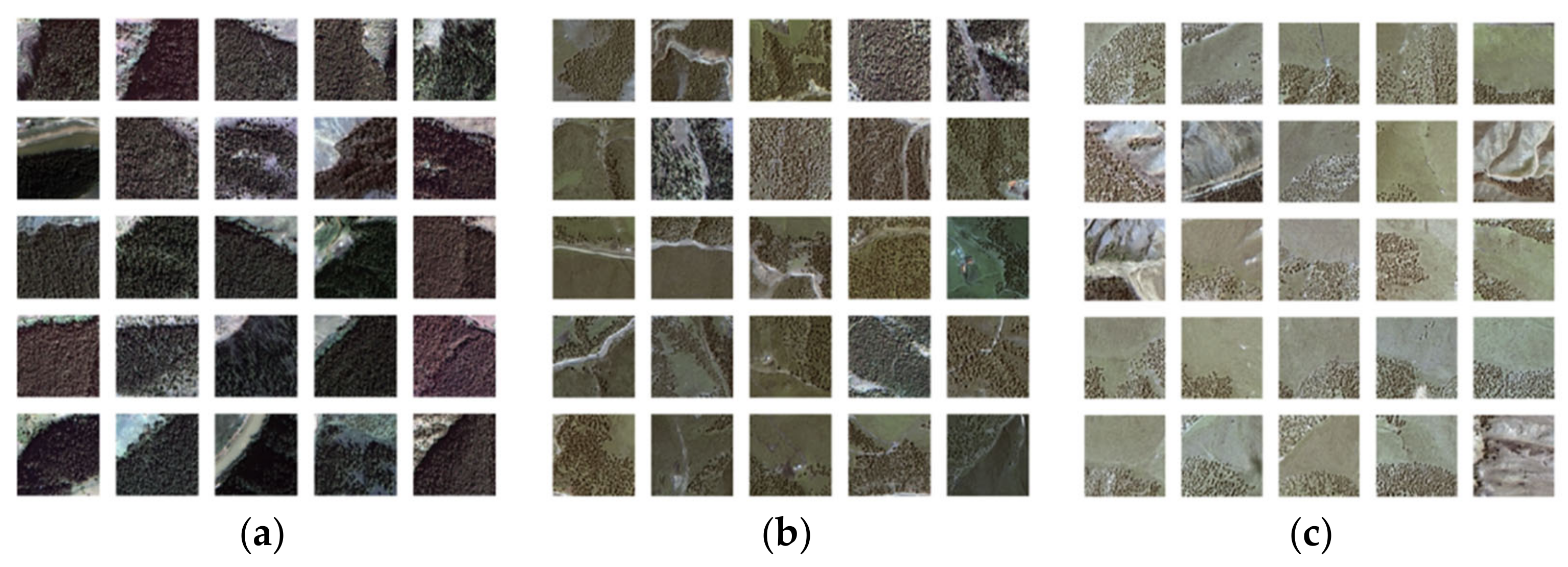
2.1. Study Area and Data
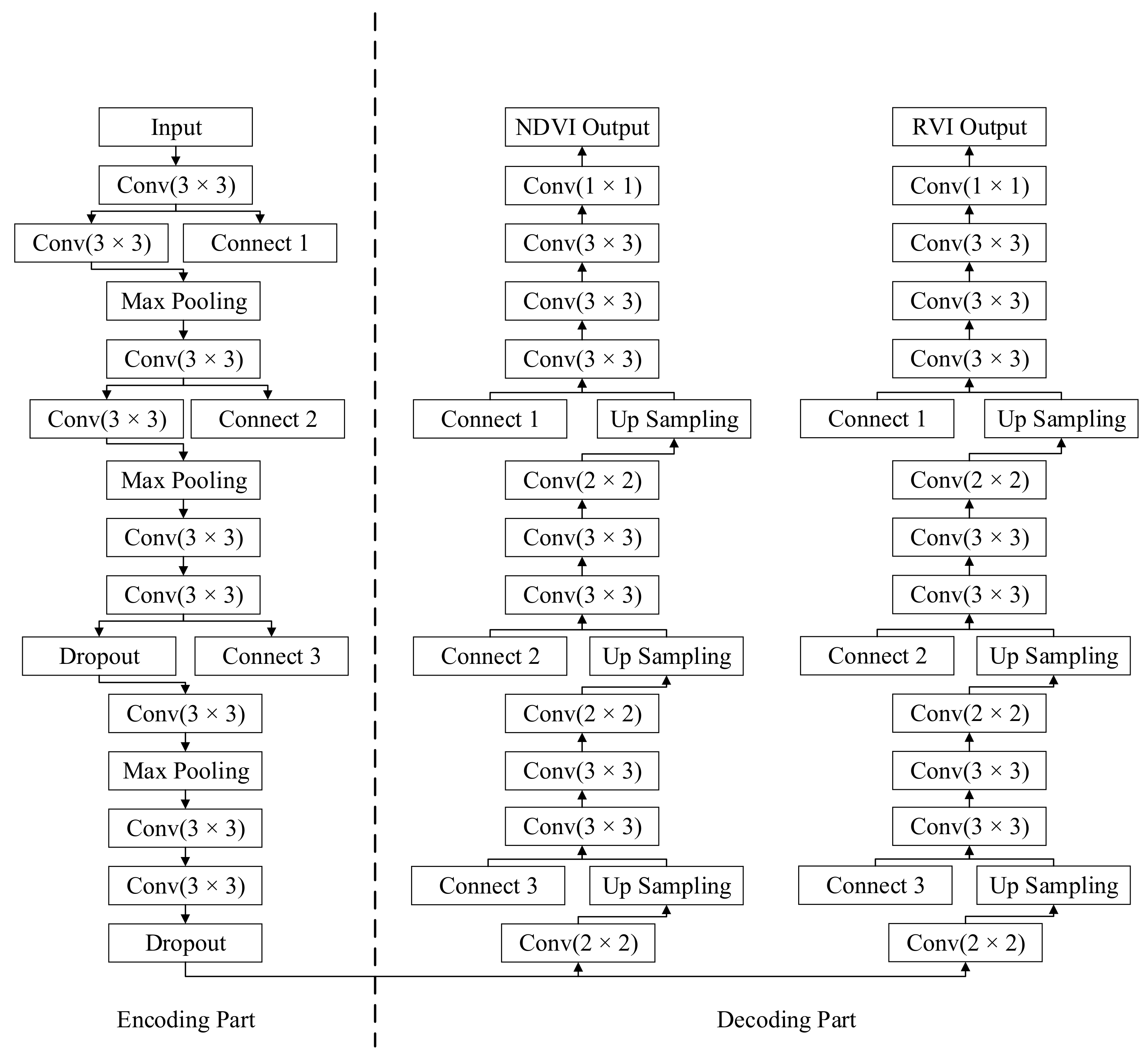
2.2. Proposed Method
2.2.1. Unsupervised Learning Based Model for Domain Knowledge Extraction
2.2.2. Semi-Supervised Learning-Based Model Fine-Tuning
2.3. Comparsion Methods
3. Results
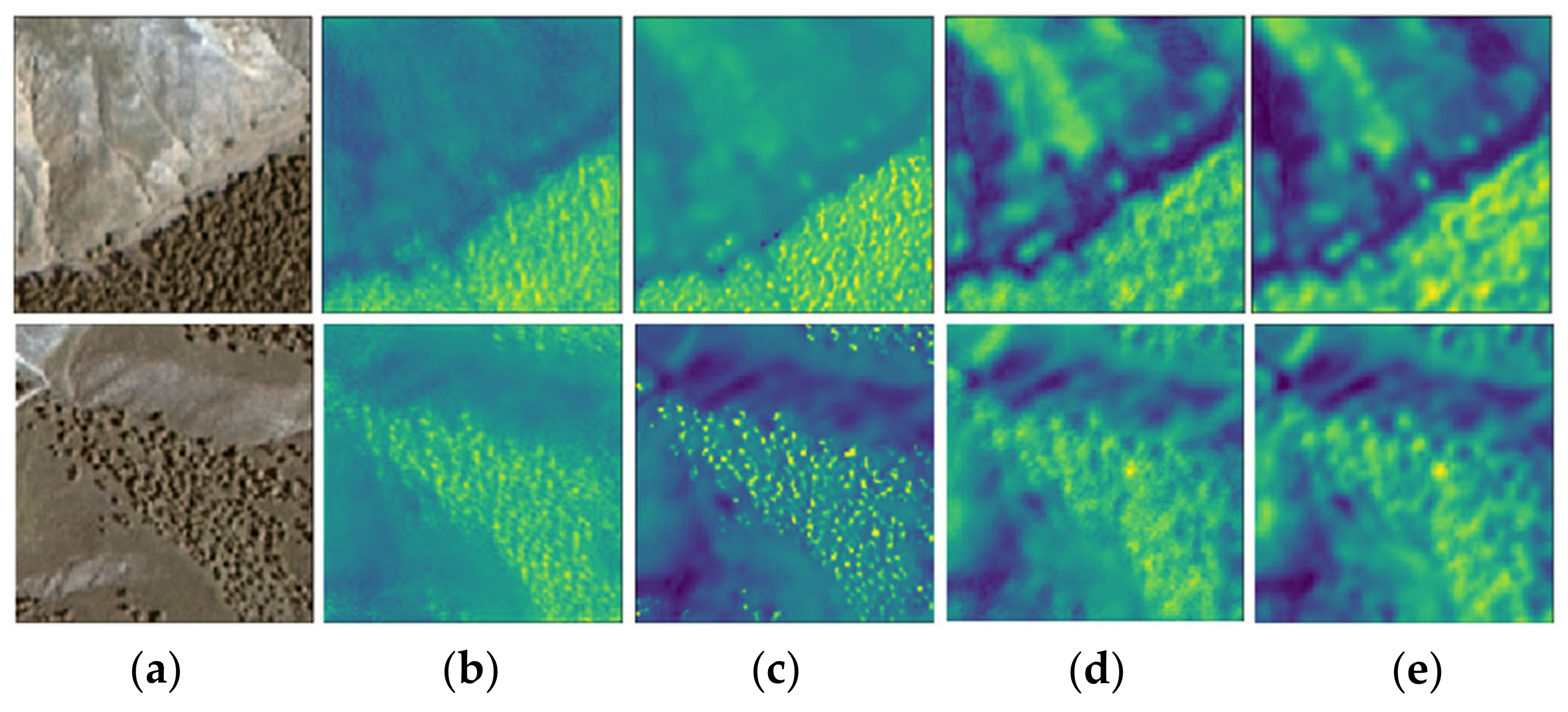
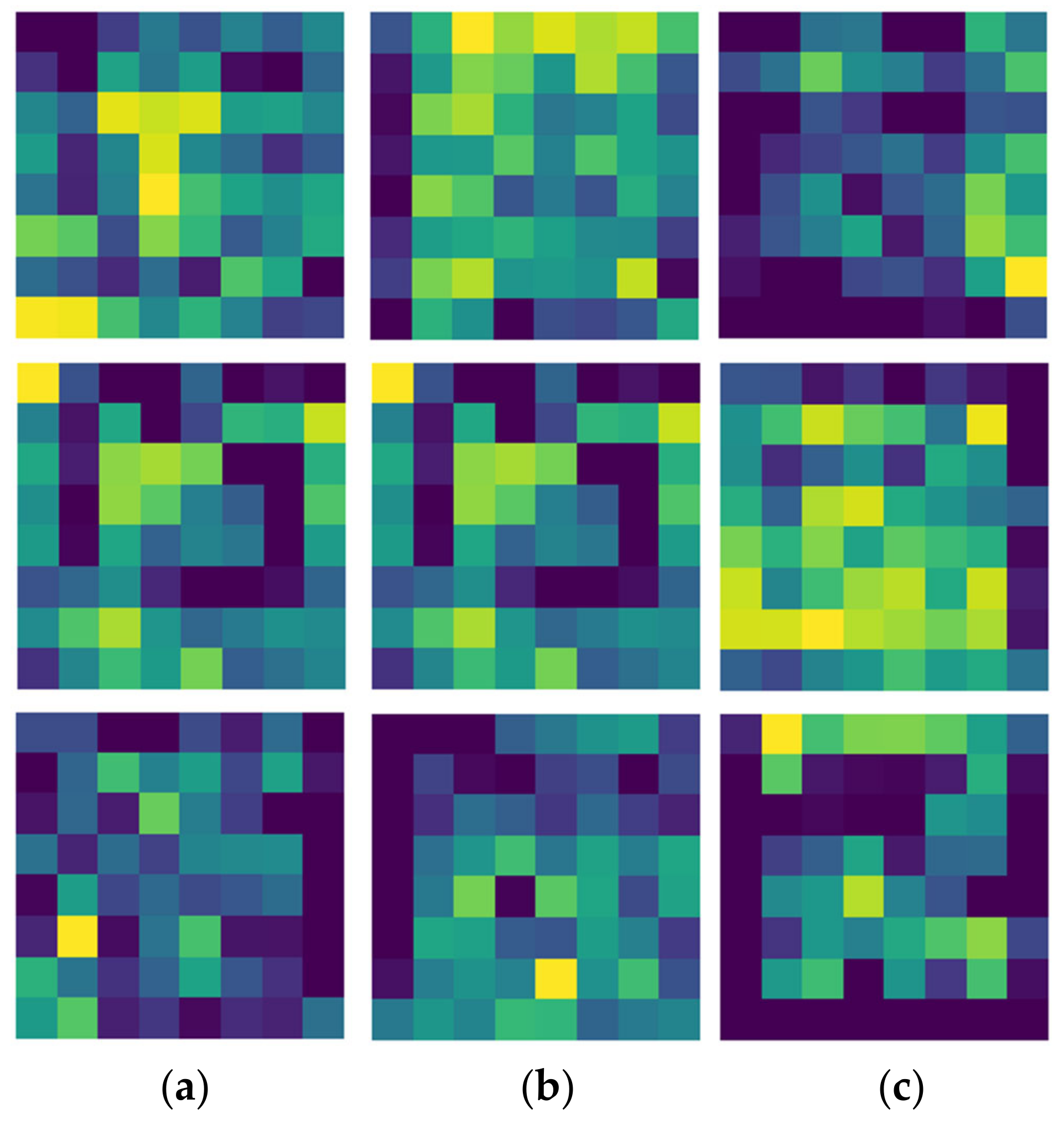
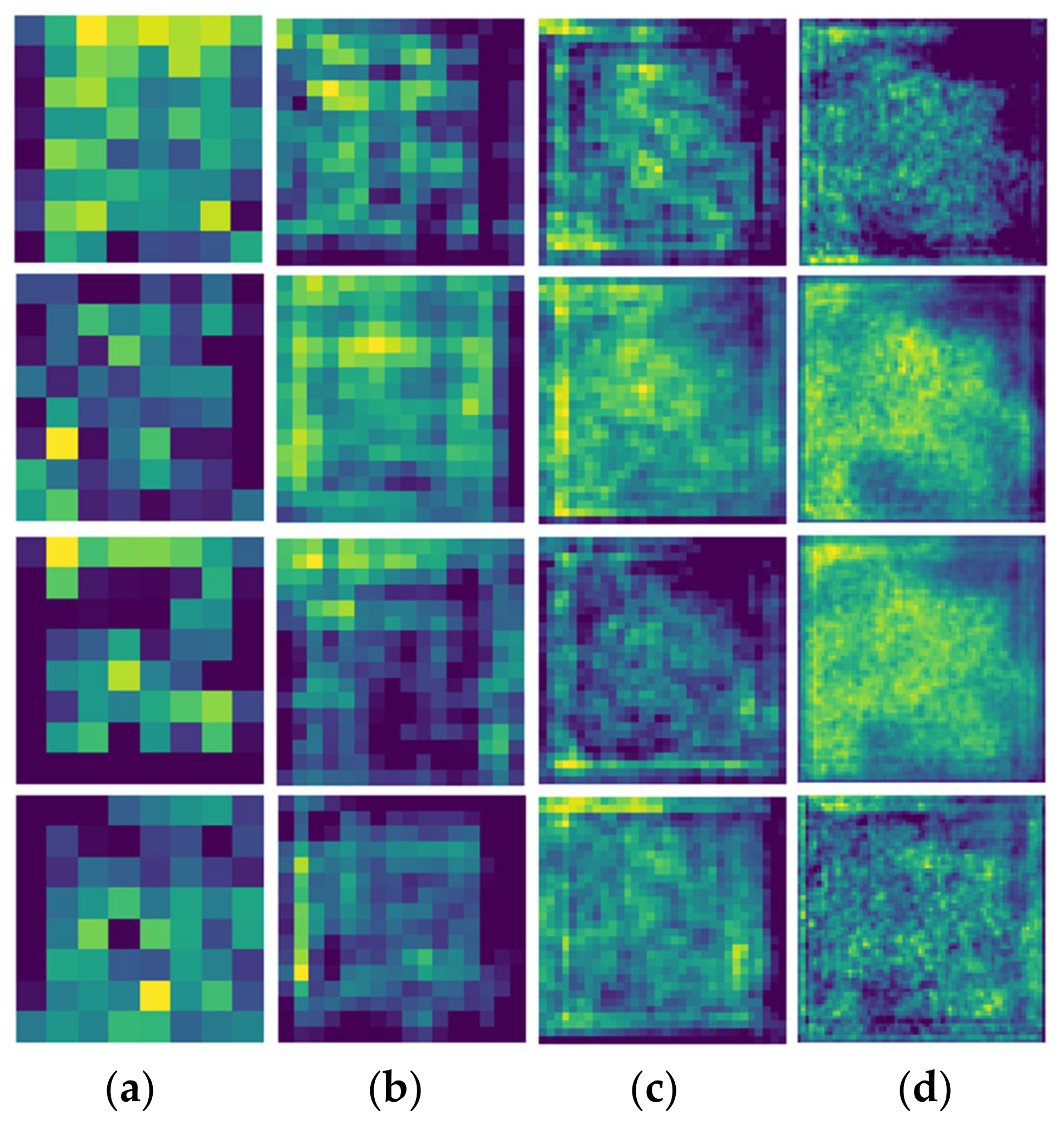
3.1. Result of Unsupervised Learning-Based Model for Domain Knowledge Extraction
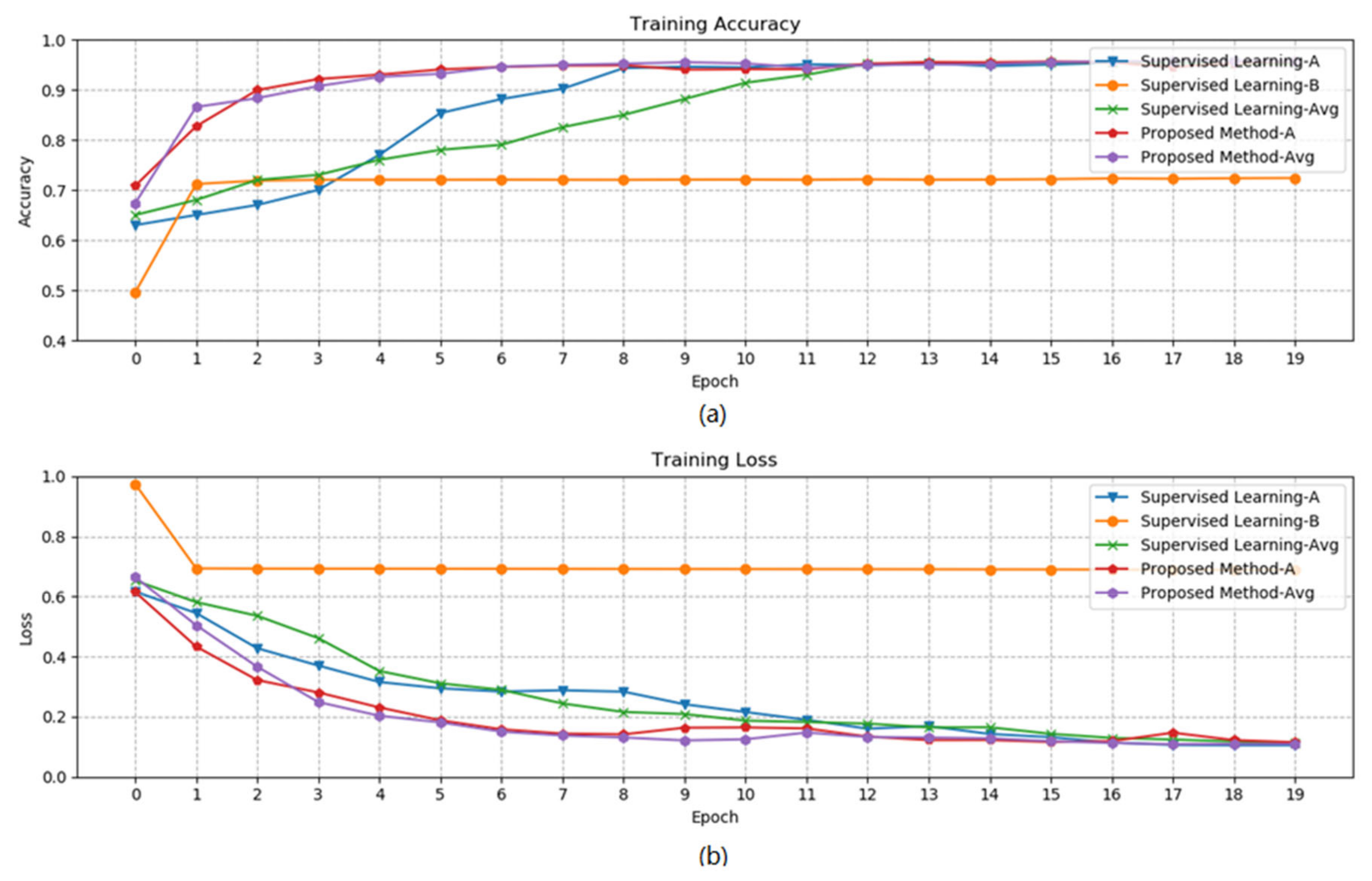
3.2. Results of Semi-Supervised Learning-Based Model Fine-Tuning
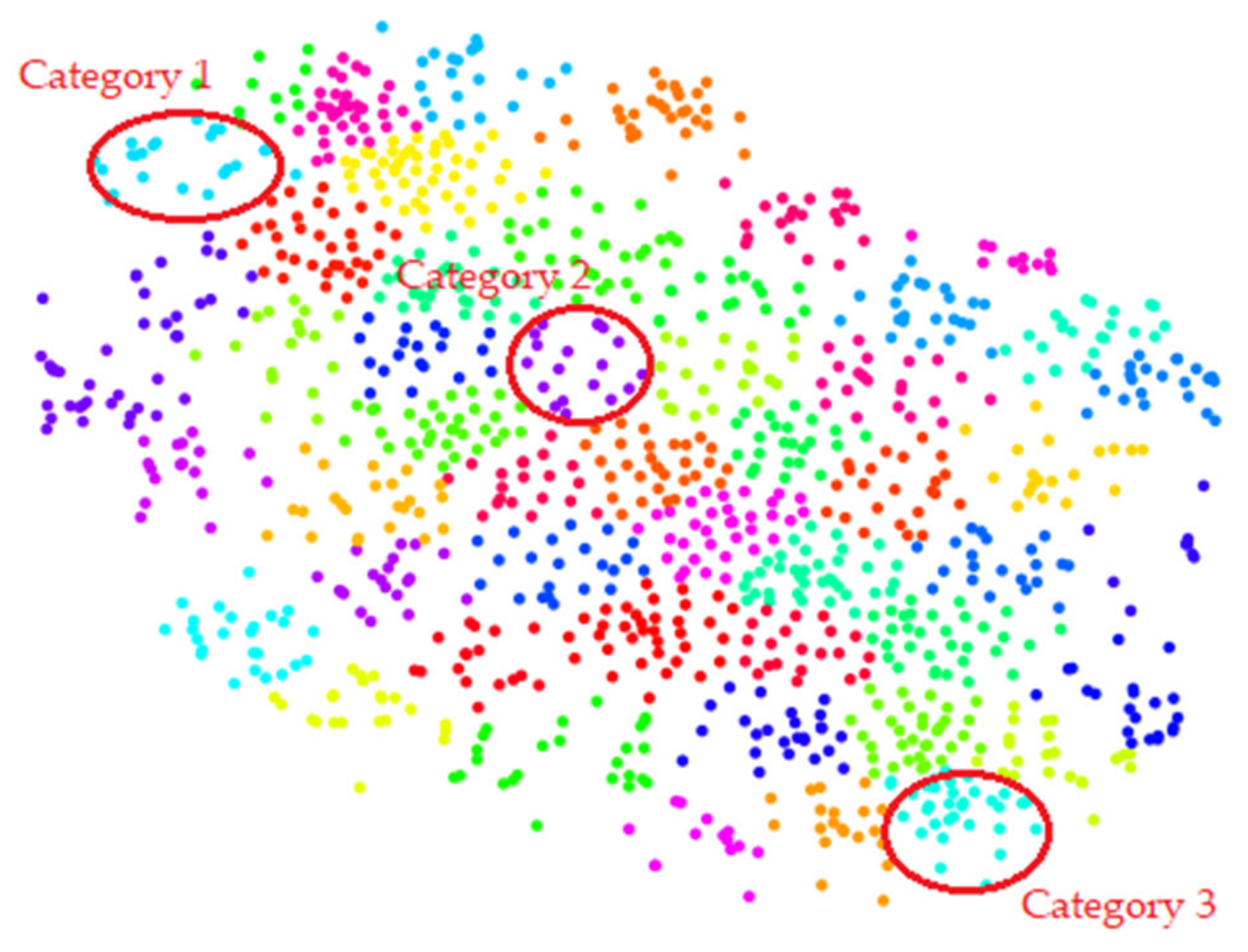
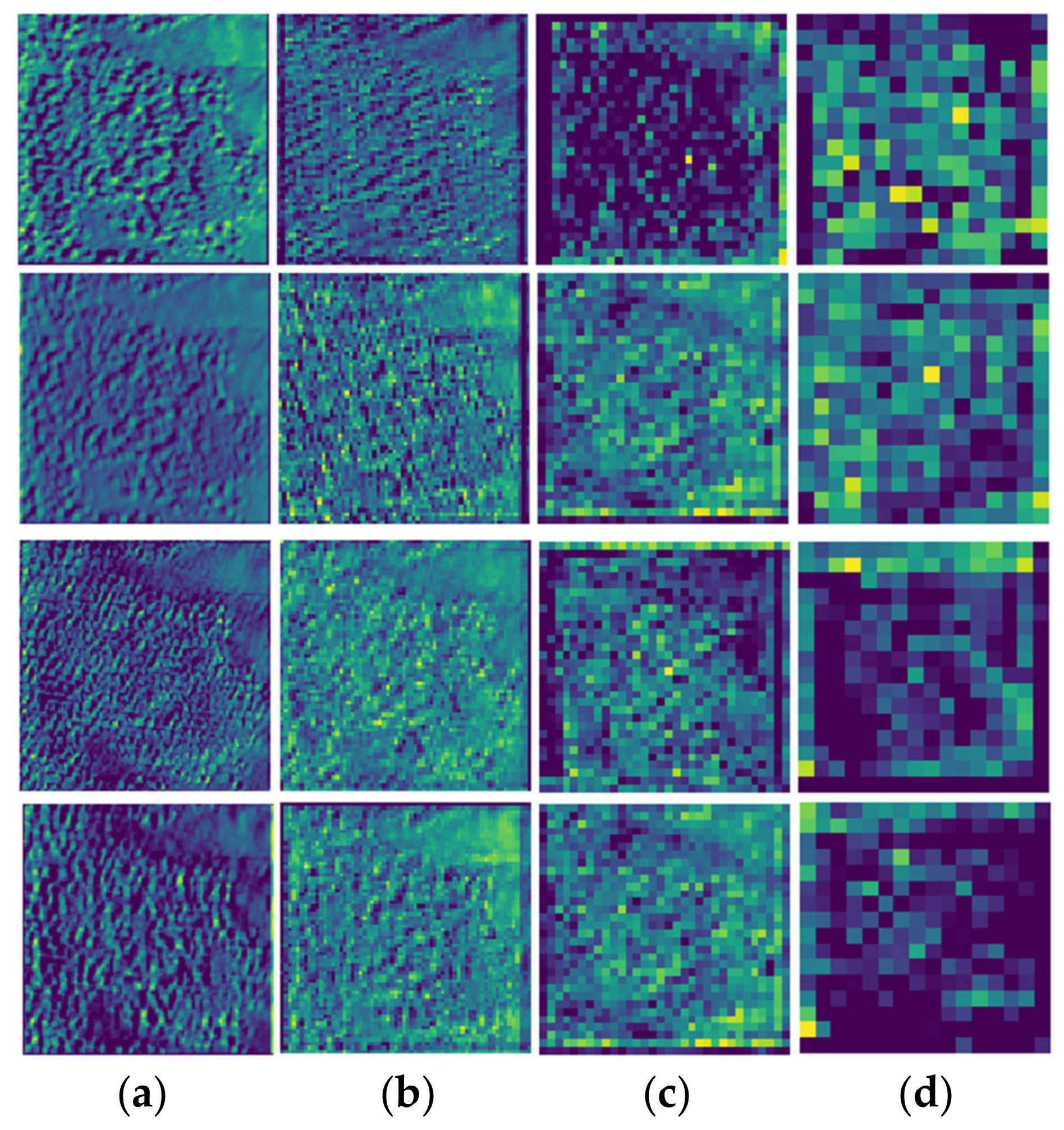
3.3. Extracted Feature Visualization
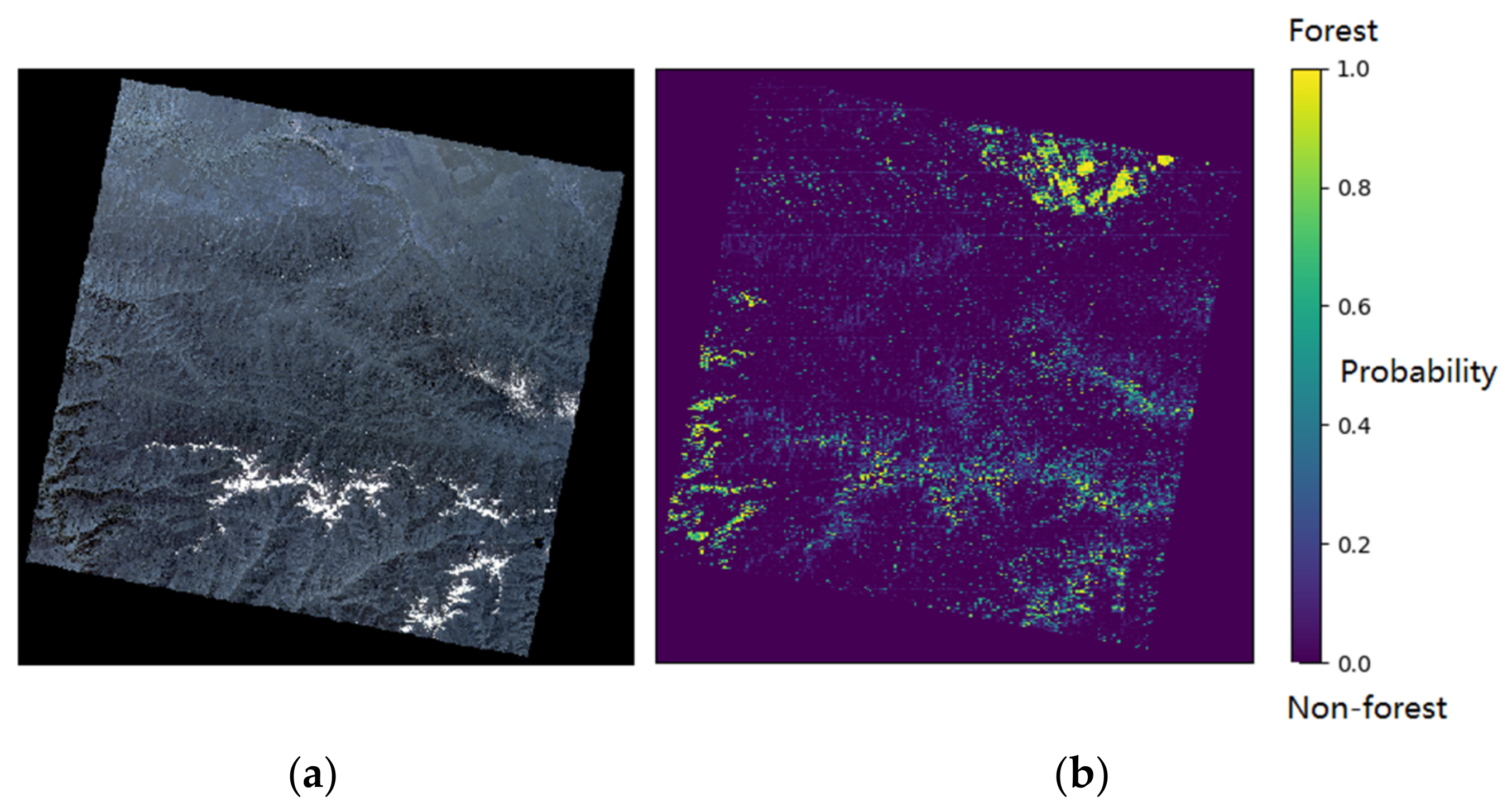
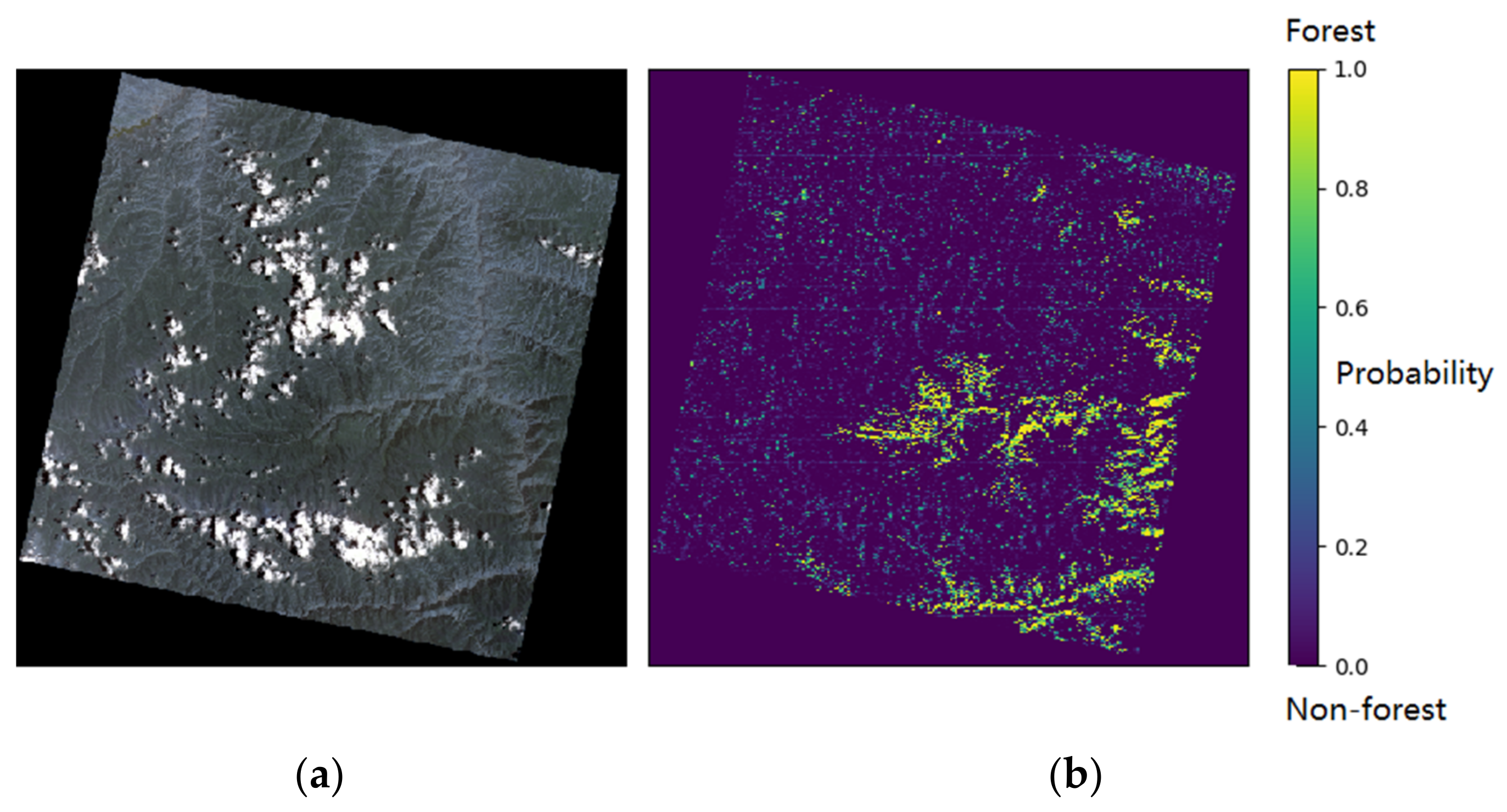
3.4. Forest Mapping for Large Region Based on Proposed Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, S.; Vailshery, L.S.; Jaganmohan, M.; Nagendra, H. Mapping urban tree species using very high resolution satellite imagery: Comparing pixel-based and objectbased approaches. ISPRS Int. J. Geo.-Inf. 2013, 2, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăgu, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, F.X.; Guo, A.H. Study on the climate change trend and its catastrophe over “Sanjiangyuan” region in recent 43 years. J. Nat. Res. 2006, 21, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Duro, D.C.; Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Han, T. Development of a large area biodiversity monitoring system driven by remote sensing. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2007, 31, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymond, C.C.; Mladenoff, D.J.; Radeloff, V.C. Phenological differences in Tasseled Cap indices improve deciduous forest classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. NDVI-Derived Land Cover Classification at a Global Scale. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3567–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arii, M.; van Zyl, J.J.; Kim, Y. A general characterization for polarimetric scattering from vegetation canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Naudiyal, N.; Wu, N.; Cui, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Q. Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Tibet. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Matsuyama, H.; Tsuzuki, H.; Sweda, T. Improving the estimation of leaf area index by using remotely sensed NDVI with BRDF signatures. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, D.; Chen, J.; Cao, X. An improved automated land cover updating approach by integrating with downscaled NDVI time series data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gim, H.-J.; Ho, C.-H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.; Feng, S.; Hayes, M.J. Improved mapping and change detection of the start of the crop growing season in the US Corn Belt from long-term AVHRR NDVI. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 294, 108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinuzzi, S.; Gould, W.A.; González, O.M.R.; Robles, A.M.; Maldonado, P.C.; Buitrago, N.P.; Cabán, J.J.F. Mapping tropical dry forest habitats integrating Landsat NDVI, Ikonos imagery, and topographic information in the Caribbean Island of Mona. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2008, 56, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, B.; Jeganathan, C.; Rathore, V.S. Improved NDVI based proxy leaf-fall indicator to assess rainfall sensitivity of deciduousness in the central Indian forests through remote sensing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Foody, G.M.; Ge, Y.; Boyd, D.S.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Atkinson, P. Mapping annual forest cover by fusing PALSAR/PALSAR-2 and MODIS NDVI during 2007–2016. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quegan, S.; Le Toan, T.; Yu, J.; Ribbes, F.; Floury, N. Multitemporal ERS SAR analysis applied to forest mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgani, F.; Bruzzone, L. Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Chi, M.; Marconcini, M. A novel transductive SVM for semisupervised classification of remote-sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, M.; Mather, P.M. Support vector machines for classification in remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Tian, J. Remote Sensing Image Fusion Using Multiscale Mapped LS-SVM. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Feng, R.; Bruzzone, L. Classification of hyperspectral remote-sensing data with primal SVM for small-sized training dataset problem. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forest Classification of Multisource Remote Sensing and Geographic Data. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS’04, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Canovas-Garcia, F.; Alonso-Sarria, F.; Gomariz-Castillo, F.; Oñate-Valdivieso, F. Modification of the random forest algorithm to avoid statistical dependence problems when classifying remote sensing imagery. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, M.M.; Miller, S.N.; Murphy, M.A. High-resolution landcover classification using Random Forest. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, T.; Kemblowski, M.; Lall, U.; Urroz, G. Support vector machines for nonlinear state space reconstruction: Application to the great salt lake time series. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuldt, C.; Laptev, I.; Caputo, B. Recognizing human actions: A local SVM approach. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 23–26 August 2004; pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, D. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging Using a Fully Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 17, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Proc. Int. Conf. Med. Image Comput. Comput.-Assist. Interv. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Li, S.; Khandelwal, A.; Nayak, G.; Karpatne, A.; Kumar, V. Spatial Context-Aware Networks for Mining Temporal Discriminative Period in Land Cover Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Calgary, AB, Canada, 2–4 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, C.; Webb, G.I.; Petitjean, F. Temporal Convolutional Neural Network for the Classification of Satellite Image Time Series. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldner, F.; Diakogiannis, F.I. Deep Learning on Edge: Extracting Field Boundaries from Satellite Images with a Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 245, 111741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, G.; Mutanga, O.; Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Adam, E. Performance of support vector machines and artificial neural network for mapping endangered tree species using WorldView-2 data in Dukuduku forest, South Africa. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4825–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Jia, K.; Jia, X.; Khandelwal, A.; Kumar, V. Global River Monitoring Using Semantic Fusion Networks. Water 2020, 12, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ziv, G.; Adami, M.; Mitchard, E.; Batterman, S.A.; Buermann, W.; Marimon, B.S.; Junior, B.H.; Reis, S.M.; Rodrigues, D.; et al. Mapping tropical disturbed forests using multi-decadal 30m optical satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Jia, K.; Jia, X.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, Z. Large-Scale River Mapping Using Contrastive Learning and Multi-Source Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendenieks, Z.; Nita, M.D.; Nikodemus, O.; Radeloff, V.C. Half a century of forest cover change along the Latvian-Russian border captured by object-based image analysis of Corona and Landsat TM/OLI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Niu, J.; Berndtsson, R.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. NDVI Dynamics and Its Response to Climate Change and Reforestation in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Negrón-Juárez, R.I.; Chambers, J.Q. Remote sensing and statistical analysis of the effects of hurricane María on the forests of Puerto Rico. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharuk, V.I.; Ranson, K.J.; Im, S.T.; Oskorbin, P.A.; Dvinskaya, M.L.; Ovchinnikov, D.V. Tree-Line Structure and Dynamics at the Northern Limit of the Larch Forest: Anabar Plateau, Siberia, Russia. Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2013, 45, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. Integrating Remote Sensing and Landscape Characteristics to Estimate Soil Salinity Using Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study from Southern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Long, D.; Hong, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, J.; Han, Z.; Liu, R.; Wan, W. Validation and reconstruction of FY-3B/MWRI soil moisture using an artificial neural network based on reconstructed MODIS optical products over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
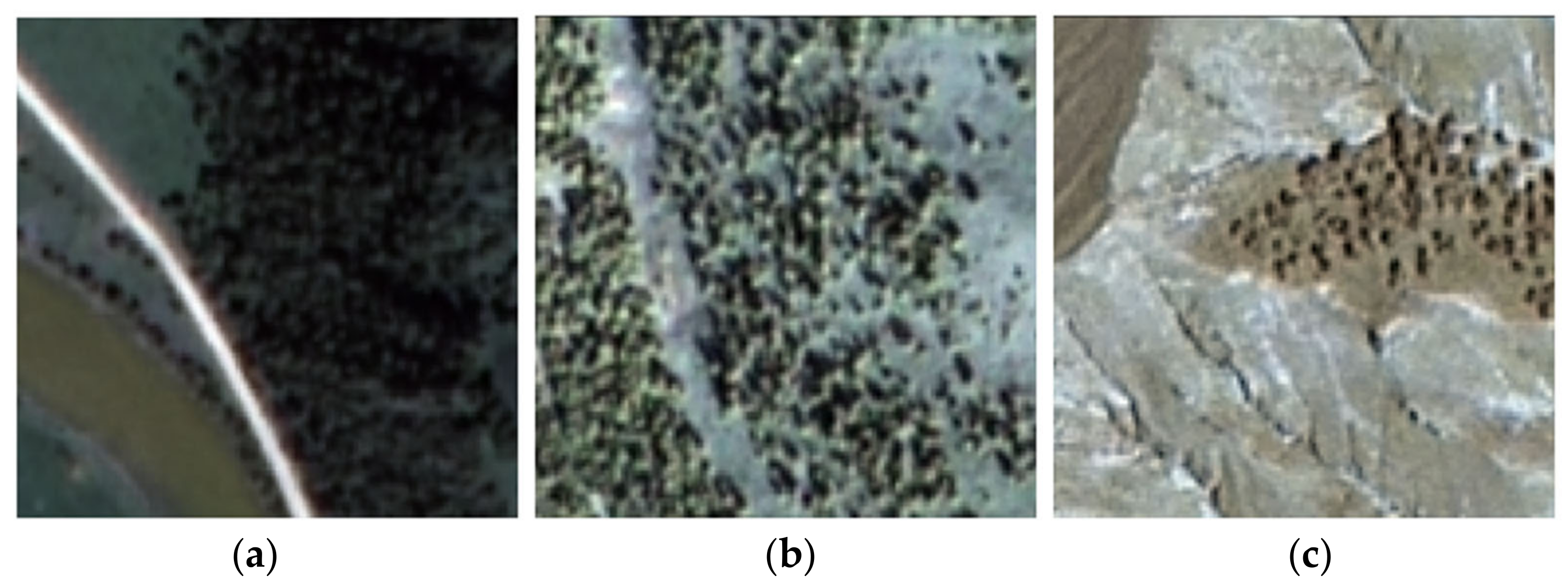
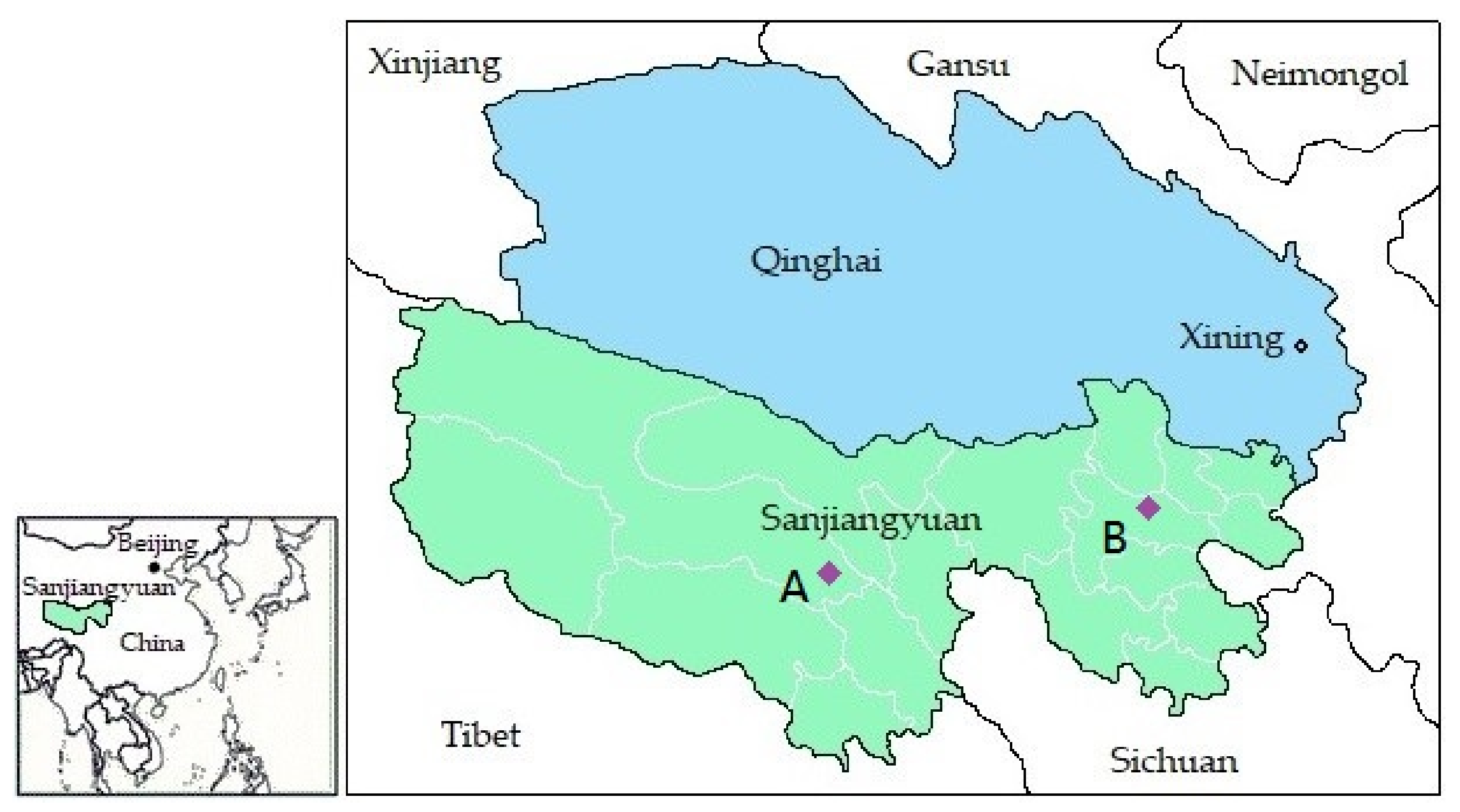
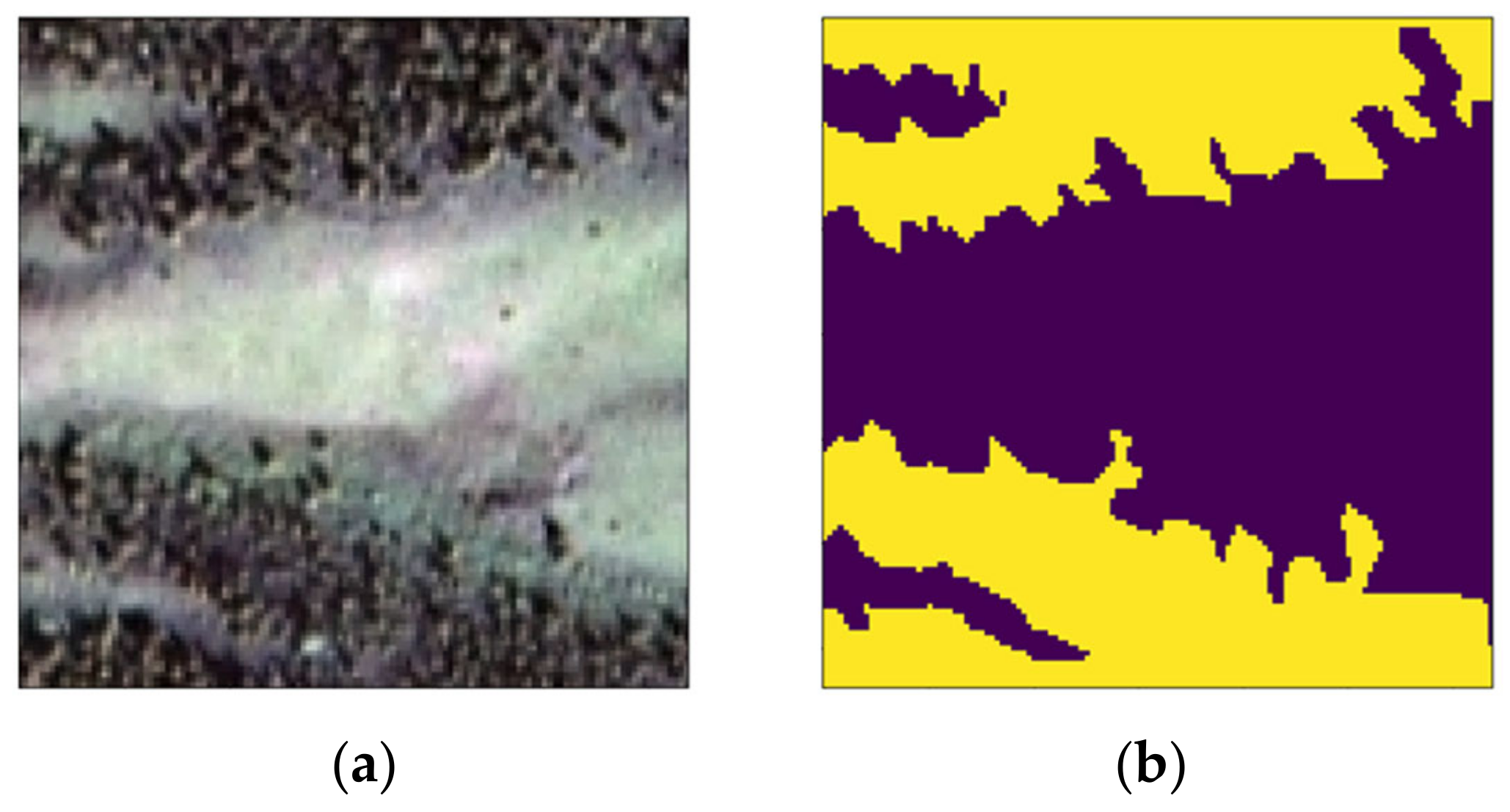







| Parameter Type | Detail |
|---|---|
| temporal resolution | 5 days |
| spatial resolution | 2 m |
| spectral range | 0.45–0.89 μm |
| orbital altitude | 505.984 km |
| Parameter Type | Detail |
|---|---|
| data sources | ZY-3 satellite imagery |
| sample | 38,708 |
| manual ground truth | 1187 |
| sample size | 128 × 128 pixels |
| manual ground truth size | 128 × 128 pixels |
| resolution for each pixel | 2 m |
| period of the data | January 2017–December 2017 |
| period of the manual ground truth | May 2017–June 2017 |
| Algorithm | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | Threshold | 0.1 |
| RVI | Threshold | 0.01 |
| RF | Criterion | Gini |
| SVM | Kernel Type | RBF |
| UNET | Learning Rate | 0.0001 |
| Loss function | Binary Cross Entropy | |
| Proposed Method | Learning Rate | 0.0001 |
| Loss function | Mean Squared Error, Binary Cross Entropy |
| Train Samples | NDVI | RVI | RF | SVM | UNET | PROPOSED | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | P | R | F1 | P | R | F1 | P | R | F1 | P | R | F1 | P | R | F1 | P | R | |
| 100 | 43.09 | 59.32 | 47.38 | 51.21 | 50.76 | 67.63 | 67.02 | 76.83 | 65.07 | 72.23 | 80.35 | 72.61 | 73.28 | 95.48 | 65.73 | 84.23 | 96.32 | 79.09 |
| 300 | 45.40 | 54.22 | 52.11 | 51.07 | 47.51 | 71.02 | 62.73 | 72.16 | 62.07 | 71.69 | 74.53 | 77.95 | 81.91 | 94.04 | 80.89 | 86.39 | 97.55 | 82.59 |
| 500 | 47.28 | 60.18 | 49.36 | 48.84 | 43.69 | 76.25 | 61.65 | 62.81 | 71.94 | 69.23 | 68.68 | 82.52 | 83.85 | 93.57 | 84.25 | 86.76 | 95.20 | 86.53 |
| 700 | 43.88 | 46.53 | 52.26 | 51.05 | 46.90 | 68.01 | 67.46 | 70.33 | 71.87 | 73.81 | 79.65 | 74.01 | 92.78 | 93.95 | 90.62 | 92.90 | 93.97 | 91.75 |
| Average | 44.91 | 55.06 | 50.28 | 50.54 | 47.22 | 70.73 | 64.72 | 70.53 | 67.74 | 71.74 | 75.80 | 76.77 | 82.96 | 94.26 | 80.37 | 87.57 | 95.76 | 84.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Z.; Jia, K.; Jia, X.; Liu, P.; Ma, Y.; Chen, T.; Feng, G. Mapping Large-Scale Plateau Forest in Sanjiangyuan Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Few-Shot Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020388
Wei Z, Jia K, Jia X, Liu P, Ma Y, Chen T, Feng G. Mapping Large-Scale Plateau Forest in Sanjiangyuan Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Few-Shot Learning. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(2):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020388
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Zhihao, Kebin Jia, Xiaowei Jia, Pengyu Liu, Ying Ma, Ting Chen, and Guilian Feng. 2022. "Mapping Large-Scale Plateau Forest in Sanjiangyuan Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Few-Shot Learning" Remote Sensing 14, no. 2: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020388
APA StyleWei, Z., Jia, K., Jia, X., Liu, P., Ma, Y., Chen, T., & Feng, G. (2022). Mapping Large-Scale Plateau Forest in Sanjiangyuan Using High-Resolution Satellite Imagery and Few-Shot Learning. Remote Sensing, 14(2), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020388








