Reconstruction of Rainfall Field Using Earth–Space Links Network: A Compressed Sensing Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The spatial clustering algorithm has been used to design the ESL network conforming to the CS principle, and the effect of the distribution of ESL on reconstructing the rainfall fields has been studied.
- (2)
- The CS technique has been used for reconstructing rainfall fields using an ESL network, and the results show that an ESL network with CS is able to reconstruct high-precision rainfall fields under sparse sampling.
2. Principles of Reconstructing Rainfall Field
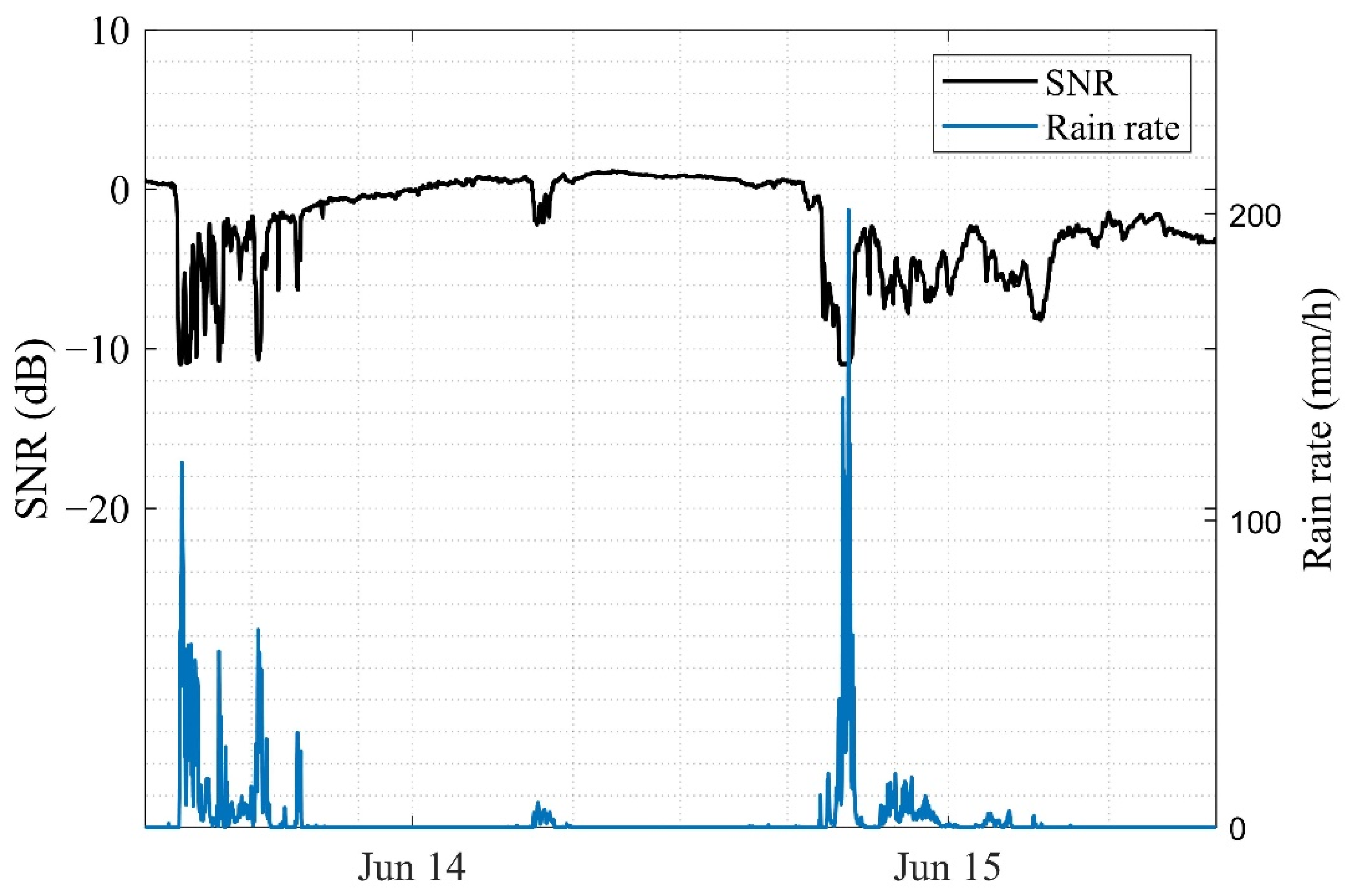
2.1. Description of Rainfall Retrieved by ESL
2.2. Algorithm for Reconstructing Rainfall Field by ESL Network
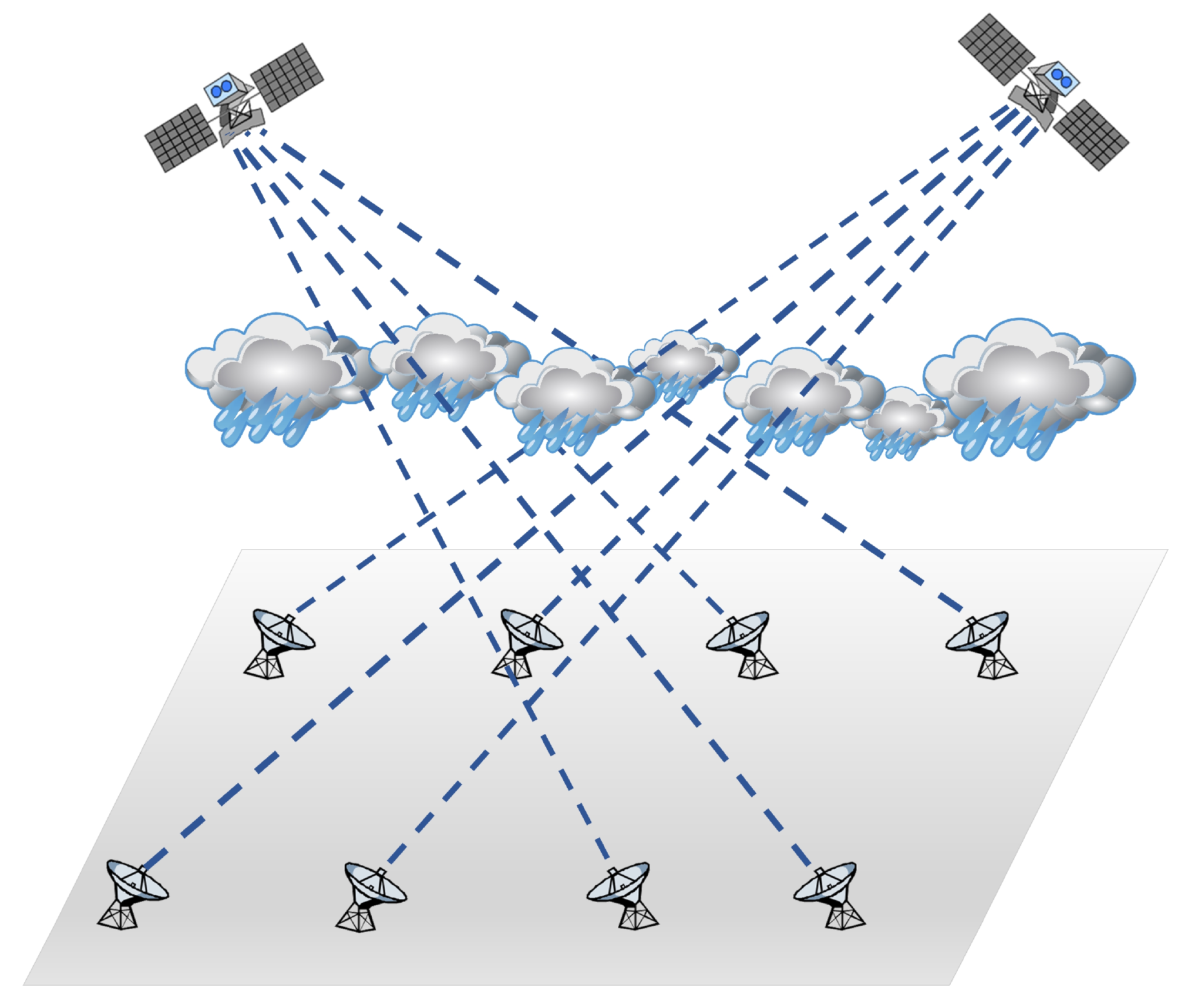
3. Design of the ESL Network
- (1)
- Randomly select m points from the n grid points in the experimental area as the initial locations of the antennas of the ESL network.
- (2)
- Calculate the distance from all grid points of the area to each antenna position of the ESL network, and divide the area into m classes based on the rule of the shortest distance.
- (3)
- The mean value of the area for each class is calculated and used as the center of the new clusters.
- (4)
- Repeat steps (2) and (3) until the clustering results no longer change. Following that, m points in the area are used as locations for the antennas of the ESL network, from which the designed ESL network can be obtained.
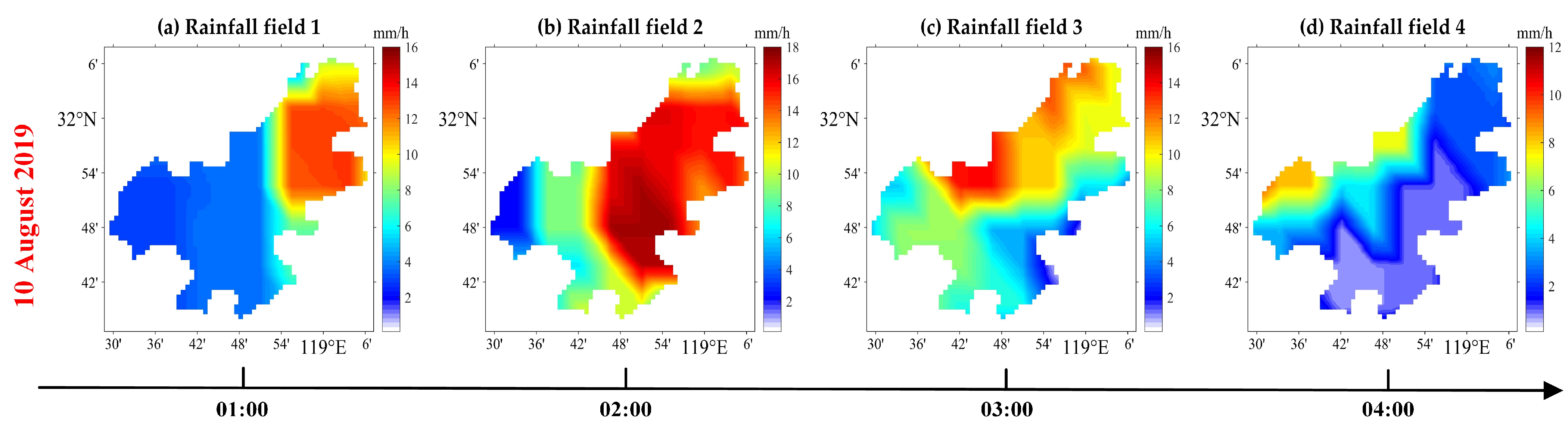
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbot, C. Precipitation Cycles. Science 1949, 110, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, P.; Rubin, Y. First Daily Mapping of Surface Moisture from Cellular Network Data and Comparison with Both Observations/ECMWF Product. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8619–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, M.F.; Rodell, M.; Alsdorf, D.E.; Miralles, D.G.; Uijlenhoet, R.; Wagner, W.; Lucieer, A.; Houborg, R.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Franz, T.E.; et al. The Future of Earth Observation in Hydrology. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3879–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandine, B.; Rieckermann, J.; Berne, A. Quality control of rain gauge measurements using telecommunication microwave links. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.C.; Gao, T.C.; Liu, L. A comparison of rainfall measurements from multiple instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, S. Dual-frequency radar ratio of nonspherical atmospheric hydrometeors. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getirana, A.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Mandarino, F.; Ottoni, M.; Arsenault, K. Potential of GPM IMERG Precipitation Estimates to Monitor Natural Disaster Triggers in Urban Areas: The Case of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tr Mel, S.; Ziegert, M.; Ryzhkov, A.V.; Chwala, C.; Simmer, C. Using Microwave Backhaul Links to Optimize the Performance of Algorithms for Rainfall Estimation and Attenuation Correction. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1748–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagit, M.; Artem, Z.; Pinhas, A. Environmental Monitoring by Wireless Communication Networks. Science 2006, 312, 713. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, K.; Liu, X.; Xian, M.; Gao, T. Machine Learning Classification of Rainfall Types Based on the Differential Attenuation of Multiple Frequency Microwave Links. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2020, 58, 6888–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, X.; Gao, T.; He, B. Raindrop Size Distribution Retrieval Using Joint Dual-Frequency and Dual-Polarization Microwave Links. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 7251870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinevich, A.; Messer, H.; Alpert, P. Frontal Rainfall Observation by a Commercial Microwave Communication Network. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2009, 48, 1317–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshtein, O.; Messer, H.; Zinevich, A. Rain Rate Estimation Using Measurements from Commercial Telecommunications Links. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2009, 57, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthès, L.; Mallet, C. Rainfall measurement from the opportunistic use of an Earth–space link in the Ku band. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnai, C.; Cuccoli, F.; Sermi, F. Rainfall estimation with a commercial tool for satellite internet in Ka band: Concept and preliminary data analysis. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Remote sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XVI, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 October 2014; Volume 9239. [Google Scholar]
- Giannetti, F.; Moretti, M.; Reggiannini, R.; Vaccaro, A. The NEFOCAST System for Detection and Estimation of Rainfall Fields by the Opportunistic Use of Broadcast Satellite Signals. IEEE Aero. El. Sys. Mag. 2019, 34, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, M.; Liu, X.; Yin, M.; Song, K.; Zhao, S.; Gao, T. Rainfall Monitoring Based on Machine Learning by Earth-Space Link in the Ku Band. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2020, 13, 3656–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Xian, M.; Gao, T. Statistical Study of Rainfall Inversion Using the Earth-Space Link at the Ku Band: Optimization and Validation for 1 Year of Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 14, 9486–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xi, S.; Huang, D.D.; Feng, X.; Wang, W. Tomographic reconstruction of rainfall fields using satellite communication links. In Proceedings of the 2017 23rd Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC), Perth, WA, USA, 11–13 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, M.; Liu, X.; Song, K.; Gao, T. Reconstruction and Nowcasting of Rainfall Field by Oblique Earth-Space Links Network: Preliminary Results from Numerical Simulation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, I.G.A.B.; Xu, S.A.C.; Wu, Y.C.D.; Bazaka, K.E. Hopes and concerns for astronomy of satellite constellations. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Pu, K.; Ye, J.; Xian, M. Research on the Method of Rainfall Field Retrieval Based on the Combination of Earth–Space Links and Horizontal Microwave Links. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Xi, S.; Huang, D.D.; Lu, J. Compressive Sensing-Based 3-D Rain Field Tomographic Reconstruction Using Simulated Satellite Signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, M.; Cheung, N.; Quek, T.Q.S. Compressed sensing of diffusion fields under heat equation constraint. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saghi, Z.; Holland, D.J.; Leary, R.; Falqui, A.; Bertoni, G.; Sederman, A.J.; Gladden, L.F.; Midgley, P.A. Three-Dimensional Morphology of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Reactive Concave Surfaces. A Compressed Sensing-Electron Tomography (CS-ET) Approach. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4666–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.L. The aRb relation in the calculation of rain attenuation. IEEE Trans. 1978, 26, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU-R. Recommendation P.838-3 Specific attenuation model for rain for use in prediction methods. Technical Report. 2005. Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/p/R-REC-P.838-3-200503-I!!PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- ITU-R. Recommendation P.839-4 Rain height model for prediction methods. Technical Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.itu.int/dms_pubrec/itu-r/rec/p/R-REC-P.839-4-201309-I!!PDF-E.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Tropp, J.A. A mathematical introduction to compressive sensing. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 2017, 54, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, R.; Peleg, T.; Elad, M. Analysis K-SVD: A Dictionary-Learning Algorithm for the Analysis Sparse Model. IEEE Trans. Signal Processing 2011, 61, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, B.; Hansen, A.C.; Poon, C.; Roman, B. Breaking the coherence barrier: A new theory for compressed sensing. Mathematics. 2013, 1, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, L. Lower bounds on the maximum cross correlation of signals. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 1974, 20, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Niu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Cheng, C. Operation rule derivation of hydropower reservoir by k-means clustering method and extreme learning machine based on particle swarm optimization. J. Hydrol. 2019, 576, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

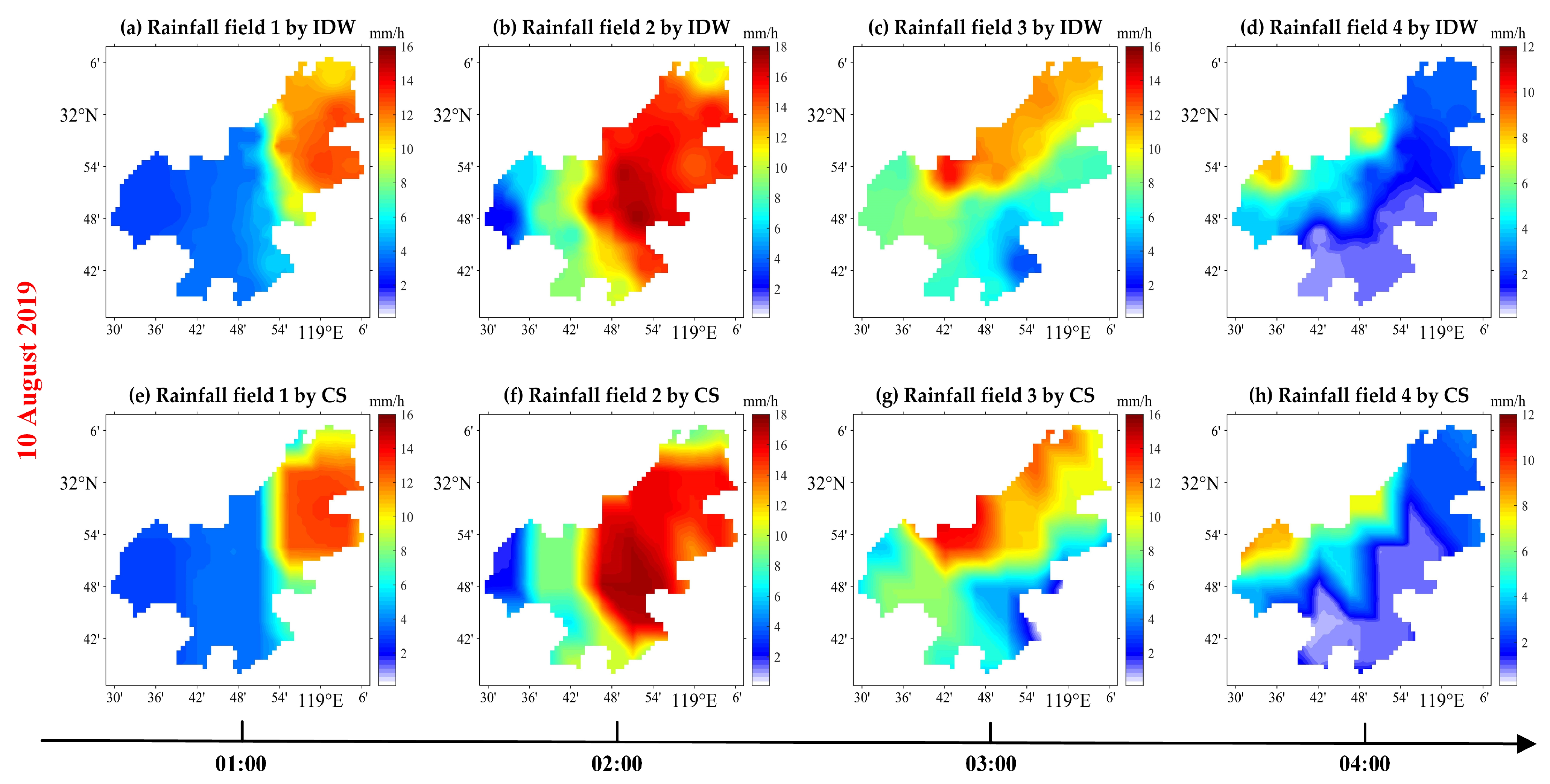

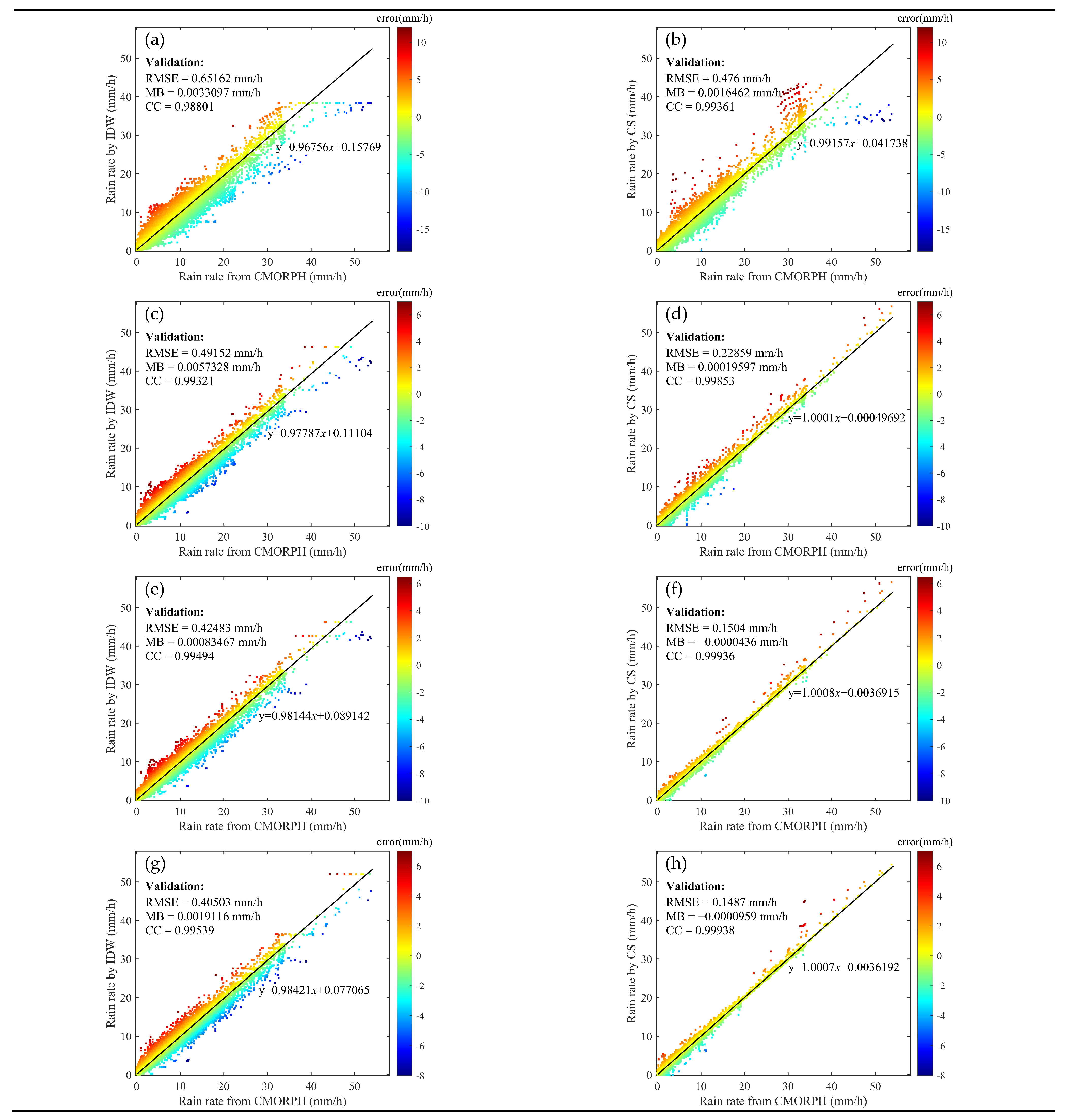
| Situations | Rainfall Fields | RMSE (mm/h) | MB (mm/h) | CC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDW | CS | IDW | CS | IDW | CS | ||
| No noise | Rainfall field 1 | 0.86 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.975 | 0.999 |
| Rainfall field 2 | 1.20 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.960 | 0.999 | |
| Rainfall field 3 | 1.03 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.934 | 0.999 | |
| Rainfall field 4 | 0.56 | 0.07 | −0.12 | 0.01 | 0.966 | 0.999 | |
| With noise | Rainfall field 1 | 0.86 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.974 | 0.998 |
| Rainfall field 2 | 1.21 | 0.25 | 0.08 | −0.05 | 0.960 | 0.998 | |
| Rainfall field 3 | 1.03 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.934 | 0.999 | |
| Rainfall field 4 | 0.57 | 0.15 | −0.12 | 0.03 | 0.965 | 0.997 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Pu, K.; Song, K. Reconstruction of Rainfall Field Using Earth–Space Links Network: A Compressed Sensing Approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194966
Zhao Y, Liu X, Liu L, Pu K, Song K. Reconstruction of Rainfall Field Using Earth–Space Links Network: A Compressed Sensing Approach. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194966
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yingcheng, Xichuan Liu, Lei Liu, Kang Pu, and Kun Song. 2022. "Reconstruction of Rainfall Field Using Earth–Space Links Network: A Compressed Sensing Approach" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194966
APA StyleZhao, Y., Liu, X., Liu, L., Pu, K., & Song, K. (2022). Reconstruction of Rainfall Field Using Earth–Space Links Network: A Compressed Sensing Approach. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4966. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194966





