Weighted Group Sparsity-Constrained Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A sparse constrained regularization is proposed to explore the sparse structure of the HSI differential image in the horizontal and vertical directions. In addition, weight coefficients are used to enhance sparsity.
- The norm is utilized to constrain the sparse regularizer, and the norm is embedded in the NTF framework to maintain the sparsity of the abundance tensor.
- The proposed algorithm WSCTF uses the alternating direction method of multipliers to iteratively optimize. Experiments on three real data prove the effectiveness of our algorithm.
2. Related Work
2.1. Notation
2.2. NTF Unmixing Method
3. Proposed Method
3.1. WSCTF Model
3.2. Optimization
| Algorithm 1 The proposed method SCLT |
Input: —the mixing hyperspectral data; P—the number of endmembers; Parameter , and .
Output: —the abundance tensor; —the endmember matrix. |
4. Experiments
4.1. Sythetic Data
4.2. Real Datasets
4.3. Parameter Analysis
4.4. Complexity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Zheng, X. A Feature Aggregation Convolutional Neural Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7894–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Zhang, B.; Plaza, A.; Chanussot, J. Graph Convolutional Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8246–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dian, R.; Fang, L.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M. Fusing hyperspectral and multispectral images via coupled sparse tensor factorization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 4118–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, L.; Yuan, Y. Subspace Clustering Constrained Sparse NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Gao, L.; Yang, L. Endmember Extraction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images Based on the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2635–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizel, F.; Benediktsson, J.A. Spatially Enhanced Spectral Unmixing Through Data Fusion of Spectral and Visible Images from Different Sensors. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, L.; Qi, H. Endmember Extraction From Highly Mixed Data Using Minimum Volume Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Bilateral Filter Regularized L2 Sparse Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, X. Spectral-Spatial Joint Sparse NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lu, X. Projection-Based NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2632–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B. NMF hyperspectral unmixing algorithm combined with spatial and spectral correlation analysis. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Wittman, T.; Osher, S. L1 unmixing and its application to hyperspectral image enhancement. In Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Orlando, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 7334, p. 73341M. [Google Scholar]
- Pauca, V.P.; Piper, J.; Plemmons, R.J. Nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral data analysis. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2006, 416, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Liang, Y. L 1/2 regularization. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2010, 53, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Chang, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, H. L1/2 regularization: A thresholding representation theory and a fast solver. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhu, F.; Guo, A.J.X. A Robust Multilinear Mixing Model with l 2,1 norm for Unmixing Hyperspectral Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Macau, China, 1–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Salehani, Y.E.; Gazor, S. Smooth and Sparse Regularization for NMF Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3677–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Meng, D.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, W.; Xu, Z. Nonconvex-Sparsity and Nonlocal-Smoothness-Based Blind Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, P.; Li, X. Manifold Regularized Sparse NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2815–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Jiao, L. Geometric Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (GNMF) for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2696–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.; Tao, D.; Luo, Z.; Yuan, B. Manifold Regularized Discriminative Nonnegative Matrix Factorization With Fast Gradient Descent. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Publ. IEEE Signal Process. Soc. 2011, 20, 2030–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; He, M.; Shen, Z.; Belkacem, B. Neighborhood preserving Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for spectral mixture analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 2573–2576. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Y.Y. Hyperspectral Unmixing via Total Variation Regularized Nonnegative Tensor Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2341–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, R.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Superpixel-Based Reweighted Low-Rank and Total Variation Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Y. Double constrained NMF for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Xiong, F.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Y.Y. Matrix-Vector Nonnegative Tensor Factorization for Blind Unmixing of Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1776–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Plemmons, R.J.; Pauca, V.P. Spectral unmixing using nonnegative tensor factorization. In Proceedings of the Southeast Regional Conference, Winston-Salem, NC, USA, 23–24 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzichristos, C.; Kofidis, E.; Morante, M.; Theodoridis, S. Blind fMRI Source Unmixing via Higher-Order Tensor Decompositions. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 315, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilius, L.B.; Pentiuc, S.G. Improving the Analysis of Hyperspectral Images Using Tensor Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Development and Application Systems (DAS), Suceava, Romania, 21–23 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Imbiriba, T.; Borsoi, R.A.; Bermudez, J.C.M. Low-Rank Tensor Modeling for Hyperspectral Unmixing Accounting for Spectral Variability. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imbiriba, T.; Borsoi, R.A.; Bermudez, J.C.M. A Low-rank Tensor Regularization Strategy for Hyperspectral Unmixing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany, 10–13 June 2018; pp. 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wu, F.; Zhan, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Jeon, B. Weighted Nonlocal Low-Rank Tensor Decomposition Method for Sparse Unmixing of Hyperspectral Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, T.Z.; Zhao, X.L.; Deng, L.J. Nonlocal Tensor-Based Sparse Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 6854–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, X. Hyperspectral Unmixing Using Nonlocal Similarity-Regularized Low-Rank Tensor Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobigeon, N.; Moussaoui, S.; Coulon, M.; Tourneret, J.; Hero, A.O. Joint Bayesian Endmember Extraction and Linear Unmixing for Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 4355–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.; Yuan, Y. Sparse Constrained Low Tensor Rank Representation Framework for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Leung, Y.; Zhao, X.L.; Meng, D. Hyperspectral Image Restoration Via Total Variation Regularized Low-Rank Tensor Decomposition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Jeon, B.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y. Hyperspectral unmixing based on L1-L2 sparsity and total variation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 4349–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.B.; Huang, T.Z.; Zhao, X.L.; Chen, Y.; He, W. Double-Factor-Regularized Low-Rank Tensor Factorization for Mixed Noise Removal in Hyperspectral Image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8450–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Z.; Yan, S.; Sun, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Y. Robust Recovery of Subspace Structures by Low-Rank Representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, L.; Lin, C.; Figueiredo, M.A.T.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M. Regularization Parameter Selection in Minimum Volume Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 9858–9877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; King, T.V.; Gallagher, A.J.; Calvin, W.M. The US Geological Survey, digital spectral reflectance library: Version 1: 0.2 to 3.0 microns. In Proceedings of the JPL, Summaries of the 4th Annual JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 25–29 October 1993; Volume 1, pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P.; Su, H.; Du, Q. Sparse and Low-Rank Constrained Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Image Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

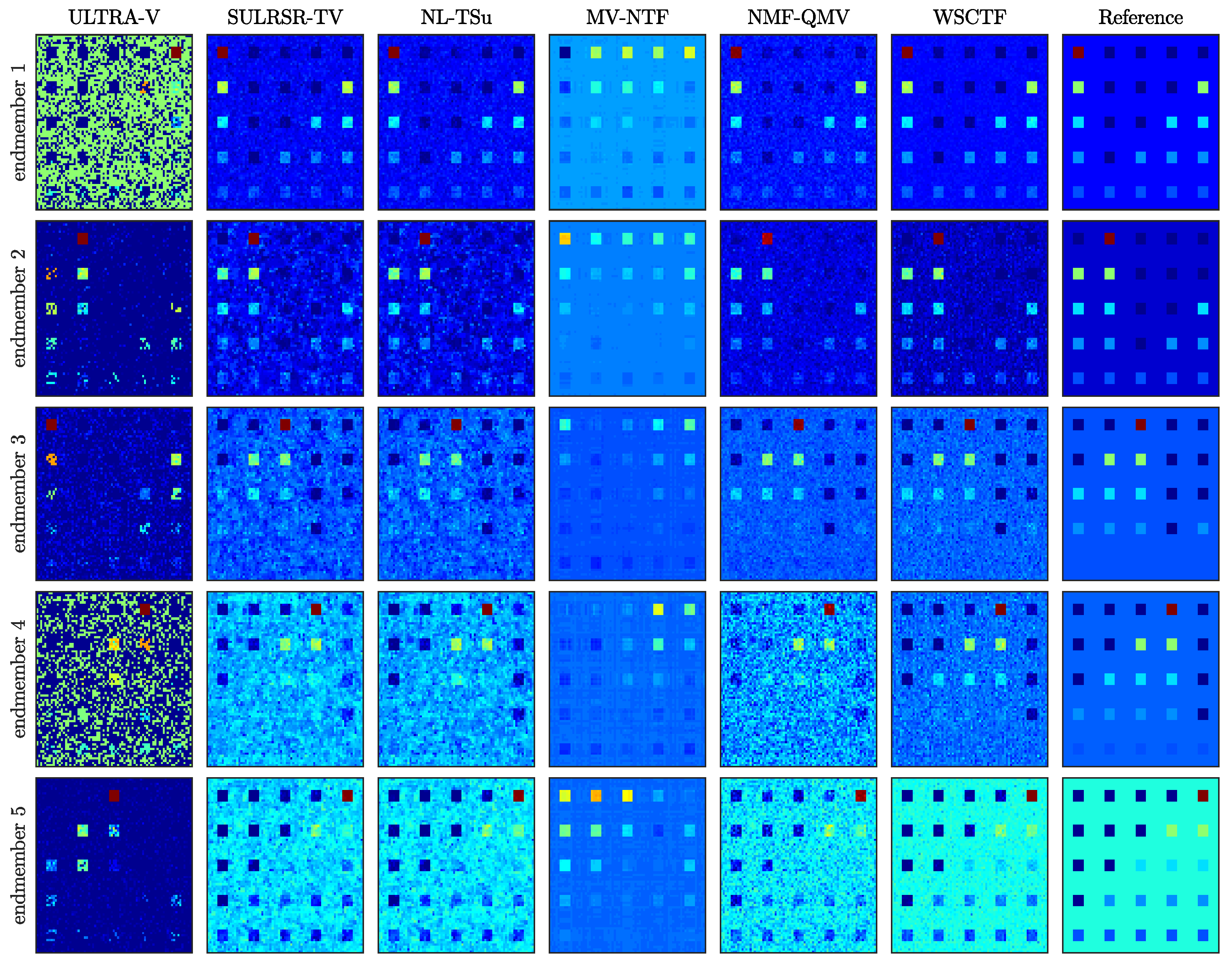
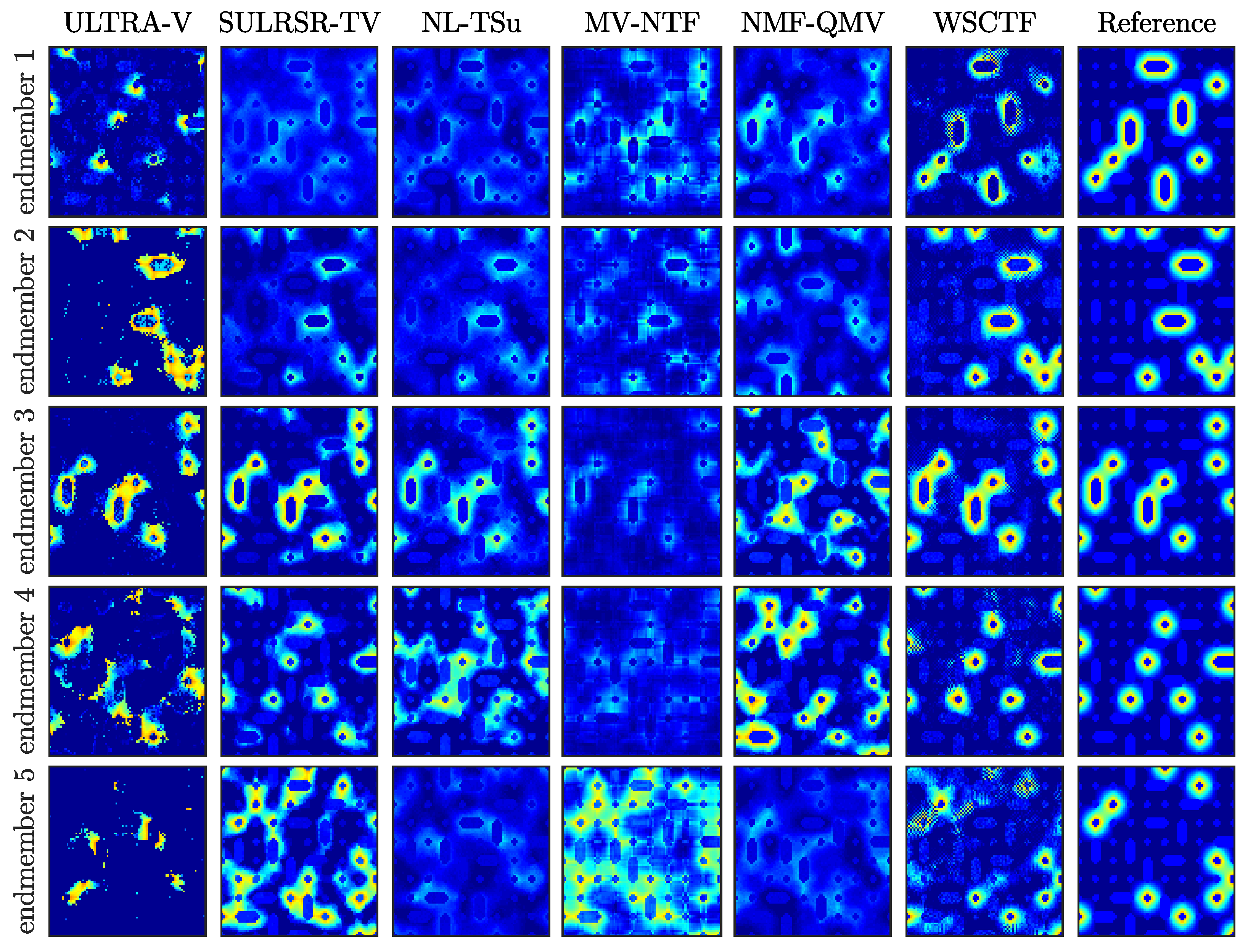

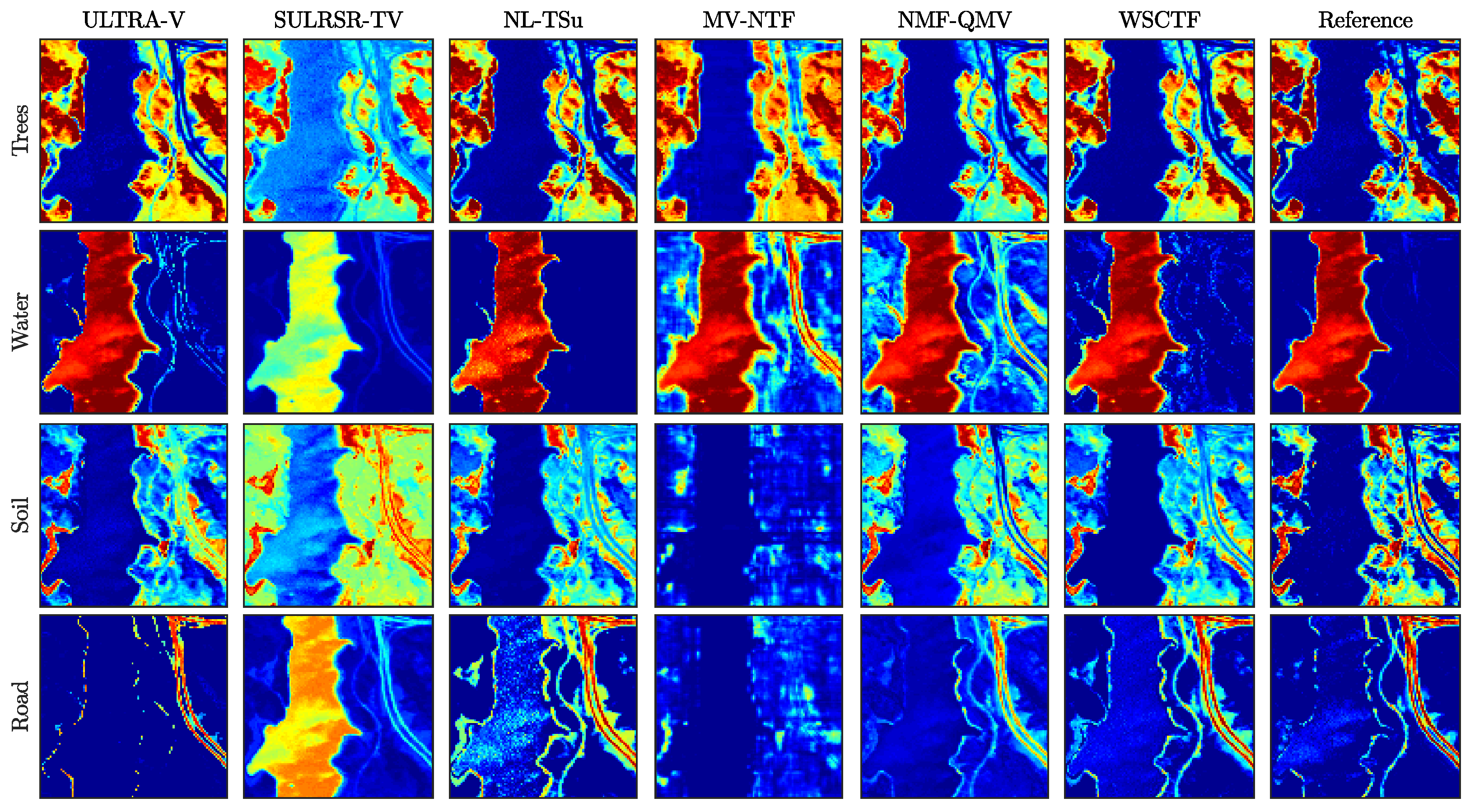

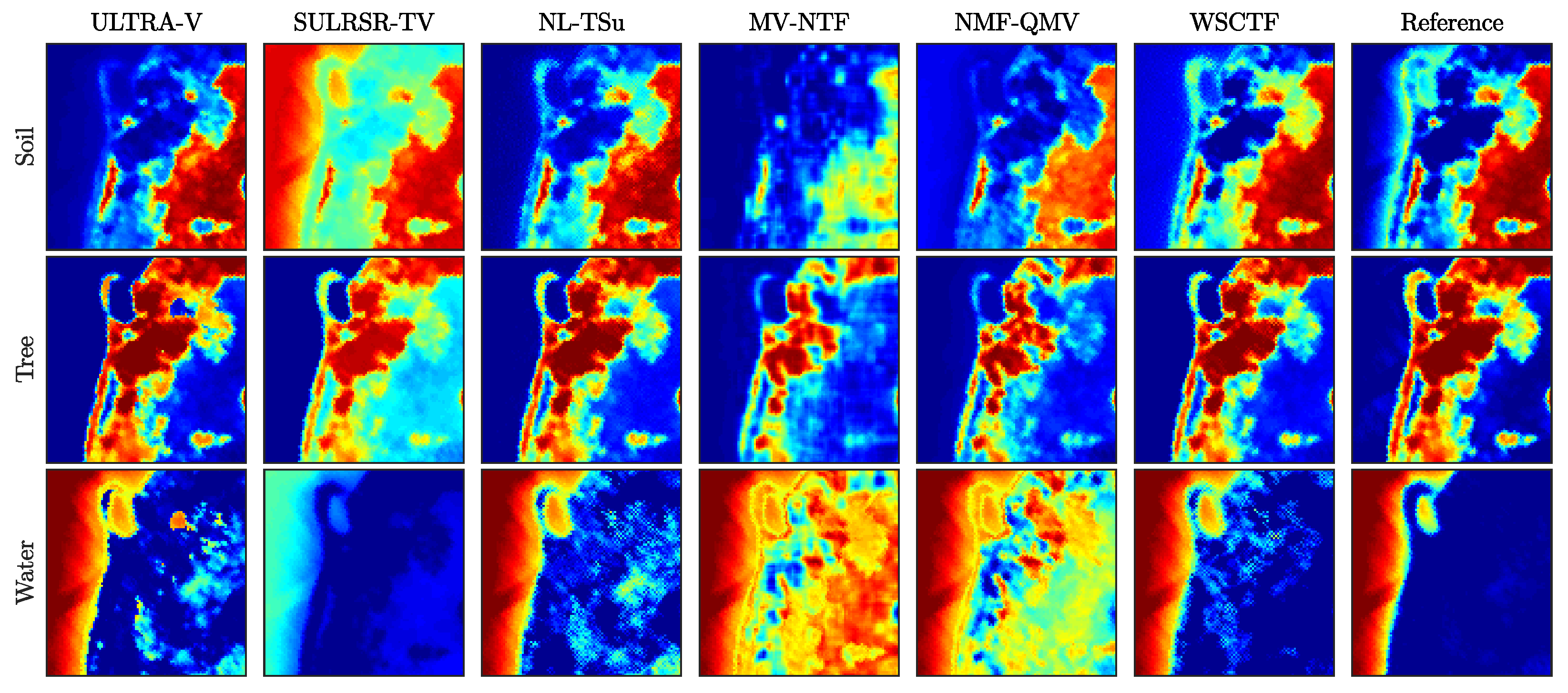



| Data | SNR | SULRSR-TV | NMF-QMV | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | WSCTF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 dB | 0.0995 ± 0.0049 | 0.0960 | 0.1906 ± 0.0041 | 0.1447 ± 0.0621 | 0.2339 ± 0.0031 | 0.0827 ± 0.0019 | |
| DS1 | 20 dB | 0.0805 ± 0.0077 | 0.0723 | 0.1500 ± 0.0420 | 0.1024 ± 0.0352 | 0.1701 ± 0.0214 | 0.0682 ± 0.0241 |
| 30 dB | 0.0797 ± 0.0051 | 0.0624 | 0.1456 ± 0.0164 | 0.0828 ± 0.0614 | 0.2291 ± 0.0510 | 0.0621 ± 0.0146 | |
| 10 dB | 0.1433 ± 0.0143 | 0.1200 | 0.1256 ± 0.0091 | 0.1326 ± 0.0312 | 0.1980 ± 0.0312 | 0.1126 ± 0.0321 | |
| DS2 | 20 dB | 0.1366 ± 0.0106 | 0.1193 | 0.1580 ± 0.0217 | 0.1273 ± 0.0318 | 0.1876 ± 0.0021 | 0.1004 ± 0.0021 |
| 30 dB | 0.1344 ± 0.0054 | 0.0942 | 0.1005 ± 0.0032 | 0.0987 ± 0.0021 | 0.1690 ± 0.0410 | 0.0911 ± 0.0039 |
| Data | SNR | SULRSR-TV | NMF-QMV | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | WSCTF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 dB | 0.1115 ± 0.0139 | 0.3624 | 0.5127 ± 0.0164 | 0.1326 ± 0.0052 | 0.1427 ± 0.0216 | 0.0920 ± 0.0031 | |
| DS1 | 20 dB | 0.0453 ± 0.0014 | 0.0867 | 0.4023 ± 0.0121 | 0.0952 ± 0.0143 | 0.1214 ± 0.0126 | 0.0434 ± 0.0108 |
| 30 dB | 0.0134 ± 0.0004 | 0.0920 | 0.3210 ± 0.0114 | 0.0623 ± 0.2432 | 0.0737 ± 0.0601 | 0.0126 ± 0.0245 | |
| 10 dB | 0.1977 ± 0.0928 | 0.2325 | 0.5232 ± 0.0088 | 0.4329 ± 0.0621 | 0.3172 ± 0.0241 | 0.1920 ± 0.0314 | |
| DS2 | 20 dB | 0.1688 ± 0.0794 | 0.0861 | 0.5161 ± 0.0128 | 0.4061 ± 0.0051 | 0.3202 ± 0.0152 | 0.0827 ± 0.0021 |
| 30 dB | 0.1423 ± 0.0366 | 0.0184 | 0.3237 ± 0.0672 | 0.2846 ± 0.0601 | 0.3110 ± 0.0031 | 0.0094 ± 0.0017 |
| SULRSR-TV | NMF-QMV | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | WSCTF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 0.2012 ± 0.0187 | 0.2571 | 0.2416 ± 0.0136 | 0.2081 ± 0.0306 | 0.0502 ± 0.0003 | 0.0495 ± 0.0476 |
| Soil | 0.2336 ± 0.0011 | 1.1890 | 0.2601 ± 0.0089 | 0.2334 ± 0.0001 | 0.1422 ± 0.0342 | 0.1071 ± 0.1660 |
| Water | 0.6194 ± 0.1761 | 0.1386 | 0.1586 ± 0.0956 | 0.4929 ± 0.2715 | 0.5641 ± 0.0013 | 0.3977 ± 0.0072 |
| Road | 0.2943 ± 0.0722 | 0.1840 | 0.4544 ± 0.0706 | 0.3665 ± 0.1179 | 0.0362 ± 0.0033 | 0.2461 ± 0.0303 |
| Mean | 0.3863 ± 0.0357 | 0.4421 | 0.3024 ± 0.0396 | 0.3723 ± 0.0482 | 0.3002 ± 0.0010 | 0.2406 ± 0.0434 |
| SULRSR-TV | NMF-QMV | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | WSCTF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 0.0247 ± 0.0121 | 0.0337 | 0.0433 ± 0.0129 | 0.0288 ± 0.0161 | 0.0340 ± 0.0272 | 0.0201 ± 0.0024 |
| Soil | 0.0495 ± 0.0011 | 0.0732 | 0.0953 ± 0.0011 | 0.0496 ± 0.0001 | 0.0566 ± 0.0090 | 0.0685 ± 0.0102 |
| Water | 0.1299 ± 0.0004 | 1.4831 | 0.2810 ± 0.0050 | 0.1289 ± 0.0003 | 0.2401 ± 0.0221 | 0.0675 ± 0.0021 |
| Mean | 0.0818 ± 0.0019 | 0.8575 | 0.1733 ± 0.0036 | 0.0825 ± 0.0026 | 0.1438 ± 0.0154 | 0.0611 ± 0.0105 |
| SULRSR-TV | NMF-QMV | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | WSCTF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alunite | 0.0966 ± 0.0739 | 0.0860 | 0.0748 ± 0.0875 | 0.0783 ± 0.0243 | 0.1897 ± 0.0722 | 0.0735 ± 0.0134 |
| Andradite | 0.1353 ± 0.0157 | 0.1212 | 0.0661 ± 0.0207 | 0.0958 ± 0.0376 | 0.0971 ± 0.0323 | 0.0631 ± 0.0369 |
| Buddingtonite | 0.0699 ± 0.0174 | 0.0797 | 0.0718 ± 0.0193 | 0.0982 ± 0.0183 | 0.1097 ± 0.0193 | 0.0669 ± 0.0217 |
| Chalcedony | 0.1482 ± 0.0230 | 0.1428 | 0.1652 ± 0.0304 | 0.1253 ± 0.0444 | 0.1212 ± 0.0307 | 0.0829 ± 0.0317 |
| Dumortierite | 0.0855 ± 0.0152 | 0.1108 | 0.0984 ± 0.0208 | 0.1709 ± 0.0240 | 0.0936 ± 0.0158 | 0.0944 ± 0.0258 |
| Kaolinite#1 | 0.0718 ± 0.0155 | 0.0795 | 0.0841 ± 0.0070 | 0.0738 ± 0.0095 | 0.1300 ± 0.0137 | 0.0859 ± 0.0104 |
| Kaolinite#2 | 0.0678 ± 0.0187 | 0.1014 | 0.0786 ± 0.0098 | 0.0625 ± 0.0126 | 0.0391 ± 0.0160 | 0.0638 ± 0.0154 |
| Montmorillonite | 0.0504 ± 0.0132 | 0.1114 | 0.0535 ± 0.0065 | 0.0720 ± 0.0124 | 0.0508 ± 0.0134 | 0.0501 ± 0.0143 |
| Muscovite | 0.1066 ± 0.0450 | 0.0811 | 0.2518 ± 0.0498 | 0.0925 ± 0.0457 | 0.1257 ± 0.0389 | 0.1719 ± 0.0461 |
| Nontronite | 0.0730 ± 0.0193 | 0.0715 | 0.1086 ± 0.0111 | 0.0813 ± 0.0156 | 0.0835 ± 0.0246 | 0.0702 ± 0.0271 |
| Pyrope | 0.1876 ± 0.0521 | 0.1812 | 0.1431 ± 0.0598 | 0.1501 ± 0.0464 | 0.1737 ± 0.0535 | 0.1326 ± 0.0574 |
| Sphene | 0.0663 ± 0.0564 | 0.1879 | 0.0700 ± 0.0673 | 0.1642 ± 0.0137 | 0.2306 ± 0.0506 | 0.0744 ± 0.0829 |
| Mean | 0.1042 ± 0.0062 | 0.1190 | 0.1176 ± 0.0135 | 0.1054 ± 0.0066 | 0.1317 ± 0.0089 | 0.0925 ± 0.0134 |
| Data | ||
|---|---|---|
| DS1 | 0.015 | 0.010 |
| DS2 | 0.015 | 0.010 |
| Jasper | 0.02 | 0.015 |
| Samon | 0.015 | 0.010 |
| Cuprite | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| SULRSR-TV | NMF-QMV | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | WSCTF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jasper Ridge Data | 6 | 10 | 170 | 55 | 26 | 5 |
| Samon Data | 5 | 9 | 135 | 29 | 14 | 4 |
| Cuprite Data | 34 | 293 | 904 | 194 | 209 | 17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Han, L.; Dong, L. Weighted Group Sparsity-Constrained Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020383
Feng X, Han L, Dong L. Weighted Group Sparsity-Constrained Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(2):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020383
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xinxi, Le Han, and Le Dong. 2022. "Weighted Group Sparsity-Constrained Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing" Remote Sensing 14, no. 2: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020383
APA StyleFeng, X., Han, L., & Dong, L. (2022). Weighted Group Sparsity-Constrained Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sensing, 14(2), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020383





