Abstract
Geo-parsing, one of the key components of geographical information retrieval, is a process to recognize and geo-locate toponyms mentioned in texts. Such a process can obtain locations contained in toponyms successfully with consistent updating of neural network models and multiple contextual features. The significant offset distance between the geo-parsed locations and the actual occurrence locations still remains. This is because the geo-parsed locations sourced from toponyms in texts always point to the centers of cities, counties, or towns, and cannot directly represent the actual occurrence locations such as factories, farms, and activity areas. Consequently, The significant offset distances between the geo-parsed locations and the actual occurrence locations limit text mining applications in micro-scale geographic discoveries. This research aims at decreasing offset distances of geo-parsed locations by proposing a novel Toponym Correction Method based on satellite Remote Sensing Images (TC-RSI). The TC-RSI method uses satellite remote sensing images to provide extra detailed spatial information that can be associated with the sentence toponym by corresponding attributes. The TC-RSI method was validated in a case study of the forest ecological pattern dataset of An’hui province from visual, statistical, and robustness assessments. The correction results show that the TC-RSI method dramatically decreases the offset distances from about 50 km to about 1 km and promotes geographical discoveries on smaller scales. A series of analyses indicated that the TC-RSI is a valid, effective, and promising method to improve the accuracy of geo-parsed locations, which allows text mining to find more accurate geographical discoveries with lower offset distances. Moreover, toponym correction promotes the use of more diverse spatial data sources, such as Lidar, domain gazetteers, Wikimedia, and streetscapes, which are expected to usher in a new era of geo-parsing with toponym corrections.
1. Introduction
Geo-parsing is a process to recognize and geo-locate toponyms from texts, which consists of two parts: toponym recognition and toponym resolution [1,2,3]. Toponym recognition detects the place mentioned in texts, while toponym resolution resolves any place name ambiguity and assigns the appropriate spatial footprint (e.g., a pair of coordinates). With these spatial footprints and various attributes among descriptions, texts can support numerous spatial analyses and applications, such as spatial distribution illustration, event evolutions, and behavior analyses, and reveal very influential geoscience discoveries [4,5,6]. This means geo-parsing is the foundation of all kinds of text-based spatial applications. In view of error transitivity, the validity and reliability of numerous spatial analyses rely on the geo-parsing quality, which means the accuracy of geo-parsed coordinates [2,7,8]. Thus, improving the accuracy of geo-parsed coordinates is a continuous research field in the GIScience.
At present, geo-parsing technology has made great progress. With the construction of deep learning models and professional toponym gazetteers, the accuracy of geo-parsing in a specific domain or data source has reached 0.9 [2,9]. More detailed geo-parsing technologies are shown in the related work section. Considering current geo-parsing accuracy, many text-based applications use geo-parsed locations to analyze further spatial distributions, patterns, behaviors, and discoveries [10,11,12,13,14]. However, the locations obtained through geo-parsing are not the actual locations of objects or events. The reason is that the geo-parsed locations are sourced from the text toponyms, which are fuzzy spatial areas. According to parsing these fuzzy spatial areas, it is hard to obtain the actual locations of objects or events. Thus, there are likely to be offsets between the geo-parsed locations and the actual locations. A detailed case of a text mining application is given in the following related work section to illustrate the offsets further in geo-parsing processes.
To address this issue, the spatial information from toponyms may be not enough, and more extra spatial information may need to be explored to correct the toponym offsets. At present, spatial information is mainly of two types: stable existing spatial data sets and dynamic earth observation systems [15,16,17]. Stable existing spatial data sets indicate domain data sets that exist the spatial information about objects or events, such as domain gazetteers, mapping data, domain knowledge base, and Wikimedia. These data usually have a specific application scope and are limited by the construction quality [17,18]. Thus, stable existing spatial data sets cannot support a large coverage and various targets. Dynamic earth observation systems refer to remote sensing-based data sets, such as satellite images and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) data, which are flexible to various targets with corresponding algorithms. Considering the large coverage and multiple application scales of geo-parsing, remote sensing images represent a global, frequency, stable, and mature spatial information data source that can ideally be qualified to do so [16,19,20,21]. Remote sensing images can directly recognize correct geographic locations with apparent spatial features. Especially, satellite remote sensing images can acquire spatial information about large-scale urban areas and their surrounding environments. Therefore, it is hypothesized that remote sensing images can be used as extra spatial information to correct geo-parsed toponyms. Moreover, the extra spatial information needs to be associated with the corresponding toponym in the sentence, which can lead to extra spatial information for each toponym. Based on the above assumption, this research explored a novel toponym correction method based on remote sensing images (TC-RSI), which is expected to usher in a new era of geo-parsing with toponym correction processes. In other words, the main contribution of this paper is to introduce the spatial information contained in remote sensing images into the fuzzy spatial location descriptions in the text, which is expected to greatly improve the spatial accuracy of geo-parsing.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Related works in geo-parsing are reviewed in Section 2. Section 3 gives the basic idea and designed processes of the proposed method. Section 4 presents the detailed experiments and corresponding results, including the study area, correction results, correction evaluations, and correction effects. Section 5 shows the toponym correction method’s attention issues, limitations, and potential development. The conclusions are presented in Section 6.
2. Related Works
2.1. Geo-Parsing Progress
Generally, the geo-parsing method has two fixed steps: recognizing toponyms by natural language processing techniques called toponym recognition, and identifying the most probable candidate toponym from gazetteers, called toponym resolution. We have improved the accuracy of geo-parsed coordinates from both two steps.
In the toponym recognition field, after the rule-based period and early deep learning period with a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Deep Belief Network (DBN), and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), the current popular method of toponym recognition uses the Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (BiLSTM) model [22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Considering the selections of different word embeddings and self-attention mechanisms, the adjusted BiLSTM models have slightly different performances and can achieve F1 values over 0.90 [29,30].
In the toponym resolution field, the same general workflow has been used: retrieving place candidates from the GeoNames gazetteer and then identifying the correct place instance among the candidates. To achieve higher performances, a series of toponym corpus, annotation platforms, adjusted embedding methods, and more features have been used to construct better toponym resolution models, such as GeoTxt, GeoCorpora, GeoAnnotator, density embedding, adapted context features, graph features, and multi-lingual features [24,31,32,33,34,35,36,37]. According to these toponym recognition and toponym resolution methods, many geo-parsers have been constructed, including GeoTxt, DM_NLP, NLPIR, Amap, Baidu, and DBpedia [2,10,24,38,39]. Moreover, partial popular geo-parsers have been evaluated by the EUPEG benchmarking platform. Results show that excellent geo-parsers can achieve over 0.9 precision and recalls on commonly used news datasets in the toponym recognition process [2].
In summary, current related works show that toponyms and corresponding coordinates are geo-parsing core spatial information sources. Moreover, the accuracy of geo-parsed locations continues to be promoted with the improvements of deep learning models, embedding methods, and features strategies. However, the toponym in texts represents a broad spatial area, which is fuzzy in pointing out its real occurrence locations. The offset between the geo-parsed location and the actual location truly exists. Thus, decreasing the offset is a key to opening a new era of geo-parsing.
2.2. A Geo-Parsing Offset Case
A text-based event mining case, in which most of the text mining research can be seen as an event mining case, is given to illustrate offsets clearly. An ecological pattern is a modern and efficient developing tendency guided by the combined principles of ecology and economics, providing specific paths to implement sustainable development goals; a forest-crop is a typical forest ecological pattern. Texts, such as news and documents, are the primary data sources to investigate ecological patterns on a national scale. The ecological pattern investigation records such as location, ecological pattern, time, and associated attributes. The locations can be obtained by geo-parsing from the text descriptions. An ecological pattern investigation process was conducted in Hefei city [40,41]. Figure 1 illustrates the geo-parsed locations (Hefei and Feixi in black squares), the actual locations of forest ecological patterns (economic forest areas in four colors), and the offsets between the geo-parsed locations and the actual locations of ecological patterns (red arrows). The geo-parsed locations are mainly the centers of cities, counties, or towns, because toponyms of text descriptions parse them. Yet the actual locations are not just centers. The huge offsets (nearly 50 km) mean the geo-parsed locations cannot represent the actual locations of objects or events. These offsets not only impact the accuracy of further spatial analyses but also cannot be improved by current adjusted geo-parsing methods, because accuracy toponyms are the best results of geo-parsing. Therefore, further methods with extra spatial information warrant study for toponym corrections.
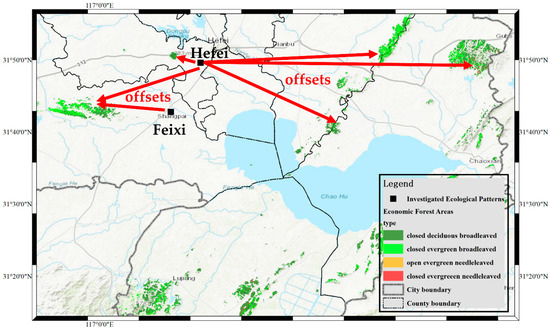
Figure 1.
Offsets between the geo-parsed locations and the actual locations of ecological patterns in the example of a Hefei forest ecological pattern investigation.
3. Methodology
3.1. Basic Idea
The basic idea to correct geo-parsed toponym location was to adopt satellite remote sensing images to provide extra detailed spatial information that could be associated with the sentence toponym by corresponding attributes. Compared with the offsets (nearly 50 km) in real space, satellite remote sensing images usually have a spatial resolution of 1 m–30 m that is much smaller than the scale of the offsets, which can provide fine spatial information for geo-parsed location. Specifically, during text mining, the target sentence usually focuses on a theme, which consists of toponyms or relevant attributes, such as object, event, time, and relevant attributes (Figure 2). For example, in the sentence “the application of forest-crop ecological pattern (object/event) has significantly improved individual incomes in Feixi county (toponym) in 2019 (time)”, Feixi county (toponym) is associated with forest-crop ecological pattern (object/event). The accuracy of actual areas of forest-crop ecological pattern (object/event) can be obtained from the remote sensing images, which are the extra spatial information.
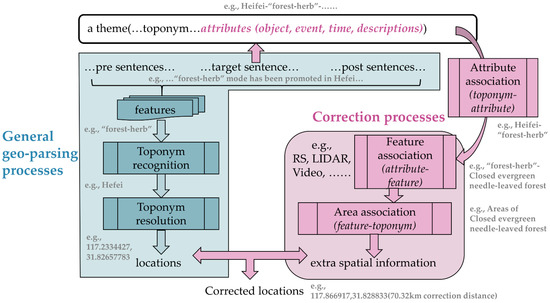
Figure 2.
The basic idea of toponym correction based on remote sensing images. An example, “forest-herb” mode in Hefei is attached to show the results of each process. The detailed data and validation of this example can be found in Section 4 with the id 5 forest ecological pattern.
Based on the above idea, the basic idea of toponym correction based on remote sensing images has two main parts: general geo-parsing processes and correction processes (Figure 2). The general geo-parsing processes include toponym recognition and toponym resolution steps based on the context features. These two processes are currently used in the geo-parsing process. The correction processes consist of attribute association, feature association, and area association. First, attribute association constructs the links between the toponyms and the attributes. Second, the feature association process set up the links between the attributes and the features. Finally, the area association process reveals the links between the target areas and the features. According to these processes, extra spatial information can further improve the accuracy of geo-parsed locations and finally achieve corrected locations.
3.2. TC-RSI Method
Based on the above basic idea, a novel Toponym Correction method based on remote sensing images (TC-RSI) was designed to correct toponym locations in geo-parsing. There are five core procedures in the TC-RSI method, including the general geo-parsing process, the attribute associating process, the remote sensing (RS) feature associating process, the remote sensing (RS) area associating process, and the location correction process (Figure 3). To illustrate the TC-RSI method clearly, the research of forest ecological pattern investigation based on text is given as an example to describe these procedures.
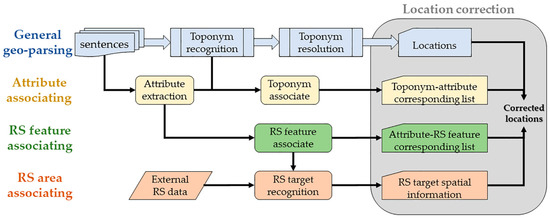
Figure 3.
Basic idea of toponym correction based on remote sensing images.
General geo-parsing procedure. This procedure includes toponym recognition and toponym resolution steps to attain locations of parsed toponyms. Because it is a classic process, the existing open-sourced tools can be directly used in this process, such as StanfordNER [42], SpaCyNER [43], and Baidu geocoding tool [44]. This procedure aims to obtain the best geo-parsing locations by current text-based geo-parsing techniques. In a forest ecological pattern investigation, the geo-parsed locations of forest ecological patterns can be obtained with these practical tools, and the record should be as in Formula (1) where indicates the sentences.
Attribute associating procedure. This procedure requires extracting attributes from the sentence, associating the extracted attributes to relevant toponyms, and obtaining a toponym-attribute corresponding list. The goal of this procedure is to get obtain the basic links between the toponyms and their attributes. For example, in a forest ecological pattern investigation, each ecological pattern can be extracted and associated with the corresponding toponym. The toponym-attribute corresponding record is shown as Formula (2).
RS feature associating procedure. This procedure associates attributes with RS features. The reason is RS features can provide additional spatial information to correct the current geo-parsed locations, which need to link additional spatial information (RS feature) with the attributes. For example, the attribute “forest-crop” indicates the crop grows under the forest. To achieve accurate RS features, forest types should be identified. In the target area, the crop refers to sweet potatoes (Dioscorea esculenta (Lour.) Burkill). Moreover, the corresponding forest is walnut trees (Juglans regia Linn.), which belongs to the closed deciduous broadleaved forest. Thus, the corresponding RS feature is “closed deciduous broadleaved forest”, which can be recorded as Formula (3).
RS area associating procedure. This procedure should obtain RS target spatial information based on the RS features. Thus, the external RS images can provide data to recognize the RS target areas. In the forest ecological pattern investigation, the areas of RS feature “closed deciduous broadleaved forest” can be recognized with mature forest recognition algorithms [45]. After data splicing, clipping, and exporting, the RS image of the target area can be obtained. Moreover, discrete small patches need to be removed with the necessary steps of image principal component analysis (PCA), image clump, and a patch sieve with 4 pixels. Finally, the associated RS areas are obtained.
Location correction procedure. To synthesize the acquired locations and links including “locations” from the general geo-parsing procedure, “toponym-attribute” from the attribute associating procedure, “attribute-RS feature” from the RS feature associating procedure, and “target area-RS feature” from the RS area associating procedure, a location correction procedure is needed, which is the algorithm center in our proposed method. In the example of a forest ecological pattern investigation, the geo-parsed toponym set indicates , the toponym-attribute (toponym-pattern) correspondence list indicates , the attribute-RS feature (pattern-ForestType) correspondence list indicates , and RS area (forest area) set indicates . Moreover, additional parameters are required to improve the correction accuracy, including the city center list and the cluster threshold . The cluster threshold aims to split the target area clusters and should be set by considering the distance between the villages. The clusters can be generated by using DBSCAN with an ArcMap tool named density-based clustering. For example, can be set to 10 km, which is the average distance between the towns in eastern China. It is noted that the toponym correction algorithm contains an AI value, which is short for Attractive Index that indicates the ability to attract the surrounding areas. An AI value can be calculated by Formula (4), where indicates the Euclidean distance between the current toponym location and the cluster center.
A detailed specific toponym correction algorithm is shown in Figure 4, which obtains the corrected toponym set with the above parameters. During the process of the Toponym Correction Algorithm, each toponym is checked to determine if it will be corrected and where it will be moved to. First, is divided into two categories (the under-city level or the city level) with different processes. Second, the target RS areas are obtained according to the related features, such as patterns and forest-area types. Third, the clusters are calculated by the Density-based Clustering ArcMap tool with the target RS areas. Finally, each toponym is checked by the Attractive Index and moved to the most probable location. The time complexity of the toponym correction algorithm is .

Figure 4.
The logic flow of the toponym correction algorithm based on remote sensing images.
4. Experiments and Results
To describe the validity and effectiveness of the TC-RSI method, this section is divided into four parts. The case study area part presents general information about the research area, the correction results show the correction results compared with previous locations, the correction evaluation section assesses the TC-RSI method in different aspects, and the correction effect section describes the improvements of the TC-RSI method. Note that due to the low complexity of the designed algorithm, the effectiveness and applicability of the algorithm are mainly discussed in the experiment.
4.1. Case Study Area
The toponym correction targets of this experiment are the geo-parsed locations of Chinese forest ecological patterns that contain apparent spatial features. The data of Chinese forest ecological patterns comes from the published dataset of the spatial distribution dataset on ecological agriculture patterns of China (2018–2020) [40]. The case study area is An’hui province, which includes 93 geo-parsed locations. To illustrate the corrected changes visually, the experiment uses Hefei city, the capital of Anhui province in eastern China, as an example. Figure 5 shows the distribution of national Chinese forest ecological patterns and the patterns in Hefei. Because of the distance offsets, only two points are shown in Figure 5. In fact, these two points represent 11 outstanding local forest ecological patterns in five categories, detailed in Table 1, which were extracted from the spatial distribution dataset on ecological agriculture patterns of China. Furthermore, the TC-RSI method uses the NLPIR as the toponym recognition algorithm and the Amap as the toponym resolution gazetteer.
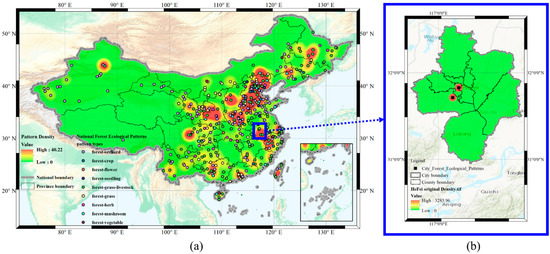
Figure 5.
Study area in experiments. (a) National Chinese forest ecological pattern distribution and density. (b) The case study city, Hefei.

Table 1.
The examples of forest ecological patterns in Hefei.
Forest ecological patterns and their detailed corresponding RS feature information are listed in Table 2, including cooperating main species, forest main species, forest types, and corresponding GRIDCODE. The cooperating main species and forest main species were obtained from the implementation outline of under-forest economic development in Anhui province (2019–2025) [46]. The forest types and corresponding GRIDCODE were sourced from the dataset of GLC_FCS30-2020 [45]. The GRIDCODE 2, 4, and 6 indicate closed evergreen broadleaved forest (id 52), closed deciduous broadleaved forest (id 62), and closed evergreen needle-leaved forest (id 72), respectively.

Table 2.
Corresponding information of forest ecological patterns and forest types in Hefei.
4.2. Correction Result
This section explains the correction results by a presentation illustrating the corrected locations and statistics showing the correction ranges.
4.2.1. Presentation
In general, the locations of forest ecological patterns were corrected by using the TC-RSI method. The city center and county center locations were moved to different clusters where forests of different types exist (Figure 6). The forest distribution shows the original locations of forest ecological patterns are not in any forest areas. This means these locations must have offsets between these locations and their actual occurrence locations. Thus, the directions of correction results in Figure 6 are correct, which point to the actual forest areas.
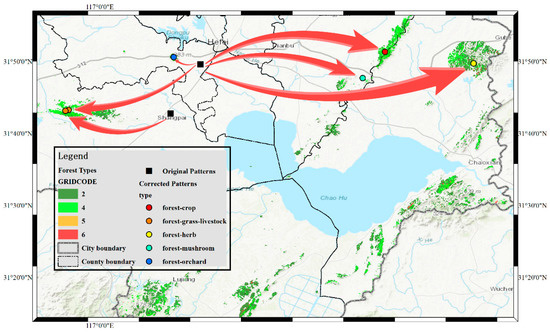
Figure 6.
Correction routes of forest ecological patterns in Hefei.
4.2.2. Correction Ranges
The correction ranges of forest ecological patterns with TC-RSI in Hefei are shown in Table 3. This shows that the records have significant correction distances, and the average correction distance reaches 37.82 km. This average correction distance is nearly the median offset distance (48 km) of current excellent geo-parsers [2]. On the one hand, the correction ranges of forest ecological patterns with the TC-RSI method is near the median offset distance (50 km) from the literature. On the other hand, the average correction distance shows the effectiveness of the TC-RSI method. The correction results also show that the county change exists over 50% of the location corrections. That means most geo-parsed locations have cross-county offsets, and the TC-RSI method has the ability to correct cross-county locations. Although the correction routes and ranges of forest ecological patterns with the TC-RSI method are shown well, validations are required to prove these corrected locations, as in the following section.

Table 3.
Correction ranges of forest ecological patterns with the TC-RSI method.
4.3. Correction Evaluation
Validation of the TC-RSI method included visual validation, statistical assessment, and robustness assessment. The reason for choosing visual validation was because only visual comparisons can prove the correction is valid and correct. Thus, visual validation shows the correction performance of the TC-RSI method. To quantify the corrections, we measured the statistical results and robustness of the provincial dataset. Note that visual validation only presents part of the results to illustrate the changes clearly. The whole validation dataset information is shown in the robustness assessment.
4.3.1. Visual Validation
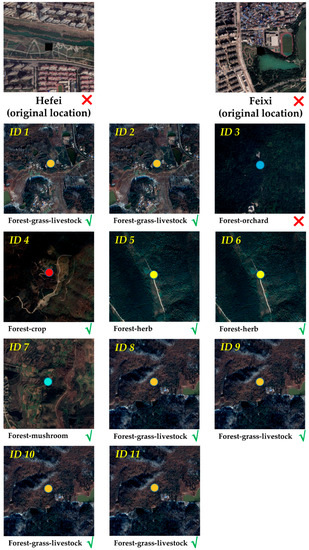
Remote sensing images from Google Earth Pro were used to validate corrected forest ecological pattern locations by visual interpretation. The images of the original and corrected locations are illustrated in Figure 7. The corresponding forest ecological patterns were double-checked by the news and documents from the official website of the Hefei forestry and garden bureau [47]. According to the results of visual interpretation, it was found that the original locations are in the city or county centers, which are not the actual locations. After correction by the TC-RSI method, over 90.9% (10/11) of corrected locations were in the place where the forest ecological pattern should be located. The corresponding forests, farm traces, houses, roads, and relevant spatial patterns appeared in the corrected locations. For example, ID 1 has the typical features of forests, barnyards, and fields for the Forest-grass-livestock pattern, and ID 5 has the typical features of closed forests, necessary paths, and storage rooms for the Forest-herb pattern. These examples prove that the correction of the TC-RSI method is valid. Most geo-parsed locations were corrected to the actual locations.
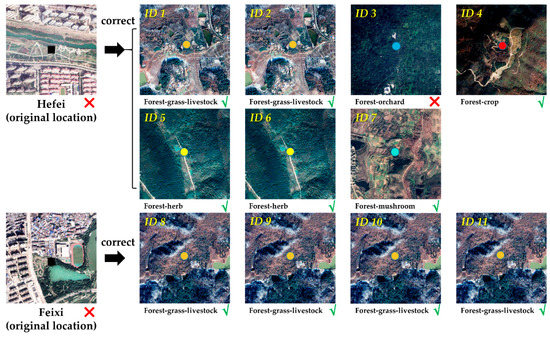
Figure 7.
Images of corrected forest ecological pattern locations. The symbol √ & × mean the corrected location is right and wrong, respectively. The centers of images mean the different ecological pattern types, which corresponds to the legend of Figture 6. Enlarged images are shown in Appendix B.
An erroneous case also occurred. In the image of ID 3, there are no orchard features around the corrected location. According to visual interpretation, the corrected location is a forest park around the city, with the same forest features as an orchard. Considering the Attractive Index (AI) mechanism in Figure 4, the forests around the city center affect the accuracy of toponym correction because of their short distances to the city center. This means the spatial features around the city affect the accuracy of the TC-RSI method.
Overall, the TC-RSI method has an excellent toponym correction effect from the visual validation process perspective.
4.3.2. Statistical Assessment
To quantify the toponym correction effect of the TC-RSI method, the offsets of each correction were calculated, as in Table 4. The shown offset distances are impressive and exciting. Because most of the corrected locations are in the actual forest ecological pattern areas, the average offset distance decreased to 0.70 km when using Formula (5). This means that the TC-RSI method dramatically improved geo-parsing performance. Note that the offset distance of ID 3 was calculated by the corrected location and the nearest area with a Forest-orchard ecological pattern. Therefore, TC-RSI is a quantitatively verified toponym correction method with excellent performance. More statistical assessment is shown in the next section with the whole An’hui province including 93 geo-parsed locations.

Table 4.
Offset distances between the corrected locations and the nearest actual locations.
4.3.3. Robustness Assessment
To verify the effectiveness and robustness of the TC-RSI method further, different toponym recognition algorithms and toponym resolution gazetteers were used. Considering the records in Hefei are few, the robustness assessment used the records in An’hui province, including 93 geo-parsed locations (containing the above 11 locations in Hefei city). Two experiment groups were set to analyze the impacts of toponym recognition algorithms and toponym resolution gazetteers (Table 5).

Table 5.
Results of robustness assessment of the TC-RSI method by different toponym recognition algorithms and toponym resolution gazetteers.
Group 1 shows the impacts of different toponym recognition algorithms. Although different toponym recognition algorithms impact the results of the TC-RSI method, the offset correction ability of the TC-RSI method was proved by decreasing the offset distance over 38 km. In addition, the value of “With the TC-RSI avg. offset” was 1.62 (±0.80) km, which has a minimal deviation value (±0.80 km). This means the TC-RSI method is stable with different toponym recognition algorithms. In the same way, Group 2, with a ±1.44 km deviation value, shows that the TC-RSI method is also stable with different toponym resolution gazetteers. Therefore, all the correction evaluations prove that the proposed TC-RSI is a stable, effective, and reliable method of toponym correction in geo-parsing.
4.4. Correction Effect
The correction effects of the TC-RSI method after the validation process are described below, showing the proposed method’s broad application prospects.
4.4.1. Improving Geo-Parsing Location Accuracy
The overall effect of the TC-RSI method is to improve the accuracy of geo-parsed locations, because the TC-RSI method contains an additional toponym correction process compared with current geo-parsers. The decreasing offset distances attained were over 38 km, and the average offset distance with the TC-RSI method was up to 0.82 km (Table 5). This is a dramatic improvement in the geo-parsing process. Therefore, these reliable values not only show the validity of the TC-RSI method but also prove the validity of the new toponym correction step in the geo-parsing process.
4.4.2. Promoting Geographical Discoveries on Small Scales
The second effect of the TC-RSI method is that corrected locations can promote more detailed geographical discoveries. After toponym corrections, more detailed patterns can be revealed on a smaller scale. Figure 8 shows pre-density and post-density maps of Hefei forest ecological patterns. In Figure 8a, the core centers of Hefei forest ecological patterns are near the center of Hefei city, whereas Figure 8b indicates that the actual core centers of Hefei forest ecological patterns are in the west and the east.
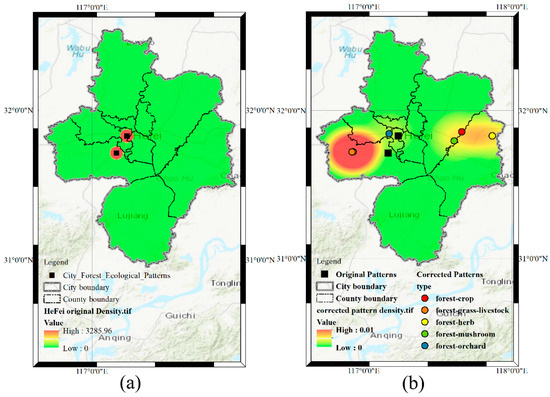
Figure 8.
Density maps of Hefei forest ecological patterns. (a) Pre-correction density pattern. (b) Post-correction density pattern.
These changing patterns indicate the validity of the proposed method, which can effectively correct geo-parsed toponym locations. Furthermore, toponym corrections provide more accurate locations and support more detailed discoveries.
5. Discussion
According to the above series of experiments, the results prove that the TC-RSI is a valid and effective method to improve the accuracy of geo-parsed locations. However, there are also some conditions and limitations to the current toponym correction method. This section discusses these limitations and suggests potential future work to further develop the toponym correction method.
5.1. Terrian Impact
Although the TC-RSI method obtained a 0.82 km average offset distance with 93 records in An’hui province, the correction results varied in different terrains. Figure 9 illustrates the corrected results in different terrains. For example, all the corrected locations in Figure 9a are the actual locations where the pattern occurred, and most of the corrected locations in Figure 9c are not actual locations. Moreover, the statistical information in Figure 9d also shows the impact of the method. Seventy percent of the records (ID 1-65) with small offset distances are plain areas, which have lower reliefs in their terrains. The reason for these differences is that large mountainous areas contain mixed forests. There are still diversified forest ecological patterns for single species of forest. For example, closed deciduous broadleaved forests can include forest-orchard, forest-grass-livestock, and forest-mushroom types. When the forest is mixed in this way, there is a lack of extra information to match these areas with the patterns. Fortunately, the distances of these patterns are very close when the forest is joined as described. Therefore, the corrected directions are always correct and the offset distances decrease.
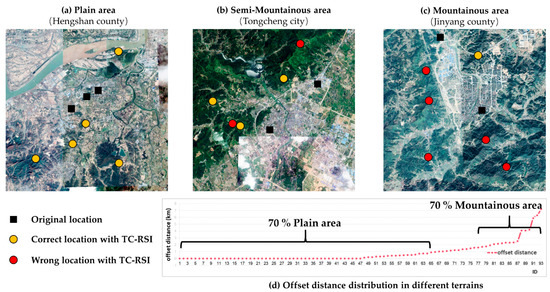
Figure 9.
Terrain impacts the TC-RSI method. (a) Corrected locations in the plain area. (b) Corrected locations in a semi-mountainous area. (c) Corrected locations in a mountainous area. (d) Offset distance distribution in different terrains in An’hui province. Note that Hengshan county, Tongcheng city, and Jinyang county belong to the experimental dataset in An’hui.
The results of the TC-RSI method are not homogeneous. Different terrains around the candidate locations impact the correct performance. However, this feature does not influence the TC-RSI method as a valid toponym correction method because of the significant decrease in offset distance.
5.2. Method Limitation
It should be noted that the promising TC-RSI method still has limitations. In terms of the mechanism of the method, there is an assumption that the candidate toponyms should describe objects or events together with attributes. In other words, the candidate toponyms must relate to the attributes with extra spatial information. Thus, the assumption leads to two limitations.
First, the TC-RSI method can only correct the toponyms containing attribute information in sentences. For example, Hefei city has attempted to plant sweet potatoes under the forest, a representative local ecological pattern (forest-crop). The toponym (Hefei city) in the above example describes the location of the forest-crop ecological pattern. The toponym with these situations can be corrected by the TC-RSI method. However, there are also many toponyms in sentences, which are not directly correlated to attributes. For example, “… including Hefei city, Nanjing city, and Hangzhou city” and “…published in March 3, Beijing”. These italic toponyms in the sentences cannot be corrected by the TC-RSI method.
Second, the TC-RSI method corrects the toponyms by the spatial information correlated with the attributes in the sentences. It indicates that the toponyms of the attributes must have spatial features that can be attained easily from remote sensing images, such as forest ecological patterns. In contrast, some attributes have no apparent spatial features, such as hybrid farming, hybrid aquaculture, and biogas recycling. Unclear spatial features or no spatial features for remote sensing images, cannot be used with the TC-RSI method. Thus, the TC-RSI method is limited by these targets. More comprehensive and universal toponym correction methods will continue to be explored.
5.3. Potential Future Work
According to the mechanism of the TC-RSI method, remote sensing image is a valid path to obtain extra spatial information required to correct geo-parsed locations. This indicates that correcting geo-parsed toponyms with extra spatial information is possible. Moreover, extra spatial information can significantly improve the accuracy of geo-parsed locations. The offsets of geo-parsed locations decreased from about 50 km down to about 1 km. Details are given in Section 4.3.3. Considering the improved performance and various types of extra spatial information, we believe that the TC-RSI method will usher in a new era of geo-parsing with toponym corrections.
Satellite remote sensing images can provide extra spatial information for the geo-parsing. This suggest that other data sources may also provide extra spatial information for the geo-parsing. For example, the sentence “Nanjing city constructs lots of agriculture parks with the agriculture-park ecological pattern, such as Guli Modern agriculture park, …” contains attribute information such as “Guli Modern agriculture park”, which may be recorded in the domain gazetteers that store the actual locations. Moreover, other sources may also have this information. Thus, domain gazetteers, low-altitude UAV images, Wikimedia, streetscapes, GNSS, InSAR, and hybrid sources may be data sources used to correct geo-parsed locations [48,49]. These need to correlate the attributes with the relevant toponyms; for example, correlating “Nanjing” with “Guli Modern agriculture park”. Sometimes, different data sources have different spatial and temporal coverages and resolutions [50]. Complex and diverse data sources require model adjustments to suit their scales, which may change algorithm performance. Thus, we will adjust the multi-source toponym correction algorithm (e.g., the dependence of features on different scales and different data sources) and release a toponym correction platform for different spatial information sources in the future.
6. Conclusions
Geo-parsing is a commonly used process to obtain locations from texts in GIScience. To further decrease the offset distances of the geo-parsed locations, this study proposes a novel Toponym Correction method based on Remote Sensing Images (TC-RSI). The experiments prove that the TC-RSI method can effectively decrease the average offset distances compared with current geo-parsed locations. Although the TC-RSI mainly provides an auxiliary correction function to improve the geo-parsing performance in the text field, it has two groundbreaking conclusions.
First, the TC-RSI is an effective toponym correction method. Using the TC-RSI method, the offset distances of current geo-parsed locations can be decreased from almost 50 km to almost 1 km. This dramatic improvement shows that the remote sensing images have powerful accurate spatial information that can be used to correct geo-parsed locations. This remarkable improvement will allow text mining to find more accurate geographical discoveries with lower offset distances.
Second, correcting locations by their relevant attributes is a valid path to decreasing the offset distances of geo-parsed locations. In this study, the remote sensing image is regarded as a spatial information dataset that correlates to the attributes, achieving impressive improvements. More types of spatial information datasets could be explored, such as domain gazetteers, Wikimedia, and streetscapes.
In short, TC-RSI shows the ability to use extra spatial information to improve the performance of geo-parsing, which is expected to usher in a new era of geo-parsing with toponym corrections and remote sensing techniques.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W. and X.Y.; data curation, S.W.; Formal analysis, S.W.; funding acquisition, S.W. and Y.Z.; investigation, S.W.; methodology, S.W. and X.Y.; resources, S.W. and X.Y.; software, X.Y.; supervision, Y.Z., J.S., K.S., W.L., L.H., Y.Q. and H.X.; validation, X.Y.; visualization, S.W.; writing–original draft, S.W.; writing–review & editing, S.W. and X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 42101467 and 42050101; Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number XDA23100101; the Informatization Plan of Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number CAS-WX2021SF-0106.
Data Availability Statement
The remote sensing images were obtained from the PIESAT platform. The PIESAT processing code, shapefiles, and national forest ecological patterns can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6362489.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers who provided insightful comments on improving this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
The forest main species and their corresponding images.
Table A1.
The forest main species and their corresponding images.
| Id | Forest Main Species (Official Latin Name) | Family Name | Generic Name | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Juglans regia Linn. | Juglandaceae | Juglans |  |
| 2 | Toxicodendron vernicifluum (Stokes) F. A. Barkl. | Anacardiaceae | Toxicodendron |  |
| 3 | Phyllostachys heterocycla (Carr.) Mitford cv. Pubescens Mazel ex H.de leh. | Gramineae | Phyllostachys |  |
| 4 | Castanea mollissima Bl. | Fagaceae | - |  |
| 5 | Pinus massoniana Lamb. | Pinaceae | Pinus |  |
| 6 | Cerasus yedoensis | Cerasus yedoensis | Cerasus Mill. |  |
References
- Purves, R.S.; Clough, P.; Jones, C.B.; Hall, M.H.; Murdock, V. Geographic Information Retrieval: Progress and Challenges in Spatial Search of Text. Found. Trends Inf. Retr. 2018, 12, 164–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y. Are we there yet? evaluating state-of-the-art neural network based geoparsers using EUPEG as a benchmarking platform. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Geospatial Humanities, Chicago, IL, USA, 5 November 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nizzoli, L.; Avvenuti, M.; Tesconi, M.; Cresci, S. Geo-semantic-parsing: AI-powered geoparsing by traversing semantic knowledge graphs. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 136, 113346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshitoyan, V.; Dagdelen, J.; Weston, L.; Dunn, A.; Rong, Z.; Kononova, O.; Persson, K.A.; Ceder, G.; Jain, A. Unsupervised word embeddings capture latent knowledge from materials science literature. Nature 2019, 571, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh Chawla, D. Text-mining tool seeks out ‘hidden data’. Nature 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Hou, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Shen, S.; Cheng, Q.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Lv, H.; et al. Geoscience knowledge graph in the big data era. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritta, M.; Pilehvar, M.T.; Limsopatham, N.; Collier, N. What’s missing in geographical parsing? Lang. Resour. Eval. 2018, 52, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Wolter, D. A reasoning model for geo-referencing named and unnamed spatial entities in natural language place descriptions. Spat. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 21, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuke, H.; Zhiyong, Z.; Hao, L.; Yingjie, H.; Fuqiang, G.; Jens, K.; Hongchao, F.; Friederike, K. Location reference recognition from texts: A survey and comparison. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.01683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, J. Earthquake Information Extraction and Comparison from Different Sources Based on Web Text. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gao, S.; Gong, L.; Kang, C.; Zhi, Y.; Chi, G.; Shi, L. Social Sensing: A New Approach to Understanding Our Socioeconomic Environments. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2015, 105, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, C.; Yu, M.; Huang, Q. Geographic context-aware text mining: Enhance social media message classification for situational awareness by integrating spatial and temporal features. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2021, 14, 1721–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, F. User-generated content: A promising data source for urban informatics. In Urban Informatics; Shi, W., Goodchild, M.F., Batty, M., Kwan, M.-P., Zhang, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 503–522. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Qian, L.; Zhu, Y.; Song, J.; Lu, F.; Zeng, H.; Chen, P.; Yuan, W.; Li, W.; Geng, W. A web text mining approach for the evaluation of regional characteristics at the town level. Trans. GIS 2021, 25, 2074–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sanz, S.; Ghamisi, P.; Piles, M.; Werner, M.; Cuadra, L.; Moreno-Martinez, A.; Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E.; Munoz-Mari, J.; Mosavi, A.; Camps-Valls, G. Machine learning information fusion in Earth observation: A comprehensive review of methods, applications and data sources. Inf. Fusion 2020, 63, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Mu, L.; Huang, L. Knowledge discovery from remote sensing images: A review. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 10, e1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson, E.; De Sabbata, S.; Purves, R.S. A quantitative analysis of global gazetteers: Patterns of coverage for common feature types. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.A.; Davis, C.A.; Borges, K.A.V.; Delboni, T.M.; Laender, A.H.F.; Society, I.C. The role of gazetteers in geographic knowledge discovery on the Web. In Proceedings of the Third Latin American Web Congress (LA-WEB’2005), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1 October–2 November 2005; pp. 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Asokan, A.; Anitha, J. Change detection techniques for remote sensing applications: A survey. Earth Sci. Inform. 2019, 12, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarian, S.; Valente, J.; van der Voort, M.; Tekinerdogan, B. Effect of Attention Mechanism in Deep Learning-Based Remote Sensing Image Processing: A Systematic Literature Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Bluemel, A.; Gebhardt, S.; Quoc, T.V.; Dech, S. Remote Sensing of Mangrove Ecosystems: A Review. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 878–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana-Bobadilla, E.; Molina-Villegas, A.; Lopez-Arevalo, I.; Reyes-Palacios, S.; Muñiz-Sanchez, V.; Arreola-Trapala, J. Adaptive Geoparsing Method for Toponym Recognition and Resolution in Unstructured Text. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewandaru, A.; Widyantoro, D.H.; Akbar, S. Event Geoparser with Pseudo-Location Entity Identification and Numerical Argument Extraction Implementation and Evaluation in Indonesian News Domain. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, M.; Pezanowski, S.; MacEachren, A.M.; Wallgrün, J.O. GeoTxt: A scalable geoparsing system for unstructured text geolocation. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Xie, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, H.; Sun, K. ChineseTR: A weakly supervised toponym recognition architecture based on automatic training data generator and deep neural network. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 1256–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Joseph, K. NeuroTPR: A neuro-net toponym recognition model for extracting locations from social media messages. Trans. GIS 2020, 24, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Du, M. Deep Belief Networks Based Toponym Recognition for Chinese Text. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Chen, X.; Yu, H. Change Detection of Geographic Features Based on Web Pages. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2013, 15, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, A.; Han, J.; Li, C. A Survey on Deep Learning for Named Entity Recognition. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, Z.; Jaffry, S.W.; Malik, M.K. Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction: State-of-the-Art. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallgrün, J.O.; Karimzadeh, M.; MacEachren, A.M.; Pezanowski, S. GeoCorpora: Building a corpus to test and train microblog geoparsers. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, M.; MacEachren, A.M. GeoAnnotator: A Collaborative Semi-Automatic Platform for Constructing Geo-Annotated Text Corpora. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Villegas, A.; Muñiz-Sanchez, V.; Arreola-Trapala, J.; Alcántara, F. Geographic Named Entity Recognition and Disambiguation in Mexican News using word embeddings. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 176, 114855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yang, C.; Hu, L.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, L.; Gong, J. The Integration of Linguistic and Geospatial Features Using Global Context Embedding for Automated Text Geocoding. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Vasardani, M.; Winter, S. Similarity matching for integrating spatial information extracted from place descriptions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gelernter, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Multi-lingual geoparsing based on machine translation. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, T.H.V.M.; Davis, C.A., Jr.; Fonseca, F.T. Reference data enhancement for geographic information retrieval using linked data. Trans. GIS 2017, 21, 683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lample, G.; Ballesteros, M.; Subramanian, S.; Kawakami, K.; Dyer, C. Neural architectures for named entity recognition. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.01360. [Google Scholar]
- Big Data Search and Mining Lab. NLPIR. Available online: http://ictclas.nlpir.org/ (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, L.; Song, J.; Yuan, W. The Spatial Distribution Dataset on Ecological Agriculture Patterns of China (2018–2020). J. Glob. Change Data Discov. 2021, 5, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, L.; Song, J.; Yuan, W.; Sun, K.; Li, W.; Cheng, Q. A novel rapid web investigation method for ecological agriculture patterns in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Stanford Natural Language Processing Group. Stanford Named Entity Recognizer (NER). Available online: https://nlp.stanford.edu/software/CRF-NER.shtml (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- spaCy. Industrial-Strength Natural Language Processing in Python. Available online: https://spacy.io/ (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Baidu. Geocoding API v2.0. Available online: https://api.map.baidu.com/lbsapi/cloud/webservice-geocoding.htm (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover product with fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2753–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anhui Forestry Bureau. Implementation Outline of Underforest Economic Development in Anhui Province (2019–2025). Available online: https://lyj.ah.gov.cn/public/9913203/39124599.html (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Hefei Forestry and Garden Bureau. Hefei Forestry and Garden Bureau Website. Available online: http://lyj.hefei.gov.cn/index.html (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Benoit, L.; Briole, P.; Martin, O.; Thom, C.; Malet, J.P.; Ulrich, P. Monitoring landslide displacements with the Geocube wireless network of low-cost GPS. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, T.; Tofani, V.; Lombardi, L.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Bertolo, D.; Thuegaz, P.; Casagli, N. Combination of GNSS, satellite InSAR, and GBInSAR remote sensing monitoring to improve the understanding of a large landslide in high alpine environment. Geomorphology 2019, 335, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwedczuk, K.; Cienkosz, D.; Apollo, M.; Borowski, L.; Lewinska, P.; Santos, C.A.G.; Eborka, K.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Romero-Andrade, R.; Sedeek, A. Challenges related to the determination of altitudes of mountain peaks presented on cartographic sources. Geod. Vestn. 2022, 66, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).