Regional Yield Estimation for Sugarcane Using MODIS and Weather Data: A Case Study in Florida and Louisiana, United States of America
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Collection
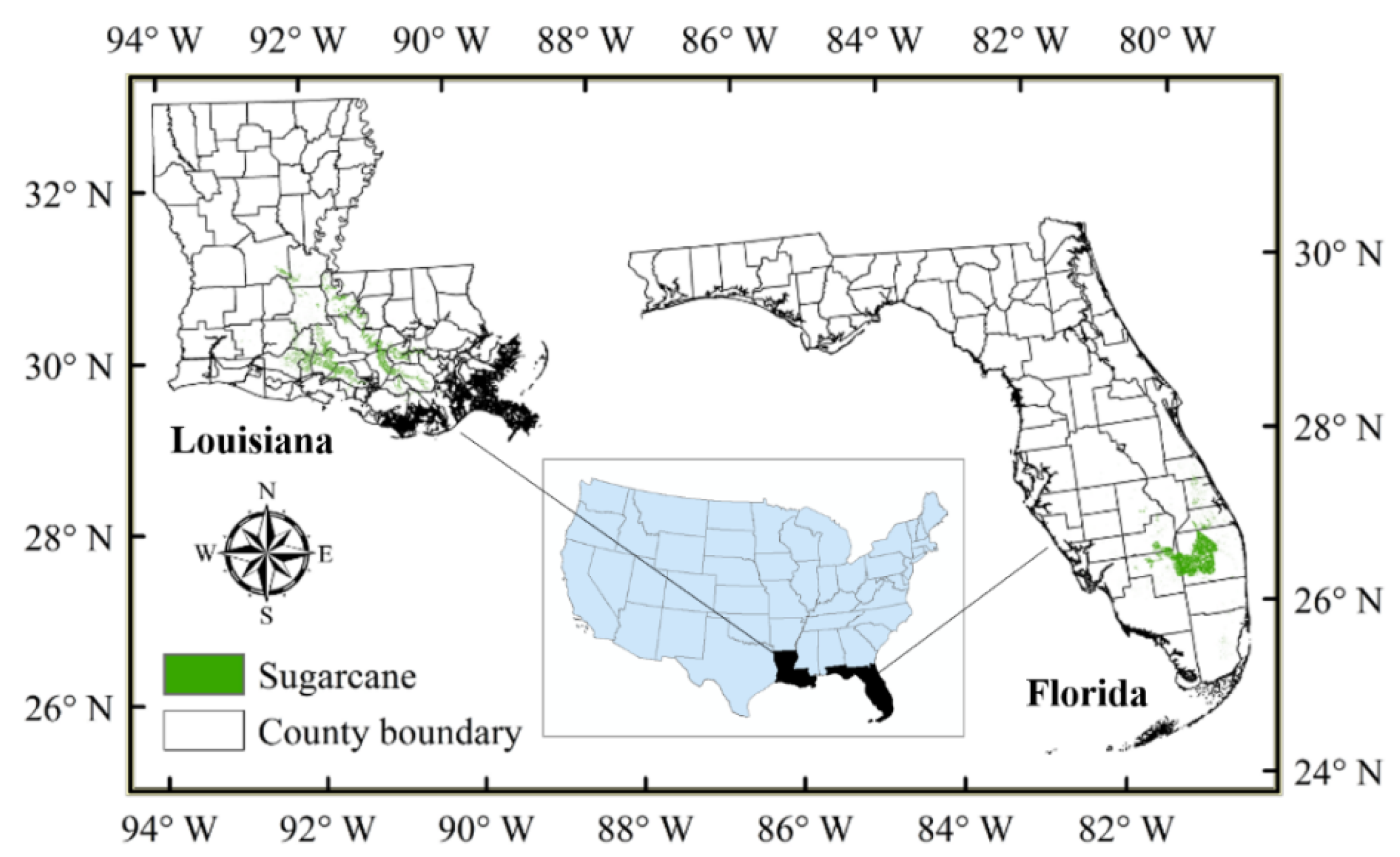
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. NDVI and LAI Data
2.2.2. Sugarcane Statistical Planting Area, Yield, and Production Data
2.2.3. Sugarcane Planting Area Map
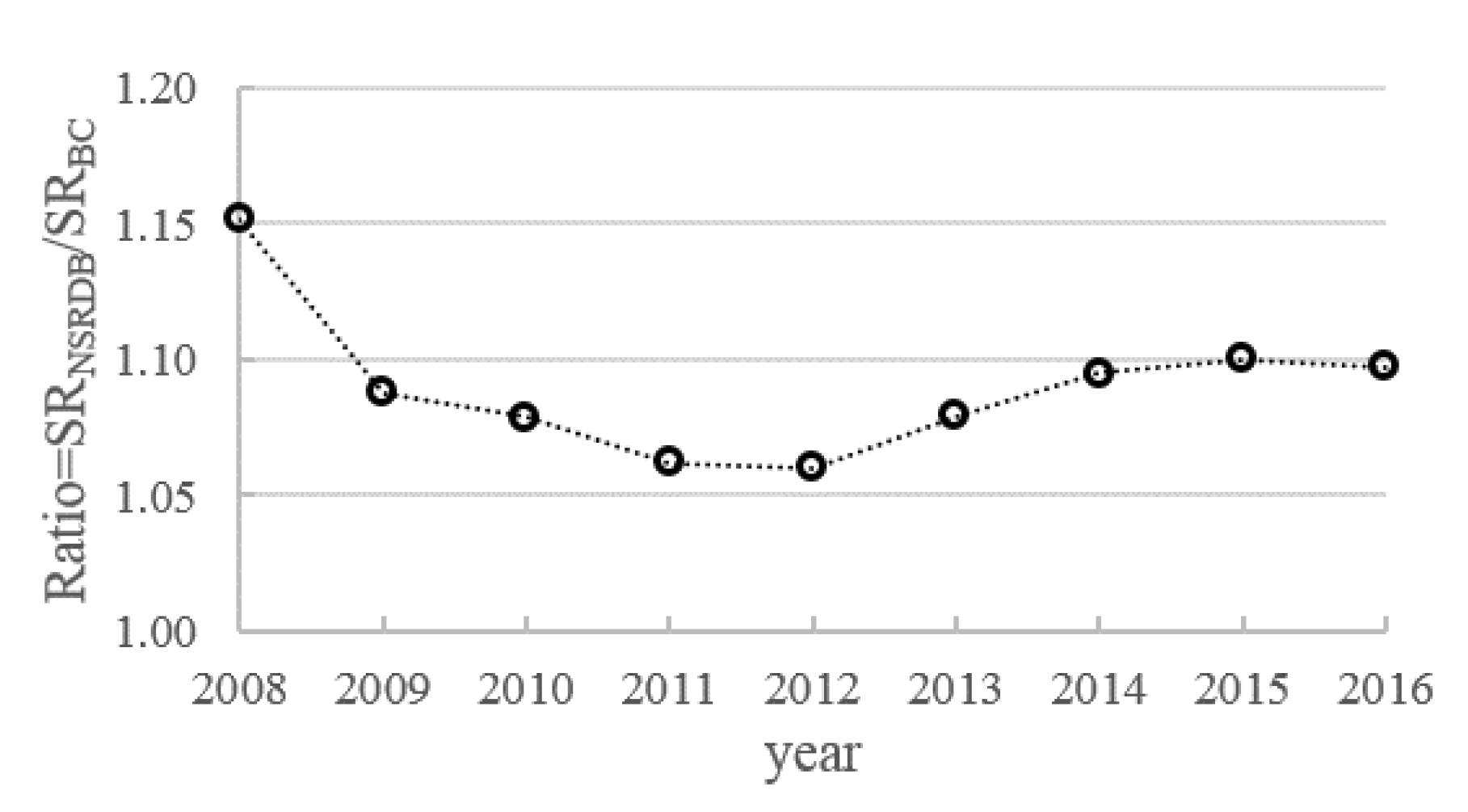
2.2.4. Meteorological and Soil Water Data
- (1)
- Solar radiation (SR) data
- (2)
- Temperature data
3. Methodology
3.1. The Length of Sugarcane Growth Period
3.2. Sugarcane Planting Area Extraction
3.3. Sugarcane Yield Prediction Models
3.3.1. CNDVI Model
3.3.2. K–M Model
3.3.3. SiPAR Model
3.4. Performance Evaluation Method
4. Result and Discussion
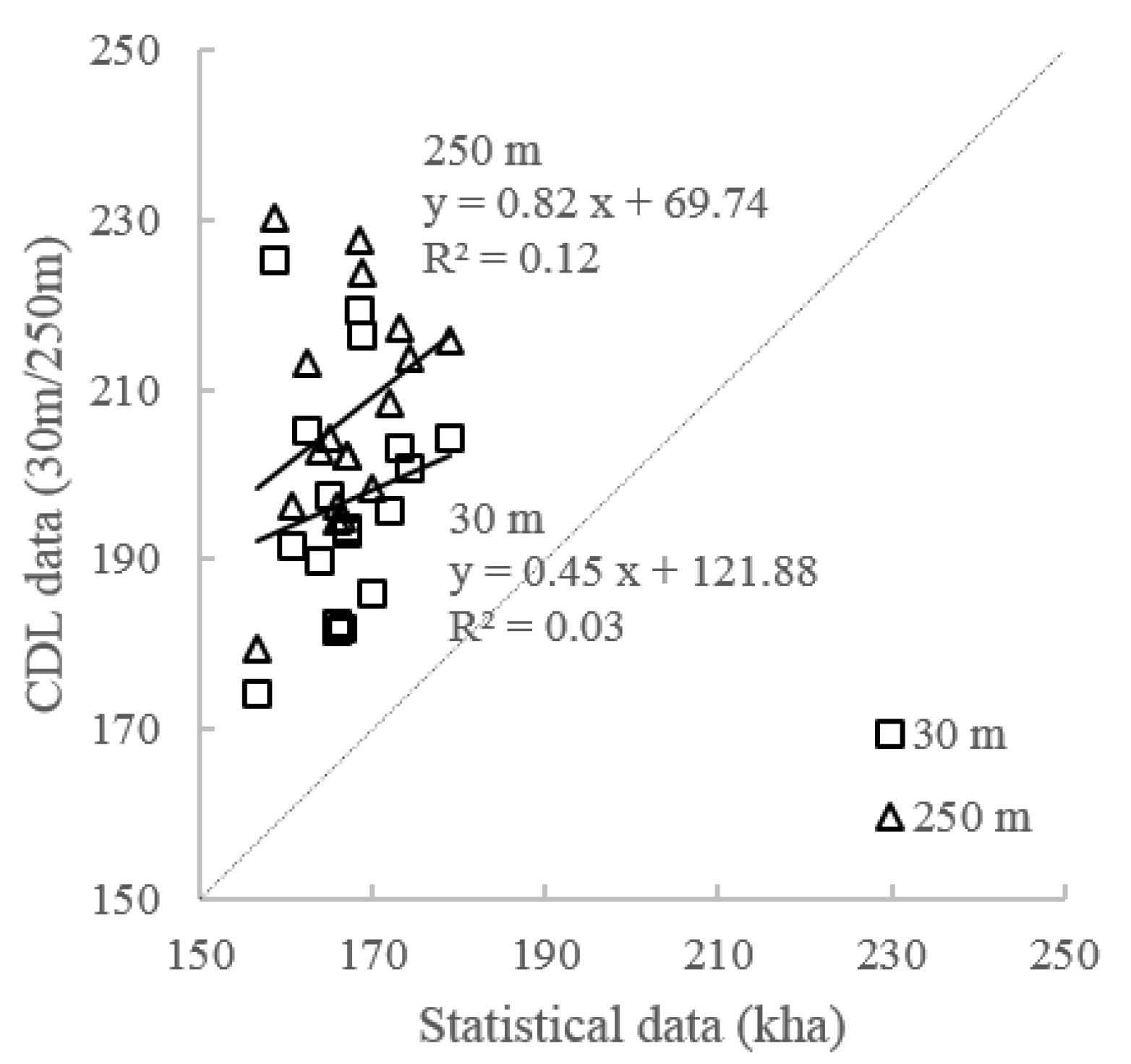
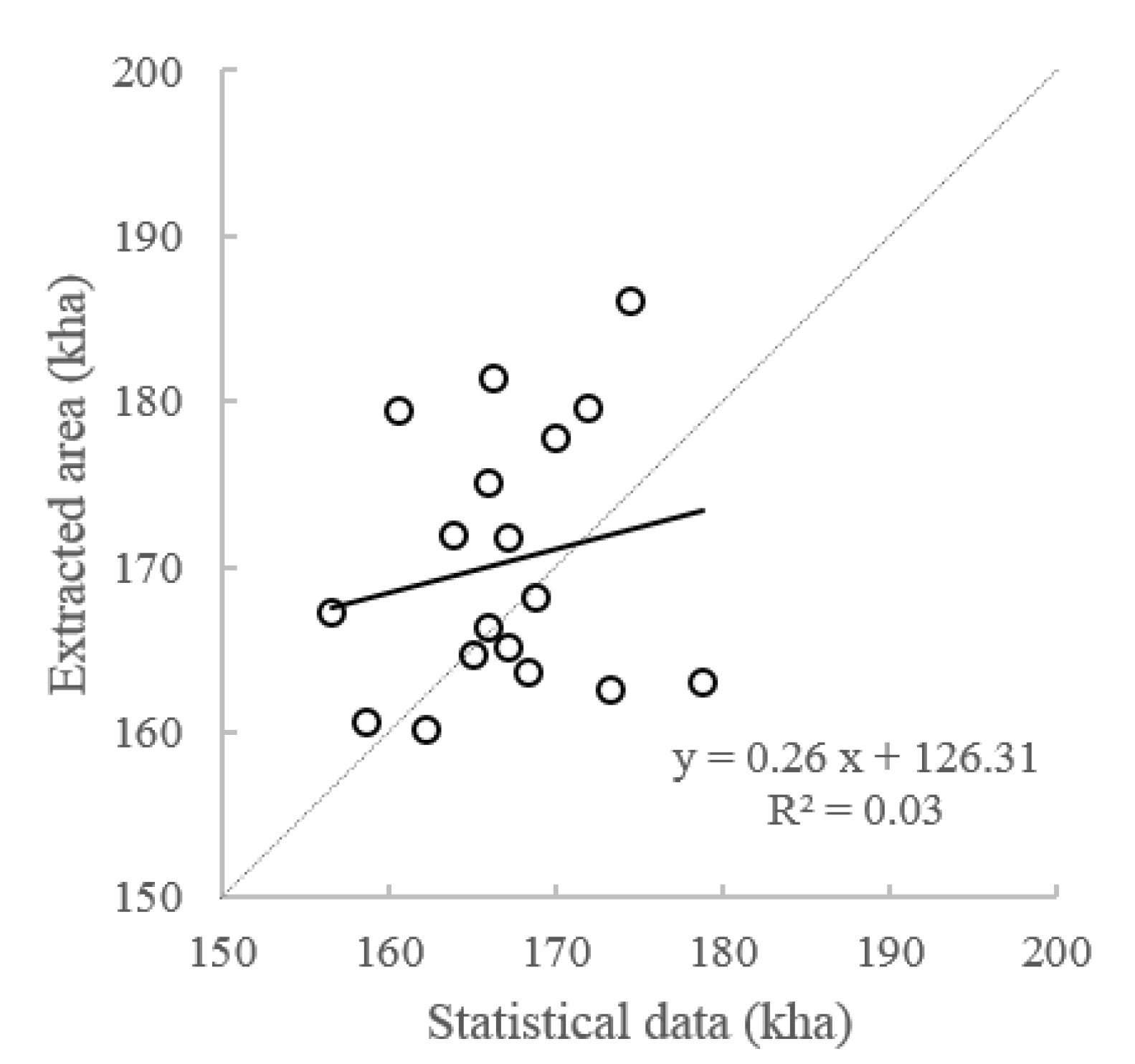
4.1. Extracted Sugarcane Planting Area at County Level
4.2. Sugarcane Yield Prediction
4.2.1. Prediction Performance at State Level
4.2.2. Prediction Performance at County Level
4.2.3. Prediction Performance in Palm Beach County
4.3. The Spatial Pattern of Sugarcane Yield
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grof, C.P.L.; Campbell, J.A. Sugarcane sucrose Metabolism: Scope for molecular manipulation. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-R.; Yang, L.-T. Sugarcane Agriculture and Sugar Industry in China. Sugar Tech 2014, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, E.; Friedman, Z.; Johnson, M. Sustainability Measurement of the American Sugarcane Industry; School of Environment and Sustainability, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2018; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Inman-Bamber, N.G. A growth model for sugarcane based on a simple carbon balance and the CERES-Maize water balance. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 1991, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inman-Bamber, N.G.; Bonnett, G.D.; Smith, D.M.; Thorburn, P.J. Sugarcane Physiology: Integrating from cell to crop to advance sugarcane production. Field Crops Res. 2005, 92, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singels, A.; Bezuidenhout, C.N. A new method of simulating dry matter partitioning in the Canegro sugarcane model. Field Crops Res. 2002, 78, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, B.A.; Robertson, M.J.; Muchow, R.C.; Huth, N.I. Modelling sugarcane production systems. I. Development and performance of the sugarcane module. Field Crops Res. 1999, 63, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Bull, T.A. Simulation of biomass and sugar accumulation in sugarcane using a process-based model. Ecol. Model. 2001, 144, 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, A.J.W.; van Diepen, C.A. Crop model data assimilation with the Ensemble Kalman filter for improving regional crop yield forecasts. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 146, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.W.; Jones, J.W. Scaling-up crop models for climate variability applications. Agric. Syst. 2000, 65, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shi, L.; Zha, Y.; Williams, M.; Lin, L. Simultaneous state-parameter estimation supports the evaluation of data assimilation performance and measurement design for soil-water-atmosphere-plant system. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 812–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shi, L.; Huang, K.; Zha, Y.; Hu, X.; Ye, H.; Yang, Q. Improvement of sugarcane crop simulation by SWAP-WOFOST model via data assimilation. Field Crops Res. 2019, 232, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ines, A.V.M.; Das, N.N.; Hansen, J.W.; Njoku, E.G. Assimilation of remotely sensed soil moisture and vegetation with a crop simulation model for maize yield prediction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauwels, V.R.N.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Lannoy, G.J.M.; Guissard, V.; Lucau, C.; Defourny, P. Optimization of a coupled hydrology-crop growth model through the assimilation of observed soil moisture and leaf area index values using an ensemble Kalman filter. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.K.; Gavli, A.S.; Yadav, S.K.; Sehgal, S.; Ray, S.S. Remote Sensing-Based Yield Forecasting for Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) Crop in India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Robson, A.J. A Novel Approach for Sugarcane Yield Prediction Using Landsat Time Series Imagery: A Case Study on Bundaberg Region. Adv. Remote Sens. 2016, 05, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudorff, B.F.T.; Batista, G.T. Yield estimation of sugarcane based on agrometeorological-spectral models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 33, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, H.S.; Gilbert, R.A.; McCray, J.M.; Perdomo, R.; Eiland, B.; Powell, G.; Montes, G. Relationships among leaf area index, visual growth rating, and sugarcane yield. J. Am. Soc. Sugar Cane Technol. 2012, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, M.D.S.; Rocha, J.V.; Lamparelli, R.A.C. Spectral variables, growth analysis and yield of sugarcane. Sci. Agric. 2005, 62, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simões, M.D.S.; Rocha, J.V.; Lamparelli, R.A.C. Growth indices and productivity in sugarcane. Sci. Agric. 2005, 62, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Rahman, E.M.; Ahmed, F.B. The application of remote sensing techniques to sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid) production: A review of the literature. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3753–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, B.; Cammarano, D.; Carfagna, E. Review of Crop Yield Forecasting Methods and Early Warning Systems; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Monteith, J.L. Solar radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 1972, 9, 744–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, M.; Monteith, J.L. Remote Sensing of Crop Growth; Academic Press: Leicester, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, J.; Todoroff, P.; Bégué, A.; Bury, A.; Martiné, J.-F.; Petit, M. Toward a Satellite-Based System of Sugarcane Yield Estimation and Forecasting in Smallholder Farming Conditions: A Case Study on Reunion Island. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6620–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horie, T. A model for evaluating climatic productivity and water balance of irrigated rice and its application to Southeast Asia. Southeast Asian Stud. 1987, 25, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, T.R.; Horie, T. Leaf nitrogen, photosynthesis and crop radiation use efficiency: A review. Crop Sci. 1989, 29, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shi, L.; Zha, Y.; Huang, K. A new sugarcane yield model using the SiPAR model. Agron. J. 2021, 114, 490–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, G.; Kanemasu, E.T.; Jackson, R.D.; Pinter, P.J. Estimation of total above-ground phytomass production using remotely sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pattey, E.; Miller, J.R.; McNairn, H.; Smith, A.; Hu, B. Estimating crop stresses, aboveground dry biomass and yield of corn using multi-temporal optical data combined with a radiation use efficiency model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, N.P.; Sentelhas, P.C. Climatic effects on sugarcane ripening under the influence of cultivars and crop age. Sci. Agric. 2013, 70, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarpari, M.S.; Beauclair, E.G.F. Sugarcane maturity estimation through edaphic-climatic parameters. Sci. Agric. 2004, 61, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarpari, M.S.; Beauclair, E.G.F. Physiological model to estimate the maturity of sugarcane. Sci. Agric. 2009, 66, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baez-Gonzalez, A.; Kiniry, J.; Meki, M.; Williams, J.; Alvarez-Cilva, M.; Ramos-Gonzalez, J.; Magallanes-Estala, A.; Zapata-Buenfil, G. Crop Parameters for Modeling Sugarcane under Rainfed Conditions in Mexico. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inman-Bamber, N.G. Temperature and seasonal effects on canopy development and light interception of sugarcane. Field Crops Res. 1994, 36, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

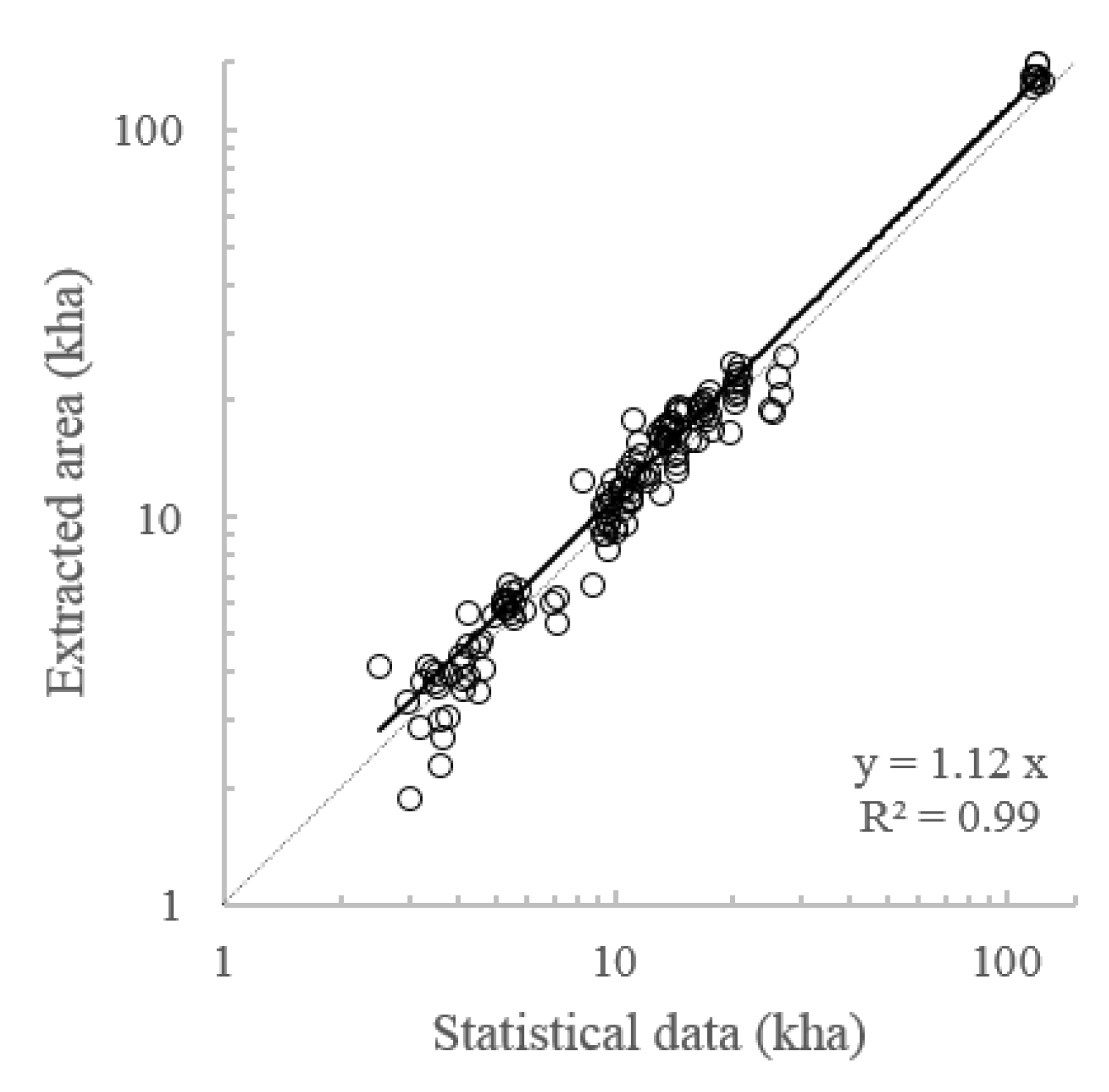
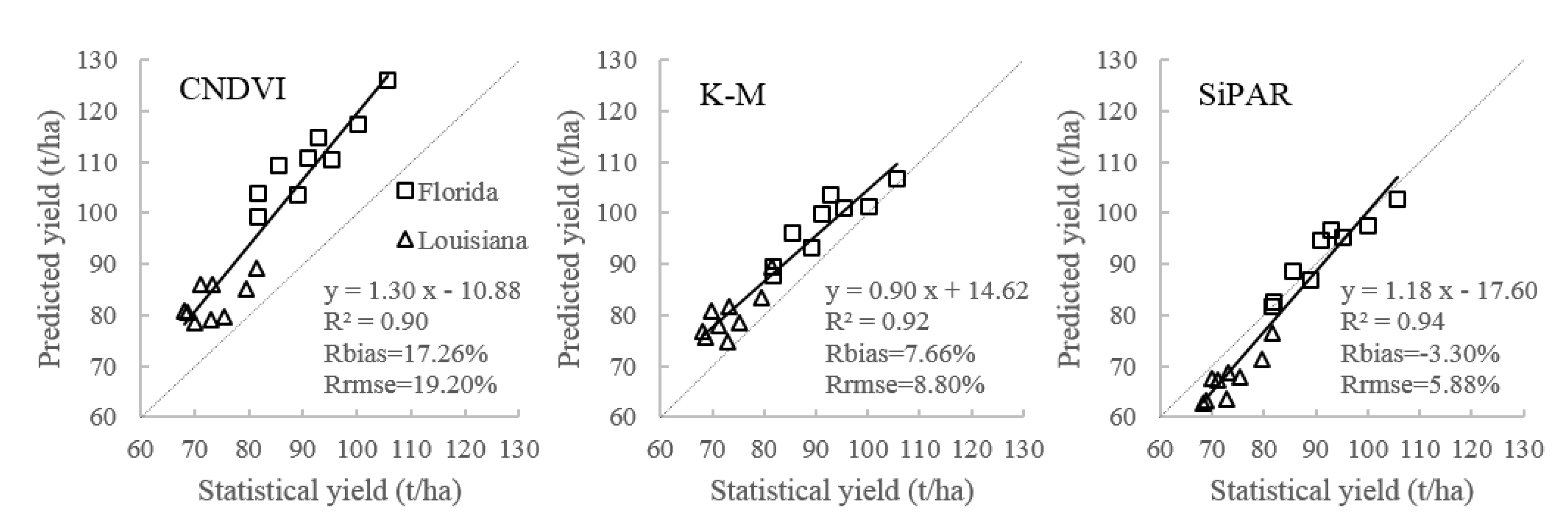

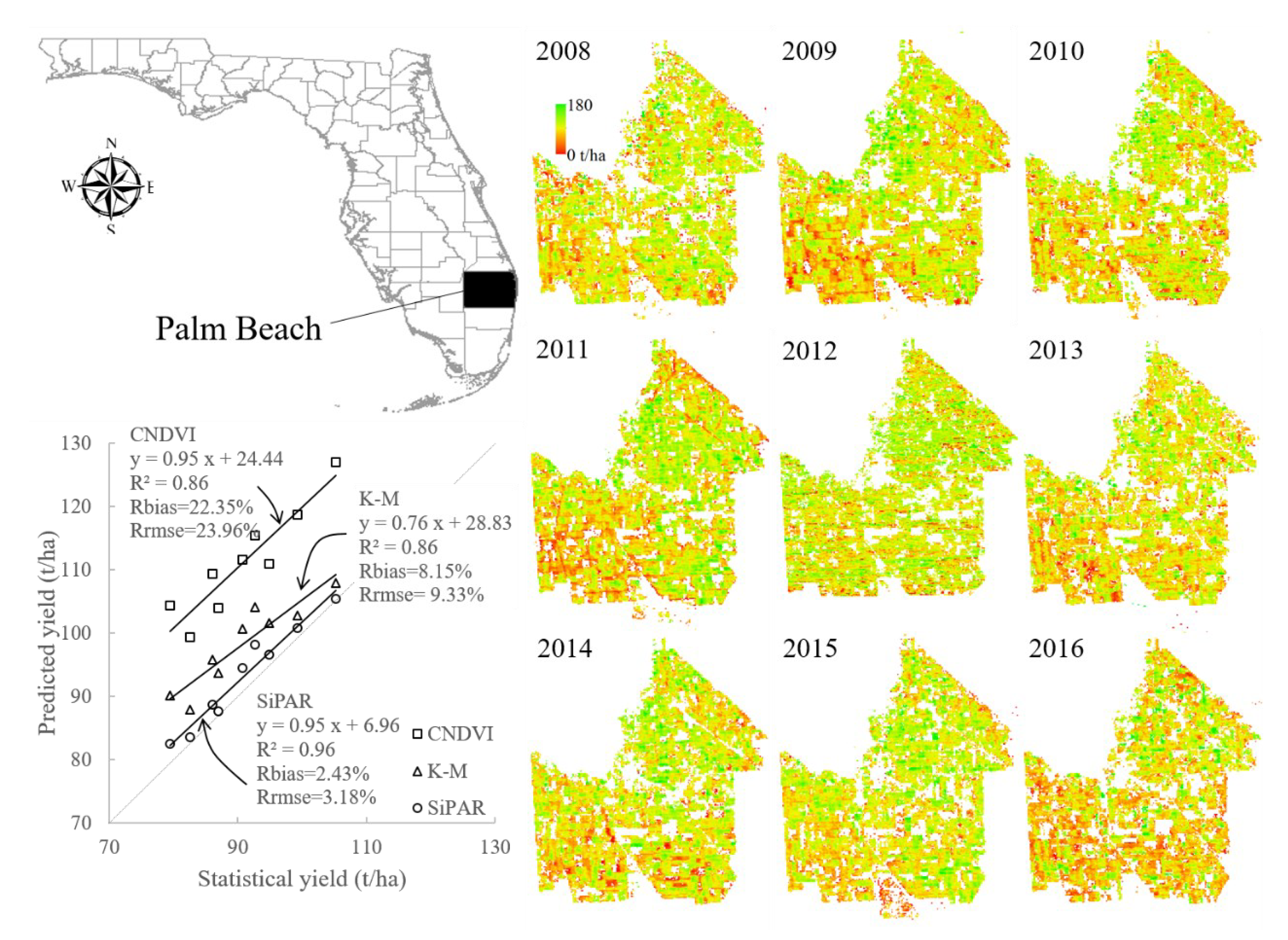
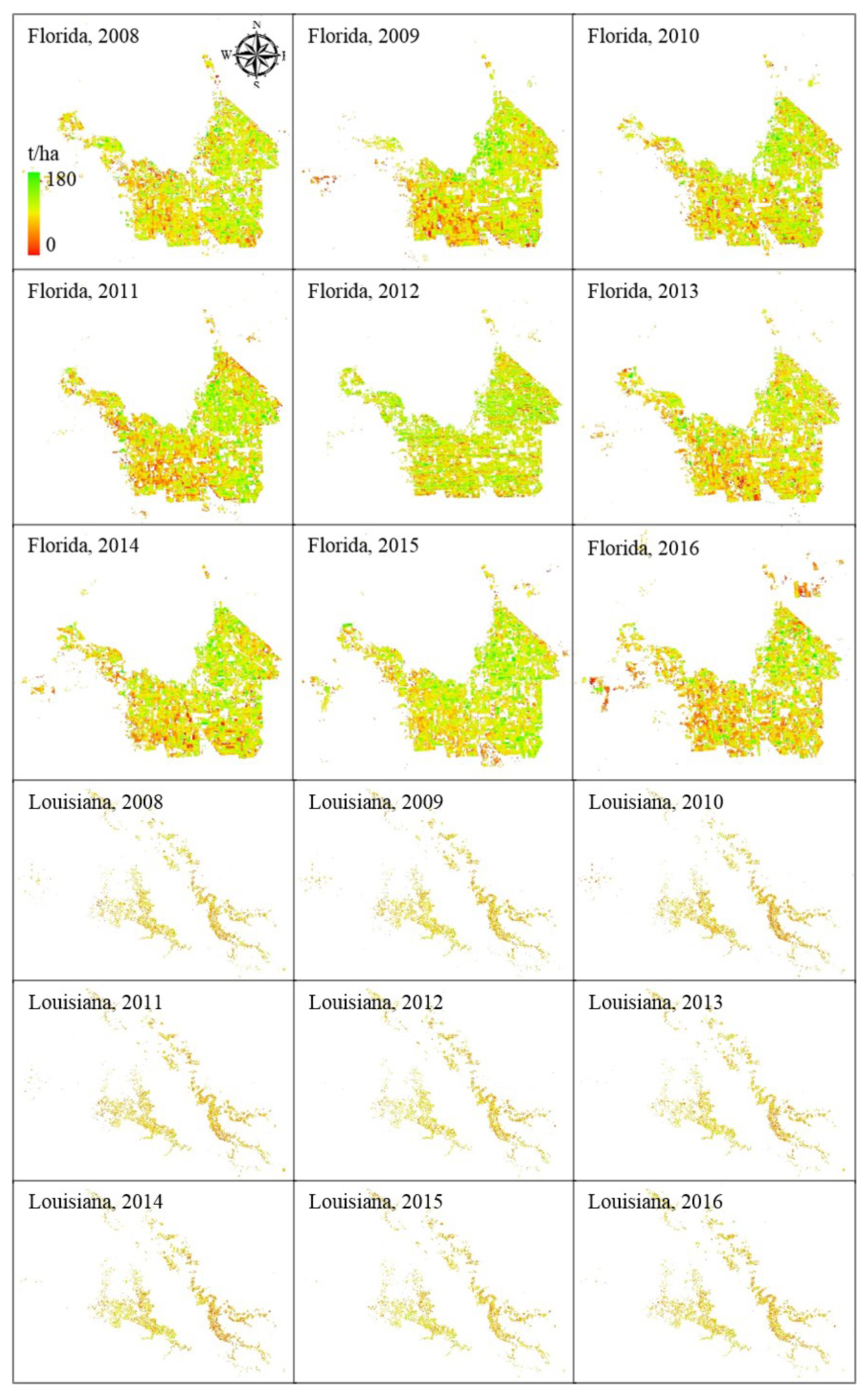
| Model | Area | Number | Slope | R2 | Rbias | Rrmse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kha | - | - | - | % | % | |
| CNDVI | >2.5 | 27F, 115L | 0.84 | 0.50 | 13.23 | 17.19 |
| >6.0 | 27F, 75L | 0.91 | 0.59 | 15.41 | 18.76 | |
| >10.0 | 21F, 64L | 0.97 | 0.64 | 14.95 | 17.80 | |
| >14.0 | 19F, 32L | 1.06 | 0.68 | 16.18 | 19.00 | |
| >18.0 | 16F, 9L | 1.10 | 0.81 | 20.54 | 22.33 | |
| K–M | >2.5 | 27F, 115L | 0.58 | 0.40 | 6.38 | 12.40 |
| >6.0 | 27F, 75L | 0.60 | 0.50 | 8.22 | 13.08 | |
| >10.0 | 21F, 64L | 0.63 | 0.53 | 7.97 | 12.16 | |
| >14.0 | 19F, 32L | 0.70 | 0.63 | 7.18 | 10.93 | |
| >18.0 | 16F, 9L | 0.66 | 0.74 | 9.25 | 11.97 | |
| SiPAR | >2.5 | 27F, 115L | 0.83 | 0.58 | −7.72 | 12.21 |
| >6.0 | 27F, 75L | 0.87 | 0.67 | −5.46 | 10.27 | |
| >10.0 | 21F, 64L | 0.89 | 0.66 | −5.62 | 10.11 | |
| >14.0 | 19F, 32L | 0.95 | 0.73 | −4.58 | 8.98 | |
| >18.0 | 16F, 9L | 0.92 | 0.80 | −0.78 | 6.58 |
| Model | Slope | R2 | Rbias | Rrmse |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | % | % | |
| CNDVI | 0.86 ± 0.39 | 0.86 ± 0.24 | −0.14 ± 2.76 | 2.93 ± 1.78 |
| K–M | 0.96 ± 0.52 | 0.87 ± 0.19 | −0.38 ± 2.90 | 2.87 ± 1.94 |
| SiPAR | 0.97 ± 0.22 | 0.95 ± 0.09 | 0.04 ± 1.35 | 1.54 ± 1.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Shi, L.; Zha, Y.; Zeng, L. Regional Yield Estimation for Sugarcane Using MODIS and Weather Data: A Case Study in Florida and Louisiana, United States of America. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163870
Hu S, Shi L, Zha Y, Zeng L. Regional Yield Estimation for Sugarcane Using MODIS and Weather Data: A Case Study in Florida and Louisiana, United States of America. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(16):3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163870
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shun, Liangsheng Shi, Yuanyuan Zha, and Linglin Zeng. 2022. "Regional Yield Estimation for Sugarcane Using MODIS and Weather Data: A Case Study in Florida and Louisiana, United States of America" Remote Sensing 14, no. 16: 3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163870
APA StyleHu, S., Shi, L., Zha, Y., & Zeng, L. (2022). Regional Yield Estimation for Sugarcane Using MODIS and Weather Data: A Case Study in Florida and Louisiana, United States of America. Remote Sensing, 14(16), 3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163870







