Using GNSS-IR Snow Depth Estimation to Monitor the 2022 Early February Snowstorm over Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
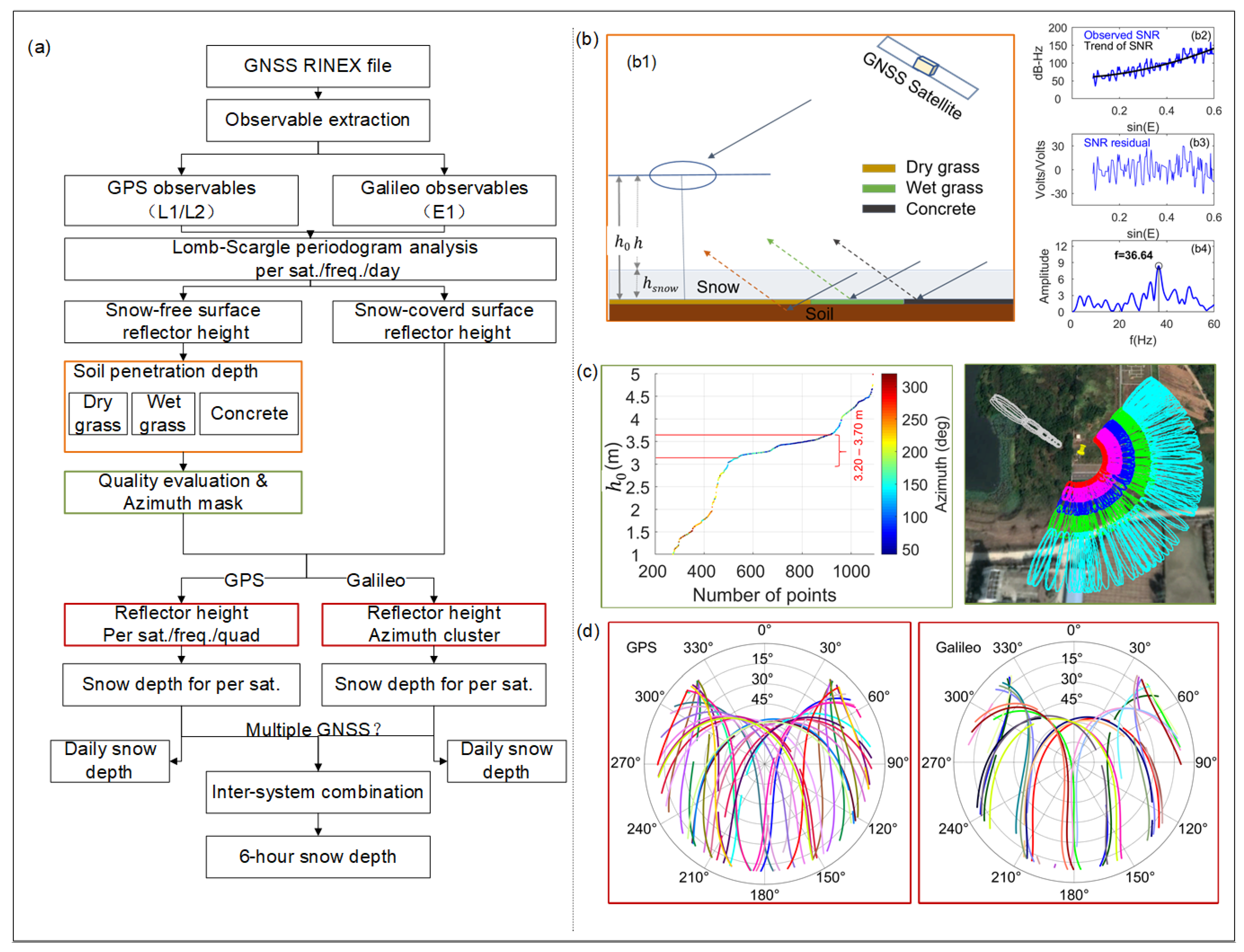
2.2. Methods of Snow Depth Retrieval
2.2.1. Quality Control of the Reference Reflector Height
2.2.2. Determination of the Soil Penetration Depth of Different Surface Conditions
2.2.3. Considerations of the Non-Repeatable Galileo Tracks to Eliminate Terrain Effects
2.2.4. Estimation of 6-h Resolution Snow Depths
3. Results and Discussion
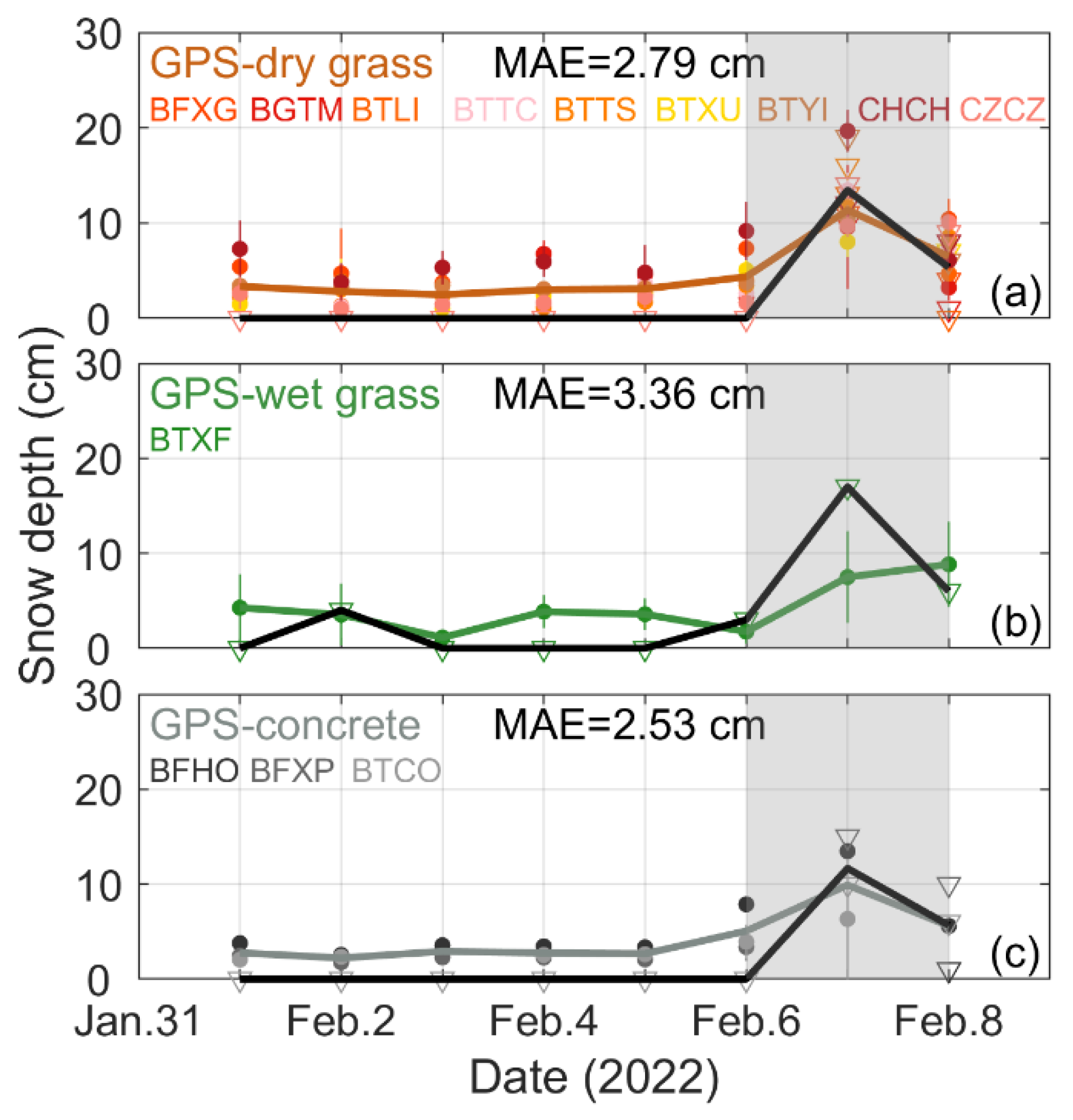
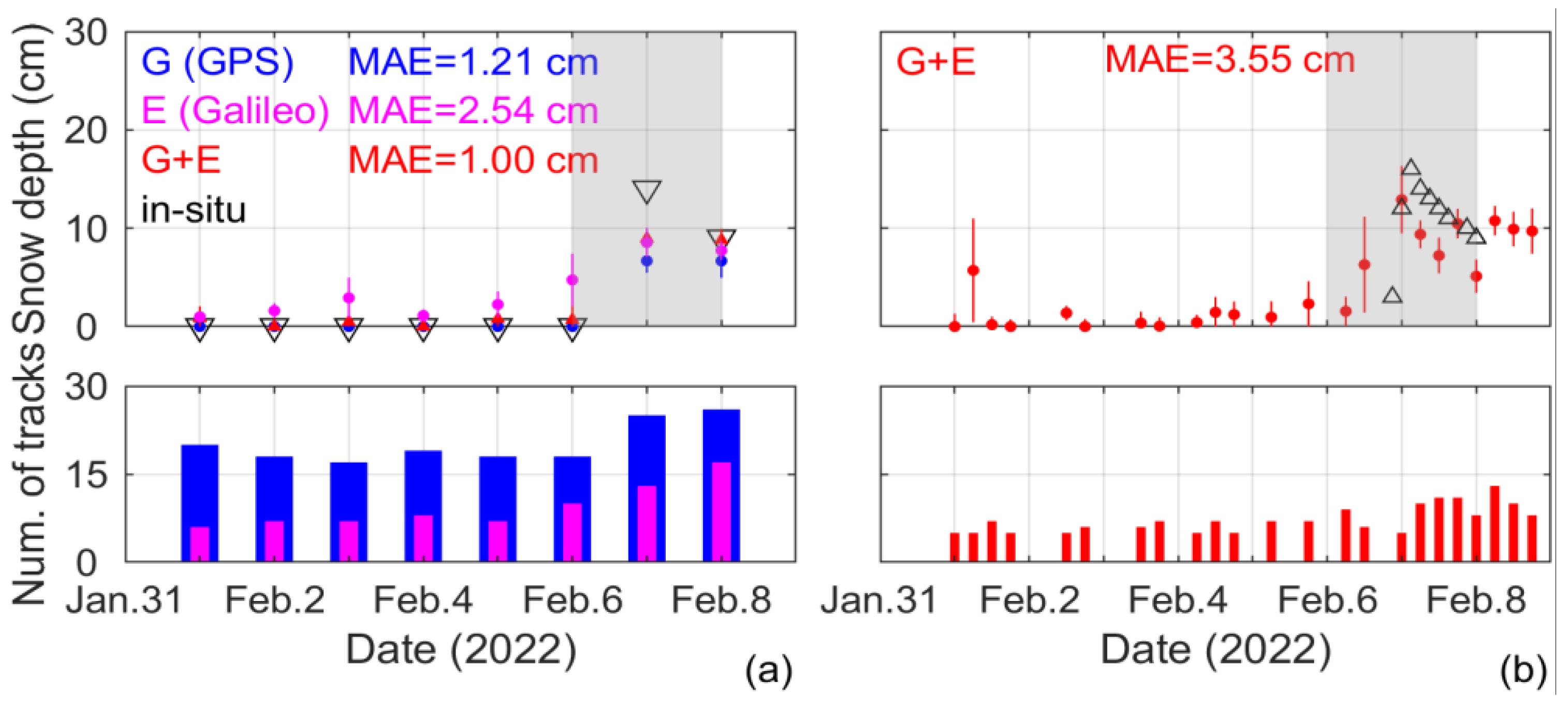
3.1. General Responses to the Snowstorm Event
3.2. Detailed Responses to the Snowstorm Event Using the 6-Hour Data
3.3. Advantages and Limitations of the Data and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J. Analysis and assessment of the risk of snow and freezing disaster in China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 19, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Boehrer, B. Variability in observed snow depth over China from 1960 to 2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 374–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L.; Liang, H.; Liu, B.; Guo, Z.; Hu, H.; Yang, T.; Zhao, L. A new snow depth data set over northern China derived using GNSS interferometric reflectometry from a continuously operating network (GSnow-CHINA v1.0, 2013-2022). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3549–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach, E.; Fabra, F.; Rius, A.; Pettinato, S.; D’Addio, S. Characterization of dry-snow sub-structure using GNSS reflected signals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Camps, A.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Bosch-Lluis, X.; Monerris, A.; Ramos-Perez, I.; Valencia, E.; Marchan-Hernandez, J.F.; Martinez-Fernandez, J.; Baroncini-Turricchia, G. Land geophysical parameters retrieval using the interference pattern GNSS-R technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 49, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Aguasca, A.; Valencia, E.; Bosch-Lluis, X.; Camps, A.; Ramos-Perez, I.; Park, H.; Vall-Llossera, M. Snow thickness monitoring using GNSS measurements. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J.; Small, E.E.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L. GPS multipath and its relation to near-surface soil moisture content. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Gutmann, E.D.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Braun, J.J.; Williams, M.W.; Nievinski, F.G. Can we measure snow depth with GPS receivers? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievinski, F.G.; Larson, K.M. Inverse modeling of GPS multipath for snow depth estimation—Part I: Formulation and simulations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6555–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievinski, F.G.; Larson, K.M. Inverse modeling of GPS multipath for snow depth estimation—Part II: Application and validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6564–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Ban, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Snow depth estimation based on multipath phase combination of GPS triple-frequency signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5100–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, M.; Heki, K. GPS snow depth meter with geometry-free linear combinations of carrier phases. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Yao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, S. A new GPS SNR-based combination approach for land surface snow depth monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.; Li, Y.; Chang, X. Snow depth estimation based on combination of pseudorange and carrier phase of GNSS dual-frequency signals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Nievinski, F.G. GPS snow sensing: Results from the EarthScope Plate Boundary Observatory. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Jin, S. Estimation of snow depth from GLONASS SNR and phase-based multipath reflectometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4817–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, S.; Geremia-Nievinski, F.; van Dam, T. Statistical comparison and combination of GPS, GLONASS, and multi-GNSS multipath reflectometry applied to snow depth retrieval. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3773–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.; Xing, Y.; Liu, L. Monitoring snow depth based on the SNR signal of GLONASS satellites. J. Remote Sens 2018, 22, 889–899. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chang, X.; Yu, K.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Estimation of snow depth using pseudorange and carrier phase observations of GNSS single-frequency signal. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X. Triple-frequency multi-GNSS reflectometry snow depth retrieval by using clustering and normalization algorithm to compensate terrain variation. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Bai, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhai, X.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; et al. FY3E GNOS II GNSS Reflectometry: Mission Review and First Results. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y. Using CYGNSS data to monitor China’s flood inundation during typhoon and extreme precipitation events in 2017. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Reager, J.T.; Small, E. CYGNSS data map flood inundation during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Gao, F.; Xu, T.; Wang, N.; Tu, J.; Jing, L.; Kong, Y. Daily Flood Monitoring Based on Spaceborne GNSS-R Data: A Case Study on Henan, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Zhang, Q. Analysis and combination of multi-GNSS snow depth retrievals in multipath reflectometry. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, X.; Xiao, R.; Song, M.; Jia, D. Millimeter to centimeter scale precision water-level monitoring using GNSS reflectometry: Application to the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wan, W.; Liang, H.; Liu, B.; Guo, Z. A comprehensive evaluation of utilizing BeiDou data to estimate snow depth from two ground-based stations. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Chew, C.C.; Braun, J.J. Using geodetic GPS receivers to measure vegetation water content. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, Q.; Wickert, J.; Jiang, Z. An SVM-based snow detection algorithm for GNSS-R snow depth retrievals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 6046–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Id | Site | Province | Lat. | Lon. | Alt. | GNSS Band | Cut-off Elev. Angle | Surface Condition during the Snowstorm | Mean VSM * in Feb., 2022 | Approx. Antenna Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Deg., N) | (Deg., E) | (m) | (Deg.) | (cm3.cm−3) | (m) | |||||
| 1 | BFXG | Hubei | 30.9 | 113.95 | 27.23 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.42 | 3.3 |
| 2 | BGTM | Hubei | 30.67 | 113.13 | 35.74 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.39 | 3.6 |
| 3 | BTLI | Hubei | 30.75 | 115.4 | 128.17 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.45 | 3.8 |
| 4 | BTTS | Hubei | 29.61 | 114.46 | 104.64 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.34 | 3.8 |
| 5 | BTXU | Hubei | 30.47 | 115.22 | 71.17 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.40 | 3.7 |
| 6 | BTYI | Hubei | 29.9 | 115.22 | 62.2 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.38 | 3.5 |
| 7 | CHCH | Anhui | 31.58 | 117.83 | 36.13 | L1, L2, E1 | 10 | dry grass | 0.43 | 5.2 |
| 8 | CZCZ | Anhui | 30.65 | 117.51 | 23.15 | L1, L2, E1 | 10 | dry grass | 0.48 | 3.8 |
| 9 | BTTC | Hubei | 29.27 | 113.88 | 150 | L1, L2 | 5 | dry grass | 0.38 | 3.4 |
| 10 | BFHO | Hubei | 30.51 | 114.94 | 29.7 | L1, L2 | 5 | concrete | 0.38 | 3.4 |
| 11 | BFXP | Hubei | 29.85 | 114.37 | 100.97 | L1, L2 | 5 | concrete | 0.29 | 3.7 |
| 12 | BTCO | Hubei | 29.54 | 114.04 | 83.12 | L1, L2 | 5 | concrete | 0.43 | 3.9 |
| 13 | BTXF | Hubei | 29.68 | 109.14 | 780.68 | L1, L2 | 5 | wet grass | 0.32 | 2.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Liang, H.; Wan, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, B. Using GNSS-IR Snow Depth Estimation to Monitor the 2022 Early February Snowstorm over Southern China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184530
Zhang J, Liu S, Liang H, Wan W, Guo Z, Liu B. Using GNSS-IR Snow Depth Estimation to Monitor the 2022 Early February Snowstorm over Southern China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jie, Shanwei Liu, Hong Liang, Wei Wan, Zhizhou Guo, and Baojian Liu. 2022. "Using GNSS-IR Snow Depth Estimation to Monitor the 2022 Early February Snowstorm over Southern China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184530
APA StyleZhang, J., Liu, S., Liang, H., Wan, W., Guo, Z., & Liu, B. (2022). Using GNSS-IR Snow Depth Estimation to Monitor the 2022 Early February Snowstorm over Southern China. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4530. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184530





